Spatiotemporal Characteristics and Rainfall Thresholds of Geological Landslide Disasters in ASEAN Countries
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Data and Methodology
2.1. Data
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Antecedent Effective Precipitation
2.2.2. Intensity–Duration Model for Rainfall
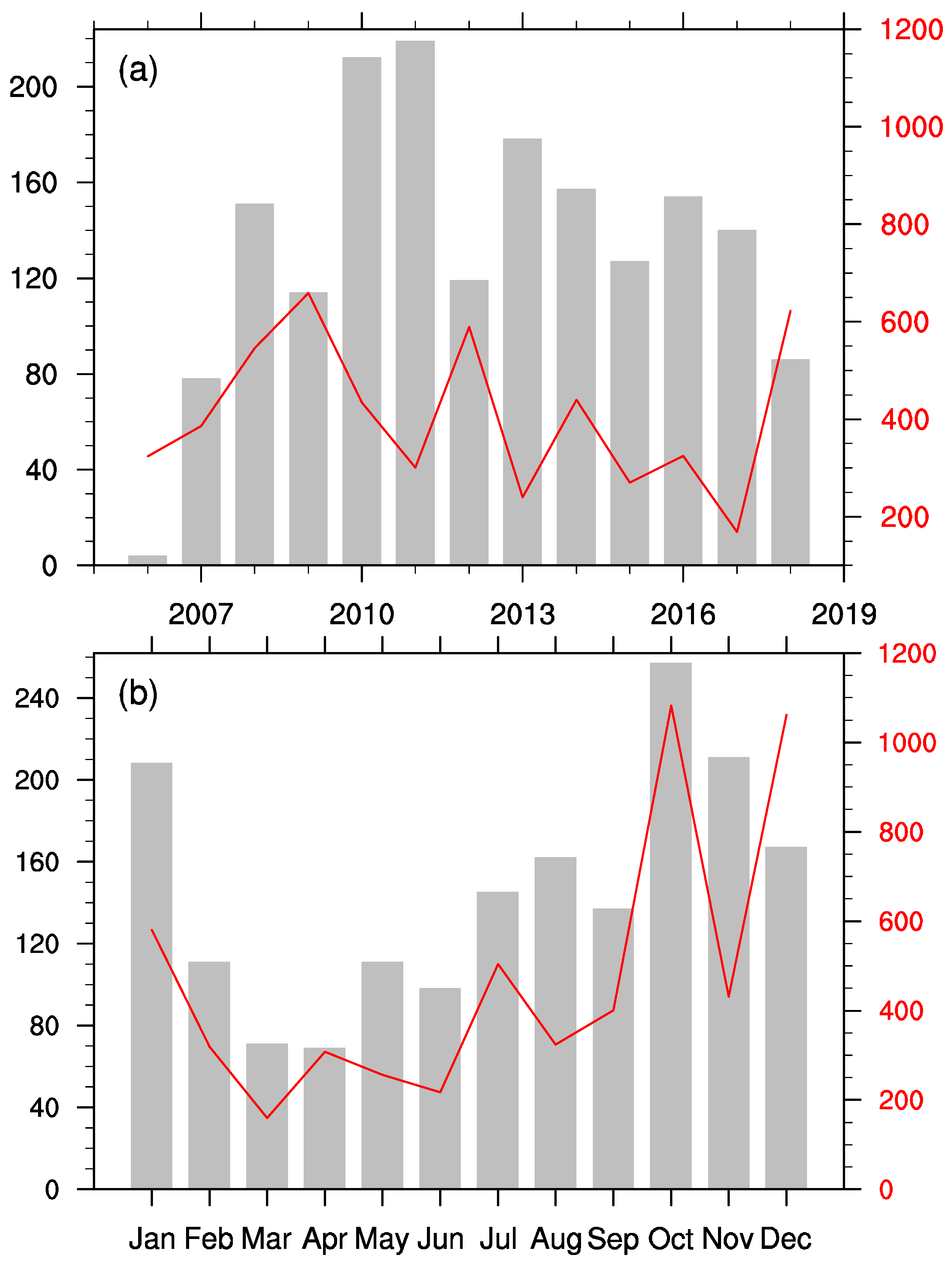
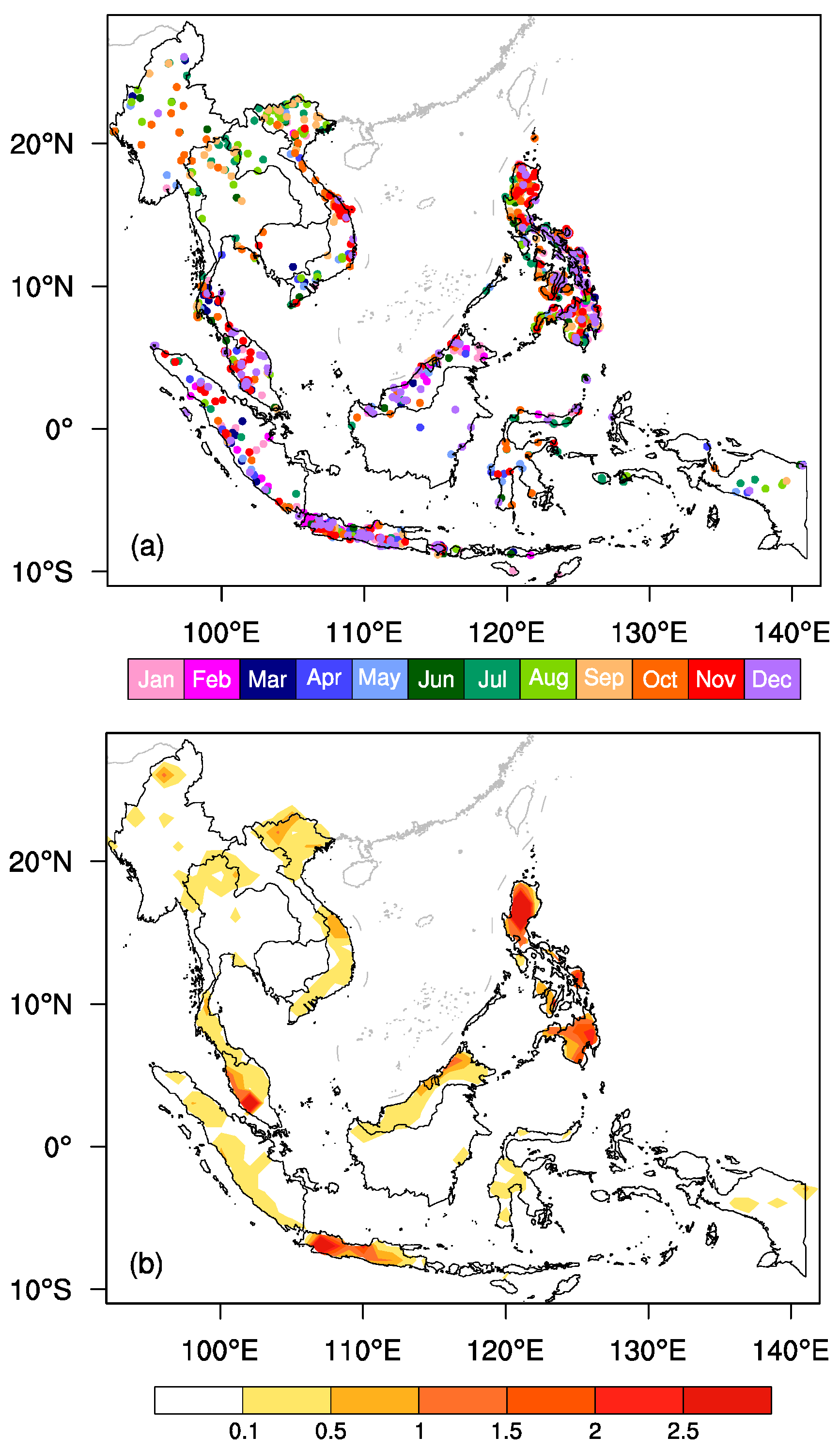
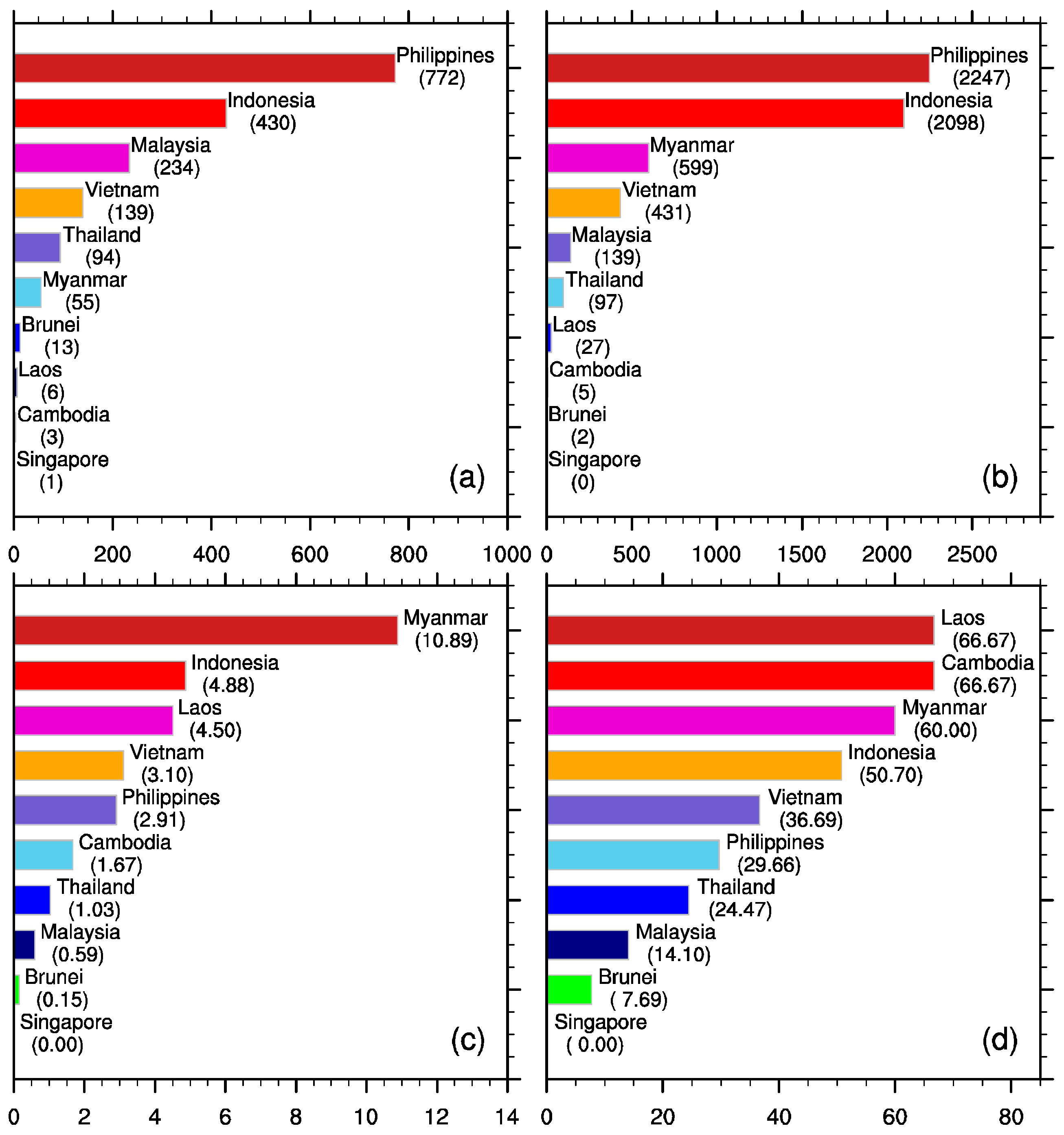
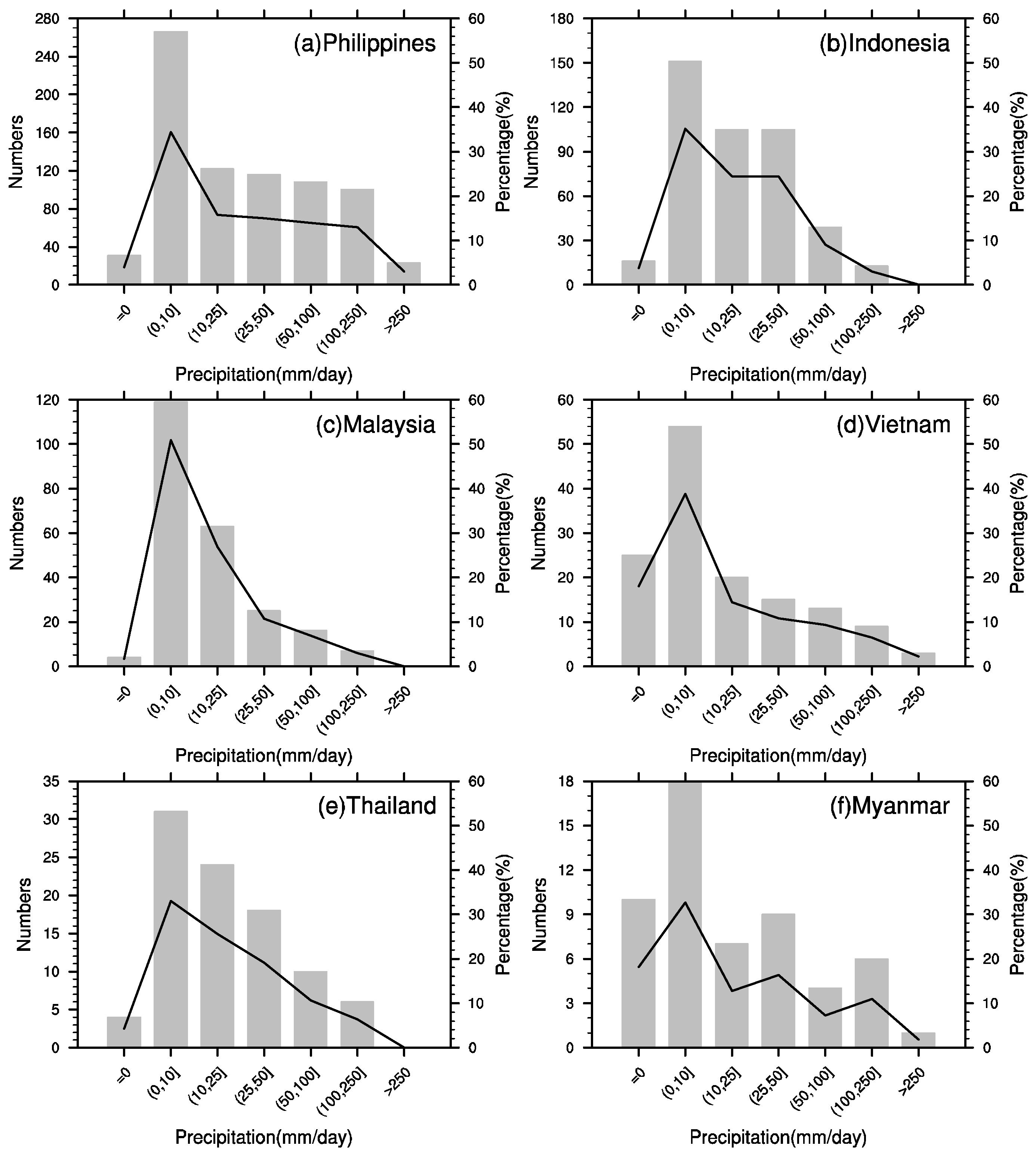
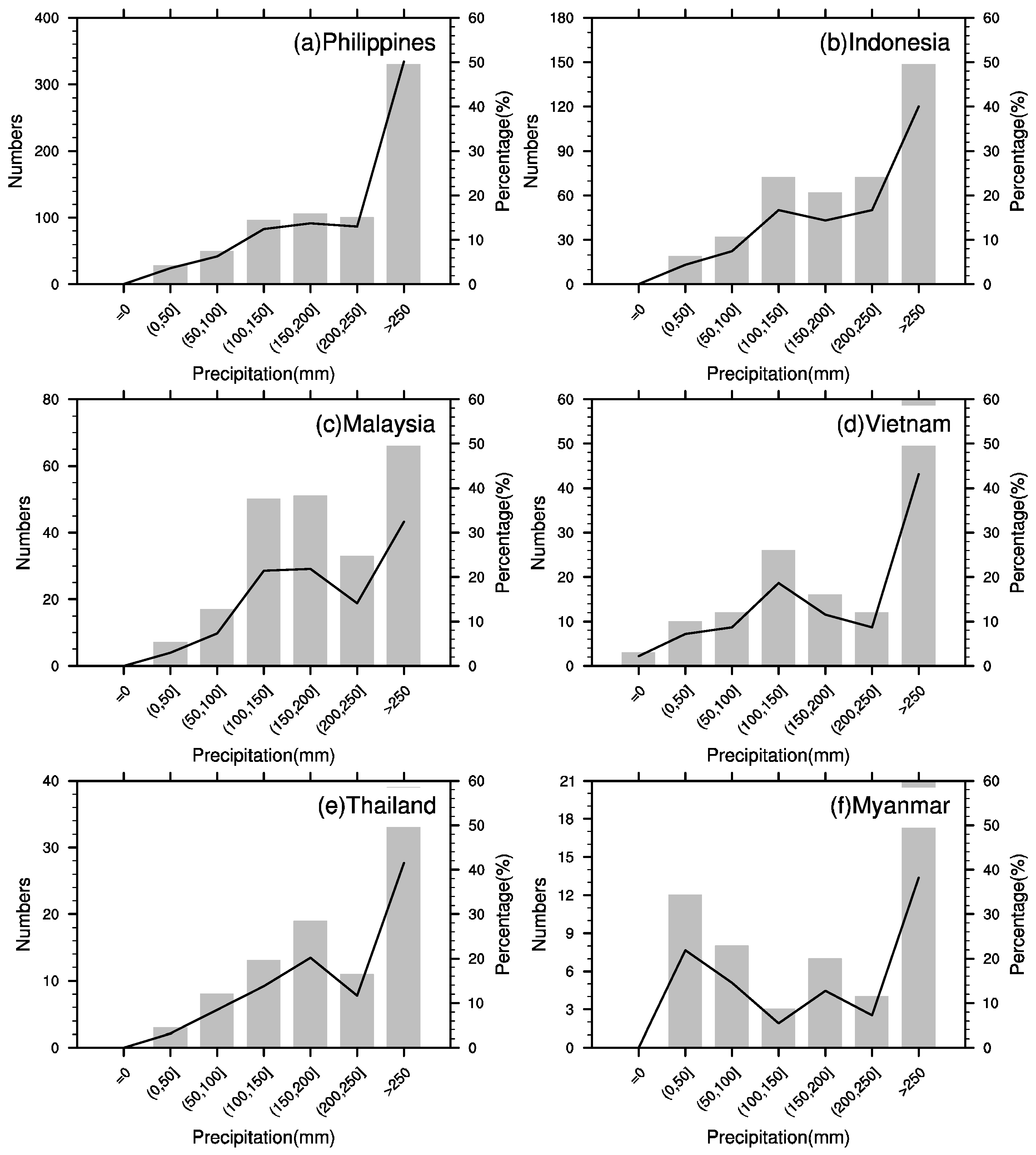
