Variations in Air Pollutant Concentrations on Dry and Wet Days with Varying Precipitation Intensity
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Data and Methodology
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Meteorological Data and Selection of Grid Points
2.3. Air Pollutant Data
2.4. Statistical Tests for Data Analysis
2.5. K-Means Clustering, Principal Component Analysis (PCA), and Multiple Regression
3. Results
3.1. Temporal Exceedance Rates of Air Pollutant Concentrations
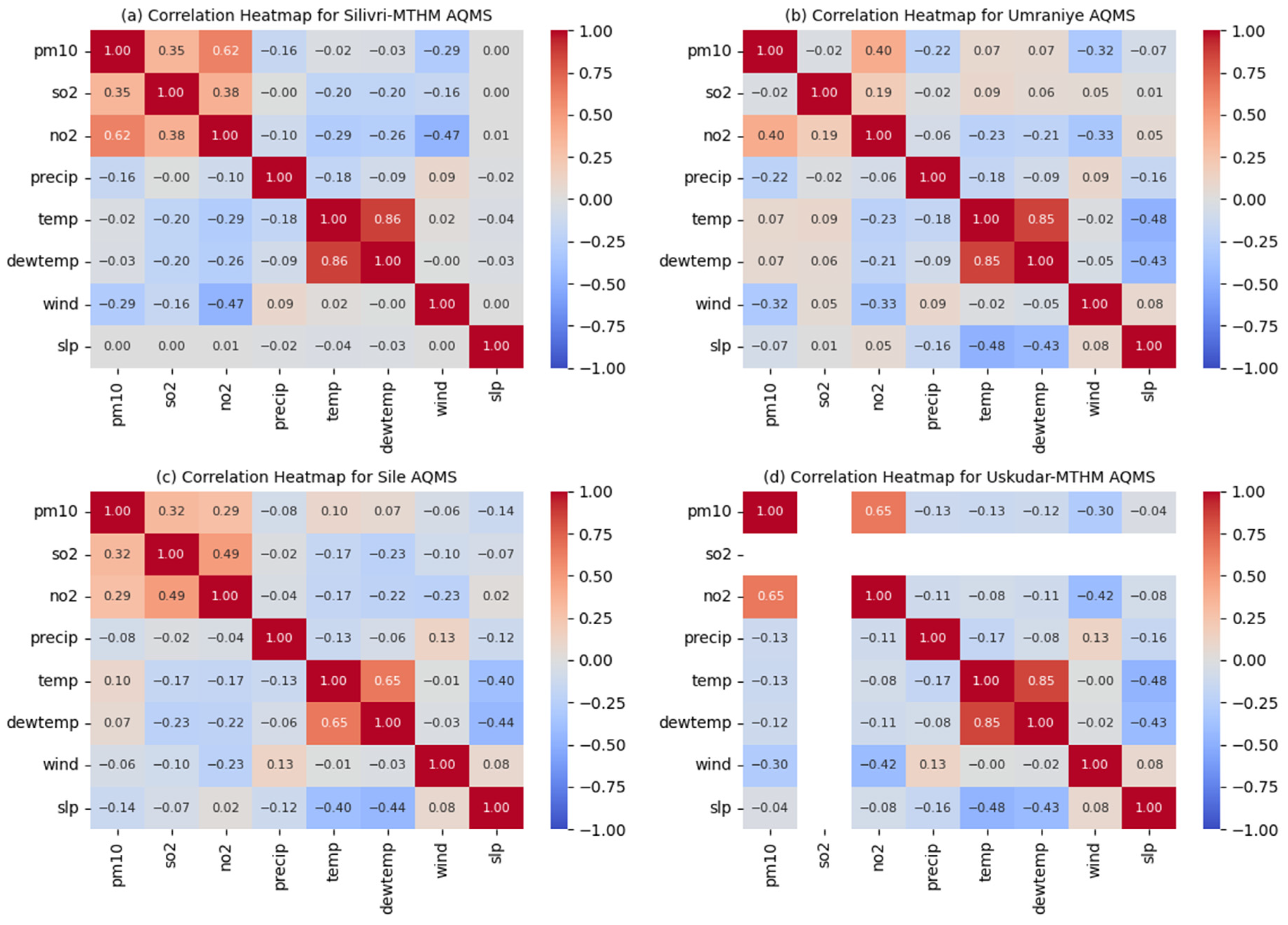
3.2. Correlation Matrices of Meteorological Variables Influencing Air Pollutant Concentrations
