Abstract
In this work, we study long-term changes in the main directions of movement (storm tracks) of extratropical cyclones in the North Atlantic for the period 1873–2021, based on the data of the MSLP (Mean Sea Level Pressure) archives from the Climatic Research Unit and NCEP/DOE AMIP-II reanalysis. It was found that in the cold half of the year, the mean latitudes of storm tracks undergo oscillations with the periods ~80–100, ~40–45, and ~22 years, which indicates their possible association with solar cyclicity. Cyclone trajectories were found to shift northward at the minimum of the Gleissberg secular cycle (~1900–1930) and southward at its maximum (~1940–1960). The secular variations are the most pronounced in the western part of the North Atlantic, with the peak-to-peak amplitude reaching ~3–5°, and disappear at longitudes east of Greenwich. On the bidecadal timescale, cyclone tracks were found to shift noticeably to the north in even solar cycles and weakly to the south in odd ones. The most significant northward shifts (~1–2°) were detected during the descending phase and the minimum of the solar cycle (from the second to the sixth year after the solar maximum) in the eastern part of the North Atlantic (longitudes 30–10° W). The detected oscillations of cyclone trajectories may be caused by long-term changes in the intensity of the stratospheric polar vortex associated with galactic cosmic ray variations and geomagnetic activity.
1. Introduction
Extratropical cyclonic activity, i.e., the formation, development, and movement of cyclones and anticyclones, is an important link of the general circulation of the atmosphere, providing mass and heat exchange between high and low latitudes (e.g., [1]). Mobile extratropical cyclones, usually forming and developing over oceans, have a major impact on the weather and climate at middle and high latitudes in both hemispheres, affecting temperature, precipitation, humidity, and winds. In the Northern Hemisphere, cyclones coming from the North Atlantic are responsible for many hazardous events over Europe associated with extreme winds and precipitation. In particular, heavy rainfall caused by cyclone Bernd in July 2021 resulted in a severe flood in Central Europe [2] with more than 200 victims. Thus, studying the influence of solar activity and related phenomena on extratropical cyclonic activity is of great importance to improve the quality of weather and climate forecasts and avoid losses associated with extreme weather events.
The influence of the 11-year solar cycle on extratropical cyclone trajectories in the North Atlantic was studied in the works [3,4]. Brown and John [3] analyzed cyclone track changes in the northeast Atlantic (longitudes from 40° W to 30° E) in winter months for five solar cycles. They revealed a solar cycle dependence of storm tracks crossing this region at latitudes north of 50° N, with the mean latitude of the tracks being 2.5° further south at solar maximum than at solar minimum. Tinsley [4] showed that this effect is most pronounced under the west phase of the quasi-biennial oscillation (QBO) of the atmosphere, with the peak-to-peak amplitude of storm track variations in the solar cycle reaching ~6°. On a longer timescale, modeling studies of circulation changes in the North Atlantic during the Maunder minimum of solar activity were carried out by Luterbacher and colleagues [5] and Raible and colleagues [6]. The results of these works suggested a southward shift of mid-latitudinal cyclone tracks associated with reduced solar activity in the studied period. The findings in [5,6] seem to be in disagreement with those obtained by Brown and John [3] and Tinsley [4], which indicate a northward shift of North Atlantic cyclones with decreasing sunspot activity on a decadal timescale. So, further research is needed to clarify the possible influence of solar activity on extratropical cyclone movement on longer timescales. For this reason, the aim of this study is to consider long-term variations in extratropical cyclone trajectories in the North Atlantic and their possible association with solar cyclicity.
2. Experimental Data
Extratropical cyclones usually arise over oceans near the eastern coasts of continents where temperature contrasts are enhanced, especially in the winter period. In the North Atlantic area, cyclone formation occurs near the eastern coasts of North America, which is a region of high temperature contrasts and has a favorable thermobaric field structure that contributes to cyclone deepening [7]. From the North American coast, cyclones move, as a rule, in the northeastern direction towards Iceland and, then, towards the Barents Sea. The occurrence frequency of cyclones increases from the coast of North America to Iceland, which indicates the predominance of cyclogenesis processes in this area [1]. In the region of Iceland, the occurrence and depth of cyclones reach maxima, but from Iceland to the Barents Sea, processes of cyclone filling (destruction) intensify and cyclone occurrence decreases.
The motion and evolution of North Atlantic cyclones results in the formation of an extended region of lowered pressure (a baric trough), which usually stretches from the coast of North America to the Arctic coasts of Eurasia, at monthly maps of sea level pressure (SLP). This region is characterized by an enhanced occurrence and intensive development of cyclones. Examples of SLP distribution are presented in Figure 1 for cold months, when extratropical cyclonic activity is the most intensive. The axis of a baric trough (the central line connecting minimal pressure values at different longitudes) corresponds to a region of predominant passages of cyclone centers (storm tracks). The data in Figure 1 show the latitudinal position of North Atlantic storm tracks, indicating that the main direction of cyclone movement varies noticeably depending on the time period.
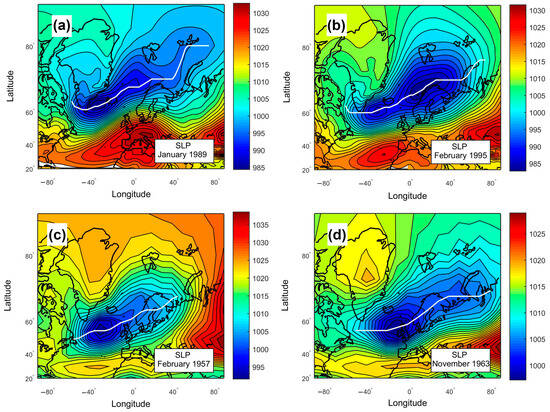
Figure 1.
Distribution of mean monthly sea level pressure (SLP; in hPa) in the North Atlantic in cold months: (a) January 1989; (b) February 1995; (c) February 1957; (d) November 1963. The baric trough axes indicating the main direction of cyclone movement (storm tracks) are shown by white lines.
As experimental data for this study, we used the gridded monthly data from the MSLP (Mean Sea Level Pressure) archives of the Climatic Research Unit, UK for 1873–1978, and NCEP/DOE AMIP-II reanalysis for 1979–2021. The study was carried out for the cold half of the year (October–March), which is the period of the most intensive cyclonic activity at middle latitudes. For each month, we plotted a monthly map of SLP showing the position of the baric trough. To determine the position of a storm track, pressure minima and their latitudes were found for the longitudes from 60° W to 20° E. Then, the latitudes of pressure minima were averaged over the cold months (October–March). Cases when a high pressure region was displaced over Iceland and no baric trough was observed were excluded. In the cases when a part of cyclones declined to the south (the situation which sometimes occurred east of the Greenwich meridian), the northern branch of the storm track was taken for the analysis.
