Electrostatic Particle Ionization for Reduction in Livestock and Potash Dust
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Electrostatic Particle Ionization System
2.2. Experimental Dust
2.3. Aerosolization of Dust Samples
2.4. Measurements
2.5. Evaluation of EPI Performance
2.6. Data and Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Collection Efficiency
3.2. Power Consumption
3.3. Ozone Production
3.4. Comparison of the Different Electrodes Based on the Various Metrics
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hartung, J.; Saleh, M. Composition of dust and effects on animals. Landbauforsch Volk 2007, 308, 111–116. [Google Scholar]
- Klein, M.O.; Reid, K.W.; Goldsmith, E.L. Air emissions at KCl facilities. In Pollution Control in Fertilizer Production; Hodge, C.A., Popovici, N.N., Eds.; Marcel Dekker, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Isaevich, A.; Semin, M.; Levin, L.; Ivantsov, A.; Lyubimova, T. Study on the dust content in dead-end drifts in the potash mines for various ventilation modes. Sustainability 2022, 14, 3030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilote, J.; Létourneau, V.; Girard, M.; Duchaine, C. Quantification of airborne dust, endotoxins, human pathogens and antibiotic and metal resistance genes in Eastern Canadian swine confinement buildings. Aerobiologia 2019, 35, 283–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirychuk, S.P.; Dosman, J.A.; Reynolds, S.J.; Willson, P.; Senthilselvan, A.; Feddes, J.J.; Classen, H.L.; Guenter, W. Total dust and endotoxin in poultry operations: Comparison between cage and floor housing and respiratory effects in workers. J. Occup. Environ. Med. 2006, 48, 741–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Government of Ontario. Current Occupational Exposure Limits for Ontario Workplaces Under Regulation 833. 2022. Available online: https://www.ontario.ca/page/current-occupational-exposure-limits-ontario-workplaces-under-regulation-833 (accessed on 13 December 2024).
- Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA). Particulates Not Otherwise Regulated, Total and Respirable Dust (PNOR). 2023. Available online: https://www.osha.gov/chemicaldata/801 (accessed on 13 December 2024).
- Markham, J.W.; Tan, L.K. Concentrations and health effects of potash dust. Am. Ind. Hyg. Assoc. J. 1981, 42, 671–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, B.L.; Dosman, J.A.; Cotton, D.J.; Weisstock, S.R.; Lappi, V.G.; Froh, F. Pulmonary function and respiratory symptoms in potash workers. J. Occup. Med. 1984, 26, 209–214. [Google Scholar]
- Rimac, D.; Macan, J.; Varnai, V.M.; Vucemilo, M.; Matković, K.; Prester, L.; Orct, T.; Trosić, I.; Pavicić, I. Exposure to poultry dust and health effects in poultry workers: Impact of mould and mite allergens. Int. Arch. Occup. Environ. Health 2010, 83, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viegas, S.; Faísca, V.M.; Dias, H.; Clérigo, A.; Carolino, E.; Viegas, C. Occupational exposure to poultry dust and effects on the respiratory system in workers. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health Part A 2013, 76, 230–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogink, N.; van Harn, J.; van Emous, R.; Ellen, H. Top layer humidification of bedding material of laying hen houses to mitigate dust emissions: Effects of water spraying on dust, ammonia and odor emissions. In Proceedings of the 2012 IX International Livestock Environment Symposium (ILES IX), Valencia, Spain, 8–12 July 2012; Available online: https://elibrary.asabe.org/abstract.asp?aid=41632 (accessed on 13 December 2024).