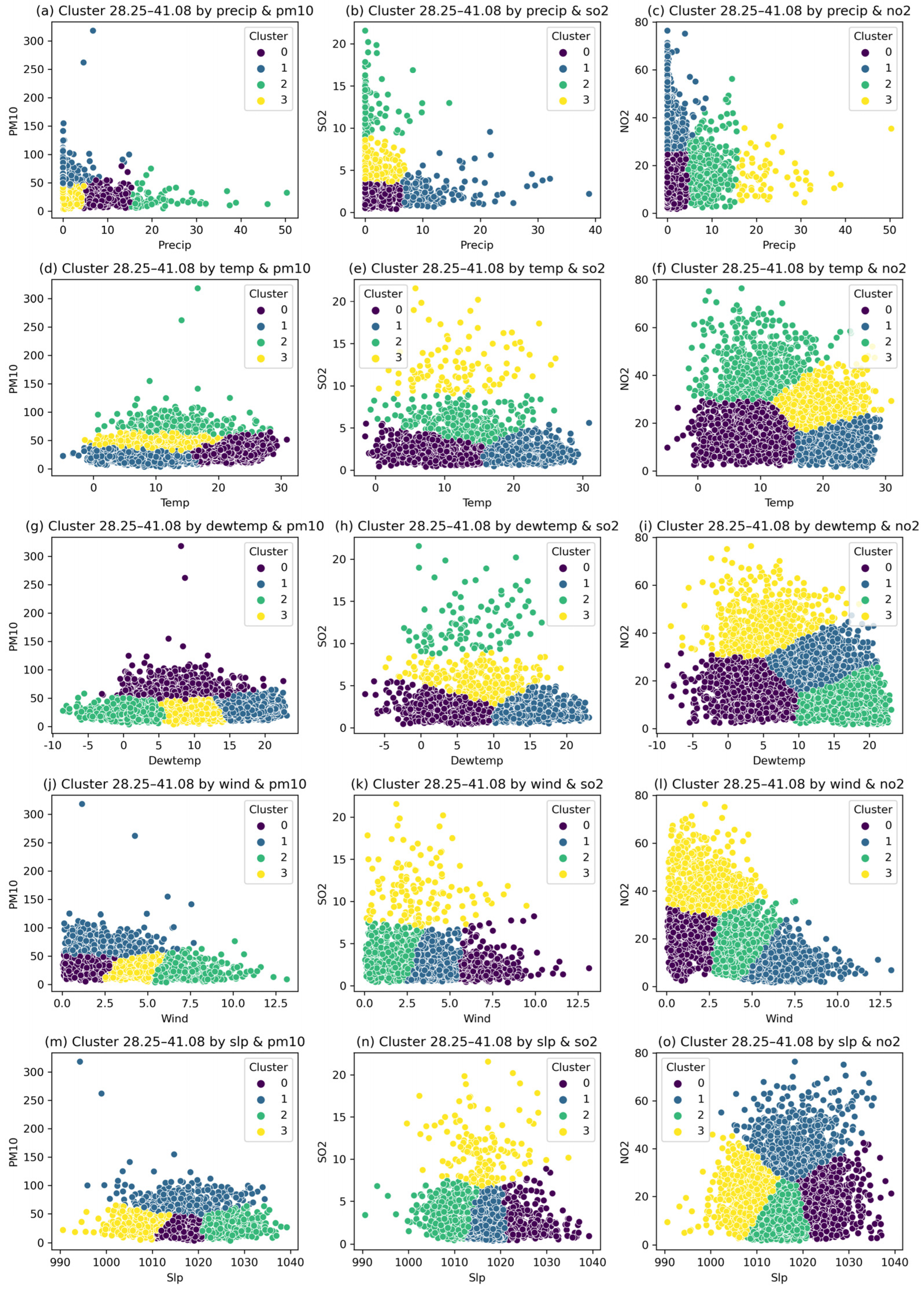
3.3. Cluster Analysis of Meteorological Variables and Air Pollutant Concentrations
3.4. Multiple Regression and Principal Component Analyses
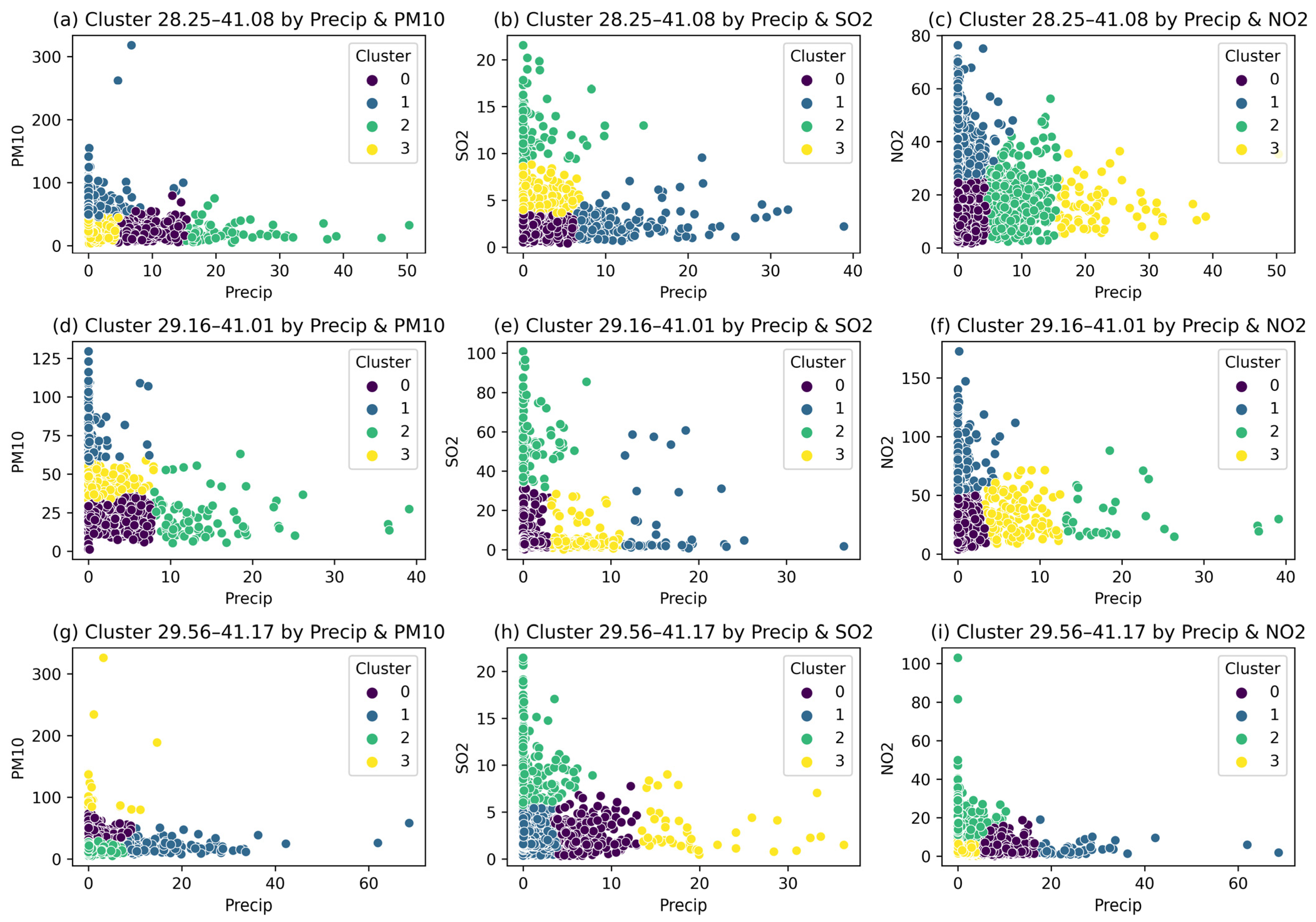
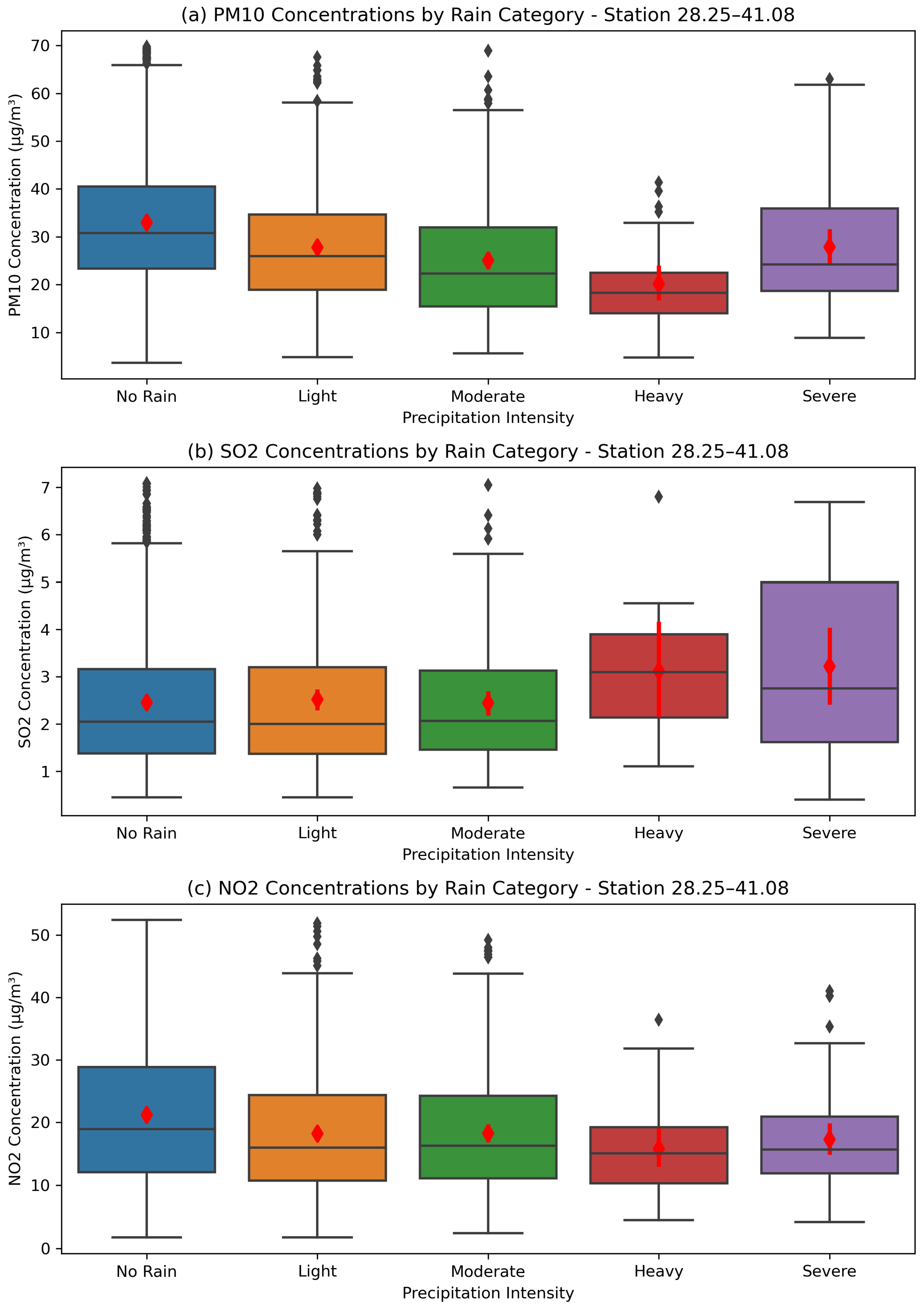
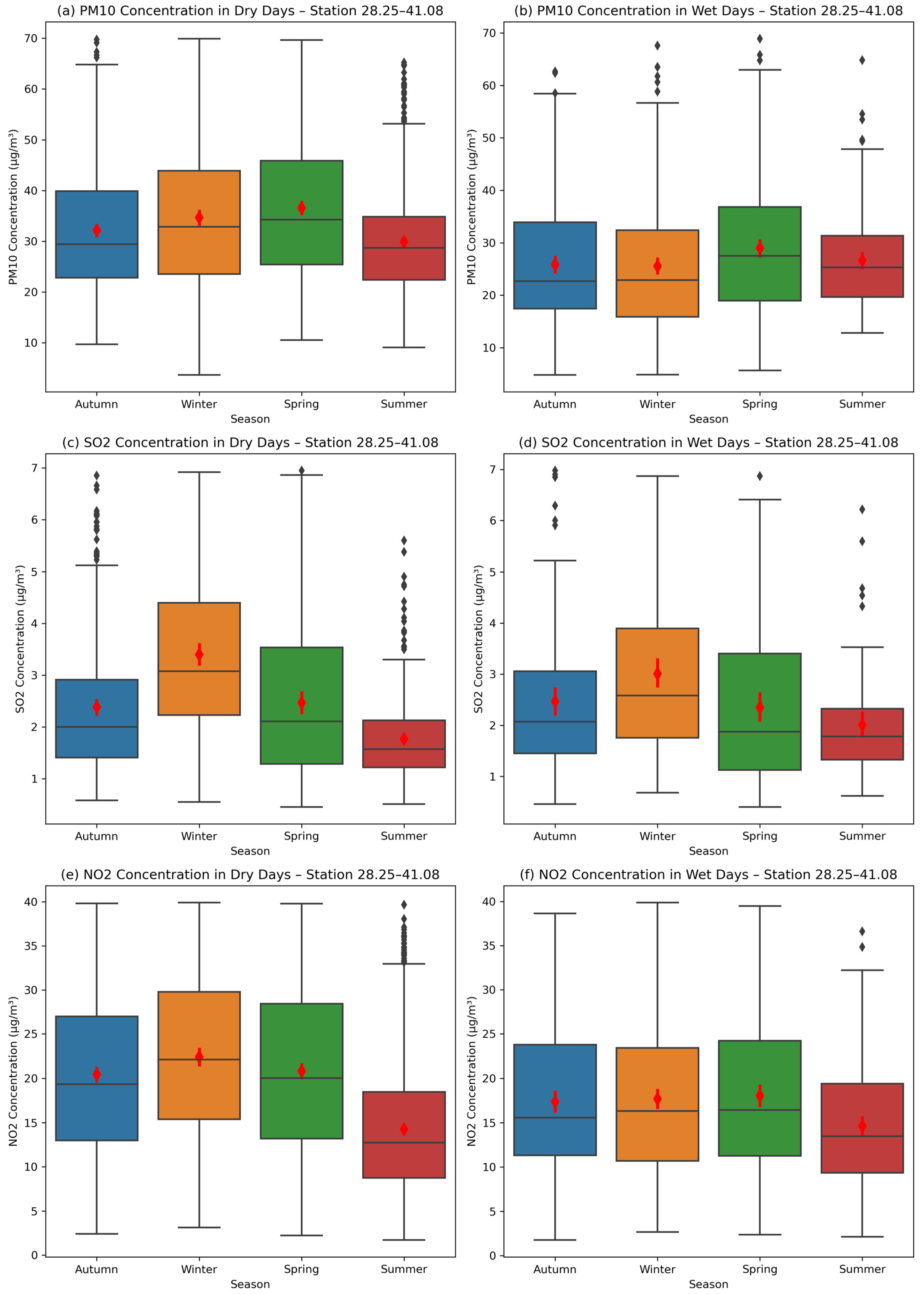
3.5. Variations in Air Pollutant Concentrations According to Precipitation Intensities
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
- In Istanbul, pollutant concentration values show significant variations based on the station. Less air pollution was observed in rural areas of the city, while higher pollution levels were detected at stations located in more urbanized and densely populated inner areas.
- Between 2013 and 2023, a marked decrease in pollutant concentration values was observed, particularly in the last few years. This is believed to be related to the COVID-19 period, during which industrial and human activities declined.
- Generally, pollutant concentrations were higher in the winter season; however, there was a notable decrease in concentration values on wet days, especially when snowfall was observed.
- Among meteorological variables, wind and precipitation were the most influential on air quality. Negative correlations were found between these two variables and air pollutant concentrations in almost all cases, indicating that increased wind and precipitation values had a positive effect on air quality.
- The highest air pollutant concentrations were observed in the winter season, when there was no precipitation and stable atmospheric conditions prevailed.
- Similar to studies in the literature, higher air pollutant concentrations were observed in the absence of precipitation and during light rainfall, while lower concentrations were found in the moderate and severe rainfall categories. This indicates that increasing precipitation intensities have a cleansing effect on air pollution.
