Observed Impacts of Ground-Mounted Photovoltaic Systems on the Microclimate and Soil in an Arid Area of Gansu, China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Domain and Background
2.2. Data Monitoring and Analysis Methods
3. Results and Discussion
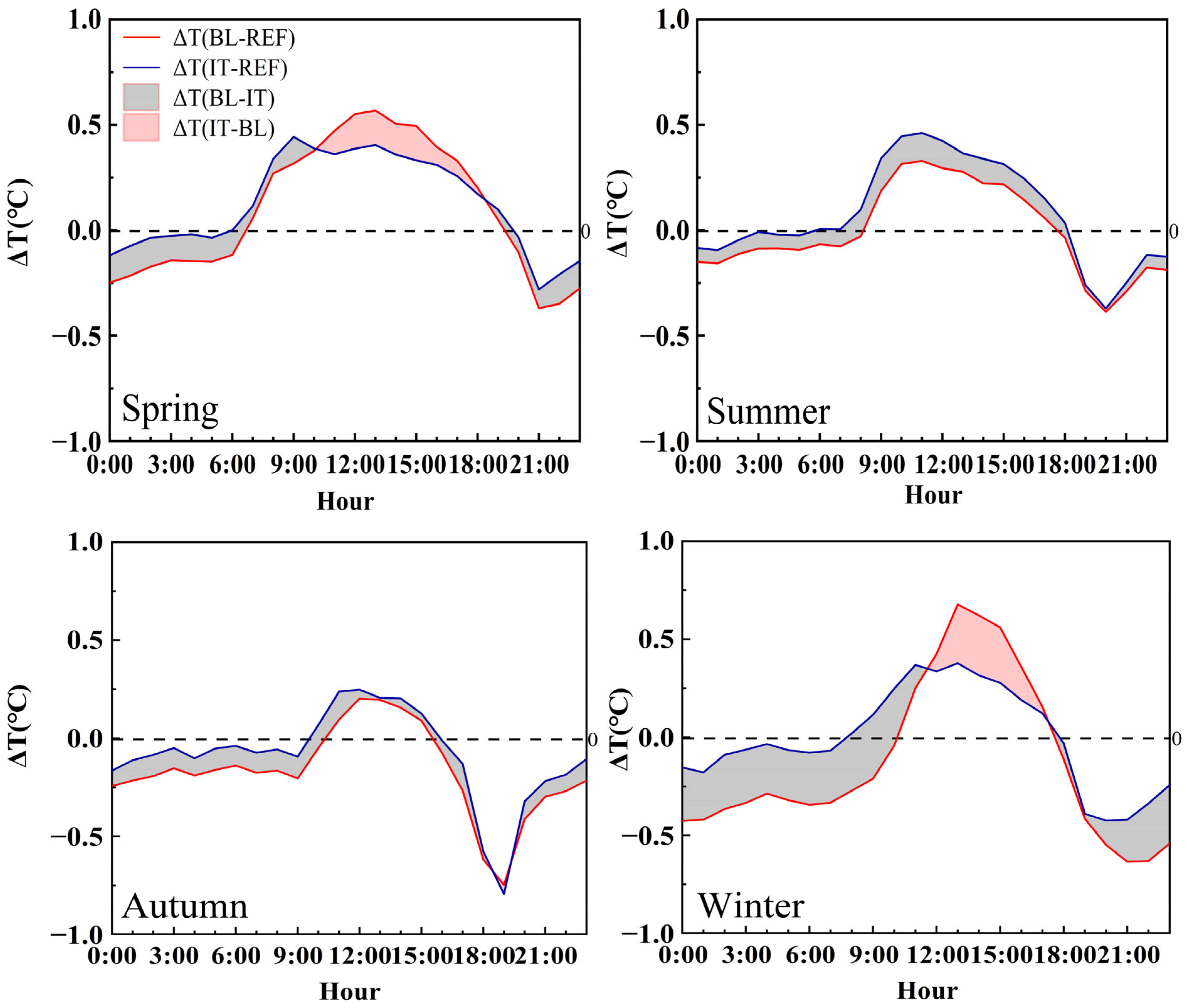
3.1. The Temperature
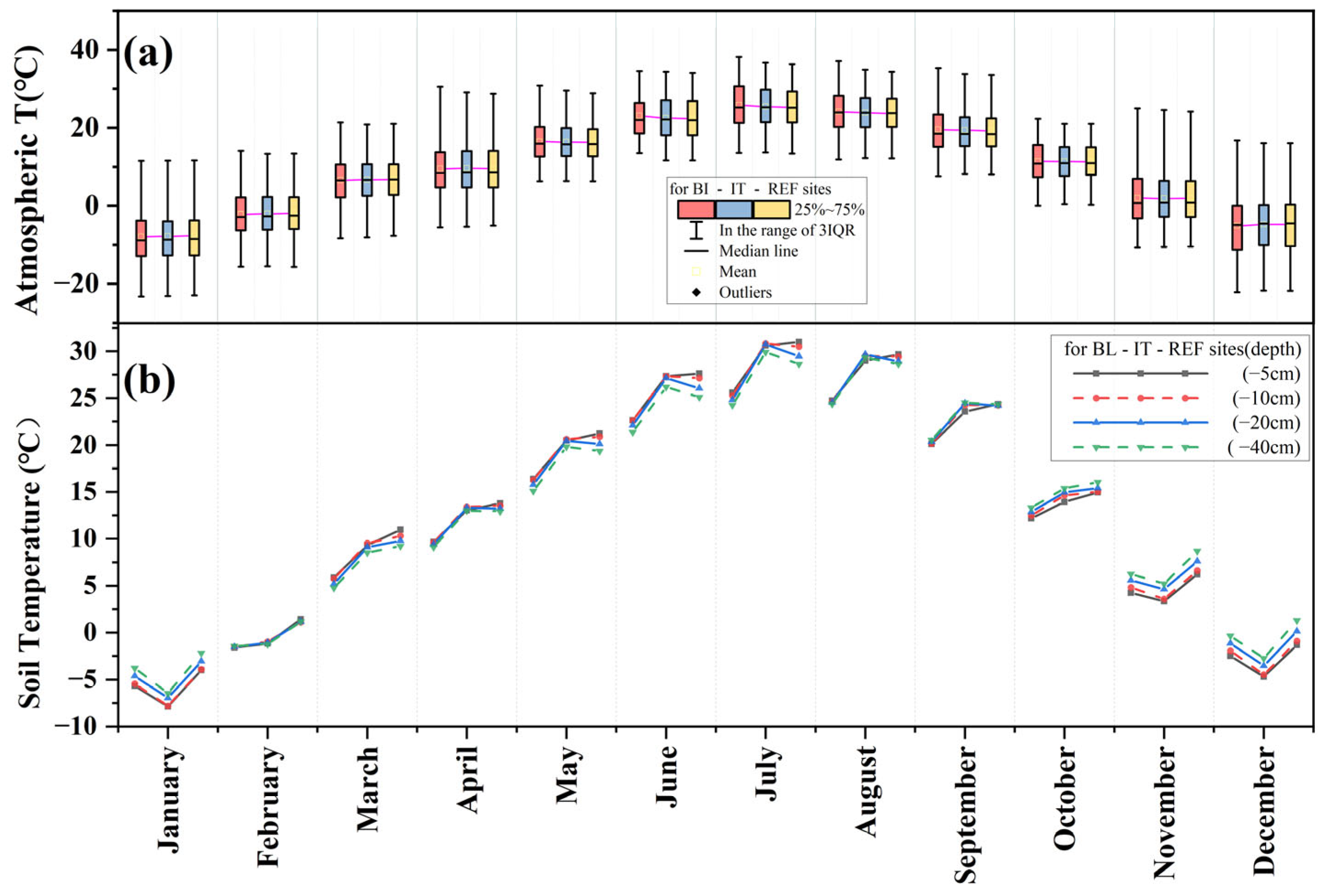
3.1.1. Atmospheric Temperature
3.1.2. Soil Temperature
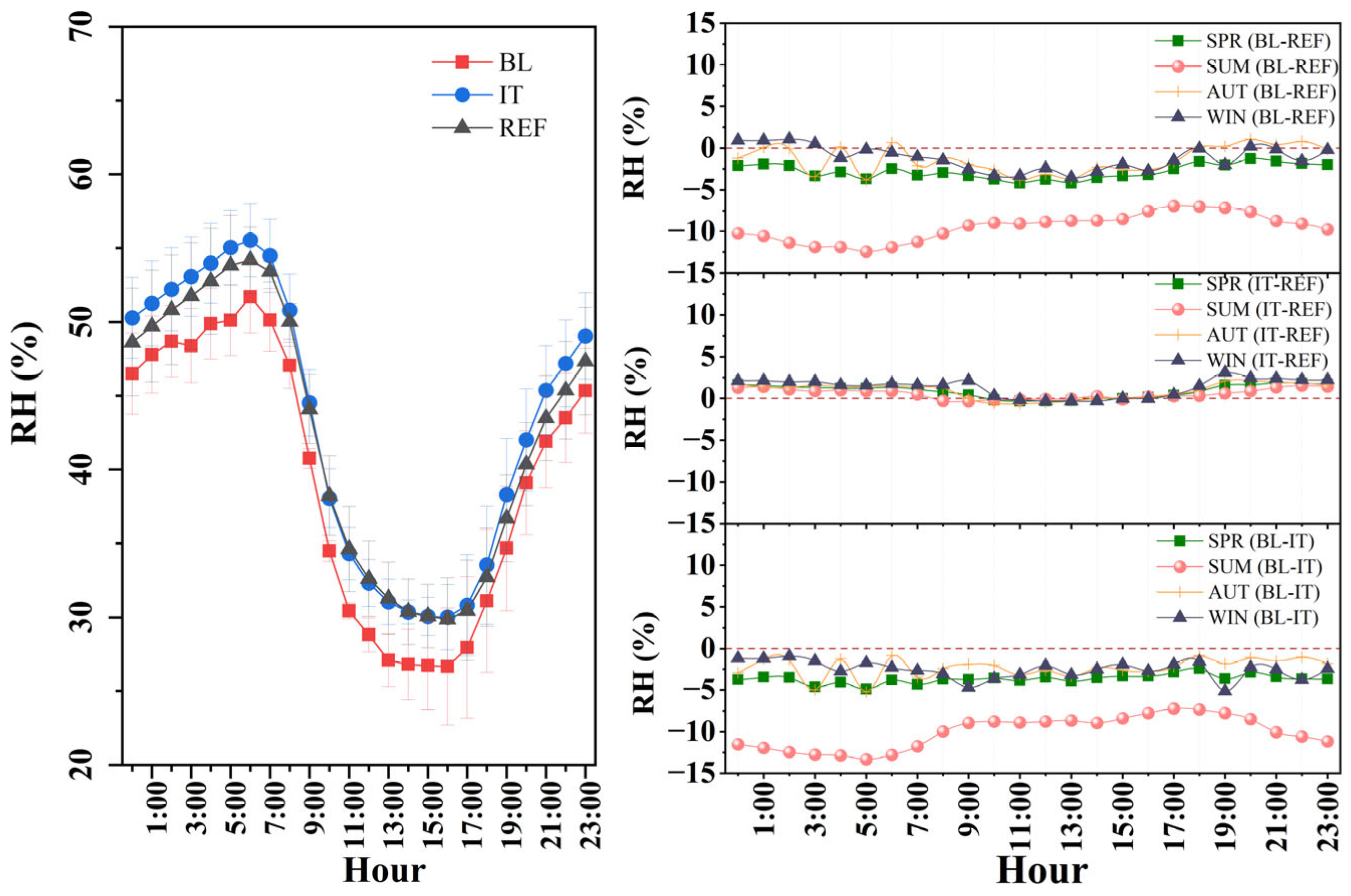
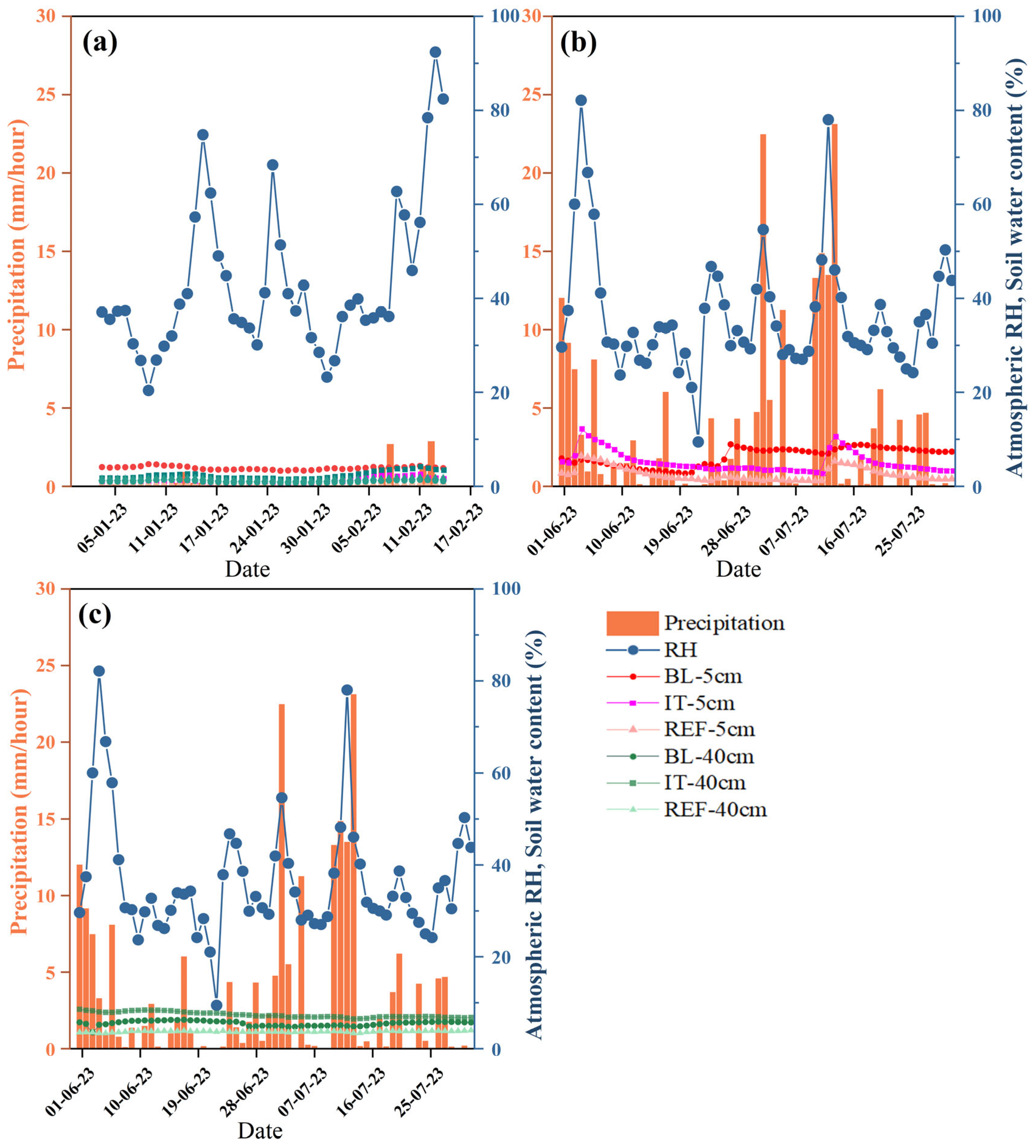
3.2. Relative Humidity
3.3. Soil Water Content
3.4. Wind Speed and Direction
4. Conclusions
- Atmospheric Temperature and Relative Humidity
- Soil Temperature and Soil Water Content
- Wind Speed and Direction
- Implications and Future Research
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Ground-mounted photovoltaic | GMPV |
| Atmospheric temperature | AT |
| Relative humidity | RH |
| Soil temperature | ST |
| Soil water content | SWC |
| Below line site | BL |
| Interval site | IT |
| Reference site | REF |
| Photovoltaic | PV |
References
- Wang, Y.; Wang, R.; Tanaka, K.; Ciais, P.; Penuelas, J.; Balkanski, Y.; Sardans, J.; Hauglustaine, D.; Liu, W.; Xing, X.; et al. Accelerating the energy transition towards photovoltaic and wind in China. Nature 2023, 619, 