Abstract
The study of the surface energy balance characteristics of different ecosystems in the Qinghai Plateau is of great significance for a deeper understanding of land surface processes, the water cycle, and global climate change. This study aims to compare the seasonal variations in energy balance and partitioning of four typical ecosystems on the Qinghai Plateau—swamp meadows, subalpine mountain meadows, alpine shrublands, and alpine deserts. Mantel analysis and path analysis were used to explore the regulatory mechanisms of meteorological elements on energy fluxes and the Bowen ratio (β). The results showed the following: (1) Net radiation (Rn), sensible heat flux (H), and latent heat flux (LE) all exhibited a single-peak pattern of change, and the energy partitioning was closely related to the hydrothermal conditions. Swamp meadows and subalpine mountain meadows were dominated by LE throughout the year and the growing season, while H dominated in the non-growing season. Meanwhile, alpine shrublands and alpine deserts were dominated by H throughout the year. (2) β reflected the characteristics of turbulent fluxes variations and the moisture level of the underlying surface. Swamp meadows and subalpine mountain meadows were relatively moist, with the value of β all being less than 1. Alpine shrublands and deserts were comparatively arid, with the values of β all exceeding 1. The energy closure rate ranged from 48% to 90%, with better energy closure conditions observed during the growing season compared to the non-growing season. (3) Meteorological factors collectively regulated the variations in energy fluxes and its partitioning, with H and LE being primarily influenced by Rn, relative humidity (RH), and soil moisture (Ms). β was significantly affected by RH, Ms, and the saturated vapor pressure deficit (VPD). The sensitivity of the ecosystems to changes in fluxes increased with decreasing moisture, especially in alpine deserts, with Ms, VPD and RH being the most affected. Swamp meadows were significantly associated with air temperature (Ta), soil temperature (Ts), and wind speed; subalpine mountain meadows with Ta and Ts; and alpine shrublands with Ta. These results provided a basis for further analyses of the energy balance characteristics and partitioning differences of different ecosystems on the Qinghai Plateau.
1. Introduction
The land surface and the atmosphere continuously exchange water vapor, heat, momentum, carbon dioxide, and other material fluxes, with the surface energy balance being the core component of the interactions between the land and the atmosphere. A thorough understanding of the surface energy balance process is crucial for regional and global climate change, energy partitioning, hydrological cycles, and ecological processes [1,2,3]. The Qinghai Plateau is acclaimed as the “Roof of the World” and the “Third Pole of the Earth”. The bulge of the Qinghai Plateau forms a powerful source of power and heat, which is an important source of thermal action for the Asian monsoon system. The land–atmosphere interaction plays a key role in global energy conversion, water cycle processes, and environmental evolution [3,4,5]. Consequently, examining the surface energy balance in the Qinghai Plateau’s ecosystems will improve our grasp of energy partitioning, material cycles, and climate change in cold regions. Since the 1970s, scholars at home and abroad have carried out many works in the Qinghai Plateau [6,7] and have successfully carried out the “Asian Monsoon Qinghai Plateau Experiment of Global Energy Water Cycle” (GAME/Tibet), the “Asia-Australia Monsoon Project on the Qinghai Plateau” (CAMP/Tibet), and “The Third Qinghai Plateau Atmospheric Science Experiment” (TIPEX-III). At the same time, many atmospheric observation instruments and flux observatories were deployed and established, and a large number of research data on radiant fluxes, energy balance, and water–heat exchange processes in the plateau region were obtained.
Energy balance closure is a critical metric for assessing the quality of observational data, with energy fluxes typically allocated to sensible heat flux, latent heat flux, soil heat flux, and other thermal storage components [8]. In theory, the sum of turbulent fluxes (the sum of sensible and latent heat fluxes) should equal the available energy (the net radiation minus the soil heat flux). However, in practical observations, many monitoring stations encounter issues with energy imbalance [9]. In different regions of the Qinghai Plateau, the radiant flux, and surface energy partitioning have obvious seasonal variations, and the energy is generally non-closure. Previous studies have analyzed the radiative fluxes, turbulent fluxes, soil heat flux, and surface energy balance closure in the underlying surfaces of alpine swamp meadows, desert steppes, the Gobi desert, shrublands, and other underlying surfaces in the alpine region [10,11,12,13,14,15]. Zhang et al. [16] analyzed the variation characteristics of surface energy fluxes and evapotranspiration of three different underlying surfaces in the northeastern Qinghai Plateau and revealed the differences in energy partitioning. Liu et al. [17] used the SHAW model to study the influence of long-term energy balance changes on the active layer in the permafrost region of the Qinghai Plateau, which provided a basis for a deeper understanding of the land–atmosphere role of the permafrost region under the background of global warming. Sun et al. [18] investigated the energy fluxes over heterogeneous underlying surfaces in the plateau from the perspectives of spatial variability and structure, and they found significant spatial variability in these fluxes. Xin et al. [15] found that the average energy balance ratio of 10 sites, using the TIPEX III flux stations, was approximately 74.2%, similar to other regions, and it exhibited a strong diurnal cycle. Sun et al. [10] analyzed the seasonal variation in surface albedo based on two sites in the permafrost region of the Qinghai Plateau and revealed the relevant effects of snowpack, active layer processes, and solar altitude angle on surface albedo. Hu et al. [19] explored the energy balance condition based on the measured data of three sites in the plateau region and evaluated the estimation level of the surface energy balance model for the land–atmosphere energy exchange on different underlying surfaces. Ma et al. [20] conducted a study on evapotranspiration in the semi-arid alpine grassland of the Qinghai Plateau using the energy balance method and explored the environmental and biophysical controls on evapotranspiration. In addition, some scholars [7,21] have used ERA5, JRA-55, MERRA-2, and other reanalysis data to simulate the long-term series turbulent fluxes over the Qinghai Plateau and revealed the applicability of land surface models in the Qinghai Plateau region. Although multi-site energy fluxes studies have been carried out on the Qinghai Plateau, most of them focus on the surface energy balance and partitioning characteristics at the interannual scale. There was a lack of research on energy closure, partitioning, and the effects of meteorological factors (net radiation, air temperature, wind speed, relative humidity, saturated water vapor pressure difference, soil moisture, soil temperature) on energy fluxes and the Bowen ratio during the growth stages of vegetation on the Qinghai Plateau in different underlying surfaces.
Scholars often used multiple regression analysis to investigate the effects of environmental variables on energy fluxes and partitioning in the Qinghai Plateau [16,20]; however, this method has certain limitations: insufficient capture of non-linear relationships, difficulty in inferring causality, and unclear direct or indirect effects of environmental variables on fluxes. Additionally, structural equation modeling and path analysis are the primary methods for studying the relationship between environmental variables and energy fluxes [22,23,24]. These methods have been commonly applied in the temperate grasslands and desert areas of northern China, as well as in the subtropical agricultural regions of southern China, but have been less frequently used in the Qinghai Plateau. Path analysis has been specifically reported in studies of the Yangtze River source area, the Maqu area, and the Beiluhe observation station [11,25]. In comparison, path analysis overcomes the limitations of multiple regression analysis and can quantitatively analyze the relationship between environmental factors and fluxes; the Mantel Test method is used as an extension of the correlation analysis method for analyzing complex relationships between multiple variables or matrices. Hence, path analysis and Mantel Test methods were used in this study to quantify the influence of meteorological factors on fluxes.
