Qualitative and Quantitative Analyses of Automotive Exhaust Plumes for Remote Emission Sensing Application Using Gas Schlieren Imaging Sensor System
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
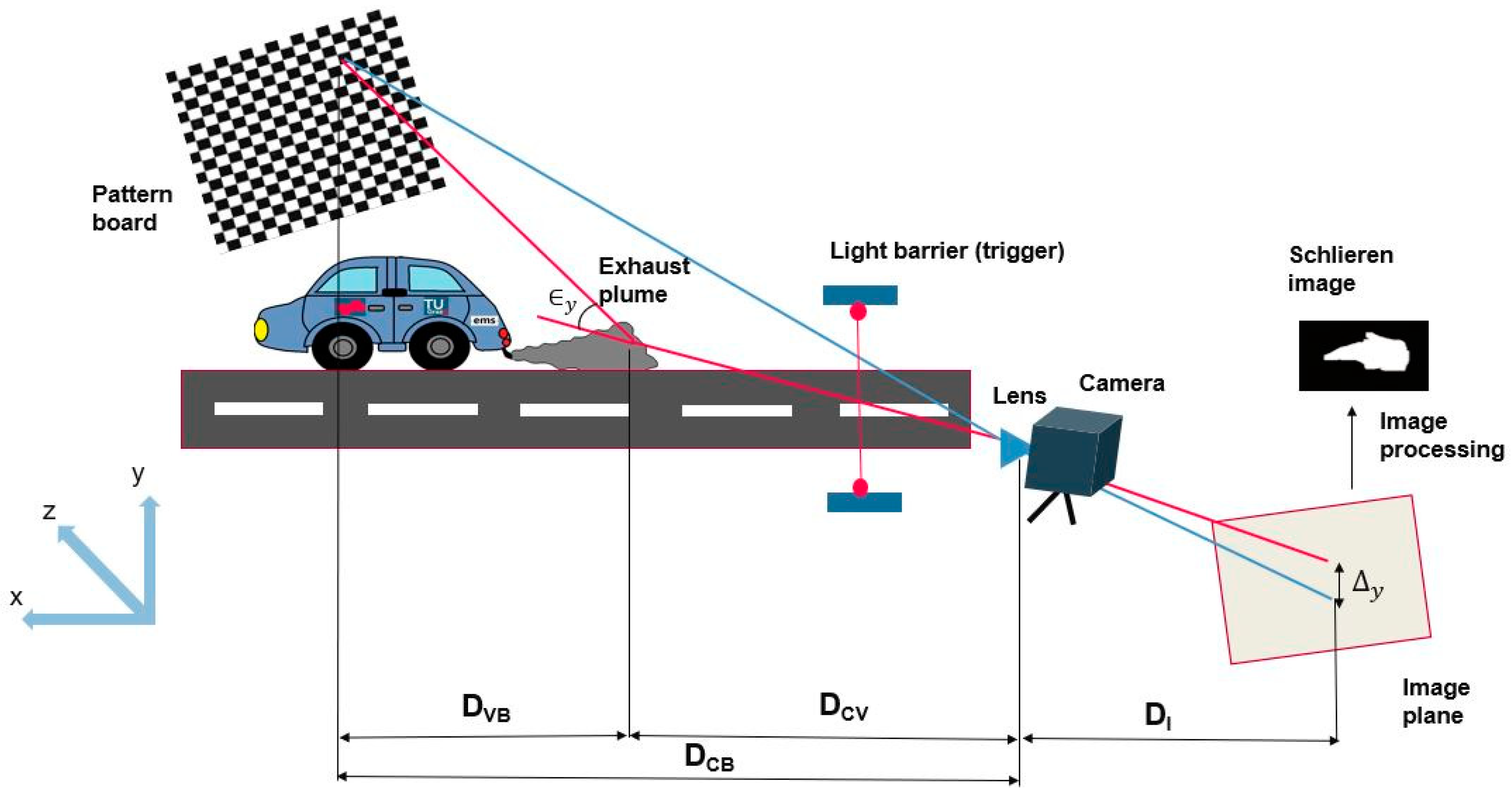
2.1. GSIS System
2.2. On-Road Measurements
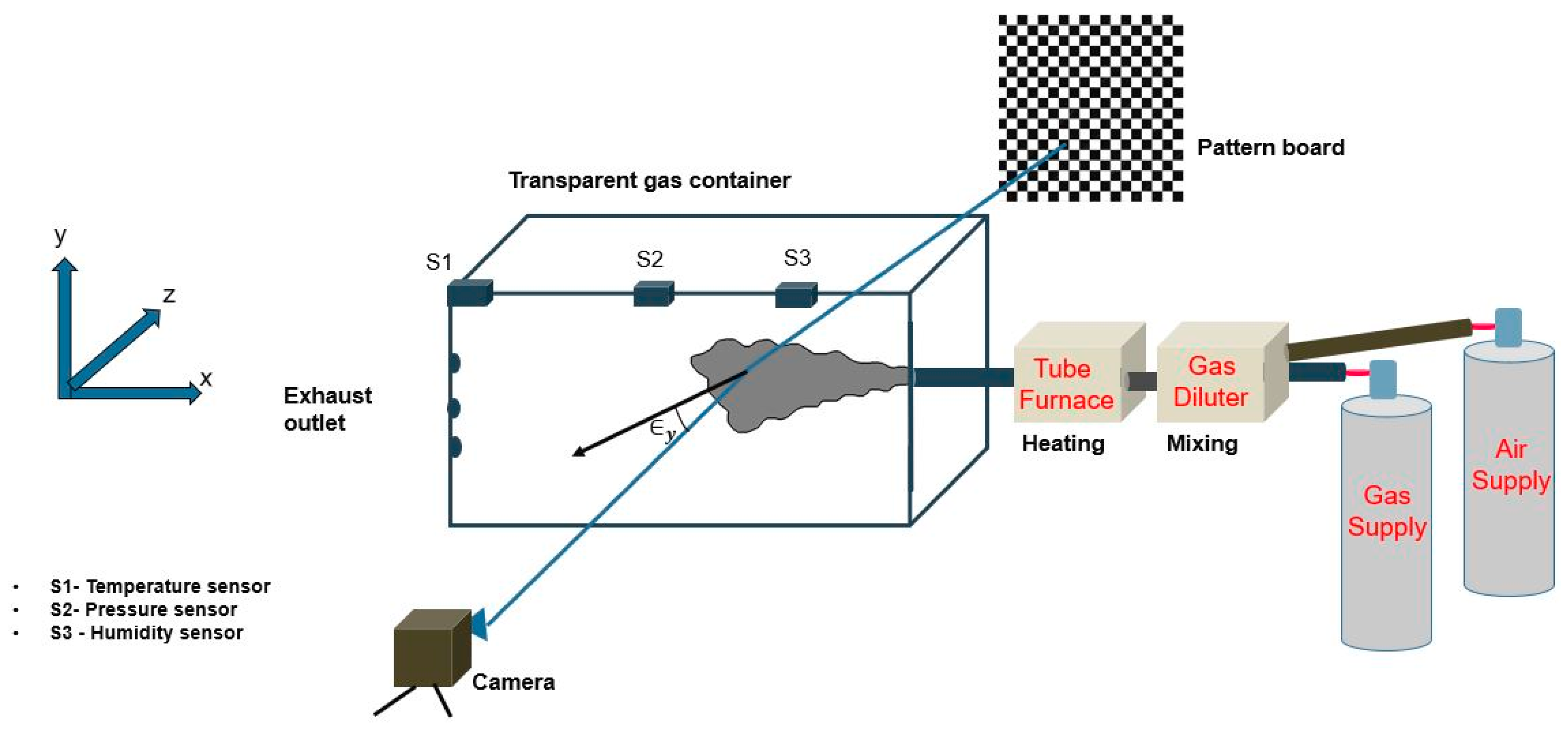
2.3. Laboratory Characterization
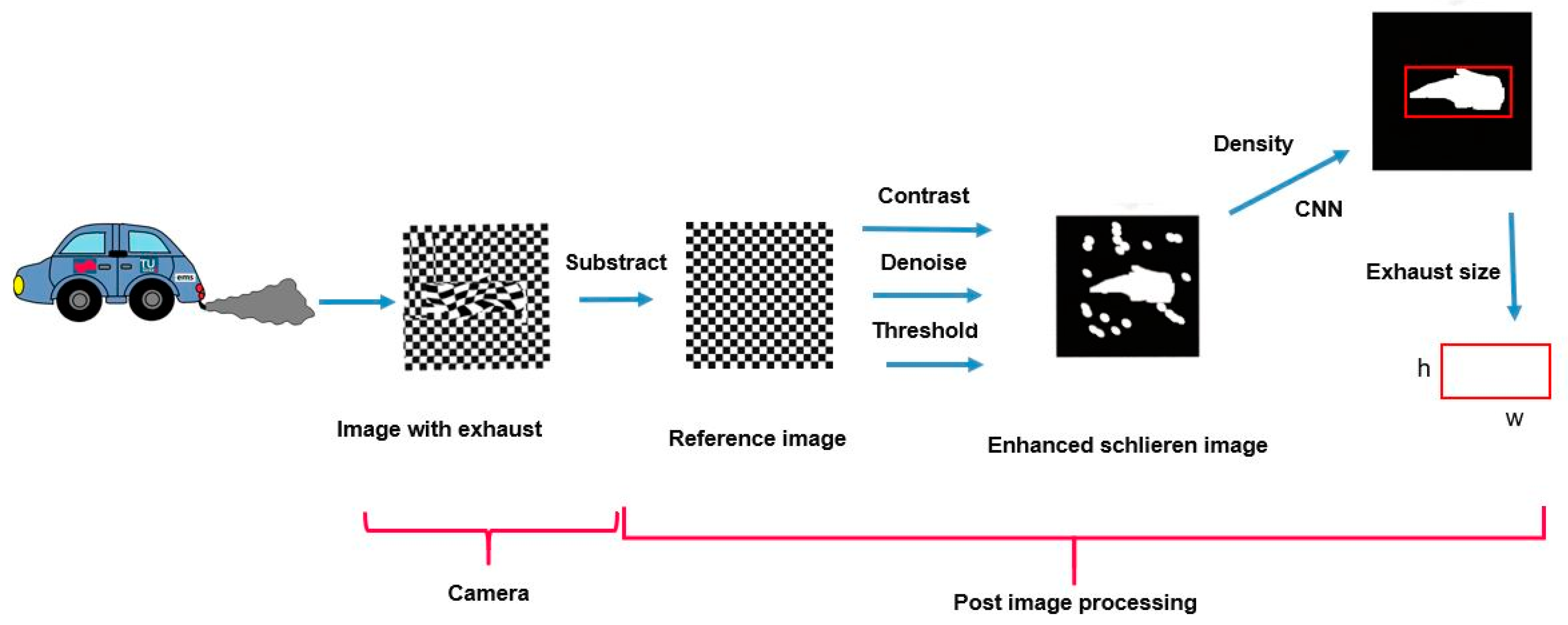
2.4. Image Processing and Exhaust Plume Detection
2.4.1. Exhaust Plume Detection with Density
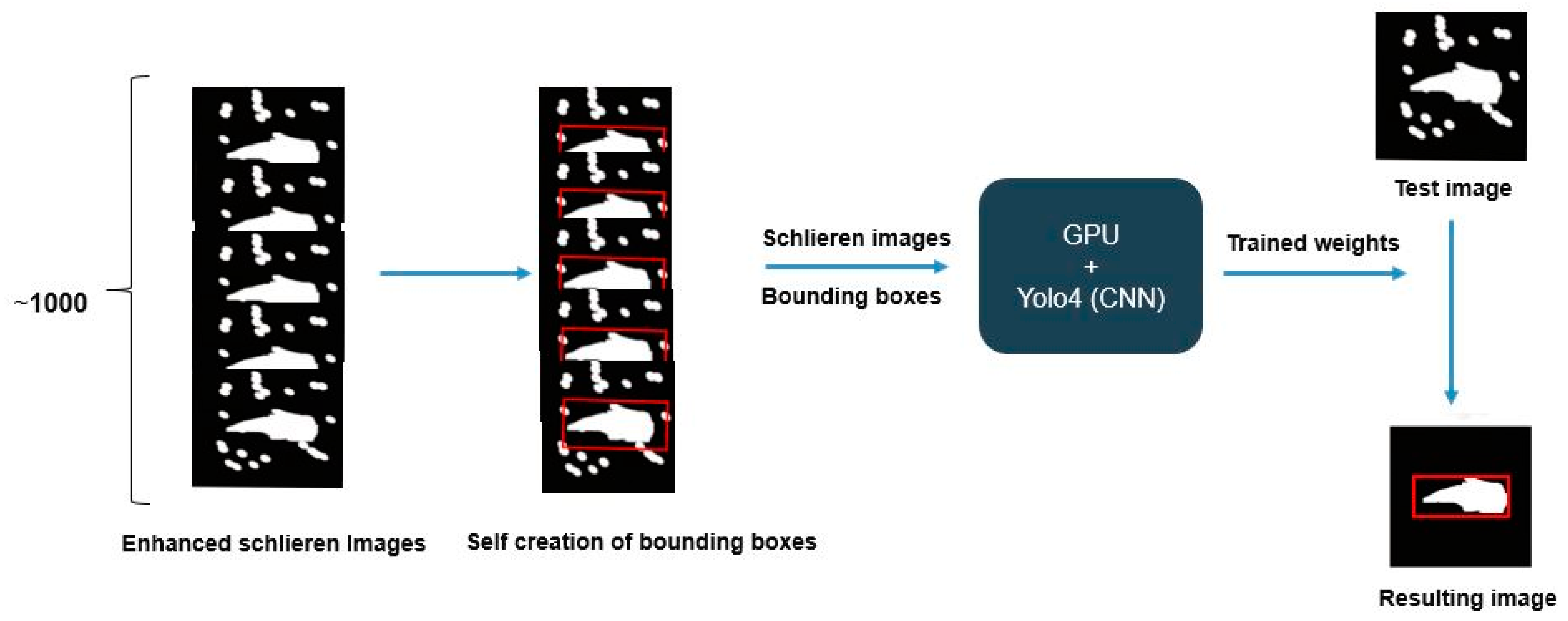
2.4.2. Exhaust Plume Detection with CNN
2.4.3. Exhaust Plume Size Calculation
2.5. GSIS—Quantitative Analysis
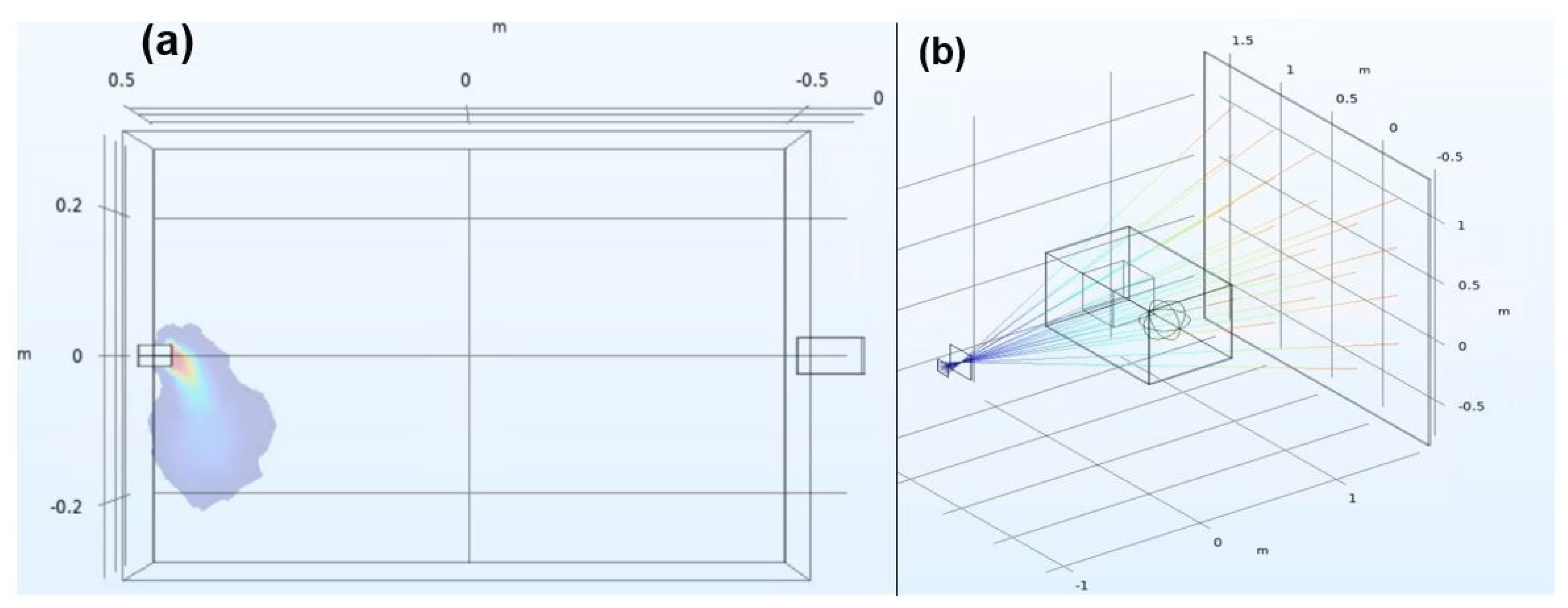
2.6. Modeling GSIS System
2.7. Calculating Direct Concentration of Pollutants Using GSIS
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Modeling vs. Laboratory Results
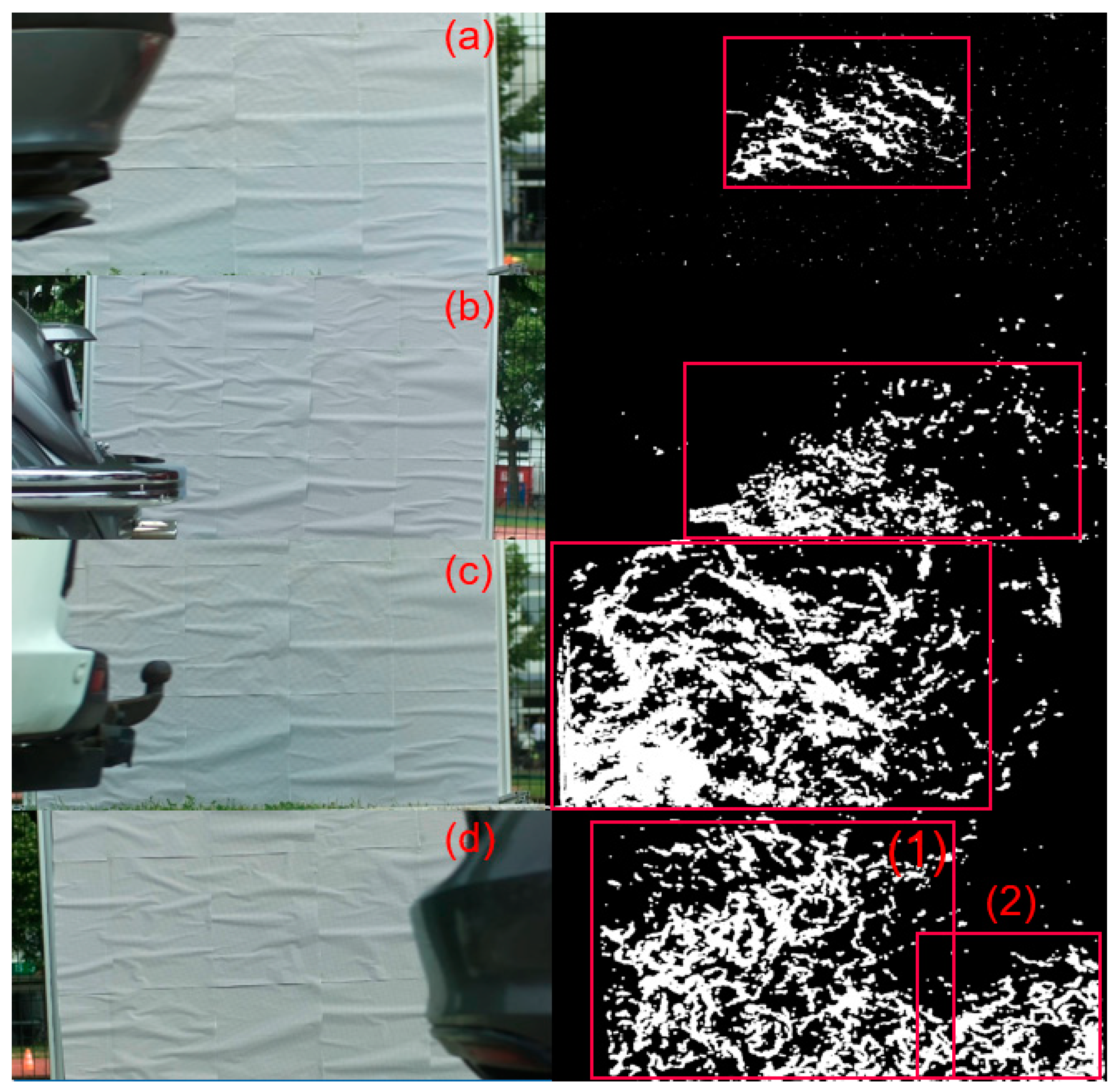
3.2. Exhaust Plume Size Meausrement of Passing Cars
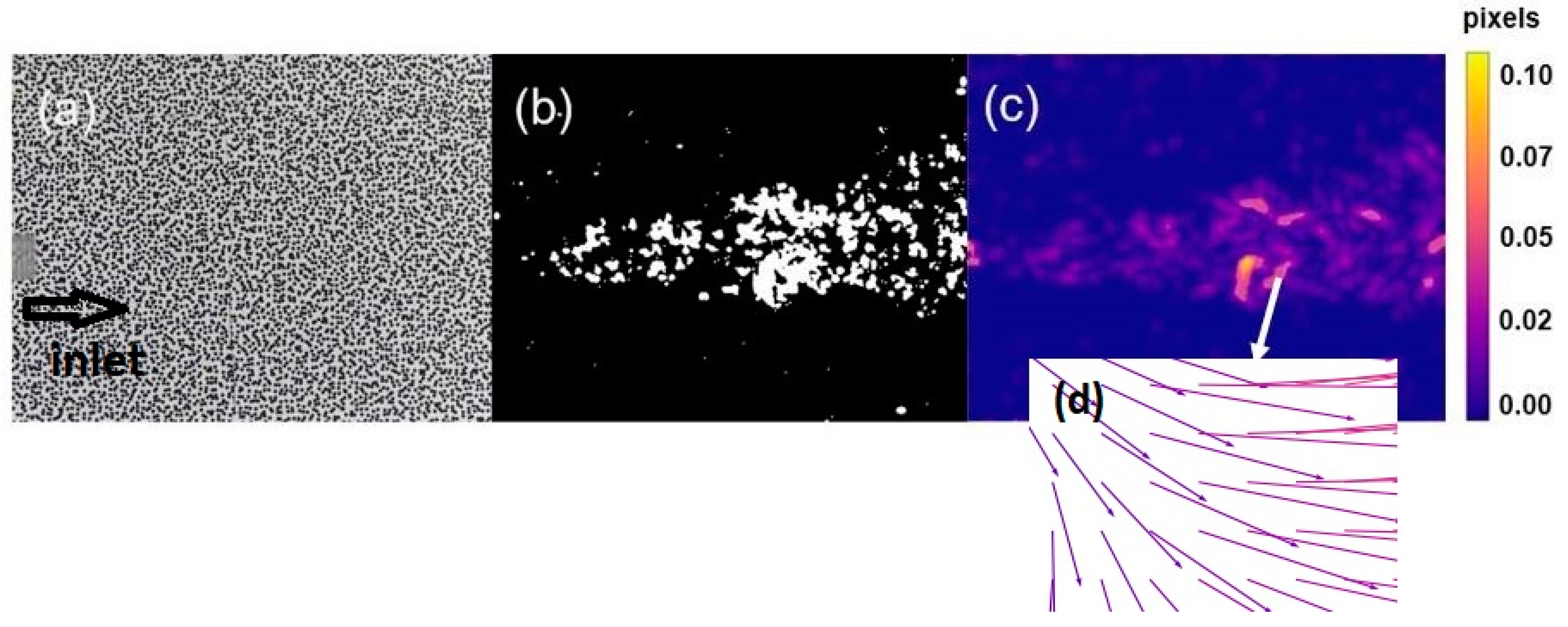
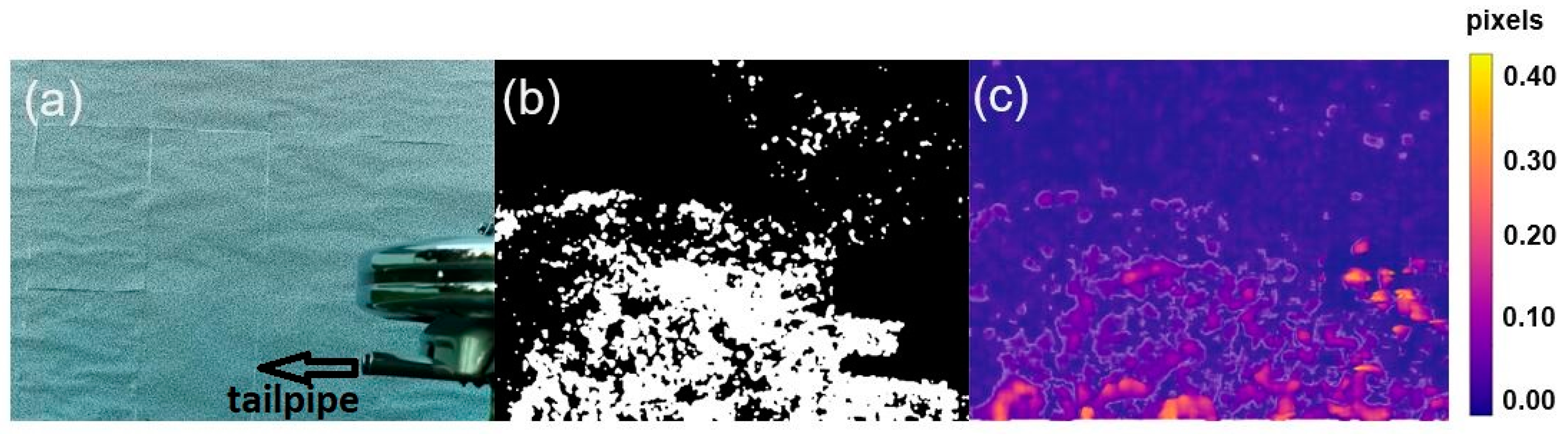
3.3. Displacement Fields of Vehicle Exhaust and Gas Flows