761–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cherp, A.; Vinichenko, V.; Tosun, J.; Gordon, J.A.; Jewell, J. National growth dynamics of wind and solar power compared to the growth required for global climate targets. Nat. Energy 2021, 6, 742–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez, R.R.; Armstrong, A.; Burney, J.; Ryan, G.; Moore-O’Leary, K.; Diédhiou, I.; Grodsky, S.M.; Saul-Gershenz, L.; Davis, R.; Macknick, J.; et al. Techno–ecological synergies of solar energy for global sustainability. Nat. Sustain. 2019, 2, 560–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Gao, X.; Chen, B. The Impact of Utility-Scale Photovoltaics Plant on Near Surface Turbulence Characteristics in Gobi Areas. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Energy Administration. Available online: https://www.nea.gov.cn/2024-02/28/c_1310765696.htm (accessed on 6 April 2024).
- Hua, Y.; Chai, J.; Chen, L.; Liu, P. The Influences of the Desert Photovoltaic Power Station on Local Climate and Environment: A Case Study in Dunhuang Photovoltaic Industrial Park, Dunhuang City, China in 2019. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez, R.R.; Easter, S.B.; Murphy-Mariscal, M.L.; Maestre, F.T.; Tavassoli, M.; Allen, E.B.; Barrows, C.W.; Belnap, J.; Ochoa-Hueso, R.; Ravi, S.; et al. Environmental impacts of utility-scale solar energy. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2014, 29, 766–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsoutsos, T.; Frantzeskaki, N.; Gekas, V. Environmental impacts from the solar energy technologies. Energy Policy 2005, 33, 289–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez, R.R.; Hoffacker, M.K.; Murphy-Mariscal, M.L.; Wu, G.C.; Allen, M.F. Solar energy development impacts on land cover change and protected areas. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 13579–13584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barron-Gafford, G.A.; Minor, R.L.; Allen, N.A.; Cronin, A.D.; Brooks, A.E.; Pavao-Zuckerman, M.A. The Photovoltaic Heat Island Effect: Larger solar power plants increase local temperatures. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 35070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Gao, X.; Lv, F.; Hui, X.; Ma, L.; Hou, X. Study on the local climatic effects of large photovoltaic solar farms in desert areas. Sol. Energy 2017, 144, 244–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Yue, S.; Zhou, X.; Guo, M.; Wang, J.; Ren, L.; Yuan, B. Observational Study on the Impact of Large-Scale Photovoltaic Development in Deserts on Local Air Temperature and Humidity. Sustainability 2020, 12, 3403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, R.; Shen, Y.; Luo, Y.; Wang, B.; Yang, Z.; Guo, P. Observed surface radiation and temperature impacts from the large-scale deployment of photovoltaics in the barren area of Gonghe, China. Renew. Energy 2018, 118, 131–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fthenakis, V.; Yu, Y. Analysis of the potential for a heat island effect in large solar farms. In Proceedings of the Photovoltaic Specialists Conference, Tampa, FL, USA, 16–21 June 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, D.Y.; Ma, L.; Qu, J.J.; Zhao, S.P.; Yu, Y.; Tan, L.; Xiao, J.H. Effect of large Photovoltaic power station microclimate of desert region in Gonghe Basin. Bull. Soil Water Conserv. 2017, 37, 15–21. [Google Scholar]
- Yue, S.; Guo, M.; Zou, P.; Wu, W.; Zhou, X. Effects of photovoltaic panels on soil temperature and moisture in desert areas. Env. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2021, 28, 17506–17518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yue, S.; Wu, W.; Zhou, X.; Ren, L.; Wang, J. The Influence of Photovoltaic Panels on Soil Temperature in the Gonghe Desert Area. Environ. Eng. Sci. 