Research on Modeling Weighted Average Temperature Based on the Machine Learning Algorithms
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Data and Methods
2.1. Data
2.2. Methods
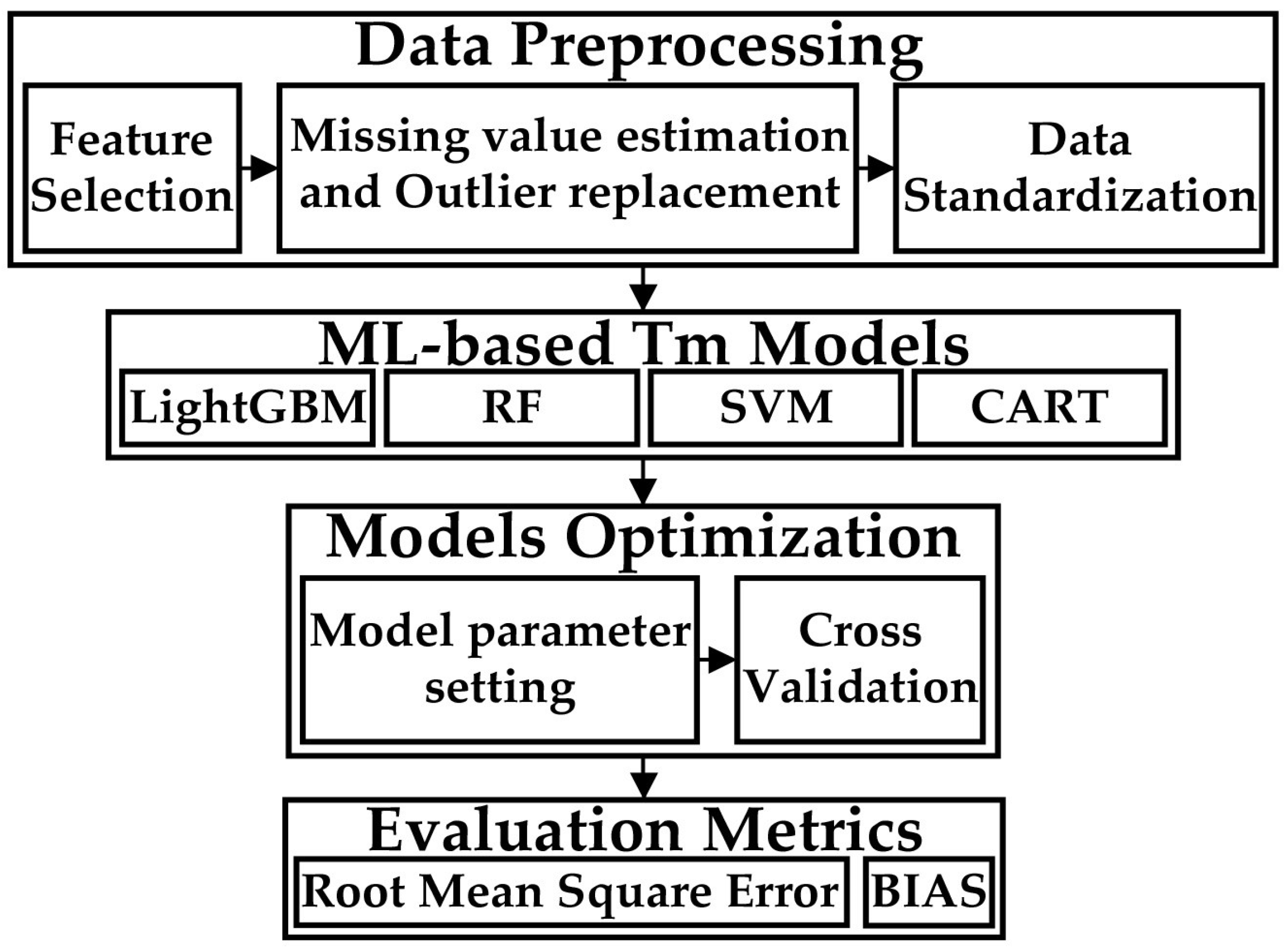
2.2.1. Machine Learning Algorithms
- 1.
