Optimization of High-Temperature CO2 Capture by Lithium Orthosilicate-Based Sorbents Using Response Surface Methodology
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sorbents Production and Characterization
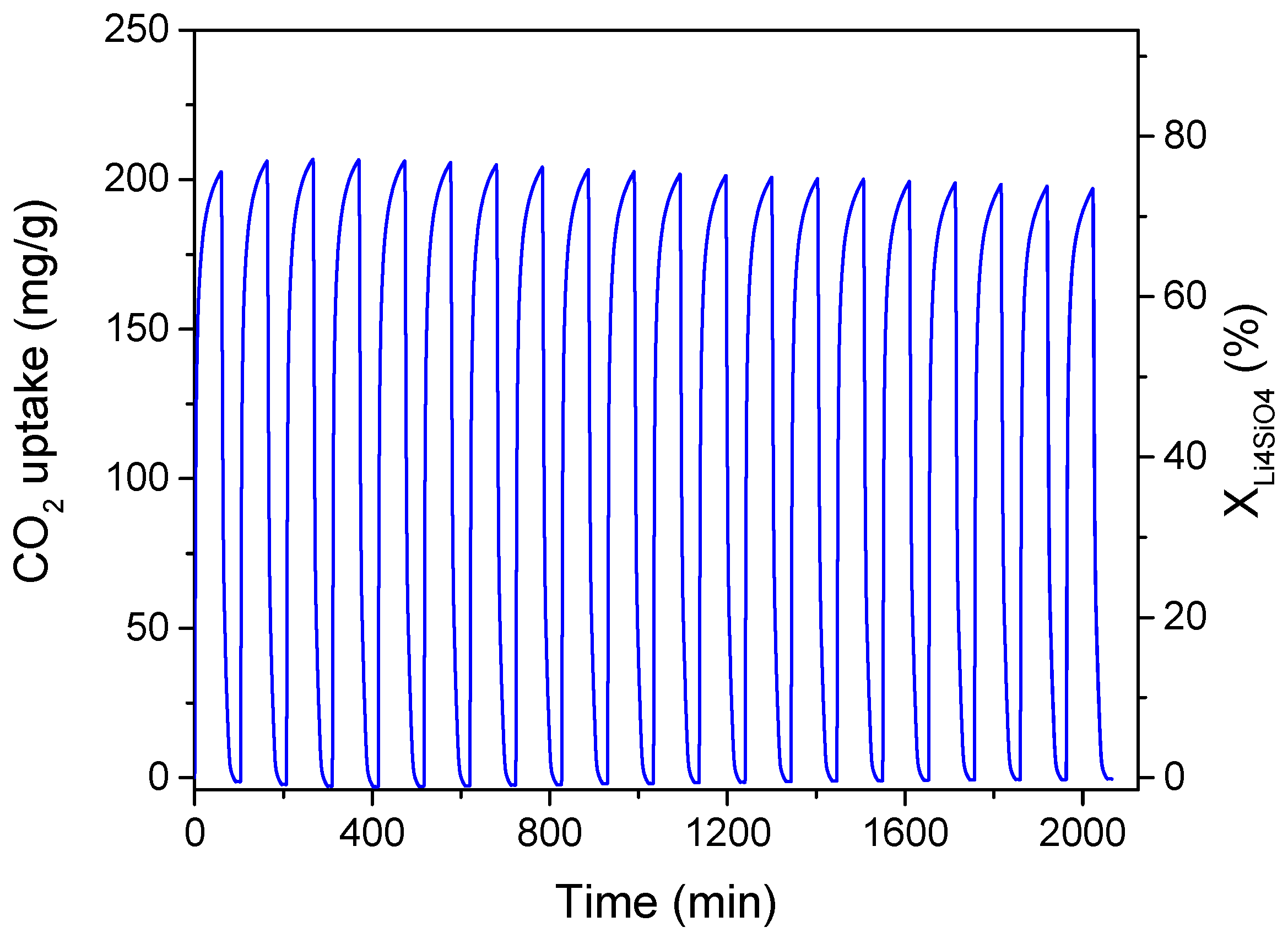
2.2. CO2 Capture Experiments Setup and Procedure
2.3. Experimental Design and Parametric Models
3. Results and Discussion
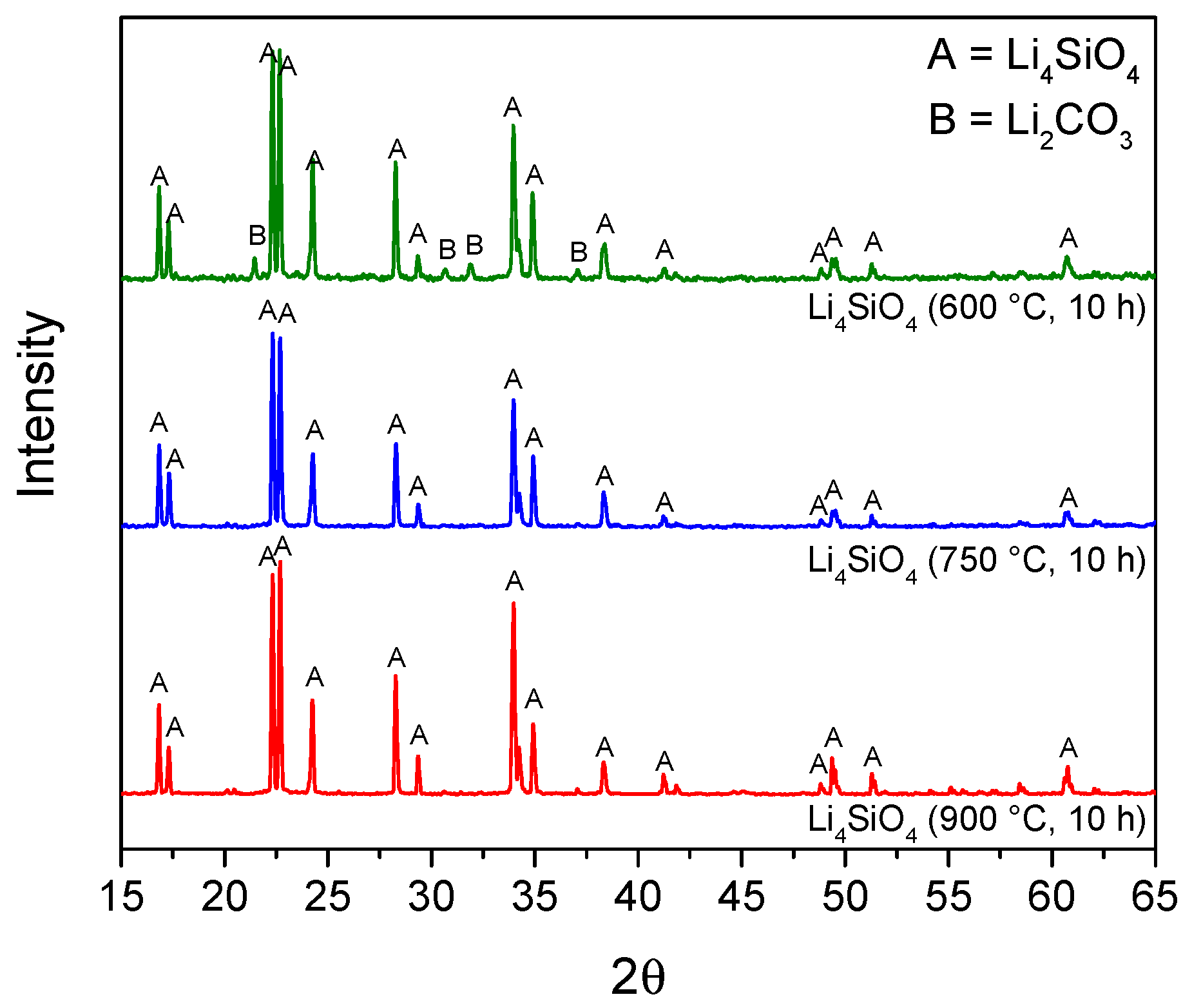
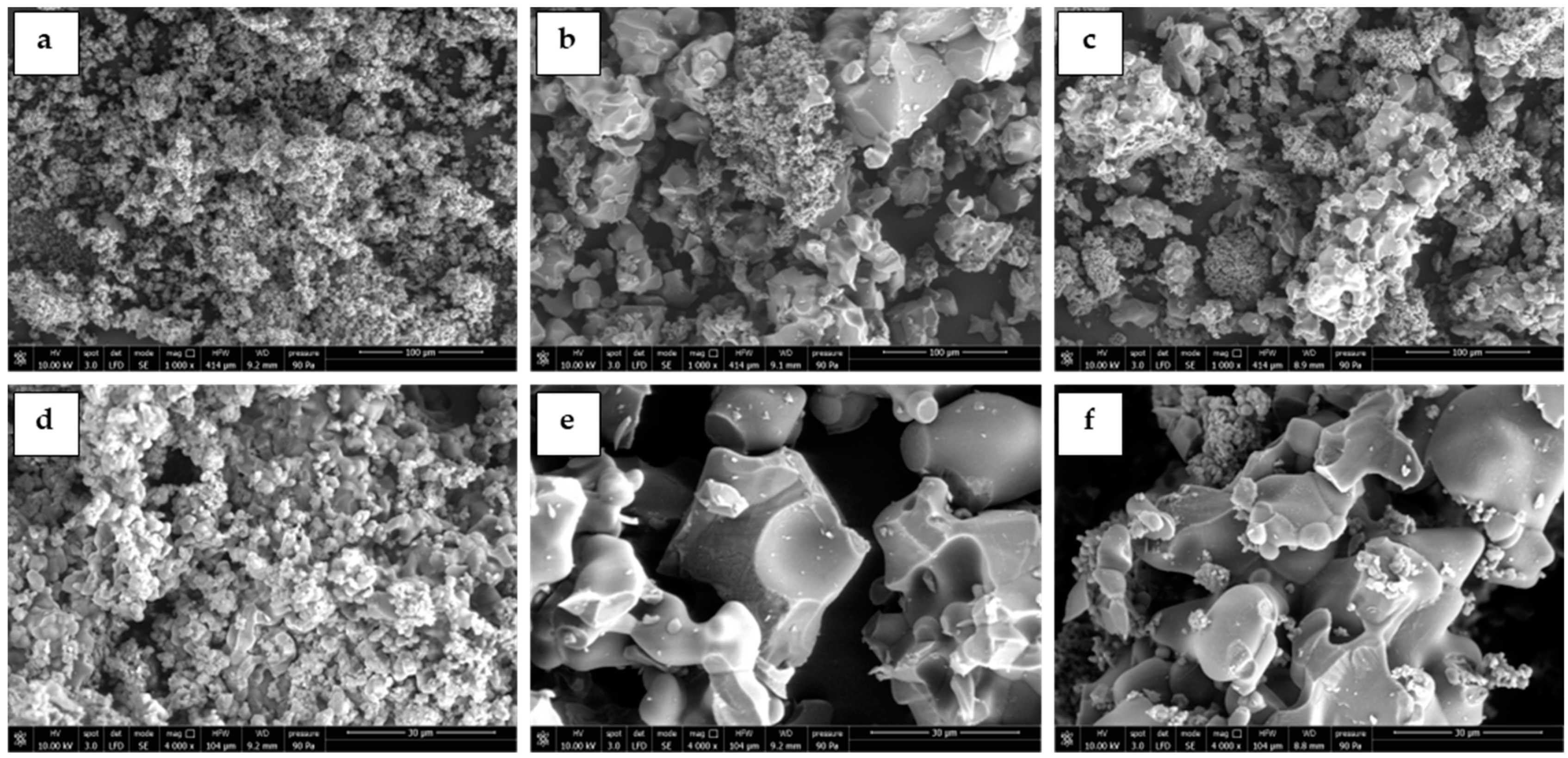
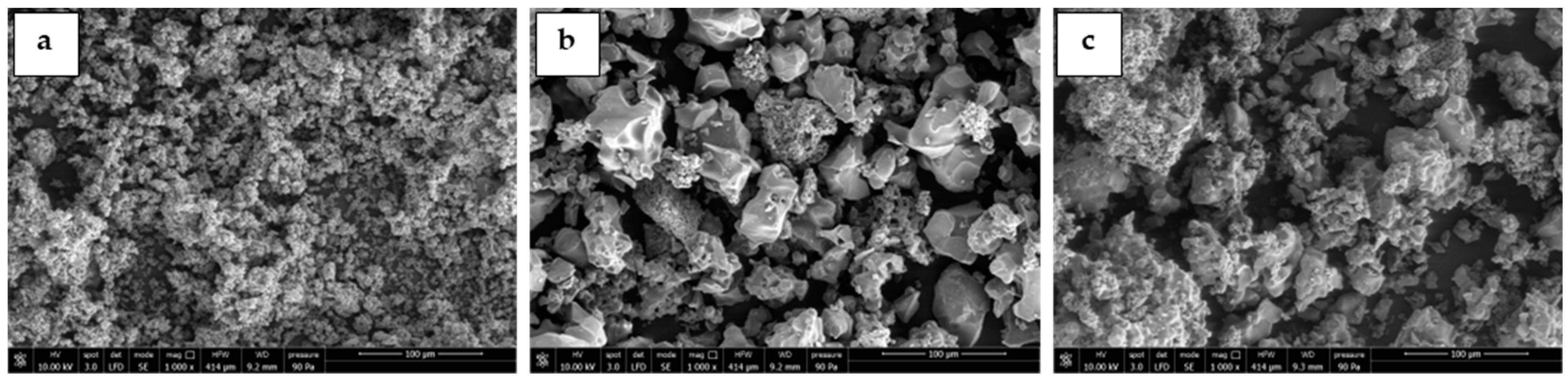
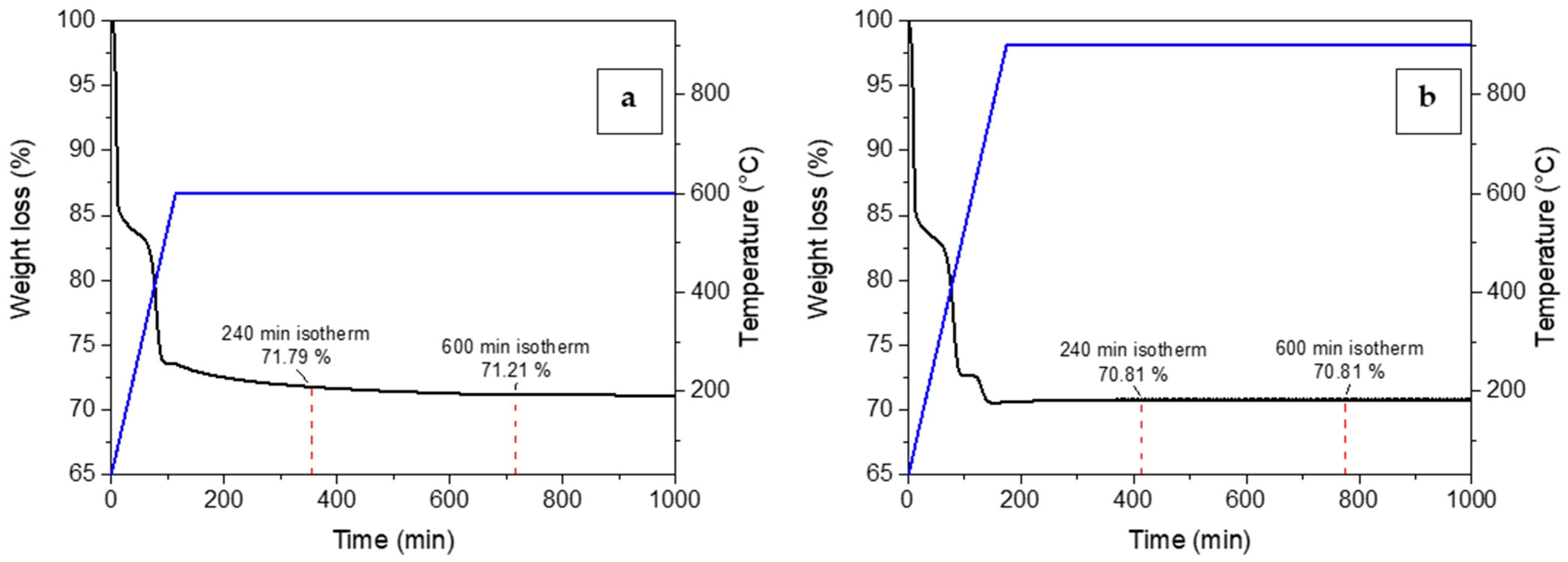
3.1. Sorbents Characterization
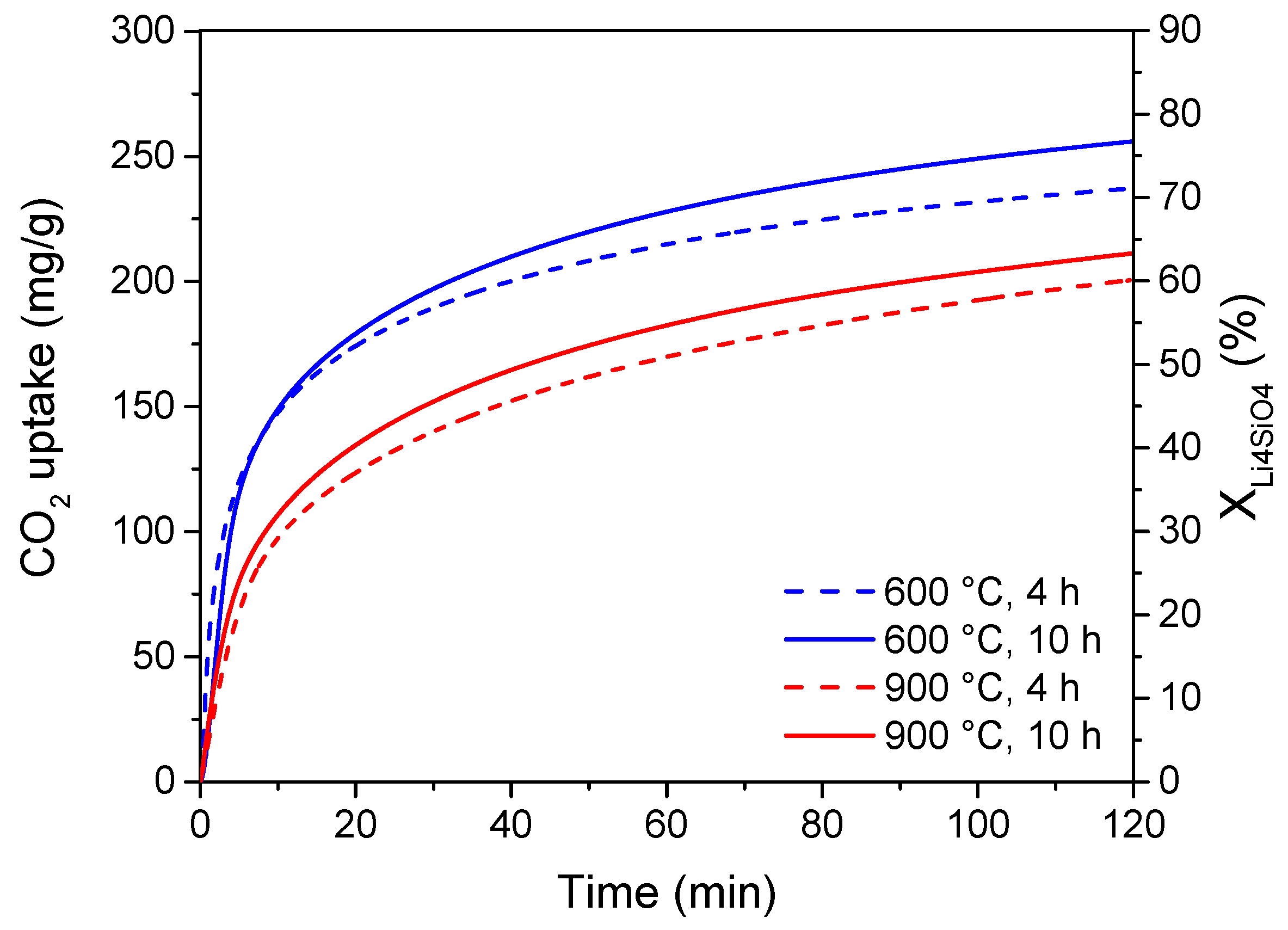
3.2. Preliminary Variables Selection for Parametric Modeling
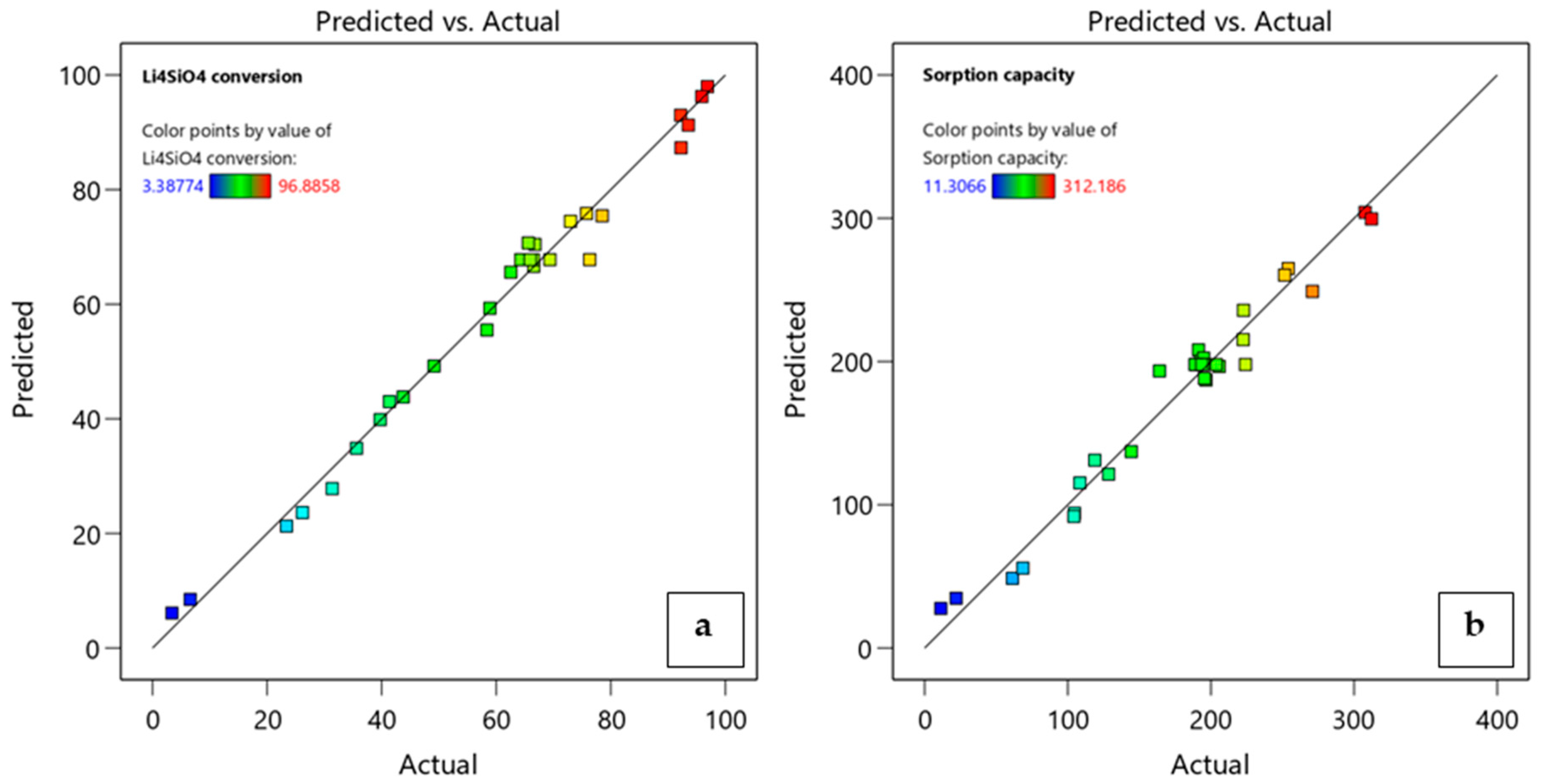
3.3. Modeling of the CO2 Adsorption Process and Statistical Analysis
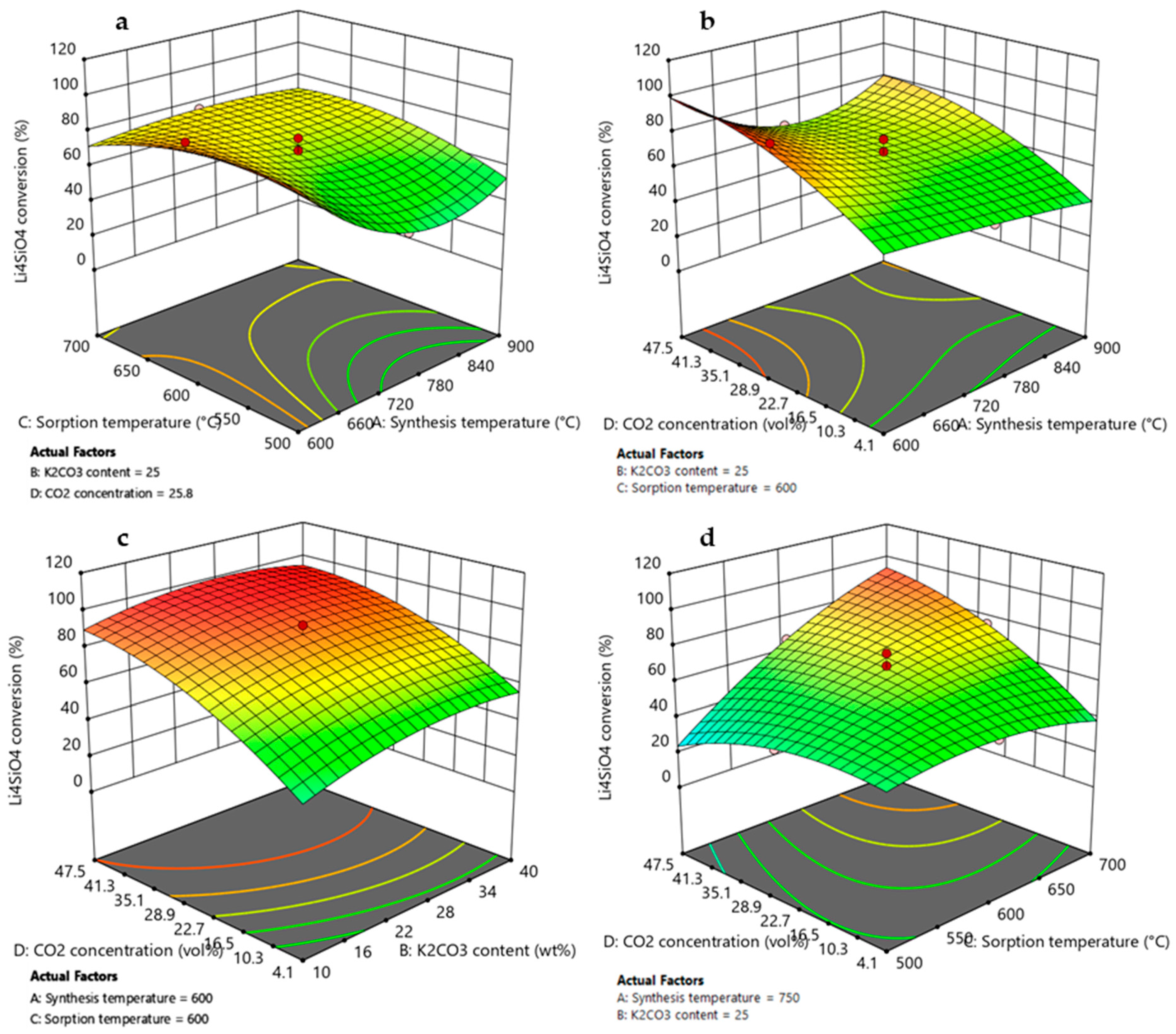
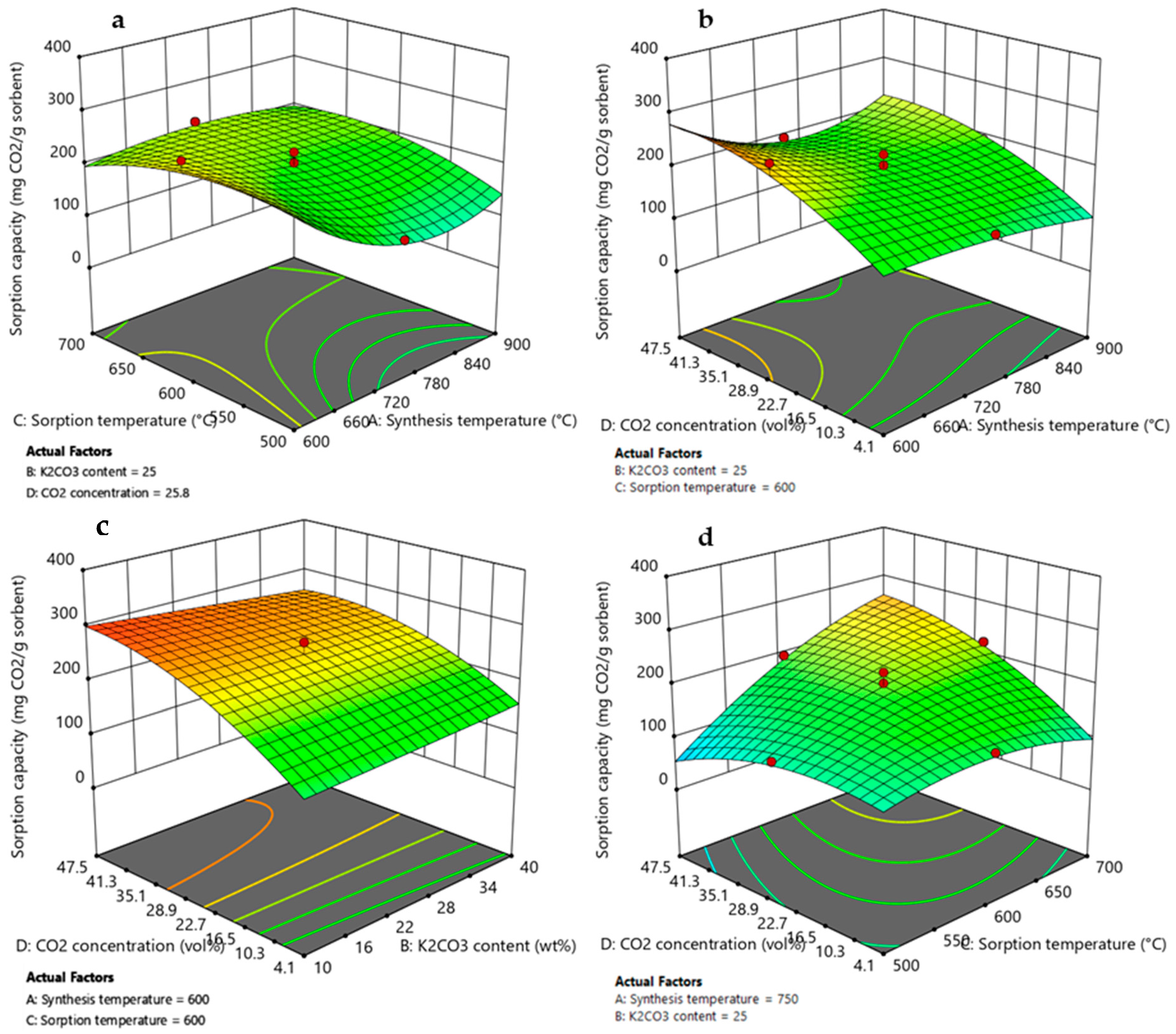
3.3.1. Effect of Synthesis Temperature
3.3.2. Effect of K2CO3 Content
3.3.3. Effect of Adsorption Temperature and CO2 Concentration
3.4. Optimization and Validation Tests
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gunawardene, O.H.P.; Gunathilake, C.A.; Vikrant, K.; Amaraweera, S.M. Carbon Dioxide Capture through Physical and Chemical Adsorption Using Porous Carbon Materials: A Review. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahimi, K.; Riahi, S.; Abbasi, M.; Fakhroueian, Z. Modification of Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotubes by 1,3-Diaminopropane to Increase CO2 Adsorption Capacity. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 242, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikolajewicz, U.; Grö, M.; Ernst, A.E.; Ae, M.-R.; Schurgers, G.; Miren, A.E.; Ae, V.; Winguth, A.M.E. Long-Term Effects of Anthropogenic CO2 Emissions Simulated with a Complex Earth System Model. Clim. Dyn. 2007, 28, 599–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharjee, P.K. Global Warming Impact on the Earth. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Dev. 2010, 1, 219–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Yoro, K.O.; Daramola, M.O. CO2 Emission Sources, Greenhouse Gases, and the Global Warming Effect. Adv. Carbon Capture Methods Technol. Appl. 2020, 3–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holechek, J.L.; Geli, H.M.E.; Sawalhah, M.N.; Valdez, R. A Global Assessment: Can Renewable Energy Replace Fossil Fuels by 2050? Sustainability 2022, 14, 4792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gernaat, D.E.H.J.; de Boer, H.S.; Daioglou, V.; Yalew, S.G.; Müller, C.; van Vuuren, D.P. Climate Change Impacts on Renewable Energy Supply. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2021, 11, 119–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okiemute Akpasi, S.; Makarfi Isa, Y. Review of Carbon Capture and Methane Production from Carbon Dioxide. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 1958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fawzy, S.; Osman, A.I.; Doran, J.; Rooney, D.W. Strategies for Mitigation of Climate Change: A Review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2020, 18, 2069–2094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajendran, A.; Subraveti, S.G.; Pai, K.N.; Prasad, V.; Li, Z. How Can (or Why Should) Process Engineering Aid the Screening and Discovery of Solid Sorbents for CO2 Capture? Acc. Chem. Res. 2023, 56, 2354–2365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, M.; Xie, J.; Li, X.; Gao, X. Investment Evaluation of CCUS Retrofitting for Coal-to-Liquid Industry in China. Atmosphere 2023, 14, 1737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilfong, W.C.; Ji, T.; Bao, Z.; Zhai, H.; Wang, Q.; Duan, Y.; Soong, Y.; Li, B.; Shi, F.; Gray, M.L. Big Data Analysis and Technical Review of Regeneration for Carbon Capture Processes. Energy Fuels 2023, 37, 11497–11531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, D.; Shen, B.; Li, Z.; Ma, J.; Liu, L. Fabrication of Robust CaO-Based Sorbent via Entire Utilization of MSW Incineration Bottom Ash for CO2 Capture. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2023, 307, 122795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Li, Y.; Duan, L.; Anthony, E.; Liu, H. CO2 Capture Performance of Calcium-Based Synthetic Sorbent with Hollow Core-Shell Structure under Calcium Looping Conditions. Appl. Energy 2018, 225, 402–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Gong, X.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, M.; Chen, B. CO2 Capture Performance of CaO-Based Sorbent Modified with Torrefaction Condensate during Calcium Looping Cycles. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 469, 144004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peltzer, D.; Salazar Hoyos, L.A.; Faroldi, B.; Múnera, J.; Cornaglia, L. Comparative Study of Lithium-Based CO2 Sorbents at High Temperature: Experimental and Modeling Kinetic Analysis of the Carbonation Reaction. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 104173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, Y.; Chen, S.; Huang, X.; He, Y.; Chen, J.; Qin, C. CO2 Capture by Li4SiO4 Sorbents: From Fundamentals to Applications. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 301, 121977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seggiani, M.; Stefanelli, E.; Puccini, M.; Vitolo, S. CO2 Sorption/Desorption Performance Study on K2CO3-Doped Li4SiO4-Based Pellets. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 339, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefanelli, E.; Vitolo, S.; Puccini, M. Single-Step Fabrication of Templated Li4SiO4-Based Pellets for CO2 Capture at High Temperature. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 108389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peltzer, D.; Mùnera, J.; Cornaglia, L.; Strumendo, M. Characterization of Potassium Doped Li2ZrO3 Based CO2 Sorbents: Stability Properties and CO2 Desorption Kinetics. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 336, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lara-Garcia, H.; Alcántar-Vázquez, B.; Duan, Y.; Pfeiffer, H. CO Chemical Capture on Lithium Cuprate, through a Consecutive CO Oxidation and Chemisorption Bifunctional Process. J. Phys. Chem. C 2016, 120, 3798–3806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Mamoori, A.; Hameed, M.; Saoud, A.; Al-Ghamdi, T.; Al-Naddaf, Q.; ALwakwak, A.A.; Baamran, K. Development of Sodium-Based Borate Adsorbents for CO2 Capture at High Temperatures. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2023, 62, 3695–3704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, G.; Yang, H.; Memon, M.Z.; Gao, Y.; Qu, B.; Fu, W.; Olguin, G.; Zhao, M.; Li, A. Recent Advances on Kinetics of Carbon Dioxide Capture Using Solid Sorbents at Elevated Temperatures. Appl. Energy 2020, 267, 114874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Liu, W.; Yang, Y.; Qu, M.; Li, H. CO2 Capture by Li4SiO4 Sorbents and Their Applications: Current Developments and New Trends. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 359, 604–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Li, Y.; Ma, X.; Zhao, J.; Wang, Z.; Yan, X.; Li, Y.; Ma, X.; Zhao, J.; Wang, Z. Performance of Li4SiO4 Material for CO2 Capture: A Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Dai, P.; Chen, Z.; Sun, X.; Ren, X. Kinetic and Thermodynamic Investigations on the Cyclic CO2 Adsorption-Desorption Processes of Lithium Orthosilicate. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 468, 143679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefanelli, E.; Puccini, M.; Vitolo, S.; Seggiani, M. CO2 Sorption Kinetic Study and Modeling on Doped-Li4SiO4 under Different Temperatures and CO2 Partial Pressures. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 379, 122307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Wang, K.; Yin, Z.; Zhao, P.; Su, Z.; Sun, J. Molten K2CO3-Promoted High-Performance Li4SiO4 Sorbents at Low CO2 Concentrations. Thermochim. Acta 2017, 655, 284–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Chen, K.; Wang, Y.; Lei, J.; Alsubaie, A.; Ning, P.; Wen, S.; Zhang, T.; Almalki, A.S.A.; Alhadhrami, A.; et al. Effect of K2CO3 Doping on CO2 Sorption Performance of Silicate Lithium-Based Sorbent Prepared from Citric Acid Treated Sediment. Chinese J. Chem. Eng. 2022, 51, 10–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Li, M.; Ning, P.; Jia, Q.; Wang, Q.; Wang, J. K2CO3 Promoted Novel Li4SiO4-Based Sorbents from Sepiolite with High CO2 Capture Capacity under Different CO2 Partial Pressures. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 380, 122515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Y.; Wei, J.; Yuan, Y.; Zhou, X.; Geng, L.; Liao, L. High Temperature Capture of Low Concentration CO2 by Na/Ca-Doped Lithium Orthosilicate with KIT-6 as Precursor. Mater. Today Commun. 2022, 33, 104685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, Y.; Zhang, M.; Guo, M. Na-Doped Li4SiO4 as an Efficient Sorbent for Low-Concentration CO2 Capture at High Temperature: Superior Adsorption and Rapid Kinetics Mechanism. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2025, 352, 128268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, H.; Li, X.; Chen, H.; Gu, X.; Cheng, Z.; Zhou, Z. Sol-Gel Derived, Na/K-Doped Li4SiO4-Based CO2 Sorbents with Fast Kinetics at High Temperature. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 382, 122807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Chen, S.; Qin, C.; Chen, S.; Yuan, W.; Zhou, X.; Ran, J. Understanding the Effect of H2S on the Capture of CO2 Using K-Doped Li4SiO4 Sorbent. Fuel 2021, 283, 119364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bararpour, S.T.; Karami, D.; Mahinpey, N. Investigation of the Effect of Alumina-Aerogel Support on the CO2 Capture Performance of K2CO3. Fuel 2019, 242, 124–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thouchprasitchai, N.; Pintuyothin, N.; Pongstabodee, S. Optimization of CO2 Adsorption Capacity and Cyclical Adsorption/Desorption on Tetraethylenepentamine-Supported Surface-Modified Hydrotalcite. J. Environ. Sci. 2018, 65, 293–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amiri, M.; Shahhosseini, S.; Ghaemi, A. Optimization of CO2 Capture Process from Simulated Flue Gas by Dry Regenerable Alkali Metal Carbonate Based Adsorbent Using Response Surface