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bainschab, M.; Schriefl, M.A.; Bergmann, A. Particle number measurements within periodic technical inspections: A first quantitative assessment of the influence of size distributions and the fleet emission reduction. Atmos. Environ. X 2020, 8, 100095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davison, J.; Bernard, Y.; Borken-Kleefeld, J.; Farren, N.J.; Hausberger, S.; Sjödin, Å.; Tate, J.E.; Vaughan, A.R.; Carslaw, D.C. Distance-based emission factors from vehicle emission remote sensing measurements. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 739, 139688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bishop, G.A.; Starkey, J.R.; Ihlenfeldt, A.; Williams, W.J.; Stedman, D.H. IR long-path photometry: A remote sensing tool for automobile emissions. Anal. Chem. 1989, 61, 671A–677A. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gastaldi, M.; Meneguzzer, C.; Giancristofaro, R.A.; Gecchele, G.; Lucia, L.D.; Prati, M.V. On-road measurement of CO2 vehicle emissions under alternative forms of intersection control. Transp. Res. Procedia 2017, 27, 476–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; He, H.; Lu, D.; Zhou, D.; Lu, C.; Fang, X.; Peng, Z. Evaluation of CO2 and NOx emissions from container diesel trucks using a portable emissions measurement system. Build. Environ. 