Based on the aforementioned research background, this study selected routine meteorological and flux data from four stations on the Qinghai Plateau: Wayanshan (WYS), ARou (AR), Haibei (HB), and Ngari (NADORS). By analyzing these data, this study investigated the characteristics of energy balance partitioning and explored the regulatory mechanisms of meteorological elements on energy fluxes and the Bowen ratio using Mantel Test and path analysis. The main objectives of his study were as follows: (1) to explore the variations in and partitioning characteristics of energy fluxes across different underlying surfaces on the Qinghai Plateau; (2) to analyze the difference of energy closure of different underlying surfaces; (3) to clarify the regulatory mechanisms of different underlying surfaces’ meteorological factors on energy fluxes and partitioning at different stages. The findings of the present study deepen our understanding of the surface energy balance and partitioning for different underlying surfaces of the Qinghai Plateau, providing an in-depth comprehension of the regulatory mechanisms by which meteorological factors influence fluxes and partitioning. This contributes to the further assessment of factors influencing surface energy partitioning and advances research in the field of global climate change.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Sites and Data Acquisition
The Qinghai Plateau (26°00′~39°47′ N, 73°19′~104°47′ E) is located in the southwest of China, with an average altitude of more than 4000 m. It has a typical plateau mountain climate, being cold in winter and cool in summer, and obvious seasonal changes. This study selected four sites on the Qinghai Plateau (Figure 1) for analysis, and detailed information and parameters of the sites are introduced in Table 1. The meteorological and eddy data of the AR and NADORS observation stations were sourced from the National Qinghai Plateau Data Center (https://data.tpdc.ac.cn/, accessed on 10 April 2024). The meteorological and eddy data of the WYS station were derived from the measured data obtained from the comprehensive observation station deployed by Qinghai Normal University in the Wayanshan wetland of the Qinghai Lake watershed; the data for the HB station were obtained from the National Ecological Science Data Centre (http://www.nesdc.org.cn/, accessed on 10 April 2024). In this study, considering the differences in data sources across various stations, we selected data from each station in the Qinghai Plateau from different years to ensure the integrity of the analysis. Specifically, the data from HB station were limited to 2012, while the data from NADORS station were more complete for 2013; both WYS and AR stations had selected data from 2017. All data underwent preprocessing and quality control before analysis. Since the focus of this study was to compare the differences in energy partitioning among stations, the issue of inconsistent data timing could thus be disregarded. According to previous studies [14,26,27,28], the Qinghai Plateau is located at a high altitude and the whole growing season is short, and the beginning and end of the growing season are inconsistent each year. Thus, the growing season of vegetation on the Qinghai Plateau was defined as May to October in this study.
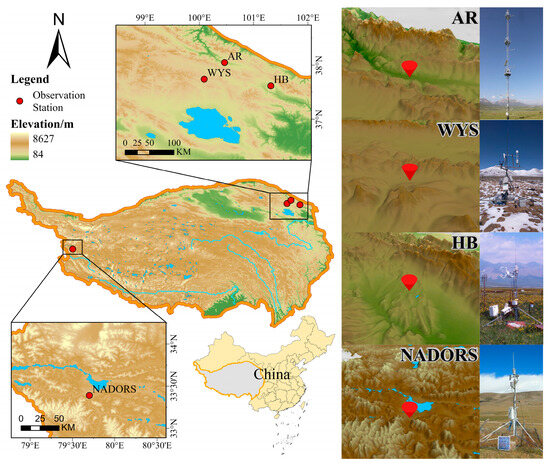
Figure 1.
A sketch map of the study area.

Table 1.
A detailed description of the four sites on the Qinghai Plateau.
2.2. Data Preprocessing Methods
2.2.1. Data Processing and Gap Filling
In this study, the meteorological and eddy covariance data collection frequencies varied across the four observation stations. At the four observation stations, AR station collected meteorological data every 10 min and eddy covariance data every 30 min. For WYS and HB stations, both types of data were gathered at 30 min intervals. For NADORS station, the data were collected hourly for both meteorological and eddy covariance measurements. To standardize the data for further analysis, all the measurements were harmonized into 1 h intervals. The eddy data of AR, HB, and WYS stations were corrected using EddyPro software (version 7.0.9), including field point removal, time lag correction, coordinate rotation, frequency response correction, ultrasonic virtual temperature correction, and density correction (WPL). And the turbulence data of NADORS station were processed and quality controlled using the TK3 software package. In addition, this study replaced data marked with a quality flag of 2 in the sensible heat (H) and latent heat (LE) fluxes from the AR station with “NAN”. It also replaced data marked with a quality flag of 7 to 9 in the H and LE fluxes from the NADORS station with “NAN”. After quality control, the effective data rates for H and LE at the AR station were 75.6% and 68.6%, respectively, while those at the NADORS station were 80.4% and 70.8%, respectively. To address the missing H and LE data, this study utilized a random forest model [29], incorporating input variables such as solar shortwave radiation, wind speed, temperature, relative humidity, and soil moisture and temperature at depths of 10 cm, 20 cm, and 40 cm. Using this approach, we were able to fill 24.3% of the missing H data and 31.3% of the LE data at the AR station, as well as 19.5% of the H data and 29.1% of the LE data at the NADORS station. For the missing soil heat flux (G) data, linear interpolation based on the valid fluxes at both ends was used to fill short gaps (≤2 h), and the daily variation method was applied to fill longer gaps (>2 h) [30], accounting for a total of 0.9% of the G data at the AR station. As the Qinghai Plateau is located at a high altitude and Rn is low in winter, the values around 0 W·m−2 generally lead to errors in data results; therefore, in this study, the values of |Rn| < 30 W·m−2, H, and LE outside the range of −100 W·m−2 to 1000 W·m−2 and the values of EBR((H + LE)/(Rn − G)) outside the range of −1 to 2 were deleted [31,32,33]. Due to the absence of G observations at the HB and NADORS stations, calculating G was not feasible. Therefore, relying on findings from previous studies [34,35], this study assumed G to be zero to simplify the analysis for the purpose of energy balance closure.
2.2.2. Radiant Fluxes Calculation
The net radiation was obtained by direct calculation from the four radiation component data:
where Rn is the net radiation, SD is the downward shortwave radiation, SU is the upward shortwave radiation, LD is the downward longwave radiation, and LU is the upward longwave radiation, and the unit of each flux is W·m−2.
The turbulent fluxes, which include sensible heat (H) and latent heat flux (LE), were obtained from the turbulent eddy covariance system. The calculation formula was as follows:
where ω′, T′, and q′ represent the turbulent fluctuations of vertical wind speed (m·s−1), air temperature (°C), and specific humidity (g·kg−1), respectively. ρ is the air density (kg·m−3), Cp is the specific heat capacity at constant pressure (MJ·kg−1·°C−1), and λ is the latent heat of the vaporization of water (MJ·kg−1).
The surface soil heat flux is typically calculated using the measured soil heat flux at a certain depth from the heat flux plate and temperature sensors. In this study, the TDEC (Thermal Dissipation of Heat Conductivity) method [36,37] was used to obtain the surface soil heat flux during the observation period. The specific formula is as follows:
where Gz is the soil heat flux (W·m−2) directly observed at the soil depth z, and the soil heat fluxes of 2 cm and 5 cm were selected here. Cs is the soil volumetric heat capacity (J·m−3), which is 1.18 × 106 J·m−3·K−1 [38].
2.2.3. Calculation of Surface Energy Balance and Closure Rate
The net radiation (Rn) is divided into H, LE, G, canopy heat storage (S), and the sum of additional energy (Q). Typically, a small value of Q is neglected. Previous studies have shown [39,40] that the canopy heat storage (S) significantly affects energy balance closure when vegetation heights surpass 8 m. However, in this study, the underlying surface vegetation height was uniformly low; therefore, S was not considered. The surface energy balance equation could be expressed as follows [41,42]:
An important basis for the evaluation of the observations is the energy balance closure. Previous studies have shown that there was a general lack of closure of the surface energy [11], so the relationships between the turbulent fluxes (H + LE) and the effective energy (Rn − G) at different stations were analyzed. In this study, the least square method (OLS) was most commonly used to calculate the energy closure rate (EBR) in order to evaluate the status of energy closure. The calculation formula was as follows [33]:
2.2.4. Parameter Calculations
The Bowen ratio (β) is the ratio of sensible heat flux to latent heat flux at a particular interface. It provides a comprehensive reflection of the impact of microclimate and hydrological conditions on the energy partitioning in the ecosystem [43]. The calculation formula is as follows:
β > 1 reflects the dominance of H in the turbulent flux, while β < 1 reflects the dominance of LE. To avoid errors in the value of β caused by weak solar radiation and other factors, according to previous studies [44,45], values of downward shortwave radiation (SD) less than 100 W·m−2 were removed.