Methodology. Energy Fuels 2017, 31, 5286–5296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amiri, M.; Shahhosseini, S. Optimization of CO2 Capture from Simulated Flue Gas Using K2CO3/Al2O3 in a Micro Fluidized Bed Reactor. Energy Fuels 2018, 32, 7978–7990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oehlert, G.W. A First Course in Design and Analysis of Experiments, 1st ed.; W. H. Freeman: New York, NY, USA, 2000; ISBN 0-7167-3510-5. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, H.; Jang, H.D.; Choi, M. Facile Synthesis of Macroporous Li4SiO4 with Remarkably Enhanced CO2 Adsorption Kinetics. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 280, 132–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.C.; Wang, C.C.; Kumta, P.N. Chemical Synthesis and Characterization of Lithium Orthosilicate (Li4SiO4). Mater. Des. 2001, 22, 617–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz, D.; Bulbulian, S.; Lima, E.; Pfeiffer, H. Kinetic Analysis of the Thermal Stability of Lithium Silicates (Li4SiO4 and Li2SiO3). J. Solid State Chem. 2006, 179, 909–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfeiffer, H.; Bosch, P.; Bulbulian, S. Synthesis of Lithium Silicates. J. Nucl. Mater. 1998, 257, 309–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seggiani, M.; Puccini, M.; Vitolo, S. Alkali Promoted Lithium Orthosilicate for CO2 Capture at High Temperature and Low Concentration. Int. J. Greenh. Gas Control 2013, 17, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavri, R.; Moore, G.D. Gas Turbine Emissions and Control; GER-4211; GE Energy Services: Atlanta, Georgia, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, C.-Y.; Kuo, C.-C.; Yang, M.-W.; Zhuang, Z.-Y.; Lin, P.-W.; Chen, Y.-F.; Yang, H.-S.; Chou, C.-T. CO2 Capture from Flue Gas of a Coal-Fired Power Plant Using Three-Bed PSA Process. Energies 2021, 14, 3582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amann, J.M.G.; Bouallou, C. CO2 Capture from Power Stations Running with Natural Gas (NGCC) and Pulverized Coal (PC): Assessment of a New Chemical Solvent Based on Aqueous Solutions of N-Methyldiethanolamine + Triethylene Tetramine. Energy Procedia 2009, 1, 909–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- David, E.; Stanciu, V.; Sandra, C.; Armeanu, A.; Niculescu, V. Exhaust Gas Treatment Technologies for Pollutant Emission Abatement from Fossil Fuel Power Plants. WIT Trans. Ecol. Environ. 