Abstract
This study presents an improved wet scavenging process for particles in air quality modeling, focusing on the Korean Peninsula. New equations were incorporated into the air quality chemical transport model (CTM) to enhance the simulation of particulate matter (PM) concentrations. The modified air quality CTM module, utilizing size-dependent scavenging formulas, was applied to simulate air quality for April 2018, a month characterized by significant precipitation. Results showed that the modified model produced more accurate predictions of PM10 and PM2.5 concentrations compared to the original air quality CTM model. The maximum monthly average differences were 5.46 µg/m3 for PM10 and 2.87 µg/m3 for PM2.5, with pronounced improvements in high-concentration regions. Time-series analyses for Seoul and Busan demonstrated better agreement between modeled and observed values. Spatial distribution comparisons revealed enhanced accuracy, particularly in metropolitan areas. This study highlights the importance of incorporating region-specific, size-dependent wet scavenging processes in air quality models. The improved model shows promise for more accurate air quality predictions, potentially benefiting environmental management and policy-making in the region. Future research should focus on integrating more empirical data to further refine the wet scavenging process in air quality modeling.
1. Introduction
Atmospheric aerosols are significantly impacted by wet scavenging processes [1]. The removal of ultrafine particles from the atmosphere through wet scavenging is crucial for their transport and dispersion [2]. Consequently, comprehending and accurately modeling the mechanisms of wet scavenging for ultrafine particles has become essential for implementing three-dimensional air quality prediction models [3]. Wet scavenging is a primary mechanism that eliminates particulate matter (PM) due to precipitation. As raindrops descend during precipitation events, they absorb and remove substances from the atmosphere [4]. The efficiency of wet scavenging depends on various factors, including the distribution, intensity, duration of precipitation, concentration, and spatial distribution of atmospheric pollutants [5]. When it rains, raindrops collect and remove PM through inertial impaction, interception, and Brownian diffusion [6]. Collection coefficients define these processes based on droplet collisions, where the total number of collisions refers to how often raindrops collide with PM over an area equivalent to the effective cross-sectional area of the raindrops [7].
Numerous studies have been conducted to measure the scavenging effects of precipitation [8,9,10,11,12,13]. In a study conducted in East Asia on Sado Island, Japan, researchers measured the atmospheric and precipitation concentrations of sulfur dioxide (SO2) and sulfate (SO42−) to investigate the scavenging coefficients of sulfur compounds due to long-range transport. The results indicated that the scavenging coefficient could be expressed as λ = aPb, where P represents the precipitation intensity. Parameter a was approximately 10−4, and parameter b ranged from 0.67 to 0.76. Recently, a study in Lanzhou, China, examined the removal characteristics of atmospheric aerosols by measuring air pollution and precipitation [14]. It was found that aerosols in the 10–1000 nm range have distinct coefficients depending on rain and snowfall, with the intensity and duration of snowfall having a significant impact. A study using high-resolution data on atmospheric and soluble inorganic salts in precipitation collected during the summer focused on the scavenging coefficient under low cloud conditions [15]. The study concluded that different scavenging coefficients should be used for different ions in chemical transport models, considering the variations in chemical composition. However, due to the complexity of air quality models, a simplified approach is necessary [16].
Various modeling approaches have been employed to simulate wet scavenging processes in different environmental contexts, with significant variations in methodologies across studies [17]. For instance, traditional models often simplify the wet scavenging process by utilizing constants or first-order equations that fail to capture the complexity of aerosol and raindrop interactions accurately [18]. More advanced models, such as the Community Multiscale Air Quality (CMAQ) model, have incorporated size-dependent scavenging coefficients that allow for a more nuanced representation of the physical processes involved. These models differentiate between aerosol particle sizes and precipitation types, leading to more accurate predictions of particulate matter (PM) concentrations. Comparative analyses between different models, such as those utilizing Lagrangian and Eulerian frameworks, have demonstrated the critical need for enhancing wet scavenging mechanisms to improve the accuracy of air quality simulations [19].
Recent advancements in wet scavenging research have focused on refining the parameters used in chemical transport models (CTMs) to better reflect real-world conditions [20,21,22]. Innovations include the development of empirical formulas that account for the size distribution of aerosols and raindrops, as well as the intensity and duration of precipitation events. These improvements have led to more accurate simulations of aerosol removal processes, particularly under varying meteorological conditions [23]. Studies have highlighted the importance of using size-resolved scavenging coefficients derived from in situ measurements, which have been shown to significantly enhance the predictive capabilities of models like CMAQ [7]. Furthermore, these advancements are increasingly being integrated into air quality models to improve their application in environmental management and policy-making.
Comprehensive research on wet scavenging processes is needed to better understand this phenomenon [24]. This study aims to evaluate the factors affecting wet scavenging and improve the modeling process by accurately formulating the transport and dispersion of particles in the atmosphere. Applying the wet scavenging mechanism to three-dimensional air quality prediction models will enhance the accuracy of particle concentration predictions in real environments [25]. Thus, by analyzing wet scavenging results and applying three-dimensional air quality prediction models, this study aims to provide more accurate and reliable information on ultrafine particles, contributing to environmental management and policy-making.
This study tries to apply the scavenging coefficient equation based on rainfall intensity using PM concentration from air quality monitoring stations collected over 5 years from 12 cities across the Korean Peninsula [26]. The research involves updating air quality prediction models by incorporating rainfall data to derive scavenging coefficients for multiple locations. Additionally, model simulations and analyses were conducted specifically for April 2018, when rainfall intensity reached its peak, to further explore this relationship.
