Hour-by-Hour Prediction Model of Air Pollutant Concentration Based on EIDW-Informer—A Case Study of Taiyuan
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Background
1.2. Literature Review
1.3. Our Contribution
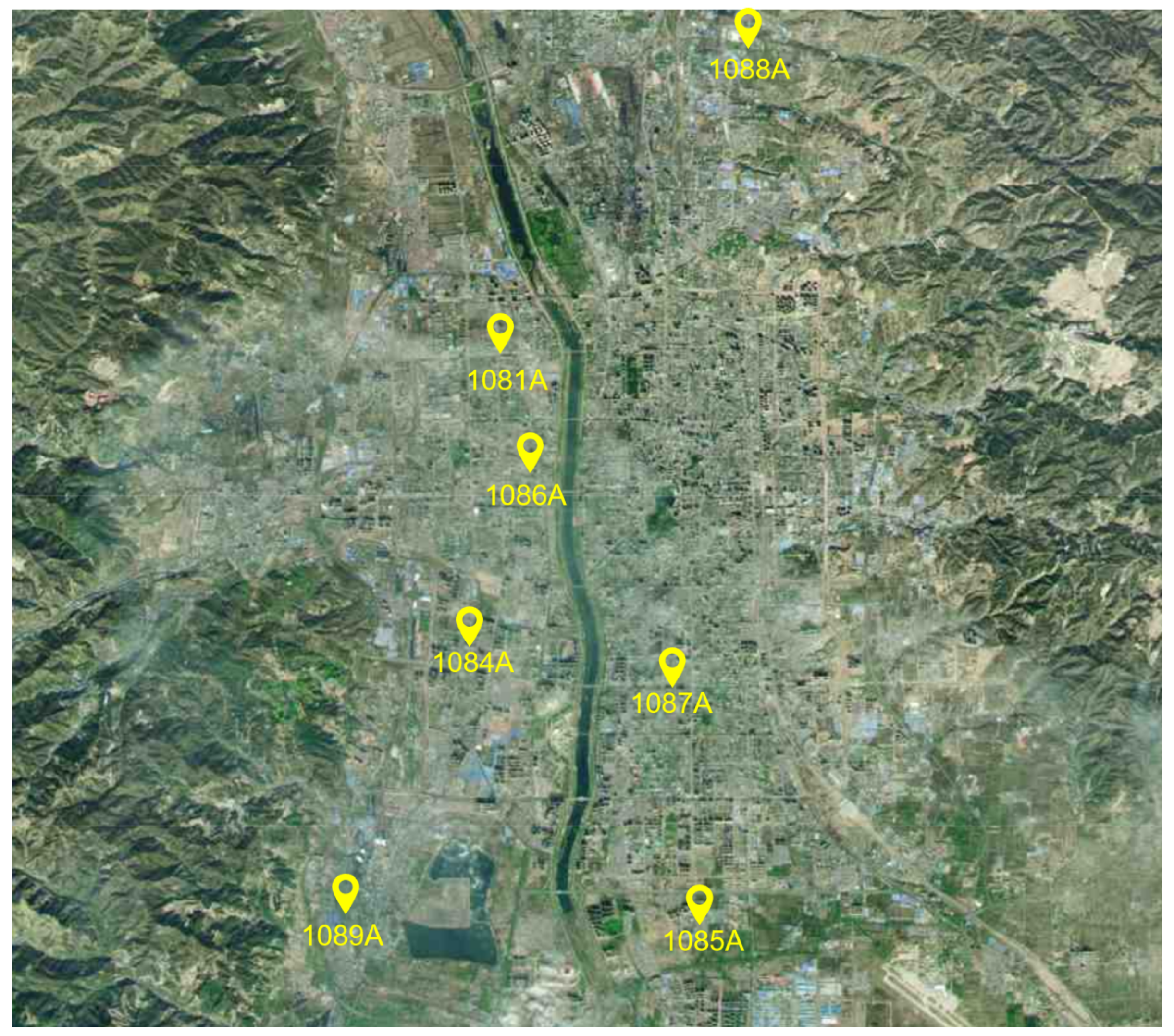
- For the first time, the environmental similarity and inverse distance weighted interpolation methods were combined to create a multi-dimensional environmental vector of historical air pollutant concentration data and meteorological data from seven environmental monitoring stations in the urban area of Taiyuan City, from which the environmental similarity between sample points was calculated, and then the missing data in the dataset were interpolated according to the combined weight of the environmental similarity and relative distance of each sample point, in order to solve the missing data problem faced in air quality prediction.
- In this study, a Transformer-based Informer model was selected to solve the problem of air quality prediction. Compared with the original model, the prediction effect of the EIDW-Informer model increased by 20%, 27%, and 43% in three time scales of 1 h, 8 h, and 72 h, respectively, and the model achieved a good balance in terms of training cost and prediction effect.