2024, 252, 111266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knoll, M.; Penz, M.; Schmidt, C.; Pöhler, D.; Rossi, T.; Casadei, S.; Bernard, Y.; Hallquist, Ǻ.M.; Sjödin, Ǻ.; Bergmann, A. Evaluation of the point sampling method and inter-comparison of remote emission sensing systems for screening real-world car emissions. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 932, 171710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sjödin, Å. On-road emission performance of late-model TWC-cars as measured by remote sensing. Air Waste 1994, 44, 397–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephens, R.D.; Cadle, S.H. Remote sensing measurements of carbon monoxide emissions from on-road vehicles. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 1991, 41, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, J.; Nelson, D.R.; Bahan, T.P.; Polchin, G.C.; Jack, M.D. Unmanned integrated optical remote emissions sensor (RES) for motor vehicles. U.S. Patent 5,726,450, 10 March 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Jack, M.D.; Ahlgren, W.; Bahan, T.P.; Gray, M.N.; Hanson, J.L.; Heidt, T.L.; Huerta, F.A.; Kennedy, A.; Nelson, D.R.; Paneral, A.J.; et al. Remote and on-board instrumentation for Automotive Emissions Monitoring. SAE Tech. Pap. Ser. 1995, 104, 796–809. [Google Scholar]
