Abstract
Identifying the types and vertical distribution of aerosols plays a significant role in evaluating the influence of aerosols on the climate system. Based on the aerosol optical properties obtained from Cloud-Aerosol Lidar and Infrared Pathfinder Satellite Observation (CALIPSO), this study analyzed the long-term aerosol characteristics of seven cities in East Asia (Ulaanbaatar, Beijing, Lanzhou, Shanghai, Lhasa, Hong Kong, and Bangkok) from 2007 to 2021, including the spatiotemporal variations of aerosol optical depth (AOD), the vertical stratification characteristics of aerosols, and the main aerosol subtype. The results showed that, except for Lhasa, the AOD values of all cities exhibited a trend of initially increasing and then decreasing over the years. Except for Shanghai, the high values of AOD in the other cities occurred in the spring and summer seasons, while the low values occurred in the autumn and winter seasons. In all four seasons, the AOD contribution within the 1–3 km range accounted for more than 50% of the total. In the autumn and winter seasons, this proportion reached over 80%. The main types of aerosols and their contributions varied at different altitudes. Overall, dust, polluted continental/smoke, polluted dust, and elevated smoke dominated in all aerosol layers across each city. On the other hand, clean marine, clean continental, and dusty marine had very small proportions, accounting for less than 5% of all the cities’ aerosol layers.
1. Introduction
Aerosols influence the climate system in direct and indirect ways. Aerosols directly scatter and absorb solar radiation, which has an impact on the atmosphere’s latent heating distribution and radiant energy transmission [1,2]. On the other hand, aerosols have an indirect impact on the weather and climate by acting as Cloud Condensation Nuclei (CCN) and Ice Nuclei (IN), thereby changing cloud properties and lifetimes [3,4,5]. In addition, aerosols harm human health [6], and reduce visibility and agricultural Total Factor Productivity (TFP) [7,8,9].
However, owing to incomplete knowledge concerning the optical and microphysical properties, spatiotemporal distributions, and vertical profiles of aerosols, these effects dominate the uncertainty in climate modeling [1,2]. Therefore, figuring out the aerosols’ optical and microphysical properties and identifying aerosol types and vertical profiles are of significance when evaluating aerosols’ roles in climate systems [3,4,5].
With the recognition of the importance of aerosols to the climate, satellite observations and ground-based measurements have been used to determine the optical types and vertical profiles of aerosols. Ground-based measurements provide a reliable and accurate representation of aerosol properties. However, they are limited by the number of sites [6]. Satellite passive sensors like Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) and Multiangle Imaging Spectroradiometer (MISR) are frequently utilized to study the two-dimensional distribution of aerosols, but they fail to provide aerosol vertical distribution properties [7]. Whereas satellite active sensors, like the Cloud-Aerosol Lidar with Orthogonal Polarization (CALIOP) on board the Cloud-Aerosol Lidar and Infrared Pathfinder Satellite Observations (CALIPSO), can continuously acquire a high-resolution vertical profile of aerosol properties and comprehensive three-dimensional spatial and temporal information about their distribution. Moreover, these sensors can determine the optical and microphysical characteristics of the aerosol [8].
CALIPSO has been used to get the aerosol types and vertical distribution in numerous investigations [9,10,11,12,13]. Liao et al. [14] presented the 3D vertical structure of aerosols over Southwest China using the CALIPSO Level 2 nighttime aerosol profile product. The research contributes to our understanding of the three-dimensional features of the development and dispersion of aerosols in Southwest China. Brakhasi et al. [7] found that aerosols increasing in altitude are caused by environmental heat and steam resulting from the climate or season, and revealed that CALIOP Vertical Feature Mask (VFM) time-series data can be used to analyze the vertical distribution and variation of aerosols, providing a means of monitoring the atmospheric vertical structure. Niu et al. [15] found the existence of tropospheric aerosol layers associated with the Asian summer monsoon by exploring the properties, spatial/vertical distributions, and annual evolution of tropopause aerosols over the South Asia region. Using CALIPSO data from 2006 to 2016, Song et al. [16] investigated the vertical spatiotemporal patterns for absorbing aerosols and predicted global absorbing aerosols‘ distribution by a neural network model. Gupta et al. [17] utilized long-term CALIPSO measurements to obtain dominant aerosol subtypes at different heights. Mehta et al. [18] demonstrated that vertical and columnar trends of aerosols were increasing in four seasons, and the vertical mixing of aerosols is higher in the upper Indo-Gangetic plain during the spring and monsoon seasons. Banerjee et al. [19] found that 51% and 41% of the total columnar aerosols in South Asian cities remained within 0–1 km and the planetary boundary layer (PBL), respectively.
East Asia is one of the largest aerosol precursors, which are caused by various aerosol sources [20,21]. These different aerosol sources may vary across areas that have different populations, climates, and elevations or are coastal or inland. A few studies have focused on the aerosols of East Asia and got confident results [21,22,23,24,25]. However, most of these studies have concentrated on the spatiotemporal dynamics or the aerosol components over the study area, but there is a lack of vertical structure aimed at different cities. In this study, seven cities in East Asia are selected. We studied the vertical structure and aerosol types of these cities and compared them using the data derived from CALIPSO from 2007 to 2021.
2. Data and Methods
2.1. Study Area
From Figure 1 and Table 1, the study area includes seven cities in East Asia: Ulaanbaatar, Lanzhou, Lhasa, Beijing, Shanghai, Hong Kong, and Bangkok. The seven cities range from low to high latitudes in East Asia. In regard to the geographical location on both land and sea, Ulaanbaatar, Lanzhou, Lhasa, and Beijing are inland cities, while Shanghai, Hong Kong, and Bangkok are coastal cities. They also have significant differences in elevation, with Lhasa at an altitude of nearly 4 km, Ulaanbaatar and Lanzhou at over 1 km, and Beijing, Shanghai, Hong Kong, and Bangkok ranging from a few meters to several dozen meters above sea level. Additionally, these seven cities are located in different climate zones. Among these seven cities, Ulaanbaatar, Beijing, and Bangkok are respectively the capitals of Mongolia, China, and Thailand, while the rest of the cities are all provincial capitals in China. Ulaanbaatar and Lhasa have populations of only around 1 million, while Beijing and Shanghai have populations exceeding 20 million. In summary, these cities are representative in terms of location, altitude, climate, and population.