2. Methods
Wet scavenging is the natural process by which airborne particles, such as cloud droplets, fog droplets, rain, and snow, are removed from the atmosphere and deposited onto the Earth’s surface [27]. This phenomenon is also known by other terms, including wet deposition, wet removal, washout, and rainout. In this research, the term “scavenging” will be primarily used. Rainout typically describes the scavenging of particles within clouds, while washout refers to the scavenging of particles below clouds by falling rain or snow [28]. The removal of PM through wet scavenging can be divided into three stages: (1) the contact between aerosols and condensed water, (2) the adsorption of aerosols, and (3) the transportation of aqueous particles to the Earth’s surface [29]. It is important to note that some wet scavenging processes are reversible, as evaporating raindrops can generate new aerosols even though they had previously scavenged particles under clouds [30]. Wet scavenged pollutants interact with various physical stages and phenomena at different scales, involving numerous steps and variables, including diverse forms such as cloud droplets, rain, snow, ice, hail, and sleet, each with distinct size resolutions [31]. Furthermore, the complexities of this process are further increased due to the presence of four media: air, cloud droplets, aerosol particles, and raindrops, with specific types of pollutants existing within each phase [32].
2.1. Theoretical Analysis of Wet Scavenging
The likelihood of collisions between raindrops and particles is contingent upon the particle size and their relative positioning [18]. Predicting the exact trajectories of particles is a complex fluid dynamics problem [33]. Wet scavenging equations utilize the concept of collision efficiency, analogous to the collision efficiency between raindrops. The collision efficiency, E, denotes the fraction of aerosols with diameter dp that are collected within the collision volume of a raindrop with diameter Dp [34]. This collision efficiency serves as a correction factor to account for the interactions between descending raindrops and atmospheric aerosols [35].
For the aerosol size distribution n(dp, t), below-cloud scavenging can be understood as a first-order approximation of how particles are transferred into raindrops. The governing equation for the wet removal of particles is given by the following:
as described by [36]. In this equation, Λ(dp) is the scavenging coefficient. This relationship illustrates that the removal rate of particles from the atmosphere via raindrops is proportional to both the scavenging coefficient and the concentration of those particles. The effectiveness of this process is influenced by particle size and their spatial distribution within the atmosphere.
As shown in Equation (2), the scavenging coefficient Λ(dp) represents the efficiency with which aerosols of diameter dp are removed by precipitation characterized by a raindrop size distribution ND. It is assumed that all raindrops in the precipitation have the same diameter Dp and a number concentration ND.
By definition, the collision efficiency E is the ratio of the total number of collisions between raindrops and aerosols to the total number of aerosol particles in the effective cross-sectional area of the raindrop. In the standard CMAQ model, E is typically assumed to be 1, indicating that all particles within the geometric cylindrical volume traversed by the falling drop are collected [37]. However, experimental data often show that the actual scavenging efficiency is less than 1, as it accounts for the degree to which particles are scavenged, depending on various factors. Our model improvements are based on these realistic assumptions, refining the CMAQ model to better reflect the actual collision efficiencies observed in empirical studies. While the standard model uses E = 1, our enhancements consider the variability in collision efficiency observed in experiments, thereby improving the model’s predictive accuracy.
Using the expression for collision efficiency (E), the wet removal rate for precipitation events, or the scavenging coefficient (Λ), can be estimated. This calculation is based on information about the aerosol size distribution below the cloud and the raindrop size distribution. The Λ represents the efficiency with which aerosols of diameter dp are removed by precipitation with a raindrop size distribution of Dp. Here, it is assumed that all raindrops in the precipitation have the same diameter Dp and a number concentration ND. The only relevant variable for aerosols of diameter Dp is the collision efficiency (E).
Moreover, the wet scavenging coefficient can be simplified using rainfall intensity (R) as shown in Equation (3). Rainfall intensity is utilized as a representative variable for removal by precipitation, and the wet Λ can be derived using air pollution monitoring data. Here, a and b are constants determined from previous studies, used to estimate the wet scavenging coefficient from rainfall intensity.
2.2. Modification of the Wet Scavenging Algorithm in Chemical Transport Models (CTMs)
To validate the study results, we aimed to apply the newly derived Λ equation from previous studies using a three-dimensional air quality chemical transport model (CTM). Accurately simulating wet scavenging processes in a model necessitates a comprehensive understanding of atmospheric meteorology [38]. However, implementing these complex wet scavenging processes in air quality models is fraught with difficulties. Most existing air quality models simplify the wet scavenging process by precipitation using constants or first-order equations [28]. This simplification arises because fully formulating all aerosol scavenging processes during precipitation is both challenging and computationally inefficient [19]. Notably, in the widely used three-dimensional air quality model CMAQ (The Community Multiscale Air Quality Modeling System), aerosol removal processes are considered one-dimensionally without distinguishing between raindrops and cloud droplets [39]. The scavenging mechanism in CMAQ targets aerosols within the accumulation mode (0.1–1 μm) and coarse mode (>10 μm), assuming complete absorption by clouds and rain. Since particles in the Aitken mode are aggregated into the accumulation mode, only the accumulation and coarse modes are considered [40]. However, this assumption is inaccurate from a physical scavenging mechanism perspective, especially for below-cloud scavenging processes that must account for the size distribution of raindrops and aerosols.