- LightGBM
- 2.
- RF
- 3.
- SVM
- 4.
- CART
2.2.2. Evaluations
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Feature Selection
3.1.1. Correlation
3.1.2. Collinearity
3.2. The ML-Based Tm Modeling
3.2.1. Data Preprocessing
3.2.2. The Model Optimization
3.3. Accuracy Analysis
3.3.1. The Daily Models
3.3.2. Quarterly and Monthly Models
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Tm | Weighted average temperature |
| Ts | Surface temperature |
| Es | Water vapor pressure |
| Ps | Atmospheric pressure |
| ML | Machine learning |
| LightGBM | Light Gradient Boosting Machine |
| SVM | Support Vector Machine |
| RF | Random Forest |
| CART | Classification and Regression Tree |
| GNSS | Classification and Regression Tree |
| RMSE | Root mean square error |
| PWV | Precipitable water vapor |
| ZTD | Zenith total delay |
| ZHD | Zenith hydrostatic delay |
| ZWD | Zenith wet delay |
| GPT | Global Pressure and Temperature Model |
| GWMT | Global Weighted Mean Temperature |
| BPNN | Back Propagation Neural Networks |
| GRNN | Generalized Regression Neural Network |
| EFB | Exclusive feature bundling |
| GOSS | Gradient-based One-Side Sampling |
| VIF | Variance Inflation Factor |
References
- Askne, J.; Nordius, H. Estimation of tropospheric delay for microwaves from surface weather data. Radio Sci. 1987, 22, 379–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, J.; Herring, T.; Shapiro, I.; Rogers, A.; Elgered, G. Geodesy by radio interferometry: Effects of atmospheric modeling errors on estimates of baseline length. Radio Sci. 1985, 20, 1593–1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Liu, Y.; Yao, W.; Yao, Y. Hourly rainfall forecast model using supervised learning algorithm. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2021, 60, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mircheva, B.; Tsekov, M.; Meyer, U.; Guerova, G. Anomalies of hydrological cycle components during the 2007 heat wave in Bulgaria. J. Atmos. Sol.-Terr. Phys. 2017, 165, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, Z.; Zhang, B.; Geng, Y. Establishment and analysis of global gridded Tm− Ts relationship model. Geod. Geodyn. 2016, 7, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bevis, M.; Businger, S.; Chiswell, S.; Herring, T.A.; Anthes, R.A.; Rocken, C.; Ware, R.H. GPS meteorology: Mapping zenith wet delays onto precipitable water. J. Appl. Meteorol. 1994, 33, 379–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Zhu, S.; Yue, S. A globally applicable, season-specific model for estimating the weighted mean temperature of the atmosphere. J. Geod. 2012, 86, 1125–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, B.; Li, L.; Xie, W.; Zhou, J.; Li, Y.; Gu, J.; Zhang, Z. Localized model fitting of weighted average temperature in the Yangtze River Delta. J. Navig. Position 2019, 7, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Chen, P.; Liu, T.; Xu, G.; Lu, Z. Development and Assessment of an ALLSSA-Based Atmospheric Weighted Mean Temperature Model with High Time Resolution for GNSS Precipitable Water Retrieval. Earth Space Sci. 2022, 9, e2021EA002089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Zhang, B.; Yao, Y. Improving the estimation of weighted mean temperature in China using machine learning methods. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Jiang, W.; Liu, L.; Chen, H.; Ye, S. A new global grid model for the determination of atmospheric weighted mean temperature in GPS precipitable water vapor. J. Geod. 2019, 93, 159–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umakanth, N.; Satyanarayana, G.C.; Simon, B.; Rao, M.; Babu, N.R. Long-term analysis of thunderstorm-related parameters over Visakhapatnam and Machilipatnam, India. Acta Geophys. 