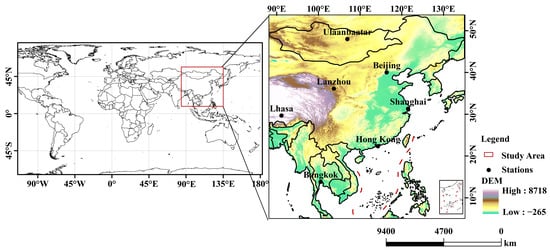
Figure 1.
The location of the study area.

Table 1.
Information of the required stations in this study.
2.2. CALIPSO
The CALIPSO satellite is the collaborative effort of the National Centre for Space Studies of France (CNES) and the U.S. National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA), launched as part of the A-Train satellite constellation [26]. It has a revisiting period of 16 days and covers almost the entire globe between 82° S and 82° N for the study of clouds and aerosols. The primary apparatus on board is CALIOP, which is a polarization-sensitive lidar with two distinct wavelengths that produce vertical profiles of backscatter at 532 and 1064 nm during both the day and night [27]. CALIOP offers a wealth of unique information on the vertical and geographical distributions of clouds and aerosols. Layer products, profile products, and the VFM are three categories of products for CALIOP level 2 data. The profile products provide retrieved profiles of extinction and backscatter within detected aerosol layers [28]. In the V4 profile product, tropospheric aerosols are separated into seven subtypes: dust, elevated smoke, clean continental, polluted continental/smoke, clean marine, polluted dust, and dusty marine [29]. A table on the classification of subtypes is shown in Appendix A. In the troposphere, spanning between 20 km and −0.5 km, aerosol profile products have a vertical spatial resolution of 60 m and a horizontal resolution of 5 km. In the stratosphere (above 20 km), these products have a vertical spatial resolution of 180 m and a horizontal resolution of 5 km. In this study, we obtained the V4.20 and V4.21 profile products from the NASA Goddard Space Flight Center (https://earthdata.nasa.gov/, accessed on 27 June 2023). The data available are from June 2006 to January 2022. To ensure the consistency of the annual and seasonal profile averages, profile products from 2007 to 2021 were used for this study.
In these products, we used the 532 nm extinction coefficient to calculate the daily, seasonal, and annual vertical aerosol distribution of these cities. In addition, the Atmospheric Volume Description (AVD) data product containing a feature classification flag was used to specify the aerosol type for each profile bin. With the help of the AVD characterization flag, the aerosol type was determined for each data point for aerosol extinction at various heights.
2.3. Methods
2.3.1. Cloud Screened and Quality Control (QC) of Extinction Profiles
The Cloud-Aerosol Discrimination (CAD) score was employed to clear clouds. The CAD score offers a numerical assessment of the reliability of the layer classification in the CALIOP CAD algorithm. The CAD algorithm has been adjusted to categorize these blended layers as clouds preventing cloud pollution of the aerosol dataset [26]. The standard CAD scores reported in the CALIPSO layer products range from −100 to 100. A positive CAD score indicates a cloud, while a negative score indicates an aerosol. The absolute value of the CAD score provides a level of confidence in the categorization. A higher CAD score corresponds to greater confidence in the accuracy of the categorization. Extinction profiles with CAD scores less than or equal to 20 and more than or equal to 100 were employed in this investigation [30]. To get accurate data, extinction profiles with the extinction QC flags of 0 (unconstrained retrieval, initial lidar ratio unchanged during solution process) and 1 (constrained retrieval) are included in this research [31].
2.3.2. Extinction Coefficient Arithmetic Rule
The 532 nm aerosol extinction coefficient was used to calculate the vertical distribution of the aerosols. To obtain more extinction coefficient data and to better represent the aerosol characteristics of these cities, we selected the extinction coefficient data within a 1° × 1° range centered on the coordinates of the cities to get their daily average data. We conducted analyses based on seasons and years. The months have been divided into four distinct seasons, for ease of presentation, spring is MAM (March, April, May), summer is JJA (June, July, August), autumn is SON (September, October, November), and winter is DJF (December, January, February). Furthermore, due to significant differences in altitude between the cities, we adopted the height above ground level for the vertical distribution analysis to better compare the vertical distribution of aerosols between cities. The range of nominal altitude is from −0.5 to 20.2 km above mean sea level.
3. Results
3.1. The Annual AOD and Vertical Extinction Distribution
Figure 2a displays the annual AOD and extinction coefficient of the seven cities from 2007 to 2021. The annual values of AOD for the seven cities showed a clear 3-level stepwise distribution. Hong Kong and Bangkok were at the highest level. The highest value in Hong Kong reached 0.581, while the lowest value was 0.416. In Bangkok, the highest value reached 0.584, with the lowest value being 0.397, showing more pronounced fluctuations overall. Their values in any given year were far higher than the average of the seven sites in that year. Beijing and Shanghai were at a slightly higher medium level. At this level, Shanghai had the lowest value of 0.244. The highest value in Beijing was 0.424. The fluctuations in value changes at this level were relatively small. In contrast, Ulaanbaatar, Lhasa, and Lanzhou had the lowest AOD values ranging from 0.200 to 0.357. Particularly, Lhasa was clearly at a stable low level among all cities, with AOD values consistently below 0.230. The AOD values of these three cities in recent years were much lower than the average value. As a whole, except for Lhasa, the other six cities showed an increasing and then decreasing trend, and most of the cities’ AOD values peaked between 2013 and 2016. Specifically, Hong Kong on the contrary showed decreasing and then increasing, and Bangkok has been on the rise, when all cities except Lhasa increased and then decreased from 2012 to 2014.
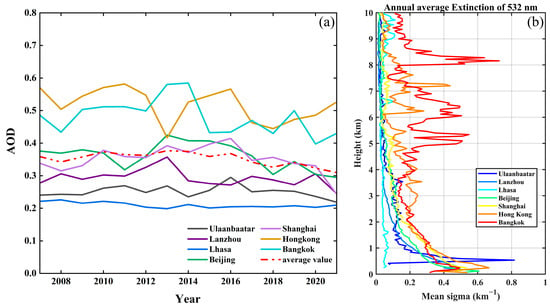
Figure 2.
Variations of (a) annual AOD (532 nm) and (b) extinction coefficient (532 nm) for seven cities.