Existing studies have simplified the precipitation-driven aerosol removal process, and the scavenging formula proposed by [8] utilizing empirically determined Λ has been widely adopted. This method employs rainfall intensity and empirically derived coefficients to simulate the scavenging of aerosols by precipitation in both Lagrangian and Eulerian air quality models. Consequently, there is a need to enhance the wet scavenging mechanism by improving the Λ, which is a critical component of the scavenging formula.
Figure 1a depicts the original mechanism used in the Community Multiscale Air Quality (CMAQ) model, where the wet scavenging process is represented using a simplified, scavenging time variable, τwash. In contrast, Figure 1b illustrates the modified mechanism introduced in this study, which incorporates a size-dependent collision efficiency [41]. While Figure 1a assumes that E remains constant and independent of particle size dp, Figure 1b demonstrates how E varies as a function of dp, reflecting the influence of diffusion, interception, and impaction processes. Meanwhile, the right panel introduces a revised equation that explicitly accounts for particle diameter (dp), underscoring its critical role in determining scavenging efficiency.
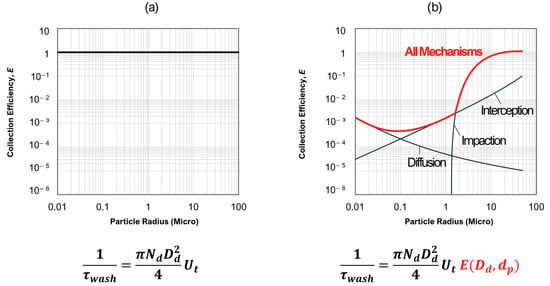
Figure 1.
Modified mechanism of wet collision efficiency. (a) Constant scavenging coefficient (b) Size-dependent scavenging coefficient.
The scavenging time (τwash) in the original CMAQ model, as represented in Figure 1a, is treated as a constant value [26]. However, in the modified approach shown in Figure 1b, τwash is dynamically influenced by particle diameter (dp). Under the condition where Dd is fixed, the collision efficiency E in Figure 1a remains constant, while in Figure 1b, E exhibits variation as a function of the particle diameter dp. This enhanced approach better reflects the complexity of the wet scavenging process, providing a more accurate representation of particle removal during precipitation events.
Additionally, the modified equation with collision efficiency (E), as presented in Figure 1b, considers both rainfall intensity and particle characteristics with Λ, offering a significant improvement over the original CMAQ model, which bases its calculations solely on precipitation duration.
The Λ values using Equation (3) were specifically derived from this extensive dataset, as reported in [26]. Data from 28,888 h of precipitation recorded between 2015 and 2019 were analyzed. To ensure the representativeness of Λ, the median value was chosen over the mean, as it better reduces the influence of outliers and extreme values that could otherwise skew the results. As shown in Figure 2, the distribution of the scavenging coefficients (Λ) for PM2.5 across 12 cities in Korea exhibits a significant number of extreme values due to the nature of the real-world measurement data. The mean value is heavily influenced by these outliers, making it less reliable for representing central tendency. In contrast, the median provides a more stable and accurate measure of central tendency in the presence of such extreme values. A preliminary comparison between the mean and median values further supports this choice, as the median consistently provided more stable and reliable coefficients.
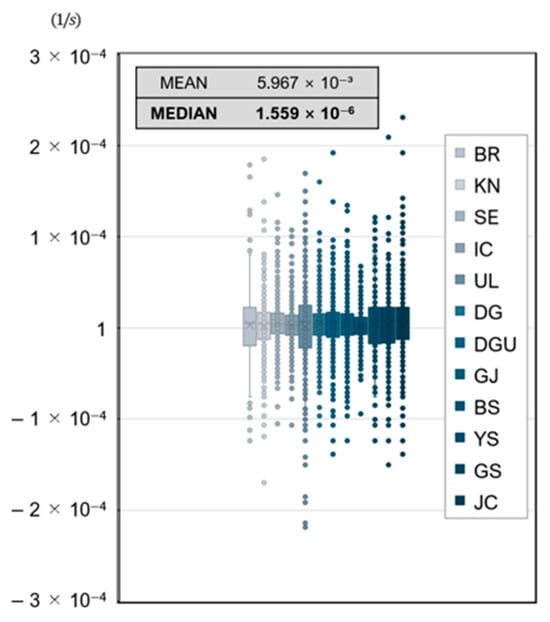
Figure 2.
Distribution of scavenging coefficient (Λ) for PM2.5 across cities, including mean and median values.
2.3. Chemical Transport Models (CTMs)
The study employed the Community Multiscale Air Quality (CMAQ) model version 5.1 for the simulation. The research concentrated on April 2018, a month characterized by significant precipitation based on observational data. To enhance the simulation’s accuracy, a pre-run period from 21 March to 31 March was included. Meteorological input data were generated using the Weather Research and Forecasting (WRF) Model, while emission data were sourced from the KORUS-AQ version 5. This modeling approach is a widely accepted methodology in air quality modeling, as it reflects realistic atmospheric conditions to predict pollutant concentrations. The modeling conditions are described in detail in Table 1. The simulation utilized stable physical settings for the meteorological and air quality modeling components.

Table 1.
CMAQ modeling options and details.