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- He, J.; Gong, S.; Yu, Y.; Yu, L.; Wu, L.; Mao, H.; Song, C.; Zhao, S.; Liu, H.; Li, X.; et al. Air pollution characteristics and their relation to meteorological conditions during 2014–2015 in major Chinese cities. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 223, 484–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- An, X.; Yan, T.; Mi, S.; Sun, Z.; Hou, Q. Association between PM10 and respiratory hospital admissions in different seasons in heavily polluted Lanzhou City. J. Environ. Health 2015, 77, 64–71. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Incecik, S.; İm, U. Air Pollution in Mega Cities: A Case Study of İstanbul. In Air Pollution—Monitoring, Modelling and Health; Intech Open Access Publisher: Rijeka, Croatia, 2012; pp. 77–116. [Google Scholar]
- Krzyzanowski, M.; Apte, J.S.; Bonjour, S.P.; Brauer, M.; Cohen, A.J.; Prüss-Ustun, A.M. Air Pollution in the Mega-cities. Curr. Environ. Health Rep. 2014, 1, 185–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çapraz, Ö.; Deniz, A.; Doğan, N. Effects of air pollution on respiratory hospital admissions in İstanbul, Turkey, 2013 to 2015. Chemosphere 2017, 181, 544–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Jiang, X.; Tong, D.; Davis, S.J.; Zhao, H.; Geng, G.; Feng, T.; Zheng, B.; Lu, Z.; Streets, D.G. Transboundary health impacts of transported global air pollution and international trade. Nature 2017, 543, 705–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Çapraz, Ö.; Deniz, A. Particulate matter (PM10 and PM2.5) concentrations during a Saharan dust episode in Istanbul. Air Qual. Atmos. Health 2021, 14, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çapraz, Ö.; Efe, B.; Deniz, A. Study on the association between air pollution and mortality in İstanbul, 2007–2012. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2016, 7, 147–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, A.; Trigo, R.M.; Martins, H.; Mendes, M.T. NO2, PM10 and O3 urban concentrations and its association with circulation weather types in Portugal. Atmos. Environ. 2014, 89, 768–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferenczi, Z.; Imre, K.; Lakatos, M.; Molnár, Á.; Bozó, L.; Homolya, E.; Gelencsér, A. Long-term Characterization of Urban PM10 in Hungary. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2021, 21, 210048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolat, İ. Effect of Forest Fires on Air Quality: Antalya example. Bartın Fac. For. J. 2022, 24, 651–666. (In Turkish) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilten, N.; Selici, A.T. Investigating the impacts of some meteorological parameters on air pollution in Balikesir, Turkey. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2008, 140, 267–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernardino, A.D.; Iannarelli, A.M.; Casadio, S.; Perrino, C.; Barnaba, F.; Tofful, L.; Campanelli, M.; Di Liberto, L.; Mevi, G.; Siani, A.M.; et al. Impact of synoptic meteorological conditions on air quality in three different case studies in Rome, Italy. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2021, 12, 76–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.T.; Gong, S.; Yu, M.; Zhao, Q.C.; Li, H.R.; He, J.J.; Zhang, J.; Li, L.; Wang, X.G.; Li, S.L.; et al. Contributions of meteorology and emission to the 2015 winter severe haze pollution episodes in Northern China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. Discuss. 2016. preprint. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, W.; Cheng, S.; Chen, X.; Wang, G.; Li, S.; Wang, X.; Liu, X. Impact of emission control on PM2.5 and the chemical composition change in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei during the APEC summit 2014. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 4509–4521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Özdemir, E.T.; Korkmaz, F.M.; Yavuz, V. Synoptic analysis of dust storm over Arabian Peninsula: A case study on February 28, 2009. Nat. Hazards 2018, 92, 805–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yavuz, V.; Özen, C.; Çapraz, Ö.; Özdemir, E.T.; Deniz, A.; Akbayır, İ.; Temur, H. Analysing of atmospheric conditions and their effects on air quality in Istanbul using SODAR and CEILOMETER. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 16213–16232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yavuz, V. An analysis of atmospheric stability indices and parameters under air pollution conditions. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2023, 195, 934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kara, Y.; Şevik, S.E.Y.; Toros, H. Comprehensive analysis of air pollution and the influence of meteorological factors: A case study of adiyaman province. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2024, 196, 525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kara, Y.; Yavuz, V.; Temiz, C.; Lupo, A.R. Exploring Spatio-Temporal Precipitation Variations in Istanbul: Trends and Patterns from Five Stations across Two Continents. Atmosphere 2024, 15, 539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibarra-Espinosa, S.; da Silva, G.A.M.; Rehbein, A.; Vara-Velaac, A.; de Freitas, E.D. Atmospheric effects of air pollution during dry and wet periods in São Paulo. Environ. Sci. Atmos. 2022, 2, 215–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emekwuru, N.; Ejohwomu, O. Temperature, Humidity and Air Pollution Relationships during a Period of Rainy and Dry Seasons in Lagos, West Africa. Climate 2023, 11, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, L.; Zhao, X.; Tao, Y.; Mi, S.; Huang, J.; Zhang, Q. The effects of air pollution and meteorological factors on measles cases in Lanzhou, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 13524–13533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Govender, P.; Sivakumar, V. Application of k-means and hierarchical clustering techniques for analysis of air pollution: A review (1980–2019). Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2020, 11, 40–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Wang, C. Objective Synoptic Weather Classification on Air Pollution during Winter Seasons in Hangzhou. J. Atmos. Sci. Res. 2021, 4, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zareba, M.; Weglinska, E.; Danek, T. Air pollution seasons in urban moderate climate areas through big data analytics. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 3058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.; Kumar, R.; Tang, W.; Pfister, G.; Xu, Y.; Qian, Y.; Brasseur, G. Air Pollution Interactions with Weather and Climate Extremes: Current Knowledge, Gaps, and Future Directions. Curr. Pollut. Rep. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.-Q.; Hao, T.-Y.; Zhang, Y.-F.; Liu, J.-L.; Li, P.-Y.; Cai, Z.-Y.; Zhang, M.; Wang, Q.