2020, 68, 921–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, T.T.K.; Lee, T.; Kim, J.-S. Increasing neurons or deepening layers in forecasting maximum temperature time series? Atmosphere 2020, 11, 1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, W.; Qie, X. Prediction of Air Pollutant Concentrations via RANDOM Forest Regressor Coupled with Uncertainty Analysis—A Case Study in Ningxia. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, M. A neural network model for predicting weighted mean temperature. J. Geod. 2018, 92, 1187–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, M.; Li, J.; Liu, L.; Huang, L.; Zhou, L.; Huang, L.; He, H. Weighted Mean Temperature Hybrid Models in China Based on Artificial Neural Network Methods. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 3762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, Y.; Sun, G.; Chen, Q.; Zhang, M.; Zhu, H.; Rehman, M.U. A model combining convolutional neural network and LightGBM algorithm for ultra-short-term wind power forecasting. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 28309–28318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saber, M.; Boulmaiz, T.; Guermoui, M.; Abdrabo, K.I.; Kantoush, S.A.; Sumi, T.; Boutaghane, H.; Nohara, D.; Mabrouk, E. Examining LightGBM and CatBoost models for wadi flash flood susceptibility prediction. Geocarto Int. 2022, 37, 7462–7487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morshed-Bozorgdel, A.; Kadkhodazadeh, M.; Valikhan Anaraki, M.; Farzin, S. A novel framework based on the stacking ensemble machine learning (SEML) method: Application in wind speed modeling. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Lin, M.; Fang, Q.; Chen, J.; Yue, Q.; Xia, J. Air temperature estimation over winter wheat fields by integrating machine learning and remote sensing techniques. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2023, 122, 103416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radhika, Y.; Shashi, M. Atmospheric temperature prediction using support vector machines. Int. J. Comput. Theory Eng. 2009, 1, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lathifah, S.N.; Nhita, F.; Aditsania, A.; Saepudin, D. Rainfall Forecasting using the Classification and Regression Tree (CART) Algorithm and Adaptive Synthetic Sampling (Study Case: Bandung Regency). In Proceedings of the 2019 7th International Conference on Information and Communication Technology (ICoICT), Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 24–26 July 2019; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Ke, G.; Meng, Q.; Finley, T.; Wang, T.; Chen, W.; Ma, W.; Ye, Q.; Liu, T.-Y. Lightgbm: A highly efficient gradient boosting decision tree. In Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 30, Proceedings of the NIPS 2017, Long Beach, CA, USA, 4–9 December 2017; Curran Associates: Montreal, QC, Canada, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Duan, H.; Huang, W.; Guo, R.; Duan, B. Classified early warning and forecast of severe convective weather based on LightGBM algorithm. Atmos. Clim. Sci. 2021, 11, 284–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, R.; Ning, Y.; Li, C.; Feng, W.; Chen, Y.; Xie, X. Numerical forecast correction of temperature and wind using a single-station single-time spatial LightGBM method. Sensors 2022, 22, 193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, T.; Yu, Y.; Yan, J.; Xu, H. Long-Term Rainfall Forecast Model Based on The TabNet and LightGbm Algorithm. 2020. Available online: https://web.archive.org/web/20201126204621id_/https://assets.researchsquare.com/files/rs-107107/v1_stamped.pdf (accessed on 25 May 2023).