From Figure 2b, it can be observed that the value of the extinction coefficient had a certain relationship with the altitude. The extinction coefficient exhibited a decreasing trend with increasing altitude. Below 5 km, only Lhasa had a stable value of extinction coefficient. The height is 0.071 and a peak occurs at 1.62 km. On the contrary, the peak values of other cities were below 1 km. The peak values for Ulaanbaatar, Hong Kong, and Beijing were approximately between 0.607 and 0.816, while the peak values for Bangkok, Shanghai, and Lanzhou were 0.465 to 0.531. Above 5 km, except for Bangkok and Hong Kong, the value of the extinction coefficient for the other cities showed a significant decreasing trend. The peak values for Lhasa, Lanzhou, Ulaanbaatar, Shanghai, and Beijing were below 0.2. The fluctuation of the variation in accordance with the increase in height was negligible. The peak value for Hong Kong was 0.437. Bangkok was the most unique, with a peak value of 0.727 above 5 km.
3.2. The Seasonal AOD and Vertical Extinction Distribution
Table 2 shows the average AOD changes in the seven different cities during different seasons. Beijing, Shanghai, Hong Kong, and Bangkok had relatively high average AOD values, all above 0.36. Comparing different cities in the same season, it was found that the highest AOD values in spring, summer, and autumn were in Hong Kong, while the highest AOD value in winter was in Bangkok. However, Lhasa’s AOD for all seasons was solidly the lowest of all cities. On the other hand, comparing the four seasons within the same city, Hong Kong exhibited more pronounced fluctuations. The volatility in Hong Kong was relatively significant. Bangkok had the highest volatility. It can be observed that except for Shanghai, the highest values for all six cities occurred in the spring (Lanzhou, Lhasa, Hong Kong, Bangkok) or summer (Ulaanbaatar, Beijing), while the lowest values occurred in the autumn (Lanzhou, Bangkok) or winter (Ulaanbaatar, Lhasa, Beijing, Hong Kong). Shanghai, on the other hand, had the highest value of 0.485 in winter and the lowest value of 0.364 in spring.

Table 2.
Average AOD values of the seven cities in four seasons.
Figure 3 illustrates the vertical distribution of AOD in seven different cities across the seasons. From the observation, the AOD values below 3 km exceeded 50% of the total value for all cities in all four seasons. Among them, the percentage of AOD below 2 km exceeded 40%. This proportion was even higher in autumn and winter, with more than 80% and 70% of the AOD below 3 km and below 2 km in all cities, respectively. However, the proportion of AOD below 1 km was generally lower in spring and summer. Overall, there has been a significant drop in the AOD percentage as the height has risen.
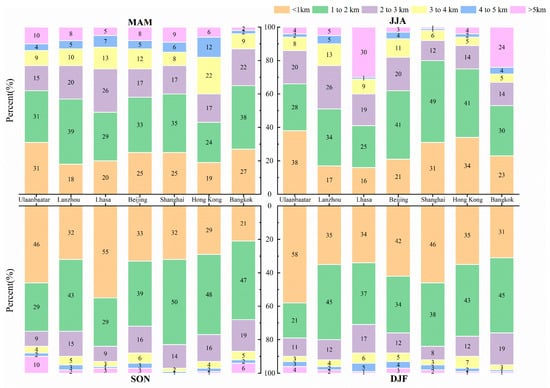
Figure 3.
The percentage of vertical distribution of AOD in seven cities during four seasons.
In comparison among the seven cities from the viewpoint of below 1 km, Ulaanbaatar had the highest percentage of AOD in all seasons except autumn, reaching 58% in winter. While in the autumn, the city with the highest percentage of AOD was Lhasa, reaching 55% at the same height. The lowest percentages of AOD in spring and summer were in Lanzhou and Lhasa, respectively, with only 18% and 16%. Meanwhile, in autumn and winter, Bangkok had the lowest AOD percentage at 21% and 31%, respectively. In terms of 1–2 km heights, compared to other cities, the highest percentage of Lanzhou was found in autumn and winter at 43% and 45%, respectively. The percentage of Lanzhou in spring was also relatively high, reaching 39% within the same height. Also, Shanghai had the highest proportion in summer and autumn, with 49% and 50%, respectively. Furthermore, the proportion of AOD at higher than 5 km was not greater than 10% for all cities across all seasons except summer, and especially in winter, the proportion was below 5%. However, Lhasa and Bangkok showed two distinct high values in summer, at 30% and 24%, respectively.
The seasonal mean extinction coefficients of the seven cities decreased with increasing altitude from 2007 to 2021 (Figure 4). Among them, the fluctuation of the extinction coefficients of Hong Kong and Bangkok was special. They showed a sudden increase in all seasons. Taking autumn as an example for analysis, the maximum degree of sudden increase in Hong Kong occurred at 3.54 km, when the mean sigma value was as high as 0.853. The maximum degree of sudden increase in Bangkok occurred at 7.08 km when the mean sigma value was as high as 0.511. Below 1 km, all the cities except Lhasa showed high values of extinction coefficient in all seasons. In particular, the maximum extinction coefficients for Ulaanbaatar, Lanzhou, Beijing, and Shanghai occurred below 1 km height. However, in four seasons the extinction coefficients measured at Lhasa remained consistently stable and low, always below 1.620. The only exception was a higher value of 6.60 recorded at 7 km during the summer.
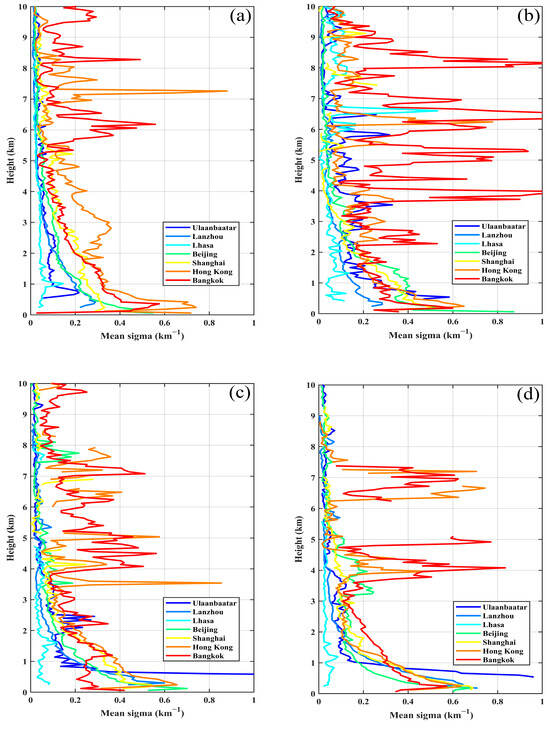
Figure 4.
