A GPU-Implemented Lattice Boltzmann Model for Large Eddy Simulation of Turbulent Flows in and around Forest Shelterbelts
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. The Numerical Model and Vegetation Drag Force Implementation
2.1. The ABLE-LBM Model
2.2. Modeling of Porous Element Drag Force in LBM System
2.3. Sub-Grid Turbulence Parameterization
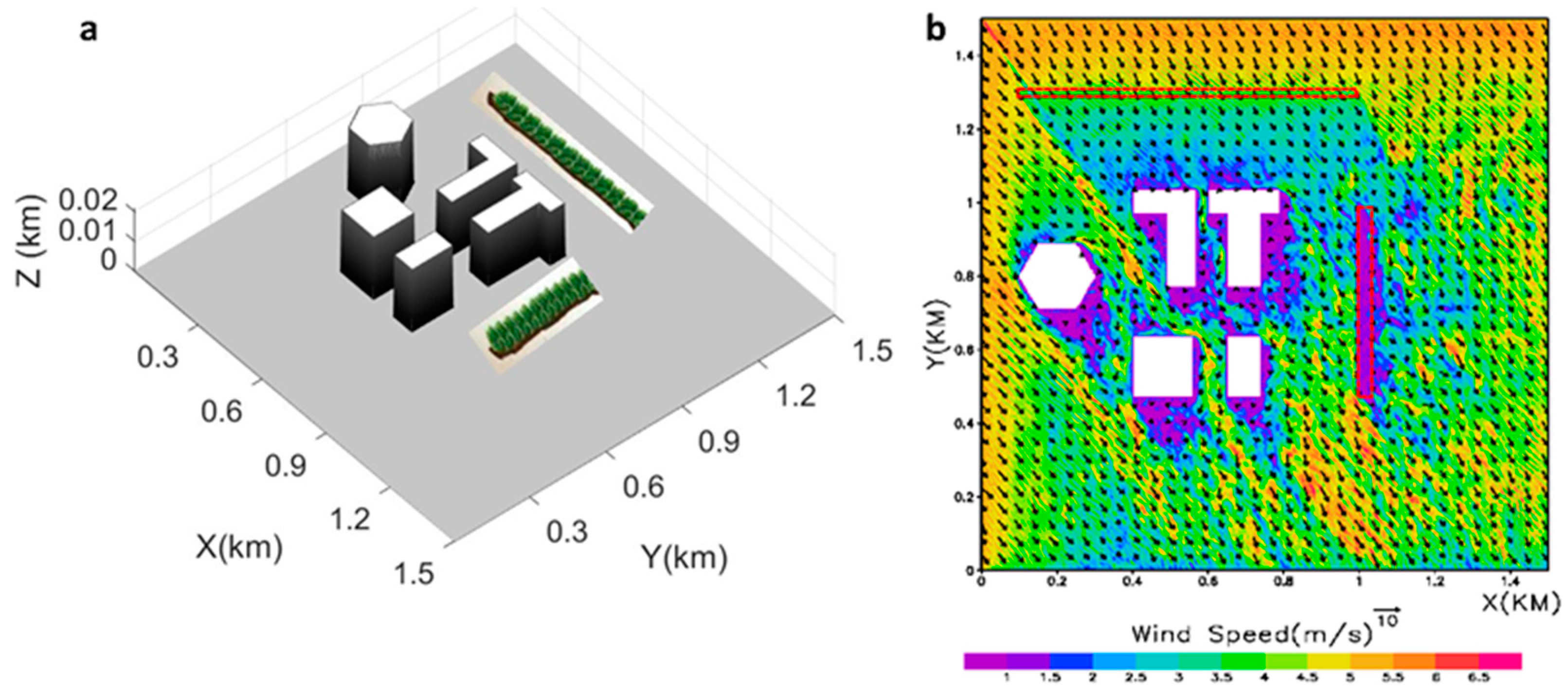
3. Results and Discussion
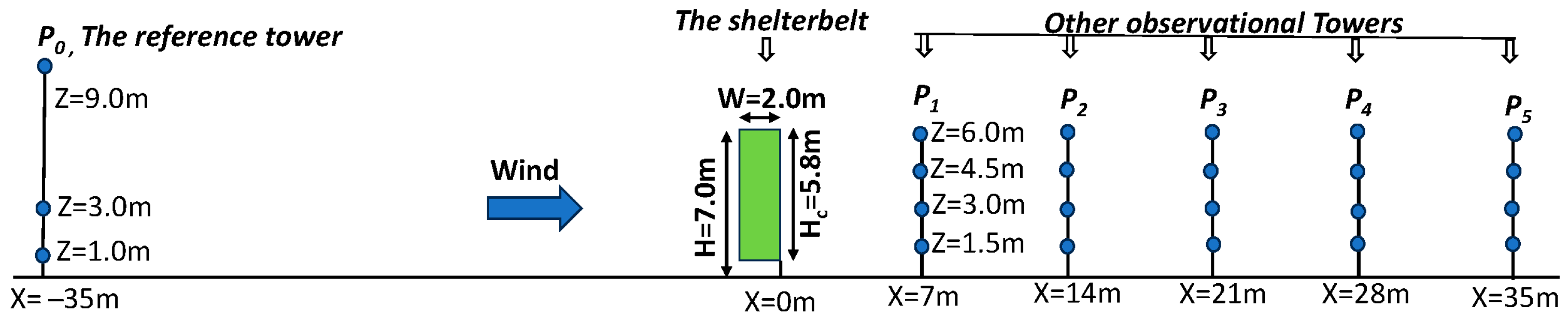
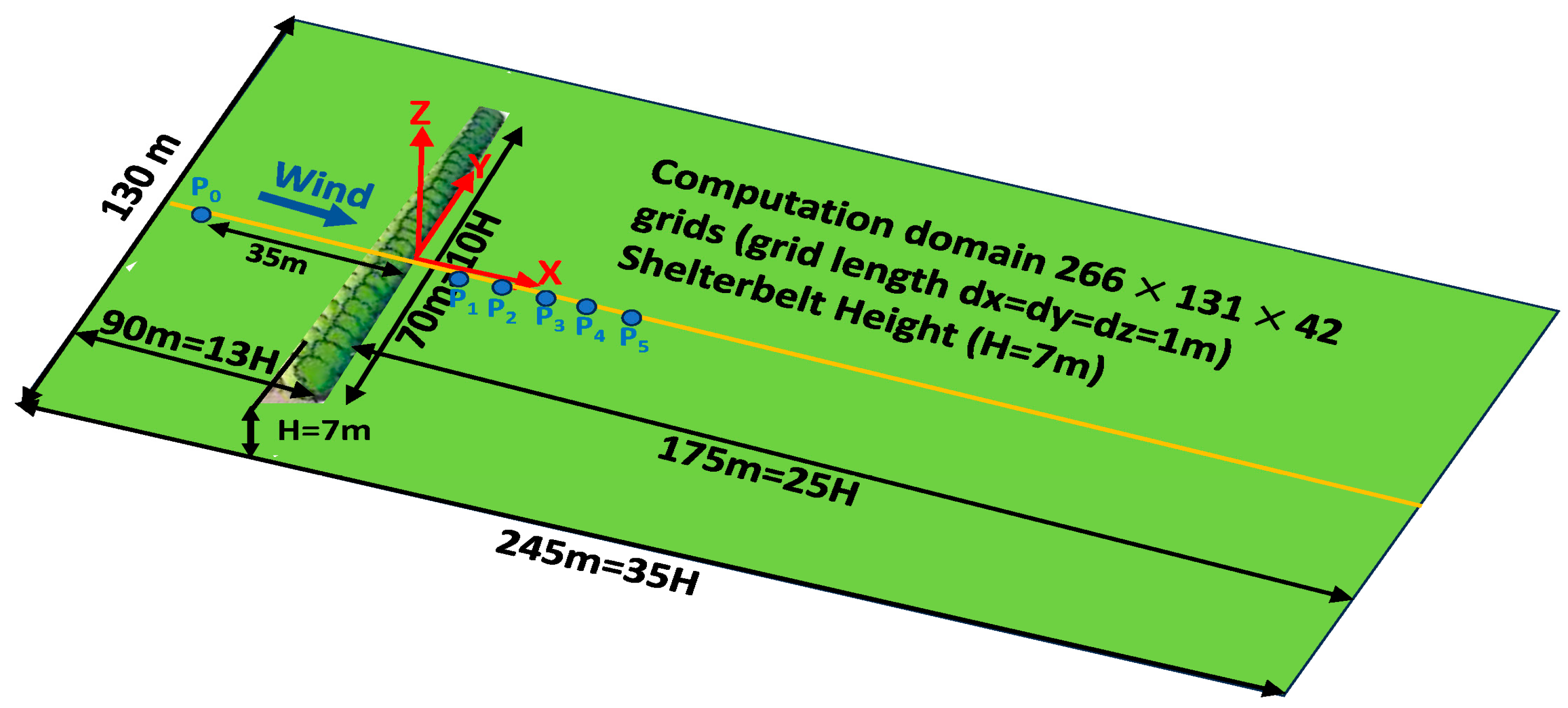
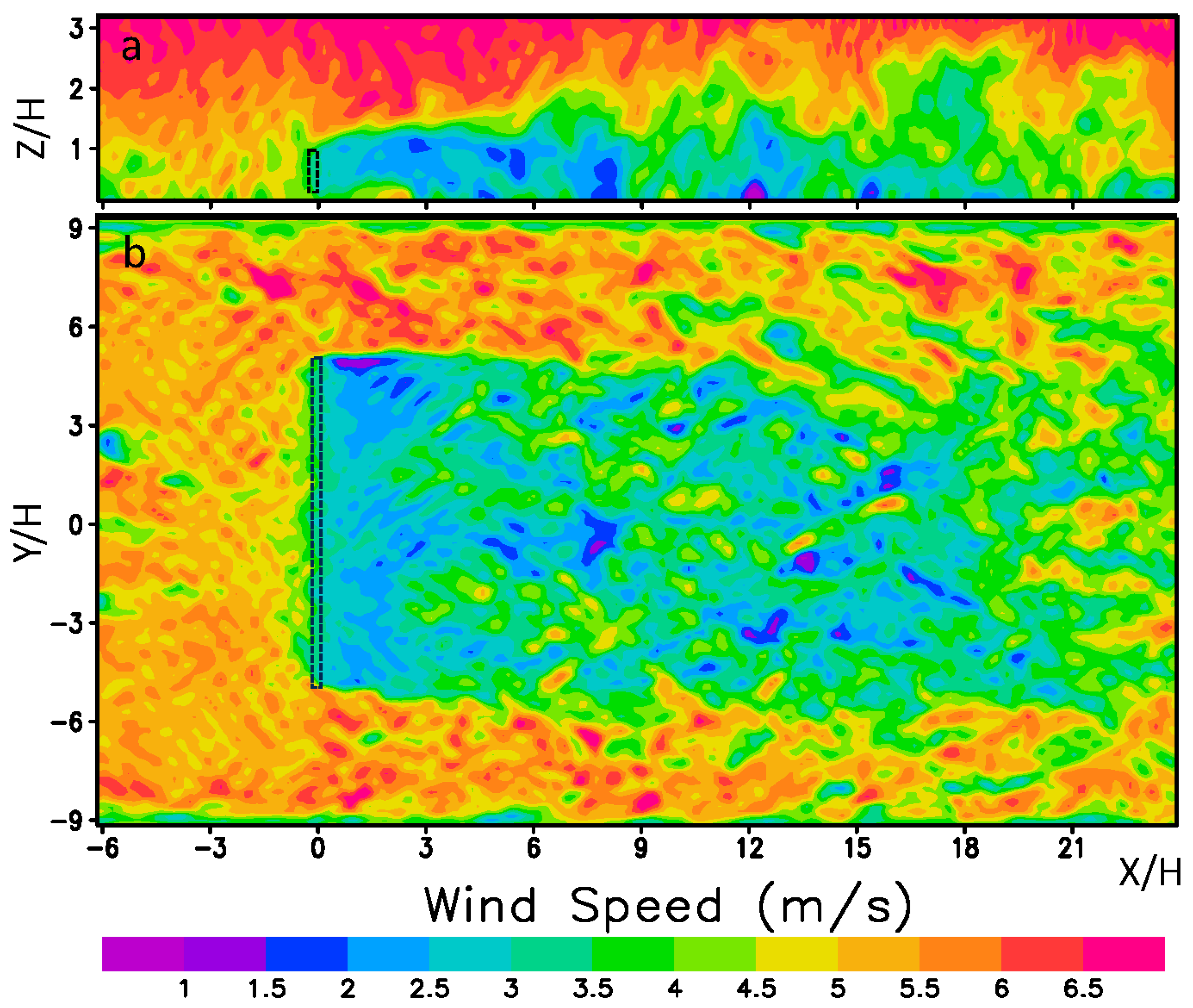
3.1. Simulation of a Forest Shelterbelt
3.2. The Sensitivity of Turbulent Flow Field to Shelterbelt Structures and Wind Directions
3.2.1. Vegetation Element Density
3.2.2. The Width of the Shelterbelt
3.2.3. The Wind Directions and Shelter Effects
3.3. GPU Implementation of the ABLE-LBM and Model Execution Speed
4. Summary and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- van Eimern, J.; Karschon, R.; Razumova, L.A.; Robertson, G.W. Windbreaks and Shelterbelts; Tech. Note No. 59; World Meteorological Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 1964; 188p. [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg, N.J. The influence and implications of windbreaks on agriculture in dry regions. In Ground Level Climatology; Shaw, R.H., Ed.; American Association for the Advancement of Science: Washington, DC, USA, 1967; pp. 327–349. [Google Scholar]
- Miller, D.R.; Rosenberg, N.J.; Bagley, W.T. Soybean water use in the shelter of a slat-fence windbreak. Agric. Meteorol. 1973, 11, 405–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogawa, Y.; Diosey, P.G. Surface roughness and thermal stratification effects on the flow behind a two-dimensional fence: II. A wind tunnel study and similarity considerations. Atmos. Environ. 1980, 14, 1309–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heisler, G.M.; Dewalle, D.R. Effects of windbreak structure on wind flow. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 1988, 22–23, 41–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurotani, Y.; Kiyota, N.; Kobayashi, S. Windbreak Effect of Tsuijimatsu in Izumo: Part. 2. Proc. Archit. Inst. Jpn. 2001, 745–746. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar]
