Abstract
The Brazilian Cerrado biome is known for its high biodiversity, and the role of groundwater recharge and climate regulation. Anthropogenic influence has harmed the biome, emphasizing the need for science to understand its response to climate and reconcile economic exploration with preservation. Our work aimed to evaluate the seasonal and interannual variability of the surface energy balance in a woodland savanna (Cerrado) ecosystem in southeastern Brazil over a period of 19 years, from 2001 to 2019. Using field micrometeorological measurements, we examined the variation in soil moisture and studied its impact on the temporal pattern of energy fluxes to distinguish the effects during rainy years compared to a severe drought spell. The soil moisture measures used two independent instruments, cosmic ray neutron sensor CRNS, and FDR at different depths. The measures were taken at the Pé de Gigante (PEG) site, in a region of well-defined seasonality with the dry season in winter and a hot/humid season in summer. We gap-filled the energy flux measurements with a calibrated biophysical model (SiB2). The long-term averages for air temperature and precipitation were 22.5 °C and 1309 mm/year, respectively. The net radiation (Rn) was 142 W/m2, the evapotranspiration (ET) and sensible heat flux (H) were 3.4 mm/d and 52 W/m2, respectively. Soil moisture was marked by a pronounced negative anomaly in the 2014 year, which caused an increase in the Bowen ratio and a decrease in Evaporative fraction, that lasted until the following year 2015 during the dry season, despite the severe meteorological drought of 2013/2014 already ending, which was corroborated by the two independent measurements. The results showed the remarkable influence of precipitation and soil moisture on the interannual variability of the energy balance in this Cerrado ecosystem, aiding in understanding how it responds to strong climate disturbances.
1. Introduction
The Brazilian Cerrado is one of the largest biomes in South America, covering 1.5 million km2 or 24% of the Brazillian land, composed of grasses and savanna forests and playing a fundamental hydrological role by containing headwaters of large rivers that recharge large deep aquifers, with a great spatial climatic variation with average temperatures ranging from 20 °C to 26 °C and precipitation from 800 to 1800 mm/year [1]. The vegetation of the Cerrado is characterized by strong seasonality, with a humid and hot summer and a dry and mild winter, which markedly controls evapotranspiration and primary productivity [2,3]. This seasonal control is generally noted in the surface energy balance pattern, especially in the partitioning of turbulent atmospheric fluxes of sensible heat H and latent heat LE, which is very different from the Amazonian forests [4]. The partitioning of available energy, for example, expressed in the Bowen ratio (β = H/LE), shows high values in the dry season and small values in the rainy season, respectively [4], associated with the high soil water deficit during the dry season [5]. The most common vegetation physiognomies in the Cerrado biome are the campo Cerrado and Cerrado sensu stricto, structurally composed of herbaceous and arboreal strata that coexist simultaneously [6]. During the dry season, many Cerrado trees show adaptation mechanisms in their senescence process to try to use moisture from deeper soil levels [7], while grasses undergo dormancy processes. Fire events in the Cerrado, which are part of its adaptive mechanisms in its evolutionary history, also influence the energy balance and soil water status temporarily [5,8].
Furthermore, on a regional scale and especially at the border of the Amazon and Cerrado biomes, deforested areas replaced by cultivated pastures have possibly promoted the reduction of evapotranspiration (ET), which has possibly influenced the reduction of rainfall at the beginning of the rainy season in recent decades [9]. In general, in terms of natural precipitation variability, Brazil has been subject to large regional-scale meteorological droughts in the last two decades, such as in the Pantanal biome in 2020 [10], in the Cerrado biome of the central-west region between 2016 and 2017 [11] and particularly in the southeastern region from 2013 to 2014 [12] with a rainfall reduction of 44%, considered an exceptional index that disrupted the socio-economic condition of 80 million people due to water consumption restrictions [13].
Soil moisture is a condition of the Cerrado state that is inherently linked to vegetation seasonality, energy partitioning at the surface and possibly interannual climate variability, whose variation depends on the precipitation, evapotranspiration and water storage in the soil [3,4,5,14]. The measurement of soil moisture can use different methods, such as direct current resistivity [15], electromagnetic induction [16] and time-domain reflectometry (FDR) [17], which, however, sample a small volume of soil at a point scale (ANNISS, 2021). The cosmic ray neutron soil moisture probe (CRNS) measures neutrons that have been thermalized by hydrogen atoms present in the soil [18], potentially within a footprint of 130–240 m radius around the probe and extending to depths from 0.15 m up to 0.83 m [19]. Joint measurements of soil moisture and energy fluxes in the Cerrado are scarce in the literature, and knowledge of the interactions between soil moisture and vegetation remains an open question, with several implications: How sensitive are the tree and grass layers to the seasonal water deficit? How does soil water deficit control the vegetation response during season transitions (from wet to dry and from dry to wet)? What is the impact of major meteorological droughts on soil moisture and energy partitioning?
Our work aimed to evaluate the seasonal and interannual variability of the surface energy fluxes in an area with woodland savanna ecosystem (Cerrado) in southeastern Brazil, using micrometeorological measurements, in a range during 19 years from 2001 to 2019, and discusses the soil moisture variability in distinguishing the effects in rainy years compared to severe drought years.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area and Micrometeorological Measurements
Our study area is located in the city of Santa Rita do Passa Quatro, São Paulo state, Brazil, in the Pé de Gigante Forest Reserve (PEG), with an area of 1060 hectares, covered with woodland savanna vegetation (Figure 1, with dense Cerrado predominantly of Cerradão and Cerrado sensu stricto physiognomies [20,21] and other small areas of campo and deciduous forest, with a surrounding eucalyptus plantation to the west and north, and crops to the east and south.
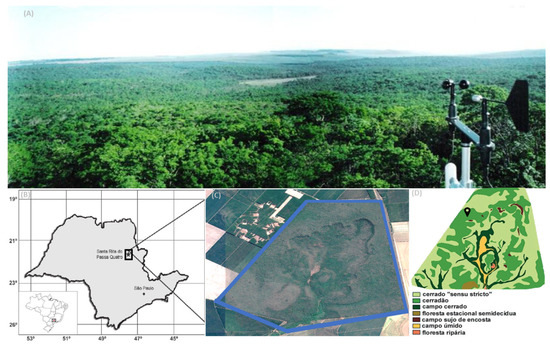
Figure 1.
(A) View from the top of the micrometeorological tower at the PEG site, in the southeast direction, with a cup anemometer/wind vane on the right; (B) map of Brazil and São Paulo state with a location box of the site in the city of Santa Rita do Passa Quatro; (C) satellite image (07/2018) of the region with the PEG site (blue polygon); (D) vegetation physiognomy at the PEG site (adapted from [22]).