2007, 102, 923–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seggiani, M.; Puccini, M.; Vitolo, S. High-Temperature and Low Concentration CO2 Sorption on Li4SiO4 Based Sorbents: Study of the Used Silica and Doping Method Effects. Int. J. Greenh. Gas Control 2011, 5, 741–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Yao, S.; Liu, W.; Hu, Y.; Li, Q.; Li, Z.; Zhou, S.; Zhou, Z. Novel Synthesis of Tailored Li4SiO4-Based Microspheres for Ultrafast CO2 Adsorption. Fuel Process. Technol. 2021, 213, 106675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izquierdo, M.T.; Turan, A.; García, S.; Maroto-Valer, M.M. Optimization of Li4SiO4 Synthesis Conditions by a Solid State Method for Maximum CO2 Capture at High Temperature. J. Mater. Chem. A 2018, 6, 3249–3257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izquierdo, M.T.; Gasquet, V.; Sansom, E.; Ojeda, M.; Garcia, S.; Maroto-Valer, M.M. Lithium-Based Sorbents for High Temperature CO2 Capture: Effect of Precursor Materials and Synthesis Method. Fuel 2018, 230, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Dai, J.; Qin, C.; Yuan, W.; Manovic, V. Adsorption and Desorption Equilibrium of Li4SiO4-Based Sorbents for High-Temperature CO2 Capture. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 429, 132236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaniwa, S.; Yoshino, M.; Niwa, E.; Yashima, M.; Hashimoto, T. Analysis of Chemical Reaction between Li4SiO4 and CO2 by Thermogravimetry under Various CO2 Partial Pressures—Clarification of CO2 Partial Pressure and Temperature Region of CO2 Absorption. Mater. Res. Bull. 2017, 94, 134–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Variables (Factors) | Unit | Levels | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| −1 | 0 | +1 | ||
| Synthesis temperature | °C | 600 | 750 | 900 |
| K2CO3 content | wt% | 10 | 25 | 40 |
| Adsorption temperature | °C | 500 | 600 | 700 |
| CO2 concentration | vol% | 4 | 27 | 50 |
| Run | Input Variables | Responses | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A Synthesis Temperature (°C) | B K2CO3 Content (wt%) | C Adsorption Temperature (°C) | D CO2 Concentration * (vol%) | Y1 XLi4SiO4 (%) | Y2 Adsorption Capacity (mg/g) | |
| 1 | 750 | 25 | 600 | 27 | 76.32 | 224.15 |
| 2 | 750 | 25 | 700 | 27 | 75.78 | 222.58 |
| 3 | 750 | 25 | 600 | 50 | 66.54 | 195.44 |
| 4 | 600 | 10 | 500 | 50 | 66.76 | 222.80 |
| 5 | 750 | 25 | 600 | 27 | 69.37 | 203.73 |
| 6 | 900 | 10 | 500 | 50 | 35.61 | 118.86 |
| 7 | 750 | 25 | 600 | 27 | 66.50 | 195.30 |
| 8 | 600 | 40 | 700 | 50 | 96.88 | 254.07 |
| 9 | 750 | 25 | 600 | 27 | 64.30 | 188.86 |
| 10 | 900 | 40 | 500 | 4 | 41.36 | 108.45 |
| 11 | 750 | 25 | 600 | 4 | 49.16 | 144.38 |
| 12 | 600 | 40 | 500 | 50 | 78.50 | 205.85 |
