Phenomenology of the Composition of PM2.5 at an Urban Site in Northern France
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
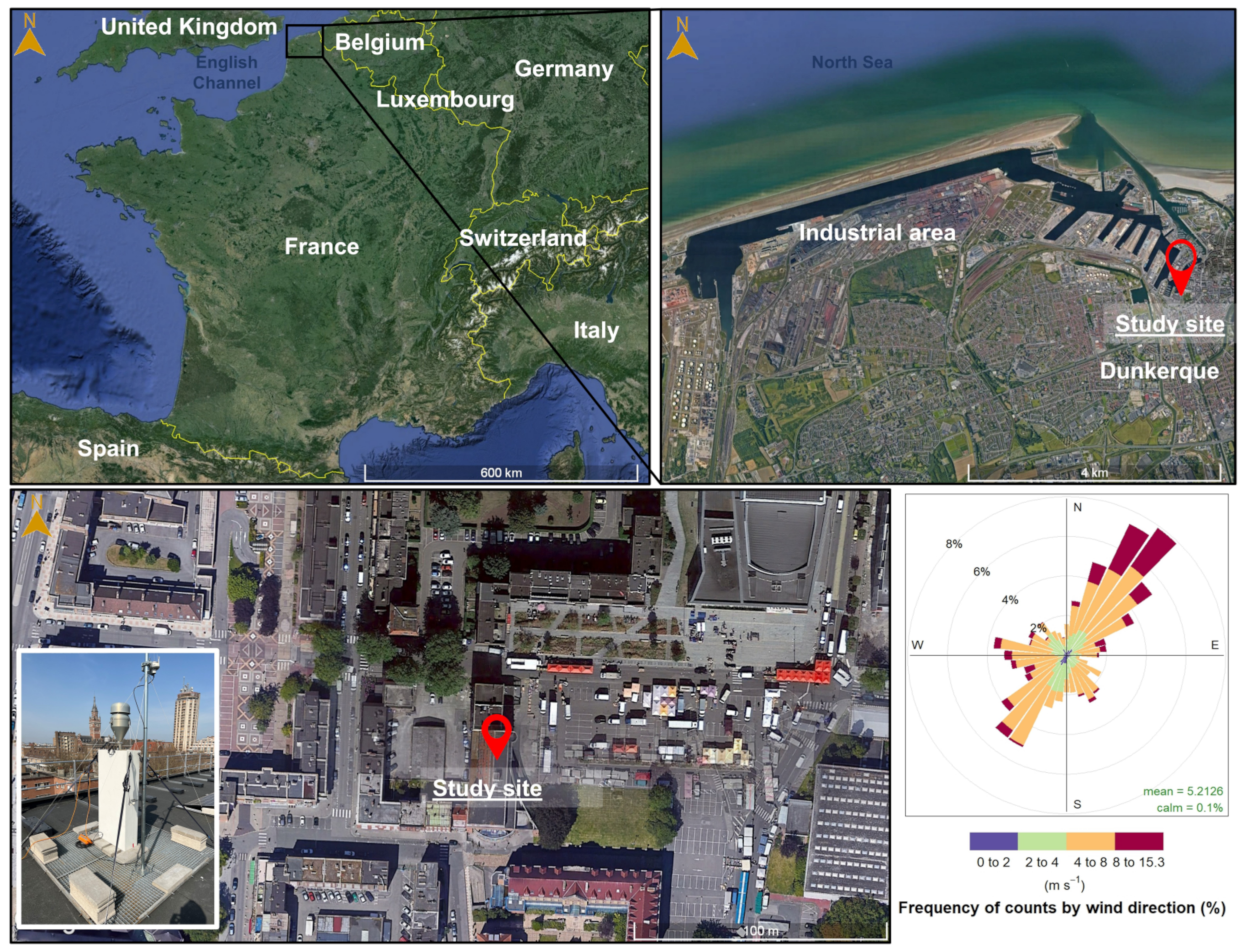
2.1. Sampling Site Description
2.2. Sampling Strategy
2.3. Analytical Procedures
2.3.1. OC and EC Analysis
2.3.2. Water-Soluble Ions, WSOC, and HULIS-C Analysis
2.3.3. Major and Trace Elements
2.4. Data Processing
2.4.1. Statistical Tests
2.4.2. Chemical Mass Closure
[EC] + [crustal dust] + [nss-Cl−] + [nss-Mg2+] + [nss-K+] + [other elements]
2.4.3. Enrichment Factor for Major and Trace Elements
2.4.4. Estimation of Secondary Formation
2.4.5. Bivariate Polar Plots Representations
2.4.6. HYSPLIT Cluster Analysis
3. Results and Discussions
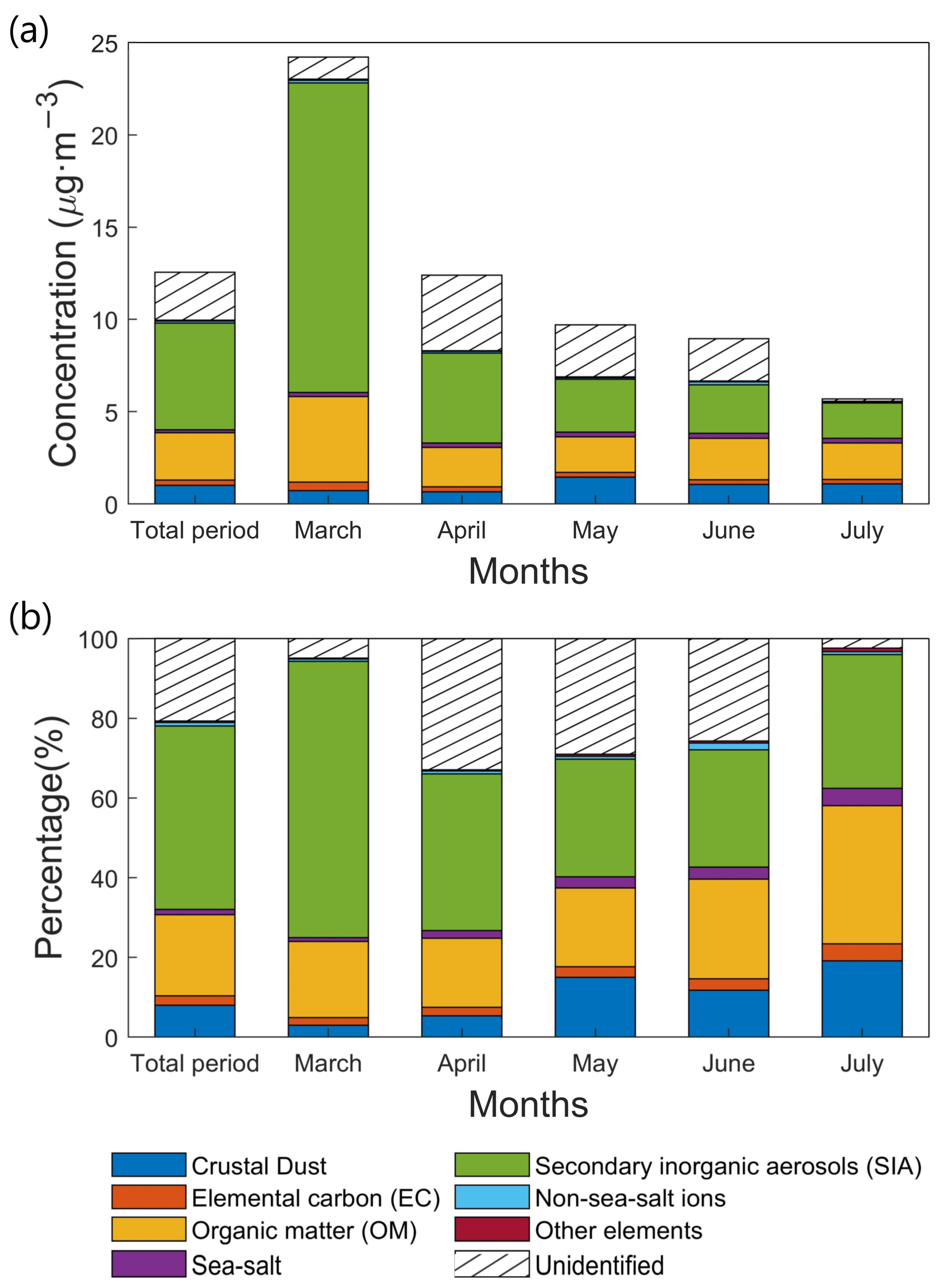
3.1. Chemical Characterization of PM2.5 and Mass Reconstruction
3.1.1. PM2.5 Concentration and Composition
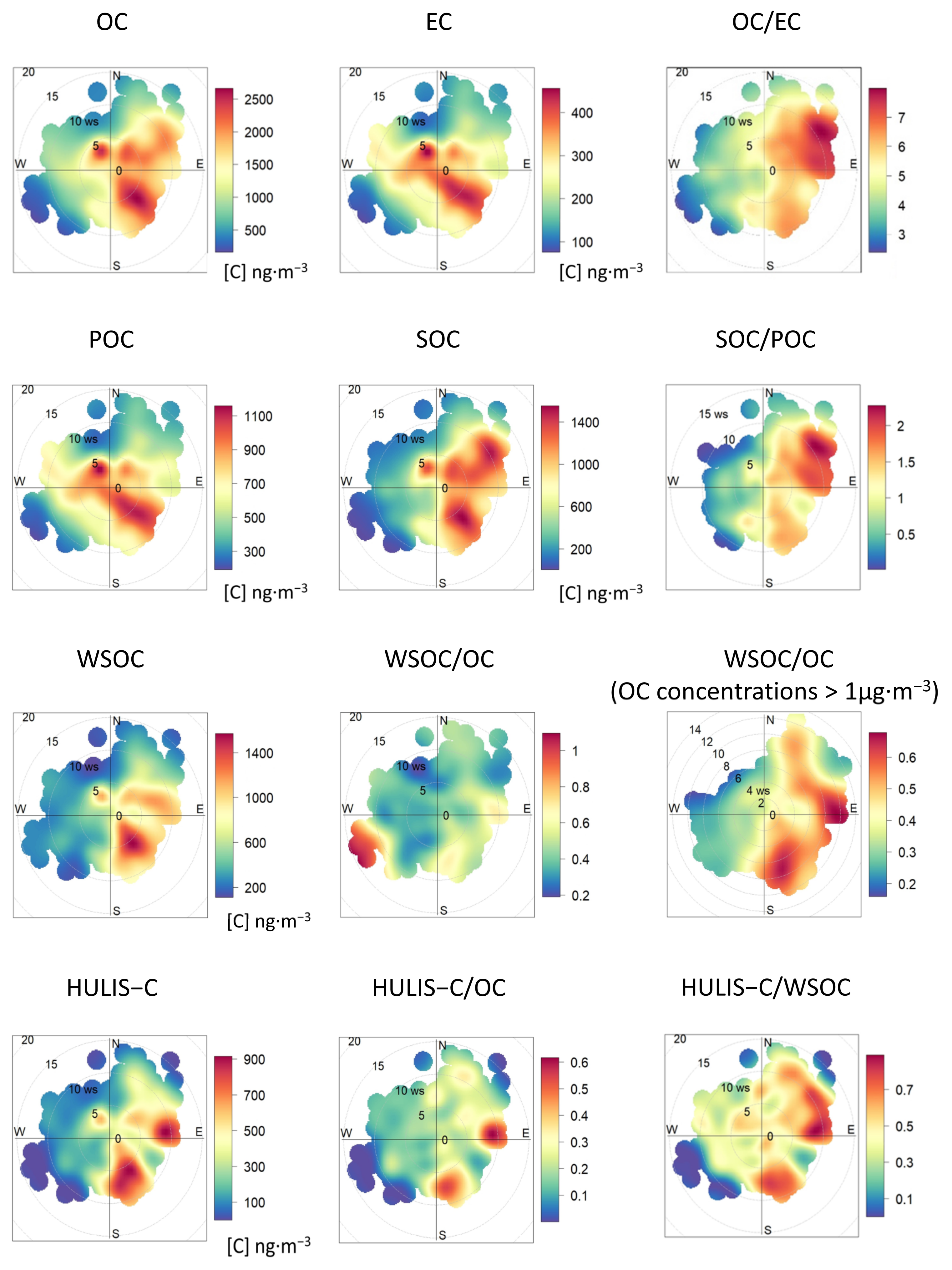
3.1.2. Carbonaceous Fraction of PM2.5
3.1.3. Concentrations of Inorganic Ions
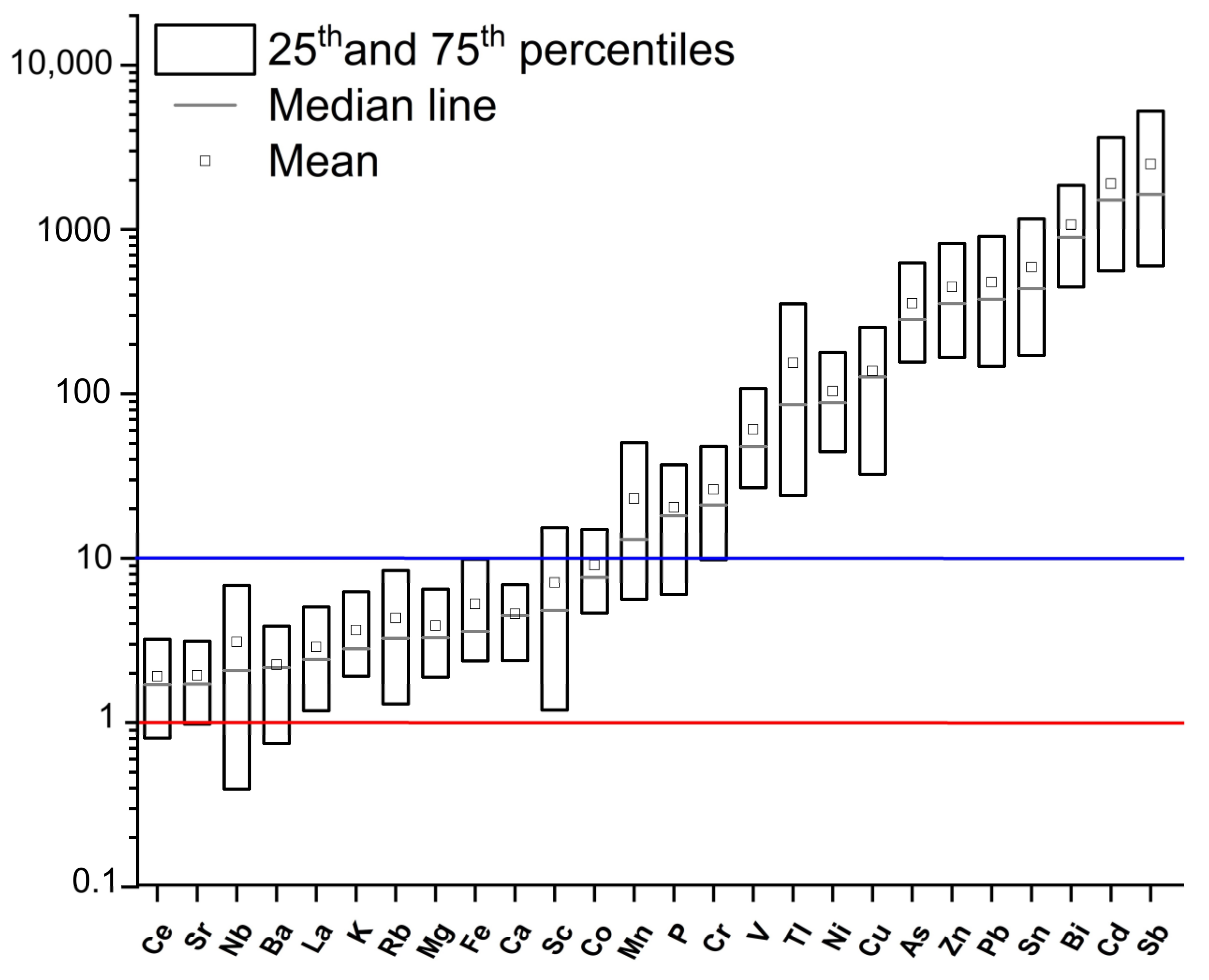
3.1.4. Concentrations of Major and Trace Elements
3.1.5. Chemical Mass Closure of PM2.5
3.2. Identifying Sources of Emissions
3.2.1. Diagnostic Ratios of Elements and Enrichment Factors
3.2.2. Diagnostic Ratios and Correlations between Carbonaceous Species
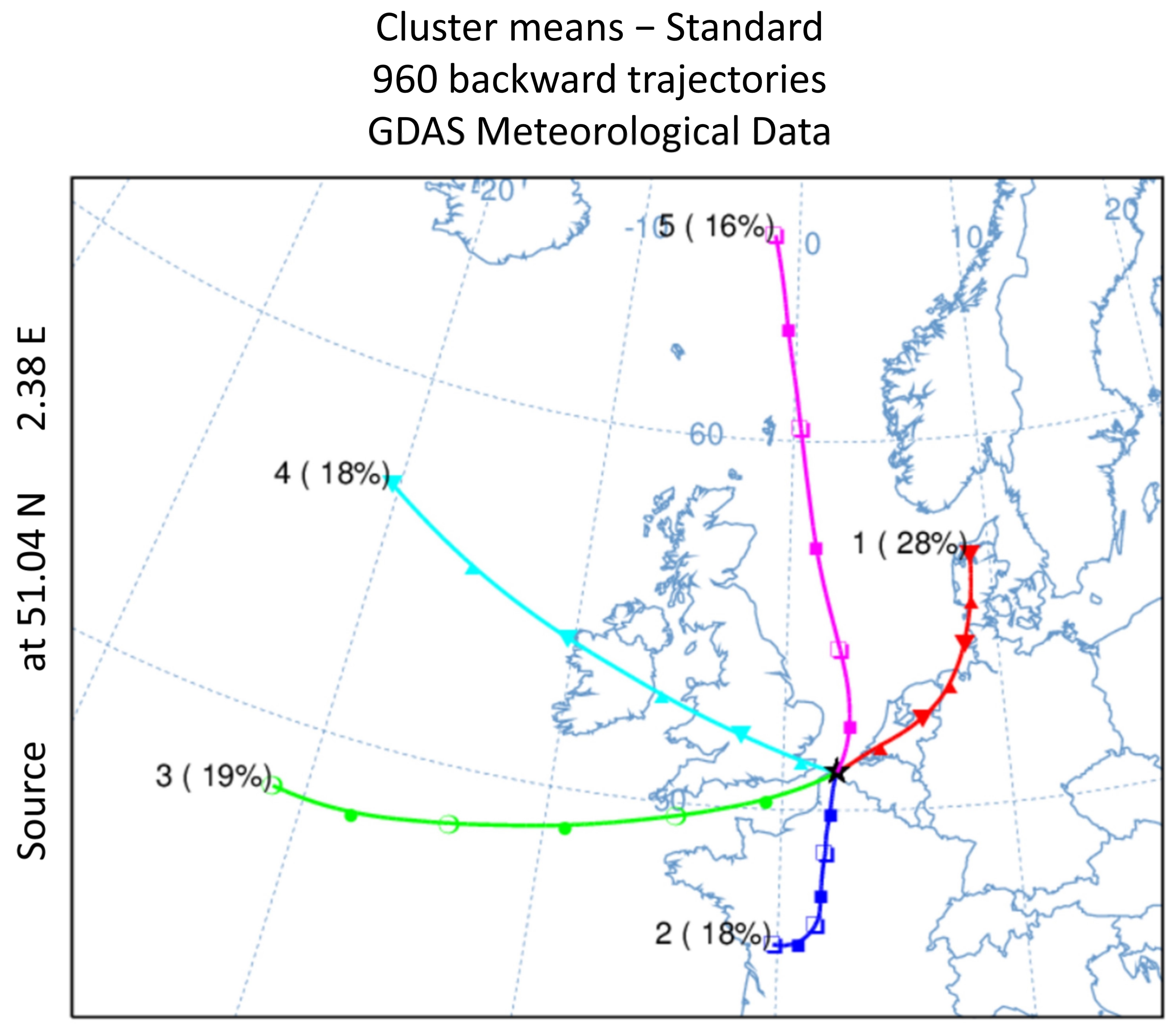
3.3. Back Trajectories Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Apte, J.S.; Marshall, J.D.; Cohen, A.J.; Brauer, M. Addressing Global Mortality from Ambient PM2.5. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 8057–8066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burnett, R.; Chen, H.; Szyszkowicz, M.; Fann, N.; Hubbell, B.; Pope, C.A.; Apte, J.S.; Brauer, M.; Cohen, A.; Weichenthal, S.; et al. Global Estimates of Mortality Associated with Long-Term Exposure to Outdoor Fine Particulate Matter. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 9592–9597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandolfi, M.; Mooibroek, D.; Hopke, P.; van Pinxteren, D.; Querol, X.; Herrmann, H.; Alastuey, A.; Favez, O.; Hüglin, C.; Perdrix, E.; et al. Long-Range and Local Air Pollution: What Can We Learn from Chemical Speciation of Particulate Matter at Paired Sites? Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2020, 20, 409–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Europe’s Air Quality Status 2022—European Environment Agency. Available online: https://www.eea.europa.eu/publications/status-of-air-quality-in-Europe-2022/europes-air-quality-status-2022 (accessed on 12 September 2022).
- OR2S Diagnostic Territorialisé Des Hauts-de-France—Territoires de Proximité. Available online: http://or2s.fr/images/PRS/2017_DiagnosticTerritorialiseDesHautsDeFrance_PRS2_HautsDeFrance.pdf (accessed on 5 March 2024).
- Juda-Rezler, K.; Reizer, M.; Maciejewska, K.; Błaszczak, B.; Klejnowski, K. Characterization of Atmospheric PM2.5 Sources at a Central European Urban Background Site. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 713, 136729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Błaszczak, B.; Juda-Rezler, K.; Rogula-Kozłowska, W.; Reizer, M.; Mathews, B.; Maciejewska, K.; Klejnowski, K. Ionic Composition of Fine Particulate Matter from Urban and Regional Background Sites in Poland. Environ. Eng. Sci. 2017, 34, 236–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, P.; Zhou, X.; Duan, J.; Tan, J.; He, K.; Yuan, C.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, Y. Chemical Characteristics of Water-Soluble Organic Compounds (WSOC) in PM2.5 in Beijing, China: 2011–2012. Atmos. Res. 2017, 183, 104–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correa-Ochoa, M.A.; Bedoya, R.; Gómez, L.M.; Aguiar, D.; Palacio-Tobón, C.A.; Colorado, H.A. A Review on the Characterization and Measurement of the Carbonaceous Fraction of Particulate Matter. Sustainability 2023, 15, 8717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massabò, D.; Prati, P. An Overview of Optical and Thermal Methods for the Characterization of Carbonaceous Aerosol. Riv. Nuovo Cimento 2021, 44, 145–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, I.; Badran, G.; Verdin, A.; Ledoux, F.; Roumié, M.; Courcot, D.; Garçon, G. Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbon Derivatives in Airborne Particulate Matter: Sources, Analysis and Toxicity. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2018, 16, 439–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samaké, A.; Jaffrezo, J.-L.; Favez, O.; Weber, S.; Jacob, V.; Canete, T.; Albinet, A.; Charron, A.; Riffault, V.; Perdrix, E.; et al. Arabitol, Mannitol, and Glucose as Tracers of Primary Biogenic Organic Aerosol: The Influence of Environmental Factors on Ambient Air Concentrations and Spatial Distribution over France. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2019, 19, 11013–11030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrivastava, M.; Cappa, C.D.; Fan, J.; Goldstein, A.H.; Guenther, A.B.; Jimenez, J.L.; Kuang, C.; Laskin, A.; Martin, S.T.; Ng, N.L.; et al. Recent Advances in Understanding Secondary Organic Aerosol: Implications for Global Climate Forcing. Rev. Geophys. 2017, 55, 509–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kroll, J.H.; Seinfeld, J.H. Chemistry of Secondary Organic Aerosol: Formation and Evolution of Low-Volatility Organics in the Atmosphere. Atmos. Environ. 2008, 42, 3593–3624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fadel, M.; Ledoux, F.; Farhat, M.; Kfoury, A.; Courcot, D.; Afif, C. PM2.5 Characterization of Primary and Secondary Organic Aerosols in Two Urban-Industrial Areas in the East Mediterranean. J. Environ. Sci. 2021, 101, 98–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahilang, M.; Deb, M.K.; Pervez, S. Biogenic Secondary Organic Aerosols: A Review on Formation Mechanism, Analytical Challenges and Environmental Impacts. Chemosphere 2021, 262, 127771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hallquist, M.; Wenger, J.C.; Baltensperger, U.; Rudich, Y.; Simpson, D.; Claeys, M.; Dommen, J.; Donahue, N.M.; George, C.; Goldstein, A.H.; et al. The Formation, Properties and Impact of Secondary Organic Aerosol: Current and Emerging Issues. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2009, 9, 5155–5236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, H.; Huang, G.; Zeng, H. Multi-Objective Optimal Dispatch Strategy for Power Systems with Spatio-Temporal Distribution of Air Pollutants. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2023, 98, 104801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Kang, S.; Tripathee, L.; Ram, K.; Rupakheti, M.; Panday, A.; Zhang, Q.; Guo, J.; Wang, X.; Pu, T.; et al. Light Absorption Properties of Elemental Carbon (EC) and Water-Soluble Brown Carbon (WS–BrC) in the Kathmandu Valley, Nepal: A 5-Year Study. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 261, 114239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.-L.; El-Haddad, I.; Huang, R.-J.; Ho, K.-F.; Cao, J.-J.; Han, Y.; Zotter, P.; Bozzetti, C.; Daellenbach, K.R.; Slowik, J.G.; et al. Large Contribution of Fossil Fuel Derived Secondary Organic Carbon to Water Soluble Organic Aerosols in Winter Haze in China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 18, 4005–4017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graber, E.R.; Rudich, Y. Atmospheric HULIS: How Humic-like Are They? A Comprehensive and Critical Review. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2006, 6, 729–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.; Song, J.; Peng, P. Comparison of Isolation and Quantification Methods to Measure Humic-like Substances (HULIS) in Atmospheric Particles—ScienceDirect. Atmos. Environ. 2012, 60, 366–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, P.; Huang, X.; He, L.; Yu, J. Abundance and Size Distribution of HULIS in Ambient Aerosols at a Rural Site in South China. J. Aerosol Sci. 2010, 41, 74–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, Y.; Sun, N.; Li, X.; Zhao, Z.; Ma, S.; Huang, H.; Ye, Z.; Ge, X. Chemical and Optical Characteristics and Sources of PM2.5 Humic-Like Substances at Industrial and Suburban Sites in Changzhou, China. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Z.; Li, Q.; Ma, S.; Zhou, Q.; Gu, Y.; Su, Y.; Chen, Y.; Chen, H.; Wang, J.; Ge, X. Summertime Day-Night Differences of PM2.5 Components (Inorganic Ions, OC, EC, WSOC, WSON, HULIS, and PAHs) in Changzhou, China. Atmosphere 2017, 8, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, T.; Li, R.; Meng, Y.; Han, Y.; Cheng, H.; Fu, H. Size-Segregated Atmospheric Humic-Like Substances (HULIS) in Shanghai: Abundance, Seasonal Variation, and Source Identification. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Han, J.; Hopke, P.K.; Hu, J.; Shu, Q.; Chang, Q.; Ying, Q. Quantifying Primary and Secondary Humic-like Substances in Urban Aerosol Based on Emission Source Characterization and a Source-Oriented Air Quality Model. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2019, 19, 2327–2341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayol-Bracero, O.; Guyon, P.; Graham, B.; Roberts, G.; Andreae, M.; Decesari, S.; Facchini, M.; Sandro, F.; Artaxo, P. Water-Soluble Organic Compounds in Biomass Burning Aerosols over Amazonia: 2. Apportionment of the Chemical Composition and Importance of the Polyacidic Fraction. J. Geophys. Res. 2002, 107, LBA-14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuang, B.Y.; Lin, P.; Huang, X.H.H.; Yu, J.Z. Sources of Humic-like Substances in the Pearl River Delta, China: Positive Matrix Factorization Analysis of PM2.5 Major Components and Source Markers. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2015, 15, 1995–2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.S.; Kim, E.S.; Kim, K.-A.; Yu, J.Z.; Kim, Y.P.; Jung, C.H.; Lee, J.Y. Temporal Variations and Characteristics of the Carbonaceous Species in PM2.5 Measured at Anmyeon Island, a Background Site in Korea. Asian J. Atmos. Environ. 2020, 14, 35–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baduel, C.; Voisin, D.; Jaffrezo, J.-L. Seasonal Variations of Concentrations and Optical Properties of Water Soluble HULIS Collected in Urban Environments. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2010, 10, 4085–4095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frka, S.; Grgić, I.; Turšič, J.; Gini, M.I.; Eleftheriadis, K. Seasonal Variability of Carbon in Humic-like Matter of Ambient Size-Segregated Water Soluble Organic Aerosols from Urban Background Environment. Atmos. Environ. 2018, 173, 239–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guilhermet, J.; Preunkert, S.; Voisin, D.; Baduel, C.; Legrand, M. Major 20th Century Changes of Water-Soluble Humic-like Substances (HULISWS) Aerosol over Europe Inferred from Alpine Ice Cores. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2013, 118, 3869–3878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kristensen, T.; Du, L.; Nguyen, Q.; Nøjgaard, J.; Bender Koch, C.; Nielsen, O.; Hallar, A.; Lowenthal, D.; Nekat, B.; Pinxteren, D.; et al. Chemical Properties of HULIS from Three Different Environments. J. Atmos. Chem. 2015, 72, 65–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krivácsy, Z.; Kiss, G.; Ceburnis, D.; Jennings, G.; Maenhaut, W.; Salma, I.; Shooter, D. Study of Water-Soluble Atmospheric Humic Matter in Urban and Marine Environments. Atmos. Res. 2008, 87, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Caravaca, A.; Crespo, J.; Galindo, N.; Yubero, E.; Juárez, N.; Nicolás, J.F. Sources of Water-Soluble Organic Carbon in Fine Particles at a Southern European Urban Background Site. Atmos. Environ. 2023, 306, 119844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voliotis, A.; Prokeš, R.; Lammel, G.; Samara, C. New Insights on Humic-like Substances Associated with Wintertime Urban Aerosols from Central and Southern Europe: Size-Resolved Chemical Characterization and Optical Properties. Atmos. Environ. 2017, 166, 286–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witkowska, A.; Lewandowska, A.U. Water Soluble Organic Carbon in Aerosols (PM1, PM2.5, PM10) and Various Precipitation Forms (Rain, Snow, Mixed) over the Southern Baltic Sea Station. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 573, 337–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hauts-de-France, Cartes de Trafics Annuels. Available online: https://www.hauts-de-france.developpement-durable.gouv.fr/?Cartes-de-trafics-annuels (accessed on 28 March 2024).