2021, 38, 910–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W. Observational Study on the Impact of Large-Scale Photovoltaic Development on Soil Temperature. In Proceedings of the IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science, Nanjing, China, 25–27 June 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Broadbent, A.M.; Krayenhoff, E.S.; Georgescu, M.; Sailor, D.J. The Observed Effects of Utility-Scale Photovoltaics on Near-Surface Air Temperature and Energy Balance. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2019, 58, 989–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, R.Q.; Huang, Z.; Cheng, Z.; López-Vicente, M.; Ma, X.R.; Wu, G.L. Solar photovoltaic panels significantly promote vegetation recovery by modifying the soil surface microhabitats in an arid sandy ecosystem. Land Degrad. Dev. 2019, 30, 2177–2186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Rbaihat, R.; Alahmer, H.; Al-Manea, A.; Altork, Y.; Alrbai, M.; Alahmer, A. Maximizing efficiency in solar ammonia–water absorption refrigeration cycles: Exergy analysis, concentration impact, and advanced optimization with GBRT machine learning and FHO optimizer. Int. J. Refrig. 2024, 161, 31–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, S.Y.; Al-Amir, Q.R.; Hamzah, H.K.; Ali, F.H.; Abed, A.M.; Al-Manea, A.; Egab, K.; Al-Rbaihat, R.; Saleh, K.; Alahmer, A. Investigation of natural convection and entropy generation of non-Newtonian flow in molten polymer-filled odd-shaped cavities using finite difference lattice Boltzmann method. Numer. Heat Transf. Part B Fundam. 2024, 29, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuting, Z.; Zhen, Z.; Jihu, M. Spatial-temporal variation of vegetation coverage in Wuwei City from 2011 to 2020. Shelter. Technol. 2022, 1, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhiguo, Z.; Hongjie, K. Spatial-temporal changes and driving forces of land use/cover in Wuwei City from 2000 to 2020. Sci. Technol. Eng. 2023, 23, 8579–8587. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Z.Y.; Hou, A.P.; Chang, C.; Huang, X.; Shi, D.Q.; Wang, Z.F. Environmental impacts of large-scale CSP plants in northwestern China. Environ. Sci. -Process. Impacts 2014, 16, 2432–2441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teuwel. SD60/SDI12 Data Collector. Available online: https://www.truwel.com/truwel_Product_2062740003.html (accessed on 19 July 2024).
- Teuwel. Product Center. Available online: https://www.truwel.com/truwel_ProClass.html (accessed on 19 July 2024).