Based on hour-scale data from observation stations, the daily scale saturated water vapor pressure deficit (VPD) can be calculated using empirical formulas [46]; the formula is as follows:
where T stands for site temperature (°C), and RH stands for relative humidity.
2.2.5. Data Analysis Methods
Mantel analysis was used to investigate the regulatory mechanisms of meteorological factors on energy fluxes and the parameter β at four sites on the Qinghai Plateau during various growth stages, and R Studio software (version 2023.12.1) was employed to plot the results of the Mantel analysis. To study in depth the complexity of the inter-relationships between meteorological factors and energy fluxes, the path analysis method was used to analyze the direct and indirect relationships generated by meteorological factors on energy fluxes during the growing season on the Qinghai Plateau.
3. Results
3.1. Variations in Energy Fluxes
The meteorological and eddy data of the four stations selected for this study were of different vintages, so only the overall variation characteristics of the energy fluxes at each station were analyzed, and the differences in radiative fluxes between the stations were not compared. Additionally, G was not analyzed for the HB and NADORS stations. Rn, H, and LE displayed pronounced seasonal variations, where Rn and LE followed a single-peaked seasonal trend, peaking during the growing season and then falling off in the non-growing season. The high values of LE at the HB and NADORS stations were mainly concentrated in the mid-growing season (Figure 2). During the growing season, the WYS and AR stations experienced a longer period where the LE surpassed the H. In contrast, the HB and NADORS stations exhibited a comparatively shorter duration with LE exceeding H. As the phenological development of vegetation progressed, the seasonal patterns of H and LE for various underlying surfaces primarily changed at different stages of the growing season. Specific analyses revealed that H remained the predominant component throughout the year in both alpine shrubland and alpine desert ecosystems. Furthermore, in the alpine shrubland ecosystem, the shift in dominance from H to LE occurred at the beginning of the growing season and persisted through to the end of the growing season; in the alpine desert ecosystem, the transition in dominance from H to LE primarily occurred during the mid-season of growth. However, in swamp meadows and subalpine mountain meadows, LE dominated throughout the year. The shift in dominance from H to LE primarily occurred at the end of the non-growing season near the growing season, early in the growing season, and the end of the growing season.
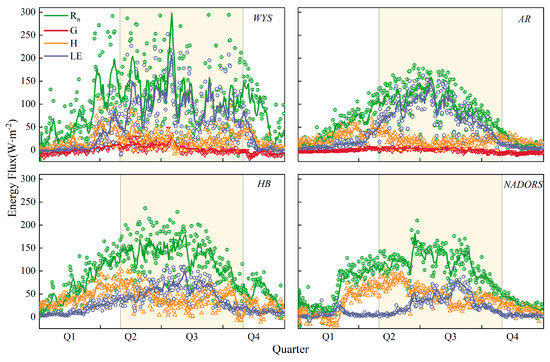
Figure 2.
The daily variation characteristics of Rn, H, LE and G at four sites on the Qinghai Plateau: the scatter plot represents the original data of each site, the line represents the 7-day moving average of the daily average energy fluxes at each site during the observation period, and the shallow yellow-shaded areas in the figure represent the regional growth season.
3.2. Seasonal Variations in Energy Partitioning
The seasonal variation in energy fluxes partitioning was significant at each site, with LE showing greater seasonal fluctuations compared to H (Figure 3). Rn was mainly consumed by H and LE. Throughout the year, swamp meadows and subalpine mountain meadows were dominated by LE, while alpine shrublands and alpine deserts were dominated by H, with alpine deserts having a greater H dominance. At the WYS, AR, HB, and NADORS stations, the values of H/Rn were 27.78%, 33.02%, 39.04%, and 44.55%, while the values of LE/Rn were 81.71%, 60.39%, 30.68%, and 21.33%, respectively. On a seasonal scale, during the growing season, Rn was predominantly allocated to LE in swamp meadows and subalpine mountain meadows, with values of LE/Rn of 95.04% and 72.61%, respectively; in the alpine shrublands, the partitioning of Rn to both H and LE was comparable, with a slight advantage for LE. During the non-growing season, Rn was primarily partitioned to H. In contrast, in both the growing and non-growing seasons of the alpine deserts, Rn was predominantly assigned to H. As the turbulent fluxes varied, β also varied, exhibiting a roughly “W”-shaped variation in the alpine deserts and a “U”-shaped curve in the rest of the underlying surfaces. The annual mean values of β at each site showed the following pattern: NADORS (2.78) > HB (1.66) > AR (0.80) > WYS (0.31). The seasonal variations in the β were pronounced. During the growing season, β remained relatively stable, with values in swamp meadows, subalpine mountain meadows, and alpine shrublands all being less than 1, indicating that LE was the dominant component of turbulent fluxes. In contrast, in alpine deserts, β values exceeded 1 in both the growing and non-growing seasons, indicating that H was the primary component of turbulent fluxes.
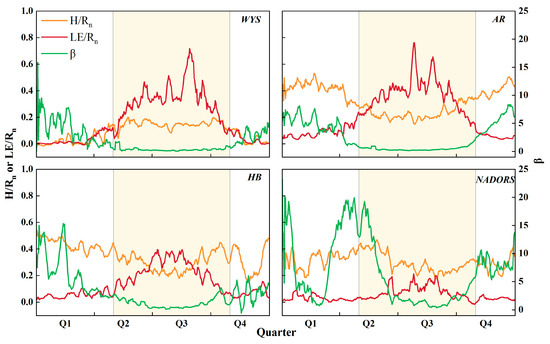
Figure 3.
The seasonal variation in energy partitioning (LE/Rn and H/Rn) and β at four sites on the Qinghai Plateau. The shallow yellow-shaded areas represent the regional growth season, and all values in the above plot are 7-day sliding averages for each site.
3.3. Energy Closure Condition
In this study, the energy balance ratio (EBR) was adopted as a key indicator for evaluating the results of eddy covariance system observations. To ensure the accuracy of the analysis, we filtered the 1 h observation data from four sites on the Qinghai Plateau, excluding data with EBR values less than 0.3 or greater than 1.3. Subsequently, we conducted a linear regression analysis on the turbulent fluxes and available energy data from each station. The slope of the regression coefficient represented the EBR, as detailed in Table 2. During the observation period, there was a significant difference in energy closure among different ecosystems. The swamp meadows had the highest degree of energy closure, followed by subalpine mountain meadows and alpine shrublands, while alpine deserts had the lowest degree of energy closure. Specifically, the mean EBR at the WYS station was 0.8, ranging from 0.61 to 0.9; at the AR station, it was 0.71, ranging from 0.62 to 0.78; at the HB station, it was 0.64, ranging from 0.61 to 0.66; and at the NADORS station, it was 0.51, ranging from 0.48 to 0.53. All stations showed a consistent pattern where the energy closure degree was higher during the growing season compared to the non-growing season.

Table 2.
Energy closure conditions at four sites on the Qinghai Plateau.
3.4. The Correlation between Climate Factors of Different Underlying Surfaces and Energy Fluxes
The Mantel Test, a non-parametric statistical method, was used to evaluate the correlation between two matrices. In this study, we constructed a flux matrix that included H, LE, and β, as well as a meteorological factors matrix comprising Ws, Ta, RH, Ms, Ts, VPD, and Rn, to explore the correlation between them. Based on the Mantel correlation coefficient, the correlation was categorized into three levels: a value of Mantel’s r < 0.2 indicated a low correlation between the two matrices, a value in the range 0.2 < Mantel’s r < 0.4 suggested a relatively high degree of overlap, and a value of Mantel’s r ≥ 0.4 signified the highest degree of overlap. When the statistical significance test for the Mantel’s p value was less than 0.01, the larger the value of Mantel’s r, the stronger the correlation [47]. The results indicated that the correlations between fluxes and β with meteorological factors varied among different growth stages of ecosystems in the Qinghai Plateau.