- Singh, N.; Chaturvedi, S.; Akhter, S. Weather forecasting using machine learning algorithm. In Proceedings of the 2019 International Conference on Signal Processing and Communication (ICSC), Dalian, China, 20–23 September 2019; pp. 171–174. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, A.; Xu, L.; Li, Y.; Xing, J.; Chen, X.; Liu, K.; Liang, Y.; Zhou, Z. Random-forest based adjusting method for wind forecast of WRF model. Comput. Geosci. 2021, 155, 104842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, N.; Fu, F.; Zuo, H.; Zheng, X.; Zheng, Q. A Municipal PM2.5 Forecasting Method Based on Random Forest and WRF Model. Eng. Lett. 2020, 28, 312–321. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Qiu, X.; Li, X.; Huang, Z.; Wu, M.; Dong, Y. Support vector machine weather prediction technology based on the improved quantum optimization algorithm. Comput. Intell. Neurosci. 2021, 2021, 6653659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nayak, M.A.; Ghosh, S. Prediction of extreme rainfall event using weather pattern recognition and support vector machine classifier. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2013, 114, 583–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R. Decision tree for the weather forecasting. Int. J. Comput. Appl. 2013, 76, 31–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geetha, A.; Nasira, G. Data mining for meteorological applications: Decision trees for modeling rainfall prediction. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE International Conference on Computational Intelligence and Computing Research, Coimbatore, India, 18–20 December 2014; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, D.; Ghose, U. A comparative study of classification algorithms for forecasting rainfall. In Proceedings of the 2015 4th International Conference on Reliability, Infocom Technologies and Optimization (ICRITO) (Trends and Future Directions), Noida, India, 2–4 September 2015; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Zhang, B.; Yao, Y.; Liu, L.; Sun, Z.; Yan, X. A refined regional model for estimating pressure, temperature, and water vapor pressure for geodetic applications in China. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Zhang, B.; Xu, C.; Yan, F. Improved one/multi-parameter models that consider seasonal and geographic variations for estimating weighted mean temperature in ground-based GPS meteorology. J. Geod. 2014, 88, 273–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Wu, S.; Wang, X.; Tian, Y.; He, C.; Zhang, K. Seasonal multifactor modelling of weighted-mean temperature for ground-based GNSS meteorology in Hunan, China. Adv. Meteorol. 2017, 2017, 3782687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isioye, O.A.; Combrinck, L.; Botai, J. Modelling weighted mean temperature in the West African region: Implications for GNSS meteorology. Meteorol. Appl. 2016, 23, 614–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miles, J. Tolerance and Variance Inflation Factor. Wiley Statsref: Statistics Reference Online. 2014. Available online: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1002/9781118445112.stat06593 (accessed on 25 May 2023).
