The Development of a Low-Cost Particulate Matter 2.5 Sensor Calibration Model in Daycare Centers Using Long Short-Term Memory Algorithms
Abstract
1. Introduction
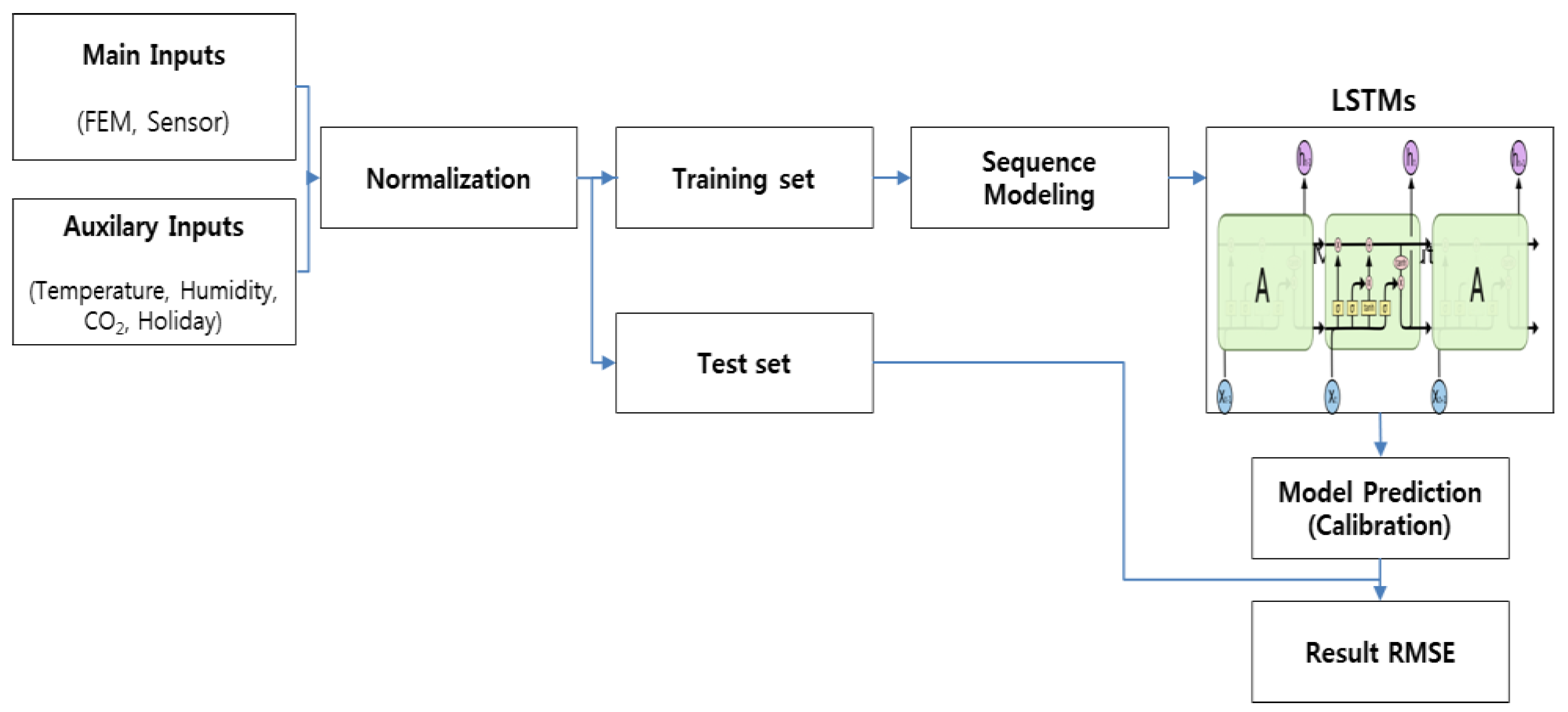
2. Materials and Methods
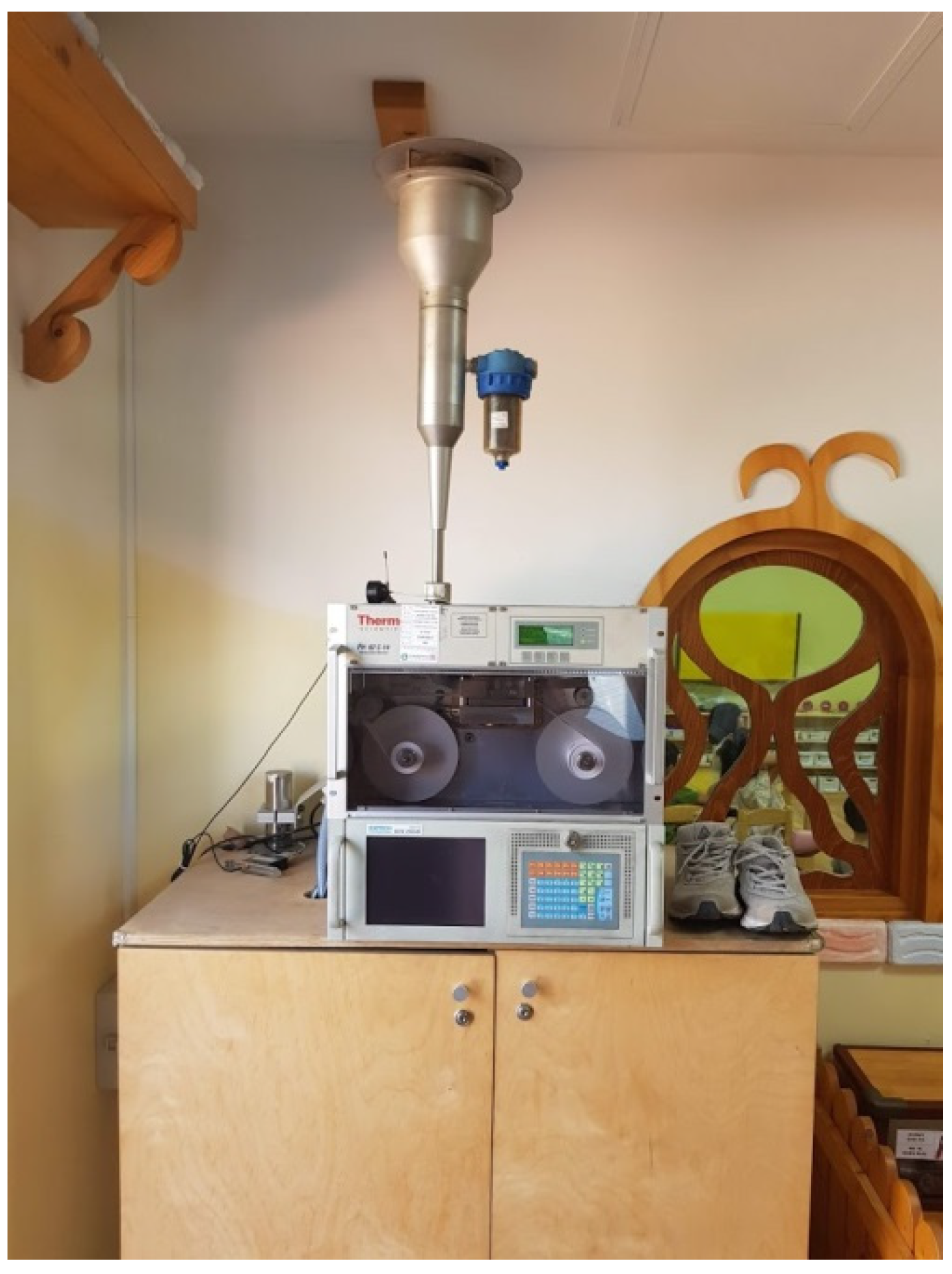
2.1. Location and Design
2.2. Evaluation and Calibration of Sensor Performance Data
2.2.1. Multiple Regression Analysis
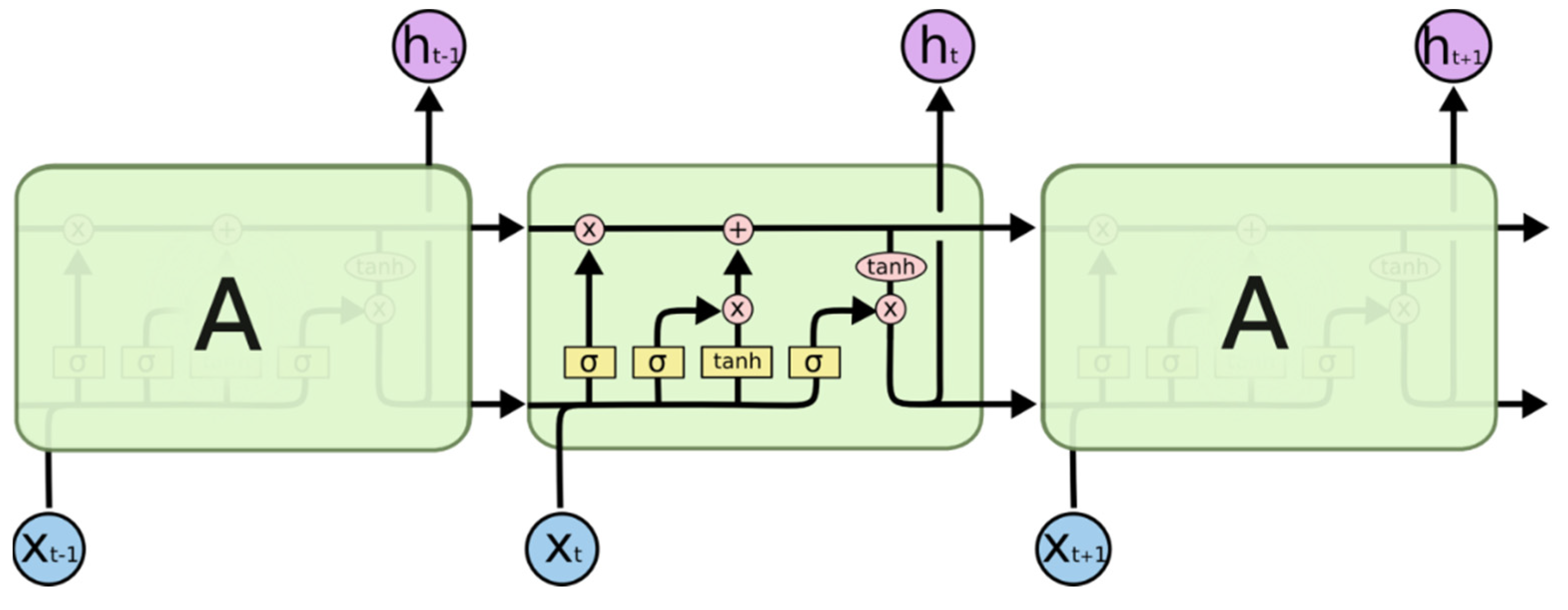
2.2.2. RNN and LSTM
2.2.3. Sequence Data Generation
2.2.4. Outlier Removal
3. Results and Discussion
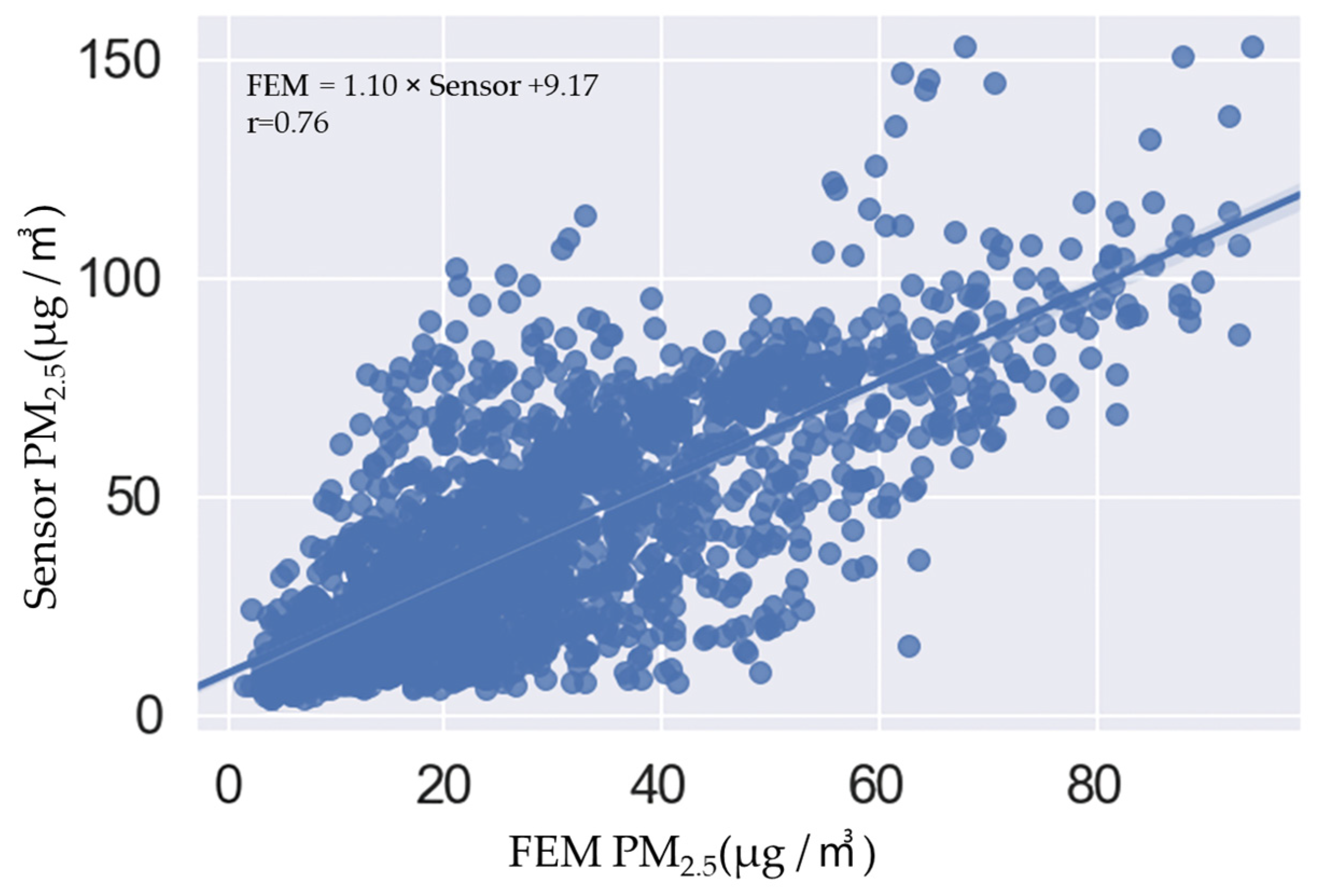
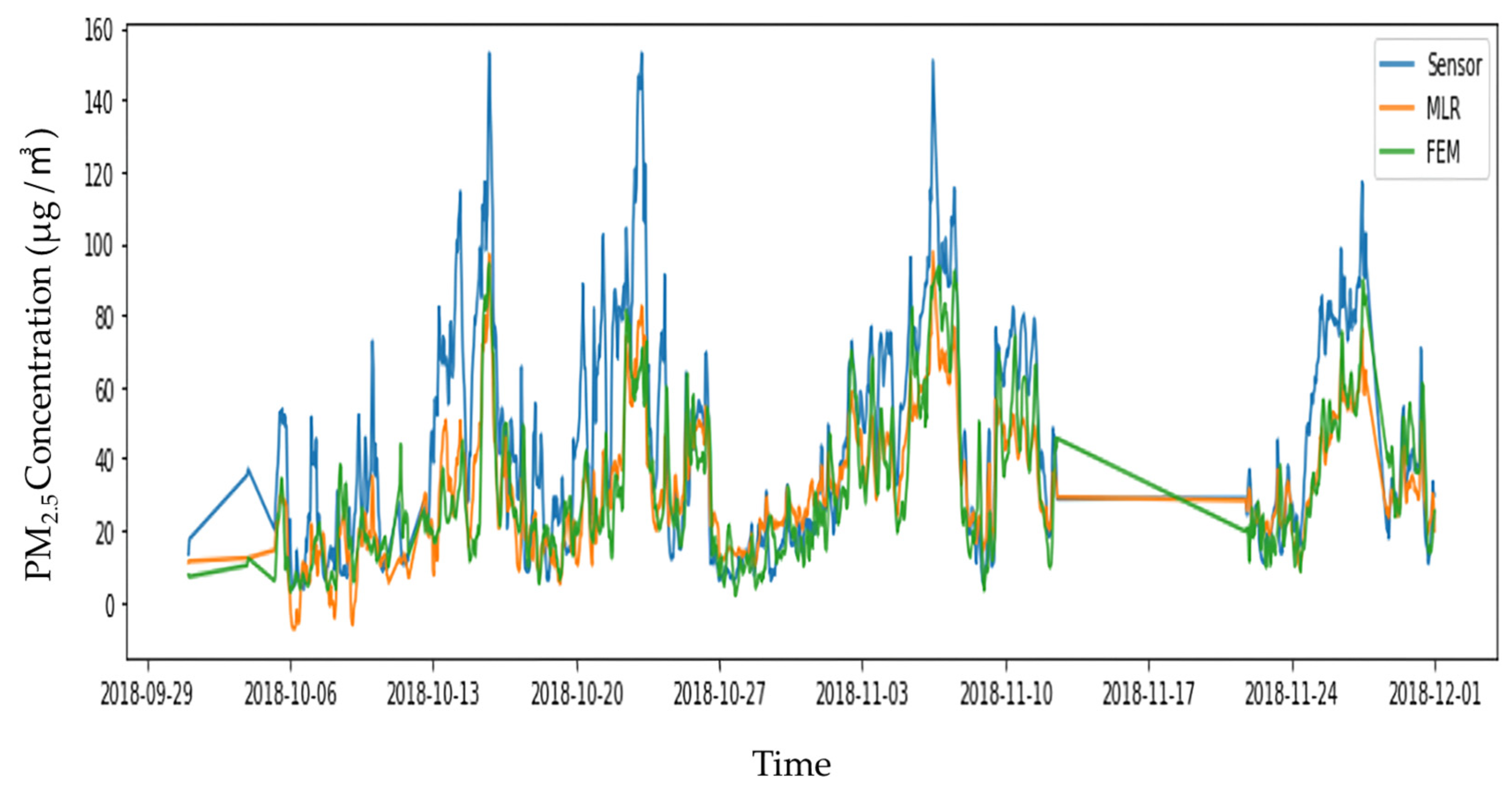
3.1. Measurement Results
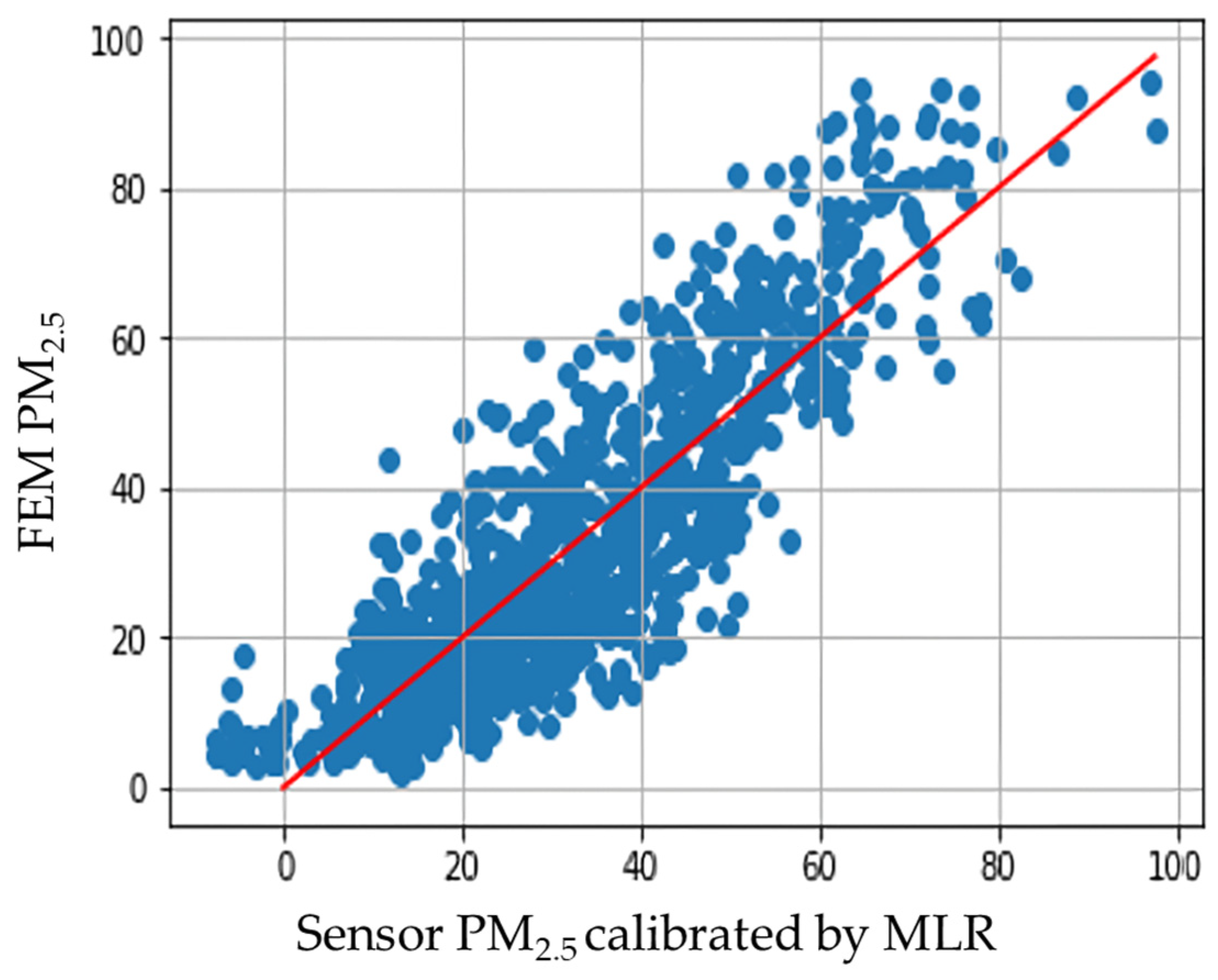
3.2. Calculation of Correction Factor
3.2.1. Linear Regression
3.2.2. Multiple Linear Regression
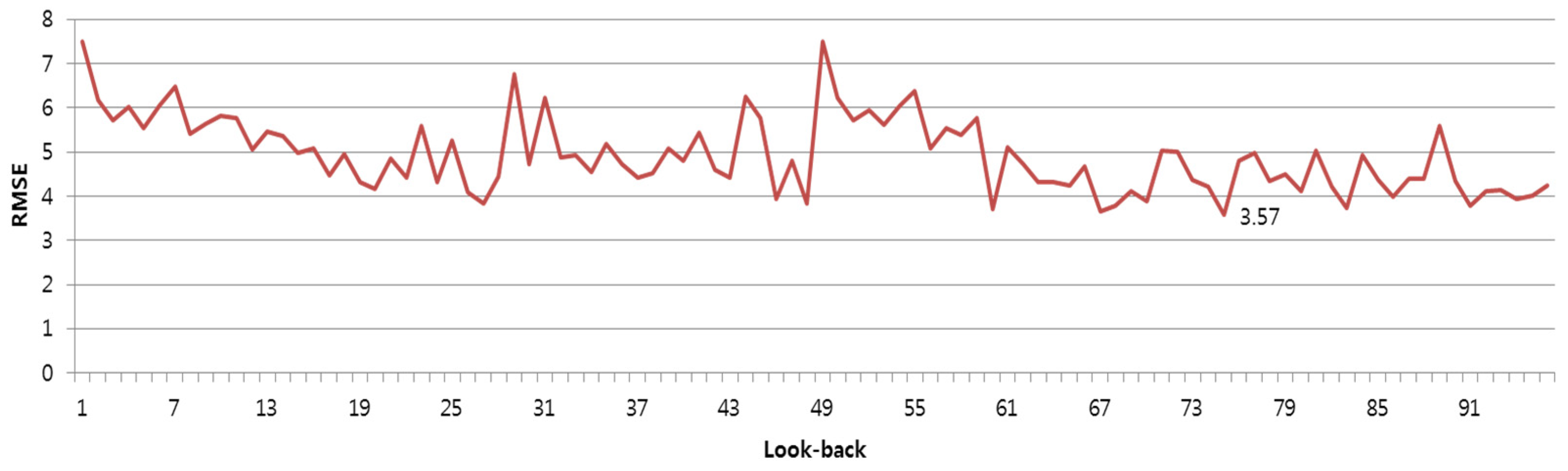
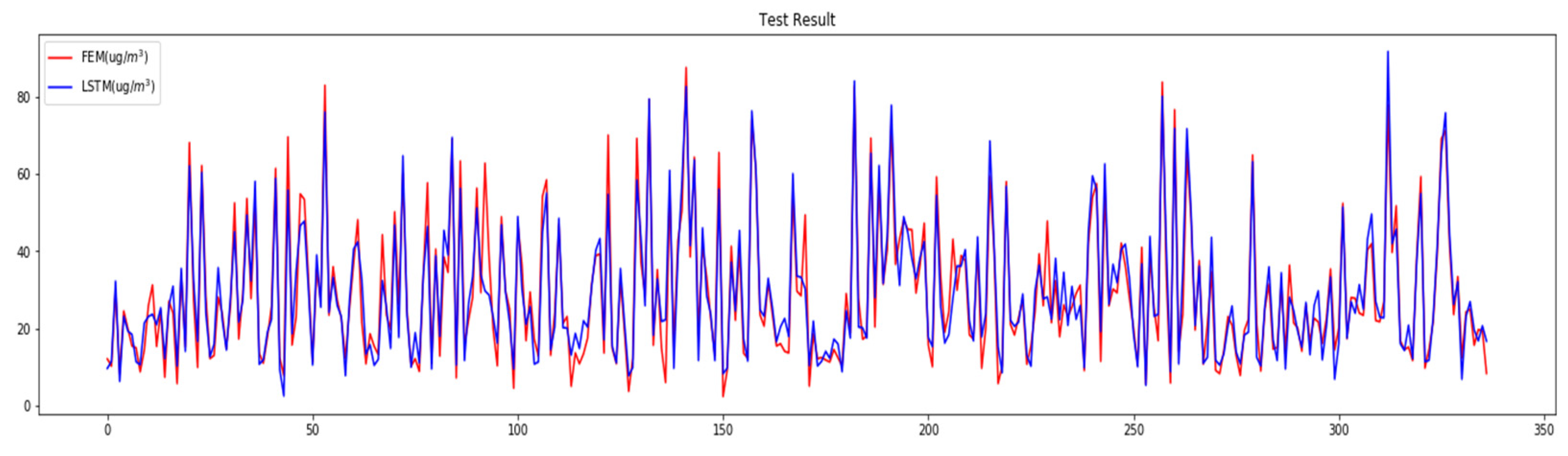
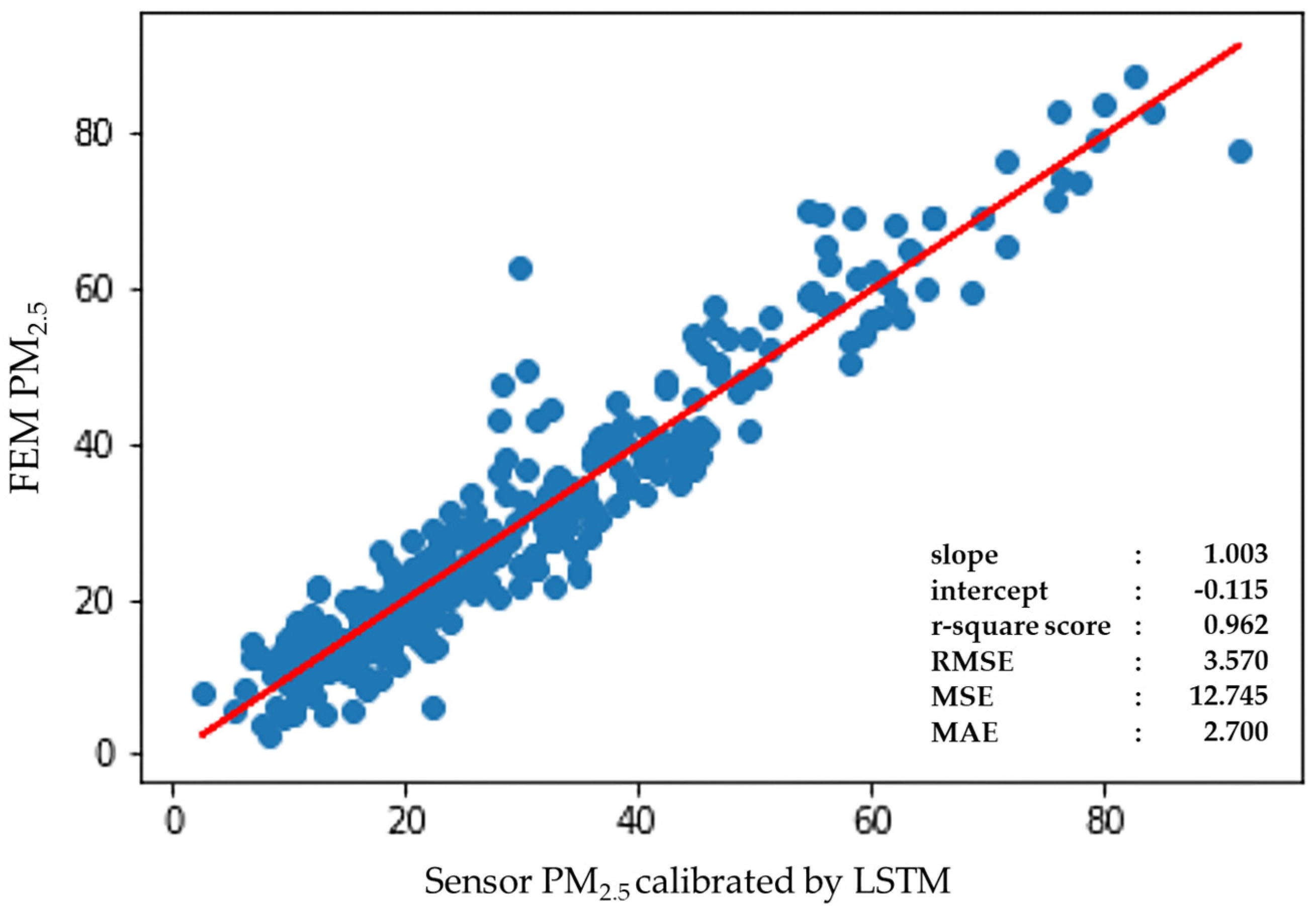
3.2.3. RNN
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Brienza, S.; Galli, A.; Anastasi, G.; Bruschi, P. A low-cost sensing system for cooperative air quality monitoring in urban areas. Sensors 2015, 15, 