During the growing season (Figure 4), at the WYS station, Ws, Ta, RH, Ms, Ts, and Rn significantly impacted H and showed significant correlations. Ta, RH, VPD, and Rn had the greatest impact on LE and showed highly significant correlations, while Ws and T significantly impacted LE and showed significant correlations. Ms had a significant effect on the β. At the AR station, Ta, RH, Ts, VPD, and Rn had the greatest impacts on H and LE and exhibited significant correlations. Ta and Ts had the most significant impacts on the β, followed by RH, Ms, VPD, and Rn. At the HB station, Ta, RH, Ts, and VPD had the most significant impact on H and exhibited a highly significant correlation. Ta, Ts, VPD, and Rn had a significant impact on both LE and β and showed significant correlations. At the NADORS station, RH and VPD had the most significant impact on H, followed by Ws and Ms, all showing significant correlations. Except for Ws, LE showed highly significant correlations with all other factors, Ta, RH, Ms, and VPD had the most significant impact on LE, followed by Ts and Rn. Except for Ts and Rn, β was significantly correlated with all other factors, RH, Ms, and VPD had the most significant impacts on β, followed by Ws and Ta. It is worth pointing out that Ms had the greatest impact on the alpine desert ecosystem.
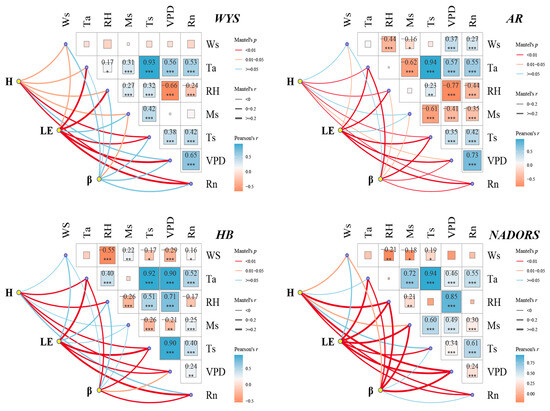
Figure 4.
Mantel analysis of daily energy fluxes and β and meteorological factors in the growing season. And * represents significant at the level of p < 0.05; ** represents significant at the level of p < 0.01 level, *** represents significant at the level of p < 0.001.
During the non-growing season (Figure 5), at the WYS, AR, and HB stations, Ta and Rn significantly affected H. At the WYS and AR stations, Ts and VPD also significantly affected H. At the WYS station, the impact of Ws on H was also significant. At the NADORS station, Ms significantly affected H. At the AR and HB stations, Ta, Ms, Ts, VPD, and Rn significantly affected LE, and RH also significantly affected LE at the AR station. At the NADORS station, RH and VPD significantly affected LE. At the WYS station, none of the factors significantly affected LE. At the WYS station, Ws significantly affected β. At the AR station, except for Ws, all factors significantly affected β. At the HB station, Ts and Rn significantly affected β. Overall, the strength of correlation between non-growing season fluxes and meteorological factors varied widely among sites.
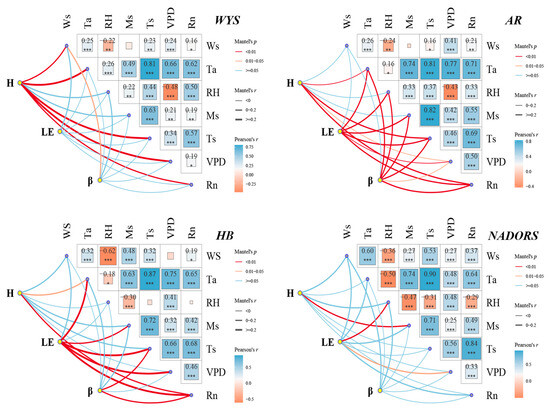
Figure 5.
Mantel analysis of daily energy fluxes and β and meteorological factors in the non-growing season. And * represents significant at the level of p < 0.05; ** represents significant at the level of p < 0.01 level, *** represents significant at the level of p < 0.001.
Throughout the year (Figure 6), at the WYS station, all factors significantly affected H; except for VPD, the rest of the meteorological factors had highly significant effects with LE. At the AR station, RH, Ts, and Ta significantly affected H; except for Ws, all factors had a highly significant effect with LE and β. At the HB station, RH significantly affected H. Ta, Ms, Ts, VPD, and Rn had a highly significant effect on LE. Ta, Ts, VPD, and Rn significantly affected β. At the NADORS station, Ws, Ms, Ta, and Rn significantly affected H; except for Ws, all factors significantly affected LE and β.
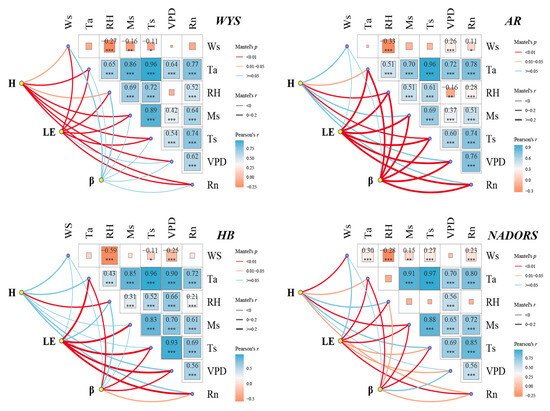
Figure 6.
Mantel analysis of daily energy fluxes and β and meteorological factors throughout the year. And * represents significant at the level of p < 0.05; ** represents significant at the level of p < 0.01 level, *** represents significant at the level of p < 0.001.
In summary, during the growing season at the WYS station, Ws, Ta, RH, Ts, and Rn significantly affected the fluxes; during the non-growing season, all meteorological factors showed no significant correlation with LE. During the growing season at the AR station, Ta, RH, Ts, VPD and Rn significantly affected the fluxes; during the non-growing season, Ta, Ts, VPD, and Rn significantly affected the fluxes; and during the two phases of the growing season and the non-growing season, Ta, RH, Ms, Ts, VPD, and Rn all significantly affected β. During the growing season at the HB station, Ta, Ts, VPD, and Rn significantly affected the fluxes; during the non-growing season, Ta and Rn significantly affected the fluxes; and during the two phases of the growing season and the non-growing season, Ts and Rn significantly affected β. During the growing season at the NADORS station, RH, Ms, VPD, and Rn significantly affected the fluxes. During the growing season and the non-growing season at both the WYS and NADORS stations, the relationship between meteorological factors and β varied significantly.
3.5. The Regulatory Pathway of Meteorological Factors on Energy Fluxes
This article used path analysis to study the impacts of meteorological factors during the growing season on energy partitioning. This method, grounded in multiple linear regression, decomposed the correlation between independent and dependent variables into direct and indirect paths of influence. In this study, we used meteorological factors (Ws, Ta, RH, Ms, Ts, VPD, and Rn) as independent variables and energy fluxes (H, LE, and β) as dependent variables to calculate the direct and indirect path coefficients of meteorological factors on energy fluxes, with larger absolute values of path coefficients indicating a greater influence of meteorological factors on fluxes. The path analysis results (Figure 7) indicated that during the growing season, Rn, RH, Ms, and Ts had a significant impact on H. RH and Ms exerted an inhibitory effect on H, while Rn and Ts exerted a positive influence on H. The research revealed that Ws, RH, Ms, Ts, VPD, and Rn primarily influenced H through direct effects. Specifically, Ws, Ts, and Rn exerted positive influences on the variations in H, while RH, Ms and VPD exerted an inhibitory effect on the changes in H. Ta positively affected H mainly by regulating other meteorological factors. LE was predominantly influenced by a combination of Rn, RH, Ms, and VPD, with all these factors contributing positively to the changes in LE. The research revealed that Ta, RH, VPD, and Rn primarily influenced the variations in LE through their direct effects. Ws, Ts, and Ms affected LE mainly by modulating other meteorological factors; Ws had an inhibitory effect, while Ts and Ms influenced LE through positive indirect effects. Compared to H and LE, the impacts of meteorological factors on the β were diminished. β was predominantly influenced by Ms, VPD, and RH, all of which exerted inhibitory effects on β. Except for Rn, which predominantly influenced β through indirect effects, the other factors primarily affected β through direct effects. Specifically, the direct influences of Ws and Ts on β were positive, whereas those of Ta, RH, Ms, and VPD were negative.
