The Relationship between the Typhoons Affecting South China and the Pacific Decadal Oscillation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Data and Methods
2.1. Data
2.2. Methods
3. Results
3.1. Climatic Characteristics of Tropical Cyclones Affecting South China and Their Relationship with the PDO Index
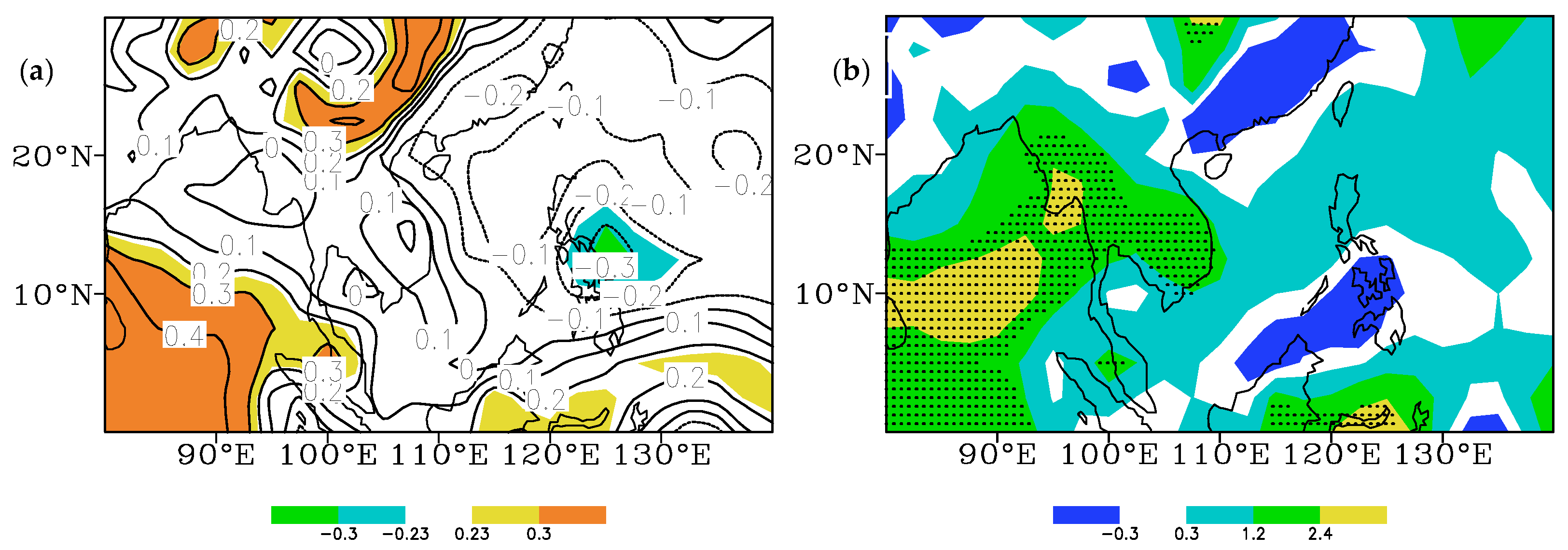
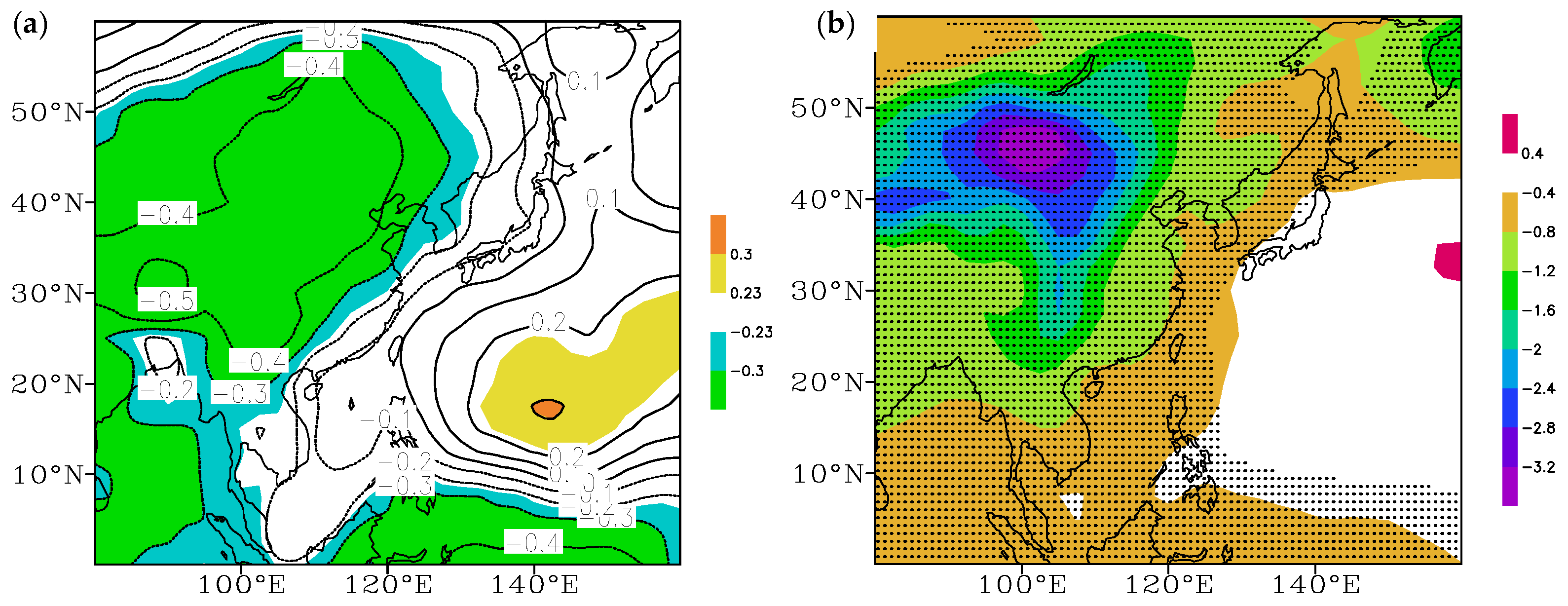
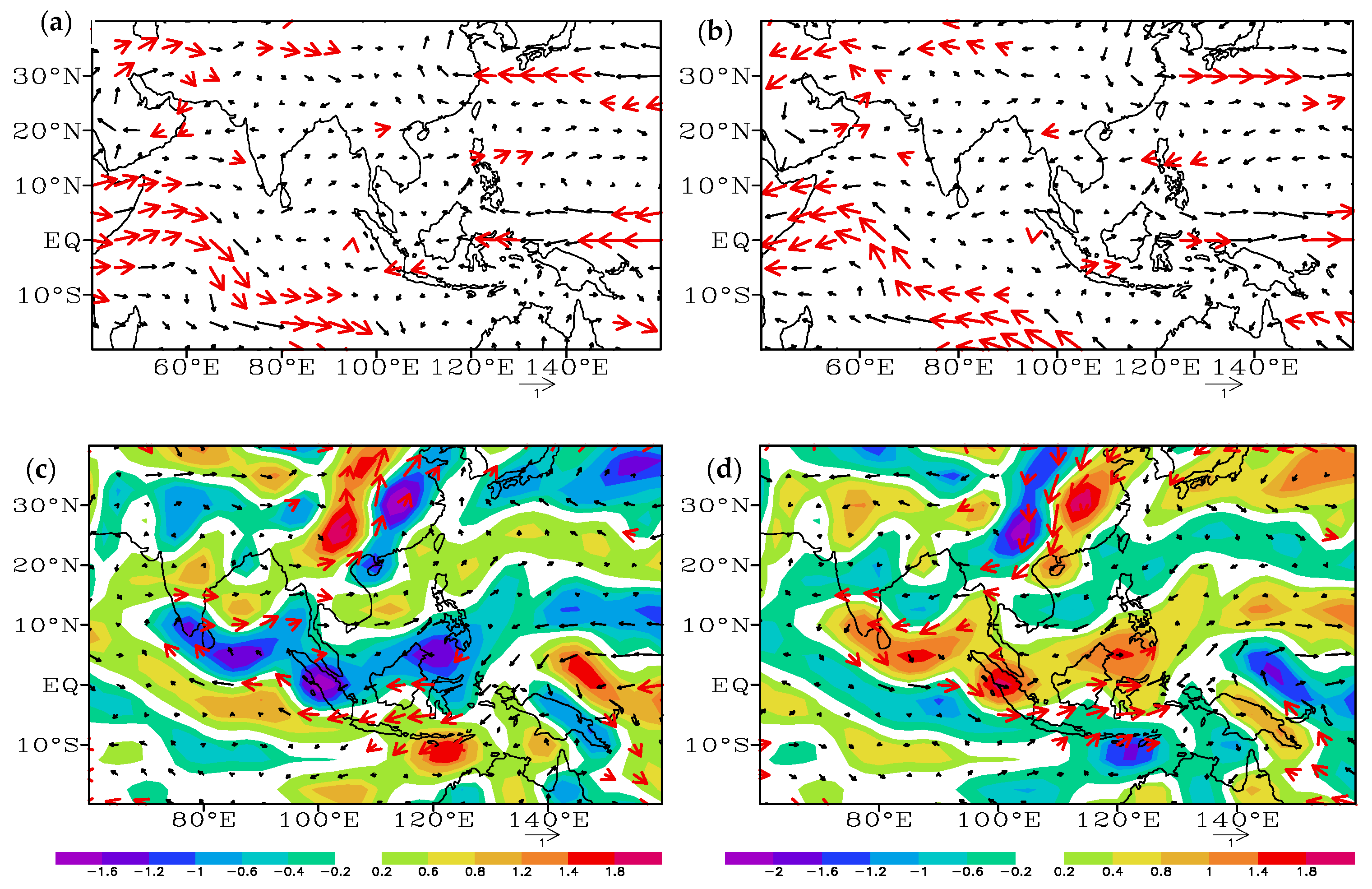
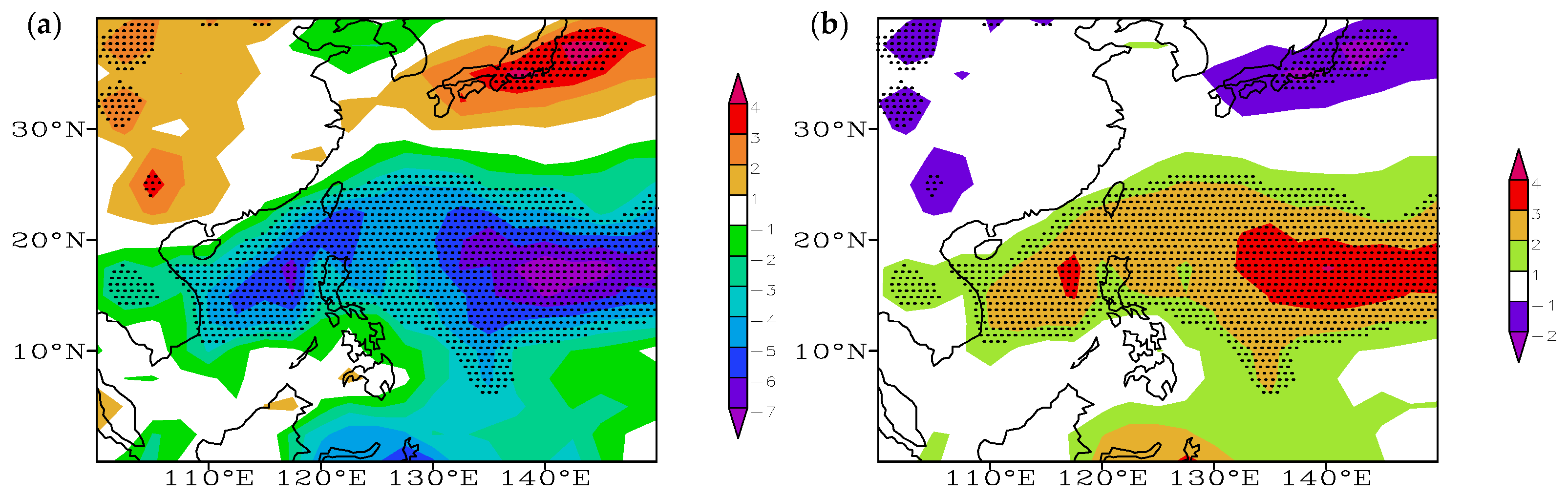
3.2. Characteristics of Ocean–Atmosphere Anomalies in Different PDO Phases and Their Relationship with the Proportion of SCTYs
3.2.1. SST
3.2.2. Subtropical High
3.2.3. Relative Humidity
3.2.4. Sea Level Pressure
3.2.5. High- and Low-Altitude Wind Fields
3.2.6. Atmospheric Convection
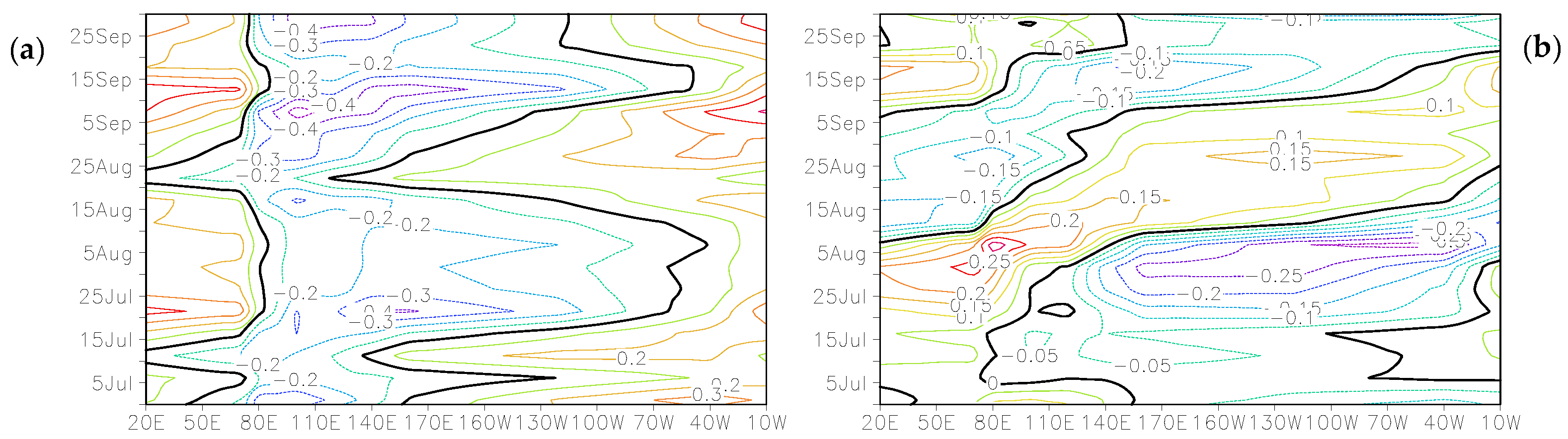
3.2.7. Madden–Julian Oscillation
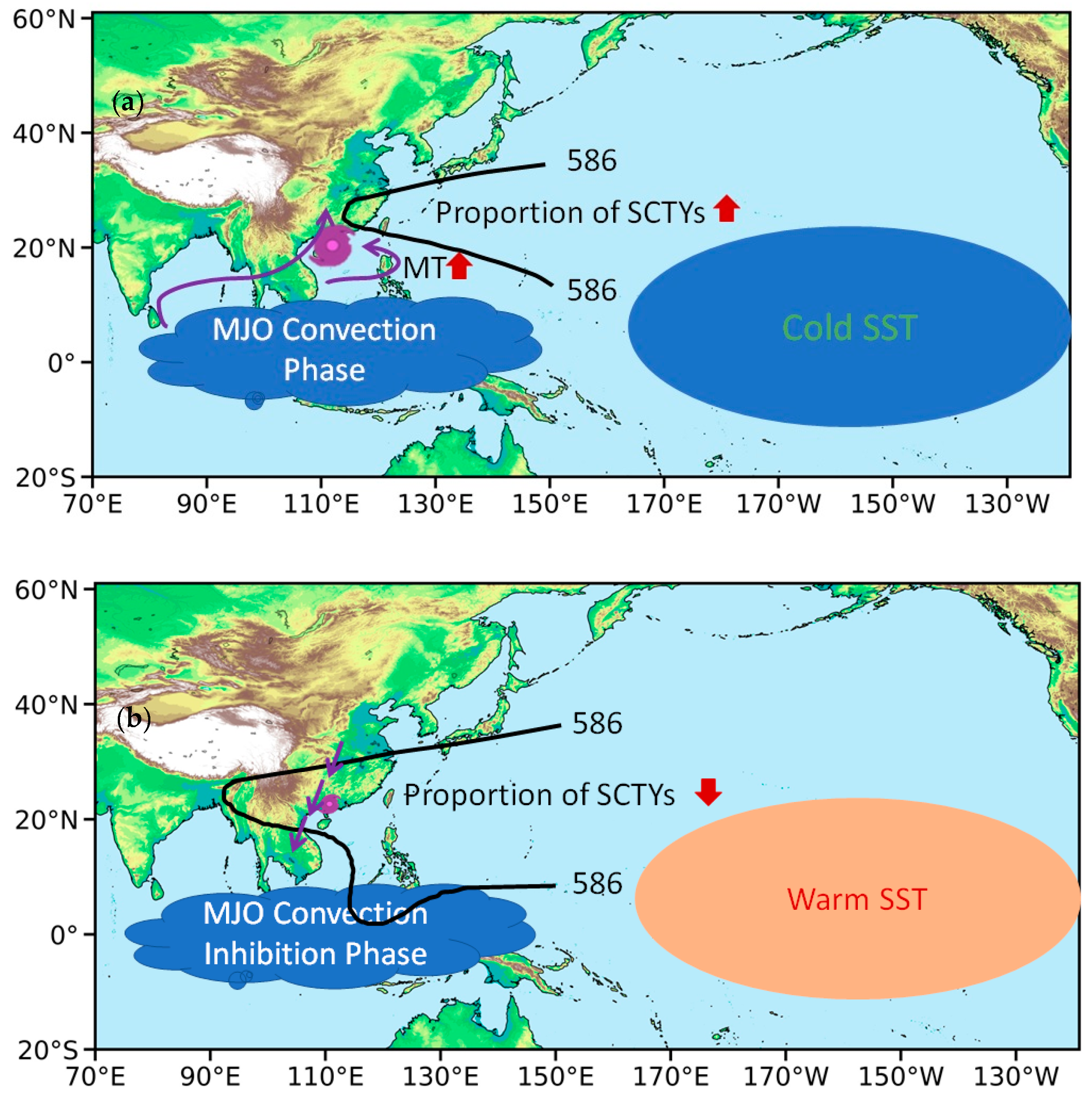
4. Discussion
4.1. Climate Change and SCTCs
4.2. SST and Subtropical High
4.3. MT and MJO
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kang, N.Y.; Elsner, J.B. Climate mechanism for stronger typhoons in a warm world. J. Clim. 2016, 29, 1051–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.K.; Duan, X.Y.; Raga, G.B.; Philip, J.K. Changes in characteristics of rapidly intensifying western North Pacific tropical cyclones related to climate regime shifts. J. Clim. 2018, 31, 8163–8179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, M.Z. Change in the occurrence frequency of landfalling and non-landfalling tropical cyclones over the Northwest Pacific. J. Clim. 2021, 34, 3145–3154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Z.Q.; Nie, G.Z.; Qiu, X.; Gu, J.F.; Zhang, Y. Outer size distribution of landfalling tropical cyclones over China changes in the recent decades. J. Clim. 2023, 