3. Spatiotemporal Characteristics of Geological Landslides within ASEAN
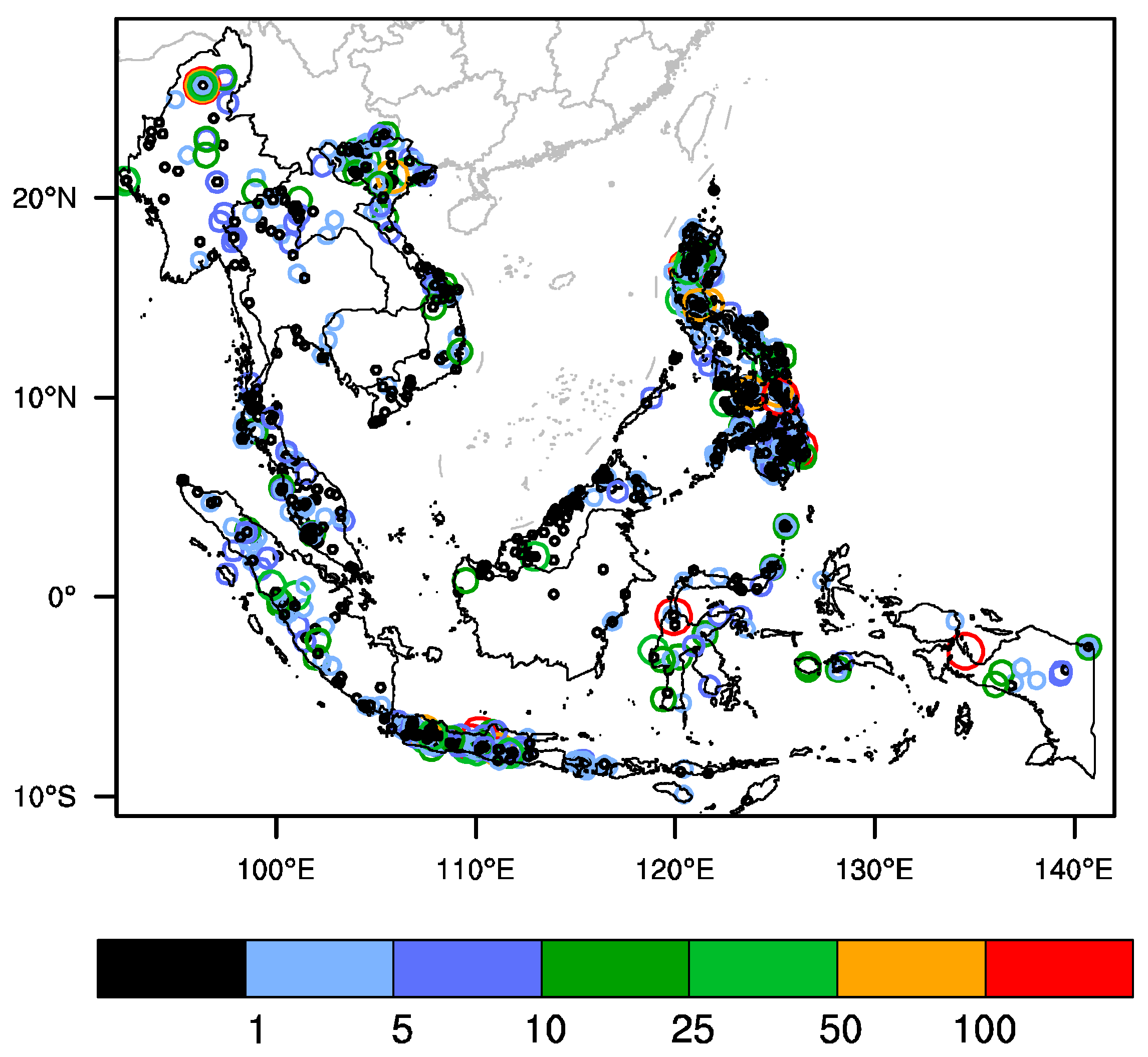
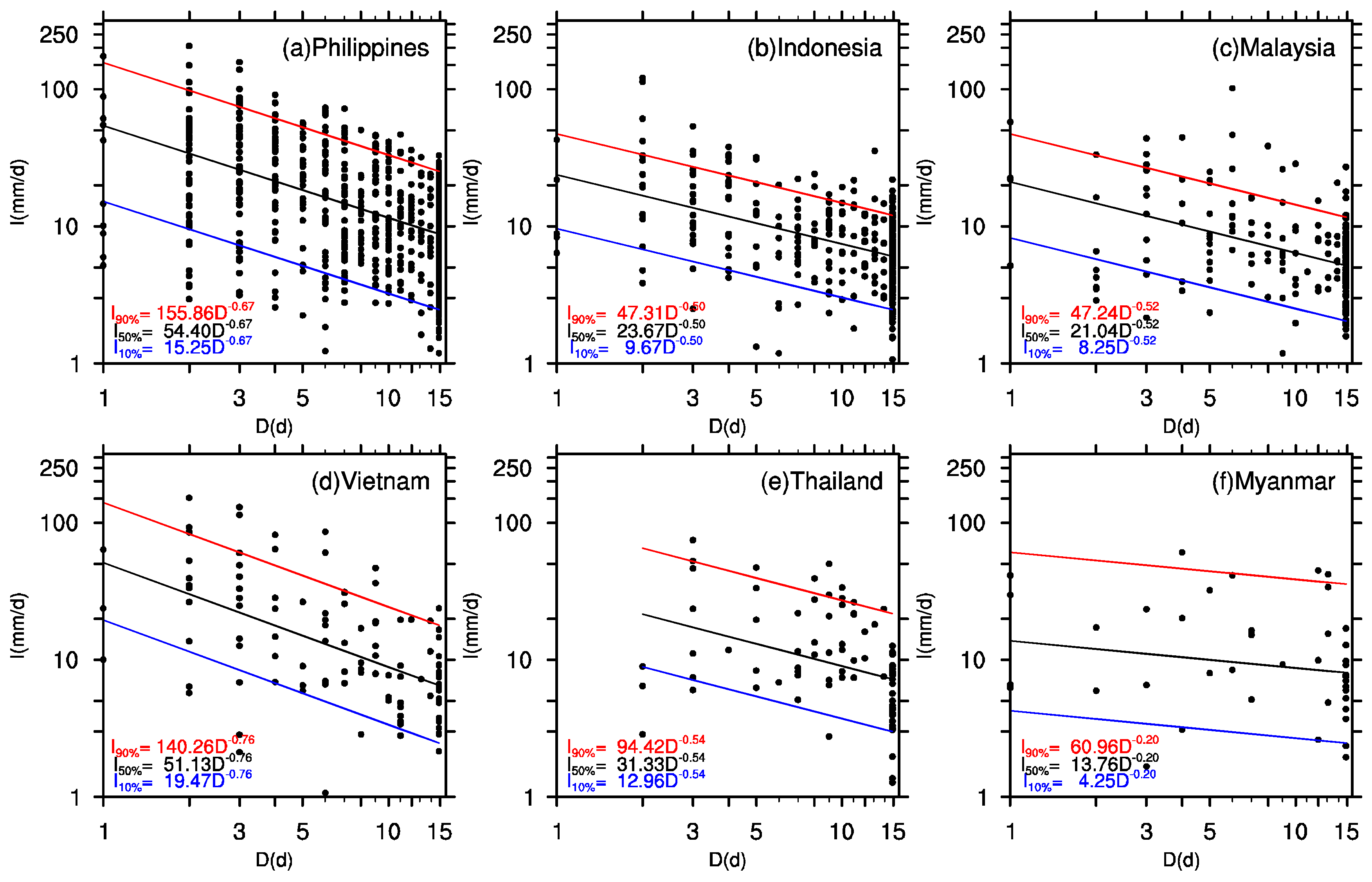
4. Rainfall Thresholds of Landslides in ASEAN Nations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Barman, J.; Soren, D.D.L.; Biswas, B. Landslide susceptibility evaluation and analysis: A review on articles published during 2000 to 2020. In Monitoring and Managing Multi-Hazards. GIScience and Geo-Environmental Modelling; Das, J., Bhattacharya, S.K., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Sim, K.B.; Lee, M.L.; Wong, S.Y. A review of landslide acceptable risk and tolerable risk. Geoenviron. Dis. 2022, 9, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keaokiriya, P.; Shivakoti, B.; Goto, T.; Sakai, H.; Dewi, A.; Jayasinghe, S.; Basnayake, S.; Kartiko, R.D.; Arambepola, N.M.S.I. Disaster risk reduction in the ASEAN region: Understanding and assessing systematic risks of floods and landslides in a river basin context. 2022. Available online: https://www.undrr.org/media/80192/download (accessed on 1 May 2024).