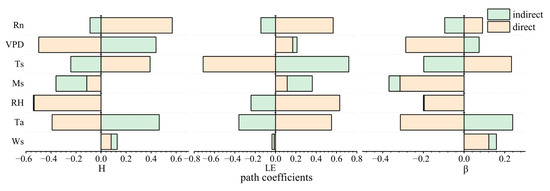
Figure 7.
Path analysis of energy fluxes and β with respect to meteorological factors.
4. Discussion
4.1. Differences in Energy Fluxes and Partitioning of Various Underlying Surfaces
At various stations on the Qinghai Plateau, Rn, LE, and H exhibited a unimodal variation pattern. However, the fluctuations in H were more pronounced under surfaces of the alpine shrublands and alpine deserts. This was mainly determined by the differences in local radiation, hydrothermal conditions, and the varying meteorological factors that affected vegetation at different growth stages [22,48]. At each station, Rn was primarily consumed by H and LE, while G showed minimal fluctuations. This was consistent with research from the typical alpine swamp meadows in the Yangtze River source area [11], the alpine grasslands in the eastern Qinghai Plateau [49], and the alpine wetlands in the central Qinghai Plateau [50]. Previous studies [51,52] showed that in semi-arid ecosystems, a reduction in vegetation cover led to an increase in albedo and a decrease in Rn, thereby affecting the land–atmosphere exchange, energy balance, and surface biophysical properties. Compared with swamp meadows and subalpine mountain meadows, alpine shrublands, and alpine deserts had lower vegetation cover. In early spring, H increased rapidly, the transition of H to processes dominated by LE was delayed, the fluctuations were greater, and the period during which H was higher than LE was extended throughout the year. At the WYS station, LE exhibited a multi-peaked characteristic, which may be related to the intense local solar radiation and the closure of plant stomata [53].
The differences between various underlying surfaces led to distinct characteristics in energy partitioning. Previous studies indicated that in areas with higher vegetation cover and soil moisture, the LE accounted for a larger proportion [42,54]. The swamp meadows and subalpine mountain meadows had better vegetation coverage and ample soil moisture, with energy predominantly present in the form of LE. Moreover, the proportion of LE at swamp meadows was larger, exceeding that in the subalpine wetlands on the eastern fringe of the Qinghai Plateau and the degraded wetlands in the central areas [55,56]. In the alpine shrublands and alpine deserts, where water was limited and vegetation cover was low, energy was primarily in the form of H. This pattern was similar to the energy allocation characteristics observed in the arid and semi-arid grasslands of the western plateau, such as at Shiquan and Gai Ze stations, as well as in the desert grasslands and semi-arid grasslands of northern China and the Artemisia shrublands of the Mu Us Sandy Land [57,58,59]. On a seasonal scale, swamp meadows and subalpine mountain meadows exhibited similar energy exchange characteristics to other regions of the Qinghai Plateau. During the growing season, energy was predominantly in the form of LE, while during the non-growing season, it was primarily H [50,60,61]. Among them, during the growing season in the swamp meadows, the value of LE/Rn (95%) was significantly higher than the corresponding ratios in the subalpine mountain meadows, as well as in the riverine marshy wetland on the Qinghai Plateau, the subalpine wetland on the eastern margin, and the degraded wetland in the hinterland in previous studies [50,56,62]. During both the growing and non-growing seasons of the alpine shrublands, H and LE were comparable, while in the alpine deserts, H was dominant throughout the same periods. The above differences were mainly due to soil moisture, vegetation, and solar radiation. The underlying surfaces of the WYS station belonged to undegraded swamp meadows, which experienced increased precipitation during the growing season, leading to the storage of large amounts of water on the ground. The strong solar radiation and unique moisture conditions resulted in strong evaporation from the soil, and thus LE was more dominant in the energy fluxes. Alpine shrublands and alpine deserts were highly water-limited and had very low vegetation cover, resulting in a small percentage of LE. The energy partitioning characteristics corresponded to the hydrothermal conditions of the subsurface.
β was a key indicator for measuring the energy balance and physical characteristics of ecosystems. It influenced the heating of surface air by energy, which in turn affected the regional microclimate and the hydrological cycle [42]. Throughout the year, the β values for swamp meadows and subalpine mountain meadows were both less than 1, while those for alpine shrublands and alpine deserts were both greater than 1. This reflected the differences in the primary modes of energy fluxes partitioning at the time. At various stations, soil moisture levels decreased sequentially from WYS to AR, HB, and NADORS stations, while the corresponding β values increased in tandem. The pattern of β variation was consistent across both the growing and non-growing seasons. Throughout the year, the β values for swamp meadows and subalpine mountain meadows were consistently less than 1, while those for alpine shrublands and alpine deserts were consistently greater than 1. This variance delineated the predominant energy fluxes allocation mechanisms at play within these distinct ecosystems. The β values in this study were consistent with the range of β values in previous studies on the Qinghai Plateau [16,49,61]. Throughout the year and during the growing season, the β values of the swamp meadows were similar to those of the agricultural lands along the Lhasa River and the Haibei swamp meadows [63,64]. The β values of the subalpine mountain meadows were all lower than those of the three alpine ecosystems in the Qinghai Lake watershed [16] but higher than those of the Horqin meadow [65]. The β values of the alpine shrublands were higher than those of similar ecosystems’ water birch shrubs in the Qinghai Lake watershed [16] but lower than those of the shrubs in the Mu Us Desert in the northern region [59]. The β values of the alpine deserts were all higher than the β values in the other aforementioned ecosystems and were similar to those of the desert grasslands in northern China [58], indicating that the region had less moisture.
4.2. Meteorological Factors Regulate the Energy Fluxes and Their Partitioning
In field observations, energy fluxes and their partitioning were influenced by atmospheric conditions, water supply status, and vegetation. Under varying surface conditions, Rn, RH, and Ms were the primary factors affecting energy fluxes and their partitioning. The positive impact of Rn on H and LE was consistent with previous studies [24,66], but it also indicated that Ta was not always the dominant controlling factor [53]. Additionally, we found that Ta, Ts, VPD, and Rn significantly influenced LE at all sites, aligning with earlier research [67]. In this study, it was discovered that VPD predominantly exerted a positive influence on LE through other meteorological factors, such as Ta, Ts, and Rn, which was similar to findings from alpine swamp meadows in the Qinghai Plateau [61] but contrasts with previous studies where VPD had an inhibitory effect on LE [45,68].
Ms was a significant factor affecting fluxes and their partitioning in ecosystems [24,48,69]. In arid and semi-arid ecosystems, soil moisture was a key limiting factor for energy partitioning, while in ecosystems with more abundant moisture, radiation and other atmospheric conditions had more significant impacts on fluxes [44,48]. According to the aridity index, the Qinghai Plateau was divided into three regions: arid, semi-arid, and semi-humid [70]. At the NADORS station, located in the arid region of the western Qinghai Plateau, soil moisture was a significant limiting factor affecting the partitioning of energy in its alpine desert ecosystem. This study found that during the growing season, LE in the alpine desert ecosystem was primarily controlled by Ms and VPD. In contrast, in swamp meadows and subalpine mountain meadows, which were well supplied with water, LE was primarily influenced by Rn and other atmospheric conditions. In alpine shrublands, although the underlying surface moisture was relatively abundant, surpassing that of the alpine deserts, the increase in LE within the energy fluxes led to a reduction in Ms. However, the intensity of its consumption had not yet reached a level sufficient to limit LE; thus, flux variations were insensitive to Ms. Meanwhile, during the growing season in alpine deserts, the fluxes were significantly affected by RH and VPD, which also indirectly demonstrated the substantial impact of moisture on these arid environments. In the swamp meadows, Ws had a significant impact on the fluxes. As Ws increased, the convection between the land and the atmosphere was enhanced, leading to more heat being transferred to the atmosphere, consequently increasing H. This finding was similar to the results of previous studies [71].