36, 6427–6445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.Y.; Zhou, W.; Shun, C.M.; Lee, T.C. Change in destructiveness of landfalling tropical cyclones over China in recent decades. J. Clim. 2017, 30, 3367–3379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, K.Y.; Yu, X.P. Variability of tropical cyclone landfalls in China. J. Clim. 2021, 34, 9235–9247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Wang, Y.Q.; Zhan, R.F.; Xu, J.; Duan, Y.H. Increasing destructive potential of landfalling tropical cyclones over China. J. Clim. 2020, 33, 3731–3743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, M.M.; Wang, C.Z. Decadal variability of the anticyclone in the western North Pacific. J. Clim. 2020, 33, 9031–9043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.H.; Zhao, H.K.; Philp, J.K.; Graciela, B.R.; Cao, J.; Wang, C. Decadal modulation of transbasin variability on extended boreal summer tropical cyclone activity in the tropical North Pacific and Atlantic Basins. J. Clim. 2021, 34, 7149–7166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Wang, C. Interdecadal modulation on the relationship between ENSO and typhoon activity during the late season in the western North Pacific. Climate dynamics: Observational, theoretical and computational research on the climate system. Clim. Dyn. 2016, 47, 315–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimada, U.D. Variability of environmental conditions for tropical cyclone rapid intensification in the western North Pacific. J. Clim. 2022, 35, 4437–4453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.H.; Han, X.; Zhao, H.K.; Klotzbach, P.J.; Wu, L.G.; Raga, G.B.; Wang, C. Enhanced predictability of rapidly intensifying tropical cyclones over the western North Pacific associated with snow