-L.; Zhang, H. Vertical observation and analysis on rapid formation and evolutionary mechanisms of a prolonged haze episode over central-eastern China. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 616–617, 135–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, W.; Zhao, T.; Bai, Y.; Kong, S.; Xiong, J.; Sun, X.; Yang, Q.; Gu, Y.; Lu, H. Importance of regional PM2.5 transport and precipitation washout in heavy air pollution in the Twain-Hu Basin over Central China: Observational analysis and WRF-Chem simulation. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 758, 143710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muñoz, R.C.; Garreaud, R.; Rutllant, J.A.; Seguel, R.; Corral, M. New Observations of the Meteorological Conditions Associated with Particulate Matter Air Pollution Episodes in Santiago, Chile. Atmosphere 2023, 14, 1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Handhayani, T. An integrated analysis of air pollution and meteorological conditions in Jakarta. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 5798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kindap, T. Identifying the Trans-Boundary Transport of Air Pollutants to the City of Istanbul under Specific Weather Conditions. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2008, 189, 279–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozcan, H.K. Long Term Variations of the Atmospheric Air Pollutants in Istanbul City. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2012, 9, 781–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baltacı, H. Spatial and temporal variation of the extreme Saharan dust event over Turkey in March 2016. Atmosphere 2017, 8, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baltacı, H.; Akkoyunlu, B.O.; Arslan, H.; Yetemen, Ö.; Özdemir, E.T. The influence of meteorological conditions and atmospheric circulation types on PM10 levels in western Turkey. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2019, 191, 466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Efe, B.; Öztaner, Y.B.; Deniz, A.; Unal, A. Analysis of air pollutants in Kagithane valley and Istanbul Metropolitan Area. Air Qual. Atmos. Health 2022, 15, 1027–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birinci, E.; Deniz, A.; Özdemir, E.T. The relationship between PM10 and meteorological variables in the mega city Istanbul. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2023, 195, 304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birinci, E.; Denizoğlu, M.; Özdemir, H.; Özdemir, E.T.; Deniz, A. Ambient air quality assessment at the airports based on a meteorological perspective. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2023, 195, 1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demirtaş, M. A comprehensive overview of PM10 levels in İstanbul: Annual and seasonal spatio-temporal variations and the long-distance transport. Anadolu Univ. J. Sci. Technol. A-Appl. Sci. Eng. 2018, 19, 219–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasparoglu, S.; Incecik, S.; Topcu, S. Spatial and temporal variation of O3, NO and NO2 concentrations at rural and urban sites in Marmara Region of Turkey. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2018, 9, 1009–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yurtseven, E.; Vehid, S.; Bosat, M.; Köksal, S.; Yurtseven, C.N. Assessment of Ambient Air Pollution in Istanbul during 2003–2013. Iran. J. Public Health 2018, 47, 1137–1144. [Google Scholar]
- TSI. Turkish Statistical Institu: Address Based Population Registration System Results. 2021. Available online: https://data.tuik.gov.tr/Bulten/Index?p=45500 (accessed on 12 March 2024).
- Hersbachi, H.; Bell, B.; Berrisford, P.; Hirahara, S.; Horányi, A.; Muñoz-Sabater, J.; Nicolas, J.; Peubey, C.; Radu, R.; Schepers, D.; et al. The ERA5 global reanalysis. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2020, 146, 1999–2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, X.; Chen, J.; Dai, R.; Zhai, Z.; He, D.; Zhao, L.; Jin, X.; Zhang, J. The Effects of Planetary Boundary Layer Features on Air Pollution Based on ERA5 Data in East China. Atmosphere 2023, 14, 1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Chen, P.; Wang, R.; An, Z.; Qiu, L. Estimation of PM2.5 concentrations with high spatiotemporal resolution in Beijing using the ERA5 dataset and machine learning models. Adv. Space Res. 2023, 71, 3150–3165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fania, A.; Monaco, A.; Pantaleo, E.; Maggipinto, T.; Bellantuono, L.; Cilli, R.; Lacalamita, A.; La Rocca, M.; Tangaro, S.; Amoroso, N.; et al. Estimation of Daily Ground Level Air Pollution in Italian Municipalities with Machine Learning Models Using Sentinel-5P and ERA5 Data. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gündoğdu, S.; Elbir, T. A data-driven approach for PM2.5 estimation in a metropolis: Random forest modeling based on ERA5 reanalysis data. Environ. Res. Commun. 2024, 6, 035029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouhi, M.; Oskouei, E.A. Understanding the spatial patterns of temperature hazards in Qazvin Province Using ERA5-Land Reanalysis data. J. Geogr. Environ. Hazards 2023, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- TMEUCC. Turkish Ministry of Environment, Urbanization and Climate Change. 2023. Available online: https://www.csb.gov.tr/en (accessed on 6 March 2024).
- WHO. World Health Organization. 2021. Available online: https://www.eea.europa.eu/en/analysis/publications (accessed on 15 April 2024).
- Aryani, W.; Mansur, M. Pengaruh Penggunaan Alat Peraga Mistar Hitung Terhadap Hasil Belajar Siswa Pokok Bahasan Penjumlahan Dan Pengurangan Bilangan Bulat. Utama J. Keilmuan Kependidikan Dasar 2017, 9, 55–78. [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro, S.S.; Wilk, M.B. An analysis of variance test for normality: Complete samples. Biometrika 1965, 52, 591–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilcoxon, F. Individual comparisons by ranking methods. Biom. Bull. 1945, 1, 80–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mann, H.B.; Whitney, D.R. On a test of whether one of two random variables is stochastically larger than the other. Ann. Math. Stat. 1947, 18, 50–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartigan, J.A.; Wong, M.A. Algorithm AS 136: A K-Means Clustering Algorithm. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. C Appl. Stat. 1979, 28, 100–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdi, H.; Williams, L.J. Principal component analysis. WIREs Comput. Stat. 2010, 2, 433–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sen, A.; Srivastava, M. Multiple Regression. In Regression Analysis: Theory, Methods, and Applications; Springer Texts in Statistics; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- TSMS. Turkish State Meteorological Service. 2024. Available online: https://www.mgm.gov.tr/site/yardim1.aspx?=HadSid (accessed on 15 April 2024).