- Urso, P.M.; Turgeon, A.; Ribeiro, F.R.B.; Smith, Z.K.; Johnson, B.J. Review: The effects of dust on feedlot health and production of beef cattle. J. Appl. Anim. Res. 2021, 49, 133–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Y.; Meng, Q.; Gao, J.; Tang, X.; Zhang, H. Effects of relative humidity on animal health and welfare. J. Integr. Agric. 2017, 16, 1653–1658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banhazi, T.M.; Saunders, C.; Nieuwe, N.; Lu, V.; Banhazi, A. Oil spraying as an air quality improvement technique in livestock buildings: Development and utilisation of a testing device. Aust. J. Mech. Eng. 2011, 8, 169–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehdizadeh, S.A.; Banhazi, T.M. Evaluating droplet distribution of spray-nozzles for dust reduction in livestock buildings using machine vision. Int. J. Agric. & Biol. Eng. 2015, 8, 58–64. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, Z.; Zhang, Y. A review of effects and control methods of particulate matter in animal indoor environments. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2004, 54, 845–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, R.; Tao, Y.; Chen, J.; Li, S.; Wang, S. Review on dust control technologies in coal mines of China. Sustainability 2024, 16, 4038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jerez, S.B.; Mukhtar, S.; Faulkner, W.; Casey, K.D.; Borhan, M.S.; Smith, R.A. Evaluation of electrostatic particle ionization and biocurtain™ technologies to reduce air pollutants from broiler houses. Appl. Eng. Agric. 2013, 29, 975–984. [Google Scholar]
- Martel, M.; Kirychuk, S.; Predicala, B.; Bolo, R.; Yang, Y.; Thompson, B.; Guo, H.; Zhang, L. Improving air quality in broiler rooms using an electrostatic particle ionization system. J. ASABE 2023, 66, 887–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bist, R.B.; Yang, X.; Subedi, S.; Ritz, C.W.; Kim, W.K.; Chai, L. Electrostatic particle ionization for suppressing air pollutants in cage-free layer facilities. Poult. Sci. 2024, 1034, 103494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cambra-López, M.; Winkel, A.; van Harn, J.; Ogink, N.W.; Aarnink, A.J. Ionization for reducing particulate matter emissions from poultry houses. Trans. ASABE 2009, 52, 17571771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pushpawela, B.; Jayaratne, R.; Nguy, A.; Morawska, L. Efficiency of ionizers in removing airborne particles in indoor environments. J. Electrostat. 2017, 90, 79–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, C.; Haghighat, F.; Feng, Z.; Kumar, P.; Cao, S.J. Impact of ionizers on prevention of airborne infection in classroom. Build. Simul. 2023, 16, 749–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romay, F.J.; Ou, Q.; Pui, D.Y.H. Effect of ionizers on indoor air quality and performance of air cleaning systems. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2024, 24, 230240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.-T.; Lu, C.-L.; Lu, S.-J.; Lee, D.-S. Electrostatic precipitator design optimization for the removal of aerosol and airborne viruses. Sustainability 2023, 15, 8432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harmon, J.D.; Hoff, S.J.; Rieck-Hinz, A.M. Animal Housing—Electrostatic Precipitation Overview. Agriculture and Environment Extension Publications. 2014. Available online: http://lib.dr.iastate.edu/extension_ag_pubs/212 (accessed on 6 January 2025).
- Bist, R.B.; Yang, X.; Subedi, S.; Paneru, B.; Chai, L. Enhancing dust control for cage-free hens with electrostatic particle charging systems at varying installation heights and operation durations. AgriEngineering 2024, 6, 1747–1759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lippmann, M. Health effects of ozone: A critical review. JAPCA 1989, 39, 672–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosentrater, K. Laboratory analysis of an electrostatic dust collection system. Agric. Eng. Int. CIGR J. 2004. Manuscript BC 03 008. Available online: https://ecommons.cornell.edu/server/api/core/bitstreams/e9b836d9-17c8-42ee-91d5-ead9227fe5d9/content (accessed on 6 January 2025).
- Shin, D.H.; Woo, C.G.; Kim, H.J.; Kim, Y.J.; Han, B. Comparison of discharging electrodes for the electrostatic precipitator as an air filtration system in air handling units. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2019, 19, 671–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.-J.; Han, B.; Kim, Y.-J.; Yoa, S.-J.; Oda, T. Integration of a nonmetallic electrostatic precipitator and a wet scrubber for improved removal of particles and corrosive gas cleaning in semiconductor manufacturing industries. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2012, 62, 905–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosentrater, K. Performance of an Electrostatic Dust Collection System In Swine Facilities. Agric. Eng. Int. CIGR J. 2003. Manuscript BC 03 003. Available online: https://pdfs.semanticscholar.org/44f9/7a41de9d0cf0d766bca5f4e75c38d963375c.pdf?_ga=2.261349773.1207055507.1569004420-713621346.1569004420 (accessed on 13 December 2024).