depth changes over the Tibetan Plateau. J. Clim. 2022, 35, 2093–2110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Wang, L.; Chen, W. How Does the east asian summer monsoon behave in the decaying phase of El Niño during different PDO phases. J. Clim. 2014, 27, 2682–2698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.K.; Chen, S.H.; Klotzbach, P.J. Recent strengthening of the relationship between the western North Pacific monsoon and western North Pacific tropical cyclone activity during the boreal summer. J. Clim. 2019, 32, 8283–8299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.M.; Ha, K.J.; Jin, F.F. Seasonality and El Niño diversity in the relationship between ENSO and western North Pacific tropical cyclone activity. J. Clim. 2019, 32, 8021–8045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patricola, C.M.; Camargo, S.J.; Klotzbach, P.J.; Saravanan, R.; Chang, P. The influence of ENSO flavors on Western North Pacific tropical cyclone activity. J. Clim. 2018, 31, 5395–5416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.Y.; Zhou, W. Interdecadal change in South China Sea tropical cyclone frequency in association with zonal sea surface temperature gradient. J. Clim. 2014, 27, 5468–5480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, X.Q.; Holloway, C.E.; Feng, X.B.; Liu, C.L.; Lyu, X.Y.; Xue, Y.F.; Bao, R.J.; Li, J.D.; Qiao, F.L. Observed interannual relationship between ITCZ position and tropical cyclone frequency. J. Clim. 2023, 36, 5587–5603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.D.; Wang, C.Z.; Zhang, L.P.; Wang, X. Multidecadal variability of tropical cyclone rapid intensification in the western North Pacific. J. Clim. 2015, 28, 3806–3820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.M.; Liu, J.L.; Zhuang, X.D.; Du, Y.D. New characteristics of tropical cyclones affecting Guangdong and proposals for their mitigation. Guangdong Meteorol. 