3. Analysis of Experimental Data
3.1. Secular Variations in North Atlantic Cyclone Trajectories
Figure 2 presents temporal variations in the average latitudes of storm tracks in the cold half of the year for different longitudes λ in the North Atlantic. One can note that the North Atlantic storm tracks are characterized by a noticeable variability both on interannual and longer timescales, including multidecadal and secular ones.
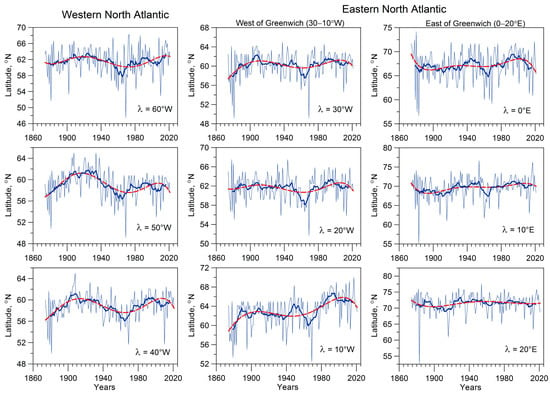
Figure 2.
Temporal variations in storm track latitudes averaged over cold months (October–March) for the different parts of the North Atlantic. Thick dark blue lines and dashed red lines show 11-year running averages and the 5th-order polynomial approximation of storm track latitudes, respectively, at different longitudes λ in the North Atlantic.
The data in Figure 2 show that secular variations in cyclone tracks are most distinctly seen in the western part of the North Atlantic (from 60 to 40° W), where cyclones usually form and develop most intensively. In the eastern part of the North Atlantic, secular variations become less pronounced. They weaken noticeably in the region of Iceland (30–10° W) and disappear east of Greenwich (0–20° E), where processes of cyclone filling are intensified.
Figure 3 presents the results of a spectral analysis of storm track latitudes in the North Atlantic, which was performed using the method of a sampling estimate of the normalized spectral density [8]. The data in Figure 3 confirm that secular variations, with periods of ~80–90 years, do really predominate in the western part of the North Atlantic and weaken in its eastern part in the region of Iceland. East of Greenwich, secular variations disappear; in this region, oscillations with periods of ~50–60 years dominate. Let us note that storm track latitudes reveal bidecadal (~22–25 years) oscillations at all the studied longitudes of the North Atlantic. One can also note multidecadal (~40–45 years) oscillations, which seem to be the most pronounced in the region of Iceland (Figure 3b).
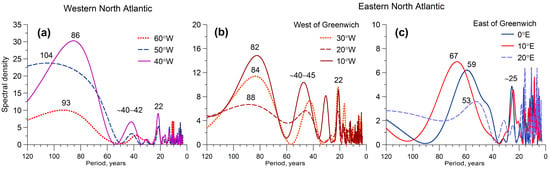
Figure 3.
Sampling estimates of the normalized spectral density of storm track latitudes in the western (a) and eastern (b,c) parts of the North Atlantic.
Thus, the above data show that cyclone track latitudes in the North Atlantic undergo oscillations with periods of ~80–90, ~40–45, and ~22 years, from which we suggest their possible association with variations in solar activity. Let us compare secular variations in cyclone trajectories with those in solar activity and related phenomena. Figure 4a presents long-term variations in storm track latitudes (11-year running averages) in the western North Atlantic, where they were found to be the most pronounced. Yearly values of sunspot numbers (SSN) (according to the new version [9]) are presented in Figure 4b. The maximal values of SSN in solar cycles are approximated by the fifth-order polynomial (red dashed line) to indicate secular variations in solar activity. Figure 4c shows detrended values of the concentration of the cosmogenic isotope 10Be in ice cores at the station Dye-3 in Greenland [10]. The 10Be is formed due to the interaction of cosmic rays with nuclei of atmospheric nitrogen and oxygen atoms, so its concentration in polar ice is used to characterize the intensity of galactic cosmic ray (GCR) fluxes in the past. GCRs are known to be strongly modulated by solar activity and penetrate deeply into the atmosphere, being the main ionization source at altitudes of 3–60 km [11]. Thus, GCRs are currently considered to be one of the most plausible agents transferring solar signals to the lower atmosphere (e.g., [12,13,14,15]).
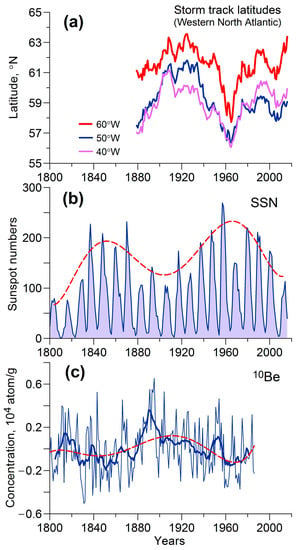
Figure 4.
(a) Long-term variations in storm track latitudes in the western North Atlantic (11-year running averages); (b) yearly values of sunspot numbers (SSN). The dashed line shows the 5th-order polynomial approximation of SSN values at maxima of the 11-year cycle; (c) concentration of the cosmogenic isotope 10Be in polar ice (after the linear trend removal). Thick blue and dashed red lines show 11-year running averages and the 5th-order polynomial approximation of the 10Be concentration, respectively.
Comparing the data in Figure 4, we can see that during the period of the secular Gleissberg cycle (~1900–1930), when the intensity of GCR fluxes was enhanced, cyclone trajectories in the western North Atlantic were noticeably shifted to the north. In the middle of the twentieth century (~1940–1960), when the maximum of the secular solar cycle took place accompanied by a decrease in GCR intensity, cyclone trajectories were shifted to the south. The peak-to-peak amplitude of the detected secular variations in storm track latitudes amounts to ~5°. Since roughly the 1960s, the descending phase of the secular solar cycle has been observed and, as we can see in Figure 4a, storm track latitudes in the western North Atlantic have been increasing again.
Thus, cyclone tracks in the North Atlantic were found to shift northward under a secular lowering of solar activity and southward under its enhancement. The detected secular variations in storm track latitudes are in good agreement with the data of Brown and John [3] and Tinsley [4], which revealed a southward shift of storm tracks in the North Atlantic at maxima of the 11-year cycle. The results obtained suggest a possible influence of solar activity and related phenomena on extratropical cyclone movement.