- Remaoun, S.-M.; Tilmatine, A.; Hammadi, N.; Miloua, F.; Medles, K. Optimisation of one stage electrostatic precipitator for welding fume filtration. Sci. Iran. 2012, 19, 1861–1864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Chen, T.-M.; Tsai, C.J.; Yan, S.-Y.; Li, S.-N. An efficient wet electrostatic precipitator for removing nanoparticles, submicron and micron-sized particles. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2014, 136, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso, C.; Raynor, P.C.; Davies, P.R.; Morrison, R.B.; Torremorell, M. Evaluation of an electrostatic particle ionization technology for decreasing airborne pathogens in pigs. Aerobiologia 2016, 32, 405–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katz, J. Factors affecting resistivity in electrostatic precipitation. J. Air Pollut. Control Assoc. 1980, 30, 195–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Lagarias, J.S. Discharge electrodes and electrostatic precipitators. J. Air Pollut. Control Assoc. 1960, 10, 271–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babatunde, O.O.; Park, C.S.; Adeola, O. Nutritional potentials of atypical feed ingredients for broiler chickens and pigs. Animals 2021, 11, 1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chai, M.; Lu, M.; Keener, T.; Khang, S.-J.; Chaiwatpongsakorn, C.; Tisch, J. Using an improved electrostatic precipitator for poultry dust removal. J. Electrostat. 2009, 67, 870–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirychuk, S.P.; Reynolds, S.J.; Koehncke, N.K.; Lawson, J.; Willson, P.; Senthilselvan, A.; Marciniuk, D.; Classen, H.L.; Crowe, T.; Just, N.; et al. Endotoxin and dust at respirable and nonrespirable particle sizes are not consistent between cage- and floor-housed poultry operations. Ann. Occup. Hyg. 2010, 54, 824–832. [Google Scholar]
- Wang-Li, L.; Cao, Z.; Li, Q.; Liu, Z.; Beasley, D.B. Concentration and particle size distribution of particulate matter inside tunnel-ventilated high-rise layer operation houses. Atmos. Environ. 2013, 66, 8–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, H.T.L.; Aarnink, A.J.A.; Cambra-López, M.; Huynh, T.T.T.; Parmentier, H.K.; Groot Koerkamp, P.W.G. Size distribution of airborne particles in animal houses. Agric. Eng. Int. CIGR J. 2014, 16, 28–42. [Google Scholar]
- Jerez, S.B.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, X. Measurement of particle size distribution in a swine building. Trans. ASABE 2011, 54, 1103–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, D.D.; Friday, W.H.; DeForest, S.S. Environmental Control for Confinement Livestock Housing. Historical Documents of the Purdue Cooperative Extension Service. Paper 1083. 2015. Available online: https://docs.lib.purdue.edu/agext/1083 (accessed on 13 December 2024).
- National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH). Best Practices for Dust Control in Metal/Nonmetal Mining—Mineral Processing Operations—Total Mill Ventilation Systems. 2018. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/niosh/engcontrols/ecd/detail194.html (accessed on 13 December 2024).
- Xu, J.; Chen, P.; Gu, Z.; Xi, J.; Cai, J. Performances of a new type high-temperature tubular electrostatic precipitator with rare-earth tungsten cathode. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 280, 119820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, J.H.; Lawless, P.A.; Yamamoto, T.; Coy, D.W.; McKenna, J.D.; Mycock, J.C.; Nunn, A.B.; Greiner, G.P.; Vatavuk, W.M. Chapter 3—Electrostatic Precipitator, Section 6—Particulate Matter Controls, EPA/452/B-02-001. 1999. Available online: https://www3.epa.gov/ttncatc1/cica/files/cs6ch3.pdf (accessed on 13 December 2024).