2015, 37, 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Mantua, N.J.; Hare, S.R.; Zhang, Y.; Wallace, J.M.; Francis, R.C. A Pacific Interdecadal Climate Oscillation with impacts on salmon production. Bull. Am. Meteor. Soc. 1997, 78, 1069–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holliday, C.R.; Thompson, A.H. Climatological characteristics of rapidly intensifying typhoons. Mon. Weather Rev. 1979, 107, 1022–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, C.Z.; Zhang, R.; Bao, S.L. Forecasting the tropical cyclone genesis over the Northwest Pacific through identifying the causal factors in cyclone–climate interactions. J. Clim. 2018, 31, 247–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuura, T.; Yumoto, M.; Iizuka, S.; Kawamura, R. Typhoon and ENSO simulation using a high-resolution coupled GCM. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1999, 26, 1755–1758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corporal-Lodangco, I.L.; Leslie, L.M.; Lamb, P.J. Impacts of ENSO on Philippine tropical cyclone activity. J. Clim. 2016, 29, 1877–1896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, Y.; Zhong, Z.; Hu, Y.J. Influences of ENSO on western North Pacific tropical cyclone kinetic energy and its meridional transport. J. Clim. 2013, 26, 322–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Wang, X. Classifying El Niño Modoki I and II by different impacts on rainfall in South China and typhoon tracks. J. Clim. 2013, 26, 1322–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goh, A.Z.C.; Chan, J.C.L. An improved statistical scheme for the prediction of tropical cyclones making landfall in South China. Weather Forecast. 