| 13 | 900 | 40 | 500 | 50 | 39.76 | 104.27 |
| 14 | 900 | 10 | 500 | 4 | 31.37 | 104.71 |
| 15 | 750 | 40 | 600 | 27 | 62.56 | 164.05 |
| 16 | 750 | 25 | 500 | 27 | 43.77 | 128.56 |
| 17 | 900 | 10 | 700 | 50 | 93.54 | 312.19 |
| 18 | 600 | 25 | 600 | 27 | 92.26 | 270.98 |
| 19 | 600 | 40 | 500 | 4 | 72.95 | 191.36 |
| 20 | 600 | 10 | 700 | 4 | 3.390 | 11.310 |
| 21 | 750 | 25 | 600 | 27 | 65.93 | 193.62 |
| 22 | 900 | 40 | 700 | 50 | 95.89 | 251.45 |
| 23 | 750 | 25 | 600 | 27 | 64.67 | 189.95 |
| 24 | 900 | 40 | 700 | 4 | 26.19 | 68.670 |
| 25 | 750 | 10 | 600 | 27 | 58.39 | 194.87 |
| 26 | 900 | 10 | 700 | 4 | 6.600 | 22.030 |
| 27 | 600 | 10 | 700 | 50 | 92.20 | 307.72 |
| 28 | 600 | 10 | 500 | 4 | 58.90 | 196.58 |
| 29 | 600 | 40 | 700 | 4 | 23.40 | 61.330 |
| 30 | 900 | 25 | 600 | 27 | 65.60 | 192.67 |
| Sum of Squares | df | Mean Square | F-Value | p-Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | 18,056.83 | 14 | 1289.77 | 80.42 | <0.0001 | significant |
| A-Synthesis temperature | 1238.99 | 1 | 1238.99 | 77.25 | <0.0001 | |
| B-K2CO3 content | 457.49 | 1 | 457.49 | 28.52 | <0.0001 | |
| C-Adsorption temperature | 512.43 | 1 | 512.43 | 31.95 | <0.0001 | |
| D-CO2 concentration | 151.10 | 1 | 151.10 | 9.42 | 0.0078 | |
| AC | 1145.37 | 1 | 1145.37 | 71.41 | <0.0001 | |
| AD | 16.81 | 1 | 16.81 | 1.05 | 0.3221 | |
| BD | 103.61 | 1 | 103.61 | 6.46 | 0.0226 | |
| CD | 5735.35 | 1 | 5735.35 | 357.60 | <0.0001 | |
| A2 | 325.90 | 1 | 325.90 | 20.32 | 0.0004 | |
| B2 | 135.92 | 1 | 135.92 | 8.48 | 0.0107 | |
| C2 | 163.32 | 1 | 163.32 | 10.18 | 0.0061 | |
| D2 | 252.20 | 1 | 252.20 | 15.73 | 0.0012 | |
| A2C | 410.97 | 1 | 410.97 | 25.62 | 0.0001 | |
| A2D | 266.52 | 1 | 266.52 | 16.62 | 0.0010 | |
| Residual | 240.57 | 15 | 16.04 | |||
| Lack of fit | 138.33 | 10 | 13.83 | 0.6765 | 0.7204 | not significant |
| Pure error | 102.24 | 5 | 20.45 | |||
| Cor Total | 18,297.40 | 29 | ||||
| Model statistics | ||||||
| R2 | 0.9869 | |||||
| Adjusted R2 | 0.9746 | |||||
| Predicted R2 | 0.9602 |
| Sum of Squares | df | Mean Square | F-Value | p-Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | 1.599∙105 | 13 | 12,300.57 | 41.24 | <0.0001 | significant |
| A-Synthesis temperature | 10,692.54 | 1 | 10,692.54 | 35.85 | <0.0001 | |
| B-K2CO3 content | 369.47 | 1 | 369.47 | 1.24 | 0.2821 | |
| C-Adsorption temperature | 4420.24 | 1 | 4420.24 | 14.82 | 0.0014 | |
| D-CO2 concentration | 1303.36 | 1 | 1303.36 | 4.37 | 0.0529 | |
| AC | 10,010.29 | 1 | 10,010.29 | 33.56 | <0.0001 | |
| AD | 137.69 | 1 | 137.69 | 0.4617 | 0.5066 | |