- Wilson, J.D. Oblique, stratified winds about a shelter fence. Part I: Measurements. J. Appl. Meteorol. 2004, 43, 1149–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Tofsted, D.; Yarbrough, J.; Quintis, D.; Brice, R.; D’Arcy, S.; Elliott, S.; Truong, T.; Davalo, M. Characterizing the Turbulent Wind Flow Near a Wind Barrier Using a Data Set Collected with an Array of Sonic Anemometers; ARL Technical Report ARL-TR-4834; Army Research Laboratory: Adelphi, MD, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Judd, M.J.; Raupach, M.R.; Finnigan, J.J. A Wind Tunnel Study of Turbulent Flow around Single and Multiple Windbreaks, Part I: Velocity Fields. Bound.-Layer Meteorol. 1996, 80, 127–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Z.; Luo, W.; Qian, G.; Wang, H. A wind tunnel simulation of the mean velocity fields behind upright porous fences. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2007, 146, 82–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torita, H.; Nemoto, M. Wind Tunnel Experiment on Densities and Widths of Shelterbelt. J. Jpn. For. Soc. 2002, 84, 85–90. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi, H. Wind tunnel test on the effect of width of windbreaks on the wind speed distribution in leeward. J. Agric. Meteorol. 1978, 33, 183–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thom, A.S. Momentum, mass and heat exchange of plant communities. Veg. Atmos. 1975, 1, 1–278. [Google Scholar]
- Wilson, N.R.; Shaw, R.H. A higher order closure model for canopy flow. J. Appl. Meteorol. 1977, 16, 1197–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raupach, M.R.; Shaw, R.H. Averaging procedures for flow within vegetation canopies. Boundary-Layer Meteorol. 1982, 22, 79–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finnigan, J.J. Turbulent transport in flexible plant canopies. In The Forest-Atmosphere Interaction; Hutchison, B.A., Hicks, B.B., Eds.; D. Reidel: Dordrecht, The Netherlands; Boston, MA, USA; Lancaster, UK, 1985; pp. 443–480. [Google Scholar]