Also, Table 2 outlines the scenarios used in this study, comparing different sets of scavenging coefficients (Λ). The MOD scenario uses Λ values derived from air quality measurements in Korean cities, providing region-specific accuracy [26]. The CMAQ module was modified by applying the previously derived Λ to simulate pollutant levels across the Korean Peninsula. This allows for a comparative analysis between the original model and the improved model with the modified module [42], offering insights into the enhancements achieved. LITERATURE refers to the use of Λ from the published literature and GEOS refers to the use of Λ from Geos-chem measurements. The LITERATURE scenario employs more generalized Λ values from broader observational studies, which may not capture local conditions as precisely [43]. The GEOS scenario uses Λ from the Geos-chem model within the Goddard Earth Observing System (GEOS), offering a global perspective but potentially less local relevance. This comparison highlights the importance of using locally derived data to improve the accuracy of air quality models for the Korean Peninsula.

Table 2.
Scenario names and details employed in this study.
3. Results
3.1. Results of Simulation CTM
This study incorporated newly derived scavenging coefficient equations to modify the CMAQ model’s wet scavenging module, enabling a more comprehensive three-dimensional air quality simulation for the East Asian region. The adjusted module, based on the newly developed size-dependent scavenging formulas, produced simulation results that differentiated between model outputs using particle size-specific scavenging coefficients for PM10 and PM2.5. The simulated regional distributions of monthly average concentrations for PM10 and PM2.5 using the modified CMAQ model are presented in Figure 2. This approach facilitated a more detailed and nuanced representation of the wet scavenging processes, which are critical for accurately modeling air quality dynamics in the East Asian region.
The domain-wide average differences were found to be 5.46 µg/m³ for PM10 and 2.87 µg/m³ for PM2.5 when comparing the modified module with the original model, with these differences being consistently observed across the domain rather than localized to specific regions. The original CMAQ model employed a single, uniform scavenging coefficient that did not account for the influence of aerosol particle size on the wet scavenging process. In contrast, the revised scavenging formulas developed in this study utilize size-dependent Λ. This refined approach recognizes that the efficiency of particle removal by raindrops is strongly dependent on the size distribution of both the aerosols and the falling raindrops.
The mechanism implemented in the modified CMAQ model reduces the deposition amount by multiplying the scavenging efficiency, which is a function of particle size, with the deposition amount. This leads to an overall increase in the simulated particulate matter concentrations compared to the original model, as the size-dependent Λ better captures the complex interplay between rainfall characteristics and aerosol properties.
The Λ in the modified model is derived based on rainfall intensity, indicating that the scavenging efficiency is significantly influenced by the temporal variation in rainfall intensity. Consequently, the monthly average values of PM concentrations may exhibit a different pattern compared to the total accumulated rainfall over the same period, as the wet scavenging process is more responsive to the temporal dynamics of precipitation rather than just the total amount. This underscores the importance of incorporating size-dependent scavenging formulas that account for the influence of both rainfall characteristics and aerosol properties for accurate air quality modeling.
Additionally, there may be limitations due to variables not accounted for in the model, such as temporal variations and spatial movement, which can also affect the results. The use of a scavenging formula based on rainfall intensity means that higher rainfall intensity leads to a more significant change in the scavenging coefficient, reflecting the simulation results.
3.2. Comparison with Observational Data
The reliability of the applied wet scavenging module was evaluated through a comprehensive comparative analysis using observational data. This study examined the concentration results from the model grid as well as the time-series analysis for an air quality monitoring station in Seoul, which are presented in Figure 3. This figure illustrates the time-series analysis of PM2.5 concentrations and modeled precipitation in Seoul (Mapo) for April 2018, comparing the original CMAQ model (BASE) with three modified scenarios: MOD, LITERATURE, and GEOS. The results indicate that the GEOS scenario, represented by the blue line, deviates most significantly from the observed data, highlighting the limitations of using global-scale scavenging coefficients for local air quality modeling. The LITERATURE scenario (green line) shows a better fit, though it still falls short in capturing local conditions accurately.
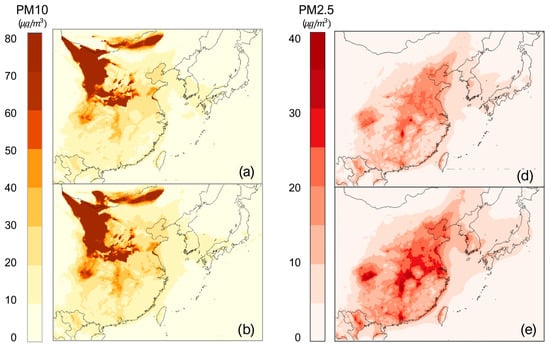
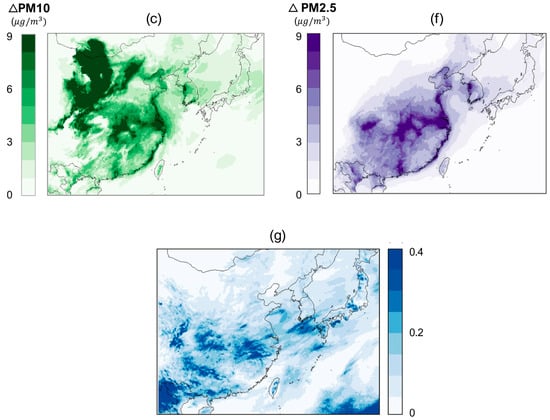
Figure 3.
BASE and modified scenario results of PM2.5 and modeled precipitant. (April 2018). (a) BASE for PM10 (b) MOD for PM10 (c) MOD10 minus BASE for PM10 (d) BASE for PM2.5 (e) MOD for PM2.5 (f) MOD2.5 minus BASE for PM2.5 (g) Modelled precipitation.