- Tian, X.; Cui, K.; Sheu, H.; Hsieh, Y.; Yu, F. Effects of Rain and Snow on the Air Quality Index, PM2.5 Levels, and Dry Deposition Flux of PCDD/Fs. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2021, 21, 210158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kluska, K.; Piotrowicz, K.; Kasprzyk, I. The impact of rainfall on the diurnal patterns of atmospheric pollen concentrations. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2020, 291, 108042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Sun, Y.; Zhao, C.; Jiang, H. Impact of Precipitation with Different Intensity on PM2.5 over Typical Regions of China. Atmosphere 2020, 11, 906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.; Xu, G.; Li, Q.; Chen, C.; Li, J. Effect of precipitation on reducing atmospheric pollutant over Beijing. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2019, 10, 1443–1453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
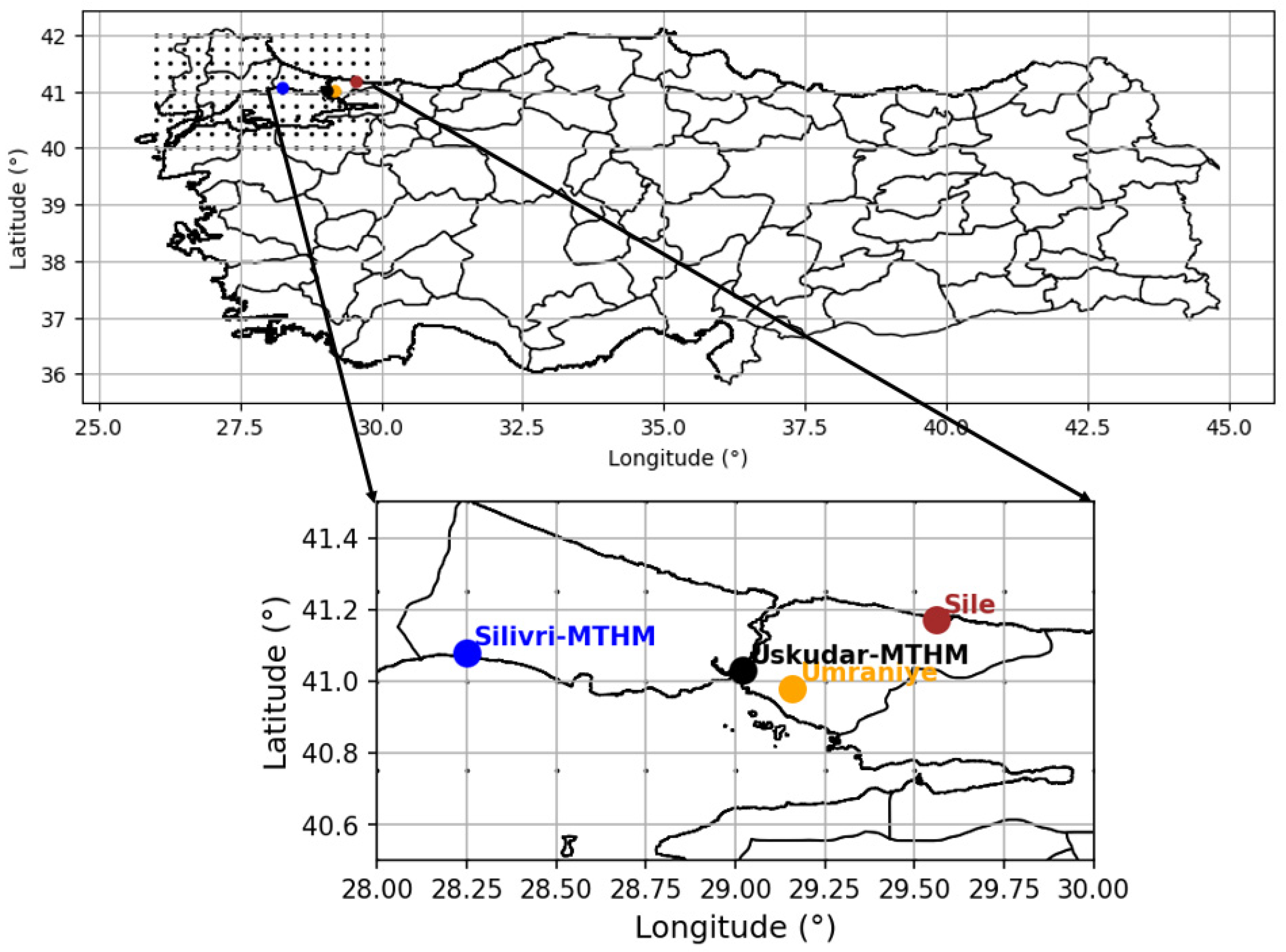
| AQMS | Lat | Lon | Nearest 0.25° Lat | Nearest 0.25° Lon | Distance to Nearest 0.25° | Selected Station |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Silivri-MTHM | 41.08° | 28.25° | 41.00° | 28.25° | 0.08° | + |
| Basaksehir | 41.10° | 28.80° | 41.00° | 28.75° | 0.15° | |
| Kagithane | 41.06° | 29.00° | 41.00° | 29.00° | 0.06° | |
| Umraniye | 41.01° | 29.16° | 41.00° | 29.25° | 0.10° | + |
| Umraniye-MTHM | 41.03° | 29.10° | 41.00° | 29.00° | 0.13° | |
| Sile | 41.17° | 29.56° | 41.25° | 29.50° | 0.14° | + |
| Uskudar-MTHM | 41.03° | 29.02° | 41.00° | 29.00° | 0.05° | + |
| Yenibosna | 41.00° | 28.83° | 41.00° | 28.75° | 0.08° | |
| Mecidiyekoy | 41.07° | 29.00° | 41.00° | 29.00° | 0.07° | |
| Kandilli | 41.06° | 29.06° | 41.00° | 29.00° | 0.12° | |
| Sirinevler | 41.00° | 28.84° | 41.00° | 28.75° | 0.09° | |
| Esenyurt | 41.03° | 28.66° | 41.00° | 28.75° | 0.12° |
| Silivri-MTHM | Umraniye | Sile | Uskudar-MTHM | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Year | PM10 | SO2 | NO2 | PM10 | SO2 | NO2 | PM10 | SO2 | NO2 | PM10 | SO2 | NO2 |
| 2013 | 24.5% | - | 0.0% | - | - | - | 5.4% | - | 0.0% | 30.1% | - | 13.2% |
| 2014 | 21.7% | - | 0.0% | - | - | - | 3.0% | - | 0.0% | 33.0% | - | 12.9% |
| 2015 | 20.5% | - | 0.0% | - | - | - | 2.0% | - | 0.6% | 24.8% | - | 4.7% |
| 2016 | 16.6% | - | 0.0% | - | - | - | 2.8% | - | 0.0% | 19.3% | - | 6.7% |
| 2017 | 20.5% | - | 0.0% | - | - | - | 5.5% | - | 0.0% | 23.6% | - | 4.5% |
| 2018 | 14.0% | 0.0% | 0.0% | - | - | - | 3.4% | 0.0% | 0.0% | 16.1% | - | 3.1% |
| 2019 | 5.3% | 0.0% | 0.0% | 12.1% | 0.0% | 8.0% | 2.8% | 0.0% | 0.0% | 14.6% | - | 2.8% |
| 2020 | 7.2% | 0.0% | 0.0% | 13.0% | 2.5% | 11.5% | 2.8% | 0.0% | 0.0% | 9.7% | - | 2.0% |
| 2021 | 12.3% | 0.0% | 0.0% | 15.6% | 1.8% | 45.7% | 3.3% | 0.0% | 0.0% | 10.4% | - | 1.8% |
| 2022 | 12.6% | 0.0% | 0.0% | 32.1% | 0.0% | 0.0% | 4.3% | 0.0% | 0.0% | 12.1% | - | 0.0% |