- Wilson, J.D. Numerical Studies of Flow through a Windbreak. J. Wind Eng. Ind. Aerod. 1985, 21, 119–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, J.D. Oblique, Stratified Winds about a Shelter Fence. Part II: Comparison of Measurements with Numerical Models. J. Appl. Meteorol. 2004, 43, 1392–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Lin, J.D.; Miller, D.R. Air flow over and through a forest edge: A steady-state numerical simulation. Bound.-Layer Meteorol. 1989, 46, 333–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Shen, J. A two-dimensional numerical study of the wind sheltering effects of shelterbelts. Acta Meteol. Sin. 1989, 3, 498–505. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Takle, E.S. A numerical simulation of boundary-layer flows near shelterbelts. Bound.-Layer Meteorol. 1995, 75, 141–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Takle, E.S. Model-simulated influences of shelterbelt shape on wind sheltering efficiency. J. Appl. Meteorol. 1997, 36, 695–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Lilly, D.K. On the numerical simulation of buoyant convection. Tellus 1962, 14, 148–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smagorinsky, J. General circulation experiments with the primitive equations. Mon. Weather Rev. 1963, 91, 99–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patton, E.G.; Shaw, R.H.; Judd, M.J.; Raupach, M.R. Large-eddy simulation of windbreak flow. Bound.-Layer Meteorol. 1998, 87, 275–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Y.; Ishihara, T. Numerical study of turbulent flow fields around of a row of trees and an isolated building by using modified k-e model and LES model. J. Wind. Eng. Ind. Aerodyn. 2018, 177, 293–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, T. LES study on the structure of coherent eddies inducing predominant perturbations in velocities in the roughness sublayer over plant canopies. J. Meteorol. Soc. Jpn. 2009, 87, 39–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Patruno, L.; Zhao, G.; Tamura, Y. Windbreak effectiveness of shelterbelts with different characteristic parameters and arrangements by means of CFD simulation. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2024, 344, 109813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Yan, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Lang, J.; Wang, X. A Numerical Study of the Effect of Vegetative Windbreak on Wind Erosion over Complex Terrain. Forests 2022, 13, 1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Doolen, G.D. Lattice Boltzmann method for fluid flows. Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 1998, 30, 329–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Shu, C. Lattice Boltzmann method and its applications in engineering. In Advances in Computational Fluid Dynamics; World Scientific Publishing Co.: Singapore, 2013; Volume 3, ISBN 978-981-4508-29-2. [Google Scholar]
- Krüger, T.; Kusumaatmaja, H.; Kuzmin, A.; Shardt, O.; Silva, G.; Viggen, E.M. The Lattice Boltzmann Method, Principles and Practice; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2017; 694p, ISBN 978-3-319-44649-3. [Google Scholar]
- Bhatnagar, P.L.; Gross, E.P.; Krook, M. A Model for collision processes in gases. I: Small amplitude processes in charged and neutral one-component system. Phys. Rev. 1954, 94, 511–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Y.H.; d’Humières, D.; Lallemand, P. Lattice BGK models for Navier-Stokes equation. Europhys. Lett. 1992, 17, 479–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Chen, S.; Matthaeus, W.H. Recovery of the Navier-Stokes equations using a lattice-gas Boltzmann method. Phys. Rev. A 1992, 45, 5339–5342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geier, M.; Greiner, A.; Korvink, J.G. Cascaded digital lattice Boltzmann automata for high Reynolds number flow. Phys. Rev. E 2006, 73, 066705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geier, M.; Schonherr, A.M.; Pasquali, A.; Krafczyk, M. The cumulant lattice Boltzmann equation in three dimensions: Theory and validation. Comput. Math. Appl. 2015, 70, 507–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacob, J.; Malaspinas, O.; Sagaut, P. A new hybrid recursive regularised Bhatnagar– Gross–Krook collision model for lattice Boltzmann method-based large eddy simulation. J. Turbul. 2018, 19, 1051–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- d’Humières, D. Generalized lattice Boltzmann equations. In Rarefied Gas Dynamics: Theory and Simulations; Shizgal, B.D., Weave, D.P., Eds.; Progress in Astronautics and Aeronautics; AIAA: Reston, VA, USA, 1992; Volume 159, pp. 450–458. [Google Scholar]