- Schifter, I.; Díaz, L.; Durán, J.; Guzmán, E.; Chávez, O.; López-Salinas, E. Remote Sensing Study of emissions from motor vehicles in the metropolitan area of Mexico City. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2002, 37, 395–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, T.L.; Ning, Z. On-road remote sensing of diesel vehicle emissions measurement and emission factors estimation in Hong Kong. Atmos. Environ. 2005, 39, 6843–6856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Borken-Kleefeld, J. Real-driving emissions from cars and light commercial vehicles—Results from 13 years remote sensing at Zurich/CH. Atmos. Environ. 2014, 88, 157–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borken-Kleefeld, J.; Dallmann, T. Remote Sensing of Motor Vehicle Exhaust Emissions; The International Council on Clean Transportation: Washington, DC, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Ropkins, K.; DeFries, T.H.; Pope, F.; Green, D.C.; Kemper, J.; Kishan, S.; Fuller, G.W.; Li, H.; Sidebottom, J.; Crilley, L.R.; et al. Evaluation of edar vehicle emissions remote sensing technology. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 609, 1464–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruening, C.; Bonnel, P.; Clairotte, M.; Giechaskiel, B.; Valverde Morales, V.; Zardini, A.; Carriero, M. Potential of Remote Sensing Devices (RSDs) to Screen Vehicle Emissions; Publications Office of the European Union: Luxembourg, 2019; ISBN 978-92-76-11820-6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hooftman, N.; Ligterink, N.; Bhoraskar, A. Analysis of the 2019 Flemish Remote Sensing Campaign; The Flemish Government—Flanders Environment Agency—Team Air Quality Policy: Aalst, Belgium, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Aosaf, M.R.; Wang, Y.; Du, K. Comparison of the emission factors of air pollutants from gasoline, CNG, LPG and diesel fueled vehicles at Idle Speed. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 305, 119296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hooke, R.; Allestry, J.; Martyn, J. Micrographia, or, some physiological descriptions of minute bodies made by magnifying glasses: With observations and inquiries thereupon. 1665. Available online: https://www.biodiversitylibrary.org/item/15485#page/5/mode/thumb (accessed on 8 August 2024).