- Li, Y.; Meng, H.; Dong, Y.; Hu, S. Main types and characteristics of geo-hazard in China-Based on the results of geo-hazard survey in 290 counties. Chin. J. Geol. Hazard Control 2004, 15, 29–34. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Bai, S.; Wang, J.; Thiebes, B.; Cheng, C.; Yang, Y. Analysis of the relationship of landslide occurrence with rainfall: A case study of Wudu County, China. Arab. J. Geosci. 2014, 7, 1277–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzzetti, F.; Peruccacci, S.; Rossi, M.; Stark, C.P. The rainfall intensity-duration control of shallow landslides and debris flows: An update. Landslide 2008, 5, 3–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Tang, M.G.; Xu, Q.; Wu, H.L.; Wang, X.M. Early warning model of rainfall-induced landslide in Chongqing of China based on rainfall threshold. Mt. Res. 2022, 40, 847–858. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.H.; Yang, H.P.; Liao, L.P.; Xiao, L. Study on the rainfall threshold of the landslide disaster in Rong County in June 2010. J. Nat. Dis. 2023, 32, 228–235. [Google Scholar]
- Glade, T.; Crozier, M.; Smith, P. Applying probability determination to refine landslide-triggering rainfall thresholds using an empirical “Antecedent Daily Rainfall Model”. Pure Appl. Geophys. 2000, 157, 1059–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.K.; Wei, L.; Tan, L. Review of research on empirical rainfall threshold of rainfall-induced landslide. J. Chongqing Jiaotong Univ. (Nat. Sci.) 2012, 31, 990–996. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Caine, N. The rainfall intensity-duration control of shallow landslides and debris flows. Geogr. Ann. 1980, 62, 23–27. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, W.; Li, Y.Y.; Xu, Y.; Lian, Z.P.; Cao, Y.; Shen, Y.F. Rainfall thresholds of rainfall-triggered landslides in Cili county, Hunan province. J. Yangtze River Sci. Res. 2020, 37, 48–54. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Xia, M.X.; Li, Y.Y.; Wu, J.M.; Lian, Z.P.; Lin, W. Research on rainfall early warming threshold of landslide disaster in Zhangjiajie city based on I-D statistical model. J. Nat. Dis. 2021, 30, 203–212. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Dai, C.R.; Huang, W.; Li, M.; Zhang, M.D.; Li, C.H.; Zhu, Y. County-level rainfall warming thresholds for rainfall-induced landslides in Yunnan. Meteorol. Sci. Technol. 2015, 43, 675–680. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Huang, J.; Ju, N.P.; Liao, Y.J.; Liu, D.D. Determination of rainfall thresholds for shallow landslides by a probabilistic and empirical method. Nat. Hazards Earth Sci. Syst. 2015, 15, 2715–2723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maturidi, A.M.A.M.; Kasim, N.; Abu Taib, K.; Azahar, W.N.A.W.; Tajuddin, H.B.A. Empirically based rainfall threshold for landslides occurrence in Peninsular Malaysia. KSCE J. Civ. Eng. 2021, 25, 4552–4566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maturidi, A.M.A.M.; Kasim, N.; Abu Taib, K.; Azahar, W.N.A.W. Rainfall-induced landslide thresholds development by considering different rainfall parameters: A review. J. Ecol. Eng. 2021, 22, 85–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.Y.; Han, T.T.; Hao, X. Regional characteristics of extreme precipitation events in Eurasia. Trans. Atmos. Sci. 2020, 43, 687–698. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, B.T.; Xu, Y.; Han, Z.Y.; Shi, Y.; Wu, J.; Li, R.K. CMIP5 projected changes in mean and extreme climate in the Belt and Road region. Trans. Atmos. Sci. 2020, 43, 255–264. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- An, D.; Eggeling, J.; Zhang, L.; He, H.; Sapkota, A.; Wang, Y.-C.; Gao, C. Extreme precipitation patterns in the Asia–Pacific region and its correlation with El Niño-Southern Oscillation (ENSO). Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 11068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirschbaum, D.B.; Stanley, T.; Zhou, Y.P. Spatial and temporal analysis of a global landslide catalog. Geomorphology 2015, 249, 4–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, Y.F.; Li, Y.Y.; Xu, Y.; Wu, J.M.; Lin, W. Prediction of rainfall-type landslides based on effective rainfall intensity and logistic regression. Hydrogeol. Eng. Geol. 2019, 46, 156–162. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Huang, F.M.; Chen, J.W.; Fan, X.M.; Huang, J.S.; Zhou, C.B. Logistic regression fitting of rainfall-induced landslide occurrence probability and continuous landslide hazard prediction modelling. Earth Sci. 2022, 47, 4609–4628. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.Z.; Ma, Z.F.; Fan, G.Z. Relationship between landslide/debris flow and rainfall in typical region of Sichuan province. Bull. Soil Water Conserv. 2016, 36, 74–77. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Brunetti, M.T.; Peruccacci, S.; Rossi, M.; Luciani, S.; Valigi, D.; Guzzetti, F. Rainfall thresholds for the possible occurrence of landslides in Italy. Nat. Hazard. Earth Syst. 2010, 10, 447–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Froude, M.J.; Petley, D.N. Global fatal landslide occurrence from 2004 to 2016. Nat. Hazard. Earth Syst. 2018, 18, 2161–2181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nolasco-Javier, D.; Kumar, L.; Tengonciang, A.M.P. Rapid appraisal of rainfall threshold and selected landslides in Baguio, Philippines. Nat. Hazard. 2015, 78, 1587–1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cullen, C.A.; Suhili, R.A.; Aristizabal, E. A landslide numerical factor derived from CHIRPS for shallow rainfall triggered landslides in Colombia. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 2239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Du, J.; Yin, K.; Zhou, C.; Huang, C.; Jiang, J.; Yu, J. Regional early warning model for rainfall induced landslide based on slope unit in Chongqing, China. Eng. Geol. 2024, 333, 107464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, R.L.; Jacobs, J.M. Relationships among remotely sensed soil moisture, precipitation and landslide events. Nat. Hazard. 2007, 43, 211–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Landslide Scale | Small Scale | Medium Scale | Large-Scale | Extra-Large Scale | Unknown |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Philippines | 10.2 | 78.9 | 7.8 | 1.3 | 1.8 |
| Indonesia | 6.3 | 70.8 | 16.3 | 1.9 | 4.9 |
| Malaysia | 24.4 | 65.4 | 5.6 | 0 | 4.7 |
| Vietnam | 7.2 | 77.0 | 10.8 | 5.0 | 0 |
| Thailand | 31.9 | 57.4 | 9.6 | 0 | 1.1 |
| Myanmar | 3.6 | 63.6 | 27.3 | 0 | 5.5 |
| Rainfall Days (d) | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Country | Philippines | 54.40 | 88.52 | 114.50 | 135.90 | 154.31 |
| Indonesia | 23.68 | 40.37 | 53.98 | 65.75 | 76.27 | |
| Malaysia | 21.04 | 35.74 | 47.66 | 57.94 | 67.09 | |
| Vietnam | 51.13 | 81.28 | 103.42 | 121.19 | 136.19 | |
| Thailand | 31.33 | 52.85 | 70.12 | 84.90 | 97.99 | |
| Myanmar | 13.76 | 25.75 | 36.84 | 47.25 | 57.24 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lu, W.; Xiao, Z.; Chen, Y.; Sun, J.; Chen, F. Spatiotemporal Characteristics and Rainfall Thresholds of Geological Landslide Disasters in ASEAN Countries. Atmosphere 2024, 15, 599. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15050599
Lu W, Xiao Z, Chen Y, Sun J, Chen F. Spatiotemporal Characteristics and Rainfall Thresholds of Geological Landslide Disasters in ASEAN Countries. Atmosphere. 2024; 15(5):599. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15050599
Chicago/Turabian StyleLu, Weiping, Zhixiang Xiao, Yuhang Chen, Jingwen Sun, and Feisheng Chen. 2024. "Spatiotemporal Characteristics and Rainfall Thresholds of Geological Landslide Disasters in ASEAN Countries" Atmosphere 15, no. 5: 599. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15050599
APA StyleLu, W., Xiao, Z., Chen, Y., Sun, J., & Chen, F. (2024). Spatiotemporal Characteristics and Rainfall Thresholds of Geological Landslide Disasters in ASEAN Countries. Atmosphere, 15(5), 599. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15050599