3.2. Variations in North Atlantic Cyclone Trajectories on the Bidecadal Timescale
As the data in Figure 3 show, the latitudes of North Atlantic storm tracks reveal noticeable variations on bidecadal and multidecadal timescales. To confirm the reliability of these periodicities, an additional spectral analysis of the high-frequency components (HFC) of the studied storm track latitudes was carried out. The HFC were calculated using the Blackman–Tukey high-frequency filter [16] with different “cut-off” frequencies, which correspond to the periods Tcut-off in the time domain. The estimates of the normalized spectral density were calculated for each HFC filtered with its own Tcut-off value and then they were superimposed on the same plot to form a composite spectral periodogram [17]. This method allows low-frequency components to be eliminated from the studied time series, as well as checking the stability of the revealed maxima of spectral density on the periodogram.
The results of the spectral analysis of high-frequency components of the storm track latitudes under study are presented in Figure 5. One can see that at all the studied longitudes in the North Atlantic, there are stable maxima of HFC spectral density at the periods ~22–25 years. The presented data confirm the reliability of bidecadal oscillations in the predominant trajectories of North Atlantic cyclones in the entire studied region. These oscillations are the most pronounced (dominating) at longitudes between 30 and 40° W and weaken to the east of Greenwich. One can also note that, along with secular and bidecadal variations, storm tracks in the eastern North Atlantic (longitudes 30–10° W) reveal multidecadal variations with periods of ~40–45 years.
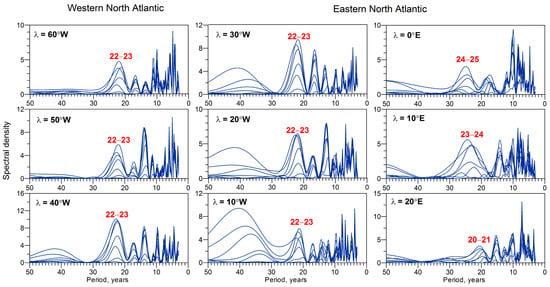
Figure 5.
Sampling estimates of the normalized spectral density of high-frequency components calculated with different cut-off parameters (Tcut-off = 7, 11, 17, 23, 29, 37, and 43 years) for storm track latitudes in different parts of the North Atlantic.
It should be noted that the detected bidecadal oscillations in storm track latitudes are close to the magnetic Hale cycle, which is observed in the magnetic polarity of both sunspots and the Sun’s polar fields (e.g., [18]). The Hale cycle consists of two consecutive 11-year cycles and lasts ~22 years, with sunspot polarity changing to the opposite at the beginning of a new cycle. Reversals of the overall magnetic field of the Sun take place near solar maxima; the polarity becomes positive in even solar cycles (according to the Zurich numbering) and negative in odd ones. To clarify what solar factors may be responsible for bidecadal oscillations of storm track latitudes, let us consider the behavior of cyclone tracks in even and odd solar cycles.
In Figure 6, the results of the superposed epoch analysis (SPEA) of variations in storm track latitudes are presented for seven even (12th to 24th) and six odd (13th to 23rd) solar cycles. The variations in storm track latitudes were obtained by subtracting secular variations (defined as the fifth-order polynomials) and then averaged over different parts of the North Atlantic. The key year is the year of the solar maximum. Red and blue lines show storm track variations when the key year is the maximum of even and odd cycles, respectively.
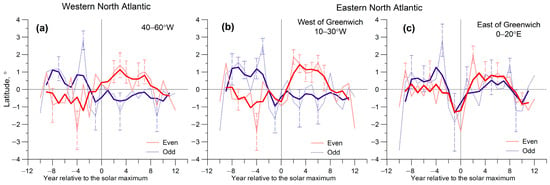
Figure 6.
Mean (SPEA) variations in storm track latitudes (after the subtraction of the 5th-order polynomial) in even and odd solar cycles for different parts of the North Atlantic: (a) 40–60° W; (b) 10–30° W; (c) 0–20° E. The year of the solar maximum is taken as a zero year for 7 even (12th to 24th) and 6 odd (13th to 23rd) solar cycles. Thick lines demonstrate 3-year running averages. Vertical dashed bars show two standard errors of the mean.
The results of the study show that variations in storm track latitudes reveal a different behavior in even and odd solar cycles, which is the most pronounced in the longitudinal range from 60° W to 0° E. In this region, trajectories of North Atlantic cyclones were found to shift noticeably (by ~1–2°) northward (relative to a secular variation) in even solar cycles, whereas in odd ones they shift insignificantly southward. The most pronounced northward shift of storm tracks in even cycles is observed in the eastern part of the North Atlantic (longitudes 10–30° W) during the descending phase and the minimum of the 11-year cycle. The deviations of cyclone tracks from secular variations noticeably exceed two standard errors of the mean in the 2nd, 3rd, and 6th years after the solar maximum. The statistical significance of the detected northward shifts of cyclone trajectories in the eastern North Atlantic (Figure 6b) was found to amount to 0.95 (2nd and 6th years) and 0.90 (3rd year) according to the modified Student’s t-test, taking into account the serial correlation in the studied time series. In the western North Atlantic (Figure 6a), the northward shift of cyclone tracks in even cycles is well pronounced, but less significant than in the eastern North Atlantic. East of Greenwich (Figure 6c), the difference between storm track variations in even and odd cycles weakens considerably.
Thus, the obtained results suggest a link of bidecadal oscillations in cyclone track latitudes with the magnetic Hale cycle on the Sun. A possible mechanism of such a link will be discussed later. Let us note that bidecadal oscillations are observed in many climatic parameters, such as drought rhythms [19], hurricane occurrence over the Atlantic and Pacific [20], summer temperatures in Northern Fennoscandia (NF) [21], etc. Recent evidence for 22-year variations in sea level pressure was obtained in [22]. It is noted (e.g., [23]), that bidecadal oscillations in climate characteristics have comparable or even larger amplitudes than decadal ones. In particular, the analysis of air temperatures in St. Petersburg/Leningrad [24] revealed stronger 22-year variations compared with 11-year ones, the correlation of them with geomagnetic activity being stressed. Summer temperatures in NF [21] revealed statistically significant bidecadal periodicities, but much weaker 11-year ones. The above data (Figure 3 and Figure 5) also show stronger bidecadal oscillations in storm track latitudes compared with those close to the 11-year cycle for most of the studied longitudes in the North Atlantic.
3.3. Amplitude Estimates of Storm Track Oscillations in the North Atlantic
To estimate the amplitude of the detected oscillations, we carried out an approximation of the studied storm track latitudes using the polyharmonic model [25], including the main quasi-periods found in the initial series. It was assumed that the initial signal (storm track latitudes at a given longitude) consists of polyharmonic and noise components and may be written as:
or
where is a constant, , and is a stationary random process (“white noise”), and ν and (k = 1, 2, 3, … ν) are the number and the value of quasi-periods, respectively. First, we determined the main quasi-periods and their number ν by constructing a composite spectral periodogram, as described above and in more detail in [17]. Then, the amplitudes and , the constant , and their confidence intervals were estimated by solving a redundant system of conditional linear equations using the least squares method [26,27].