In contrast, the MOD scenario (orange line), which uses region-specific scavenging coefficients derived from in situ measurements across Korean cities, aligns most closely with the observed PM2.5 values (blue circles). This suggests that the MOD scenario effectively captures the local meteorological and pollution dynamics, providing the most accurate representation among the scenarios. The comparison underscores the importance of using locally derived data in air quality models to improve predictive accuracy and highlights the potential limitations of relying on generalized or global-scale models like GEOS for regional applications.
Additionally, this study investigated the relationship between the modeled precipitation and the corresponding concentration differences within the grid domain for the same time period, as shown in Figure 4. This supplementary analysis provided further insights into the model’s capacity to capture the dynamics between meteorological factors and pollutant concentrations, further validating the superiority of the MOD scenario in reflecting local atmospheric conditions.
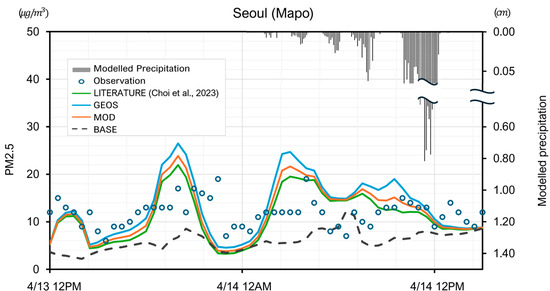
Figure 4.
Time-serial results of BASE and scenario [43] of PM2.5 and precipitant (April 2018).
The time-series analysis spanning the entire study period was carried out for both the Seoul and Busan locations, as shown in Figure 5 and Figure 6, respectively. Compared to the observational data, the modified modeling module exhibited a greater level of agreement with the measured values. This improved agreement suggests that the enhanced wet scavenging process incorporated into the revised CMAQ module better captures the real-world dynamics of particulate matter removal by precipitation. The more detailed representation of the scavenging process, which accounts for the influence of rainfall intensity and aerosol particle size, appears to provide a closer match to the observed PM concentrations at these monitoring sites. This indicates that the modified model is better able to simulate the spatiotemporal variations in pollutant levels.
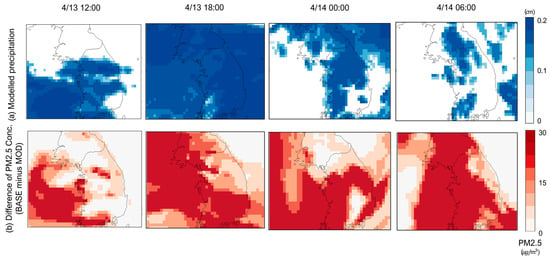
Figure 5.
Comparison of the precipitation amount and PM2.5 concentration (April 2018).
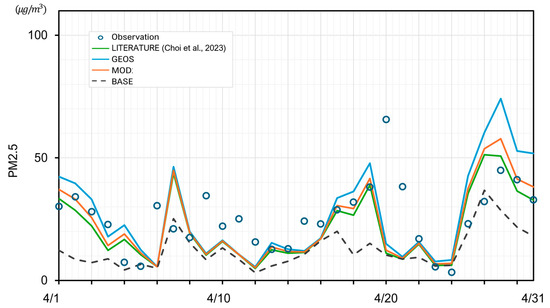
Figure 6.
Default and modified [43] CMAQ time-serial results of PM2.5 and precipitant in Seoul (April 2018).
The modified model exhibits marked improvements in capturing the spatial patterns of PM concentrations compared to the original model, as shown in Figure 7, which compares the simulation results from the original and modified CMAQ models against the measured results from air quality monitoring stations nationwide. By incorporating the size-dependent Λ, the revised CMAQ module is better able to simulate the complex interplay between rainfall characteristics and aerosol properties, leading to a more accurate representation of the wet scavenging process. This improved accuracy is particularly evident in high-concentration areas, such as the metropolitan region encompassing Seoul and Incheon, where the modified model significantly reduces the underestimations observed in the original model. The enhanced spatial distribution of simulated PM concentrations showcases the potential of the developed scavenging formulas to better reflect the real-world dynamics of air pollution and its removal by precipitation, which is crucial for effective air quality management and policy development in the region.
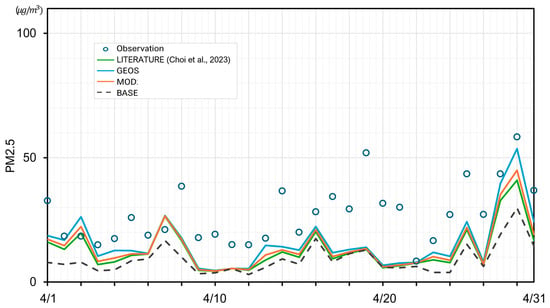
Figure 7.
Default and modified [43] CMAQ time-serial results of PM2.5 and precipitant in Busan (April 2018).
To validate the accuracy improvements achieved through the new wet scavenging coefficients, the simulated concentration values were compared against empirical air quality measurements. As shown in Figure 8, the monthly average concentrations of PM10 and PM2.5 in Seoul for April 2018 were calculated from observational data. The figure presents the observed values, the original model simulations, and the simulations utilizing the modified Λ. In Figure 9, it is evident that while all models generally underestimated the observations, the modified models exhibited some corrections, resulting in closer agreement with the measured values. Notably, the agreement for PM2.5 was significantly enhanced. These findings demonstrate the promising potential of the developed wet scavenging process in air quality modeling, which has shown the capability to improve the accuracy of simulation results [38].