The site is located ≃ 300 km from the coast and 700 m above sea level, with climatological normals (interval 1961–1990) at the Santa Rita do Passa Quatro meteorological station (21°43′09″ S; 47°28′22″ W, 715 m) reporting Cwa climate (Koeppen classification), average temperature ranging from 17.6 °C (July) to 23.5 °C (February), a dry season centered in winter from May to August and a rainy season centered in summer, from September to April with average precipitation of 1478 mm/year. The canopy height of vegetation in PEG varies from approximately 10 to 12 m. The soil in the region is predominantly Neossolo Quartzarênico (94%), sandy with good rooting capacity and low natural fertility, with reduced levels of nutrients. Its superficial layer horizon A is characterized by the decomposing organic layer, and horizon B presents a higher concentration of clay [23].
Micrometeorological measurements (Table 1) were performed automatically between 2001 and 2019 on two micrometeorological towers, the first after 2001 (21.619238° S, 47.632327° W) at 21 m height, and the second (21.618609° S and 47.633810° W) from 2010 on and about 100 m southeast of the first, at 13 m height. The positioning was designed so that the tower fetch took advantage of the predominant wind direction, usually from the east and northeast during the day and from the southeast at night, and thus representative of the Cerrado vegetation area.

Table 1.
Field measurements at PEG site.
With the installation of a 2.5 m horizontal mast at 18 m high, we measured net radiation (Rn, LITE, Kipp and Zonen, Delft, The Netherlands), global solar incoming radiation (Rg, CM3, Kipp and Zonen) and the incident and reflected fluxes of photosynthetically active radiation (PAR, LITE, Kipp and Zonen). At a height of 21 m, we measured precipitation (TB4, Hydrological Services Pty. Ltd., Sydney, NSW, Australia), wind speed (RM Young) and air temperature and humidity (HMP45 Vaisala, Helsinki, Finland). The soil heat flux (G) was measured using four heat plates (REBS, Seattle, WA, USA). The turbulent heat fluxes (LE) and (H) were estimated using the Eddy Covariance (EC) method, using a sonic anemometer (CSAT3 Campbell Sci) and an open-path gas analyzer (LI-7500 Licor Inc., Lincoln, NE, USA), with acquisition at 10 Hz with a CR1000 datalogger. The data processing was performed using EddyPro 7 software (Li-Cor, Lincoln, NE, USA). The data were converted from binary format to ASCII using Card-Convert software (Campbell Inc., Logan, UT, USA) and processed in 30 min blocks. To calculate the fluctuations, block averaging, linear trend elimination and moving average were applied. Time lag compensation was performed by maximizing the covariance, axis rotation for the correction of inclination through double rotation calculation, fluctuation and density compensation [24], sensor heating correction and high-pass and low-pass filters https://www.licor.com/env/support/EddyPro (accessed on 10 January 2001).
To address uncertainties in the estimation of energy fluxes due to energy balance closure, we used the correction of [25], assuming that the available energy measurements represented the coverage area of the EC and using criteria based on the observed Bowen ratio:
where Ho = observed sensible heat flux; LEo = observed latent heat flux; and the corrected fluxes Hc and LEc were estimated as:
where Rn = net radiation; G = soil heat flux; Sa = sensible and latent heat storage change in the air column.
β = Ho/LEo
LEc = (Rn − G − Sa − Sb)/(1 + β)
Hc = Rn − G − LEc − Sa
2.2. Soil Moisture
The soil moisture was measured by two instruments, one using vertical profile scanning with frequency domain reflectometry (FDR) (CS615 Campbell Sci) at depths of 10, 20, 50, 80, 100, 150, 200 and 250 cm, from October/2000 to 2009 and CS616 (Campbell Sci) from 2010 to 2019, and the second using horizontal/vertical scanning with a cosmic ray neutron sensor (CRNS) (Hydroinnova LLC, Albuquerque, NE, USA), installed in July/2011 and available until August/2018. The sensors were calibrated with local soil gravimetric samples (BRUNO 2004). The CRNS sensor represents a technological innovation that reaches a much wider horizontal extent of surface soil moisture and prioritizes estimates at shallower soil depths. We are not aware of previous reports of publications using CRNS measurements in savanna areas in Brazil. The estimation of soil moisture by CRNS went through calibration steps, due to interactions with water molecules present in the atmosphere, biomass and minerals. The raw data from the CRNS sensor were obtained from the website http://cosmos.hwr.arizona.edu/Probes/StationDat/044/index.php (accessed on 2 February 2012), with the following variables used: neutron count (MOD), correction factor that considers the size of the probe (PROBE), correction factor due to atmospheric pressure (PRESS) and correction factor that considers changes in the intensity of cosmic rays as a function of time (INTEN). Air temperature, relative humidity and precipitation data from the EC tower located at PEG, and the calculation of absolute air humidity (ρ_v) were also used in the correction process. In the first correction step, based on the neutron count according to vapor pressure (fh), it was assumed that:
Fh = 1 + 0.0054 × ρ_v;
The second step, biomass, was based on the process described by [26]. Literature values for the Brazilian Cerrado region [27] were also used to establish the average soil organic matter content. As a result of the processes described above, we obtained the corrected neutron count (Npihv). Thus, soil moisture was obtained by the equation:
Θ = (α0/(Npihv/N_0 − α1) − α2 − lw − SOC) × BD;
α0 = 0.0808 (cm3/g), α1 = 0.372 and α2 = 0.115 (cm3/g) are fixed, with lw = 1.7% being the water content in soil minerals, SOC is the water content in soil organic matter, BD is the soil bulk density and N_0 is obtained from the available calibration data at (http://cosmos.hwr.arizona.edu/Probes/StationDat/044/calib.php, accessed on 25 May 2024).
After correction, the calibration process was based on soil moisture data obtained by the gravimetric method.
The daily averaged volumetric water content data (θ, in m3/m3) were used to evaluate the Soil Wetness Index (SWI) and soil wetness (W), respectively, given by:
SWI = ((θi − θmin))/((θmax − θmin))
W = θi/θs
θi = soil moisture measured on day i; θmin = absolute minimum moisture content of the daily average series; θmax = absolute maximum moisture content of the daily average series; and θs = soil porosity, described here as θmax.
We noticed that the comparison of the CRNS sensor showed a strong correlation with the FDR sensor measurements at the shallower soil depths of 10 cm and 20 cm, respectively, as shown in Figure 2, while at deeper FDR depths (50 to 250 cm), the correlation was weak (not shown). Knowing in advance that the vertical sampling of the CRNS is relatively shallow, it was useful to note that the FDR sensors, which have a weakness in horizontal sampling, compared well with the CRNS at the shallower depths. This suggests that there was adequate representation of surface moisture in the study area with both measurement approaches, at least in the shallow soil.
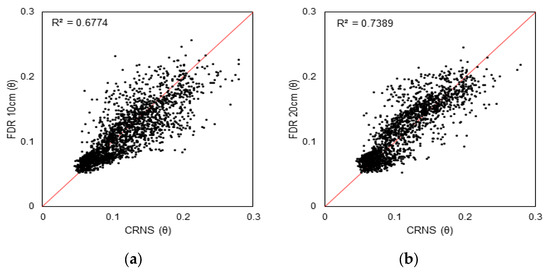
Figure 2.