Figure 7 shows the longitudinal variation in the obtained polyharmonic model parameters (the amplitudes and their standard deviations) for secular, multidecadal, and bidecadal oscillations. One can see that the amplitudes of secular variations (with periods varying from ~84 to ~104 years depending on a longitude) are the most pronounced in the western North Atlantic, the amplitudes reaching ~1.5° at the longitudes 40° W and 50° W. The amplitude of secular variations in this area noticeably exceeds those of bidecadal (~0.5–0.8°) and multidecadal (~0.5–0.6°) oscillations. In the eastern part of the North Atlantic (longitudes from 30 to 10° W), the amplitude of secular variations decreases to ~1°, whereas the amplitude of bidecadal (~21–22 years) and multidecadal (~40–45 years) oscillations increases, reaching ~1–1.2° at the longitude 10° W. In the most eastern North Atlantic (east of Greenwich), secular variations disappear, the amplitude of bidecadal oscillations decreases to 0.4–0.6°, and the amplitude of multidecadal (~50–60 years) oscillations is about 0.8–0.9°.
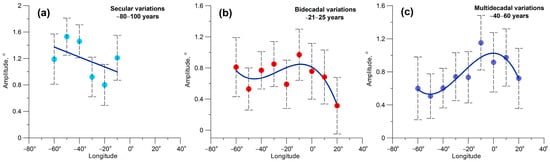
Figure 7.
Longitudinal dependence of the amplitudes for secular (a), bidecadal (b), and multidecadal (c) oscillations in storm track latitudes. The thick blue lines show the linear approximation (a) and polynomial approximation of the 3rd order (b,c). The dashed vertical bars show 2 standard deviations.
Thus, the estimates confirmed that secular variations in storm track latitudes are the strongest in the western part of the North Atlantic, which is the region of the most intensive cyclogenesis, with the amplitude reaching 1.5° (i.e., the peak-to-peak amplitude is ~3°, which agrees with the data in Figure 4), and decrease in the eastern part of the North Atlantic (the region, where cyclone destruction becomes frequent). Bidecadal variations in cyclone track latitudes are most pronounced west of Greenwich, with the amplitude increasing from west to east and reaching maximal values ~1° (the peak-to-peak amplitude ~2°) in the eastern North Atlantic at the longitude 10° W. Then, the bidecadal oscillations sharply weaken east of Greenwich. On the multidecadal timescale, oscillations with periods of ~40–45 years are observed west of Greenwich, strengthening up to ~1° in the eastern North Atlantic. East of Greenwich, both secular and multidecadal (~40–45 years) oscillations vanish, but oscillations with periods ~50–60 years appear, the maximal amplitude being ~0.9°. Thus, the above data show that the farther northeast cyclone trajectories pass, the weaker the secular variations and the stronger the bidecadal and multidecadal ones are, reaching maxima near Greenwich. This may suggest the influence of different solar activity agents influencing cyclone movement in different regions.
4. Discussion of the Results
This study revealed that the latitudinal position of the predominant trajectories of North Atlantic cyclones undergoes long-term variations with periods of ~80–90, ~40–45 and ~22–25 years, which are close to those observed in solar activity. A secular Gleissberg cycle is manifested in variations in the amplitude of the 11-year sunspot cycle (Figure 4b). Another important characteristic of solar activity is a roughly 22-year (Hale) cycle observed in the polarity of the Sun’s magnetic field (e.g., [18]). Multidecadal variations with periods of ~40–45 years were detected in the north–south asymmetry of sunspot activity on the Sun [28]. In [29], multidecadal oscillations were revealed in the sunspot cycle length, the 42-year harmonic being the second largest after the 80-year one in the power spectrum. Thus, the revealed periodicities in cyclone track latitudes suggest a possible influence of solar cyclicity on the development of cyclonic processes at extratropical latitudes.
Let us consider possible reasons for the detected variations in cyclone trajectories. It is known that extratropical cyclones usually move along isohypses of the 500 hPa level in the zone of maximal temperature contrasts (e.g., [1,7]). So, their movement is closely related to the position of the polar jet stream, which is a narrow band of strong winds (>30 m/s) in the middle and upper troposphere. The position of the polar jet stream is influenced by the stratospheric polar vortex, which is a large-scale cyclonic circulation forming above the 500 hPa level and spanning the entire stratosphere of the polar region in the cold half of the year. Under a strong vortex, the polar jet strengthens and shifts poleward, resulting in a poleward shift of storm tracks in the troposphere, whereas under a weak vortex, the polar jet weakens, meanders, and shifts towards the equator (e.g., [30]). Thus, oscillations in storm track latitudes in the North Atlantic detected on bidecadal, multidecadal, and secular timescales provide evidence for similar oscillations in intensity of the stratospheric polar vortex and the polar jet position. The polar vortex seems to be strengthened at the minimum of the secular Gleissberg cycle and weakened at the maximum of this cycle, which results in the shift of North Atlantic storm tracks to the north and south, respectively. On a bidecadal timescale, the polar vortex seems to be enhanced in even solar cycles, contributing to the northward shift of cyclone trajectories.
What agents related to solar activity may be responsible for the variations in the polar vortex strength? It was noted [31] that the area of the polar vortex formation creates favorable conditions for influences of different kinds of energetic charged particles (solar and galactic cosmic rays, auroral and radiation belt electrons). Due to low values of geomagnetic cutoff rigidity Rc < 2–3 GV, this area is accessible for galactic cosmic ray particles in a wide energy range, including their low energy component, strongly modulated by solar activity. GCRs are the main ionization source at altitudes of ~3–60 km and undergo variations on different timescales [11]. According to the reconstruction in [32], variations in GCR fluxes with energies >0.1 GeV in a secular solar cycle may amount to about ±15–20% relative to the trend values. Secular variations in GCR fluxes are clearly manifested in the concentration of the cosmogenic isotope 10Be in polar ice (Figure 4c).
On the bidecadal timescale, GCRs reveal variations associated with the changes in the polarity of the Sun’s overall magnetic field [33,34]. Figure 8a shows cosmic particle fluxes in the stratosphere at the mid-latitudinal station Dolgoprudny in Moscow region (geomagnetic cutoff rigidity Rc = 2.4 GV) according to the data from balloon measurements [35]. One can see that GCR intensity is characterized by the alternation of peaked and flat (dome-shaped) maxima depending on the sign of the overall magnetic field of the Sun. When the polarity is positive (A > 0), i.e., magnetic field lines come out from the north pole and enter the south one, an increase in cosmic ray fluxes after the solar maximum starts earlier compared with that under the negative polarity, which results in a dome-shaped peak in GCR intensity [33]. The polarity reversal occurs at or just after the sunspot maximum: in even (odd) cycles the polarity becomes positive (negative).