12242–12259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. Ambient Air Pollution-A Global Assessment of Exposure and Burden of Disease; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2016; ISBN 9789241511353. [Google Scholar]
- Graham, L.M. All I need is the air that I breath: Outdoor air quality and asthma. Paediatr. Respir. Rev. 2004, 5 (Suppl. A), S59–S64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, H.-J. Effects of short-term exposure to PM10 and PM2.5 on mortality in Seoul. Korean J. Environ. Health Sci. 2014, 40, 346–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.B.; Park, S.; Lee, Y.; Lee, S.; Kim, J.; Park, D. Prediction of concentration change and influence analysis of indoor/outdoor in subway station using indoor air quality monitoring data. J. Korean Soc. Atmos. Environ. 2022, 38, 30–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Kang, H.-S.; Son, Y.S.; Yoon, S.-L.; Kim, J.-C.; Kim, G.-S.; Kim, I. Compensation of light scattering method for real-time monitoring of particulate matters in subway stations. J. Korean Soc. Atmos. Environ. 2010, 26, 533–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, J.; Jeong, S.; Kim, G.; Park, W.; Park, S. Evaluation of measurement reliability of light-scattering PM2.5 monitor applied with referenced-channel calibration technology. J. Korean Soc. Atmos. Environ. 2022, 38, 341–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, D.; Yoo, G.W.; Park, S.H.; Lee, J.H. Assessment and calibration of a low-cost PM2.5 sensor using machine learning (hybridlSTM neural network): Feasibility study to build an air quality monitoring system. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morawska, L.; Thai, P.K.; Liu, X.; Asumadu-Sakyi, A.; Ayoko, G.; Bartonova, A.; Bedini, A.; Chai, F.; Christensen, B.; Dunbabin, M.; et al. Applications of low-cost sensing technologies for air quality monitoring and exposure assessment: How far have they gone? Environ. Int. 2018, 116, 286–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maag, B.; Zhou, Z.; Thiele, L. A survey on sensor calibration in air pollution monitoring deployments. IEEE Internet Things J. 2018, 5, 