- Jiang, J.; Gao, X.; Lv, Q.; Li, Z.; Li, P. Observed impacts of utility-scale photovoltaic plant on local air temperature and energy partitioning in the barren areas. Renew. Energy 2021, 174, 157–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armstrong, A.; Ostle, N.J.; Whitaker, J. Solar park microclimate and vegetation management effects on grassland carbon cycling. Environ. Res. Lett. 2016, 11, 074016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambert, Q.; Bischoff, A.; Cueff, S.; Cluchier, A.; Gros, R. Effects of solar park construction and solar panels on soil quality, microclimate, CO2 effluxes, and vegetation under a Mediterranean climate. Land Degrad. Dev. 2021, 32, 5190–5202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seneviratne, S.I.; Hirschi, M.; Schwingshackl, C. Quantifying Spatiotemporal Variations of Soil Moisture Control on Surface Energy Balance and Near-Surface Air Temperature. J. Clim. 2017, 30, 7105–7124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makaronidou, M. Assessment on the Local Climate Effects of Solar Parks. Ph.D. Thesis, Lancaster University, Bailrigg, UK, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Yun, J.D.; Cui, X.X.; Meng, Z.J. Study on Particle Size Characteristics of Surface Soil under Photovoltaic Panel in Kubuqi Desert. J. Inn. Mong. For. Sci. Technol. 2019, 45, 22–29. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, Z.; Liu, S.; Fu, J.; Wang, Q.; Wang, F.; Sun, T.; Liu, S.; Wang, F. Effect of desert photovoltaic on sand prevention and control—Taking Gansu Gulang Zhenfa photovoltaic DC field as an example. In Proceedings of the IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science, Weihai, China, 28–30 August 2020. [Google Scholar]

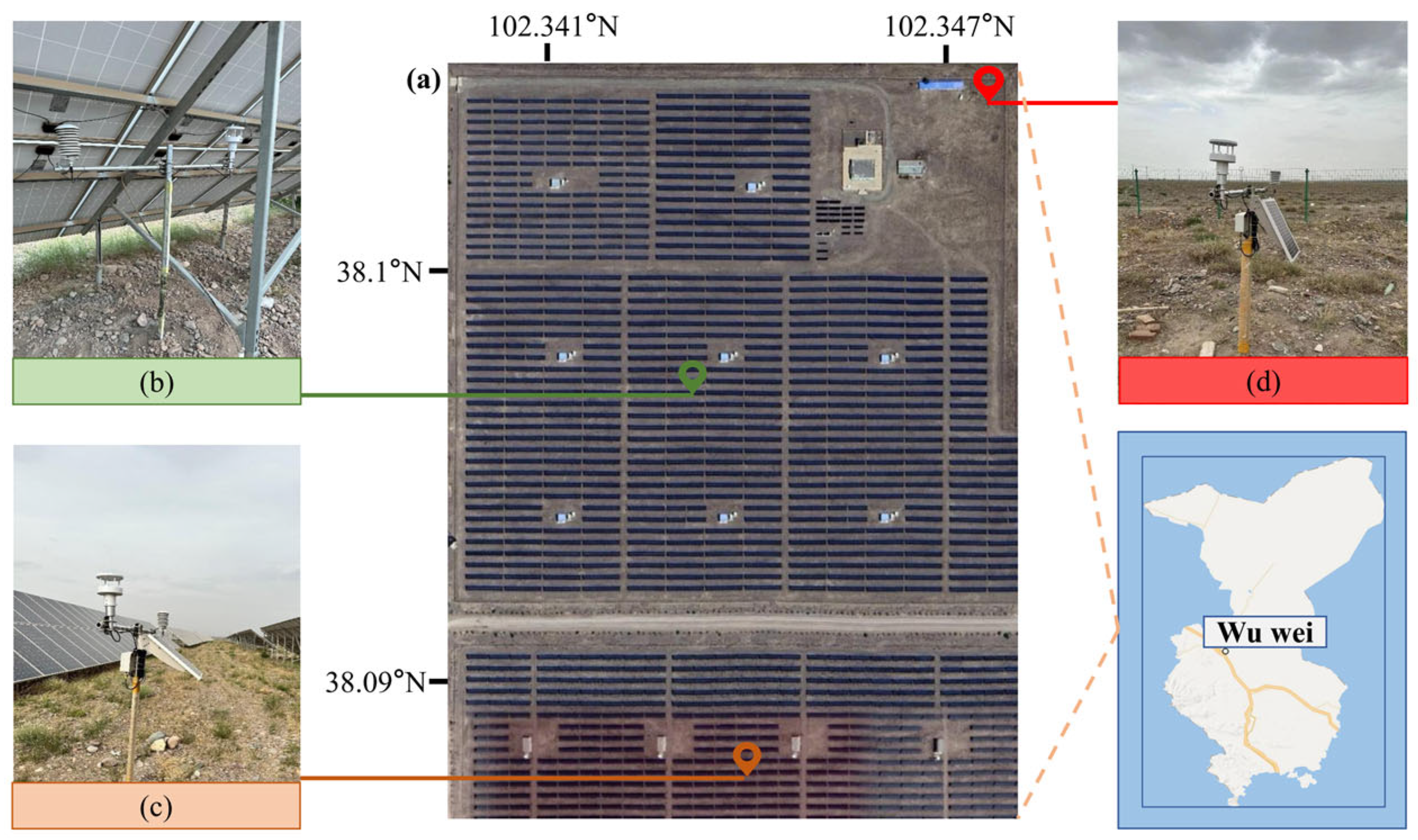


| Categories | Detailed Feature Description |
|---|---|
| Location | Western Gansu Province, eastern end of Hexi Corridor |
| Climactic | The average annual temperature: 7.8 °C Annual precipitation: 60–610 mm Evaporation capacity: 1400–3010 mm Sunshine duration: 2200–3030 h Solar radiation: 127–138 kcal/cm2 |
| Landform | The southern Qilian Mountains, the central corridor plain, and the northern desert; elevation of 1020–4874 m |