| 2023 | 7.5% | 0.0% | 0.0% | 29.0% | 0.0% | 5.3% | 0.3% | 0.0% | 0.0% | 13.5% | - | 0.0% |
| Silivri-MTHM | Umraniye | Sile | Uskudar-MTHM | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Season | PM10 | SO2 | NO2 | PM10 | SO2 | NO2 | PM10 | SO2 | NO2 | PM10 | SO2 | NO2 |
| Spring | 23% | 0% | 0% | 19% | 0% | 2% | 5% | 0% | 0% | 27% | - | 10% |
| Summer | 5% | 0% | 0% | 15% | 1% | 5% | 1% | 0% | 0% | 3% | - | 2% |
| Autumn | 14% | 0% | 0% | 19% | 2% | 6% | 5% | 0% | 0% | 18% | - | 4% |
| Winter | 18% | 0% | 0% | 24% | 0% | 17% | 3% | 0% | 0% | 28% | - | 3% |
| PM10 | SO2 | NO2 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Silivri-MTHM | MAE | 117.5 | 1.9 | 58.1 | |
| R2 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.3 | ||
| Intercept | 34.4 | 3.5 | 29.8 | ||
| Coefficients | PRE | −0.6 | 0.0 | −0.2 | |
| T | 0.1 | 0.0 | −0.2 | ||
| Td | 0.0 | 0.0 | −0.1 | ||
| Ws | −1.4 | −0.1 | −0.2 | ||
| SLP | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | ||
| Umraniye | MAE | 210.4 | 3.2 | 210.1 | |
| R2 | 0.1 | 0.0 | 0.3 | ||
| Intercept | 363.5 | 10.8 | 300.8 | ||
| Coefficients | PRE | −1.0 | 0.0 | −0.3 | |
| T | 0.2 | 0.0 | −0.7 | ||
| Td | −0.3 | 0.0 | −0.3 | ||
| Ws | −1.6 | 0.0 | −2.4 | ||
| SLP | −0.3 | 0.0 | −0.2 | ||
| Sile | MAE | 71.7 | 2.3 | 6.5 | |
| R2 | 0.0 | 0.1 | 0.2 | ||
| Intercept | 80.0 | 68.7 | 138.3 | ||
| Coefficients | PRE | −0.4 | 0.0 | 0.0 | |
| T | 0.1 | 0.0 | 0.0 | ||
| Td | 0.0 | −0.1 | −0.1 | ||
| Ws | 0.0 | −0.1 | −0.4 | ||
| SLP | −0.1 | −0.1 | −0.1 | ||
| Uskudar-MTHM | MAE | 133.2 | − | 91.6 | |
| R2 | 0.1 | − | 0.2 | ||
| Intercept | 159.3 | − | 156.3 | ||
| Coefficients | PRE | −0.7 | − | −0.2 | |
| T | 0.1 | − | −0.3 | ||
| Td | −0.1 | − | −0.2 | ||
| Ws | −1.0 | − | −1.0 | ||
| SLP | −0.1 | − | −0.1 |
| Precipitation Intensity Category | Precipitation Amount |
|---|---|
| No Rain | <1 mm |
| Light Rain | 1–5 mm |
| Moderate Rain | 6–20 mm |
| Heavy Rain | 21–50 mm |
| Severe Rain | >50 mm |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yavuz, V. Variations in Air Pollutant Concentrations on Dry and Wet Days with Varying Precipitation Intensity. Atmosphere 2024, 15, 896. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15080896
Yavuz V. Variations in Air Pollutant Concentrations on Dry and Wet Days with Varying Precipitation Intensity. Atmosphere. 2024; 15(8):896. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15080896
Chicago/Turabian StyleYavuz, Veli. 2024. "Variations in Air Pollutant Concentrations on Dry and Wet Days with Varying Precipitation Intensity" Atmosphere 15, no. 8: 896. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15080896
APA StyleYavuz, V. (2024). Variations in Air Pollutant Concentrations on Dry and Wet Days with Varying Precipitation Intensity. Atmosphere, 15(8), 896. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15080896