Daily average volumetric water content (θ) measured by CRNS sensor versus FDR sensor at a depth of (a) 10 cm and (b) 20 cm in the Cerrado sensu stricto (woodland savanna) area of the PEG site.
2.3. Gap-Filling the Observational Series
To fill in the gaps in the historical series of energy fluxes at hourly resolution, we used the SiB2 model [28] as a predictor of net radiation and atmospheric fluxes H and LE. The SiB2 model was run in offline mode, forced with field meteorological data (incoming solar radiation, air temperature and humidity, horizontal wind speed, precipitation and CO2 concentration) at a time step of 1 h, and it calculated the fluxes of net radiation, sensible heat flux, latent heat flux and its components (soil evaporation, transpiration, and rainfall interception evaporation), soil heat flux, soil temperature and soil moisture and gross and net CO2 assimilation. The meteorological data used to force the model were checked for consistency to eliminate spurious values due to sensor malfunctioning. The inconsistencies and gaps were filled using data from the ERA5-Land reanalysis [29], downscaled to the micrometeorological tower scale, with a linear regression method of hourly percentiles of measurements with the reanalysis. From 2001 to 2019, the filling totaled 5.1% for incoming solar radiation, 4.4% for air temperature, 4.6% for water vapor pressure and 7.6% for horizontal wind speed.
2.4. Estimating Model Parameters with Remote Sensing
The approach involved prescribing some model parameters from remote sensing of leaf area index (LAI) and the fraction of absorbed photosynthetically active radiation (FPAR) [29]. As the first step in parameter estimation during calibration, the time-variant parameters (monthly based) of LAI, FPAR, canopy greenness fraction (N) and land cover fraction (V) were estimated using the adapted MAPPER algorithm [30], as:
where k = mean extinction coefficient of photosynthetically absorbed radiation in the vegetation canopy; Lst = stem and trunk area index; LAI_max = maximum leaf area index; NDVI = normalized difference vegetation index.
LAI = LAImax * NDVI
FPAR = Vc N [1 − exp(−kLAI/V)];
N = LAI/(LAI + Lst)
V = LAI/LAI_max
The NDVI data were obtained of Landsat-8 time series from 2013 to 2020, with a 30 m spatial resolution. Due to the relevance that vegetation cover has on the energy partitioning of ecosystems [31], we used maps with detailed vegetation type [32].
The parameters described in Table 2 influence the time-mean PAR extinction coefficient (12), and consequently, the fraction of canopy PAR absorbed (FPAR) (13), the CO2 assimilation (14–16) and the water vapor canopy conductance (17), as follows:
where = time-mean leaf projection; = leaf dispersion coefficient of photosynthetically active radiation absorbed by the canopy.
where = fraction of photosynthetically active radiation absorbed by the canopy; k = term belonging to the extinction coefficient (()).
where = net leaf CO2 assimilation; Wc = photosynthetic enzyme RuBisCO efficiency; We = amount of PAR captured by chlorophyll; Ws = leaf capacity to export products of photosynthesis; and Rp = plant respiration that depends on the Rubisco-limited rate of assimilation (mol/m2s),
where = maximum catalytic capacity of Rubisco (mol/m2s); = canopy temperature stress factor; = soil moisture stress factor, and
where = leaf stomatal conductance (m/s); = slope coefficient proportional to leaf water use efficiency; = partial CO2 pressure on the leaf surface (Pa); = atmospheric pressure (Pa); and b = intercept coefficient = 0.01 for C3 plants and 0.04 for C4 plants.
An0 = f(Wc,We,Ws) − Rp

Table 2.
Initial and optimized parameters for optimization of net radiation and for the LE flux (physiology).
The temporal and spatial average NDVI field in summer and winter (Figure 3) showed a large deviation between them within the polygon boundaries of PEG site, predominantly with high values in January around 0.85 and lower values in August around 0.70, as expected due to the strong seasonal effect on Cerrado vegetation. In both months, a small area with a field physiognomy, close to the center of the polygon, showed a much-reduced NDVI compared to the total area, with the absence of trees. Except for this localized minimum, there was a certain spatial heterogeneity of NDVI, for both months, but that did not correspond to a very clear association with the patterns of other dominant physiognomies in the area (Figure 1D). The establishment of correlation between the Cerrado physiognomies proves to be complex, not only in relation to NDVI as previously mentioned, but also floristically and by the analyzed soil characteristics [33]. Reference [23] also reinforced that for PEG, the detailed taxonomic classes of soils were also insufficient for a complete understanding of the spatial variation of vegetation.
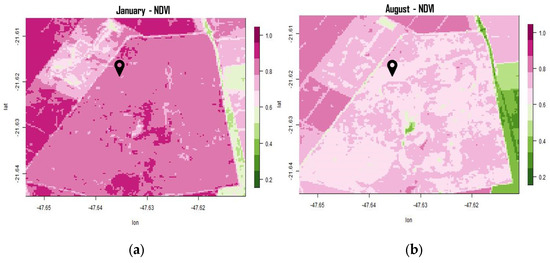
Figure 3.
Temporal average NDVI between 2013 and 2020, tower location under marked black pin, for the months of (a) January and (b) August.
Similarly, the averaged LAI (Figure 4) and FPAR (Figure 5) in summer and winter also showed modest but significant seasonal variation. In the total area covered with Cerrado, the LAI varied from approximately 4.60 m2/m2 in January to 4.25 m2/m2 in winter, as shown in Figure 4b. The FPAR parameter also varied in the same direction, from approximately 0.975 in January to 0.955 in August. The seasonality of vegetation in the site was already noticed in situ, with increasing litterfall during the dry season [34]. The leaf fraction, the most important component of litter, is extremely sensitive to meteorological variables such as precipitation, humidity and air temperature, that are possibly associated to structural changes of the canopy [20].
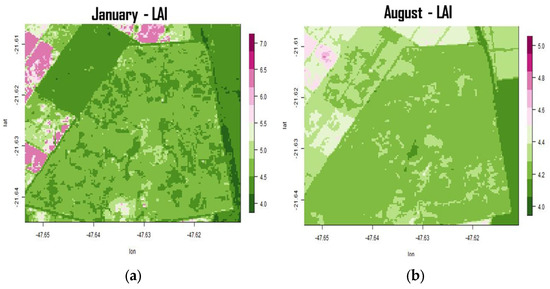
Figure 4.
Temporal average LAI between 2013 and 2020, for the months of (a) January and (b) August.
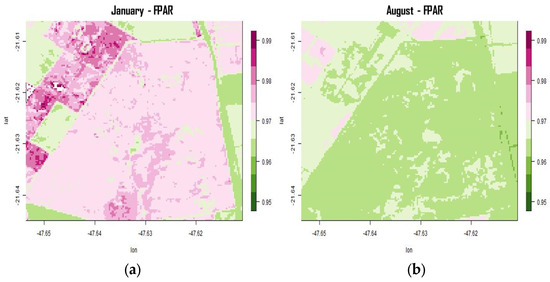
Figure 5.
Temporal average FPAR between 2013 and 2020, for the months of (a) January and (b) August.
2.5. Model Calibration
The model calibration proceeded with the prescription of time-variation parameters (Section 2.4) and soil physical properties (Table 2). The next steps were the optimization of parameters with the calculation of the net radiation (Rn) and latent heat flux (LE). The optimization was based on the method of Non-Linear Least-Square Minimization and Curve-Fitting for Python (LMFIT) [35], which minimizes the squared deviation of the simulated variable from the measurement. For a more accurate and computationally efficient search for the minimum error space across the range of each parameter to be optimized, the fit was performed in two steps. In the first step, we calculated the deviations across a thresholded range of the parameter (min and max) for discrete values of the parameter equally spaced in the range, called the brute computational estimate. In the second step, from the results of the first step, a sub-range was selected for refined search of the minimum deviation, using the Levenberg–Marquardt method (leastqr routine), under a nonlinear procedure adjustment. In summary, the calibration followed serial steps: (i) estimation of time-variant parameters LAI, N and FPAR with remote sensing; (ii) prescription of time-invariant parameters; (iii) optimization of optical parameters for net radiation; (iv) optimization of physiological parameters for latent heat flux.
The calibration of optical parameters with optimization of the net radiation (Rn) used data in the time interval from 2010 to 2017 and was performed simultaneously for 11 parameters (Table 2). For the LE flux, the optimization was performed in the summer months from January to March, and in the winter months from June to August, to accommodate the seasonality of the optimized parameters and the soil moisture initialization in the year 2011 with selected days without precipitation. The optimized parameters of slope of photosynthetic conductance, average leaf time projection and green fraction of the canopy were interpolated for the other months of the year. The improvement in performance with calibration was quite adequate for Rn (Figure 6) and LE (Figure 7).
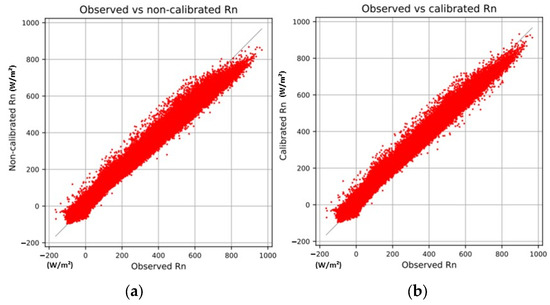
Figure 6.
Observed and calculated net radiation (Rn) by the SiB2 model: (a) using default initial parameter values; (b) using optimized parameter values. RMSE varied from 34.5 to 30.5, and Nash–Sutcliffe efficiency coefficient (NSE) ranged from 0.97 to 0.9 in the initial and optimized cases, respectively.
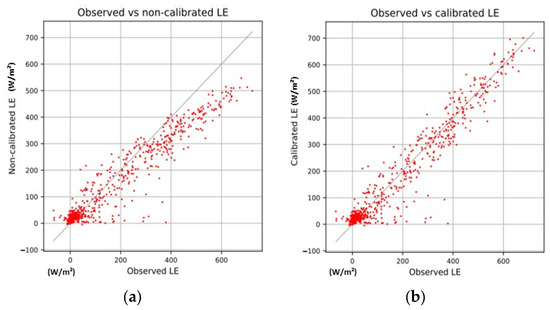
Figure 7.
Observed and calculated net radiation (Rn) by the SiB2 model using (a) default initial parameter values; (b) optimized parameter values. RMSE varied from 72.8 to 66.7, and Nash–Sutcliffe efficiency coefficient (NSE) ranged from 0.72 to 0.76 in the initial and optimized cases, respectively.
3. Results
3.1. Climatic Characterization
We discussed the climate variability of monthly average field measurements of incoming solar radiation, air temperature and humidity, wind speed and precipitation between 2001 and 2019. In general, all variables showed a well-marked seasonality (Figure 8), with pronounced differences between dry and rainy seasons (Table 3), starting with the solar radiation, which ranged from ≃ 150 to 300 (W/m2) from winter to summer, respectively, representing a two-fold factor. The seasonality of rainfall, humidity and wind was also quite pronounced, with vapor pressure maxima/minima occurring in January/August, ranging from ≃10 to 21 hPa (Figure 8c), and wind speed maxima/minima occurring in August/February, ranging from ≃ 2 to 3.5 m/s on average (Figure 8d).
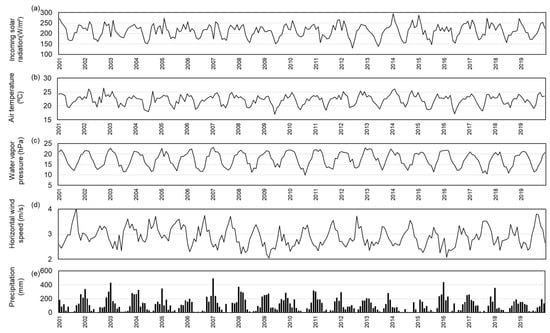
Figure 8.
Monthly average of field measurements at the PEG Cerrado tower for the years 2001–2019: (a) incoming solar radiation (W m−2); (b) air temperature (°C); (c) water vapor pressure (hPa); (d) horizontal wind speed (m/s); and (e) precipitation (mm/month).

Table 3.
Long-term average of meteorological and flux variables for the range 2001–2019.
The average rainfall was 1309 mm/year (Figure 8e, Table 3), slightly below the climatological normal (1478 mm/year) (Figure 9), that was most recurrently caused from the year 2010 on, when the rainfall was above normal only in 2016. The year 2014 was notable for the meteorological drought and the largest negative deviation of 488 mm/year, followed by several years of below-average rainfall that persisted until 2019.
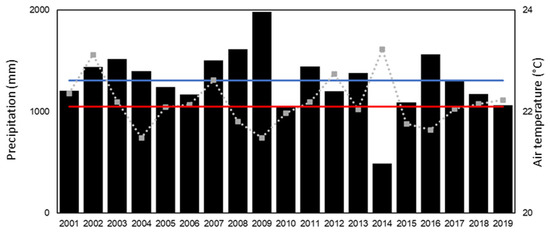
Figure 9.
Average annual air temperature (°C) (dashed line), precipitation (mm) (bars) and mean temperature (red line) at the PEG site for the years 2001–2019. The climatological normal of precipitation is shown with the blue line.
Throughout the period, the average temperature was 22.1 °C, with extremes ranging from ≃17 °C to 26 °C on a monthly basis. During 2014, we noted the highest annual average temperature of 23.2 °C (Figure 9).
We also noted a pronounced variability in the mean diurnal cycle and concurrent with seasonality, based on the comparison of the hot/wet months January–February–March (JFM) and the cold/dry months July–August–September (JJA) (Figure 10). In JFM, the incoming solar radiation (Figure 10a) was higher, caused by higher elevation angle compared to JJA and by the greater hourly variability due to the presence of cloudiness.
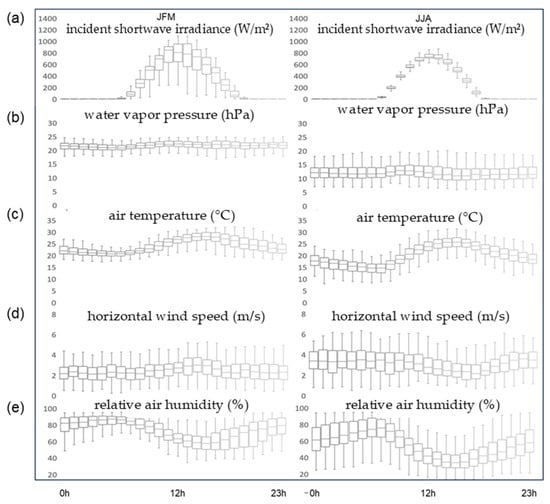
Figure 10.
Diurnal cycle of (a) incoming solar radiation (W/m2), (b) water vapor pressure (hPa), (c) air temperature (°C), (d) horizontal wind speed (m/s) and (e) relative air humidity (%) for the PEG site, calculated during the years 2001–2019.
The hourly median temperature (Figure 10c) varied between 22 °C and 28 °C in JFM, and from 15 °C to 25 °C in JJA, respectively, showing a larger amplitude in winter due to the cooler minima. The water vapor pressure median was generally lower in winter, ranging from about 22 hPa in JFM to 12 hPa in JJA, with little daily variation in both seasons (Figure 10b). Likewise, the minimum daily median relative humidity varied between about 37% in JJM, with many events reaching as low as 20%, and 60% in JJA, when it never fell below 40% (Figure 10e). The average wind speed was 3.5 m/s in JJA, higher than the 2.5 m/s observed in JFM (Figure 10d), reflecting the seasonality of large-scale wind patterns. During summer, wind speeds tended to increase during the daytime due to stronger radiative forcing.
3.2. Soil Moisture
We compared the mean monthly soil moisture measured by CRNS with FDR measurements estimated as an average between depths of 10 and 100 cm (referred to as FDR10–100 cm) and an average between depths of 150 and 200 cm (referred to as FDR150–200cm) in Figure 11. The seasonality of SWI (Soil Water Index) demonstrated a similar variability pattern between the CRNS, FDR10–100 cm and FDR150–200 cm. The minimum Soil Wetness Index (SWI) typically occurred around August, which usually marked the end of the dry season. With the onset of the rainy season after September, soil recharge began, usually reaching its maximum in January, which coincided with the rainiest month. From January onwards, there was a gradual depletion of soil moisture in both the CRNS and FDR above 200 cm, concurrent with a reduction in rainfall.
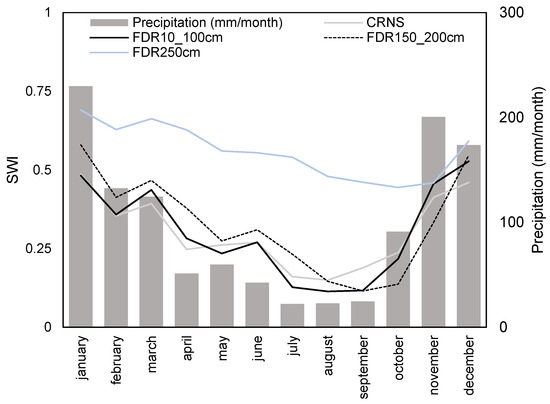
Figure 11.
Mean monthly precipitation (mm) and soil water index (SWI) for CRNS and FDR for the averaged layer, including levels 10, 20, 50, 80 and 100 cm (black line) (referred to as FDR10_100 cm); levels 150 and 200 cm (black dashed line) (referred to as FDR150_200 cm); and at 250 cm (light blue line), calculated over the common data range at the PEG site.
For soil moisture at greater depths down to 250 cm, the pattern indicated that soil recharge, after the onset of the rainy season, was slightly slower than at shallower depths. This delay is typical in tropical regions with highly permeable soils, as also observed in Amazonia [36].
Given the distinct seasonal patterns above and below the 200 cm depth, we restricted the calculation of the average annual SWI for the aforementioned layers to the months of January–February–March (JFM), July–August–September (JAS) and October–November (ON). These ranges correspond to stages of maximum and minimum seasonal moisture, and soil recharge, respectively. Overall, there was a pronounced decline in soil moisture in 2014 due to the meteorological drought, particularly in the summer (JFM), as estimated by the FDR (Figure 12a—black line) across all soil layers and by the CRNS (Figure 12b—black lines). During the winter (JAS) and seasonal transition (ON), 2014 also showed low moisture levels; however, the depletion of moisture apparently extended into the following years (2016 and 2017), in contrast to the summer when there was some recovery.
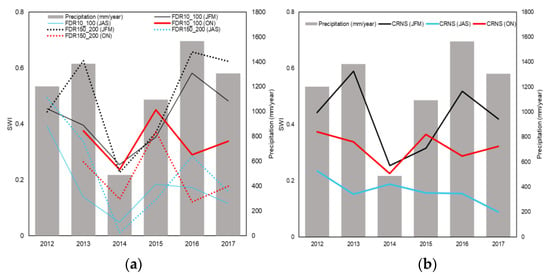
Figure 12.
Annual precipitation (bars) in mm/year, and mean SWI measured at the PEG site, estimated for three ranges of the year: January–February–March (JFM—solid and dotted black lines), July–August–September (JAS—solid and dotted blue lines) and October–November (ON—solid and dotted red lines), for (a) FDR measurements, including depths from 10 to 100 cm, from 150 to 200 cm, and (b) CRNS measurements.
3.3. Turbulent Fluxes of Heat and Water Vapor
On average, over the interval 2001–2019, the evapotranspiration (ET) calculated by the SiB2 model was partitioned into the components, ET = Et + Es + Ei, that showed transpiration (Et) with the greatest contribution of 68%, while soil evaporation (Es) and interception losses (Ei) contributed with 20% and 12%, respectively (Figure 13).
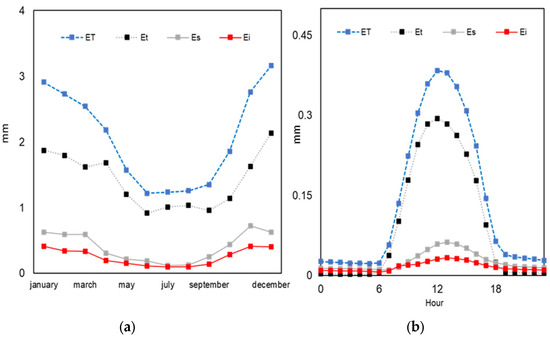
Figure 13.
(a) Monthly and (b) hourly evapotranspiration (ET), Et (transpiration), Es (soil evaporation) and Ei (interception loss of rainfall), calculated by the SIB2 model for PEG, averaged for the years 2011–2019.
In terms of seasonality, the component partition was close to the annual average during the rainy season; however, in the dry season the percentages change a little, with a drop in Es (11%) and Ei (7%), while Et increased (81%) (Figure 13a) as a result from less rainfall and surface soil moisture.
The mean calculated ET was 3.46 mm/d, which is close to another estimate (3.36 mm/d) at the same experimental site, despite of the different temporal interval used (2010–2012) [14].
The variation of monthly net radiation, LE and H, showed a clear seasonal pattern and significant difference in magnitude between LE and H fluxes (Figure 14). The variation in monthly net radiation, LE and H showed a clear seasonal pattern and a significant difference in magnitude between LE and H (Figure 14).
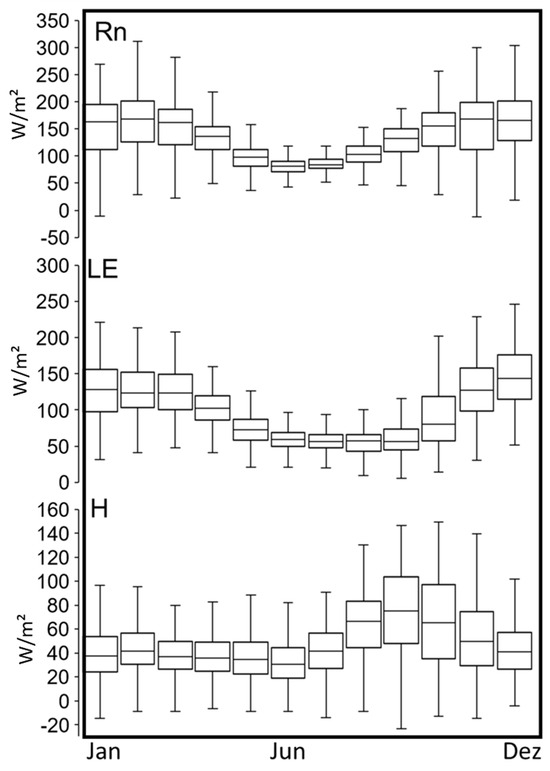
Figure 14.
Boxplot of the daily time series of flows Rn (W/m2), LE (W/m2) and H (W/m2) for PEG, in the range from 2001 to 2019. Dez—December.
During the hottest and most humid months, net radiation was higher due to increased global solar radiation. Combined with greater soil moisture, this resulted in a higher latent heat flux. A variation in the median LE was observed around 125 W/m2, with a wide range of intra-month variance. Additionally, during this period, the H flux tended to be lower throughout the year (Figure 14).
In winter and during the late dry season (August–September), the median H flux varied between approximately 40 and 80 W/m2, with intra-monthly values reaching up to 140 W/m2. Meanwhile, LE showed minimum values throughout the year, close to 60 W/m2, and exhibited low intramonthly amplitude (Figure 14).
A break in the temporal pattern of the LE and H fluxes occurred particularly in 2014, during the drought, which extended into 2015. In the dry seasons of 2014 and 2015, the H term was significantly higher than in other years, while the LE term was lower, as noted in the monthly variation (Figure 15). A common factor in these two years was the marked reduction in soil moisture (Figure 15), indicating the lasting effects of the 2014 drought that also manifested in the following year’s dry season.
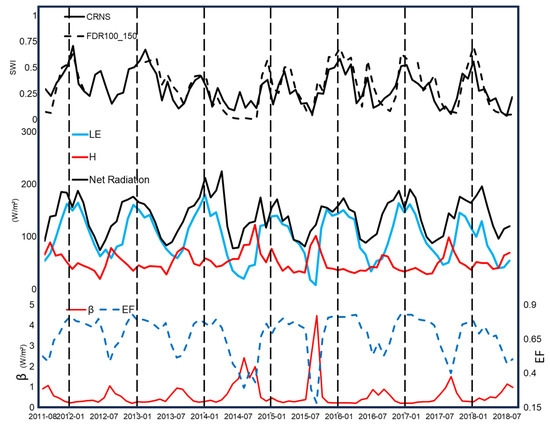
Figure 15.
Monthly mean of soil wetness index (SWI) of FDR100_150 cm (deep) and CRNS (shallow) (in top); net radiation (black line in middle), latent heat flux (LE) (blue line in middle), sensible heat flux (H) (red line in middle), Bowen ratio (β) and evaporative fraction (EF) (red and dashed blue lines in bottom) for the PEG site during the range from 2011 to 2018.
This disturbance in turbulent energy flux due to drought was further analyzed using two other indices: the evaporative fraction (EF = LE/Rn) and the Bowen ratio (β = H/LE). Before 2014 and again from 2016 onwards, the EF term typically varied between 0.5 in the dry season and 0.75 in the rainy season, indicating greater efficiency in using available radiative energy for evapotranspiration (ET) during the summer, and the opposite in winter. Similarly, the β term varied from approximately 0.25 in the rainy season, exhibiting quite stable patterns, and increased to values around 1 at the end of the dry season, usually in the form of peaks (Figure 15). During anomalous events associated with meteorological drought, it was noted that the β value exceeded 2 during the dry season of 2014 and went above 4 in 2015, indicating a pronounced inter-annual oscillation. Between 2009 and 2012, no estimates of β above 2 were reported [14]; these estimates only manifested later with the event of a great drought.
4. Discussion
Over the 19-year sampling period, we observed a decrease in annual precipitation in our investigation site since 2010, with more emphasis from 2014 on, when recurrent negative rainfall anomalies were manifested. These were not just local events but were likely serial droughts on a regional scale in southeastern Brazil, that is, of interannual natural variability and manifested as hydrological droughts at larger scales [37]. Our results have shown a significant influence of soil moisture on the response of ET in the Cerrado denso ecosystem. This effect was observed not only on a seasonal scale, as is well documented [2,4,5,14], but also on an inter-annual scale, where clear temporal propagations were evident.
In particular, during the dry seasons of 2014 and 2015, we observed minimum β owen ratio (β) values above 2. It is acknowledged that ET in the Cerrado ecosystem is significantly influenced by the available surface energy [4,14]. However, soil moisture is also closely correlated to the net radiation, resulting in complex and interdependent control mechanisms where variables do not act independently [3]. This understanding is partially attributed to the vegetation’s adaptive characteristics, particularly to water stress. The seasonal phenological changes in the vegetation, including foliar senescence in most tree species and dormancy in the herbaceous layer, typically occur during the dry season. These changes lead to a reduction in the vegetation’s photosynthetic capacity and transpiration rates [2,34].
The temporal variability in green leaf cover composition could account for some of the observed phenomena where heightened soil moisture levels did not lead to proportionate increases in ET. For instance, we documented several isolated rainfall events during the dry season, resulting in significant soil moisture pulses lasting several days, such as those in June 2013, July 2014 and June 2017. Despite these disruptions in soil moisture levels, the declining trend of ET throughout the dry season appeared unaffected, possibly due to a pronounced restriction in transpirational capacity dependent on the state of the vegetation’s foliage.
Various forms of disturbance are widespread throughout the Cerrado ecosystem on a continental scale, including occurrences such as fires followed by subsequent regeneration [38,39,40]. Recurrent fires have the potential to alter the physiognomy of the Cerrado, often leading to the transformation of its landscape into open fields [39], thereby impacting the water balance [40]. At the PEG site, we have no records of burning for approximately 50 years, and thus we precluded this type of influence on our measurements.
5. Conclusions
Our study aimed to offer an original perspective on heat and water fluxes within a dense Cerrado ecosystem. We examined surface energy partitioning and the influence of soil moisture on its temporal variability using a contemporary array of field instruments over an extensive time span. Soil moisture measurements were conducted using two independent systems, with CRNS measurements demonstrating strong agreement with FDR sensors at shallow depths, thereby bolstering their suitability in representing local conditions. Furthermore, CRNS data exhibited temporal synchrony with FDR measurements down to depths of 100 cm, indicating its capacity to effectively capture water conditions across a substantial soil profile of up to 1 m in depth. This enabled us to explore the impact of significant climate events, such as a major meteorological drought.
In general, the estimates showed the long-term average Rn of 142 W/m2, ET of 3.5 mm/d and the H flux of 52 W/m2. ET was heavily seasonal, influenced by surface energy availability, but soil moisture was also tightly correlated to net radiation, creating complex control mechanisms. The vegetation’s adaptive traits, also in response to water stress, contributed to this understanding.
We emphasize the soil moisture’s sensitivity to significant rainfall anomalies, such as those observed in 2014. Interestingly, the soil moisture anomaly persisted into the subsequent year despite the alleviation of the meteorological drought. This anomalous soil moisture likely contributed to the sustained elevation of the Bowen ratio, which persisted into the following dry season.
In light of the scientific insights gained, we conclude that a thorough assessment of soil moisture and surface energy fluxes can enhance our understanding of natural tropical ecosystem dynamics and their responses to climate disturbances.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, L.F.C.d.C. and H.R.d.R.; methodology, L.F.C.d.C., H.R.d.R., R.R., O.M.R.C., H.C.d.F. and N.V.N.; data curation L.F.C.d.C.; writing—original draft preparation, L.F.C.d.C.; writing—review and editing, L.F.C.d.C. and H.R.d.R.; visualization, L.F.C.d.C.; supervision, H.R.d.R.; project administration, H.R.d.R.; funding acquisition, H.R.d.R. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
Sao Paulo Research Foundation (FAPESP) grants 2015/50682-6 and 2021/11762-5, IAEA/CRP D12014/Contract 23713 and Agência Nacional de Aguas (ANA) project grant 88887.144979/2017-00. Additional support from the project Brazilian Experimental datasets for MUlti-Scale interactions in the critical zone under Extreme Drought (BEMUSED; grant number NE/R004897/1) and the COSMIC-SWAMP IoT Enabled Cosmic Ray Sensors for Irrigation Monitoring (grant no. NE/W004364/1), both funded by the Natural Environment Research Council (NERC) in partnership with FAPESP; and also from the International Atomic Energy Agency of the United Nations (IAEA/UN; under project no. CRP D12014).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author. The data are not publicly available due to privacy.
Acknowledgments
We thank the comments to earlier discussions from Laura Borma, Marcelo Zeri and Celso von Randow.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Oliveira-Filho, A.T.; Ratter, J.A. Vegetation physiognomies and woody flora of the cerrado biome. In The Cerrados of Brazil; Oliveira, P.S., Marquis, R.J., Eds.; Columbia University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2002; pp. 91–120. [Google Scholar]
- Vourlitis, G.L.; Da Rocha, H.R. Flux dynamics in the cerrado and cerrado–forest transition of Brazil. In Ecosystem Function in Global Savannas: Measurement and Modeling at Landscape to Globalscales; Hill, M.J., Hanan, N.P., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2011; pp. 97–116. [Google Scholar]
- Alberton, B.; Torres, R.S.; Silva, T.S.F.; da Rocha, H.R.; Moura, M.S.B.; Morellato, L.P.C. Leafing Patterns and Drivers across Seasonally Dry Tropical Communities. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Rocha, H.R.; Manzi, A.O.; Cabral, O.M.; Miller, S.D.; Goulden, M.L.; Saleska, S.R.; Coupe, N.R.; Wofsy, S.C.; Borma, L.S.; Artaxo, P.; et al. Patterns of water and heat flux across a biome gradient from tropical forest to savanna in Brazil. J. Geophys. Res. Biogeosci. 2009, 114, G00B12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quesada, C.A.; Miranda, A.C.; Hodnett, M.G.; Santos, A.J.B.; Miranda, H.S.; Breyer, L.M. Seasonal and depth variation of soil moisture in a burned open savanna (campo sujo) in central Brazil. Ecol. Appl. 2004, 14, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardner, T.A. Tree-Grass Coexistence in the Brazilian Cerrado: Demographic Consequences of Environmental Instability. J. Biogeogr. 2006, 33, 448–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bucci, S.J.; Scholz, F.G.; Goldstein, G.; Meinzer, F.C.; Franco, A.C.; Zhang, Y.; Hao, G.-Y. Water relations and hydraulic architecture in Cerrado trees: Adjustments to seasonal changes in water availability and evaporative demand. Braz. J. Plant Physiol. 2008, 20, 233–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, A.J.B.; Silva, G.T.D.A.; Miranda, H.S.; Miranda, A.C.; Lloyd, J. Effects of fire on surface carbon, energy and water vapour fluxes over campo sujo savanna in central Brazil. Funct. Ecol. 2003, 17, 711–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, M.H.; Pires, G.F. Effects of Amazon and Central Brazil deforestation scenarios on the duration of the dry season in the arc of deforestation. Int. J. Climatol. 2010, 30, 1970–1979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marengo, J.A.; Cunha, A.P.; Cuartas, L.A.; Leal, K.R.D.; Broedel, E.; Seluchi, M.E.; Michelin, C.M.; Baião, C.F.D.P.; Angulo, E.C.; Almeida, E.K.; et al. Extreme drought in the Brazilian Pantanal in 2019–2020: Characterization, causes, and impacts. Front. Water 2021, 3, 639204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunha, A.P.M.A.; Brito, S.S.B.; Neto, G.G.R.; Alvalá, R.C.S. Drought between 1963 and 2017 in the Federal District, Brazil. Anu. Inst. Geoci. Ufrj. 2018, 41, 487–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otto, F.E.L.; Haustein, K.; Uhe, P.; Coelho, C.A.S.; Aravequia, J.A.; Almeida, W.; King, A.; de Perez, E.C.; Wada, Y.; van Oldenborgh, G.J.; et al. Factors other than climate change, main drivers of 2014/15 water shortage in southeast Brazil. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2016, 96, S35–S40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nobre, C.A.; Marengo, J.A.; Seluchi, M.E.; Cuartas, L.A.; Alves, L.M. Some characteristics and impacts of the drought and water crisis in Southeastern Brazil during 2014 and 2015. J. Water Resour. Prot. 2016, 8, 252–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabral, O.M.; da Rocha, H.R.; Gash, J.H.; Freitas, H.C.; Ligo, M.A. Water and energy fluxes from a woodland savanna (cerrado) in southeast Brazil. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2015, 4, 22–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furman, A.; Ferre, T.P.A.; Warrick, A.W. A sensitivityanalysis of electrical resistivity tomography array types using analyticalelement modeling. Vadose Zone J. 2003, 2, 416–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mcneill, J.D. (Ed.) Electromagnetic Terrain Conductivity Measurement Atlow Induction Numbers; Tech. Note TN-6; Geonics Limited of Mississagua: Mississagua, ON, Canada, 1980. [Google Scholar]