The extinction coefficients (532 nm) for the seven cities from 2007 to 2021 in (a) spring, (b) summer, (c) autumn, and (d) winter.
3.3. The Annual AOD Subtype’s Vertical Distribution
It was found that the proportions of clean marine, clean continental, and dusty marine were very small, accounting for less than 5% of all the cities’ aerosol layers, by comparing the proportions of annual AOD (532 nm) subtype’s vertical distribution (Figure 5). Whereas dust, polluted continental/smoke, polluted dust, and elevated smoke played a dominant role in the various aerosol layers in the different cities, with more differences. In six cities except Ulaanbaatar, the proportions of dust and polluted continental/smoke in the aerosol layers showed increasing and decreasing with increasing heights, respectively. Meanwhile, in the six cities, polluted continental/smoke seemed to decrease with heights, excluding Hong Kong and Bangkok. However, elevated smoke showed a trend of rising and then falling, except for in Lanzhou and Lhasa, which always had low values. Ulaanbaatar differed from the other six cities in that the proportions of the four aerosol subtypes varied more dramatically and complexly with increasing heights.
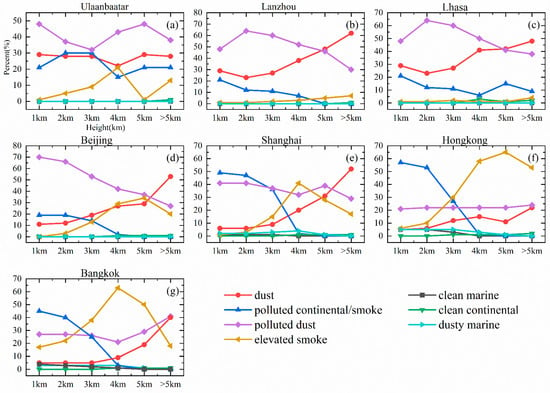
Figure 5.
The percentage of annual AOD (532 nm) subtype’s vertical distribution for (a) Ulaanbaatar, (b) Lanzhou, (c) Lhasa, (d) Beijing, (e) Shanghai, (f) Hong Kong, and (g) Bangkok from 2007 to 2021.
At the same height, the percentage of aerosol subtypes varied from city to city. The four inland cities, Ulaanbaatar, Lanzhou, Lhasa, and Beijing, had significantly higher percentages of dust and polluted dust than the three coastal cities, Shanghai, Hong Kong, and Bangkok. In contrast, the three coastal cities had slightly higher percentages of polluted continental/smoke, elevated smoke, clean marine, clean continental, and dusty marine than the other four coastal cities. However, at higher heights, there are some exceptions. At heights of 4 km and above, polluted continental/smoke was largely higher in inland cities than in coastal cities. In addition, Shanghai and Bangkok had a significant spike in dust at heights above 5 km, which was equal to or higher than inland cities.
4. Discussion
4.1. Analysis of Annual AOD and Vertical Extinction Distribution
From Figure 2a, the annual mean AOD values of the seven cities showed a clear three-stage stepwise distribution. Bangkok and Hong Kong are located in coastal low-lying areas, which likely results in higher AOD values owing to the hygroscopicity of aerosols [32] and the high-humidity climate environment. Additionally, as low-altitude areas are major population centers on Earth [33], the emissions of gas are likely to be even higher. Atmospheric aerosols in low-altitude areas are more difficult to disperse because the surrounding relatively higher-altitude areas can hinder their propagation. In addition to geographical factors, anthropogenic factors such as economic development and industrial emissions in Hong Kong and Bangkok also affect their values. Particulate air pollution in Hong Kong has become increasingly serious with rapid economic development [34]. Bangkok and its surrounding area are one of the largest urban agglomerations in Southeast Asia. Rapid urbanization and industrialization have resulted in favorable economic growth, but also in deteriorating air quality [35]. Furthermore, due to the impact of the financial crisis and government policy requirements, the value of Hong Kong had intense fluctuation [36]. For Bangkok, the fluctuation has been caused by changes in the smoke layer generated from biomass burning [37].
Beijing and Shanghai’s value was relatively low. While developing their economies, they pay great attention to environmental improvement [38]. For Shanghai, since winning the hosting rights of the World Expo, the implemented environmental initiatives and comprehensive actions, with a focus on reducing air pollution, have been effective [39].
Ulaanbaatar, Lhasa, and Lanzhou are located in inland areas with relatively dry climates. The lower level of economic development and relatively low population size result in less anthropogenic emissions in the atmosphere. Furthermore, these regions have high altitudes in the kilometer range, making it difficult for external atmospheric factors to have an impact [40]. As a result, the AOD values in these areas are the lowest [41], especially in Lhasa. Lhasa has the lowest AOD because there are almost no signs of human habitation and low anthropogenic emissions in the Tibetan Plateau. Lhasa’s high altitude prevents the frequent long-range transport of aerosols from the outer reaches [42]. Another phenomenon worth discussing is that, after 2013, there has been a clear trend of decreasing AOD values in mainland Chinese cities. In 2013, China launched the first “Action Plan for the Prevention and Control of Air Pollution” and subsequently has implemented a number of measures to reduce pollution [43].
In the analysis of the Figure 2b extinction coefficient (532 nm) for seven cities, it can be observed that the extinction coefficient exhibited a decreasing trend with increasing altitude except for Bangkok and Hong Kong. Bangkok and Hong Kong show more idiosyncratic fluctuations. On the one hand, both Bangkok and Hong Kong are coastal cities located in the tropics with relatively high humidity in the surface vertical atmosphere, and the relative humidity is positively correlated with the atmospheric extinction coefficient [44]. On the other hand, the fluctuation of aerosol extinction coefficient values in Hong Kong and Bangkok in each of the four seasons is also drastic, which can be obtained by combining Section 3.2. The extinction coefficient of Ulaanbaatar, Lanzhou, Lhasa, Beijing, and Shanghai showed a decreasing trend with increasing altitude. In all seasons, it can be observed globally that the average extinction coefficient for aerosols tends to decrease as the altitude increases [45]. It can be seen that the fluctuation of aerosol extinction coefficient values in Ulaanbaatar, Lanzhou, Lhasa, Beijing, and Shanghai in each of the four seasons also largely fits the pattern. The extinction coefficients for the seven cities in four seasons will be explained in depth in Section 4.2.