- Cavalli, F.; Viana, M.; Yttri, K.E.; Genberg, J.; Putaud, J.-P. Toward a Standardised Thermal-Optical Protocol for Measuring Atmospheric Organic and Elemental Carbon: The EUSAAR Protocol. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2010, 3, 79–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kfoury, A.; Ledoux, F.; Roche, C.; Delmaire, G.; Roussel, G.; Courcot, D. PM2.5 Source Apportionment in a French Urban Coastal Site under Steelworks Emission Influences Using Constrained Non-Negative Matrix Factorization Receptor Model. J. Environ. Sci. 2016, 40, 114–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ledoux, F.; Courcot, L.; Courcot, D.; Aboukaïs, A.; Puskaric, E. A Summer and Winter Apportionment of Particulate Matter at Urban and Rural Areas in Northern France. Atmos. Res. 2006, 82, 633–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chow, J.C.; Lowenthal, D.H.; Chen, L.-W.A.; Wang, X.; Watson, J.G. Mass Reconstruction Methods for PM2.5: A Review. Air Qual. Atmos. Health 2015, 8, 243–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bressi, M.; Sciare, J.; Ghersi, V.; Bonnaire, N.; Nicolas, J.B.; Petit, J.-E.; Moukhtar, S.; Rosso, A.; Mihalopoulos, N.; Féron, A. A One-Year Comprehensive Chemical Characterisation of Fine Aerosol (PM2.5) at Urban, Suburban and Rural Background Sites in the Region of Paris (France). Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2013, 13, 7825–7844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.H.H.; Bian, Q.; Ng, W.M.; Louie, P.K.K.; Yu, J.Z. Characterization of PM2.5 Major Components and Source Investigation in Suburban Hong Kong: A One Year Monitoring Study. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2014, 14, 237–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esmaeilirad, S.; Lai, A.; Abbaszade, G.; Schnelle-Kreis, J.; Zimmermann, R.; Uzu, G.; Daellenbach, K.; Canonaco, F.; Hassankhany, H.; Arhami, M.; et al. Source Apportionment of Fine Particulate Matter in a Middle Eastern Metropolis, Tehran-Iran, Using PMF with Organic and Inorganic Markers. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 705, 135330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Genga, A.; Ielpo, P.; Siciliano, T.; Siciliano, M. Carbonaceous Particles and Aerosol Mass Closure in PM2.5 Collected in a Port City. Atmos. Res. 2017, 183, 245–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sciare, J.; Oikonomou, K.; Cachier, H.; Mihalopoulos, N.; Andreae, M.O.; Maenhaut, W.; Sarda-Estève, R. Aerosol Mass Closure and Reconstruction of the Light Scattering Coefficient over the Eastern Mediterranean Sea during the MINOS Campaign. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2005, 5, 2253–2265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fakhri, N.; Fadel, M.; Öztürk, F.; Keleş, M.; Iakovides, M.; Pikridas, M.; Abdallah, C.; Karam, C.; Sciare, J.; Hayes, P.L.; et al. Comprehensive Chemical Characterization of PM2.5 in the Large East Mediterranean-Middle East City of Beirut, Lebanon. J. Environ. Sci. 2023, 133, 118–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galindo, N.; Yubero, E.; Clemente, A.; Nicolás, J.F.; Navarro-Selma, B.; Crespo, J. Insights into the Origin and Evolution of Carbonaceous Aerosols in a Mediterranean Urban Environment. Chemosphere 2019, 235, 636–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chester, R.; Murphy, K.J.T.; Lin, F.J.; Berry, A.S.; Bradshaw, G.A.; Corcoran, P.A. Factors Controlling the Solubilities of Trace Metals from Non-Remote Aerosols Deposited to the Sea Surface by the ‘Dry’ Deposition Mode. Mar. Chem. 1993, 42, 107–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hans Wedepohl, K. The Composition of the Continental Crust. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1995, 59, 1217–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, H.-J.; Turpin, B.J.; Edgerton, E.; Hering, S.V.; Allen, G.; Maring, H.; Solomon, P. Semicontinuous Aerosol Carbon Measurements: Comparison of Atlanta Supersite Measurements. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2003, 108, 8419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, X.; Talifu, D.; Ding, X.; Wang, X.; Abulizi, A.; Zhao, Q.; Liu, B. Secondary Formation and Influencing Factors of WSOC in PM2.5 over Urumqi, NW China. Atmos. Environ. 2023, 293, 119450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carslaw, D. OpenAir Manual|PDF|R (Programming Language)|Data Analysis. Available online: https://www.scribd.com/document/366730673/OpenAir-Manual (accessed on 3 April 2024).