2010, 25, 587–593. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Q.; Wang, X.; Tao, L. Interannual and interdecadal impact of western North Pacific subtropical high on tropical cyclone activity. Clim. Dyn. 2020, 54, 2237–2248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.S.; Chan, C.L. Interdecadal variability of western North Pacific tropical cyclone tracks. J. Clim. 2008, 21, 4464–4476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.S.; Chan, C.L. Inactive period of western North Pacific tropical cyclone activity in 1998–2011. J. Clim. 2013, 26, 2614–2630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camargo, S.J.; Emanuel, K.A.; Sobel, A.H. Use of a genesis potential index to diagnose ENSO effects on tropical cyclone genesis. J. Clim. 2007, 20, 4819–4834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.P.; Tan, Z.M. Impacts of the boreal spring Indo-Pacific Warm Pool Hadley Circulation on tropical cyclone activity over the western North Pacific. J. Clim. 2018, 31, 1361–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.; Wu, L.G.; Gu, G.J. Rapid weakening of tropical cyclones in monsoon gyres over the tropical western North Pacific. J. Clim. 2018, 31, 1015–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuura, T.; Yumoto, M.; Iizuka, S. A Mechanism of interdecadal variability of tropical cyclone activity over the western North Pacific. Clim. Dyn. 2003, 21, 105–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, R.H.; Huang, J.L.; Wu, L.; Feng, T.; Chen, G.H. Research on the interannual and interdecadal variabilities of the monsoon trough and their impacts on tropical cyclone genesis over the western North Pacific Ocean. J. Trop. Meteor. 2018, 24, 395–420. [Google Scholar]