4.2. Seasonal AOD Vertical Stratification and Vertical Extinction Distribution Analysis
As can be seen in Table 2, in different seasons, Beijing, Shanghai, Hong Kong, and Bangkok had relatively high average AOD values. These four cities also have relatively high levels of economic development. Beijing exhibited a relatively stable state throughout the four seasons, with little variation. Shanghai, on the other hand, showed a slow upward trend. The level of suspended particulates in the air is lower in winter than in spring and autumn due to weaker convection and surface temperatures, stronger winds, and precipitation. Coupled with the high precipitation in summer in Hong Kong, the mean dwell time of aerosols in the atmosphere is shorter, thus lowering the average AOD value [46]. This resulted in significant differences in AOD in summer and autumn. Meanwhile, from May to October, the AOD values decreased in summer and autumn and were high in spring and winter due to lower aerosol concentrations in Bangkok caused by clean air movement, dehumidification, and reduced biomass burning [47]. The variability of AOD values in Bangkok exhibits a seasonal pattern [48]. Lhasa has the lowest average AOD compared to other cities, with values below 0.1, reaching the highest value of 0.09 in spring and gradually decreasing thereafter, reaching the lowest value in winter. Notwithstanding the possibility of a modest rise in windy weather during spring, the AOD in Lhasa remains low and steady all year round [49].
From Figure 3, the proportion of AOD is significantly high in the lower atmospheric region below 3 km, across various vertical heights. Above 5 km, the proportion is small in all seasons except summer, especially winter. This is because, in various seasons across the globe, the average value of aerosols decreases with increasing altitude [45]. In urban areas situated below the 1 km altitude mark, the proportion of winter in Ulaanbaatar is significantly higher than that of other cities, while the proportion of autumn in Lhasa is significantly higher than that of other cities. Ulaanbaatar uses sulfur-rich coal for heating and cooking in the winter, and the air quality is very poor, with fine particulate matter concentrations often far exceeding the daily maximum levels set by the World Health Organization [50]. Autumn is the non-monsoon season on the Tibetan Plateau with less precipitation [51]. The cleaning effect on aerosols at this time of year is weaker with lower rainfall of autumn. Lanzhou and Lhasa have lower proportions in spring and summer than other cities. Spring and summer coincide with the monsoon period, and the low particulate matter concentrations during the monsoon period mainly reflect the dilution of atmospheric aerosols in Lhasa by precipitation [52]. In the case of Lanzhou, higher levels of turbulence and convection in the spring and summer blow the air layer to higher levels, resulting in a lower percentage below 1 km [41]. Bangkok has the lowest rate in the autumn and winter compared to other cities. Across India, AOD was significantly negatively correlated to rainfall in autumn [53]. May through October is the rainy season in Thailand [54]. This has contributed in part to Bangkok’s higher precipitation in the autumn. Bangkok is located in the southern part of the Indochina Peninsula, and Sooktawee et al. [55] studies have shown that the southern part of the Central South Peninsula receives more precipitation in winter than, for example, the mainland of the Central South Peninsula. Between 1–2 km, in autumn and winter, the aerosol extinction coefficient in Lanzhou is higher than in spring and summer. This is due to the larger amount of pollutant emissions during the comprehensive heating process and the poorer diffusion conditions in autumn and winter. The reason for the higher percentage in Shanghai in summer and autumn is that smog and marine aerosols are the main pollutants and are more polluted during these seasons [56].
Observing Figure 4, the most notable phenomenon is that the values of the extinction coefficients were higher in all seasons in the cities below 1 km except Lhasa, while the high value in Lhasa occurred at 7 km in summer. By considering the main components of dust and polluted dust in the atmospheric aerosols at altitudes higher than 5 km in Lhasa, it is possible to investigate the factors contributing to the occurrence of the maximum extinction coefficient value. Dust spreads from the deserts near northern India to the southern slopes of the Indo-Gangetic Plain in late spring and early summer. The southwestern monsoon may help to facilitate the spread of dust from the Indo-Gangetic Plain to the southern Tibetan Plateau in summer [57]. This elucidates the reasons behind the relatively high extinction coefficient during the summer season in Lhasa. By observing the extinction coefficients (532 nm) for the other six cities in four seasons above 5 km, the extinction coefficient values for Hong Kong and Bangkok showed the maximum fluctuations in spring and summer, respectively. Combined with the analysis in Section 3.3, it can be seen that the major aerosol subtype over the atmosphere above 5 km in Hong Kong was elevated smoke and in Bangkok was dust, polluted dust, and elevated smoke. The elevation of elevated smoke indicates that smoke produced by burning biomass is located above the PBL. This suggests to some extent that the thick layer of aerosols across the greater Bay Area is caused by transported smoke from biomass burning [58]. Regarding the distribution of aerosol subtypes above 5 km in Bangkok, a study of the smoke layer over Bangkok in the summer of 2011 found that a part of the smoke came from agricultural burning and fossil fuel combustion in the southern Indian subcontinent [37]. Furthermore, Gui et al. [59] study showed the dominant aerosol subtypes throughout East Asia are dust, polluted dust, and smoke, and Bangkok is no exception to this rule.
4.3. Analysis of the Annual AOD Subtype’s Vertical Distribution
The four inland cities, Ulaanbaatar, Lanzhou, Lhasa, and Beijing, had a much higher proportion of dust and polluted dust values at altitudes of 5 km and below than the three coastal cities, Shanghai, Hong Kong, and Bangkok. This may be due to the highly seasonal nature of dust aerosol production and transport in East Asia. The enormous dry and semi-arid Gobi in northern China and southern Mongolia, as well as the sandy Taklamakan area in northwest China, are the primary producers of dust in East Asia [60]. Dust from coastal areas can only be transported over long distances from continental sources, and during transportation [61]. Coastal cities have a slightly higher proportion of polluted continental/smoke, elevated smoke, clean marine, clean continental, and dusty marine, and clean marine may come from the ocean [62].
Furthermore, there were special circumstances regarding the polluted continental/smoke. Ulaanbaatar and Lhasa had a significantly higher proportion of this subtype at altitudes of 5 km and above compared to other cities. This is related to polluted continental/smoke originating from the Qaidam Basin and the Indus Ganges Basin in India. Research has shown that polluted continental/smoke originating from the basin can be transported to altitudes of 6 km or higher [14].