- Weinstein, L.M.; Settles, G.S. Schlieren. Opt. Metrol. Fluids Combust. Solids 2003, 1–36. [Google Scholar]
- Foucault, L. Memoire sur la construction des telescopes en verre argente. Ann. I’Observatoire Imp. Paris 1859, 5, 197–237. [Google Scholar]
- Toepler, A. Observations after a New Optical Method in Contribution to the Experimental Physics; M. Cohen & Son: Bonn, Germany, 1864. [Google Scholar]
- Schardin, H. Toepler’s Schlieren Method: Basic Principles for Its Use and Quantitative Evaluation; Navy Dept., David Taylor Model Basin: Washington, DC, USA, 1947. [Google Scholar]
- Sutherland, B.R.; Dalziel, S.B.; Hughes, G.O.; Linden, P.F. Visualization and measurement of internal waves by ‘synthetic schlieren’. Part 1. Vertically Oscillating Cylinder. J. Fluid Mech. 1999, 390, 93–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meier, G.E.A. Hintergrund-Schlierenmeßverfahren. DE 199 42 856, 21 June 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Raffel, M.; Tung, C.; Richard, H.; Yu, Y.; Meier, G.E.A. Background oriented stereoscopic schlieren (BOSS) for full-scale helicopter vortex characterization. In Proceedings of the 9th International Symposium on Flow Visualization, Edinburgh, UK, 22–25 August 2000; Volume 450, pp. 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Richard, H.; Raffel, M.; Rein, M.; Kompenhans, J.; Meier, G.E. Demonstration of the applicability of a background oriented Schlieren (BOS) method. Laser Tech. Fluid Mech. 2002, 145–156. [Google Scholar]
- Elsinga, G.E.; van Oudheusden, B.W.; Scarano, F.; Watt, D.W. Assessment and application of quantitative schlieren methods: Calibrated color Schlieren and background oriented schlieren. Exp. Fluids 2003, 36, 309–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popova, E.; Kompenhans, J.; Skornyakova, N. Investigation of the Accuracy of the Background Oriented Schlieren Method. In Proceedings of the 13th International Symposium on Flow Visualization, Nice, France, 1–4 July 2008; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Yevtikhiyeva, O.A.; Skornyakova, N.M.; Udalov, A.V. An investigation of the error of the background schlieren method. Meas. Tech. 2009, 52, 1300–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schröder, A.; Over, B.; Geisler, R.; Bulit, A.; Schwane, R.; Kompenhans, J. Measurements of Density Fields in Micro Nozzle Plumes in Vacuum by Using an Enhanced Tomographic Background Oriented Schlieren (BOS) Technique; Institute of Aerodynamics and Flow Technology: Gottingen, Germany, 2009; pp. 1–272. [Google Scholar]
- Hargather, M.J.; Settles, G.S. Background-oriented Schlieren visualization of heating and ventilation flows: HVAC-Bos. HVAC R Res. 2011, 17, 771–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hargather, M.J.; Settles, G.S. A comparison of three quantitative Schlieren techniques. Opt. Lasers Eng. 2012, 50, 8–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizukaki, T.; Tsukada, H.; Wakabayashi, K.; Matsumura, T.; Nakayama, Y. Quantitative visualization of open-air explosions by using background-oriented schlieren with natural background. In 28th International Symposium on Shock Waves; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; pp. 465–470. [Google Scholar]