1.4. Dataset
2. EIDW Method
2.1. Interpolation Methods
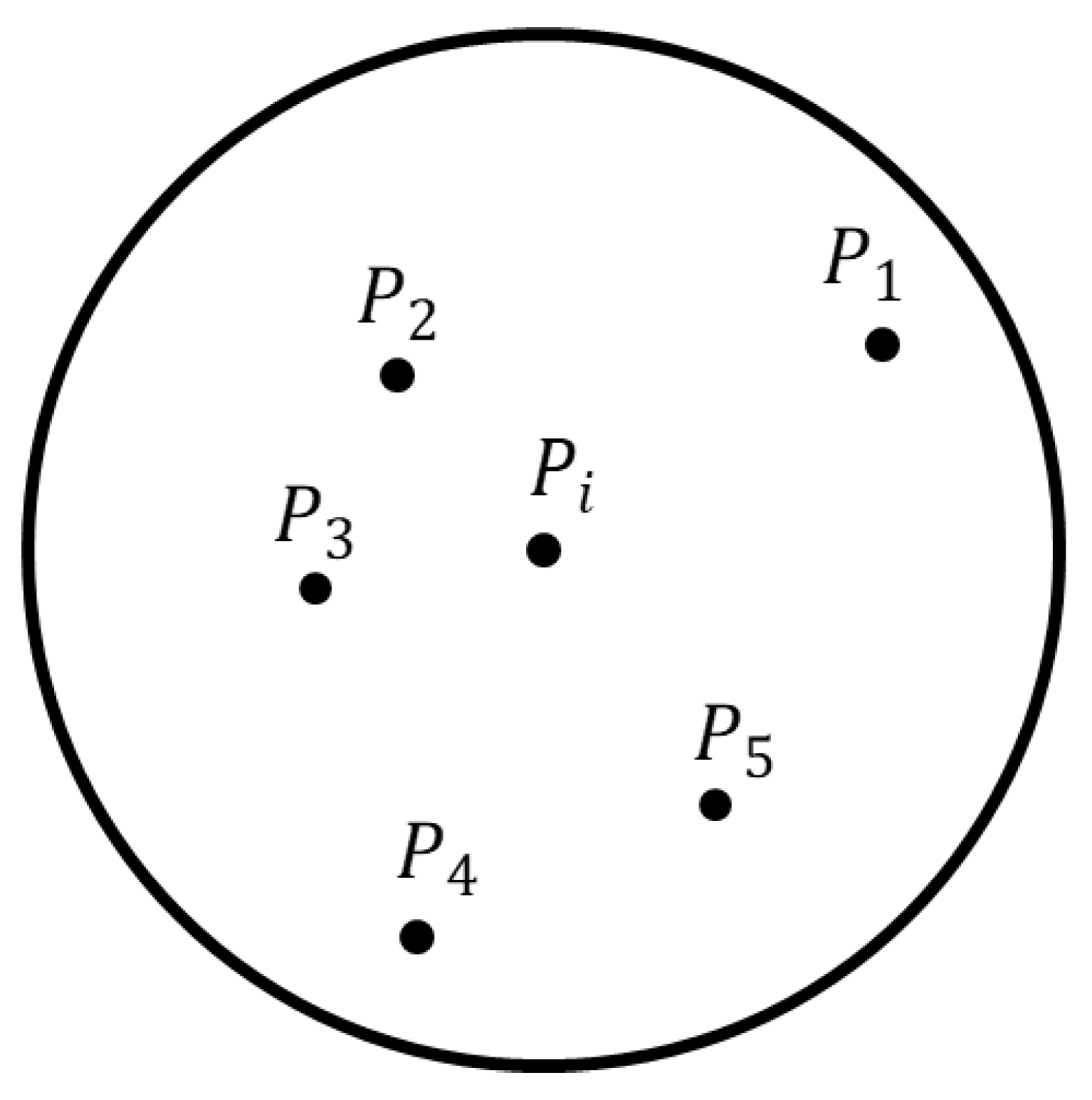
2.2. Environmental Similarity
2.3. Interpolation Method Verification
2.3.1. Correlation Analysis
2.3.2. Evaluation Indicators