| Hydrology | Yellow River Basin with a cross-border water flow of 23.15 billion cubic meters; Shiyang River Basin area: 29,100 square kilometers |
| Biodiversity | High coverage areas mainly in the southern Qilian Mountain area, medium coverage areas mainly in the central oasis agricultural areas, low coverage areas mainly in the northern desert |
| Soil type | Sandy soils with low moisture retention and high permeability |
| Parameter (unit) | Sensor | Height/ Depth | Working Range | Accuracy | Rate (min) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AT (°C) | TRB3 a | 1.5 m | −40 °C~ +70 °C | ±0.2 °C | 30 |
| RH (%) | TRB3 | 1.5 m | 0–100% | ±1.5% | 30 |
| SWC (%) | SM926 b | 5 cm, 10 cm, 20 cm, 40 cm | 0–100% | ±0.03 | 30 |
| ST (°C) | SM926 | 5 cm, 10 cm, 20 cm, 40 cm | −40~55 °C | ±0.3 | 30 |
| Wind speed & direction | WXA 100-02S c | 1.5 m | 0–60 m/s | 0.05 m/s | 30 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, J.; Li, Z.; Tao, J.; Ge, Y.; Zhong, Y.; Wang, Y.; Yan, B. Observed Impacts of Ground-Mounted Photovoltaic Systems on the Microclimate and Soil in an Arid Area of Gansu, China. Atmosphere 2024, 15, 936. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15080936
Zhang J, Li Z, Tao J, Ge Y, Zhong Y, Wang Y, Yan B. Observed Impacts of Ground-Mounted Photovoltaic Systems on the Microclimate and Soil in an Arid Area of Gansu, China. Atmosphere. 2024; 15(8):936. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15080936
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Jia, Zaixin Li, Junyu Tao, Yadong Ge, Yuzhen Zhong, Yibo Wang, and Beibei Yan. 2024. "Observed Impacts of Ground-Mounted Photovoltaic Systems on the Microclimate and Soil in an Arid Area of Gansu, China" Atmosphere 15, no. 8: 936. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15080936
APA StyleZhang, J., Li, Z., Tao, J., Ge, Y., Zhong, Y., Wang, Y., & Yan, B. (2024). Observed Impacts of Ground-Mounted Photovoltaic Systems on the Microclimate and Soil in an Arid Area of Gansu, China. Atmosphere, 15(8), 936. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15080936