Overall, clean marine, clean continental, and dusty marine account for a small proportion of the seven cities, while dust, polluted continental/smoke, polluted dust, and elevated smoke dominate. This is because airborne mineral dust has been an important contributor to macro aerosols in Asia and globally [60,63]. Furthermore, Gui, et al. [59] have also demonstrated in their study that dust, polluted dust, and smoke all contributed significantly to the aerosol concentration found in the East Asian region.
5. Conclusions
Using the aerosol optical properties obtained from CALIPSO, we analyzed the long-term aerosol characteristics, including the spatiotemporal variations of AOD, the aerosol vertical stratification properties, and the main aerosol subtype in the seven cities of East Asia.
- Except for Lhasa’s AOD which is steadily low, the AOD values of all the other cities showed an increasing and then decreasing trend during 2007–2021. The peak values occurred mostly in spring and summer, while the lowest values occurred in autumn and winter.
- In all seasons, the proportion of AOD at the altitude of 1–3 km exceeded 50% of the total, with this proportion being even higher than 80% in autumn and winter.
- Except for Lhasa, higher extinction coefficient values were observed below 1 km in all other cities during all four seasons. The highest extinction coefficient value in Lhasa occurred at an altitude of approximately 7 km during summer.
- Dust, polluted continental/smoke, polluted dust, and elevated smoke played dominant roles in various aerosol layers in all cities. On the other hand, the proportions of clean marine, clean continental, and dusty marine were very small, all below 5% in all aerosol layers of all cities.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Q.T.; methodology, Y.Z. and Q.T.; software, Y.Z. and Q.T.; validation, Q.T. and Y.Z.; formal analysis, Q.T.; investigation, Y.Z. and Q.T.; resources, Q.T.; data curation, Y.Z. and Q.T.; writing—original draft preparation, Q.T., Y.Z. and Y.H.; writing—review and editing, Q.T., Y.Z., Y.H., Q.Y. and T.L.; visualization, Y.Z.; supervision, Q.T.; project administration, Q.T.; funding acquisition, Q.T., Q.Y. and T.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31800367) and the Natural Foundation of Shandong province of China (ZR2021MD090 and ZR2017MD017).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Datasets analyzed during the current study mainly include V4.20 profile products from the NASA Goddard Space Flight Center and other influencing factor data. The CALIPSO V4.20 dataset is available at the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) Goddard Space Flight Center (https://www.earthdata.nasa.gov/, accessed on 27 June 2023).
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank the NASA Earth data website (https://www.earthdata.nasa.gov/, accessed on 27 June 2023) for providing CALIPSO aerosol and auxiliary products.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Appendix A. AOD Subtypes in CALIPSO V4 Profile Products

Table A1.
AOD subtypes and Denotations.
Table A1.
AOD subtypes and Denotations.
| Subtype | Denotation |
|---|---|
| dust | Desert dust |
| polluted continental/smoke | Urban/industrial pollution and biomass burning aerosols below 2.5 km |
| polluted dust | Episodes of dust mixed with biomass burning smoke |
| elevated smoke | Biomass burning aerosols above 2.5 km |
| clean marine | Sea salt |
| clean continental | Clean background |
| dusty marine | Mixtures of dust and marine aerosol |
References
- Kahn, R.A.; Andrews, E.; Brock, C.A.; Chin, M.; Feingold, G.; Gettelman, A.; Levy, R.C.; Murphy, D.M.; Nenes, A.; Pierce, J.R.; et al. Reducing Aerosol Forcing Uncertainty by Combining Models with Satellite and Within-The-Atmosphere Observations: A Three-Way Street. Rev. Geophys. 2023, 61, e2022RG000796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Jiang, J.H.; Tackett, J.L.; Su, H.; Fu, R. Seasonal and diurnal variations of aerosol extinction profile and type distribution from CALIPSO 5-year observations. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2013, 118, 4572–4596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmeisser, L.; Andrews, E.; Ogren, J.A.; Sheridan, P.; Jefferson, A.; Sharma, S.; Kim, J.E.; Sherman, J.P.; Sorribas, M.; Kalapov, I.; et al. Classifying aerosol type using in situ surface spectral aerosol optical properties. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2017, 17, 12097–12120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Z.; Li, Z.; Li, P.; Li, J.; Sun, H.; Yang, Y.; Gao, X.; Ren, G.; Ren, R.; Wei, J. Vertical distributions of aerosol microphysical and optical properties based on aircraft measurements made over the Loess Plateau in China. Atmos. Environ. 2022, 270, 118888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mhawish, A.; Sorek-Hamer, M.; Chatfield, R.; Banerjee, T.; Bilal, M.; Kumar, M.; Sarangi, C.; Franklin, M.; Chau, K.; Garay, M.; et al. Aerosol characteristics from earth observation systems: A comprehensive investigation over South Asia (2000–2019). Remote Sens. Environ. 2021, 259, 112410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Niu, F.; Lee, K.H.; Xin, J.; Hao, W.M.; Nordgren, B.; Wang, Y.; Wang, P. Validation and understanding of Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer aerosol products (C5) using ground-based measurements from the handheld Sun photometer network in China. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2007, 112, D22S07. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brakhasi, F.; Hajeb, M.; Mielonen, T.; Matkan, A.; Verbesselt, J. Investigating aerosol vertical distribution using CALIPSO time series over the Middle East and North Africa (MENA), Europe, and India: A BFAST-based gradual and abrupt change detection. Remote Sens. Environ. 2021, 264, 112619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhang, M.; Bilal, M.; Su, B.; Zhang, C.; Guo, L. Comparison of MODIS- and CALIPSO-Derived Temporal Aerosol Optical Depth over Yellow River Basin (China) from 2007 to 2015. Earth Syst. Environ. 2020, 4, 535–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Chin, M.; Winker, D.M.; Omar, A.H.; Liu, Z.; Kittaka, C.; Diehl, T. Global view of aerosol vertical distributions from CALIPSO lidar measurements and GOCART simulations: Regional and seasonal variations. J. Geophys. Res. 2010, 115, D00H30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burton, S.P.; Ferrare, R.A.; Vaughan, M.A.; Omar, A.H.; Rogers, R.R.; Hostetler, C.A.; Hair, J.W. Aerosol classification from airborne HSRL and comparisons with the CALIPSO vertical feature mask. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2013, 6, 1397–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Han, Z. Aerosol vertical distribution over east China from RIEMS-Chem simulation in comparison with CALIPSO measurements. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 143, 177–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, H.; Wang, X.; Liu, Y.; Wu, G. An evaluation of cloud vertical structure in three reanalyses against CloudSat/cloud-aerosol lidar and infrared pathfinder satellite observations. Atmos. Sci. Lett. 2019, 20, e906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, M.; Singh, N.; Anshumali, N. Global trends of columnar and vertically distributed properties of aerosols with emphasis on dust, polluted dust and smoke—Inferences from 10-year long CALIOP observations. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 208, 120–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, T.; Gui, K.; Li, Y.; Wang, X.; Sun, Y. Seasonal distribution and vertical structure of different types of aerosols in southwest China observed from CALIOP. Atmos. Environ. 2021, 246, 118145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, H.; Kang, S.; Gao, W.; Wang, Y.; Paudyal, R. Vertical distribution of the Asian tropopause aerosols detected by CALIPSO. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 253, 207–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Z.; He, X.; Bai, Y.; Wang, D.; Hao, Z.; Gong, F.; Zhu, Q. Changes and Predictions of Vertical Distributions of Global Light-Absorbing Aerosols Based on CALIPSO Observation. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, G.; Ratnam, M.V.; Madhavan, B.L.; Prasad, P.; Narayanamurthy, C.S. Vertical and spatial distribution of elevated aerosol layers obtained using long-term ground-based and space-borne lidar observations. Atmos. Environ. 2020, 246, 118172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, M.; Khushboo, R.; Raj, R.; Singh, N. Spaceborne observations of aerosol vertical distribution over Indian mainland (2009–2018). Atmos. Environ. 2021, 244, 117902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, T.; Anchule, A.; Sorek-Hamer, M.; Latif, M.T. Vertical stratification of aerosols over South Asian cities. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 309, 119776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.H.; Kim, Y.J. Satellite remote sensing of Asian aerosols: A case study of clean, polluted, and Asian dust storm days. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2010, 3, 1771–1784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakata, M.; Mukai, S.; Yasumoto, M. Seasonal and Regional Characteristics of Aerosol Pollution in East and Southeast Asia. Front. Environ. Sci. 2018, 6, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Allen, D.J.; Pickering, K.E.; Li, Z.; He, H. Impact of aerosol direct effect on East Asian air quality during the EAST-AIRE campaign. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2016, 121, 6534–6554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Yi, B. Aerosols over East and South Asia: Type Identification, Optical Properties, and Implications for Radiative Forcing. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 2058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huimin, C.; Bingliang, Z.; Jane, L.; Yinan, Z.; Yaxin, H.; Yang, C.; Yiman, G.; Wen, W.; Huijuan, L.; Shu, L.; et al. Absorbing Aerosol Optical Properties and Radiative Effects on Near-Surface Photochemistry in East Asia. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 2779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Wang, L.; Gong, W.; Ma, Y.; Liu, B. Aerosol Optical Properties and Direct Radiative Effects over Central China. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winker, D.M.; Vaughan, M.A.; Omar, A.; Hu, Y.; Powell, K.A.; Liu, Z.; Hunt, W.H.; Young, S.A. Overview of the CALIPSO Mission and CALIOP Data Processing Algorithms. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2009, 26, 2310–2323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winker, D.M.; Hunt, W.H.; McGill, M.J. Initial performance assessment of CALIOP. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2007, 34, L19803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winker, D.M.; Pelon, J.; Coakley, J.A.; Ackerman, S.A.; Charlson, R.J.; Colarco, P.R.; Flamant, P.; Fu, Q.; Hoff, R.M.; Kittaka, C.; et al. The CALIPSO Mission: A Global 3D View of Aerosols and Clouds. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2010, 91, 1211–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.H.; Omar, A.H.; Tackett, J.L.; Vaughan, M.A.; Winker, D.M.; Trepte, C.R.; Hu, Y.; Liu, Z.; Poole, L.R.; Pitts, M.C.; et al. The CALIPSO version 4 automated aerosol classification and lidar ratio selection algorithm. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2018, 11, 6107–6135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalluri, R.O.R.; Gugamsetty, B.; Kotalo, R.G.; Nagireddy, S.K.R.; Tandule, C.R.; Thotli, L.R.; Shaik, N.H.; Maraka, V.R.; Rajuru, R.R.; Surendran Nair, S.B. Seasonal variation of near surface black carbon and satellite derived vertical distribution of aerosols over a semi-arid station in India. Atmos. Res. 2017, 184, 77–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, S.A.; Vaughan, M.A.; Garnier, A.; Tackett, J.L.; Lambeth, J.D.; Powell, K.A. Extinction and optical depth retrievals for CALIPSO’s Version 4 data release. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2018, 11, 5701–5727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boucher, O.; Quaas, J. Water vapour affects both rain and aerosol optical depth. Nat. Geosci. 2012, 6, 4–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, J.E.; Small, C. Hypsographic demography: The distribution of human population by altitude. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 14009–14014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chengcai, L.; Lau, A.K.H.; Jietai, M.; Chu, D.A. Retrieval, validation, and application of the 1-km aerosol optical depth from MODIS measurements over Hong Kong. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2005, 43, 2650–2658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aman, N.; Manomaiphiboon, K.; Suwattiga, P.; Assareh, N.; Limpaseni, W.; Suwanathada, P.; Soonsin, V.; Wang, Y. Visibility, aerosol optical depth, and low-visibility events in Bangkok during the dry season and associated local weather and synoptic patterns. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2022, 194, 322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, X.; Wong, M.S.; Liu, C.H. Multi-spatiotemporal AOD trends and association with land use changes over the Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area during 2001–2021. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2023, 30, 44782–44794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bridhikitti, A. Atmospheric aerosol layers over Bangkok Metropolitan Region from CALIPSO observations. Atmos. Res. 2013, 127, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, S.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, B.; Wang, S.; Chang, X.; Hao, J. The impact of the “Air Pollution Prevention and Control Action Plan” on PM2.5 concentrations in Jing-Jin-Ji region during 2012–2020. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 580, 197–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Q.; Gao, W.; Xiang, W.; Shi, R.; Liu, C.; Zhai, T.; Huang, H.-L.A.; Gumley, L.E.; Strabala, K. Analysis of air quality variability in Shanghai using AOD and API data in the recent decade. Front. Earth Sci. 2013, 7, 159–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, X.; Che, H.; Zhu, J.; Chen, H.; Cong, Z.; Deng, X.; Fan, X.; Fu, Y.; Goloub, P.; Jiang, H.; et al. Ground-based remote sensing of aerosol climatology in China: Aerosol optical properties, direct radiative effect and its parameterization. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 124, 243–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Wang, Z.; Tian, P.; Wang, J.; Zhang, L.; Quan, X. Statistics of aerosol extinction coefficient profiles and optical depth using lidar measurement over Lanzhou, China since 2005–2008. J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transf. 2013, 122, 150–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Huang, J.; Zhao, C.; Qian, Y.; Leung, L.R.; Yang, B. Modeling the transport and radiative forcing of Taklimakan dust over the Tibetan Plateau: A case study in the summer of 2006. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2013, 118, 797–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Xu, X.; Ding, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, H.; Wang, Y.; Zhong, J. The impact of meteorological changes from 2013 to 2017 on PM2.5 mass reduction in key regions in China. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2019, 62, 1885–1902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, K.R.O.; Zhang, X.; Bi, L. Seasonal aerosol variations over a coastal city, Zhoushan, China from CALIPSO observations. Atmos. Res. 2019, 218, 117–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honglin, P.; Jianping, H.; Kanike Raghavendra, K.; Linli, A.; Jinxia, Z. The CALIPSO retrieved spatiotemporal and vertical distributions of AOD and extinction coefficient for different aerosol types during 2007–2019: A recent perspective over global and regional scales. Atmos. Environ. 2022, 274, 118986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Q.; Li, C.; Mao, J.; Lau, A.K.-H.; Chu, D.A. Analysis of aerosol vertical distribution and variability in Hong Kong. J. Geophys. Res. 2008, 113, D14211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahu, L.K.; Kondo, Y.; Miyazaki, Y.; Pongkiatkul, P.; Kim Oanh, N.T. Seasonal and diurnal variations of black carbon and organic carbon aerosols in Bangkok. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2011, 116, D15302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumharn, W.; Sudhibrabha, S.; Hanprasert, K. Aerosol Optical Depth: A study using Thailand based Brewer Spectrophotometers. Adv. Space Res. 2015, 56, 2384–2388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Xin, J.; Li, Z.; Wang, S.; Wang, P.; Hao, W.M.; Nordgren, B.L.; Chen, H.; Wang, L.; Sun, Y. Seasonal variations in aerosol optical properties over China. J. Geophys. Res. 2011, 116, D18209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franklin, M.; Enebish, T.; Chau, K. Ulaanbaatar, Mongolia’s coal-driven air pollution crisis and its role on adverse birth outcomes. In AGU Fall Meeting Abstracts; American Geophysical Union: Washington, DC, USA, 2019; p. GH31A–08. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, L.; Yu, W.; Schuster, P.F.; Wen, R.; Cai, Z.; Wang, D.; Shao, L.; Cui, J.; Guo, X. Control of seasonal water vapor isotope variations at Lhasa, southern Tibetan Plateau. J. Hydrol. 2020, 580, 124237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Chen, P.; Kang, S.; Yan, F.; Hu, Z.; Qu, B.; Sillanpää, M. Concentrations and light absorption characteristics of carbonaceous aerosol in PM 2.5 and PM 10 of Lhasa city, the Tibetan Plateau. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 127, 340–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramachandran, S.; Kedia, S. Aerosol-Precipitation Interactions over India: Review and Future Perspectives. Adv. Meteorol. 2013, 2013, 649156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostro, B.; Chestnut, L.; Vichit-Vadakan, N.; Laixuthai, A. The Impact of Particulate Matter on Daily Mortality in Bangkok, Thailand. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2011, 49, 100–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sooktawee, S.; Humphries, U.; Limsakul, A.; Wongwises, P. Spatio-Temporal Variability of Winter Monsoon over the Indochina Peninsula. Atmosphere 2014, 5, 101–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Liu, Q.; Geng, F.; Zhang, H.; Cai, C.; Xu, T.; Ma, X.; Li, H. Vertical distribution of optical and micro-physical properties of ambient aerosols during dry haze periods in Shanghai. Atmos. Environ. 2012, 50, 50–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Wu, H.; Yang, X.; Xie, L. Distribution and transport characteristics of dust aerosol over Tibetan Plateau and Taklimakan Desert in China using MERRA-2 and CALIPSO data. Atmos. Environ. 2020, 237, 117670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, X.; Li, S.; Xing, J.; Yang, J.; Wang, Q.; Song, G.; Teng, M.; Zhou, D.; Lu, J. CALIPSO-observed Southeast Asia biomass-burning influences on aerosol vertical structure in Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area. Atmos. Res. 2023, 289, 106755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gui, L.; Tao, M.; Wang, Y.; Wang, L.; Chen, L.; Lin, C.; Tao, J.; Wang, J.; Yu, C. Climatology of aerosol types and their vertical distribution over East Asia based on CALIPSO lidar measurements. Int. J. Climatol. 2022, 42, 6042–6054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proestakis, E.; Amiridis, V.; Marinou, E.; Georgoulias, A.K.; Solomos, S.; Kazadzis, S.; Chimot, J.; Che, H.; Alexandri, G.; Binietoglou, I.; et al. Nine-year spatial and temporal evolution of desert dust aerosols over South and East Asia as revealed by CALIOP. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 18, 1337–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bibi, M.; Saad, M.; Masmoudi, M.; Laurent, B.; Alfaro, S.C. Long-term (1980–2018) spatial and temporal variability of the atmospheric dust load and deposition fluxes along the North-African coast of the Mediterranean Sea. Atmos. Res. 2020, 234, 104689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.H.; Kim, S.W.; Yoon, S.C.; Omar, A.H. Comparison of aerosol optical depth between CALIOP and MODIS-Aqua for CALIOP aerosol subtypes over the ocean. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2013, 118, 13241–13252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Lin, B.; Minnis, P.; Wang, T.; Wang, X.; Hu, Y.; Yi, Y.; Ayers, J.K. Satellite-based assessment of possible dust aerosols semi-direct effect on cloud water path over East Asia. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2006, 33, L19802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).