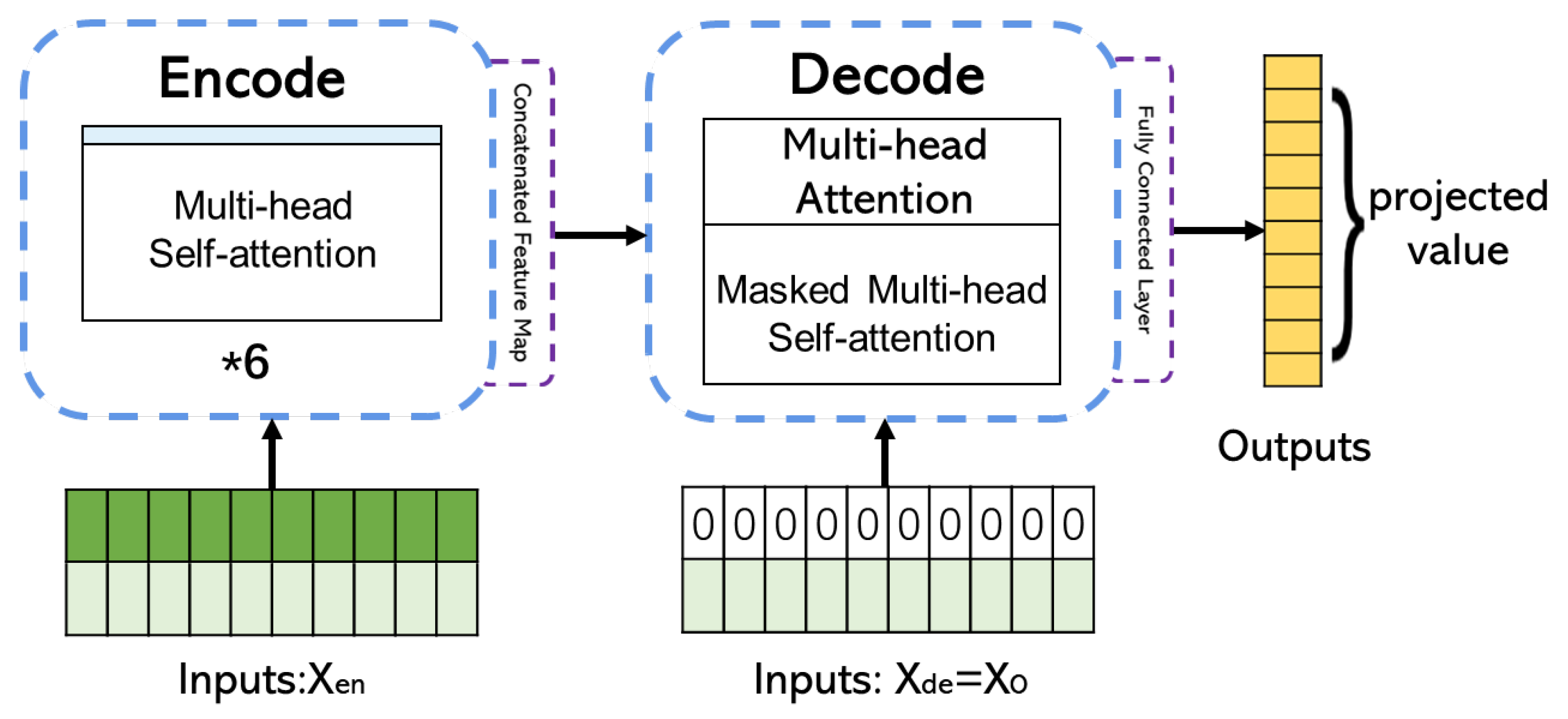
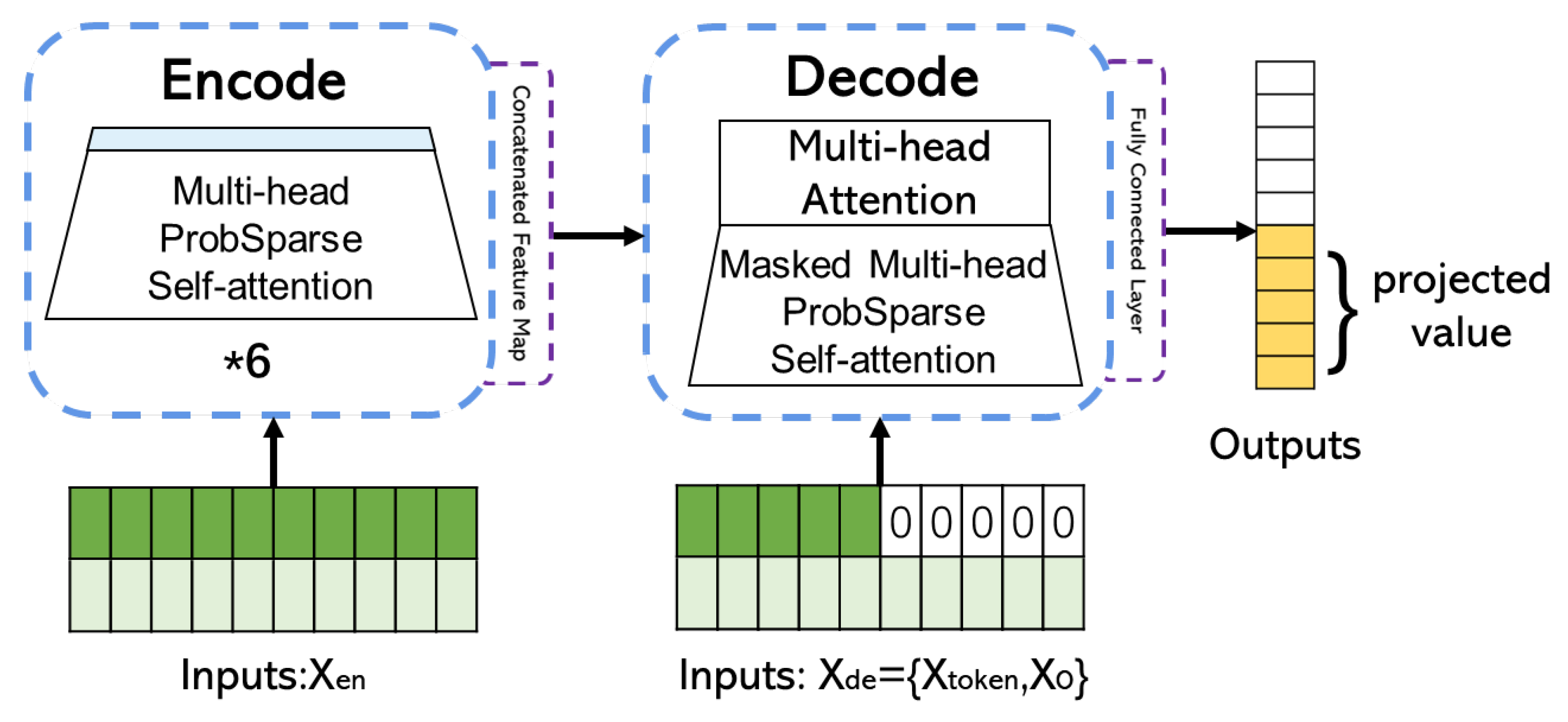
3. Prediction Methodology
3.1. Prediction Model
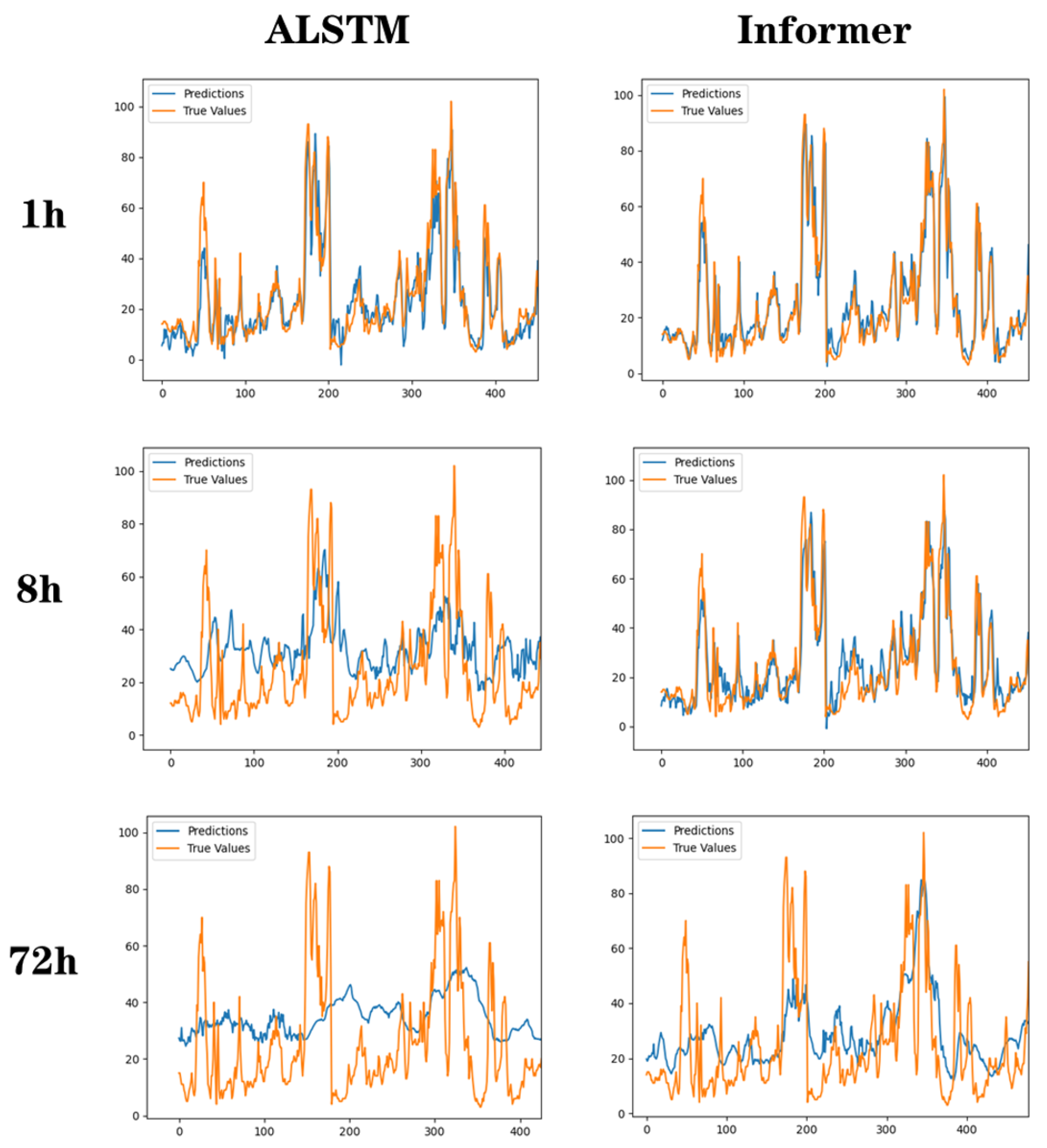
3.2. Predictive Performance Evaluation
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Health Organization. Ambient (Outdoor) Air Quality and Health [EB/OL]. Available online: http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs313/en/ (accessed on 31 October 2018).