| BD | 3633.50 | 1 | 3633.50 | 12.18 | 0.0030 | |
| CD | 51,918.23 | 1 | 51,918.23 | 174.08 | <0.0001 | |
| A2 | 2018.70 | 1 | 2018.70 | 6.77 | 0.0193 | |
| C2 | 2485.75 | 1 | 2485.75 | 8.33 | 0.0107 | |
| D2 | 3527.27 | 1 | 3527.27 | 11.83 | 0.0034 | |
| A2C | 3563.28 | 1 | 3563.28 | 11.95 | 0.0032 | |
| A2D | 2536.04 | 1 | 2536.04 | 8.50 | 0.0101 | |
| Residual | 4771.81 | 16 | 298.24 | |||
| Lack of fit | 3889.86 | 11 | 353.62 | 2.00 | 0.2288 | not significant |
| Pure error | 881.95 | 5 | 176.39 | |||
| Cor Total | 1.647∙105 | 29 | ||||
| Model statistics | ||||||
| R2 | 0.9710 | |||||
| Adjusted R2 | 0.9475 | |||||
| Predicted R2 | 0.8237 |
| Process Variable | Optimum Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 4 vol% CO2 | 27 vol% CO2 | 50 vol% CO2 | |
| A-Synthesis temperature (°C) | 600 | 600 | 600 |
| B-K2CO3 content (wt%) | 36.9 | 28.5 | 17.1 |
| C-Adsorption temperature (°C) | 500 | 557 | 662 |
| CO2 Concentration | Response | Predicted Value | Experimental Result | Error (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4 vol% | Y1: Li4SiO4 conversion (%) | 75.6 | 73.2 | 1.86 |
| Y2: Adsorption capacity (mg/g) | 206.0 | 196.4 | 3.44 | |
| 27 vol% | Y1: Li4SiO4 conversion (%) | 89.9 | 83.7 | 5.15 |
| Y2: Adsorption capacity (mg/g) | 252.2 | 239.2 | 3.41 | |
| 50 vol% | Y1: Li4SiO4 conversion (%) | 98.5 | 94.3 | 4.25 |
| Y2: Adsorption capacity (mg/g) | 300.1 | 295.6 | 1.47 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Stefanelli, E.; Francalanci, F.; Vitolo, S.; Puccini, M. Optimization of High-Temperature CO2 Capture by Lithium Orthosilicate-Based Sorbents Using Response Surface Methodology. Atmosphere 2024, 15, 908. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15080908
Stefanelli E, Francalanci F, Vitolo S, Puccini M. Optimization of High-Temperature CO2 Capture by Lithium Orthosilicate-Based Sorbents Using Response Surface Methodology. Atmosphere. 2024; 15(8):908. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15080908
Chicago/Turabian StyleStefanelli, Eleonora, Flavio Francalanci, Sandra Vitolo, and Monica Puccini. 2024. "Optimization of High-Temperature CO2 Capture by Lithium Orthosilicate-Based Sorbents Using Response Surface Methodology" Atmosphere 15, no. 8: 908. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15080908
APA StyleStefanelli, E., Francalanci, F., Vitolo, S., & Puccini, M. (2024). Optimization of High-Temperature CO2 Capture by Lithium Orthosilicate-Based Sorbents Using Response Surface Methodology. Atmosphere, 15(8), 908. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15080908