- Draxler, R.; Stunder, B.; Rolph, G.; Stein, A.; Taylor, A.; Zinn, S.; Loughner, C.; Crawford, A. HYSPLIT User’s Guide. 2023. Available online: https://www.arl.noaa.gov/documents/reports/hysplit_user_guide.pdf (accessed on 12 February 2024).
- Atmo Hauts-de-France Mesures Des Stations|Atmo Hauts-de-France. Available online: https://www.atmo-hdf.fr/acceder-aux-donnees/mesures-des-stations (accessed on 28 March 2024).
- Cesari, D.; Donateo, A.; Conte, M.; Merico, E.; Giangreco, A.; Giangreco, F.; Contini, D. An Inter-Comparison of PM2.5 at Urban and Urban Background Sites: Chemical Characterization and Source Apportionment. Atmos. Res. 2016, 174–175, 106–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kassomenos, P.A.; Vardoulakis, S.; Chaloulakou, A.; Paschalidou, A.K.; Grivas, G.; Borge, R.; Lumbreras, J. Study of PM10 and PM2.5 Levels in Three European Cities: Analysis of Intra and Inter Urban Variations. Atmos. Environ. 2014, 87, 153–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shikha; Rajouriya, K.; Pipal, A.S.; Taneja, A. Chemical Characterization and Health Risk Assessment of Particulate Matter Near National Highway at Urban and Semi-Urban Locations of Northern India. Aerosol Sci. Eng. 2023, 7, 517–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Gao, W.; Yu, Y.; Hu, B.; Xin, J.; Sun, Y.; Wang, L.; Wang, G.; Bi, X.; Zhang, G.; et al. Characteristics of PM2.5 Mass Concentrations and Chemical Species in Urban and Background Areas of China: Emerging Results from the CARE-China Network. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 18, 8849–8871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Council. On Ambient Air Quality and Cleaner Air for Europe 2008/50/EC. Off. J. Eur. Union 2008, 1, 1–44. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization. WHO Global Air Quality Guidelines: Particulate Matter (PM2.5 and PM10), Ozone, Nitrogen Dioxide, Sulfur Dioxide and Carbon Monoxide; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2021; ISBN 978-92-4-003422-8. [Google Scholar]
- Blaszczak, B.; Rogula-Kozlowska, W.; Mathews, B.; Juda-Rezler, K.; Klejnowski, K.; Rogula-Kopiec, P. Chemical Compositions of PM2.5 at Two Non-Urban Sites from the Polluted Region in Europe. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2016, 16, 2333–2348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remoundaki, E.; Kassomenos, P.; Mantas, E.; Mihalopoulos, N.; Tsezos, M. Composition and Mass Closure of PM2.5 in Urban Environment (Athens, Greece). Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2013, 13, 72–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friman, M.; Aurela, M.; Saarnio, K.; Teinilä, K.; Kesti, J.; Harni, S.D.; Saarikoski, S.; Hyvärinen, A.; Timonen, H. Long-Term Characterization of Organic and Elemental Carbon at Three Different Background Areas in Northern Europe. Atmos. Environ. 2023, 310, 119953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hama, S.; Ouchen, I.; Wyche, K.P.; Cordell, R.L.; Monks, P.S. Carbonaceous Aerosols in Five European Cities: Insights into Primary Emissions and Secondary Particle Formation. Atmos. Res. 2022, 274, 106180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mbengue, S.; Fusek, M.; Schwarz, J.; Vodička, P.; Šmejkalová, A.H.; Holoubek, I. Four Years of Highly Time Resolved Measurements of Elemental and Organic Carbon at a Rural Background Site in Central Europe. Atmos. Environ. 2018, 182, 335–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Li, T.; Chen, Y.; Yang, F. Seasonal Variation of Carbonaceous Species of PM2.5 in a Small City in Sichuan Basin, China. Atmosphere 2020, 11, 1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravindra, K.; Singh, T.; Mandal, T.K.; Sharma, S.K.; Mor, S. Seasonal Variations in Carbonaceous Species of PM2.5 Aerosols at an Urban Location Situated in Indo-Gangetic Plain and Its Relationship with Transport Pathways, Including the Potential Sources. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 303, 114049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sandrini, S.; Sandro, F.; Piazzalunga, A.; Prati, P.; Bonasoni, P.; Cavalli, F.; Bove, M.; Calvello, M.; Cappelletti, D.; Colombi, C.; et al. Spatial and Seasonal Variability of Carbonaceous Aerosol across Italy. Atmos. Environ. 2014, 99, 587–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bougiatioti, A.; Zarmpas, P.; Koulouri, E.; Antoniou, M.; Theodosi, C.; Kouvarakis, G.; Saarikoski, S.; Mäkelä, T.; Hillamo, R.; Mihalopoulos, N. Organic, Elemental and Water-Soluble Organic Carbon in Size Segregated Aerosols, in the Marine Boundary Layer of the Eastern Mediterranean. Atmos. Environ. 2013, 64, 251–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timonen, H.; Saarikoski, S.; Tolonen-Kivimäki, O.; Aurela, M.; Saarnio, K.; Petäjä, T.; Aalto, P.P.; Kulmala, M.; Pakkanen, T.; Hillamo, R. Size Distributions, Sources and Source Areas of Water-Soluble Organic Carbon in Urban Background Air. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2008, 8, 5635–5647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viana, M.; Maenhaut, W.; Chi, X.; Querol, X.; Alastuey, A. Comparative Chemical Mass Closure of Fine and Coarse Aerosols at Two Sites in South and West Europe: Implications for EU Air Pollution Policies. Atmos. Environ. 2007, 41, 315–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salma, I.; Mészáros, T.; Maenhaut, W. Mass Size Distribution of Carbon in Atmospheric Humic-like Substances and Water Soluble Organic Carbon for an Urban Environment. J. Aerosol Sci. 2013, 56, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.-M.; Lee, S.P.; Li, Y.; Yu, J.Z.; Kim, J.Y.; Kim, Y.P.; Lee, J.Y. Characterization of Seasonal Difference of HULIS-C Sources from Water Soluble PM2.5 in Seoul, Korea: Probing Secondary Processes. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2021, 21, 200233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, T.; Zhao, M.; Xiu, G.; Yu, J. Seasonal Variations of Water Soluble Composition (WSOC, Hulis and WSIIs) in PM1 and Its Implications on Haze Pollution in Urban Shanghai, China. Atmos. Environ. 