Rn exerted an effect on β by varying the magnitudes of H, LE, and Ms. Among the different underlying surfaces of the Qinghai Plateau, the effects of Ms and VPD on β were found to be greater. During the growing season, as Ta continuously rose, the VPD also showed a sustained increase, correlating negatively with β. This correlation was consistent with findings from past studies in meadows, typical needle grasslands, and shrubland ecosystems [59,67,72].
4.3. Evaluation of Energy Balance Closure for Different Underlying Surfaces
In field observations, achieving closure in the energy balance has always been a challenging issue, and it is essential to consider the question of energy partitioning when studying energy closure [1]. Generally consistent with the findings of prior researches [73,74], in this study, an energy imbalance of approximately 30% was observed at each site. The mean value of the energy balance closure ratio for the four sites was 0.67, which was consistent with the results (0.5–0.8) from a large number of field stations [11,75]. Differences in the hydrological and thermal conditions of the underlying surfaces led to varying degrees of energy closure, with the closure rate decreasing in the order of WYS, AR, HB, and NADORS.As soil moisture in the underlying surfaces decreased, closure rate also decreased. Accounting for G can improve the energy closure rate. At HB and NADORS stations, G was set to zero when calculating the energy closure, which also contributed to the lower energy closure rate. In the swamp meadow ecosystem, the highest energy closure rate was observed, noting the superior local hydrothermal conditions that facilitated a considerable LE exchange as a proportion of Rn, thereby substantially enhancing the ecosystem’s energy closure efficiency. The differences in energy closure shown at the four sites may also be related to differences in sensor and measurement heights, systematic instrumentation errors, and turbulent fluxes showing losses at low or high frequencies [76]. At the seasonal scale, energy closure conditions were more favorable during the growing season compared to the non-growing season. This may have been related to extreme weather, a lack of heat, or mechanical actions that led to insufficient turbulence fluxes during the non-growing season [9].
5. Conclusions
This study was based on eddy and meteorological data obtained from the correlation system to investigate the energy partitioning characteristics and closure conditions across various ecosystems of the Qinghai Plateau, and it discussed the differences in the impacts of various meteorological conditions on energy fluxes and the Bowen ratio at each station. The main conclusions are as follows:
- H, LE, and Rn exhibited unimodal variations. In alpine shrublands and alpine deserts, H showed greater fluctuations, with high values mainly concentrated at the beginning or end of the growing season, while high values of LE were concentrated in the mid-growing season. Swamp meadows and subalpine mountain meadows were dominated by LE in terms of energy consumption throughout the year. Seasonal characteristics of energy allocation were obvious, Rn was mainly converted to LE in the growing season, with values of LE/Rn of 95.05% and 72.61%, respectively, and Rn was mainly converted to H in the non-growing season, with values of H/Rn of 51.07% and 65.13%, respectively. In alpine shrublands and alpine deserts, energy consumption was dominated by H throughout the year. During the growing season in alpine shrublands, Rn was predominantly converted into LE, while in the non-growing season, it was mainly converted into H. In contrast, in the drier alpine deserts, energy was predominantly in the form of H during both the growing and non-growing seasons.
- Soil moisture decreased in the order of WYS, AR, HB, and NADORS, with a corresponding increase in β. During both the growing and non-growing seasons of swamp meadows and subalpine mountain meadows, the β was less than 1. Energy fluxes for the four types of underlying surfaces exhibited an approximate 30% closure discrepancy, with energy closure rates being higher during the growing season compared to the non-growing season.
- Meteorological factors collectively regulated energy fluxes and the β. During the growing season, Rn, RH, and Ms had the greatest impact on H, primarily through direct effects on the fluxes; RH, VPD, Rn, and Ms had the greatest impacts on LE, with RH, VPD, and Rn mainly regulating the fluxes through direct effects, while Ms primarily influenced the fluxes through indirect effects. The β was mainly influenced by Ms, VPD, and RH. Although the fluxes of each ecosystem were affected by the same meteorological factors, alpine deserts were particularly sensitive to moisture, showing significant relationships mainly with Ms, VPD, and RH. Swamp meadows were notably influenced by Ws, Ta, and Ts; alpine shrublands were influenced by Ta; while subalpine mountain meadows were influenced by Ta and Ts.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, X.L., L.Z. and L.G.; methodology, X.L., L.Z. and L.G.; data processing, X.L.; writing—original draft preparation, X.L. and Z.D.; writing—review and editing, X.L. and Z.D. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Project No. 42171467) and the Natural Science Foundation Project of Qinghai Province (2022-ZJ-711).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author. The data are not publicly available due to privacy.
Acknowledgments
We thank our teachers and reviewers and editors for their valuable comments.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- McGloin, R.; Šigut, L.; Havránková, K.; Dušek, J.; Pavelka, M.; Sedlák, P. Energy balance closure at a variety of ecosystems in Central Europe with contrasting topographies. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2018, 248, 418–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.M.; Hu, Z.Y.; Wang, B.B.; Ma, W.Q.; Cheng, X.L.; Han, C.B.; Li, M.S.; Zhong, L.; Gu, L.L.; Sun, F.L.; et al. The Review of the Observation Experiments on Land-Atmosphere Interaction Progress on the Qinghai-Xizang (Tibetan) Plateau. Plateau Meteorol. 2021, 40, 1241–1262. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, L.L.; Yao, J.M.; Hu, Z.Y.; Zhao, L. Comparison of the surface energy budget between regions of seasonally frozen ground and permafrost on the Tibetan Plateau. Atmos. Res. 2015, 153, 553–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Wu, H.X.; Qin, J.; Lin, C.G.; Tang, W.J.; Chen, Y.Y. Recent climate changes over the Tibetan Plateau and their impacts on energy and water cycle: A review. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2014, 112, 79–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.X.; Zhang, Y.S. Tibetan Plateau Forcing and the Timing of the Monsoon Onset over South Asia and the South China Sea. Mon. Weather. Rev. 1998, 126, 913–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.M.; Yao, T.D.; Wang, J.M. Experimental study of energy and water cycle in Qinghai Plateau-The progress introduction on the study of GAME/Tibet and CAMP/Tibet. Plateau Meteorol. 2006, 25, 344–351. [Google Scholar]
- Li, N.; Zhao, P.; Wang, J.F.; Deng, Y. The Long-Term Change of Latent Heat Flux over the Western Tibetan Plateau. Atmosphere 2020, 11, 262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Cui, Y.L.; Luo, Y.F.; Shi, Y.Z.; Liu, M.; Liu, F.P. Energy partitioning and evapotranspiration over a rotated paddy field in Southern China. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2019, 276–277, 107626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, K.; Goldstein, A.; Falge, E.; Aubinet, M.; Baldocchi, D.; Berbigier, P.; Bernhofer, C.; Ceulemans, R.; Dolman, H.A.J.; Field, C.; et al. Energy balance closure at FLUXNET sites. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2002, 113, 223–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.C.; Zhao, L.; Li, R.; Xiao, Y. Seasonal changes and major influencing factors of surface albedo in the permafrost regions of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau Hinterland. Mt. Res. 2020, 38, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.N.; Wang, S.Y.; Ye, H.L.; He, X.B.; Ding, Y.J.; Hong, X.F.; Fu, H. Characteristics of surface energy budget of typical alpine swamp meadows in the source region Yangtze River and its influencing factors. J. Glaciol. Geocryol. 2023, 45, 1501–1515. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.G.; Lyu, S.H.; Ao, Y.H.; Wen, L.J.; Zhao, L.; Wang, S.Y. Long-term energy flux and radiation balance observations over Lake Ngoring, Qinghai Plateau. Atmos. Res. 2015, 155, 13–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.B. Characteristics of Surface Energy Balance and Parameterization of Turbulent Fluxes in the Gobi Region of the Western Qinghai Plateau. Ph.D. Thesis, Nanjing University of Information Science and Technology, Nanjing, China, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, F.W.; Han, Y.; Li, H.Q.; Li, Y.N.; Cao, G.M.; Zhou, H.K. Turbulent heat exchange and partitioning and its environmental controls between the atmosphere and an alpine potentilla fruticosa shrublands over the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Chin. J. Agrometeorol. 2020, 41, 76–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, Y.F.; Chen, F.; Zhao, P.; Barlage, M.; Blanken, P.; Chen, Y.L.; Chen, B.; Wang, Y.J. Surface energy balance closure at ten sites over the Tibetan plateau. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2018, 259, 317–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.Y.; Li, X.Y.; Zhao, G.Q.; Huang, Y.M. Surface energy fluxes and controls of evapotranspiration in three alpine ecosystems of Qinghai Lake Watershed, NE Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Ecohydrology 2015, 9, 267–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.K.; Yao, J.M.; Gu, L.L.; Li, R.; Wu, X.D.; Wu, T.H.; Xie, C.W.; Zou, D.F.; Qiao, Y.P.; Hu, G.J.; et al. The surface energy budget process and preliminary analysis of its impact on the active layer in the permafrost region of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. J. Glaciol. Geocryol. 2022, 44, 1773–1783. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, G.H.; Hu, Z.Y.; Wang, J.M.; Ma, W.Q.; Gu, L.L.; Sun, F.L.; Xie, Z.P.; Yan, X.Q. The spatial heterogeneity of land surface conditions and its influence on surface fluxes over a typical underlying surface in the Tibetan Plateau. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2019, 135, 221–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.Y.; Zhong, L.; Ma, Y.M.; Zou, M.J.; Huang, Z.Y.; Xu, K.P.; Feng, L. Model estimation and validation of the surface energy fluxes at typical underlying surfaces over the Qinghai-Plateau. Plateau Meteorol. 2018, 37, 1499–1510. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, N.; Zhang, Y.S.; Guo, Y.H.; Gao, Y.H.; Gao, H.F.; Zhang, H.B.; Wang, Y.F. Environmental and biophysical controls on the evapotranspiration over the highest alpine steppe. J. Hydrol. 2015, 529, 980–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.Z.; Ma, Y.M.; Liu, Y.X. Simulation of sensible and latent heat fluxes on the Tibetan Plateau from 1981 to 2018. Atmos. Res. 2022, 271, 106129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.G.; Zhao, B.S.; Yan, H.F.; Su, J.B. Energy Partitioning and Latent Heat Flux Driving Factors of the CAM Plant Pineapple (Ananas Comosus (L.) Merril) Grown in the South Subtropical China. Plants 2023, 13, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, Y.M.; Xiao, H.J.; Xin, Z.M.; Li, J.R.; Miri, A.; Cao, Q.Q. Characteristics of Energy Distribution in a Desert Ecosystem in Inner Mongolia, Northern China. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10, 939782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; You, C.H.; Gao, Y.H.; Li, Y.Q.; Niu, Y.L.; Shao, C.L.; Wang, X.; Xin, X.P.; Yu, G.R.; Han, X.G.; et al. Seasonal variations and drivers of energy fluxes and partitioning along an aridity gradient in temperate grasslands of northern China. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2023, 342, 109736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, J.; Yu, Y.; Xie, J.; Zan, B.L. A study on responses of surface energy partitioning to climatic factors on two types of underlying surface over Qinghai-Xizang Plateau. Chin. J. Atmos. Sci. 2017, 41, 918–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.H.; Wu, K.; Hu, Z.M.; Yang, H. Spatio-temporal variability of vegetation sensitivity on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau during the growing season from 2000 to 2021. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2023, 43, 4054–4065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.Q.; Zhu, J.B.; Zhang, F.W.; He, H.D.; Yang, Y.S.; Li, Y.N.; Cao, G.M.; Zhou, H.K. Growth stage-dependant variability in water vapor and CO2 exchanges over a humid alpine shrubland on the northeastern Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2019, 268, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, M.G.; Wang, S.P.; Jiang, N.; Sun, J.P.; Cao, R.Y.; Ling, X.F.; Fang, B.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, L.H.; Xu, X.Y.; et al. Plant phenology changes and drivers on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Nat. Rev. Earth Environ. 2022, 3, 633–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.Y.; Zhang, Y.; Meng, X.H.; Song, M.H.; Shang, L.Y.; Su, Y.Q.; Li, Z.G. Fill the gaps of eddy covariance fluxes using machine learning algorithms. Plateau Meteorol. 2020, 39, 1348–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falge, E.; Baldocchi, D.; Olson, R.; Anthoni, P.; Aubinet, M.; Bernhofer, C.; Burba, G.; Ceulemans, R.; Clement, R.; Dolman, H.; et al. Gap filling strategies for long term energy flux data sets. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2001, 107, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, W.H.; Chui, T. Temporal and spatial variations of energy balance closure across FLUXNET research sites. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2019, 271, 12–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aubinet, M.; Grelle, A.; Ibrom, A.; Rannik, Ü.; Moncrieff, J.; Foken, T.; Kowalski, A.S.; Martin, P.; Berbigier, P.; Bernhofer, C.; et al. Estimates of the annual net carbon and water exchange of forests: The EUROFLUX methodology. In Advances in Ecological Research; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1999; Volume 30, pp. 113–175. ISBN 978-0-12-013930-8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoy, P.; Mauder, M.; Foken, T.; Marcolla, B.; Boegh, E.; Ibrom, A.; Arain, M.; Arneth, A.; Aurela, M.; Bernhofer, C.; et al. A data-driven analysis of energy balance closure across FLUXNET research sites: The role of landscape-scale heterogeneity. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2013, 171–172, 137–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.L.; Xia, J.; Xu, C.Y.; Chen, Y.Q. Applicability of Six Potential Evapotranspiration Estimation Methods in Haihe Basin. Water Resour. Power 2015, 3, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, W.; Lin, W.J.; Wang, G.L. Study on the Distribution of the Real Evapotranspiration in Hetao Plain Based on Remote Sense. Remote Sens. Inf. 2009, 6, 28–31+42. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, K.; Wang, J.M. A temperature prediction correction method for calculating surface soil heat flux based on soil temperature and humidity data. Science in China. Ser. D Earth Sci. 2008, 38, 243–250. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, L.; Zhong, L.; Ma, Y.M.; Fu, Y.F.; Zou, M.J. Estimation of soil heat flux over the northern Qinghai-Xizang Plateau based on in-situ soil temperature and moisture data. Plateau Meteorol. 2016, 35, 297–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Zhao, L.; Li, R.; Yao, J.M. Seasonal variation characteristics of surface energy budget components in permafrost regions in the hinterland of Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. J. Glaciol. Geocryol. 2011, 33, 1033–1039. [Google Scholar]