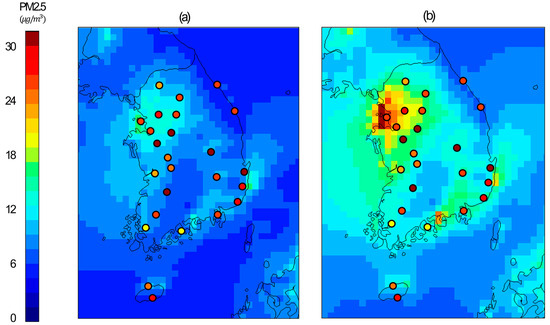
Figure 8.
Default and modified CMAQ results and measurements of PM2.5 in Korea (April 2018). (a) BASE (b) MOD.
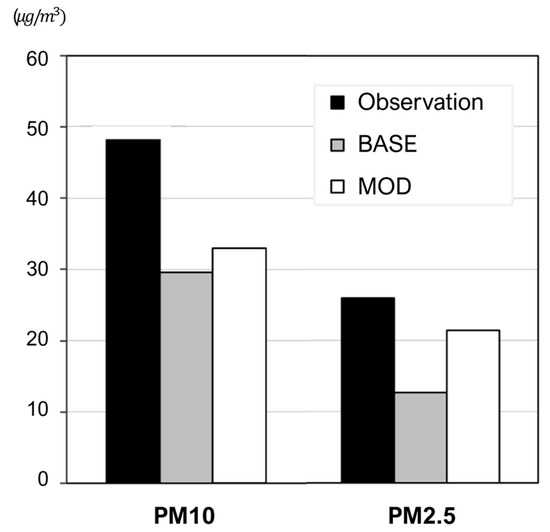
Figure 9.
Comparison of measured and simulated monthly average PM concentration in Seoul (April 2018).
Table 3 presents performance statistics comparing the BASE and MOD scenarios against observed data in Seoul (April 2018). The metrics include Mean Bias (MB), Mean Absolute Gross Error (MAGE), Mean Normalized Bias Error (MNBE), Root Mean Square Error (RMSE), and Index of Agreement (IOA). MB reflects the average difference between modeled and observed values, with negative values indicating underestimation. MAGE quantifies the average magnitude of errors regardless of their direction, while MNBE expresses bias as a percentage of the observed values. RMSE measures the standard deviation of prediction errors, and IOA gauges the overall agreement between model predictions and observations, with values closer to 1, indicating better agreement.

Table 3.
Performance statistics by scenarios compared with observation data in Seoul (April 2018).
The analysis reveals that the MOD scenario outperforms the BASE scenario. Specifically, the MOD scenario shows a reduced MB from −18.62 to −12.15 and a substantial improvement in MNBE from −38.76% to −2.50%, indicating a significant reduction in model bias. While RMSE remains nearly unchanged, the MOD scenario provides a more accurate and reliable representation of observed data, as evidenced by these metrics.
4. Discussion
This study has demonstrated the effectiveness of incorporating empirical, size-dependent wet scavenging coefficients into the CMAQ model for improved air quality predictions in the Korean Peninsula. The modified model showed significant improvements in simulating PM10 and PM2.5 concentrations, particularly in high-concentration regions and during precipitation events. The enhanced spatial distribution of simulated PM concentrations showcases the potential of the developed scavenging formulas to better reflect the real-world dynamics of air pollution and its removal by precipitation, which is crucial for effective air quality management and policy development in the region.
Moreover, this study’s findings emphasize the importance of refining air quality modeling techniques to accurately capture the dynamics of pollutant behavior in the atmosphere. The ability of the modified CMAQ model to simulate these processes more accurately highlights the potential benefits of continued model refinement. Future research should focus on the derivation of more localized scavenging coefficients, the expansion of the model’s application to different geographical areas, and its use in local-scale modeling. These efforts will continue to enhance the accuracy and applicability of air quality models, ultimately contributing to improved air quality and public health.
Finally, this study has revealed the significance of size-dependent scavenging coefficients in accurately representing wet deposition processes. This finding suggests that future air quality models should consider particle size distribution more carefully when simulating wet scavenging processes. By advancing our understanding of pollutant behavior and refining modeling techniques, this research contributes to more effective air quality management and environmental stewardship in the Korean Peninsula and beyond.
5. Conclusions
The incorporation of empirical data and the modified CMAQ module in this study has provided valuable insights into the characteristics of the scavenging process, particularly in the Korean Peninsula. The simulation results indicate significant potential for improvement in modeling PM2.5 concentrations, with differences of up to 26.7 µg/m3 lower than the original model on a monthly average. As more empirical data are collected, the model is expected to better reflect the scavenging characteristics specific to the Korean Peninsula, highlighting the importance of continuous data collection and model refinement in improving air quality predictions.
This study not only provides a framework for enhancing the modeling of air quality and meteorological conditions in the Korean Peninsula but also sets the stage for continued advancements in the field. The potential synergies between air quality modeling, empirical data collection, and policy development underscore the need for ongoing interdisciplinary research efforts to address the complex challenges of air pollution.