2015, 123, 306–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arruti, A.; Fernández-Olmo, I.; Irabien, A. Regional Evaluation of Particulate Matter Composition in an Atlantic Coastal Area (Cantabria Region, Northern Spain): Spatial Variations in Different Urban and Rural Environments. Atmos. Res. 2011, 101, 280–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ledoux, F.; Roche, C.; Delmaire, G.; Roussel, G.; Favez, O.; Fadel, M.; Courcot, D. Measurement Report: A 1-Year Study to Estimate Maritime Contributions to PM10 in a Coastal Area in Northern France. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2023, 23, 8607–8622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chesselet, R.; Morelli, J.; Buat-Menard, P.; Orelli, J. Variations in Ionic Ratios between Reference Sea Water and Marine Aerosols. J. Geophys. Res. 1972, 77, 5116–5131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, B.; Wang, T.; Zhang, G.; Liang, Y.; Lv, C.; Hu, Y.; Li, L.; Zhou, Z.; Wang, X.; Bi, X. A Review of Atmospheric Aging of Sea Spray Aerosols: Potential Factors Affecting Chloride Depletion. Atmos. Environ. 2022, 290, 119365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crawford, J.; Cohen, D.D.; Chambers, S.D.; Williams, A.G.; Atanacio, A. Impact of Aerosols of Sea Salt Origin in a Coastal Basin: Sydney, Australia. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 207, 52–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, L.; Zhang, Y.-Y.; Xiao, H.-Y.; Xiao, H.-W.; Zheng, N.-J.; Zhang, Z.-Y.; Xie, Y.-J.; Liu, C. Spatial Distributions and Sources of Inorganic Chlorine in PM2.5 across China in Winter. Atmosphere 2019, 10, 505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hleis, D.; Fernández-Olmo, I.; Ledoux, F.; Kfoury, A.; Courcot, L.; Desmonts, T.; Courcot, D. Chemical Profile Identification of Fugitive and Confined Particle Emissions from an Integrated Iron and Steelmaking Plant. J. Hazard. Mater. 2013, 250–251, 246–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, B.; Ma, Y.; Li, H.; Feng, F.; Zhang, Y.; Qin, P. Water-Soluble Ions and Source Apportionment of PM2.5 Depending on Synoptic Weather Patterns in an Urban Environment in Spring Dust Season. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 21953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ledoux, F.; Kfoury, A.; Delmaire, G.; Roussel, G.; El Zein, A.; Courcot, D. Contributions of Local and Regional Anthropogenic Sources of Metals in PM2.5 at an Urban Site in Northern France. Chemosphere 2017, 181, 713–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poulakis, E.; Theodosi, C.; Bressi, M.; Sciare, J.; Ghersi, V.; Mihalopoulos, N. Airborne Mineral Components and Trace Metals in Paris Region: Spatial and Temporal Variability. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 14663–14672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fadel, M.; Courcot, D.; Seigneur, M.; Kfoury, A.; Oikonomou, K.; Sciare, J.; Ledoux, F.; Afif, C. Identification and Apportionment of Local and Long-Range Sources of PM2.5 in Two East-Mediterranean Sites. Atmos. Poll. Res. 2023, 14, 101622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sillanpää, M.; Hillamo, R.; Saarikoski, S.; Frey, A.; Pennanen, A.; Makkonen, U.; Spolnik, Z.; Van Grieken, R.; Braniš, M.; Brunekreef, B.; et al. Chemical Composition and Mass Closure of Particulate Matter at Six Urban Sites in Europe. Atmos. Environ. 2006, 40, 212–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petit, J.-E.; Pallarès, C.; Favez, O.; Alleman, L.Y.; Bonnaire, N.; Rivière, E. Sources and Geographical Origins of PM10 in Metz (France) Using Oxalate as a Marker of Secondary Organic Aerosols by Positive Matrix Factorization Analysis. Atmosphere 2019, 10, 370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sterk, G.; Goossens, D. Emissions of Soil Dust and Related Problems in Europe: An Overview. In Proceedings of the Dustconf International Conference, Maastricht, The Netherlands, 23–24 April 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Ni, T.; Li, P.; Han, B.; Bai, Z.; Ding, X.; Wang, Q.; Huo, J.; Lu, B. Spatial and Temporal Variation of Chemical Composition and Mass Closure of Ambient PM10 in Tianjin, China. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2013, 13, 1832–1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogula-Kozłowska, W.; Klejnowski, K.; Rogula-Kopiec, P.; Ośródka, L.; Krajny, E.; Błaszczak, B.; Mathews, B. Spatial and Seasonal Variability of the Mass Concentration and Chemical Composition of PM2.5 in Poland. Air Qual. Atmos. Health 2014, 7, 41–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Cao, J.; Shen, Z.; Han, Y.; Lee, S.; Huang, Y.; Zhu, C.; Wang, Q.; Xu, H.; Huang, R. Spatial and Seasonal Variations of PM2.5 Mass and Species during 2010 in Xi’an, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 508, 477–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, W.; Fu, Q.; Yang, X.; Li, C.; Zhou, B.; Yu, Q.; Chen, L. Characteristics and Ship Traffic Source Identification of Air Pollutants in China’s Largest Port. Atmos. Environ. 2013, 64, 277–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viana, M.; Hammingh, P.; Colette, A.; Querol, X.; Degraeuwe, B.; de Vlieger, I.; van Aardenne, J. Impact of Maritime Transport Emissions on Coastal Air Quality in Europe. Atmos. Environ. 2014, 90, 96–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nigam, A.; Welch, W.; Miller, J.; Cocher, D.R., III. Effect of Fuel Sulphur Content and Control Technology on PM Emission from Ship’s Auxiliary Engine. In Proceedings of the International Aerosol Conference, St. Paul, MN, USA, 10–15 September 2006; pp. 1531–1532. [Google Scholar]