- Raffel, M. Background-oriented schlieren (BOS) techniques. Exp. Fluids 2015, 56, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolas, F.; Todoroff, V.; Plyer, A.; Le Besnerais, G.; Donjat, D.; Micheli, F.; Champagnat, F.; Cornic, P.; Le Sant, Y. A direct approach for instantaneous 3D density field reconstruction from background-oriented schlieren (BOS) measurements. Exp. Fluids 2015, 57, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Settles, G.S.; Hargather, M.J. A review of recent developments in Schlieren and Shadowgraph Techniques. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2017, 28, 042001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aminfar, A.; Cobian-Iñiguez, J.; Ghasemian, M.; Rosales Espitia, N.; Weise, D.R.; Princevac, M. Using background-oriented schlieren to visualize convection in a propagating wildland fire. Combust. Sci. Technol. 2019, 192, 2259–2279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, H.; Song, Y.; Ji, Y.; Li, Z.; He, A. Direct background-oriented schlieren tomography using radial basis functions. Opt. Express 2022, 30, 19100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amjad, S.; Soria, J.; Atkinson, C. Three-dimensional density measurements of a heated jet using laser-speckle tomographic background-oriented schlieren. Exp. Therm. Fluid Sci. 2023, 142, 110819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, P.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, X.; Dong, S.; Chen, Q.; Yuan, Y. Reconstruction method of 3D turbulent flames by background-oriented Schlieren Tomography and analysis of time asynchrony. Fire 2023, 6, 417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gojani, A.; Kamishi, B.; Obayashi, S. Measurement sensitivity and resolution for background oriented Schlieren during image recording. J. Vis. 2013, 16, 201–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mier, F.A.; Hargather, M.J. Color gradient background-oriented Schlieren imaging. Exp. Fluids 2016, 57, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, M.; Lu, Y.; Hou, W.; Matskin, M. Yolov4-object: An efficient model and method for Object Discovery. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE 45th Annual Computers, Software, and Applications Conference (COMPSAC), Madrid, Spain, 12–16 July 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Vinnichenko, N.A.; Uvarov, A.V.; Plaksina, Y.Y. Accuracy of background oriented schlieren for different background patterns and means of refractive index reconstruction. In Proceedings of the 15th International Symposium on Flow Visualization, Minsk, Belarus, 25–28 June 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, S.M.; Kim, W.H.; Côté, D.; Park, C.-W.; Lee, H. Blood cell assisted in vivo particle image velocimetry using the confocal laser scanning microscope. Opt. Express 2011, 19, 4357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farnebäck, G. Two-frame motion estimation based on polynomial expansion. Image Anal. 2003, 2749, 363–370. [Google Scholar]