- Rigan, P.J.; Fuller, R.; Acosta, N.J.R.; Adeyi, O.; Arnold, R.; Basu, N.N.; Baldé, A.B.; Bertollini, R.; Bose-O’Reilly, S.; Boufford, J.I.; et al. The Lancet Commission on pollution and health. Lancet 2017, 391, 462–512. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, B.; Kurisu, K.; Hanaki, K. Influential Factors of Public Intention to Improve the Air Quality in China. J. Cleaner Prod. 2019, 209, 595–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Ebenstein, A.; Greenstone, M.; Li, H. Evidence on the Impact of Sustained Exposure to Air Pollution on Life Expectancy from China’ s Huai River Policy. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 12936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burki, T. WHO Introduces Ambitious New Air Quality Guidelines. Lancet 2021, 398, 1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuzzi, S.; Baltensperger, U.; Carslaw, K.; Decesari, S.; Gon, H.D.v.; Facchini, M.C.; Fowler, D.; Koren, I.; Langford, B.; Lohmann, U.; et al. Particulate matter, air quality and climate: Lessons learned and future needs. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2015, 15, 8217–8299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castell, N.; Dauge, F.R.; Schneider, P.; Vogt, M.; Lerner, U.; Fishbain, B.; Broday, D.; Bartonova, A. Can commercial low-cost sensor platforms contribute to air quality monitoring and exposure estimates? Atmos. Environ. 2017, 99, 293–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.; Labzovskii, L.D.; Mak, H.W.L.; Fung, J.C.H.; Lau, A.K.H.; Kenea, S.T.; Bilal, M.; Hey, J.D.V.; Lu, X.; Ma, J. Observation of PM2.5 using a combination of satellite remote sensing and low-cost sensor network in Siberian urban areas with limited reference monitoring. Environ. Int. 2020, 227, 117410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Donkelaar, A.; Martin, R.V. Global Estimates of Fine Particulate Matter using a Combined Geophysical-Statistical Method with Information from Satellites, Models, and Monitors. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 3762–3772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motlagh, N.H.; Lagerspetz, E.; Nurmi, P.; Li, X.; Varjonen, S.; Mineraud, J.; Siekkinen, M.; Rebeiro-Hargrave, A.; Hussein, T.; Petaja, T.; et al. Toward Massive Scale Air Quality Monitoring. IEEE Commun. Mag. 2020, 58, 54–59. [Google Scholar]
- Box, G.E.P.; Jenkins, G.M.; Reinsel, G.C.; Ljung, M.G. Time Series Analysis: Forecasting and Control; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2015; pp. 47–88. [Google Scholar]
- Pandey, G.; Zhang, B.; Jian, L. An application of arima model to predict submicron particle concentrations from meteorological factors at a busy An application of arima model to predict submicron particle concentrations from meteorological factors at a busy roadside in hangzhou, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2012, 426, 336–345. [Google Scholar]