- Alves, C.; Evtyugina, M.; Vicente, E.; Vicente, A.; Rienda, I.C.; de la Campa, A.S.; Tomé, M.; Duarte, I. PM2.5 Chemical Composition and Health Risks by Inhalation near a Chemical Complex. J. Environ. Sci. 2023, 124, 860–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penkała, M.; Ogrodnik, P.; Rogula-Kozłowska, W. Particulate Matter from the Road Surface Abrasion as a Problem of Non-Exhaust Emission Control. Environments 2018, 5, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piscitello, A.; Bianco, C.; Casasso, A.; Sethi, R. Non-Exhaust Traffic Emissions: Sources, Characterization, and Mitigation Measures. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 766, 144440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrari, C.P.; Hong, S.; Van de Velde, K.; Boutron, C.F.; Rudniev, S.N.; Bolshov, M.; Chisholm, W.; Rosman, K.J.R. Natural and Anthropogenic Bismuth in Central Greenland. Atmos. Environ. 2000, 34, 941–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, K.S.; Cheng, Z.L.; Kot, S.C.; Tsang, C.W. Chemical Characteristics of Aerosols at Coastal Station in Hong Kong. II. Environmental Behavior of Trace Elements during the April 1995 to April 1996. J. Environ. Sci. China 2004, 16, 212–221. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Valotto, G.; Rampazzo, G.; Visin, F.; Gonella, F.; Cattaruzza, E.; Glisenti, A.; Formenton, G.; Tieppo, P. Environmental and Traffic-Related Parameters Affecting Road Dust Composition: A Multi-Technique Approach Applied to Venice Area (Italy). Atmos. Environ. 2015, 122, 596–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Uexull, O.; Skerfving, S.; Doyle, R.; Braungart, M. Antimony in Brake Pads—A Carcinogenic Component? J. Clean. Prod. 2005, 13, 19–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.-C.; Tsai, C.-J.; Wu, Y.-C.; Zhang, R.; Chi, K.-H.; Huang, Y.-T.; Lin, S.-H.; Hsu, S.-C. Characteristics of Trace Metals in Traffic-Derived Particles in Hsuehshan Tunnel, Taiwan: Size Distribution, Potential Source, and Fingerprinting Metal Ratio. SALAMEH 2015, 15, 4117–4130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mancilla, Y.; Mendoza, A. A Tunnel Study to Characterize PM2.5 Emissions from Gasoline-Powered Vehicles in Monterrey, Mexico. Atmos. Environ. 2012, 59, 449–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pant, P.; Harrison, R.M. Estimation of the Contribution of Road Traffic Emissions to Particulate Matter Concentrations from Field Measurements: A Review. Atmos. Environ. 2013, 77, 78–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.-Y.; Hu, M.; Huang, X.-F.; Yu, B.-D.; Zhang, Y.-H.; Liu, D.-Q. Measurement of Emissions of Fine Particulate Organic Matter from Chinese Cooking. Atmos. Environ. 2004, 38, 6557–6564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, J.Z.; Sun, L.; Tian, Y.; Shi, G.; Feng, Y. Chemical Characterization and Source Apportionment of PM1 and PM2.5 in Tianjin, China: Impacts of Biomass Burning and Primary Biogenic Sources. J. Environ. Sci. 2021, 99, 196–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salameh, D.; Detournay, A.; Pey, J.; Pérez, N.; Liguori, F.; Saraga, D.; Bove, M.C.; Brotto, P.; Cassola, F.; Massabò, D.; et al. PM2.5 Chemical Composition in Five European Mediterranean Cities: A 1-Year Study. Atmos. Res. 2015, 155, 102–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreae, M.O.; Merlet, P. Emission of Trace Gases and Aerosols from Biomass Burning. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 2001, 15, 955–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Favez, O.; El Haddad, I.; Piot, C.; Boréave, A.; Abidi, E.; Marchand, N.; Jaffrezo, J.-L.; Besombes, J.-L.; Personnaz, M.-B.; Sciare, J.; et al. Inter-Comparison of Source Apportionment Models for the Estimation of Wood Burning Aerosols during Wintertime in an Alpine City (Grenoble, France). Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2010, 10, 5295–5314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waked, A.; Favez, O.; Alleman, L.Y.; Piot, C.; Petit, J.-E.; Delaunay, T.; Verlinden, E.; Golly, B.; Besombes, J.-L.; Jaffrezo, J.-L.; et al. Source Apportionment of PM10 in a North-Western Europe Regional Urban Background Site (Lens, France) Using Positive Matrix Factorization and Including Primary Biogenic Emissions. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2014, 14, 3325–3346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Favez, O.; Cachier, H.; Sciare, J.; Sarda-Estève, R.; Martinon, L. Evidence for a Significant Contribution of Wood Burning Aerosols to PM2.5 during the Winter Season in Paris, France. Atmos. Environ. 2009, 43, 3640–3644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruce, D.; Karl, M.; Herdis, L.; Christer, J.; Aarnio, M.; Karppinen, A.; Kukkonen, J.; Ketzel, M.; Peter, W. Estimating Domestic Wood Burning Emissions of Particulate Matter in Two Nordic Cities by Combining Ambient Air Observations with Receptor and Dispersion Models. Chem. Ind. Chem. Eng. Q. 2010, 16, 237–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reche, C.; Viana, M.; Amato, F.; Alastuey, A.; Moreno, T.; Hillamo, R.; Teinilä, K.; Saarnio, K.; Seco, R.; Peñuelas, J.; et al. Biomass Burning Contributions to Urban Aerosols in a Coastal Mediterranean City. Sci. Total Environ. 2012, 427–428, 175–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kauhaniemi, M.; Karppinen, A.; Härkönen, J.; Kousa, A.; Alaviippola, B.; Koskentalo, T.; Aarnio, P.; Elolähde, T.; Kukkonen, J. Evaluation of a Modelling System for Predicting the Concentrations of PM2.5 in an Urban Area. Atmos. Environ. 2008, 42, 4517–4529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ChooChuay, C.; Pongpiachan, S.; Tipmanee, D.; Deelaman, W.; Suttinun, O.; Wang, Q.; Xing, L.; Li, G.; Han, Y.; Palakun, J.; et al. Long-Range Transboundary Atmospheric Transport of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons, Carbonaceous Compositions, and Water-Soluble Ionic Species in Southern Thailand. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2020, 20, 1591–1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sciare, J.; Oikonomou, K.; Favez, O.; Liakakou, E.; Markaki, Z.; Cachier, H.; Mihalopoulos, N. Long-Term Measurements of Carbonaceous Aerosols in the Eastern Mediterranean: Evidence of Long-Range Transport of Biomass Burning. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2008, 8, 5551–5563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Liu, Z.; Hecobian, A.; Zheng, M.; Frank, N.H.; Edgerton, E.S.; Weber, R.J. Spatial and Seasonal Variations of Fine Particle Water-Soluble Organic Carbon (WSOC) over the Southeastern United States: Implications for Secondary Organic Aerosol Formation. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2012, 12, 6593–6607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suto, N.; Kawashima, H. Measurement Report: Source Characteristics of Water-Soluble Organic Carbon in PM2.5 at Two Sites in Japan, as Assessed by Long-Term Observation and Stable Carbon Isotope Ratio. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2021, 21, 11815–11828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rastogi, N.; Patel, A.; Singh, A.; Singh, D. Diurnal Variability in Secondary Organic Aerosol Formation over the Indo-Gangetic Plain during Winter Using Online Measurement of Water-Soluble Organic Carbon. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2015, 15, 2225–2231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Win, M.S.; Tian, Z.; Zhao, H.; Xiao, K.; Peng, J.; Shang, Y.; Wu, M.; Xiu, G.; Lu, S.; Yonemochi, S.; et al. Atmospheric HULIS and Its Ability to Mediate the Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS): A Review. J. Environ. Sci. 2018, 71, 13–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, P.; Engling, G.; Yu, J.Z. Humic-like Substances in Fresh Emissions of Rice Straw Burning and in Ambient Aerosols in the Pearl River Delta Region, China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2010, 10, 6487–6500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samara, C.; Voutsa, D.; Kouras, A.; Eleftheriadis, K.; Maggos, T.; Saraga, D.; Petrakakis, M. Organic and Elemental Carbon Associated to PM10 and PM 2.5 at Urban Sites of Northern Greece. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2014, 21, 1769–1785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, W.; Lee, H.; Kim, J.; Jeong, U.; Kweon, J. Estimation of Seasonal Diurnal Variations in Primary and Secondary Organic Carbon Concentrations in the Urban Atmosphere: EC Tracer and Multiple Regression Approaches. Atmos. Environ. 2012, 56, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, H.Y.; Kim, K.A.; Kim, Y.P.; Jung, C.H.; Shin, H.J.; Moon, K.J.; Park, S.M.; Lee, J.Y. Validation of SOC Estimation Using OC and EC Concentration in PM2.5 Measured at Seoul. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2022, 22, 210388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potier, E.; Waked, A.; Bourin, A.; Minvielle, F.; Péré, J.C.; Perdrix, E.; Michoud, V.; Riffault, V.; Alleman, L.Y.; Sauvage, S. Characterizing the Regional Contribution to PM10 Pollution over Northern France Using Two Complementary Approaches: Chemistry Transport and Trajectory-Based Receptor Models. Atmos. Res. 2019, 223, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viana, M.; Maenhaut, W.; ten Brink, H.M.; Chi, X.; Weijers, E.; Querol, X.; Alastuey, A.; Mikuška, P.; Večeřa, Z. Comparative Analysis of Organic and Elemental Carbon Concentrations in Carbonaceous Aerosols in Three European Cities. Atmos. Environ. 2007, 41, 5972–5983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
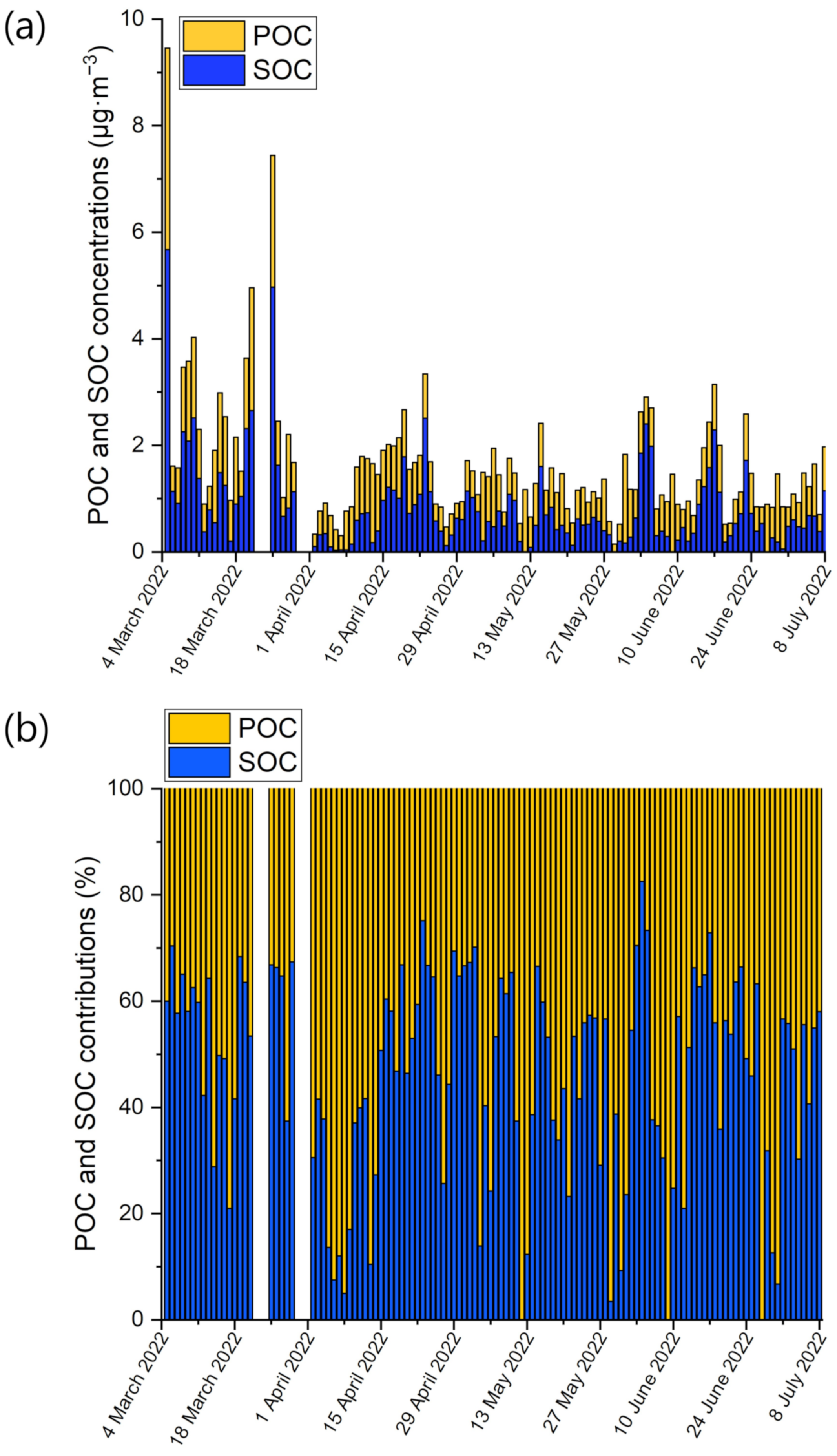
| Species | µA | µG | Median | SD | Min | Max |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PM2.5 (µg·m−3) | 12.6 | 10.3 | 10.0 | 9.5 | 3.6 | 60.7 |
| Carbonaceous fraction (µg·m−3) | ||||||
| OC | 1.6 | 1.3 | 1.4 | 1.2 | 0.1 | 9.4 |
| WSOC | 0.7 | 0.5 | 0.4 | 0.8 | 0.02 | 5.6 |
| HULIS-C | 0.4 | 0.1 | 0.2 | 0.5 | <D.L. | 3.1 |
| EC | 0.3 | 0.3 | 0.3 | 0.2 | 0.05 | 1.5 |
| Water-soluble ions (µg·m−3) | ||||||
| NO3− | 2.2 | 0.8 | 0.06 | 4.8 | 0.07 | 32.9 |
| NH4+ | 1.1 | 0.7 | 0.6 | 1.7 | 0.06 | 11.7 |
| SO42− | 1.1 | 0.9 | 0.1 | 0.7 | 0.2 | 4.5 |
| Ca2+ | 0.2 | 0.04 | 0.08 | 0.2 | <D.L. | 1.3 |
| Cl− | 0.09 | 0.02 | 0.05 | 0.1 | <D.L. | 0.8 |
| Na+ | 0.06 | 0.03 | 0.04 | 0.05 | <D.L. | 0.3 |
| K+ | 0.04 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.08 | <D.L. | 0.6 |
| Mg2+ | 0.03 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.03 | <D.L. | 0.2 |
| Major and trace elements (ng·m−3) | ||||||
| Fe | 114 | 56.9 | 59.0 | 135 | <D.L. | 653 |
| Al | 39.7 | 15.5 | 25.9 | 54.2 | <D.L. | 485 |
| Zn | 14.4 | 8.1 | 9.3 | 15.8 | <D.L. | 98.4 |
| Mn | 10.4 | 3.8 | 4.04 | 16.1 | <D.L. | 86.8 |
| P | 7.8 | 4.4 | 6.2 | 7.2 | <D.L. | 40.3 |
| Pb | 5.0 | 2.5 | 3.5 | 5.4 | <D.L. | 29.4 |
| V | 2.1 | 1.3 | 1.6 | 2.1 | 0.01 | 14.9 |
| Ti | 2.1 | 1.2 | 1.4 | 2.3 | <D.L. | 12.0 |
| Ni | 1.3 | 0.7 | 1.0 | 1.5 | <D.L. | 11.1 |
| Cu | 1.3 | 0.5 | 1.1 | 1.6 | <D.L. | 9.9 |
| Ba | 1.2 | 0.3 | 0.7 | 1.7 | <D.L. | 10.6 |
| Sn | 0.8 | 0.5 | 0.6 | 0.9 | <D.L. | 4.6 |
| Sb | 0.7 | 0.1 | 0.3 | 1.1 | <D.L. | 4.9 |
| Cr | 0.6 | 0.3 | 0.4 | 0.7 | <D.L. | 4.3 |
| Rb | 0.4 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.8 | <D.L. | 6.7 |
| As | 0.4 | 0.3 | 0.3 | 0.4 | 0.01 | 2.1 |
| Sr | 0.4 | 0.2 | 0.3 | 0.3 | <D.L. | 1.7 |
| Nb | 0.2 | 0.02 | 0.05 | 1.1 | <D.L. | 12.4 |
| Tl | 0.1 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.2 | <D.L. | 1.2 |
| Cd | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 | <D.L. | 0.7 |
| Co | 0.1 | 0.04 | 0.05 | 0.06 | <D.L. | 0.3 |
| Bi | 0.08 | 0.05 | 0.1 | 0.08 | <D.L. | 0.6 |
| Ce | 0.08 | 0.05 | 0.1 | 0.07 | <D.L. | 0.4 |
| La | 0.05 | 0.03 | 0.05 | 0.05 | <D.L. | 0.2 |
| Sc | 0.04 | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.06 | <D.L. | 0.4 |
| Clusters | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PM2.5 | 22.2 | 13.0 | 6.9 | 8.3 | 12.0 |
| OM | 4.4 | 3.0 | 1.5 | 2.1 | 1.8 |
| WSOC | 1.6 | 0.9 | 0.2 | 0.5 | 0.5 |
| HULIS-C | 0.8 | 0.5 | 0.1 | 0.4 | 0.3 |
| SOC | 1.8 | 0.9 | 0.3 | 0.6 | 0.6 |
| EC | 0.4 | 0.4 | 0.3 | 0.3 | 0.2 |
| SIA | 10.3 | 4.2 | 1.5 | 2.0 | 3.8 |
| Sea-salt | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.5 | 0.2 | 0.2 |
| Crustal dust | 0.9 | 0.7 | 1.5 | 1.3 | 0.7 |
| OC/EC | 7.1 | 5.2 | 3.3 | 4.8 | 5.2 |
| WSOC/OC | 0.6 | 0.5 | 0.2 | 0.4 | 0.5 |
| SOC/POC | 1.8 | 1.0 | 0.6 | 0.9 | 0.7 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Allouche, Y.; Fadel, M.; Ferté, A.; Verdin, A.; Ledoux, F.; Courcot, D. Phenomenology of the Composition of PM2.5 at an Urban Site in Northern France. Atmosphere 2024, 15, 603. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15050603
Allouche Y, Fadel M, Ferté A, Verdin A, Ledoux F, Courcot D. Phenomenology of the Composition of PM2.5 at an Urban Site in Northern France. Atmosphere. 2024; 15(5):603. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15050603
Chicago/Turabian StyleAllouche, Yamina, Marc Fadel, Amélie Ferté, Anthony Verdin, Frédéric Ledoux, and Dominique Courcot. 2024. "Phenomenology of the Composition of PM2.5 at an Urban Site in Northern France" Atmosphere 15, no. 5: 603. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15050603
APA StyleAllouche, Y., Fadel, M., Ferté, A., Verdin, A., Ledoux, F., & Courcot, D. (2024). Phenomenology of the Composition of PM2.5 at an Urban Site in Northern France. Atmosphere, 15(5), 603. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15050603