- Aiyyer, A.; Thorncroft, C. Interannual-to-multidecadal variability of vertical shear and tropical cyclone activity. J. Clim. 2011, 24, 2949–2962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, R.F.; Wang, Y.Q.; Ding, Y.H. Impact of the western Pacific tropical easterly jet on tropical cyclone genesis frequency over the western North Pacific. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2022, 39, 235–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madden, R.A.; Julian, P.R. Detection of a 40–50 day oscillation in the zonal wind in the tropical Pacific. J. Atmos. Sci. 1971, 28, 702–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madden, R.A.; Julian, P.R. Description of global scale circulation cells in the tropics with 40–50 day period. J. Atmos. Sci. 1972, 29, 1109–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schreck, C.J.; Molinari, J.; Mohr, K.I. Attributing tropical cyclogenesis to equatorial waves in the western North Pacific. J. Atmos. Sci. 2011, 68, 195–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.H.; Chou, C. Joint Contribution of multiple equatorial waves to tropical cyclogenesis over the western north Pacific. Mon. Weather Rev. 2014, 142, 79–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schreck, C.J. Kelvin waves and tropical cyclogenesis: A global survey. Mon. Weather Rev. 2015, 143, 3996–4011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, M.S.; Kim, H.S.; Ho, C.H.; Elsberry, R.L.; Lee, M.I. Tropical cyclone Mekkhala’s (2008) formation over the South China Sea: Mesoscale, synoptic-scale, and large-scale contributions. Mon. Weather Rev. 2015, 143, 88–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Klotzbach, P.J. The Madden–Julian Oscillation’s impact on global tropical cyclone activity. J. Clim. 2014, 27, 2317–2330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.K.; Yoshida, R.J.; Raga, G.B. Impact of the Madden–Julian Oscillation on Western North Pacific tropical cyclogenesis associated with large-scale patterns. J. Appl. Meteor. Climatol. 