- Mizuno, A. Electrostatic precipitation. IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 2000, 7, 615–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jedrusik, M.; Swierczok, A. Design efficiency of ESP. In Air Pollution: Monitoring, Modelling, Health and Control; Khare, M., Ed.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2012; pp. 197–220. [Google Scholar]
- Sudrajada, A.; Yusof, A.F. Review of electrostatic precipitator device for reduce of diesel engine particulate matter. Energy Procedia 2015, 68, 370–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grigoriu, C.; Wang, W.-N.; Martin, D.; Biswas, P. Capture of particles from an iron and steel smelter with a pulse-energized electrostatic precipitator. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2012, 12, 673–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boelter, K.J.; Davidson, J.H. Ozone generation by indoor, electrostatic air cleaners. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 1997, 27, 689–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yehia, A.; Mizuno, A. Suppression of the ozone generation in the positive and negative DC corona discharges. Int. J. Plasma Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 2, 44–49. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, H.J.; Han, B.; Kim, Y.J.; Oda, T.; Won, H. Submicrometer particle removal indoors by a novel electrostatic precipitator with high clean air delivery rate, low ozone emissions, and carbon fiber ionizer. Indoor Air 2013, 23, 369–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manuzon, R.; Zhao, L.; Gecik, C. An optimized electrostatic precipitator for air cleaning of particulate emissions from poultry facilities. ASHRAE Trans. 2014, 120, 490–503. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.; Chai, L.; Richardson, B.; Xin, H. Field evaluation of an electrostatic air filtration system for reducing incoming particulate matter of a hen house. Trans. ASABE 2018, 61, 295–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aponte, I.A.; Esser, B.; Dickens, J.C.; Mankowski, J.J.; Neuber, A.A. Fundamental investigation of unipolar and RF corona in atmospheric air. Phys. Plasmas 2021, 28, 123502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowke, J.J.; D’Alessandro, F. Onset corona fields and electrical breakdown criteria. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys 2003, 36, 2673–2682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altamimi, G.; Illias, H.A.; Mokhtar, N.; Mokhlis, H.; Bakar, A.H.A. Corona discharges under various types of electrodes. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE International Conference on Power and Energy (PECon), Kuching, Malaysia, 1–3 December 2014; pp. 5–8. [Google Scholar]
- Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA). Ozone. 2021. Available online: https://www.osha.gov/chemicaldata/9 (accessed on 13 December 2024).
- Cardello, N.; Volckens, J.; Tolocka, M.P.; Wiener, R.; Buckley, T.J. Technical note: Performance of a personal electrostatic precipitator particle sampler. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2002, 36, 162–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]

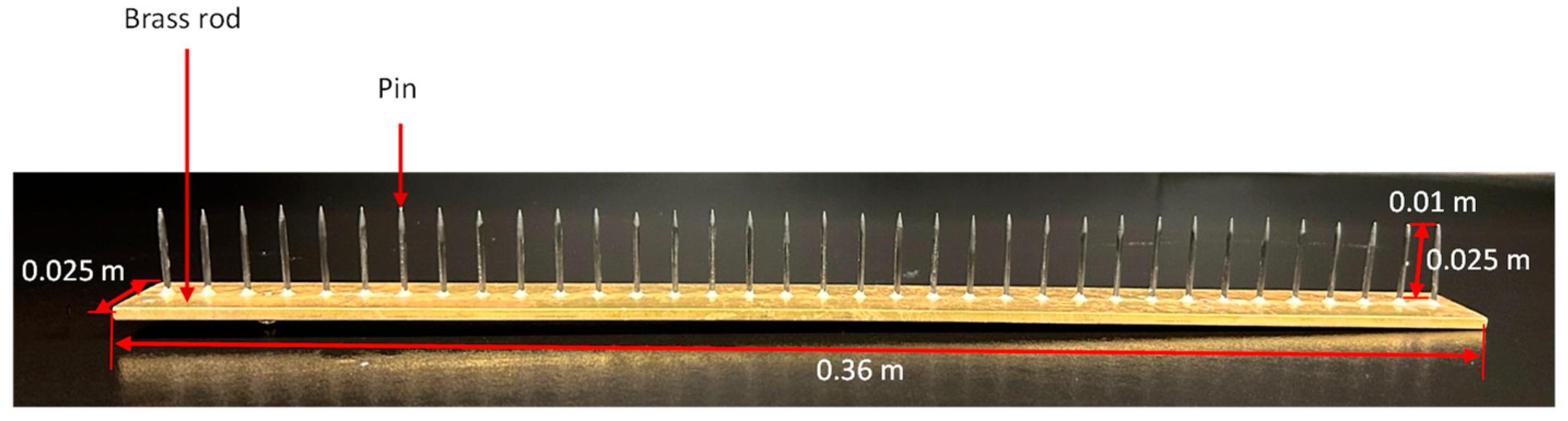

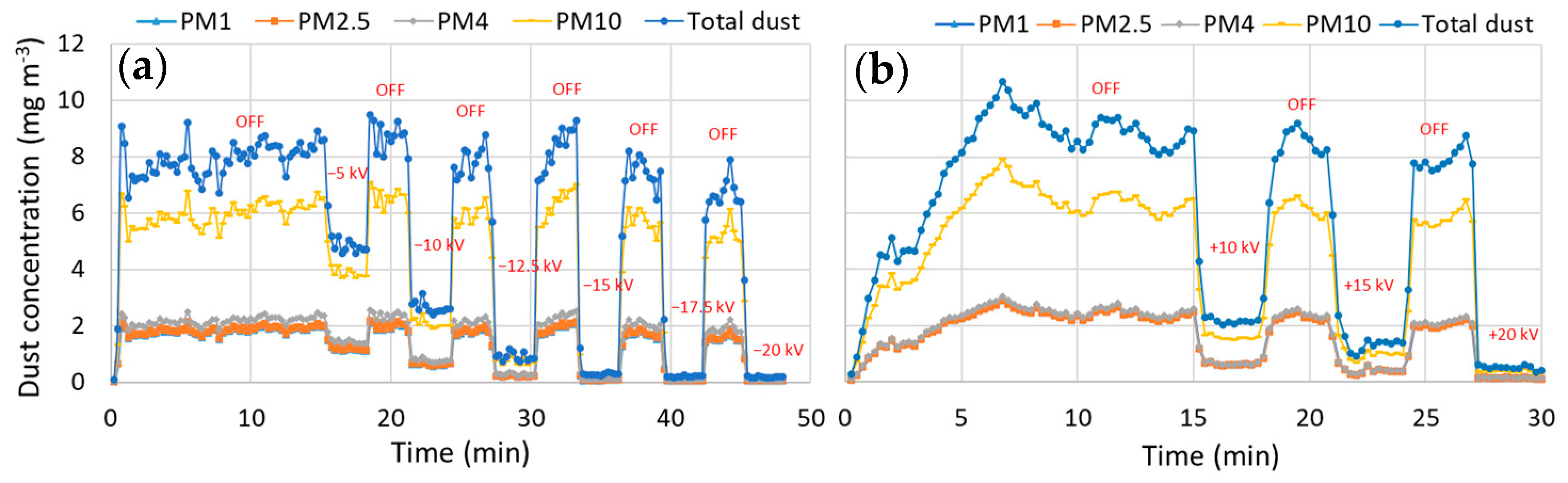
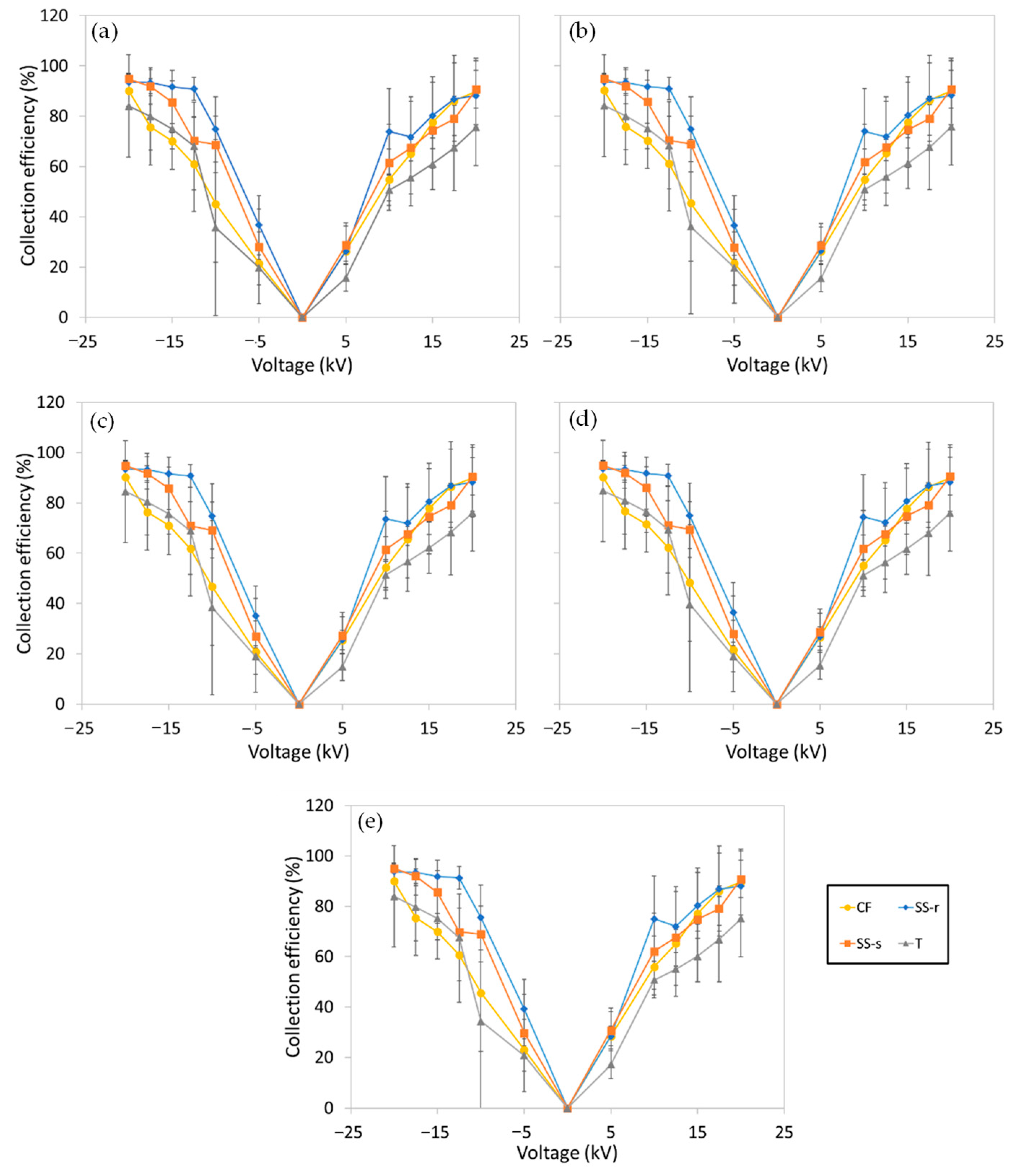
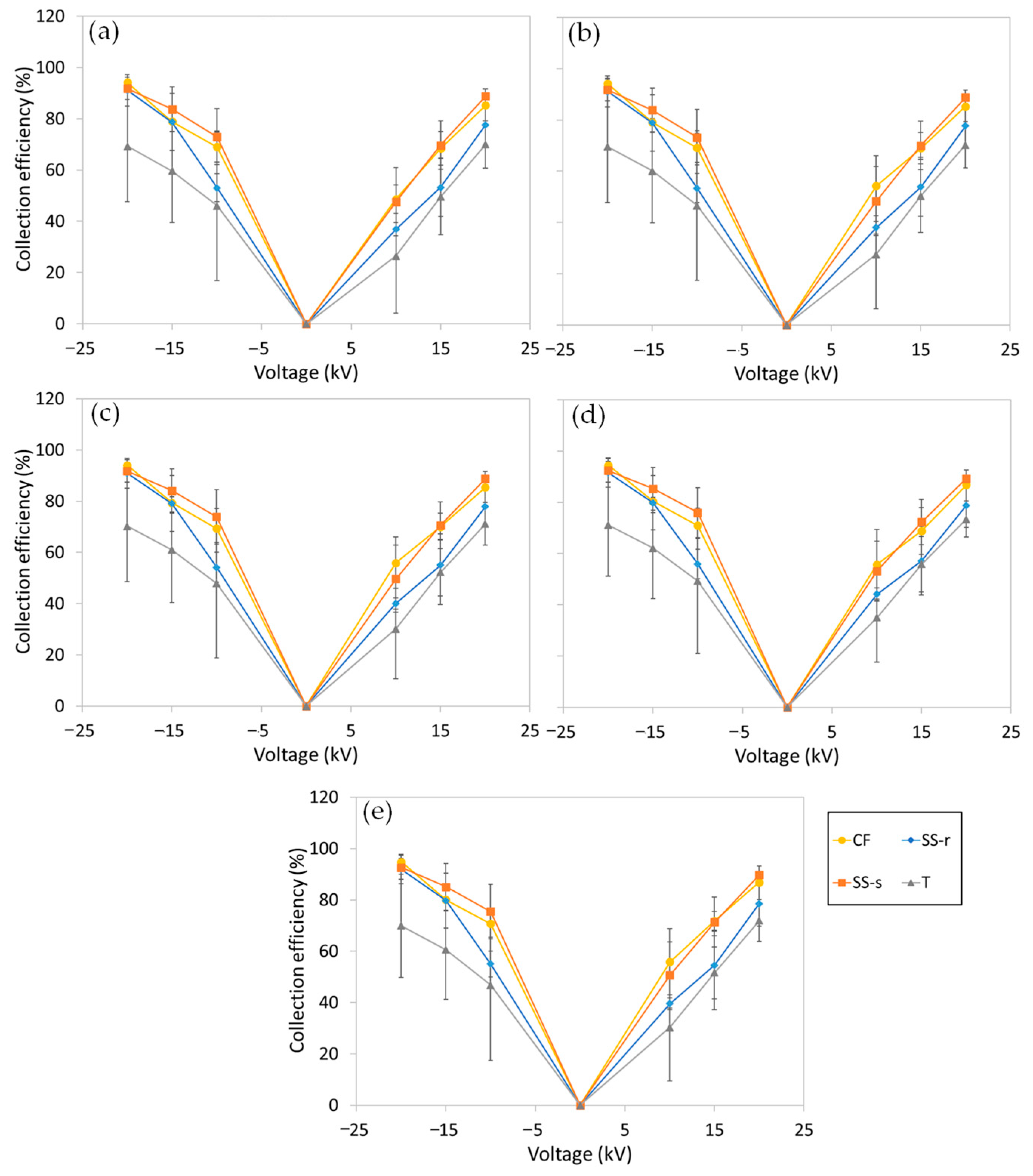

| Dust | PSD (%) | MMD (µm) | Reference | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| <10 µm | >10 µm | |||
| Sieved wheat flour | 13 | 87 | 21.8 | This study |
| Poultry dust | 23–60 | 40–77 | 7.3–26.1 | [41,42,43] |
| Swine dust | 8 | 90 | 31.6 | [44] |
| Operating and Design Conditions | Levels/Types Evaluated |
|---|---|
| Shape and material type of discharge electrode | Stainless steel, round pins Stainless steel, square pins Tungsten, round pins Carbon fiber, round pins |
| Distance between discharge electrode and collection surfaces (m) | 0.05 |
| Voltage level (kV) and polarity | ±5.0, ±10.0, ±12.5, ±15.0, ±17.5, and ±20.0 a |
| Dust concentration (mg m−3) | ~8 |
| Air changes per hour | 25 |
| Electrode Type | Collection Efficiency (%) | Power Consumption (W) | Ozone Generation (ppb) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wheat Flour | Potash Dust | |||
| Carbon fiber | 64 | 77 | 1.07 | 44 |
| Stainless steel (round) | 76 | 67 | 1.14 | 93 |
| Stainless steel (square) | 71 | 78 | 1.30 | 364 |
| Tungsten | 57 | 55 | 1.39 | 385 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Martel, M.; Taylor, M.; Kirychuk, S.; Choi, K.; Guo, H.; Zhang, L. Electrostatic Particle Ionization for Reduction in Livestock and Potash Dust. Atmosphere 2025, 16, 87. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16010087
Martel M, Taylor M, Kirychuk S, Choi K, Guo H, Zhang L. Electrostatic Particle Ionization for Reduction in Livestock and Potash Dust. Atmosphere. 2025; 16(1):87. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16010087
Chicago/Turabian StyleMartel, Myra, Matthew Taylor, Shelley Kirychuk, Kwangseok Choi, Huiqing Guo, and Lifeng Zhang. 2025. "Electrostatic Particle Ionization for Reduction in Livestock and Potash Dust" Atmosphere 16, no. 1: 87. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16010087
APA StyleMartel, M., Taylor, M., Kirychuk, S., Choi, K., Guo, H., & Zhang, L. (2025). Electrostatic Particle Ionization for Reduction in Livestock and Potash Dust. Atmosphere, 16(1), 87. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16010087