- Popa, D.; Udrea, F. Towards integrated mid-infrared gas sensors. Sensors 2019, 19, 2076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





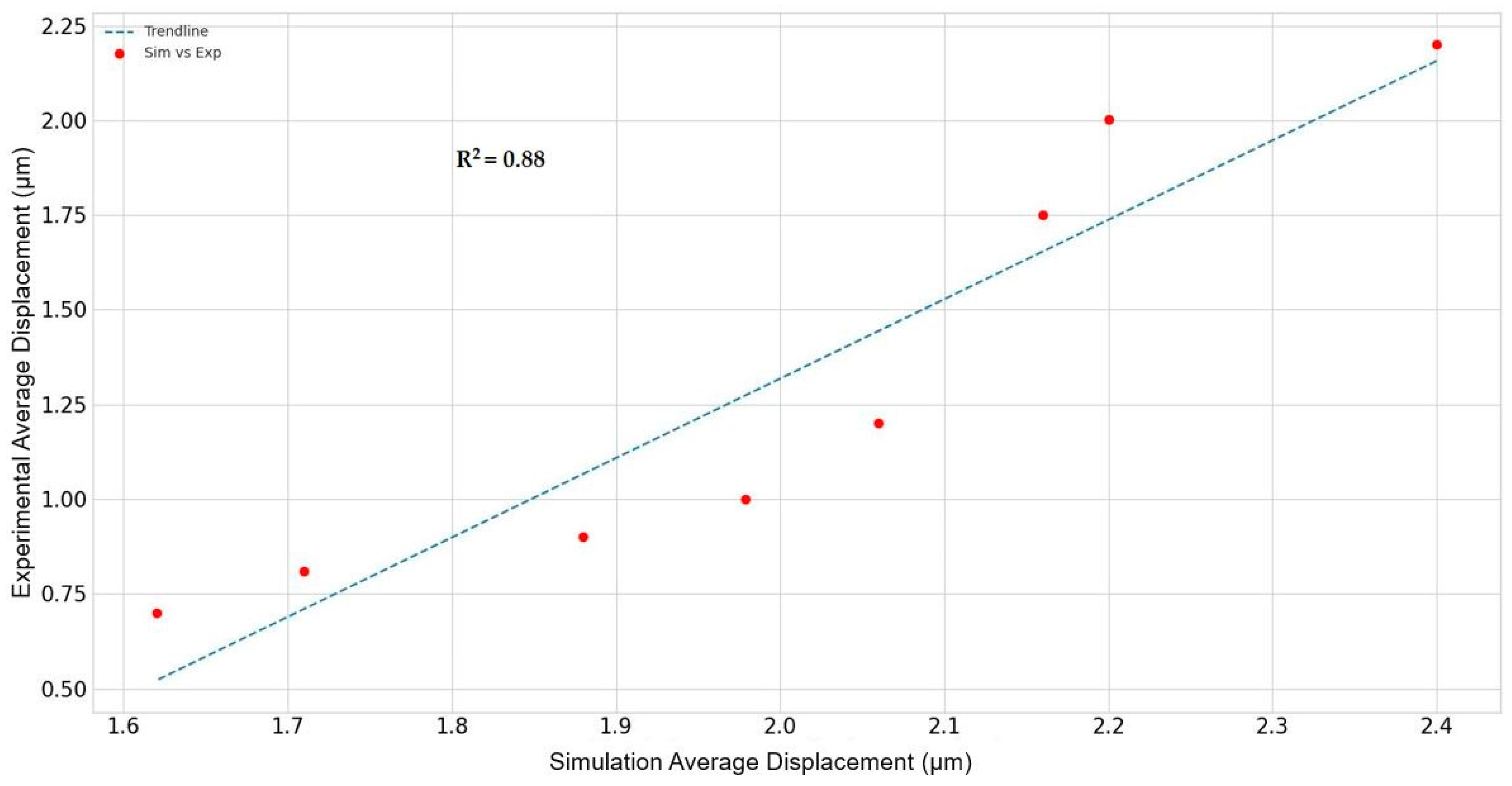
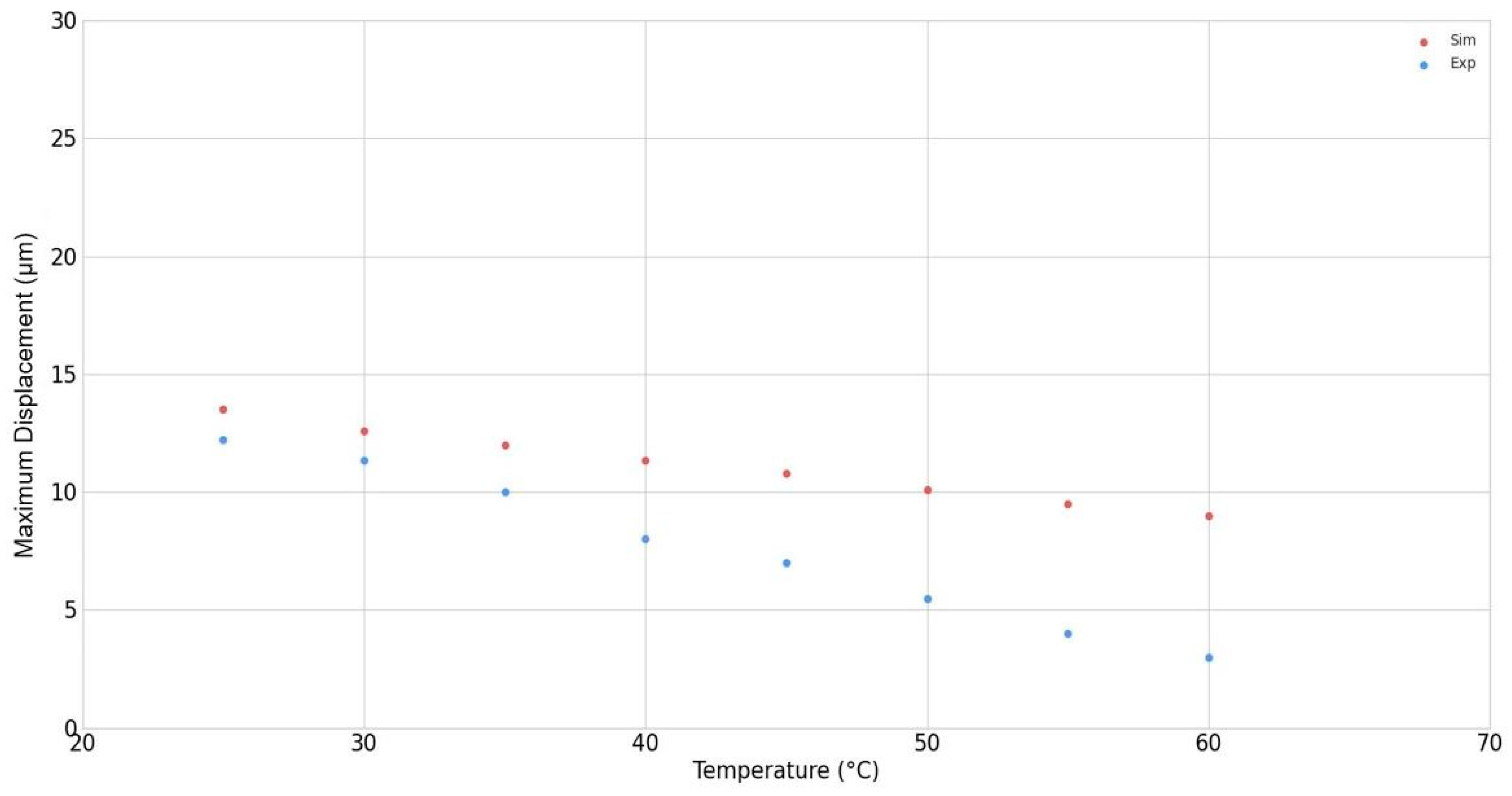
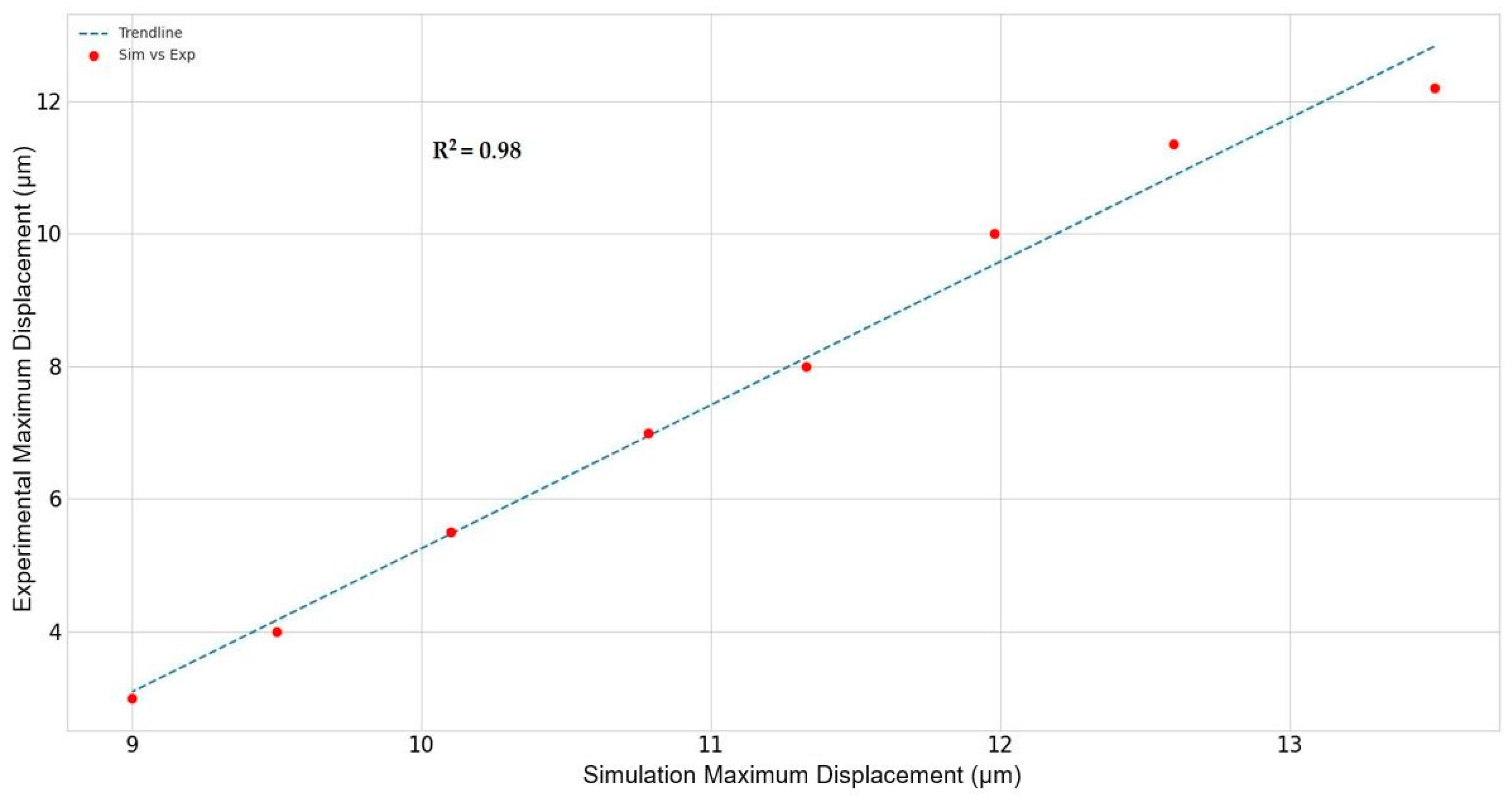

| Temperature (°C) | Average Displacement (µm) (~50,000 Displaced Pixels) | RSE (%), Average ± 95% Confidence Interval (µm) |
|---|---|---|
| 25 | 2.200 | 0.321, 2.213, 2.186 |
| 30 | 2.002 | 0.321, 2.014, 1.989 |
| 35 | 1.750 | 0.360, 1.762, 1.738 |
| 40 | 1.200 | 0.350, 1.208, 1.192 |
| 45 | 1.001 | 0.392, 1.008, 0.993 |
| 50 | 0.901 | 0.201, 0.904, 0.897 |
| 55 | 0.810 | 0.175, 0.813, 0.807 |
| 60 | 0.700 | 0.180, 0.702, 0.698 |
| Temperature (°C) | Average Displacement (µm) (~50,000 Displaced Pixels) | RSE (%), Average ± 95% Confidence Interval (µm) |
|---|---|---|
| 25 | 2.400 | 0.540, 2.425, 2.374 |
| 30 | 2.200 | 0.560, 2.224, 2.175 |
| 35 | 2.160 | 0.550, 2.183, 2.136 |
| 40 | 2.060 | 0.540, 2.081, 2.038 |
| 45 | 1.979 | 0.550, 2.000, 1.957 |
| 50 | 1.880 | 0.550, 1.900, 1.859 |
| 55 | 1.710 | 0.580, 1.729, 1.690 |
| 60 | 1.620 | 0.580, 1.638, 0.601 |
| Vehicle | Height of Plume (m) ± 7% | Width of Plume (m) ± 7% |
|---|---|---|
| (a) | 0.25 | 0.41 |
| (b) | 0.36 | 0.70 |
| (c) | 0.45 | 0.67 |
| (d-1) | 0.45 | 0.57 |
| (d-2) | 0.35 | 0.43 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Imtiaz, H.H.; Schaffer, P.; Liu, Y.; Hesse, P.; Bergmann, A.; Kupper, M. Qualitative and Quantitative Analyses of Automotive Exhaust Plumes for Remote Emission Sensing Application Using Gas Schlieren Imaging Sensor System. Atmosphere 2024, 15, 1023. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15091023
Imtiaz HH, Schaffer P, Liu Y, Hesse P, Bergmann A, Kupper M. Qualitative and Quantitative Analyses of Automotive Exhaust Plumes for Remote Emission Sensing Application Using Gas Schlieren Imaging Sensor System. Atmosphere. 2024; 15(9):1023. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15091023
Chicago/Turabian StyleImtiaz, Hafiz Hashim, Paul Schaffer, Yingjie Liu, Paul Hesse, Alexander Bergmann, and Martin Kupper. 2024. "Qualitative and Quantitative Analyses of Automotive Exhaust Plumes for Remote Emission Sensing Application Using Gas Schlieren Imaging Sensor System" Atmosphere 15, no. 9: 1023. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15091023
APA StyleImtiaz, H. H., Schaffer, P., Liu, Y., Hesse, P., Bergmann, A., & Kupper, M. (2024). Qualitative and Quantitative Analyses of Automotive Exhaust Plumes for Remote Emission Sensing Application Using Gas Schlieren Imaging Sensor System. Atmosphere, 15(9), 1023. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15091023