2015, 54, 1413–1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, S.J.; Zhang, F.Q. Influence of equatorial waves on the genesis of super typhoon Haiyan (2013). J. Atmos. Sci. 2015, 72, 4591–4613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.K.; Seo, K.H. Cluster analysis of tropical cyclone tracks over the western North Pacific using a self-organizing map. J. Clim. 2016, 29, 3731–3751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Mei, W.; Xie, S.P. Effects of tropical sea surface temperature variability on northern hemisphere tropical cyclone genesis. J. Clim. 2022, 35, 4719–4739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.M.; Liu, H.L.; Wang, X.D.; Li, H.; Zhang, Z.R.; Zuo, J.C. PDO modulation on the relationship between ENSO and typhoon tracks. J. Clim. 2022, 35, 6703–6720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, K.Y.; Chu, P.S.; Yu, X.P. Interdecadal change of tropical cyclone translation speed during peak season in South China sea:observed evidence, model results, and possible mechanism. J. Clim. 2023, 36, 4531–4541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.X.; Lu, R.Y.; Dong, B.W.; Hong, X.W.; Liu, J.Q.; Sun, J.Q. Tropical anomalies associated with the interannual variability of the cross-equatorial flows over the maritime continent in boreal summer. J. Clim. 2022, 35, 5591–5603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.C.; Zhou, W. Modulation of Western North Pacific Tropical Cyclone Activity by the ISO. Part I: Genesis and Intensity. J. Clim. 2013, 26, 