- García, C.; García, J.; López Martín, M.; Salmerón, R. Collinearity: Revisiting the variance inflation factor in ridge regression. J. Appl. Stat. 2015, 42, 648–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Qu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Ma, J.; Cao, Y. Application of machine-learning-based fusion model in visibility forecast: A case study of Shanghai, China. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 2096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yong, Z.; Youwen, L.; Shixiong, X. An improved KNN text classification algorithm based on clustering. J. Comput. 2009, 4, 230–237. [Google Scholar]
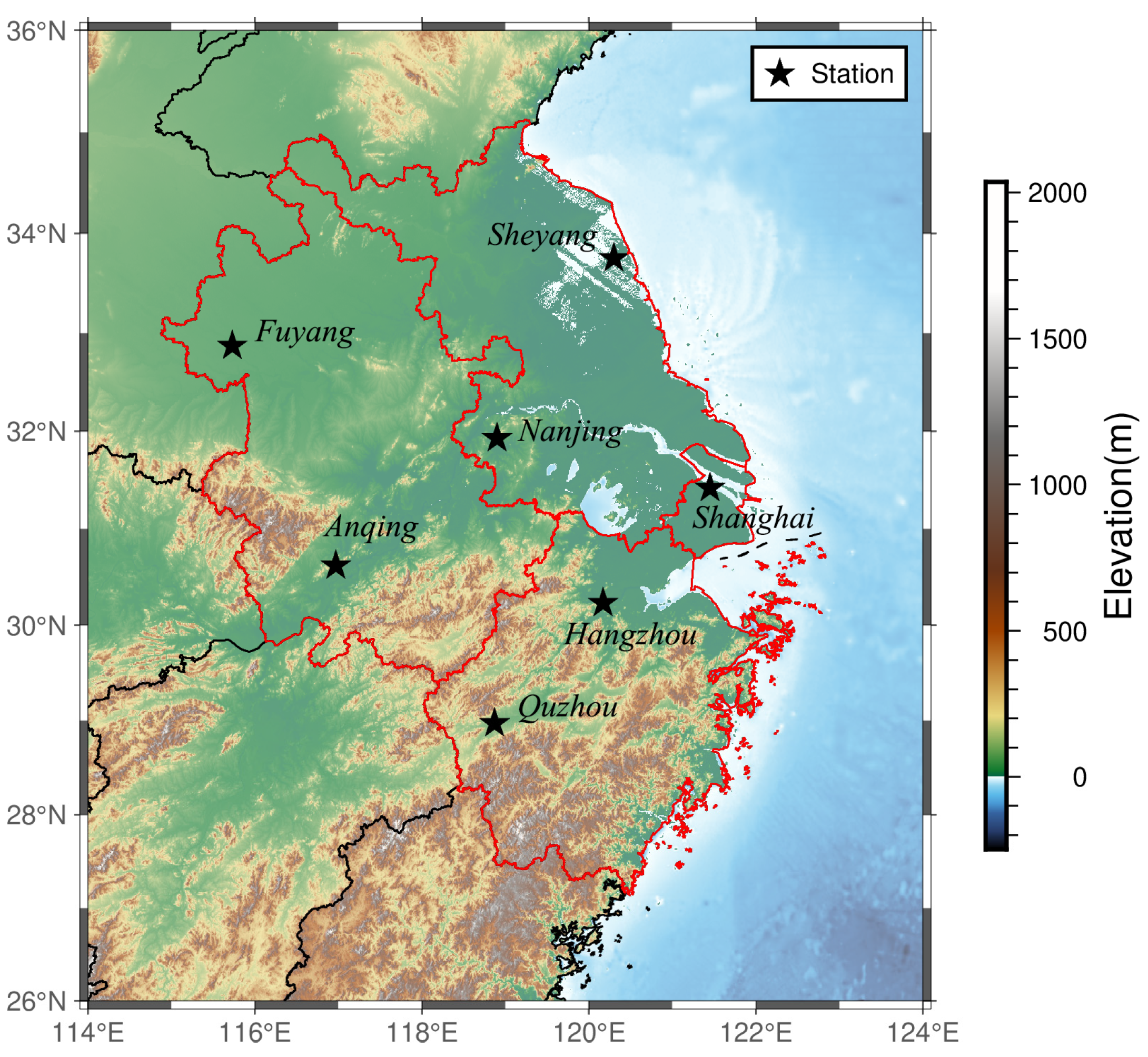







| Region | Site Number | Location [°] | Elevation [m] |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hangzhou | 58457 | (30.23° N, 120.16° E) | 43.00 |
| Quzhou | 58633 | (28.96° N, 118.86° E) | 71.00 |
| Shanghai | 58362 | (31.40° N, 121.46° E) | 4.00 |
| Anqing | 58424 | (30.53° N, 117.05° E) | 20.00 |
| Fuyang | 58203 | (32.86° N, 115.73° E) | 33.00 |
| Nanjing | 58238 | (32.00° N, 118.80° E) | 7.00 |
| Sheyang | 58150 | (33.76° N, 120.25° E) | 7.00 |
| Dependent Variable | Independent Variable | R | Independent Variable | Independent Variable | R | R2 | Tol | VIF |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tm | Ts | 0.95 | Ts | Ps | −0.85 | 0.68 | 0.32 | 3.1 |
| Tm | Ps | −0.87 | Ts | Es | 0.91 | 0.83 | 0.17 | 5.9 |
| Tm | Es | 0.96 | Ps | Es | −0.85 | 0.70 | 0.30 | 3.3 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, K.; Li, L.; Hu, A.; Pan, J.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, M. Research on Modeling Weighted Average Temperature Based on the Machine Learning Algorithms. Atmosphere 2023, 14, 1251. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14081251
Li K, Li L, Hu A, Pan J, Ma Y, Zhang M. Research on Modeling Weighted Average Temperature Based on the Machine Learning Algorithms. Atmosphere. 2023; 14(8):1251. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14081251
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Kai, Li Li, Andong Hu, Jianping Pan, Yixiang Ma, and Mingsong Zhang. 2023. "Research on Modeling Weighted Average Temperature Based on the Machine Learning Algorithms" Atmosphere 14, no. 8: 1251. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14081251
APA StyleLi, K., Li, L., Hu, A., Pan, J., Ma, Y., & Zhang, M. (2023). Research on Modeling Weighted Average Temperature Based on the Machine Learning Algorithms. Atmosphere, 14(8), 1251. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14081251