4857–4870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castell, N.; Dauge, F.R.; Schneider, P.; Vogt, M.; Lerner, U.; Fishbain, B.; Broday, D.; Bartonova, A. Can commercial low-cost sensor platforms contribute to air quality monitoring and exposure estimates? Environ. Int. 2017, 99, 293–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castell, N.; Schneider, P.; Grossberndt, S.; Fredriksen, M.F.; Sousa-Santos, G.; Vogt, M.; Bartonova, A. Localized real-time information on outdoor air quality at kindergartens in Oslo, Norway using low-cost sensor nodes. Environ. Res. 2018, 165, 410–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matte, T.D.; Ross, Z.; Kheirbek, I.; Eisl, H.; Johnson, S.; Gorczynski, J.E.; Kass, D.; Markowitz, S.; Pezeshki, G.; Clougherty, J.E. Monitoring intraurban spatial patterns of multiple combustion air pollutants in New York City: Design and implementation. J. Expo. Sci. Environ. Epidemiol. 2013, 23, 223–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, P.; Morawska, L.; Martani, C.; Biskos, G.; Neophytou, M.; Di Sabatino, S.; Bell, M.; Norford, L.; Britter, R. The rise of low-cost sensing for managing air pollution in cities. Environ. Int. 2015, 75, 199–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rai, A.C.; Kumar, P.; Pilla, F.; Skouloudis, A.N.; Di Sabatino, S.; Ratti, C.; Yasar, A.; Rickerby, D. End-user perspective of low-cost sensors for outdoor air pollution monitoring. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 607–608, 691–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jovašević-Stojanović, M.; Bartonova, A.; Topalović, D.; Lazović, I.; Pokrić, B.; Ristovski, Z. On the use of small and cheaper sensors and devices for indicative citizen-based monitoring of respirable particulate matter. Environ. Pollut. 2015, 206, 696–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, K.E.; Whitaker, J.; Petty, A.; Widmer, C.; Dybwad, A.; Sleeth, D.; Martin, R.; Butterfield, A. Ambient and laboratory evaluation of a low-cost particulate matter sensor. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 221, 491–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillooly, S.E.; Zhou, Y.; Vallarino, J.; Chu, M.T.; Michanowicz, D.R.; Levy, J.I.; Adamkiewicz, G. Development of an in-home, real-time air pollutant sensor platform and implications for community use. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 244, 440–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.; Lee, J.; Woo, U.; Choi, H. Evaluation of Low-cost Light Scattering Devices for Ultrafine Dust Based on Relative Humidity. J. Korean Soc. Living Environ. Syst. 2022, 29, 271–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, V.; Yedavalli, P.; Mohanty, S.; Nakhat, U. Deep Air: Forecasting Air Pollution in Beijing, China. Available online: https://www.ischool.berkeley.edu/sites/default/files/sproject_attachments/deep-air-forecasting_final.pdf (accessed on 14 June 2023).
- Ahn, J.; Shin, D.; Kim, K.; Yang, J. Indoor air quality analysis using deep learning with sensor data. Sensors 2017, 17, 2476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.H.; Yoo, S.J.; Kim, K.J.; Gu, Y.H.; Lee, K.H.; Son, U.H. PM10 density forecast model using long short term memory. In Proceedings of the 2017 Ninth International Conference on Ubiquitous and Future Networks (ICUFN), Milan, Italy, 4–7 July 2017; pp. 576–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Deng, F.; Cai, Y.; Chen, J. Long short-term memory–Fully connected (LSTM-FC) neural network for PM2.5 concentration prediction. Chemosphere 2019, 220, 486–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Peng, L.; Yao, X.; Cui, S.; Hu, Y.; You, C.; Chi, T. Long short-term memory neural network for air pollutant concentration predictions: Method development and evaluation. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 231, 997–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benammar, M.; Abdaoui, A.; Ahmad, S.H.M.; Touati, F.; Kadri, A. A modular IoT platform for real-time indoor air quality monitoring. Sensors 2018, 18, 581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hagan, D.H.; Isaacman-VanWertz, G.; Franklin, J.P.; Wallace, L.M.M.; Kocar, B.D.; Heald, C.L.; Kroll, J.H. Calibration and assessment of electrochemical air quality sensors by co-location with regulatory-grade instruments. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2018, 11, 315–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayahi, T.; Butterfield, A.; Kelly, K.E. Long-term field evaluation of the Plantower PMS low-cost particulate matter sensors. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 245, 932–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmerman, N.; Presto, A.A.; Kumar, S.P.N.; Gu, J.; Hauryliuk, A.; Robinson, E.S.; Robinson, A.L.; Subramanian, R. A machine learning calibration model using random forests to improve sensor performance for lower-cost air quality monitoring. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2018, 11, 291–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, G. Implementation of indoor air quality monitoring system for subway stations. J. Semicond. Technol. Sci. 2013, 50, 294–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spinelle, L.; Aleixandre, M.; Gerboles, M. Protocol of Evaluation and Calibration of Low- Cost Gas Sensors for the Monitoring of Air Pollution; Publications Office of the European Union: Luxembourg, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, N.; Kim, H.; Kang, P. Evaluating variable selection techniques for multivariate linear regression. J. Korean Inst. Ind. