Abstract
It is of great scientific value to study the spatial differences and influencing factors of carbon emission intensity (CEI) in urban agglomerations (UAs), and it also has reference significance for China in formulating energy-saving and emission-reduction policies to achieve the target of carbon neutrality. Taking 165 prefecture-level cities in 19 UAs in China from 2007 to 2019 as the research object, this study investigated the spatial differences of CEI in UAs using exploratory spatial data analysis and explored the influencing factors of CEI via Geodetector. The results showed the following: (1) The CEI of the UAs showed a downward trend. (2) The CEI of the UAs has typical spatial agglomeration characteristics, where the North comprises mainly high-high and low-high types, whereas the South is primarily high-low and low-low types. (3) The influencing factors of CEI have undergone a transformation from industrial structure to population urbanization.
1. Introduction
Global warming, caused by the increase of greenhouse gas emissions, as represented by carbon dioxide, has attracted worldwide attention. According to the “State of the Global Climate 2021” issued by the World Meteorological Organization, the global average temperature in 2021 was 1.11 ± 0.13 °C higher than that in 1850–1900 [1]. Global warming has further led to a series of problems, such as extreme weather, water resource shortages, glacier retreat, and the attenuation of ecosystem functions [2,3]. Therefore, reducing the carbon emission intensity (CEI) has become the direction of many countries and international organizations around the world [4,5]. Since 2007, China has surpassed the United States and become the largest emitter of greenhouse gases in the world [6,7]. The Statistical Review of World Energy 2022 has presented data on carbon emissions, revealing that China’s total carbon emissions will represent 31.06% of the global total in 2021. This is an increase of 5.8% compared to 2020, and it reflects a consistent upward trend from 2007 to 2021. The disparity in economic growth and carbon emissions across different regions in China is growing. The Chinese government has incorporated carbon emission reduction as a key objective of ecological civilization construction in its national development plan, with a commitment to reach the peak of carbon emissions by 2030 and achieve carbon neutrality by 2060. This is in response to the global responsibility of addressing climate change [8]. Therefore, reducing the CEI has become a major challenge for China [9,10]. Urban agglomerations (UAs), which represent an advanced type of spatial organization for urban development and are regions with a thriving economy and a high population density, are a source and agglomeration of carbon emissions [11,12,13]. With the rapid development of urbanization, 19 UAs have formed in China (Figure 1), including five national, eight regional, and six local levels [14,15,16,17]. Therefore, exploring the spatial differences and influencing factors of CEI in these UAs is significant for China to achieve the target of carbon neutrality.
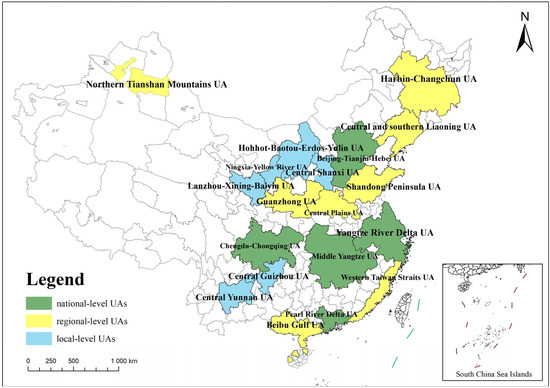
Figure 1.
19 UAs in China.
In recent years, significant progress has been made in CEI research, which involves the evaluation, spatial differences, and influencing factors of CEI. Regarding CEI assessment, the existing literature has estimated CEI based on the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) or the China Emission Accounts and Datasets (CEADs). Wang [18] estimated China’s CEI using the carbon emission coefficients of eight fossil fuels provided by the IPCC and found that CEI showed a continuous downward trend from 2001 to 2019. Chen [19] measured the CEI of 57 cities along the Yellow River Economic Belt based on CEADs and found that the CEI of the Yellow River Basin decreased slowly in a fluctuating manner from 2005 to 2017. Yang [20] used the text-mining method to measure manufacturing enterprises’ digitization and the level of enterprises’ CEI from 2011 to 2021 and found that digitization can significantly reduce the CEI of Chinese manufacturing enterprises; the effect showed a trend of “marginal increase”.
Regarding the spatial difference of CEI, the existing literature mainly uses the coefficient of variation [21,22], the Theil index [23,24], spatial autocorrelation [25,26], and the Gini coefficient [27] to reveal the differences of regional CEI. Yang [28] used the Theil index to study CEI’s spatial and temporal distribution and regional differences from 2000 to 2019 in China and found that the decrease in CEI from 2000 to 2019 showed an obvious imbalance in spatial and temporal distribution, in which the gap between the North and the South was larger than that between the East and the West. Xu [22] used the coefficient of variation and spatial autocorrelation to study CEI’s spatial and temporal characteristics in the Yangtze River Delta from 1997 to 2017 and found that the CEI of cities in the Yangtze River Delta had a strong positive spatial correlation concerning CEI, and it decreased from north to south. Zhao [29] used the spatial panel data model to study the regional differences between 30 provinces in China from 1991 to 2010 and found a significant spatial agglomeration on CEI. Liu [30] used kernel density estimation, a spatial Markov chain, and a spatial variogram model to study the temporal and spatial dynamic evolution characteristics of CEI in 41 counties of Qinghai Province, and found that the CEI of most counties showed a downward trend.
As for the influencing factors of CEI, the existing literature has covered the impact of economic scale [31,32], urbanization rate [33,34], industrial structure [35,36], foreign trade [37,38], technical progress [39,40], environmental regulation [41], and land use efficiency [42]. Shi [43] used nighttime light data, statistical energy consumption data, and urban area data to assess spatiotemporal variations of urban CO2 emissions in China from national scale to regional and UA scales between 1997 and 2012 and determined that urban CO2 emissions in China have a significant positive correlation with urban GDP and urban population at multiple scales. Huang [44] used the panel data of 30 provinces in China from 1998 to 2017 to establish a spatial panel lag model and a quantile regression model, which showed that the impact of heterogeneous human capital on CEI differed across five quantiles. Xiao [45] used the computable general equilibrium model to explore the driving factors of CO2 emission and concluded that energy structure, economic structure, and energy efficiency are the three key factors affecting CO2 emissions in China.
The existing literature has made essential progress in improving the theoretical system of CEI and provided a reference for formulating CEI policies. However, the current literature mainly selects cities across the whole country of China or a specific region as the research object, and research on the spatial differences and influencing factors of CEI in UAs requires further improvement, as it is of great scientific value under the goal of carbon neutrality. It is also of great practical significance to enrich and improve the theoretical system of CEI and formulate emission reduction policies to achieve the goal of emission peak. Therefore, this paper selects 19 UAs in China from 2007 to 2019 as the research object, uses exploratory spatial data analysis (ESDA) to study the spatial differences of CEI, and uses Geodetector to study the influencing factors of CEI in the UAs.
The contribution of this study in the field of carbon emission intensity research is mainly reflected in the following aspects. Firstly, this study addresses the lack of research on the CEI of city clusters in China by selecting 19 city clusters as the research focus. It broadens the scope of the study and offers a fresh perspective for a more thorough and comprehensive understanding of the CEI of city clusters. Secondly, through the application of ESDA, we examine the variations in CEI among urban agglomerations. This analysis allows us to uncover the spatial distribution characteristics and clustering patterns of CEI levels across different urban agglomerations. These findings serve as a valuable reference for the future formulation of carbon emission policies. Finally, by employing Geodetectors, we conduct a more thorough analysis of the factors that impact CEI of urban agglomerations. This allows us to uncover the mechanisms and interrelationships between different factors in the formation of the CEI and offer theoretical backing and policy recommendations for the economic advancement of urban agglomerations.
The rest of this paper is organized as follows: Section 2 presents the methodology and data and introduces the ESDA and Geodetector used in this study, as well as the required data source. Section 3 presents the results of the analyses of the spatial differences and influencing factors of CEI in China’s UAs. Section 4 gives the conclusions of the study and certain policy implications according to the research results.
2. Methodology and Data
2.1. CEI
The measurement of CEI in this study is expressed as the ratio of total carbon emissions to Gross Domestic Product (GDP) for each county [46], and the unit is million tones CO2/ten thousand RMB Yuan.
where is the CEI in year . is carbon emissions in year is a numerical value for the level of economic development in year is a numerical value for the level of economic development in year.
2.2. ESDA
ESDA is a collection of spatial data analysis techniques and methods that reflect the spatial structure, correlation, and aggregation characteristics of attribute values through visual expression and reveal the spatial interaction mechanism between phenomena [47,48]. ESDA includes the global Moran index (global Moran’s I) and the local Moran index (local Moran’s I). The global Moran’s I mainly explores the degree of CEI spatial agglomeration degree in each UA. Its index range is [–1, 1], and the absolute value means the strength of the correlation. The research object has evident spatial agglomeration if the global Moran’s I is greater than 0. If the global Moran’s I is less than 0, it shows that the research object has evident spatial dispersion [49,50]. The global Moran’s I is calculated as follows:
where n is the number of cities in the UA; and are the carbon emissions of cities and , respectively; is the average value of the CEI of all cities; and is the spatial weight matrix of units and j. If there is a common boundary between units i and j, = 1; otherwise = 0.
At the same time, the global Moran’s I is tested for significance using the standardized statistic value. The calculation formula is as follows:
where E(I) is the mathematical expectation of the global Moran’s I, and is the variance of the global Moran’s I. When is 0, it means that the observed values are distributed independently and randomly. When is significantly positive, it means that the observed values are clustered in space, and when is significantly negative, it means that the observed values are dispersed in space.
The global Moran’s I determines whether the research object has spatial autocorrelation. In contrast, the local Moran’s I can further study the autocorrelation characteristics of the research object in local space. For spatial unit i, the local Moran’s I is calculated as follows:
In Equation (4), the significance level of the local Moran’s I can also be measured by . By comparing the symbols of and the significance level ), spatial units can be divided into four types of spatial autocorrelation: if is significantly positive and > 0, it is a “high-high” type, which means the CEI of this city and its adjacent cities are relatively high. If is significantly positive and < 0, it is a “low-low” type, which means the CEI of this city and its adjacent cities are relatively low. If is significantly negative and > 0, it is a “high-low” type, which means cities with a high CEI are surrounded by adjacent cities with a low CEI. If is significantly negative and < 0, it is a “low-high” type, and adjacent cities with a high CEI surround cities with a low CEI. Among them, when is significantly positive, it indicates a significant local spatial positive correlation, showing spatial aggregation. If is significantly negative, it indicates a significant local spatial negative correlation, showing spatial dispersion. From the perspective of differences, if the number of “low-low” and “high-high” types is large, it shows that the spatial difference of CEI is small; if the number of “low-high” and “high-low” types is large, it shows that the spatial difference of CEI is large.
2.3. Geodetector
The geographic detector is a statistical method used to detect the spatial stratification heterogeneity of research objects and reveal the main driving factors of variables [51,52,53]. This study uses Geodetector’s factor detection and interactive detection to explore the impact of different factors on CEI. In particular, factor detection is used to analyze the impact of a single factor on the spatial differentiation of CEI, while interactive detection is used to identify whether the interaction between factors strengthens or weakens the explanatory power of CEI. The model is as follows:
where is the detection power value of the driving factor of UA’s CEI, and the value range of is [0, 1]; the larger the value, the stronger the explanatory power of this factor to the UA’s CEI. m represents the number of layers for factor . refers to the number of cities, which included the 165 cities. and are the variances of the research object and layer , respectively.
2.4. Data Source
This paper selects 19 UAs in China as the research objects. The carbon emissions of cities in the UAs are derived from the carbon emission inventory of China’s cities from 1997 to 2019 provided by CEADs (https://ceads.net/data/city/, accessed on 1 May 2023). Due to the long research timespan and the lack of data in some cities, this paper finally obtained the carbon emission data of 165 cities at the prefecture level or above in 19 UAs. Referring to Refs. [54,55,56], this paper further uses the proportion of carbon emissions in regional GDP to express their intensity. Other basic data related to the influencing factors of CEI, such as economic scale, population urbanization, industrial structure, scientific, and technological progress, opening to the outside world and residents’ income are derived from the China City Statistical Yearbook (2008–2020) (https://data.cnki.net/, accessed on 1 May 2023). Table 1 gives descriptive statistics of the data.

Table 1.
Descriptive statistics of data.
3. Results
3.1. Analysis of Time Evolution of CEI in China’s UAs
Figure 2 reports the time evolution diagram of CEI in various regions and each UA type.
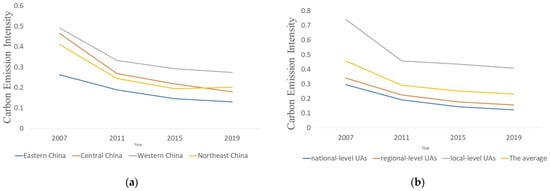
Figure 2.
Time evolution diagram of CEI in various regions and each UA type. (a) By grade; (b) By region.
Figure 2a shows the evolution results of CEI in the state-, regional-, and local-level UAs according to development level. Compared with 2007, the CEIs in 2019 showed a downward trend, with state-level UAs dropping from 0.4593 to 0.2312, state-level UAs dropping from 0.2956 to 0.1249, regional-level UAs dropping from 0.3412 to 0.1582, and local-level UAs dropping from 0.7412 to 0.4102. From the comparison of CEI, the trend of “state-level<regional-level<local-level” is exhibited over the years. State-level UAs have the lowest CEI, which effectively reduces the proportion of energy consumption in economic growth because of the high quality of economic development and energy utilization efficiency. The CEI of local-level UAs is the highest, which shows that the economic development of local-level UAs is highly dependent on regional energy resources, and the development mode is relatively extensive, resulting in a higher CEI.
Figure 2b shows the evolution of the CEI of the UAs in four regions: east, middle, west, and northeast. From the overall trend, the CEI of the four regional UAs also shows a downward trend. The eastern UAs decreased from 0.2531 to 0.1305, the central UAs decreased from 0.4664 to 0.1793, the western UAs decreased from 0.4927 to 0.2752, and the northeast UAs decreased from 0.4116 to 0.2022. From the comparison of the UAs’ CEI in the four regions, the trend of “East<Northeast<Central<West” was observed from 2007 to 2015, but the UAs’ CEI in Northeast China surpassed those in Central China from 2015 to 2019, showing the trend of “East<Central<Northeast<West.” The eastern UAs have the lowest CEI because of their high economic development and energy efficiency. In contrast, the western UAs have the highest CEI because of their high dependence on resource elements and limited economic growth by energy consumption. The Northeast UAs mainly rely on heavy industry, but it is difficult for heavy industry and energy structures to change significantly in a short time, leading to a gradually declining trend of CEI in the northeastern UAs. At the same time, due to the large population loss in the northeastern UAs in recent years, the lack of a labor force has led to an increase in CEI, rather than a decrease. Influenced by the “Thirteenth Five-Year Plan,” the central UAs have gradually gathered in the South with medium-high economic growth, reducing the central UAs’ carbon consumption per unit output value.
3.2. Spatial Difference of CEI in China’s UAs
Using ArcGIS 10.2 software, a global spatial autocorrelation test of CEI of China’s UAs from 2007 to 2019 was carried out, with the results shown in Table 2. The global Moran’s I is positive and passes the 1% significance test, which indicates that the CEIs of the UAs have similar spatial agglomeration characteristics. However, the Moran index is not large, and the highest year has a value of only 0.0930, which shows that the global spatial autocorrelation of the carbon emissions of UAs in China is not significant, meaning the mutual influence of CEI between UAs is weak.

Table 2.
Global Moran’s index of the CEIs of China’s UAs from 2007 to 2019.
In addition, we compute the local Moran’s I index for the UAs’ CEI in China. We specifically choose four significant time intervals in 2007, 2011, 2015, and 2019. To visualize the results, we utilize ArcGIS 10.2 software to generate a local autocorrelation diagram, depicted in Figure 3. Between 2007 and 2019, the distribution, position, and quantity of various types of CEI in China’s UAs remained consistent, exhibiting distinct local spatial autocorrelation characteristics.
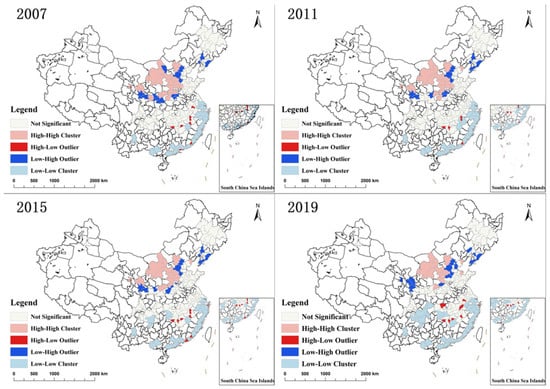
Figure 3.
Local spatial autocorrelation of the CEIs of China’s UAs from 2007 to 2019.
There are a few “high-low” types, mainly distributed in Middle Yangtze UA. The “high-high” type presents a cluster distribution, which is mainly distributed in the Hohhot–Baotou–Erdos–Yulin, the Central Shanxi, the Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei, and Central Plains UAs. The “low-low” type is mainly distributed in the eastern coastal UAs such as the Yangtze River Delta, the Western Taiwan Straits, the Pearl River Delta, and the Beibu Gulf UAs. The “low-high” type distribution is scattered, mainly distributed in the Guanzhong, Central Plains, and Central and Southern Liaoning UAs. From a regional perspective, the UAs in the North are mainly “high-high” and “low-high” types, and the spatial differences of CEI are noticeable. In contrast, the UAs in the South are mainly “high-low” and “low-low” types, and the spatial difference of CEI is slight.
Nan Ke [26] examined the regional variations and evolutionary patterns of city-level CEI in China from 2000 to 2017 using ESDA They ultimately discovered that China’s city-level CEI exhibited positive spatial autocorrelation, with “high-high” and “low-low” cities dominating the geographically aggregated areas. Both the number of ”high-high” and ”low-low” exhibited an upward trajectory from 2000 to 2017. “High-high” is primarily found in the western regions of China, while “low-low” is predominantly distributed in the eastern and central parts of the country. On the other hand, “high-low” and “low-high” are mainly dispersed in decentralized areas. This study examined the carbon emission intensity of Chinese urban agglomerations from 2007 to 2019. The findings reveal that the carbon emission intensity of Chinese urban agglomerations exhibits distinct spatial agglomeration characteristics, with “high-high” and “low-low” cities dominating the spatially agglomerated areas. In terms of geography, the urban agglomerations in the northern regions are mostly characterized by the “high-high” and “low-high” kinds, while those in the southern regions are generally characterized by the “high-low” and “low-low” types.
3.3. Influencing Factors of CEI in China’s UAs
It is known that a series of factors can influence CEI. Referring to the existing research and combining the urban development characteristics of China [57,58,59,60], this paper selected six indicators—economic scale, industrial structure, population urbanization, residents’ income, technological progress, and opening degree—as the detection factors of carbon emissions of the UAs.
GDP expresses the economic scale of a region. GDP and CEI have an inverted U-shaped relationship [61], where the expansion of the economic scale will lead to the increase of carbon emissions within a certain time. However, when the economic growth reaches a certain stage (i.e., after the inflection point of the environmental Kuznets curve), the expansion of economic scale may lead to reducing carbon emissions with the changes in technical level and production mode [62].
The proportion of the secondary industry’s added value represents the industrial structure. Among the three major sectors, the industry and transportation in the secondary industry are important sources of carbon dioxide emissions [63,64]. With the rapid development of China’s economy, the secondary industry will inevitably go through the leading stage in the process of industrial structure evolution. Carbon emissions have increased with the development of the secondary industry and the expansion of the production scale.
Population urbanization is expressed by the proportion of the urban population to the total population. With the continuous improvement of economic development, the urban population and land area have increased rapidly [65,66]. On the one hand, the early stage of urbanization may be accompanied by the extensive expansion of urban land, thus causing a corresponding increase in carbon emissions. At the same time, when the urbanization rate reaches a certain level (i.e., an appropriate urban form), the improvement of energy efficiency and the implementation of a low-carbon green city development model are all conducive to reducing carbon emissions.
The average wage of urban workers is used to express residents’ income. On the one hand, with the increase in urban residents’ income, residents’ awareness of energy conservation will also increase, which is conducive to reducing carbon emissions [59]. Meanwhile, an increase in urban residents’ income will increase consumer demand, which may stimulate the production of more carbon-consuming products.
The level of scientific and technological expenditure is used to express technological progress. Technological progress has positive and negative effects on energy consumption. On the one hand, technological progress can improve energy efficiency and thus effectively reduce the intensity of carbon emissions in the production process. Meanwhile, technological progress may stimulate economic activities, thus increasing energy consumption [67].
Opening degree is expressed by the amount of utilized foreign capital. Opening to the outside world is conducive to attracting foreign-funded enterprises with higher energy-saving and emission-reduction technologies, as well as increasing the income of developing countries, thus helping developing countries to invest more money in carbon emission reduction. However, at the same time, pollution-intensive industries may move from countries with strict environmental supervision to countries with weak supervision, thus causing more serious environmental problems [68,69].
Table 3 shows q values of the influencing factors of the CEI of the UAs by different indicators. In addition to being the largest contribution of industrial structure to the UAs’ CEI in 2007, the contribution of population urbanization to the UAs’ CEI from 2011 to 2019 is higher than the other factors. In addition, residents’ income, technological progress, and opening up have the same impact on the CEI of the UAs.

Table 3.
q detection results of CEI influencing factors of China’s UAs by different indicators.
In 2007, the key element driving the UAs’ CEI in China was the industrial structure, which was primarily dominated by the secondary industry. Since the implementation of economic reforms and opening-up policies, China’s economy has experienced significant growth, with the secondary industry playing a dominant role in the industrial structure for an extended period of time [70]. The industrial and transportation sectors within the secondary industries play a crucial role in generating carbon emissions, which have contributed significantly to China’s widespread economic growth characterized by high consumption and high pollution levels. The industrial structure significantly influences the UAs’ CEI in China. Between 2011 and 2019, the urbanization of the population took over as the primary driving force behind the UAs’ CEI in China, replacing the industrial structure. China’s urbanization has experienced significant development, surpassing 50% for the first time in 2011, due to economic expansion. China’s urban population has exceeded its rural population, resulting in significant effects on the country’s economic and social progress. This demographic shift has also led to an increased influence on China’s CEI.4. Conclusions and Policy Implications.
4. Conclusions and Policy Implications
4.1. Conclusions
In this paper, 165 Chinese prefecture-level cities in 19 UAs were taken as the research objects. The spatial differences of the UAs’ CEI were studied by ESDA, and the influencing factors of UAs’ CEI were studied by Geodetector. The conclusions are as follows:
First, through the analysis of time series evolution, it was found that CEI in China’s UAs showed a downward trend from 2007 to 2019. From the development level, the higher the UA, the lower its CEI. In terms of UA regions, the East had the lowest CEI, whereas the West had the highest.
Second, from the CEI spatial differences of the UAs, the CEI of UAs in China has typical spatial agglomeration characteristics. Among the local spatial autocorrelation types, the spatial difference of UAs’ CEI in the North is large, mainly the “high-high” type and the “low-high” type, whereas that in the South is small, mainly the “high-low” type and the “low-low” type.
Third, the influencing factors of UAs’ CEI have transformed from industrial structure to population urbanization. In 2007, industrial structure contributed the most to the UAs’ CEI, whereas population urbanization contributed the most from 2011 to 2019.
There are several areas that require enhancement in future studies on carbon emissions, particularly in relation to city clusters, in order to effectively tackle climate change and advance sustainable development. The following are some of the areas that require enhancement:
Technologies for reducing carbon emissions. Future research should focus on enhancing the study and implementation of carbon emission reduction technologies, such as renewable energy technologies, carbon capture and storage technologies, and carbon trading mechanisms. Specifically, while examining carbon emissions in urban areas, it is crucial to investigate and encourage strategies for reducing emissions. These strategies may include implementing low-carbon urban planning, constructing environmentally friendly structures, and improving public transportation. By doing so, the overall carbon emissions in urban areas can be decreased.
Collaboration across different academic disciplines. Research on carbon emissions and urban agglomeration carbon emissions necessitates multidisciplinary collaboration, integrating expertise and approaches from various disciplinary domains, including climate science, urban planning, and environmental science. Enhancing multidisciplinary research collaboration can facilitate holistic approaches to addressing carbon emission issues and bolster the formulation of comprehensive strategies for reducing carbon emissions.
Researching and implementing policies. Future research should prioritize the investigation and implementation of carbon emission policies. By conducting a thorough study of the efficacy and viability of carbon emission policies, we may offer more scientifically based policy suggestions to governments and businesses, thereby facilitating the achievement of carbon emission reduction objectives. To promote the sustainable development of urban agglomerations, it is crucial to enhance the evaluation and optimization of carbon emission reduction programs in urban areas.
Global collaboration and interactions: Research on carbon emissions and urban agglomeration carbon emissions is a global concern that necessitates more international collaboration and knowledge sharing. By collaborating with other nations and areas, we can exchange knowledge, collectively tackle the obstacles posed by climate change, and advance the achievement of worldwide targets for reducing carbon emissions.
Overall, it is imperative to enhance future research on carbon emissions and carbon emissions from urban agglomerations in various aspects, including emission reduction technologies, interdisciplinary collaboration, policy research, and international cooperation. This is crucial for advancing the comprehensive development of carbon emission reduction and achieving the objective of sustainable development.
4.2. Policy Implications
First, UAs must work together to reduce their CEI. From the perspective of UAs with different levels and regions, the government should formulate energy-saving and emission-reduction policies to achieve a synergistic emission-reduction effect in UAs and achieve the goal of carbon neutrality in China. The government can fully use the characteristics of the scattered distribution of UAs of different levels to build a green emission cooperation linkage mechanism according to regional divisions and level differences. High-level UAs play the role of radiation driving and expanding the production scale of low-carbon industries, whereas low-level UAs develop low-carbon industries, which will promote industrial green transformation and improve the development level of the urban green economy.
Second, reducing the UAs’ CEI in Northeast China is a complex problem. First, Northeast China, an old industrial base in China, is highly dependent on energy resources. Therefore, UAs in Northeast China should actively adjust their energy structures and improve their production technology. Second, the economic recession and brain-drain in Northeast China have increased carbon emissions due to the lack of labor. Therefore, UAs in Northeast China should optimize the industrial structure, increase employment benefits to attract high-quality talents, and achieve green and low-carbon development.
Third, importance should be attached to the role of population urbanization in reducing the intensity of carbon emissions. UAs with a high level of population urbanization should pay attention to the coordinated development of population urbanization and land urbanization to avoid problems such as resource waste and environmental pollution caused by excessive urban population density. In UAs, where the level of population urbanization is rapidly advancing, local governments should avoid energy consumption caused by extensive expansion of urban land while increasing population density and exerting population scale effect and agglomeration effect.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, K.L.; methodology, Y.W.; software, X.H.; validation, K.L.; formal analysis, K.L.; investigation, Y.W.; resources, K.L.; data curation, X.H.; writing—original draft prepa-ration, Y.W.; writing—review and editing, K.L.; visualization, X.H.; supervision, Y.W.; project administration, K.L.; funding acquisition, K.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the “Shandong Provincial Education Department, China, grant number 2022RW064”.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data will be made available on request. The data are not publicly available due to privacy.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Association, W. State of the Global Climate 2021; CID: 20.500.12592/khwc9c; World Meteorological Association: Geneva, Switzerland, 2022; Available online: https://policycommons.net/artifacts/2434625/1290_statement_2021_en/3456217/ (accessed on 17 July 2023).
- Azam, A.; Rafiq, M.; Shafique, M.; Zhang, H.; Yuan, J. Analyzing the effect of natural gas, nuclear energy and renewable energy on GDP and carbon emissions: A multi-variate panel data analysis. Energy 2021, 219, 119592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Qi, S.; Tan, X. Decomposition and prediction of China’s carbon emission intensity towards carbon neutrality: From perspectives of national, regional and sectoral level. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 825, 153839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andiappan, V.; Foo, D.C.Y.; Tan, R.R. Process-to-Policy (P2Pol): Using carbon emission pinch analysis (CEPA) tools for policy-making in the energy sector. Clean. Technol. Environ. 2019, 21, 1383–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Wu, F.; Chen, L. Harmonious allocation of carbon emission permits based on dynamic multiattribute decision-making method. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 248, 119184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, F.; Li, X.; Long, R.; Liu, X. Regional carbon emission performance in China according to a stochastic frontier model. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2013, 28, 525–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Feng, L.; Palmer, P.I.; Liu, Y.; Fang, S.; Bösch, H.; O Dell, C.W.; Tang, X.; Yang, D.; Liu, L.; et al. Large Chinese land carbon sink estimated from atmospheric carbon dioxide data. Nature 2020, 586, 720–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Li, S.; Ji, Q. Regional differences and driving factors analysis of carbon emission intensity from transport sector in China. Energy 2021, 224, 120178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, W.; Li, L.; Wang, F.; Li, D. Driving factors of CO2 emission inequality in China: The role of government expenditure. China Econ. Rev. 2020, 64, 101545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Da, Y. The decomposition of energy-related carbon emission and its decoupling with economic growth in China. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2015, 41, 1255–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Cheng, Z.; Zhang, H. Does industrial agglomeration promote the increase of energy efficiency in China? J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 164, 30–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Xue, Y.; Chen, Z.; Miao, Y.; Shi, J. Economic spatial structure of China’s urban agglomerations: Regional differences, distribution dynamics, and convergence. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2022, 87, 104253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Fan, W.; Liu, J.; Wang, G.; Chai, W. The effect of urbanization and spatial agglomeration on carbon emissions in urban agglomeration. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 24329–24341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, K.; Xue, M.; Peng, M.; Wang, C. Impact of spatial structure of urban agglomeration on carbon emissions: An analysis of the Shandong Peninsula, China. Technol. Forecast. Soc. 2020, 161, 120313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Wu, Y.; Wang, X.; Wang, C. Impact of spatial structure of urban agglomerations on air pollution in China. China Popul. Resour. Environ. 2020, 30, 28–35. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, W.; Wang, Y.; Sun, S.; Yao, L.; Li, T.; Fu, X. Spatiotemporal heterogeneity of PM2.5 and its driving difference comparison associated with urbanization in China’s multiple urban agglomerations. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 29689–29703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, C.; Li, M.; Zhang, G.; Chen, J.; Zhang, R.; Cao, Y. Spatiotemporal characteristics and determinants of internal migrant population distribution in China from the perspective of urban agglomerations. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e246960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Yu, S.; Li, M.; Cheng, Y.; Wang, C. Study of the Impact of Industrial Restructuring on the Spatial and Temporal Evolution of Carbon Emission Intensity in Chinese Provinces—Analysis of Mediating Effects Based on Technological Innovation. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 13401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Meng, Q.; Shi, J.; Liu, Y.; Sun, J.; Shen, W. Regional Differences and Convergence of Carbon Emissions Intensity in Cities along the Yellow River Basin in China. Land 2022, 11, 1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.; Wang, F.; Deng, F.; Xiang, X. Impact of Digital Transformation on Enterprise Carbon Intensity: The Moderating Role of Digital Information Resources. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 2178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Jin, X.; Luo, X.; Zhou, Y. Multi-scale variations and impact factors of carbon emission intensity in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 857, 159403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Li, Y.; Hu, F.; Wang, L.; Wang, K.; Ma, W.; Ruan, N.; Jiang, W. Spatio-Temporal Variation of Carbon Emission Intensity and Spatial Heterogeneity of Influencing Factors in the Yangtze River Delta. Atmosphere 2023, 14, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, G.; Baležentis, T.; Zeng, S. Per capita CO2 emission inequality of China’s urban and rural residential energy consumption: A Kaya-Theil decomposition. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 331, 117265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Fan, D. The Spatial-Temporal Evolution of China’s Carbon Emission Intensity and the Analysis of Regional Emission Reduction Potential under the Carbon Emissions Trading Mechanism. Sustainability 2022, 14, 7442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.; Li, S.; Cao, X.; Li, Y. Carbon Emission Intensity Characteristics and Spatial Spillover Effects in Counties in Northeast China: Based on a Spatial Econometric Model. Land 2022, 11, 753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, N.; Lu, X.; Kuang, B.; Zhang, X. Regional disparities and evolution trend of city-level carbon emission intensity in China. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2023, 88, 104288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, L.; Wang, Q. Spatial and Temporal Distribution and the Driving Factors of Carbon Emissions from Urban Production Energy Consumption. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 12441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, M.; Liu, Y.; Tian, J.; Cheng, F.; Song, P. Dynamic Evolution and Regional Disparity in Carbon Emission Intensity in China. Sustainability 2022, 14, 4052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Burnett, J.W.; Fletcher, J.J. Spatial analysis of China province-level CO2 emission intensity. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2014, 33, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Song, J.; Dai, T.; Shi, A.; Xu, J.; Wang, E. Spatio-temporal dynamic evolution of carbon emission intensity and the effectiveness of carbon emission reduction at county level based on nighttime light data. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 362, 132301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mardani, A.; Streimikiene, D.; Cavallaro, F.; Loganathan, N.; Khoshnoudi, M. Carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions and economic growth: A systematic review of two decades of research from 1995 to 2017. Sci Total Environ. 2019, 649, 31–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, J.; Tao, H.; Cheng, C.; Brindha, K.; Zhan, M.; Ding, J.; Mu, G. Analysis of Factors Influencing Carbon Emissions in the Energy Base, Xinjiang Autonomous Region, China. Sustainability 2020, 12, 1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.; Cao, T.; Sun, T. Analysis on the variation rule and influencing factors of energy consumption carbon emission intensity in China’s urbanization construction. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 238, 117958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Wang, Z.; Li, S.; Zhang, H. Impact of Land Urbanization on Carbon Emissions in Urban Agglomerations of the Middle Reaches of the Yangtze River. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, D.; Zhang, Y.; Bethel, B.J. An Analysis of Disparities and Driving Factors of Carbon Emissions in the Yangtze River Economic Belt. Sustainability 2019, 11, 2362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, X.; Bai, F.; Jia, J.; Liu, Y.; Shi, F. Realizing low-carbon development in a developing and industrializing region: Impacts of industrial structure change on CO2 emissions in southwest China. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 233, 728–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Xiao, H.; Zikhali, P.; Lv, Y. Carbon Emissions in China: A Spatial Econometric Analysis at the Regional Level. Sustainability 2014, 6, 6005–6023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Zhou, X. Does foreign direct investment lead to lower CO2 emissions? Evidence from a regional analysis in China. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 58, 943–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, F.; Yu, B.; Hadachin, T.; Dai, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, S.; Long, R. Drivers of carbon emission intensity change in China. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2018, 129, 187–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Xu, Y.; Liu, C.; Fang, Z.; Guo, J. Spatial Effects of Technological Progress and Financial Support on China’s Provincial Carbon Emissions. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 1743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Deng, X.; Zhang, H.; Liu, Y.; Yue, T.; Liu, G. Energy endowment, environmental regulation, and energy efficiency: Evidence from China. Technol. Forecast. Soc. 2022, 177, 121528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Jin, G.; Deng, X. Dynamic interactive effects of urban land-use efficiency, industrial transformation, and carbon emissions. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 270, 122547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, K.; Chen, Y.; Li, L.; Huang, C. Spatiotemporal variations of urban CO2 emissions in China: A multiscale perspective. Appl. Energ. 