While this study primarily focused on regional-scale simulations, the methodology developed here holds significant potential for application at the local scale. Adapting the model for finer resolution simulations could involve modifying input parameters and enhancing the spatial and temporal resolution of meteorological and emissions data. By deriving more detailed, locally specific scavenging coefficients, the model could capture the unique regional characteristics that influence wet scavenging processes. This would enhance the model’s predictive capabilities for specific areas, offering more accurate and reliable forecasts at the local level. Such adaptations would be invaluable for local air quality management and policy-making, ensuring that interventions are based on the most precise data available.
Furthermore, the limitations of the current study, including the need for more extensive validation across diverse meteorological conditions and geographical locations, provide direction for future research. The potential application of this improved model to local-scale simulations presents an exciting avenue for further investigation, promising advancements in air quality modeling and public health outcomes.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Y.S. and C.H.J.; methodology, C.H.J.; software, D.-S.P.; validation, C.H.J., Y.S. and D.-S.P.; formal analysis, D.-S.P.; investigation, D.-S.P.; resources, Y.C.; data curation, Y.C.; writing—original draft preparation, D.-S.P.; writing—review and editing, C.H.J.; visualization, D.-S.P.; supervision, Y.S.; project administration, Y.S.; funding acquisition, C.H.J. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The Ministry of Science and ICT (No. 2020M3G1A1114617).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author. The data are not publicly available due to concerns related to the sensitive nature of the information.
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge the support of the FRIEND (Fine Particle Research Initiative in East Asia Considering National Differences) Project through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Hales, J. Wet removal of sulfur compounds from the atmosphere. Atmos. Environ. 1978, 12, 389–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Tsai, W.T.; Altwicker, E.R.; Asman, W.A.H. Numerical simulation of wet scavenging of air pollutants—II. Modeling of rain composition at the ground. Atmos. Environ. Part A Gen. Top. 1990, 24, 2485–2498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, H.S.; Ryu, M.H.; Carlsten, C. Ultrafine particles: Unique physicochemical properties relevant to health and disease. Exp. Mol. Med. 2020, 52, 318–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schumann, T. Large discrepancies between theoretical and field-determined scavenging coefficients. J. Aerosol Sci. 1989, 20, 1159–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.; Huo, T.; Yang, F.; Wang, B.; Chen, Y.; Wang, H. Characteristics of Water-soluble Inorganic Ions in Aerosol and Precipitation and their Scavenging Ratios in an Urban Environment in Southwest China. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2021, 21, 200513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.; Sera, K. The Chemical Nature of Individual Size-Resolved Raindrops and Their Residual Particles Collected During High Atmospheric Loading for PM2.5. Asian J. Atmos. Environ. 2017, 11, 176–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chate, D.M.; Murugavel, P.; Ali, K.; Singh, S.; Beig, G. Below-cloud rain scavenging of atmospheric aerosols for aerosol deposition models. Atmos. Res. 2011, 99, 528–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slinn, W. Some approximations for the wet and dry removal of particles and gases from the atmosphere. Water Air Soil Pollut. 1977, 7, 513–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levine, S.Z.; Schwartz, S.E. In-cloud and below-cloud scavenging of Nitric acid vapor. Atmos. Environ. 1982, 16, 1725–1734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volken, M.; Schumann, T. A Critical review of below-cloud aerosol scavenging results on Mt. Rigi. Water Air Soil Pollut. 1993, 68, 15–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andronache, C. Estimated variability of below-cloud aerosol removal by rainfall for observed aerosol size distributions. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2003, 3, 131–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mircea, M.; Ştefan, S.; Fuzzi, S. Precipitation scavenging coefficient: Influence of measured aerosol and raindrop size distributions. Atmos. Environ. 2000, 34, 5169–5174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCully, C.R.; Fisher, M.; Langer, G.; Rosiński, J.; Glaess, H.; Werle, D. Scavenging Action of Rain on Air-borne Particulate Matter. Ind. Eng. Chem. 1956, 48, 1512–1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Yu, Y.; He, J.; Yin, D.; Wang, B. Below-cloud scavenging of aerosol particles by precipitation in a typical valley city, northwestern China. Atmos. Environ. 2015, 102, 70–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Ge, B.; Wang, Z.; Sun, Y.; Chen, Y.; Ji, D.; Yang, T.; Ma, Z.; Cheng, N.; Hao, J.; et al. Below-cloud wet scavenging of soluble inorganic ions by rain in Beijing during the summer of 2014. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 230, 963–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.; Chai, J.; Kai, W.; Xiang, Y.; Wan, Z.; Zhang, J. Experimental and model research on chloride ion gas–solid distribution in the process of desulfurization wastewater evaporation. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 26283–26292. [Google Scholar]
- Oduber, F.; Calvo, A.I.; Blanco-Alegre, C.; Castro, A.; Alves, C.; Cerqueira, M.; Lucarelli, F.; Nava, S.; Calzolai, G.; Martin-Villacorta, J.; et al. Towards a model for aerosol removal by rain scavenging: The role of physical-chemical characteristics of raindrops. Water Res. 2021, 190, 116758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García, E.; Díaz, J.J.D.C.; Ordóñez, C.; Taboada, J. A Mathematical Approach to Selective Scavenging of the Different Classes of Typical Atmospheric Aerosols by Rainout and Health Impact. Environ. Technol. 2006, 27, 337–348. [Google Scholar]