- Ferré, P.A.; Rudolph, D.L.; Kachanoski, R.G. Spatial averaging of water contet by time domain reflectometry: Implications for twin rod probes with and without dielectric coating. Water Resour. Res. 1996, 32, 271–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zreda, M.; Desilets, D.; Ferré, T.P.A.; Scott, R.L. Measuring SMC non-invasively at intermediate spatial scale using cosmic-ray neutrons. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2008, 35, L21402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franz, T.E.; Zreda, M.; Ferre, T.P.A.; Rosolem, R.; Zweck, C.; Stillman, S.; Shuttleworth, W.J. Measurement depth of the cosmic ray soil moisture probe affected by hydrogen from various sources. Water Resour. Res. 2012, 48, W08515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valenti, M.W.; Cianciaruso, M.V.; Batalha, M.A. Seasonality of litterfall and leaf decomposition in a cerrado site. Braz. J. Biol. 2008, 68, 459–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latansio-Aidar, S.R.; Oliveira, A.C.P.D.; Rocha, H.R.D.; Aidar, M.P.M. Fitossociologia de um Cerrado denso em área de influência de torre de fluxo de carbono, Pé-de-Gigante, Parque Estadual de Vassununga, SP. Biota Neotrop. 2010, 10, 195–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pivello, V.R.; Batalha, M.A.; Bitencourt, M.D.; de Mesquita, H.N., Jr. Banco de Dados em SIG para Ecologia Aplicada: Exemplo do Cerrado Pé-de-Gigante, S.P. Cad. Informações Georreferenciadas-CIG 1999, 1. Available online: http://www.cpa.unicamp.br/revista/cigv1n3a4.html (accessed on 16 February 2024).
- Cooper, M.; Ruggiero, P.G.C.; Sparovek, G.; Pires Neto, A.G. Solos da Gleba Cerrado Pé-de-Gigante. O Cerrado Pé-de-Gigante: Ecologia e Conservação–Parque Estadual de Vassununga. Parte 1: Caracterização Física do Cerrado Pé-de-Gigante e Uso das Terras na Região; SMA: São Paulo, Brazil, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Webb, E.K.; Pearman, G.I.; Leuning, R. Correction of flux measurements for density effects due to heat and water vapor transfer. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 1980, 106, 85–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Twine, T.E.; Kustas, W.P.; Norman, J.M.; Cook, D.R.; Houser, P.R.; Meyers, T.P.; Prueger, J.H.; Starks, P.J.; Wesely, M.L. Correcting Eddy-Covariance Flux Underestimates over a Grassland. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2000, 103, 279–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baatz, R.; Bogena, H.; Franssen, H.-J.H.; Huisman, J.; Qu, W.; Montzka, C.; Vereecken, H. Calibration of a catchment scale cosmic-ray probe network: A comparison of three parameterization methods. J. Hydrol. 2014, 516, 231–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roquette, J.G. Distribuição da biomassa no cerrado e a sua importância na armazenagem do carbono. Ciência Florest. 2018, 28, 1350–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sellers, P.J.; Randall, D.A.; Collatz, G.J.; Berry, J.A.; Field, C.B.; Dazlich, D.A.; Zhang, C.; Collelo, G.; Bounoua, L. A revised land surface parameterization (SiB2) for atmospheric GCMs. Part I: Model formulation. J. Clim. 1996, 9, 676–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabater, M.J. ERA5-Land hourly data from 1981 to present, Copernicus Climate Change Service (C3S) Climate Data Store (CDS). Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2019, 13, 4349–4383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sellers, P.J.; Tucker, C.J.; Collatz, G.J.; Los, S.O.; Justice, C.O.; Dazlich, D.A.; Randall, D.A. A revised land surface parameterization (SiB2) for atmospheric GCMs. Part II: The generation of global fields of terrestrial biophysical parameters from satellite data. J. Clim. 1996, 9, 706–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, T.R.; Vourlitis, G.L.; Lobo, F.A.; Oliveira, R.G.; Nogueira, J.S. Seasonal variation in energy balance and canopy conductance for a tropical savanna ecosystem of south central Mato Grosso, Brazil. J. Geophys. Res. Biogeosci. 2014, 119, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Projeto Mapbiomas—Collection 3 of the Annual Series of Land Cover and Land Use Maps in Brazil. Available online: https://mapbiomas.org/ (accessed on 18 June 2022).
- Ruggiero, P.G.; Batalha, M.A.; Pivello, V.R.; Meirelles, S.T. Soil-vegetation relationships in cerrado (Brazilian savanna) and semideciduous forest, Southeastern Brazil. Plant Ecol. 2002, 160, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocha, H.R.; Freitas, H.C.; Rosolem, R.; Juárez, R.I.; Tannus, R.N.; Ligo, M.A.; Cabral, O.M.; Dias, M.A. Measurements of CO2 exchange over a woodland savanna (Cerrado sensu stricto) in southeast Brazil. Biota Neotrop. 2002, 2, 1–11. Available online: https://www.biotaneotropica.org.br/v2n1/pt/abstract?article+BN01702012002 (accessed on 10 February 2023). [CrossRef]
- Newville, M.; Stensitzki, T.; Allen, D.B.; Rawlik, M.; Ingargiola, A.; Nelson, A. Lmfit: Non-Linear Least-Square Minimization and Curve-Fitting for Python; Zenodo: Honolulu, HI, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruno, R.D.; DARocha, H.R.; DEFreitas, H.C.; Goulden, M.L.; Miller, S.D. Soil moisture dynamics in an eastern Amazonian tropical forest. Hydrol. Process. Int. J. 2006, 20, 2477–2489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domingues, L.M.; De Abreu, R.C.; DARocha, H.R. Hydrologic Impact of Climate Change in the Jaguari River in the Cantareira Reservoir System. Water 2022, 14, 1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klink, C.A.; Machado, R.B. Conservation of the Brazilian cerrado. Conserv. Biol. 2005, 19, 707–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miranda, H.S.; Bustamante, M.M.; Miranda, A.C. The Fire Factor. In The Cerrado of Brazil: Ecology and Natural History of a Neotropical Savanna; Oliveira, P.S., Marquis, R.J., Eds.; Columbia University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2002; pp. 69–88. [Google Scholar]
- Belcher, C.M. Fire Phenomena and the Earth System: An Interdisciplinary Guide to Fire Science an Interdisciplinary Guide to Fire Science; College of Life and Environmental Sciences, University of Exeter: Exeter, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).