- Williams, B.M.; Hoel, L.A. Modeling and forecasting vehicular traffic flow as a seasonal arima process:Theoretical basis and empirical results. J. Transp. Eng. 2003, 129, 664–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voynikova, D.S.; Gocheva-Ilieva, S.G.; Ivanov, A.V.; Iliev, I.P. Studying the effect of meteorological factors on the SO2 and PM10 pollution levels with refined versions of the sarima model. In Proceedings of the Aip Conference, AIP Publishing LLC, Albena, Bulgaria, 28 June–3 July 2015; Volume 112. [Google Scholar]
- Jianwei, W.; Xiaohui, C.; Feng, X.; Weiliang, L.; Jin, M. Comparative study of two different prediction models for winter aod. In Proceedings of the 2017 Eighth International Conference on Intelligent Control and Information Processing(ICICIP), Marrakesh, Morocco, 11–16 December 2017; pp. 39–43. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, L.J.; Zhang, C.J.; Ma, L.E.M. A dynamic model for short-term PM2.5 concentration forecasting based on machine learning. Comput. Appl. 2017, 37, 3057–3063. [Google Scholar]
- Bengio, Y.; Simard, P.; Frasconi, P. Learning long-term dependencies with gradient descent is difficult. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. 1994, 5, 157–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hochreiter, S.; Schmidhuber, J. Long short term memory. Neural Comput. 1997, 9, 1735–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Peng, L.; Yao, X. Long short-term memory neural network for air pollutant concentration predictions: Method development and evaluation. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 997–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, C.; Liu, S.; Yao, X.; Peng, L.; Li, X.; Hu, Y.; Chi, T. A novel spatiotemporal convolutional long short-term neural network for air pollution prediction. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 654, 1091–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Li, Z.; Cheng, J. Air quality prediction at new stations using spatially transferred bidirectional long short-term memory network. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 705, 135771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Lee, S.Y. Air pollution forecasting based on attention-based LSTM neural network and ensemble learning. Expert Syst. 2019, 37, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaswani, A.; Shazeer, N.; Parmar, N.; Uszkoreit, J.; Jones, L.; Gomez, A.N.; Kaiser, L.; Polosukhin, I. Attention Is All You Need. In Proceedings of the 31st International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Long Beatch, CA, USA, 4–9 December 2017; pp. 6000–6010. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, H.; Zhang, S.; Peng, J.; Zhang, S.; Li, J.; Xiong, H.; Zhang, W. Informer: Beyond Efficient Transformer for Long Sequence Time-Series Forecasting. Proc. Aaai Conf. Artif. Intell. 2021, 35, 11106–11115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shepard, D. A Two-Dimensional Interpolation Function for Computer Mapping of Irregularly Spaced data. Geography and the Properties of Surfaces. In Proceedings of the ACM National Conference, New York, NY, USA, 27–29 August 1968. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.T.; Shao, Z.D. A review of spatial interpolation analysis algorithms. Comput. Syst. Appl. 2019, 28, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, G.Y.; Wong, D.W. An adaptive inverse-distance weighting spatial interpolation technique. Comput. Geosci. 2008, 34, 1044–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- A-Xing, Z.; J, L.; Fei, D.; J, Z.S.; Cheng-Zhi, Q.; Jim, B.; Thorsten, B.; Thomas, S. Predictive soil mapping with limited sample data. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2015, 66, 535–547. [Google Scholar]
- Lotrecchiano, N.; Sofia, D.; Giuliano, A.; Barletta, D.; Poletto, M. Spatial interpolation techniques for innovative air quality monitoring systems. Chem. Eng. Trans. 2021, 86, 391–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buccolieri, R.; S.; berg, M.; Sabatino, S.D. City breathability and its link to pollutant concentration distribution within urban-like geometries. Atmos. Environ. 2010, 44, 1894–1903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Liu, F.; Hsieh, H.P. Uair:When urban air quality inference meets big data. In Proceedings of the 19th ACM SIGKDD international conference on Knowledge discovery and data mining, Chicago, IL, USA, 11–14 August 2013; pp. 1436–1444. [Google Scholar]
- Nan, S.; Liang, M.; Shi, J. Analysis of the impact of heavy pollution in Taiyuan City based on Hysplit backward trajectory model. Shanxi Sci. Technol. 2018, 33, 3. [Google Scholar]
- Wei-Wu, W.; Chao, C. A quantitative analysis on spatial distribution of the pollutants in the urban air and their impact factors based on geostatistics and GIS: A case study of Hangzhou city. Geogr. Res. 2008, 27, 241–249. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep Residual Learning for Image Recognition. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Fine, T.; Jordan, M.; Lawless, J. Feedforward Neural Network Methodology, 3rd ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1999; pp. 18–156. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.; Jin, X.; Xuan, Y.; Zhou, X.; Chen, W.; Wang, Y.; Yan, X. Enhancing the locality and breaking the memory bottleneck of transformer on time series forecasting. In Proceedings of the NIPS’19: Proceedings of the 33rd International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 8–14 December 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, T.; Ma, Z.; Wen, Q.; Wang, X.; Sun, L.; Jin, R. FEDformer: Frequency Enhanced Decomposed Transformer for Long-term Series Forecasting. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, Baltimore, MD, USA, 25–27 July 2022; pp. 27268–27286. [Google Scholar]
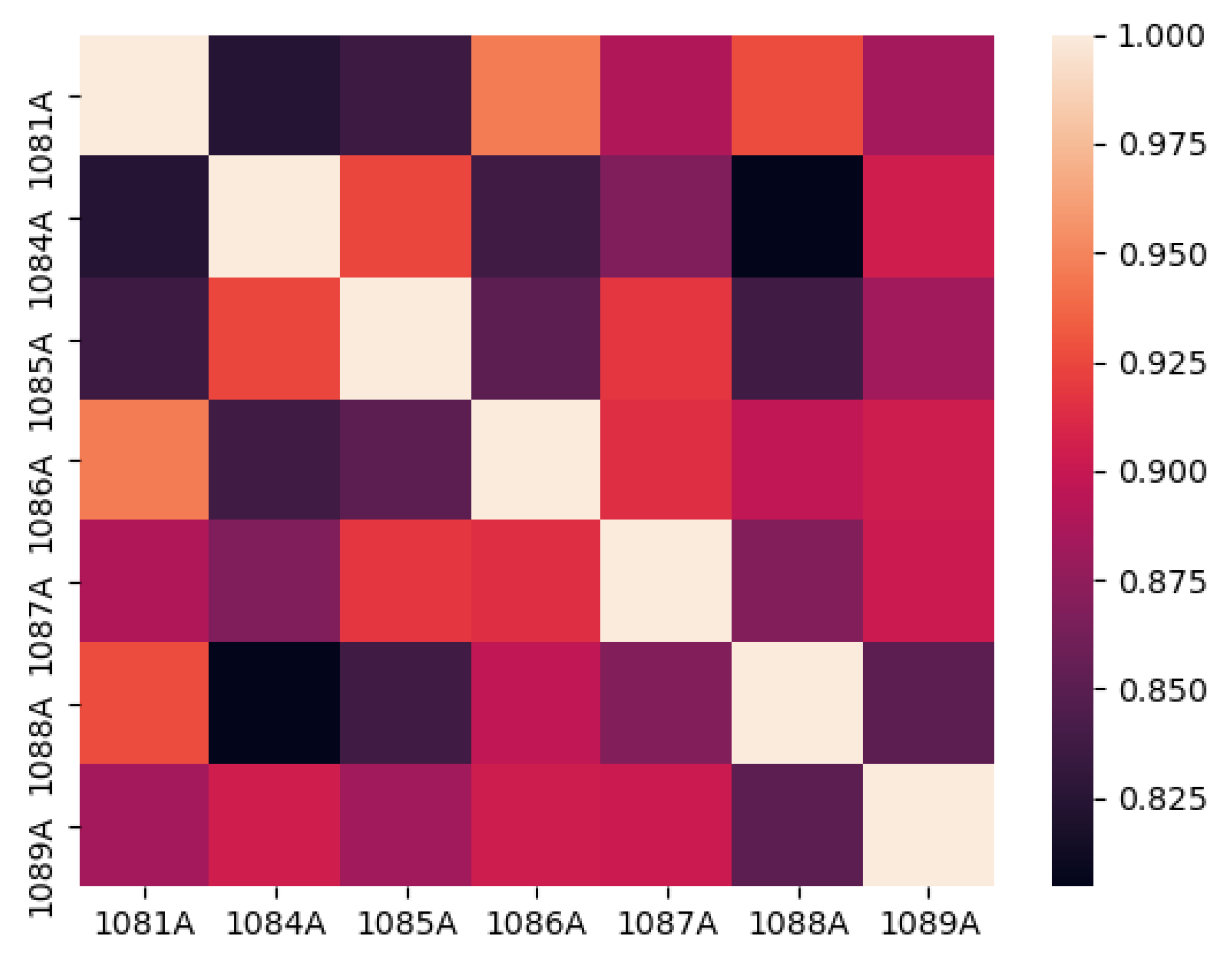
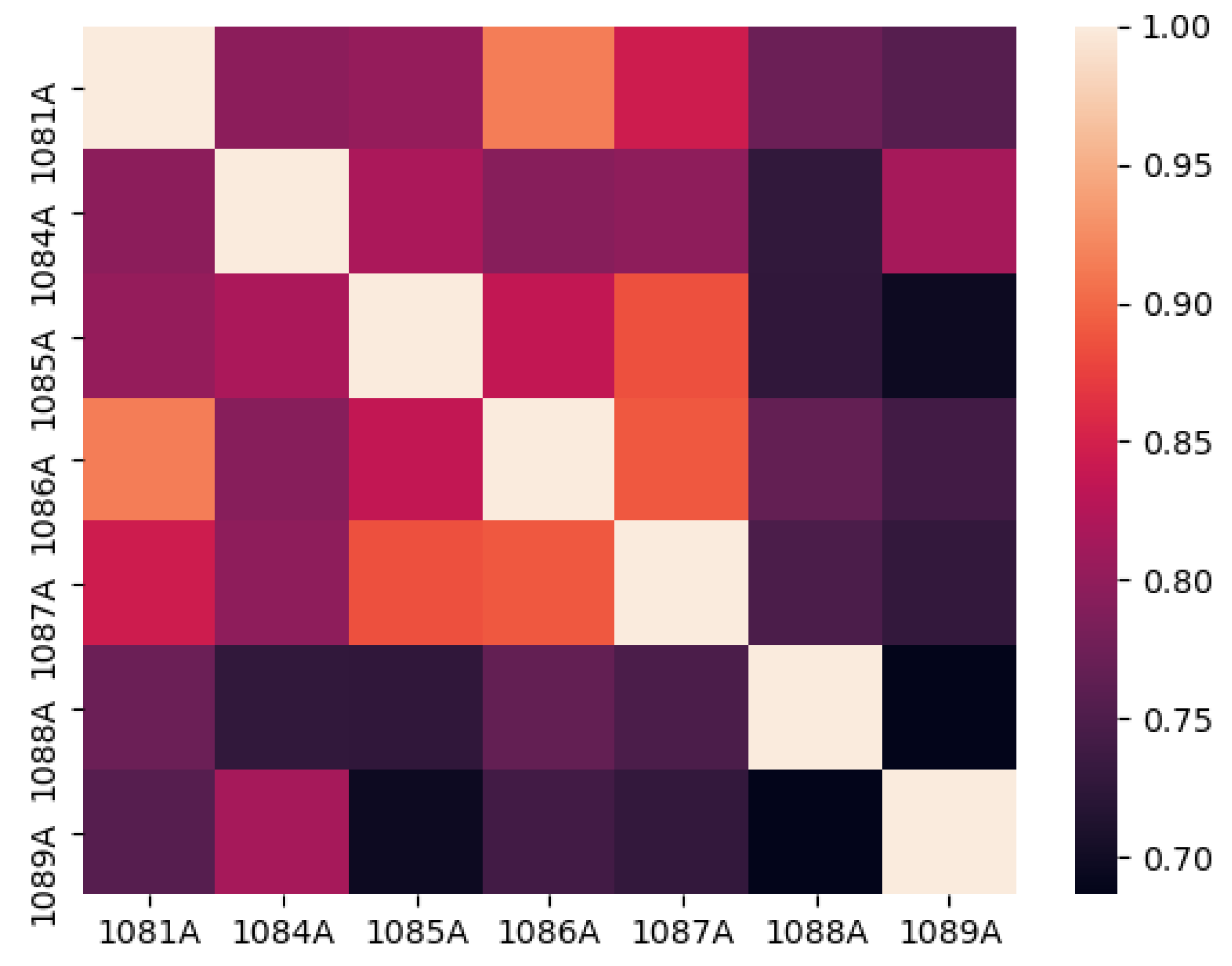

| Interpolation Method | Evaluation Indicators | PM2.5 | NO2 | O3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EIDW | RMSE | 16.32 | 18.01 | 26.14 |
| MAE | 12.90 | 16.95 | 24.23 | |
| IDW | RMSE | 18.30 | 22.43 | 27.93 |
| MAE | 15.72 | 20.38 | 25.11 |
| Pollutant | Evaluation Indicators | 1 h | 8 h | 72 h |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PM2.5 | RMSE | 7.21 | 16.44 | 19.33 |
| MAE | 4.86 | 12.56 | 16.65 | |
| NO2 | RMSE | 9.92 | 18.97 | 21.09 |
| MAE | 6.89 | 14.19 | 15.58 | |
| O3 | RMSE | 11.46 | 21.10 | 30.28 |
| MAE | 7.76 | 18.81 | 22.72 |
| Models | Evaluation Indicators | 1 h | 8 h | 72 h |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Informer | RMSE | 7.21 | 16.44 | 24.67 |
| MAE | 4.86 | 12.56 | 21.05 | |
| LSTM | RMSE | 10.92 | 25.69 | 48.06 |
| MAE | 8.97 | 18.87 | 32.43 | |
| CNN-LSTM | RMSE | 8.75 | 22.35 | 46.11 |
| MAE | 5.89 | 15.12 | 29.51 | |
| ALSTM | RMSE | 8.34 | 20.54 | 41.64 |
| MAE | 6.10 | 14.82 | 26.10 | |
| ALSTM (IDW) | RMSE | 9.03 | 22.61 | 43.04 |
| MAE | 6.76 | 16.17 | 27.87 | |
| Informer (IDW) | RMSE | 7.95 | 18.09 | 28.02 |
| MAE | 5.94 | 13.24 | 24.85 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lai, K.; Xu, H.; Sheng, J.; Huang, Y. Hour-by-Hour Prediction Model of Air Pollutant Concentration Based on EIDW-Informer—A Case Study of Taiyuan. Atmosphere 2023, 14, 1274. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14081274
Lai K, Xu H, Sheng J, Huang Y. Hour-by-Hour Prediction Model of Air Pollutant Concentration Based on EIDW-Informer—A Case Study of Taiyuan. Atmosphere. 2023; 14(8):1274. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14081274
Chicago/Turabian StyleLai, Kefu, Huahu Xu, Jun Sheng, and Yuzhe Huang. 2023. "Hour-by-Hour Prediction Model of Air Pollutant Concentration Based on EIDW-Informer—A Case Study of Taiyuan" Atmosphere 14, no. 8: 1274. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14081274
APA StyleLai, K., Xu, H., Sheng, J., & Huang, Y. (2023). Hour-by-Hour Prediction Model of Air Pollutant Concentration Based on EIDW-Informer—A Case Study of Taiyuan. Atmosphere, 14(8), 1274. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14081274