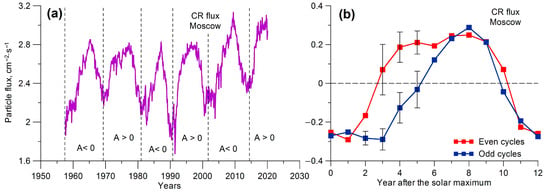
Figure 8.
(a) Monthly values of cosmic ray fluxes in the stratosphere at the station Dolgoprudny (Moscow region, Rc = 2.4 GV) at middle latitudes. Vertical dashed lines show approximate periods of the reversals of the overall magnetic field polarity on the Sun. (b) Mean (SPEA) variations in yearly values (detrended) of cosmic ray fluxes in the stratosphere at the station Dolgoprudny for even and odd solar cycles. The year of the solar maximum is taken as a zero year. Vertical bars show two standard errors of the mean.
Figure 8b presents yearly values of cosmic ray fluxes, the linear trend being removed, at the station Dolgoprudny, which were averaged over three even (20th to 24th) solar cycles and three odd (19th to 23rd) ones. One can see a noticeable difference between GCR fluxes in the stratosphere in even and odd solar cycles, which is observed during the descending branch of the cycle (from 2nd to 6th year). Comparing with the data in Figure 6, we can note that the most pronounced northward shift of storm tracks in even cycles takes place when the GCR influx is significantly increased compared with that in odd cycles. The bidecadal oscillations of GCR intensity are confirmed by the results of the spectral analysis of the 10Be concentration in Greenland polar ice according to the data in [10]. Figure 9 shows stable maxima of the spectral density of the 10Be concentration at periods ~22–23 years both for the initial time series and the high-frequency components.
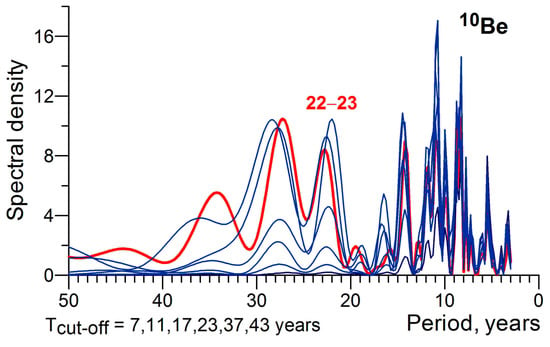
Figure 9.
Sampling estimate of the normalized spectral density of the concentration of the cosmogenic isotope 10Be in Greenland ice cores for the initial series (red line) and the high-frequency components with different cut-off parameters (blue lines).
The data presented above show that northward shifts of North Atlantic cyclone tracks, which indicate a strengthening of the stratospheric polar vortex, take place under the enhanced intensity of GCRs which is observed at the minimum of the secular Gleissberg cycle and during the descending branch of even solar cycles. At the secular maximum, as well as during the descending branch of odd cycles, when the GCR influx in the atmosphere is lower, the polar vortex seems to weaken and cyclone trajectories shift to the south. This suggests an important role of GCR variations in the formation of both secular and bidecadal oscillations of cyclone track latitudes.
Let us consider possible mechanisms of the polar vortex strengthening under an increase in GCR intensity. One of the mechanisms involves changes in the chemical composition of the polar atmosphere which influence its temperature regime. An increase in the ionization rate contributes to additional production of odd nitrogen (NOx = N+ NO + NO2) and odd hydrogen (HOx = H + OH + HO2) species (e.g., [36,37]), which are known to catalytically destroy ozone [38]. So, an enhanced production of these minor compounds can contribute to a decrease in ozone content in the polar stratosphere. In turn, ozone is a radiatively active gas participating in a heating of the atmosphere. It can influence significantly not only shortwave, but also longwave radiation fluxes. Under sunlight conditions, ozone absorbs ultraviolet radiation in a broad Hartley band (~200–320 nm). At the same time, it is also an efficient greenhouse gas due to a number of vibrational–rotational bands in the infrared range, with the 9.6 μm band being the strongest [38]. Thus, under polar night conditions, ozone absorbs the outgoing longwave radiation emitted by the Earth and the atmosphere, which contributes to the stratospheric heating. This suggests that ozone depletion associated with ionization increases due to cosmic ray variations may result in a cooling of the stratosphere. This cooling can contribute to an increase in temperature contrasts between polar and middle latitudes and, then, to the intensification of the polar vortex. A possibility of this mechanism is confirmed by model studies [39], showing an intensification of the polar vortex due to a combined effect of different kinds of energetic charged particles, including galactic and solar cosmic rays, on ozone content. The intensification of the polar vortex, which was revealed during major solar proton events of January 2005 and December 2006, as well as a number of events with particle energies above 100 MeV [40,41], also confirms a possible influence of ionization changes due to cosmic ray variations on the middle atmosphere dynamics at high latitudes.
Another possible mechanism may involve effects of GCR-related ionization changes on electric characteristics of the atmosphere, which, in turn, influence cloud formation. According to the mechanism suggested by Tinsley [42], an ionization increase due to a GCR flux increase enhances atmospheric conductivity, affecting the density of vertical electric currents which flow from the ionosphere to the Earth’s surface. Electric currents, when flowing through a low-conducting cloud layer, contribute to space charge accumulation on its edges and, then, to the intensification of microphysical processes, in particular, collection of aerosols by cloud droplets (electro-scavenging), which results in more intensive cloud formation. GCRs’ influence on cloud processes seems to be confirmed by the data in [43,44,45], showing a correlation between GCR intensity and cloud cover.
In turn, cloudiness is known to be the main regulator of radiative processes in the atmosphere, influencing significantly the thermal regime of the Earth–atmosphere system. Clouds decrease both the incoming shortwave solar radiation and the outgoing longwave radiation of the Earth and the atmosphere, with the net effect depending on the latitude, season, cloud type, and surface character. At high latitudes in winter, when the incoming solar radiation is reduced, clouds regulate mainly longwave fluxes, contributing to a warming in the underlying atmospheric layer and a cooling above the clouds. Thus, an enhancement in cloud cover in association with an increase in GCR intensity may contribute to changes in the temperature regime both of the troposphere and upper levels, influencing the polar jet stream’s position. In particular, radiative forcing of cloud cover changes may contribute to an increase in temperature contrasts in the region near the southeastern Greenland coast where cyclones usually travel. Indeed, this region is characterized by a noticeable difference in outgoing radiation fluxes over the icy Greenland surface and the warmer ocean surface, which, according to climatological data in [46] amount to ~140–150 W·m−2 and ~180–200 W·m−2, respectively, in cold months. So, a warming effect of GCR-related variations in cloud cover may be stronger over the ocean, which can increase temperature contrasts in this region and, thus, the polar jet stream characteristics. According to [47], temperature contrasts in the layer 1000–500 hPa near the southeastern coast of Greenland (longitudes 30 and 40° W) do really reveal ~22-year oscillations, the temperature contrasts increasing in even cycles and lowering in odd ones. The mechanism involving GCRs’ influence on cloud cover and the related radiative thermal balance via variations in the density of electric currents seems to be more efficient in autumn months when the polar vortex just starts to form and is not well developed. The effects of electric currents on cirrus cloud formation and longwave radiation fluxes at polar latitudes were detected in [48,49].