2904–2918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molinari, J.; Vollaro, D. What Percentage of Western North Pacific Tropical Cyclones Form within the Monsoon Trough? Mon. Weather Rev. 2013, 141, 499–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Zong, H.; Liang, J. Observational Analysis of Tropical Cyclone Formation Associated with Monsoon Gyres. J. Atmos. Sci. 2013, 70, 1023–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zong, H.; Wu, L. Synoptic-Scale Influences on Tropical Cyclone Formation within the Western North Pacific Monsoon Trough. Mon. Weather Rev. 2015, 143, 3421–3433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serinaldi, F.; Kilsby, C.G.; Lombardo, F. Untenable nonstationarity: An assessment of the fitness for purpose of trend tests in hydrology. Adv. Water Resour. 2017, 111, 132–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Qin, W.; Cai, Y.; He, L. The Relationship between the Typhoons Affecting South China and the Pacific Decadal Oscillation. Atmosphere 2024, 15, 285. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15030285
Qin W, Cai Y, He L. The Relationship between the Typhoons Affecting South China and the Pacific Decadal Oscillation. Atmosphere. 2024; 15(3):285. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15030285
Chicago/Turabian StyleQin, Weijian, Yuexing Cai, and Liyang He. 2024. "The Relationship between the Typhoons Affecting South China and the Pacific Decadal Oscillation" Atmosphere 15, no. 3: 285. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15030285
APA StyleQin, W., Cai, Y., & He, L. (2024). The Relationship between the Typhoons Affecting South China and the Pacific Decadal Oscillation. Atmosphere, 15(3), 285. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15030285