- d’Humières, D.; Ginzburg, I.; Krafczyk, M.; Lallemand, P.; Luo, L.-S. Multiple-relaxation-time lattice Boltzmann models in three dimension. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. A 2002, 360, 437–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lallemand, P.; Luo, L.-S. Theory of the lattice Boltzmann method: Dispersion, dissipation, isotropy, Galilean invariance and stability. Phys. Rev. E 2000, 61, 6546–6562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Luo, L.-S. Theory of lattice Boltzmann method: From the Boltzmann equation to the lattice Boltzmann equation. Phys. Rev. E 1997, 56, 6811–6817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, Z.; Shi, B. Multiple-relaxation-time lattice Boltzmann method for the Navier-Stokes and nonlinear convection-diffusion equations: Modeling, analysis, and elements. Phys. Rev. E 2020, 102, 023306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, T.; Shimoyama, K.; Kawashima, M.; Inagaki, A. Large-Eddy Simulation of Neutrally-Stratified Turbulent Flow within and above Plant Canopy Using the Central-Moments-Based Lattice Boltzmann Method. Bound.-Layer Meteorol. 2020, 176, 35–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, X.; Santasmasas, M.C.; Xue, X.; Niu, J.; Davidson, L.; Revell, A.J.; Yao, H.-D. Near-wall modeling of forests for atmosphere boundary layers using lattice Boltzmann method on GPU. Eng. Appl. Comput. Fluid Mech. 2022, 16, 2143–2156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; MacCall, B.; Hocut, C.; Zeng, X.; Fernando, H.J.S. Simulation of stratified flows over a ridge using a lattice Boltzmann model. Environ. Fluid Mech. 2018, 20, 1333–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Benson, M. Large-eddy simulation of turbulent flows over an urban building array with the ABLE-LBM and comparison with 3D MRI observed data sets. Environ. Fluid Mech. 2020, 21, 287–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Decker, J.; Pardyjak, E. Large-eddy simulations of turbulent flows around buildings using a Lattice Boltzmann model. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2020, 59, 885–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enoki, K.; Ishihara, T. A generalized canopy model and its application to the prediction of urban wind climate. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2012, 68, 28–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Guo, Z.L.; Zheng, C.G.; Shi, B.C. Discrete lattice effects on the forcing term in the lattice Boltzmann method. Phys. Rev. E 2002, 65, 046308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Luo, L.-S.; Girimaji, S. LES of turbulent square jet flow using an MRT Lattice Boltzmann model. Comput. Fluids 2006, 35, 957–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, Z.; Zhao, T.S. Effect of the forcing term in the multiple-relaxation-time lattice Boltzmann equation on the shear stress or the strain rate tensor. Phys. Rev. E 2012, 86, 023306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Intel X5650 CPU (Hours) | Nvidia P100 GPU (Hours) | Nvidia V100 GPU (Hours) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 236.82 | 1.84 | 0.78 | |
| CPU/GPU time ratio | 129 | 303 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Y.; Zeng, X.; Decker, J.; Dawson, L. A GPU-Implemented Lattice Boltzmann Model for Large Eddy Simulation of Turbulent Flows in and around Forest Shelterbelts. Atmosphere 2024, 15, 735. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15060735
Wang Y, Zeng X, Decker J, Dawson L. A GPU-Implemented Lattice Boltzmann Model for Large Eddy Simulation of Turbulent Flows in and around Forest Shelterbelts. Atmosphere. 2024; 15(6):735. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15060735
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Yansen, Xiping Zeng, Jonathan Decker, and Leelinda Dawson. 2024. "A GPU-Implemented Lattice Boltzmann Model for Large Eddy Simulation of Turbulent Flows in and around Forest Shelterbelts" Atmosphere 15, no. 6: 735. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15060735
APA StyleWang, Y., Zeng, X., Decker, J., & Dawson, L. (2024). A GPU-Implemented Lattice Boltzmann Model for Large Eddy Simulation of Turbulent Flows in and around Forest Shelterbelts. Atmosphere, 15(6), 735. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15060735