Geomagnetic activity and related electron precipitation is another possible agent which may influence the chemical composition and the radiative thermal balance of the middle atmosphere. Precipitations of auroral electrons (1–30 keV) contribute to the production of odd hydrogen HOx and odd nitrogen NOx families at lower thermosphere altitudes. Unlike hydrogen oxides, nitrogen oxides are long-lived under polar night conditions, so they can be transported downward to stratospheric altitudes and participate in ozone destruction. Model studies [50] showed that ozone depletion in winter months associated with auroral precipitations may reach 20% in the upper stratosphere, contributing to a temperature lowering by 3–4 K and an increase in the NAM (Northern Annular Mode) index, characterizing the polar vortex intensity.
Geomagnetic activity is known to intensify during the descending branch of the solar cycle due to enhancement in the activity of coronal holes, which are sources of high-speed streams of solar wind [51]. As Figure 6 shows, at this stage, maximum deviations of cyclone tracks from a secular variation are observed, which suggests a possible contribution of geomagnetic activity. Cliver and colleagues [52] revealed ~22-year variations in geomagnetic activity based on the aa-index [53]. According to their data, geomagnetic activity differs in even and odd solar cycles, which is manifested in higher activity during the second half of even cycles, whereas in odd cycles the peak of activity is observed during the first half. The results of a spectral analysis of yearly values of the geomagnetic aa-index presented in Figure 10a reveal bidecadal, as well as multidecadal, oscillations. Thus, we can suggest that geomagnetic activity may be an additional factor which contributes to the intensification of the polar vortex and the northward shift of cyclone tracks during the declining phase and the minimum of even solar cycles. Indeed, cyclone paths in the North Atlantic coincide rather well with the auroral zone, which is an area of maximum occurrence of auroras produced by precipitation of magnetospheric electrons. In the North Atlantic, the auroral zone is known to pass through the Arctic coasts of North America, the southern part of Greenland, the region of Iceland, and Northern Scandinavia.
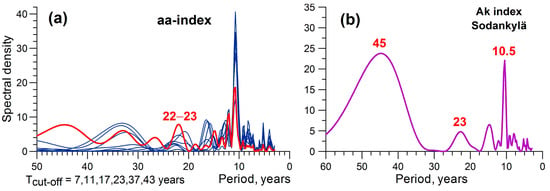
Figure 10.
Sampling estimate of the normalized spectral density of: (a) geomagnetic aa-index (yearly values) for the initial series (red line) and high-frequency components with different cut-off parameters (blue lines); (b) geomagnetic Ak-index (yearly values) at the station Sodankylä (Φ = 64.1°).
One should also note multidecadal oscillations in geomagnetic activity. Figure 10b presents the results of a spectral analysis of the local geomagnetic Ak-index at the high-latitudinal station Sodankylä (geomagnetic latitude Φ = 64.1°), the data being available since 1914. One can see pronounced variations with periods of about 40–45 years close to those revealed in storm track latitudes in the eastern North Atlantic (Figure 5). This also confirms a possible role of geomagnetic activity and related electron precipitations in variations in the polar vortex intensity and corresponding changes in storm tracks.
One should also note a possible influence of other factors of solar activity on the temperature field of the lower atmosphere and variations in cyclone tracks. On a secular timescale, variations in total solar irradiance (TSI) associated with solar activity may be of significant importance for the Earth’s climatic system (e.g., [54]). Wavelet and Fourier analysis applied to the TSI according to the reconstruction in [55] revealed both secular (~80 years) and mutidecadal (~50–60 years) variations [56]. This suggests a possible influence of long-term variations in TSI on the formation of cyclone trajectories, with processes in the ocean–atmosphere system being involved. The TSI contribution may be most significant in the western part of the North Atlantic, where high temperature contrasts between continental and ocean surfaces are observed, contributing to cyclone formation and development.
Thus, the study revealed long-term oscillations in storm track latitudes in the North Atlantic on timescales from bidecadal to secular, with oscillation periods of ~80–100, ~40–45 and, ~22 years, close to those observed in different solar characteristics. This suggests the influence of the Sun’s cyclicity on cyclonic activity, which, in turn, significantly influences weather and climate at extratropical latitudes. The detected variations in cyclone trajectories provide evidence for changes in the strength of the stratospheric polar vortex, which seems to be an important link between processes on the Sun and circulation in the lower atmosphere [31]. The physical mechanism of the oscillations in the polar vortex intensity, which are close to the main periodicities observed on the Sun, is not clear and needs further study. However, we can suggest that a possible reason for the intensification of the polar vortex may be enhancements in the ionization rate in the polar atmosphere associated with variations in energetic charged particles, in particular, galactic cosmic rays and auroral electrons, on different timescales. Ionization increases result in changes in the chemical composition (ozone depletion) of the polar atmosphere, as well as the density of vertical electric currents, influencing cloud formation. In turn, changes in ozone content and cloud properties may influence the radiative thermal balance in the high-latitudinal atmosphere, resulting in temperature changes and related changes in the polar vortex strength and the position of the polar jet stream. On a secular timescale, an important part in the formation of storm track oscillations may be played by long-term variations of total solar irradiance. Thus, the detected variations in cyclone trajectories seem to be caused by a combined effect of different factors associated with solar cyclicity on different timescales, and further studies are needed to clarify the contribution of each factor.
5. Conclusions
The results of this study showed the following.
The mean latitudes of North Atlantic storm tracks in the cold months (October–March) reveal oscillations on secular and bidecadal timescales, with the periods being of ~80–100 and ~22 years, which suggests their possible association with the solar cycles of Gleissberg and Hale, respectively.
On a secular timescale, cyclone trajectories lay further north at the minimum of the Gleissberg cycle (~1900–1930) and further south at its maximum (~1940–1960). During the current descending branch of the Gleissberg cycle, cyclone trajectories have been shifting northward again. Secular variations in storm track latitudes were found to be most pronounced west of Greenwich, the peak-to-peak amplitude reaching ~3–5° in the western part of the North Atlantic, and to disappear east of Greenwich.
On a bidecadal timescale, a northward shift in cyclone trajectories was found during the descending branch and the minimum of even-numbered solar cycles, the effect being the most significant (peak-to-peak amplitude ~2°) in the eastern part of the North Atlantic. Multidecadal oscillations in cyclone tracks were found in the eastern North Atlantic, with the periods being ~40–45 years west of Greenwich and ~50–60 years east of Greenwich.
A possible reason for the detected oscillations in cyclone tracks is long-term changes in the intensity of the stratospheric polar vortex influencing the position of the polar jet stream. The obtained results suggest oscillations in the polar vortex intensity from bidecadal to secular, which may be caused by ionization changes in the polar atmosphere due to variations in fluxes of energetic charged particles (galactic cosmic rays and auroral electrons). A possible mechanism of the vortex intensification may involve changes in chemical composition and cloudiness state influencing the temperature regime of the polar atmosphere.
Author Contributions
S.V.: conceptualization, data preparation and analysis, writing—original draft preparation; P.D.: data analysis, writing—review and editing. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
MSLP data were provided by the Climatic Research Unit, University of East Anglia, UK, at https://crudata.uea.ac.uk/cru/data/pressure (last accessed on 8 August 2004) and NOAA/OAR/ESLR PSL, Boulder, Colorado, USA https://psl.noaa.gov/data/gridded/data.ncep.reanalysis2.surface.html (last accessed on 26 January 2022). Sunspot numbers were taken from World Data Center WDC-SILSO, Royal Observatory of Belgium at http://www.sidc.be/silso/datafiles (last accessed on 16 May 2018). Cosmic ray fluxes in the stratosphere were provided by Lebedev Physical Institute, Moscow, Russia, at https://sites.lebedev.ru/ru/sites/DNS_FIAN.html (last accessed on 30 March 2022). Geomagnetic aa-indices were taken from World Data Center for Solar-Terrestrial Physics, Moscow, Russia, http://www.wdcb.ru/stp/geomag/geomagn_aa_Aa_ind.html (last accessed on 16 February 2022). Geomagnetic Ak indices were obtained from Sodankylä geophysical observatory, Finland, at https://www.sgo.fi/Data/Magnetometer/magnData.php (last accessed on 2 June 2023).
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to anonymous referees for evaluating the article and providing helpful comments.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Vorobjev, V.I. Synoptic Meteorology; Gidrometeoizdat: Leningrad, Russia, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Dietze, M.; Bell, R.; Ozturk, U.; Cook, K.L.; Andermann, C.; Beer, A.R.; Damm, B.; Lucia, A.; Fauer, F.S.; Nissen, K.M.; et al. More than heavy rain turning into fast-flowing water—A landscape perspective on the 2021 Eifel floods. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2022, 22, 1845–1856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, G.M.; John, J.I. Solar cycle influences on tropospheric circulation. J. Atmos. Terr. Phys. 1979, 41, 42–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tinsley, B.A. The solar cycle and the QBO influences on the latitude of storm tracks in the North Atlantic. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1988, 15, 409–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luterbacher, J.; Rickli, R.; Xoplaki, E.; Tinguely, C.; Beck, C.; Pfister, C.; Wanner, H. The late Maunder Minimum (1675–1715)—A key period for studying decadal scale climatic change in Europe. Clim. Chang. 2001, 49, 441–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raible, C.C.; Yoshimori, M.; Stocker, T.F.; Casty, C. Extreme midlatitude cyclones and their implications for precipitation and wind speed extremes in simulations of the Maunder Minimum versus present day conditions. Climate Dyn. 2007, 28, 409–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pogosyan, K.P. General Circulation of the Atmosphere; Gidrometeoizdat: Leningrad, Russia, 1972. [Google Scholar]
- Jenkins, G.; Watts, D. Spectral Analysis and Its Application; Holden-Day: San Francisco, CA, USA, 1968. [Google Scholar]
- Clette, F.; Lefevre, L. The new Sunspot Number: Assembling all corrections. Sol. Phys. 2016, 29, 2629–2651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beer, J.; Blinov, A.; Bonani, G.; Finkel, R.C.; Hofmann, H.J.; Lehmann, B.; Oeschger, H.; Sigg, A.; Schwander, J.; Staffelbach, T.; et al. Use of 10Be in polar ice to trace the 11-year cycle of solar activity. Nature 1990, 347, 164–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazilevskaya, G.A.; Usoskin, I.G.; Flückiger, E.O.; Harrison, R.G.; Desorgher, L.; Bütikofer, R.; Krainev, M.B.; Makhmutov, V.S.; Stozhkov, Y.I.; Svirzhevskaya, A.K.; et al. Cosmic Ray Induced Ion Production in the Atmosphere. Space Sci. Rev. 2008, 137, 149–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ney, E.P. Cosmic radiation and weather. Nature 1959, 183, 451–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pudovkin, M.I.; Veretenenko, S.V. Variations of the cosmic rays as one of the possible links between the solar activity and the lower atmosphere. Adv. Space Res. 1996, 17, 161–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tinsley, B.A.; Brown, G.M.; Scherrer, P.H. Solar variability influences on weather and climate: Possible connection through cosmic ray fluxes and storm intensification. J. Geophys. Res. 1989, 94, 14783–14792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svensmark, H. Cosmic rays and Earth’s climate. Space Sci. Rev. 2000, 93, 175–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alavi, A.S.; Jenkins, G.M. An example of digital filtering. Appl. Stat. 1965, 14, 70–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dmitriev, P.B.; Kudryavtsev, I.V.; Lazunkov, V.P.; Matveev, G.A.; Savchenko, M.I.; Skorodumov, D.V.; Charikov, Y.E. Solar flares registered by the “IRIS” spectrometer onboard the Coronas-F satellite: Peculiarities of the X-ray emission. Sol. Syst. Res. 2006, 2, 142–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hathaway, D.H. The Solar Cycle. Living Rev. Sol. Phys. 2015, 12, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, E.R.; Meko, D.M.; Stockton, C.W. A new assessment of possible solar and lunar forcing of bidecadal drought rhythm in the western United States. J. Climate 1997, 10, 1343–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendoza, B.; Pazos, M. A 22yr hurricane cycle and its relation with geomagnetic activity. J. Atmos. Sol.-Terr. Phys. 2009, 71, 2047–2054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogurtsov, M.; Veretenenko, S.V.; Helama, S.; Jalkanen, R.; Lindholm, M. Assessing the signals of the Hale solar cycle in temperature proxy records from Northern Fennoscandia. Adv. Space Res. 2020, 66, 2113–2121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, F.; Courtillot, V.; Le Mouël, J.-L. Triskeles and Symmetries of Mean Global Sea-Level Pressure. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raspopov, O.M.; Dergachev, V.A.; Kolström, T. Hale cyclicity of solar activity and its relation to climate variability. Sol. Phys. 2004, 224, 445–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pudovkin, M.I.; Lyubchich, A.A. Manifestation of solar and magnetic activity cycles in air temperature variations in Leningrad. Geomagn. Aeron. 1989, 29, 326–329. [Google Scholar]