2018, 211, 218–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Zhang, X.; Liu, K. Effects of human capital structural evolution on carbon emissions intensity in China: A dual perspective of spatial heterogeneity and nonlinear linkages. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2021, 135, 110258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, B.; Niu, D.; Wu, H. Exploring the impact of determining factors behind CO2 emissions in China: A CGE appraisal. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 581–582, 559–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, P.; Liu, L.; Xu, X.; Zhao, Y.; Niu, J.; Zhang, Q. Carbon footprint and carbon emission intensity of grassland wind farms in Inner Mongolia. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 313, 127878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, J.; Ding, G.; Zhang, L. Heterogeneous Dynamic Correlation Research among Industrial Structure Distortion, Two-Way FDI and Carbon Emission Intensity in China. Sustainability 2022, 14, 8988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z. The Spatiotemporal Dynamics and Socioeconomic Factors of SO2 Emissions in China: A Dynamic Spatial Econometric Design. Atmosphere 2019, 10, 534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Z. Assessing urban atmospheric environmental efficiency and factors influencing it in China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 594–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Chen, R.; Zang, P.; Huang, L.; Ma, S.; Wang, S. Spatiotemporal patterns of global carbon intensities and their driving forces. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 818, 151690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, S.; Xue, Y.; Ren, G.; Liu, K. Urban Green Innovation Efficiency in China: Spatiotemporal Evolution and Influencing Factors. Land 2023, 12, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Xue, Y.; Chen, Z.; Miao, Y. The spatiotemporal evolution and influencing factors of urban green innovation in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 857, 159426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, L.; Du, H.; Zhang, X. Driving forces of carbon dioxide emissions in China’s cities: An empirical analysis based on the geodetector method. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 287, 125169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, U.; Guo, Q.; Kartal, M.T.; Nurgazina, Z.; Khan, Z.A.; Sharif, A. The impact of renewable and non-renewable energy consumption on carbon emission intensity in China: Fresh evidence from novel dynamic ARDL simulations. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 320, 115782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, Y.; Yuan, W.; Zhang, B.; Wang, S. Does improvement of environmental efficiency matter in reducing carbon emission intensity? Fresh evidence from 283 prefecture-level cities in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 373, 133878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Sun, X.; Reiner, D.M.; Wu, M. Changing trends of the elasticity of China’s carbon emission intensity to industry structure and energy efficiency. Energy Econ. 2020, 86, 104679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Meng, C.; Cao, Q. Measurement and Influencing Factors of Low Carbon Urban Land Use Efficiency—Based on Non-Radial Directional Distance Function. Land 2022, 11, 1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Qu, J.; Maraseni, T.N.; Niu, Y.; Zeng, J.; Zhang, L.; Xu, L. Household CO2 Emissions: Current Status and Future Perspectives. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 7077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Fu, H.; Liu, H.; Liao, C. Urban development sustainability, industrial structure adjustment, and land use efficiency in China. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2023, 89, 104338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; He, Z.; Long, R.; Chen, H.; Han, H.; Zhang, W. Comparative analysis of the regional contributions to carbon emissions in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 127, 406–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Lin, X.; Zhang, J.; He, Q.; Yan, P. Simulation Analysis of Factors Affecting Energy Carbon Emissions in Fujian Province. Sustainability 2022, 14, 13757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quan, C.; Cheng, X.; Yu, S.; Ye, X. Analysis on the influencing factors of carbon emission in China’s logistics industry based on LMDI method. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 734, 138473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, X.; Cao, F. Analysis of Economic Efficiency and Influencing Factors of Urban Construction Land in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei under Carbon Emission Constraints. Land 2022, 11, 1926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; He, C.; Yang, L.; Yi, J.; Ke, B.; Mu, H.; Tu, P.; Ye, Z.; Hong, S. Spatiotemporal Dynamic Correlation Characteristics and Driving Factors of Major Air Pollutant Emissions in China. Atmosphere 2023, 14, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, J.; Sun, P.; Wei, G. Spatial Driven Effects of Multi-Dimensional Urbanization on Carbon Emissions: A Case Study in Chengdu-Chongqing Urban Agglomeration. Land 2022, 11, 1858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, L.; Zhang, T.; Chen, L.; Li, L.; Wang, S.; Hu, S.; Yuan, L.; Wang, J.; Wen, M. Investigating the Impacts of Urbanization on PM2.5 Pollution in the Yangtze River Delta of China: A Spatial Panel Data Approach. Atmosphere 2020, 11, 1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Yin, F.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, X. An empirical research on the influencing factors of regional CO2 emissions: Evidence from Beijing city, China. Appl. Energy 2012, 100, 277–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Zhang, F.; Li, R. Revisiting the environmental kuznets curve hypothesis in 208 counties: The roles of trade openness, human capital, renewable energy and natural resource rent. Environ. Res. 2023, 216, 114637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Xu, H. The Effect of FDI Agglomeration on Carbon Emission Intensity: Evidence from City-Level Data in China. Sustainability 2023, 15, 1716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Ren, G.; Dong, S.; Xue, Y. The synergy between pollution reduction and carbon reduction in Chinese cities and its influencing factors. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2024, 106, 105348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).