- Bae, S.Y.; Park, R.J.; Kim, Y.P.; Woo, J. Effects of below-cloud scavenging on the regional aerosol budget in East Asia. Atmos. Environ. 2012, 58, 14–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.D.; Lee, S.; Kim, J.-J.; Lee, S.-H.; Lee, D.; Lee, J.-B.; Choi, J.-Y.; Kim, M.-J. Effect of Wet Deposition on Secondary Inorganic Aerosols Using an Urban-Scale Air Quality Model. Atmos. Environ. 2021, 12, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, C.; Isaacman-VanWertz, G. Estimated Timescales for Wet Deposition of Organic Compounds as a Function of Henry’s Law Constants. Environ. Sci. Atmos. 2022, 2, 1526–1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimadera, H.; Hayami, H.; Chatani, S.; Morino, Y.; Mori, Y.; Morikawa, T.; Yamaji, K.; Ohara, T. Sensitivity analyses of factors influencing CMAQ performance for fine particulate nitrate. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2014, 64, 374–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, H.; Zhang, K.; Vogl, C.J.; Woodward, C.S.; Easter, R.C.; Rasch, P.J.; Feng, Y.; Wang, H. Numerical coupling of aerosol emissions, dry removal, and turbulent mixing in the E3SM Atmosphere Model version 1 (EAMv1), part I: Dust budget analyses and the impacts of a revised coupling scheme. Geosci. Model Dev. 2024, 17, 1387–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hales, J. Wet Removal of Pollutants from Gaussian Plumes: Basic Linear Equations and Computational Approaches. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2002, 41, 905–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Z.; Bai, X. The Impact of Convective Transport and Wet Deposition of Airborne Dust Particles on the Numerical Simulation of Northeast Asian Storms. In Proceedings of the 2006 IEEE International Symposium on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, Denver, CO, USA, 31 July–4 August 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Park, D.; Choi, Y.; Sunwoo, Y.; Jung, C. A Study on the Wet Scavenging Characteristics of Atmospheric Aerosol in the Korean Peninsula Using NAMIS (National Ambient Air Quality Monitoring Information System) Data and Its Application to Air Quality Modeling System. Korean Soc. Atmos. Environ. 2023, 39, 437–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieto, P.G.; García, B.; Dı, J.; Braña, M.R. Parametric study of selective removal of atmospheric aerosol by below-cloud scavenging. Atmos. Environ. 1994, 28, 2335–2342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, W.T.; Altwicker, E.R. Numerical simulation of wet scavenging of air pollutants—I. Modeling of sequential precipitation rates at the ground. Atmos. Environ. Part A Gen. Top. 1990, 24, 2473–2483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yalamov, Y.I.; Vasiljeva, L.; Schukin, E. The study of various mechanisms of in-cloud scavenging of large, moderately large, and small aerosol particles. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1977, 62, 503–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pruppacher, H.R.; Jaenicke, R. The processing of water vapor and aerosols by atmospheric clouds, a global estimate. Atmos. Res. 1995, 38, 283–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mircea, M.; Ştefan, S. A theoretical study of the microphysical parameterization of the scavenging coefficient as a function of precipitation type and rate. Atmos. Environ. 1998, 32, 2931–2938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, J.; Misra, A.; Sundar, S.; Naresh, R. Effect of rain on removal of a gaseous pollutant and two different particulate matters from the atmosphere of a city. Math. Comput. Model. 2008, 48, 832–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naresh, R.; Sundar, S.; Shukla, J. Modeling the removal of gaseous pollutants and particulate matters from the atmosphere of a city. Nonlinear Anal. Real World Appl. 2007, 8, 337–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berthet, S.; Leriche, M.; Pinty, J.; Cuesta, J.; Pigeon, G. Scavenging of aerosol particles by rain in a cloud resolving model. Atmos. Res. 2010, 96, 325–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, L.; Moran, M.D. Bulk or modal parameterizations for below-cloud scavenging of fine, coarse, and giant particles by both rain and snow. J. Adv. Model. Earth Syst. 2014, 6, 1301–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seinfeld, J.H.; Pandis, S.N. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics: From Air Pollution to Climate Change; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Chate, D.M.; Kamra, A.K. Collection efficiencies of large water drops collecting aerosol particles of various densities. Atmos. Environ. 1997, 31, 1631–1635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazir, M.; Khan, F.; Husain, T. Revised estimates for continuous shoreline fumigation: A PDF approach. J. Hazard. Mater. 2005, 118, 53–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, W.; Stroud, C.; Zhang, L. Cloud Processing of Gases and Aerosols in Air Quality Modeling. Atmosphere 2011, 2, 567–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binkowski, F.S.; Roselle, S.J. Models-3 Community Multiscale Air Quality (CMAQ) model aerosol component 1. Model description. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2003, 108, 4183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, C.H.; Lee, H.-M.; Park, D.; Yoon, Y.J.; Choi, Y.; Um, J.; Lee, S.S.; Lee, J.Y.; Kim, Y.P. Parameterization of below-cloud scavenging for polydisperse fine mode aerosols as a function of rain intensity. J. Environ. Sci. 2023, 132, 43–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, C.H.; Kim, Y.P.; Lee, K. A moment model for simulating raindrop scavenging of aerosols. J. Aerosol Sci. 2003, 34, 1217–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.; Jung, C.H.; Ahn, J.; Park, S.-M.; Han, K.M.; Jun, J.; Lee, G.; Kim, J.; Lim, Y.; Kang, K.-S.; et al. Empirical estimation of size-resolved scavenging coefficients derived from in-situ measurements at background sites in Korea during 2013–2020. Atmos. Res. 2023, 295, 106971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).