- Serebrennikov, M.T.; Pervosvansky, A.A. Hidden Periodicity Determination; Nauka: Moscow, Russia, 1965. [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton, W. Statistics in Physical Science; Ronald Press: New York, NY, USA, 1964. [Google Scholar]
- Agekyan, T.A. Fundamentals of the Error Theory for Astronomers and Physicists; Nauka: Moscow, Russia, 1972. [Google Scholar]
- Obridko, V.N.; Nagovitsyn, Y.A. Solar Activity, Cyclicity and Prediction Methods; VVM: St. Petersburg, Russia, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Jelbring, H. Analysis of sunspot cycle phase variations—Based on D. Justin-Schove’s proxy data. J. Coast. Res. 1995, 17, 363–369. [Google Scholar]
- Kidston, J.; Scaife, A.A.; Hardiman, S.C.; Mitchell, D.M.; Butchart, N.; Baldwin, M.P.; Gray, L.J. Stratospheric influence on tropospheric jet streams, storm tracks and surface weather. Nat. Geosci. 2015, 8, 433–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veretenenko, S. Stratospheric polar vortex as an important link between the lower atmosphere circulation and solar activity. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stozhkov, Y.I.; Okhlopkov, V.P.; Svirzhevsky, N.S. Cosmic ray fluxes in present and past times. Sol. Phys. 2004, 224, 323–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, S.R.; Owens, M.J.; Lockwood, M. The 22-year Hale cycle in cosmic ray flux—Evidence for direct heliospheric modulation. Sol. Phys. 2014, 289, 407–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stozhkov, Y.I.; Makhmutov, V.S.; Bazilevskaya, G.A.; Svirzhevsky, N.S.; Svirzhevskaya, A.K.; Philippov, M.V. Modulation effects in cosmic rays during a period of anomalously low solar activityl. Bull. Russ. Acad. Sci. Phys. 2021, 85, 1049–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stozhkov, Y.I.; Svirzhevsky, N.S.; Bazilevskaya, G.A.; Kvashnin, A.N.; Makhmutov, V.S.; Svirzhevskaya, A.K. Long-term (50 years) measurements of cosmic ray fluxes in the atmosphere. Adv. Space Res. 2009, 44, 1124–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rusch, D.W.; Gerard, J.-C.; Solomon, S.; Crutzen, P.J.; Reid, G.C. The effect of particle precipitation events on the neutral and ion chemistry of the middle atmosphere I. Odd nitrogen. Planet. Space Sci. 1981, 29, 767–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solomon, S.; Rusch, D.W.; Gerard, J.-C.; Reid, G.C.; Crutzen, P.J. The effect of particle precipitation events on the neutral and ion chemistry of the middle atmosphere: II. Odd hydrogen. Planet. Space Sci. 1981, 29, 885–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brasseur, G.P.; Solomon, S. Aeronomy of the Middle Atmosphere; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Rozanov, E.; Calisto, M.; Egorova, T.; Peter, T.; Schmutz, W. Influence of the precipitating energetic particles on atmospheric chemistry and climate. Surv. Geophys. 2012, 33, 483–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veretenenko, S. Effects of Solar Proton Events of January 2005 on the middle atmosphere dynamics in the Northern hemisphere. Adv. Space Res. 2021, 68, 1814–1824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veretenenko, S.V. Effects of energetic Solar Proton Events of solar cycle 23 on intensity of the stratospheric polar vortex. Geomagn. Aeron. 2021, 61, 985–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tinsley, B.A. The global atmospheric electric circuit and its effects on cloud microphysics. Rep. Progr. Phys. 2008, 71, 66801–66900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pudovkin, M.I.; Veretenenko, S.V. Cloudiness decreases associated with Forbush-decreases of galactic cosmic rays. J. Atmos. Terr. Phys. 1995, 57, 1349–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svensmark, J.; Enghoff, M.B.; Shaviv, N.J.; Svensmark, H. The response of clouds and aerosols to cosmic ray decreases. J. Geophys. Res. 2016, 121, 8152–8181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, H.; Svensmark, H.; Enghoff, M.B. Effects of Forbush decreases on clouds determined from PATMOS-x. J. Atmos. Sol.–Terr. Phys. 2022, 230, 105845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NOAA PSL. Available online: htpps://psl.noaa.gov/data/gridded/data.olrcdr.interp/html (accessed on 25 January 2023).
- Veretenenko, S.V.; Dergachev, V.A.; Dmitriyev, P.B. Solar rhythms in the characteristics of the Arctic frontal zone in the North Atlantic. Adv. Space Res. 2010, 45, 391–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frederick, J.E.; Tinsley, B.A. The response of longwave radiation at the South Pole to electrical and magnetic variations: Links to meteorological generators and the solar wind. J. Atmos. Sol.-Terr. Phys. 2018, 179, 214–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frederick, J.E.; Tinsley, B.A.; Zhou, L. Relationships between the solar wind magnetic field and ground-level longwave irradiance at high northern latitudes. J. Atmos. Sol.-Terr. Phys. 2019, 193, 105063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumgaertner, A.J.G.; Seppälä, A.; Jöckel, P.; Clilverd, M.A. Geomagnetic activity related NOx enhancements and polar surface air temperature variability in a chemistry climate model: Modulation of the NAM index. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2011, 11, 4521–4531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsurutani, B.T.; Gonzalez, W.D.; Gonzalez, A.L.C.; Guarnieri, F.L.; Gopalswamy, N.; Grande, M.; Kamide, Y.; Kasahara, Y.; Lu, G.; Mann, I.; et al. Corotating solar wind streams and recurrent geomagnetic activity: A review. J. Geophys. Res. 2006, 111, A07S01. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cliver, E.V.; Boriakoff, V.; Bounar, K.H. The 22-year cycle of geomagnetic and solar wind activity. J. Geophys. Res. 1996, 101, 27091–27109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayaud, P.N. The aa indices: A 100 year series characterizing the magnetic activity. J. Geophys. Res. 1972, 77, 6870–6874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, L.J.; Beer, J.; Geller, M.; Haigh, J.D.; Lockwood, M.; Matthes, K.; Cubasch, U.; Fleitmann, D.; Harrison, G.; Hood, L.; et al. Solar influences on climate. Rev. Geophys. 2010, 48, RG4001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scafetta, N.; Willson, R.C. ACRIM total solar irradiance satellite composite validation versus TSI proxy models. Astrophys. Space Sci. 2014, 350, 421–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veretenenko, S.; Ogurtsov, M. Manifestation and possible reasons of ~60-year oscillations in solar-atmospheric links. Adv. Space Res. 2019, 64, 104–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).