- McCaughey, J.H. Energy balance storage terms in a mature mixed forest at Petawawa, Ontario ? A case study. Bound.-Layer Meteorol. 1985, 31, 89–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, C.J. Frequency Response Corrections for Eddy Correlation Systems. Bound.-Layer Meteorol. 1986, 37, 17–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.B.; You, C.H.; Tan, X.R.; Chen, B.Y.; Xu, M.Z.; Chen, S.P. Seasonal and interannual variations in energy balance closure over arid and semi-arid grasslands in northern China. Chin. J. Plant Ecol. 2022, 46, 1448–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.Y.; Dong, G.; Chen, J.Q.; Jiang, S.C.; Qu, L.P.; Legesse, T.; Zhao, F.U.; Tong, Q.; Shao, C.L.; Han, X.G. Energy balance and partitioning over grasslands on the Mongolian Plateau. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 135, 108560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, X.Y.; Zhang, Q.; Yue, P.; Yang, J.H.; Wang, S. Environmental and Biophysical Effects of the Bowen Ratio over Typical Farmland Ecosystems in the Loess Plateau. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 1897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, X.; Zha, T.S.; Gong, J.N.; Wu, B.; Zhang, Y.Q.; Qin, S.G.; Chen, G.P.; Feng, W.; Kellomki, S.; Peltola, H. Energy partitioning over a semi-arid shrubland in northern China. Hydrological Process 2016, 30, 972–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.G.; Eugster, W.; Asanuma, J.; Kotani, A.; Davaa, G.; Oyunbaatar, D.; Sugita, M. Energy partitioning and its biophysical controls above a grazing steppe in central Mongolia. Agric. Forest. Meteorol. 2006, 137, 89–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, Z.Y.; Xu, X.L.; Yang, D.; Xu, C.H.; Li, X.Z.; Li, Z.W. Temporal variation of vapor pressure deficit and its influencing factors in southwest China. Res. Agric. Mod. 2022, 43, 172–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Yang, X.G.; Wang, L.; Song, N.P.; Zheng, S.; Wu, M.Y. Characteristics of evapotranspiration components of different plant communities in desert steppe and its relationship with environmental factors. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2024, 44, 330–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, P.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, L.; Li, H.Y.; Yang, Y.; Zeng, J.; Wang, S. Long-term variations in energy partitioning and evapotranspiration in a semiarid grassland in the Loess Plateau of China. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2019, 278, 107671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, L.Y.; Zhang, Y.; Lyu, S.H.; Wang, S.Y. Energy exchange of an alpine grassland on the eastern Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Sci. Bull. 2015, 60, 435–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.X.; Zhang, Y.S.; Qiang, Y.H.; Guo, Y.H. Evapotranspiration and energy partitioning of a typical alpine wetland in the central Tibetan Plateau. Atmos. Res. 2021, 267, 105931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.Q.; Tian, L.; Zhang, Y.J. Growing season carries stronger contributions to albedo dynamics on the Tibetan Plateau. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0180559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, X.H.; Goulden, M.; Hollinger, D.; Barr, A.; Black, A.; Bohrer, G.; Bracho, R.; Drake, B.; Goldstein, A.; Gu, L.H.; et al. Observed increase in local cooling effect of deforestation at higher latitudes. Nature 2011, 479, 384–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.L.; Zhu, Y.T.; Zhu, G.F.; Zhang, Y.; He, L.Y.; Xu, C.; Zhang, K.; Wang, J.; Ayyamperumal, R.; Fan, H.; et al. Energy partitioning over an irrigated vineyard in arid northwest China: Variation characteristics, influence degree, and path of influencing factors. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2024, 350, 109972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Li, S.G.; Yu, G.R.; Asanuma, J.; Sugita, M.; Zhang, L.; Hu, Z.; Wei, Y. Seasonal and interannual variations in water vapor exchange and surface balance over a grazed steppe in central Mongolia. Agric. Water Manag. 2010, 97, 857–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Zhou, B.R.; Qi, D.L.; Zhou, W.F.; Xiao, H.B.; Xiao, R.X. Study of surface energy budget over alpine wetland in Longbao, Yushu Prefecture, Qinghai Province. J. Glaciol. Geocryol. 2015, 37, 916–923. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, C.H.; Wang, B.; Xiang, J.; Du, J.; Zhang, S.F.; Qiu, G. Seasonal and interannual variability of surface energy fluxes and evapotranspiration over a subalpine horizontal flow wetland in China. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2020, 288–289, 107996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.P.; Duan, T.Y.; Wu, G.F. The Intersity of Surface Heat Source and Surface Heat Balance on the Western Qinghai-Xizang Plateau. Sci. Geogr. Sin. 2003, 23, 13–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, X.Y.; Zhang, Q.; Yue, P.; Yang, J.H.; Yan, X.Y. Study on Energy Partitioning and its Environmental Factors of Four Types of Typical Underlying Surfaces in North China. Plateau Meteorol. 2021, 40, 109–122. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, S.Y. Characteristics and Influencing Factors of Surface Energy Balance in an Artemisia Ordosica Shrub Ecosystem in the Mu Us Desert. Master’s Thesis, Beijing Forestry University, Beijing, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Liu, H.Z.; Shao, Y.P.; Liu, Y.; Sun, J.H. Water and CO2 fluxes over semiarid alpine steppe and humid alpine meadow ecosystems on the Tibetan Plateau. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2018, 131, 547–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.Y.; Wang, G.X.; Sun, X.Y.; Huang, K.W.; Song, C.L.; Li, Y.; Sun, S.Q.; Sun, J.Y.; Lin, S. Energy partitioning and controlling factors of evapotranspiration in an alpine meadow in the permafrost region of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. J. Plant Ecol. 2024, 17, rtae002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.P.; Wang, L.; Chen, D.L.; Yang, K.; Wang, A.H. Seasonal evapotranspiration changes (1983–2006) of four large basins on the Tibetan Plateau. J. Geophys. Res. 2014, 119, 13079–13095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Z.; Ouyang, H.; Xu, X.; Song, M.H.; Duan, D.; Zhang, X. Water and heat balance and water use of shrub grassland and crop fields in Lhasa River Valley. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2009, 64, 303–314. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, F.W.; Li, H.Q.; Li, Y.N.; Zhang, L. Surface energy partitioning in alpine swamp meadow in the Qinghai Tibetan Plateau. Pratacul Tural Sci. 2008, 25, 14–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.D.; Guan, D.X.; Yuan, F.H.; Ren, Y.; Wang, A.Z.; Jin, C.J.; Wu, J.B. Diurnal and seasonal variations of energy balance over Horqin meadow. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2014, 25, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.L.; Wang, K.C. Biological and EnvironmentalControls on Evaporative Fractions at AmeriFlux Sites. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2016, 55, 145–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, S.; Tang, Y.H.; Cui, X.Y.; Kato, T.; Du, M.Y.; Li, Y.N.; Zhao, X.Q. Energy exchange between the atmosphere and a meadow ecosystem on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2005, 129, 175–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aires, L.M.; Pio, C.A.; Pereira, J.S. The effect of drought on energy and water vapour exchange above a mediterranean C3/C4 grassland in Southern Portugal. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2008, 148, 565–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Pan, Z.H.; Huang, B.X.; Liang, J.; Wang, J.L.; Zhang, Z.Y.; Jiang, K.; Huang, N.; Han, G.L.; Long, B.J.; et al. Influence paradigms of soil moisture on land surface energy partitioning under different climatic conditions. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 916, 170098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, M.S.; Meng, X.H.; Sheng, D.R.; Niu, H.L.; Wu, P.L.; Li, Z.G.; Zhao, L.; Chen, H.; Shang, L.Y.; Wang, S.Y.; et al. Observed surface heat fluxes partitioning during the local growing season over the Tibetan Plateau. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2024, 356, 110186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.X.; Wang, K.; Li, L.; Zhang, H.; Ma, L.; Yao, Z.S.; Zhang, W.; Hu, Z.H.; Zhen, X.H. Study on surface energy exchange and evapotranspiration in alpine meadows of the Zoige Plateau. Chin. J. Agrometeorol. 2021, 42, 642–656. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.Y.; Wang, L.X.; Yuan, H.Y. Seasonal differences of energy fluxes among crop and grass ecosystems in semiarid region of southern Ningxia. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2005, 25, 2333–2340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mauder, M.; Foken, T.; Cuxart, J. Surface-Energy-Balance Closure over Land: A Review. Bound.-Layer Meteorol. 2020, 177, 395–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foken, T. The Energy Balance Closure Problem: An Overview. Ecol. Appl. 2008, 18, 1351–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.Q.; Yu, G.R.; Wen, X.F.; Zhang, L.M.; Ren, C.Y.; Fu, Y.L. Evaluation of the energy balance closure of the China Flux Observation Network (China FLUX). Sci. China Ser. D Earth Sci. 2004, 34, 46–56. [Google Scholar]
- Stannard, D.I.; Blanford, J.H.; Kustas, W.P.; Nichols, W.D.; Amer, S.A.; Schmugge, T.J.; Weltz, M.A. Interpretation of surface flux measurements in heterogeneous terrain during the Monsoon ’90 experiment. Water Resour. Res. 1994, 30, 1227–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).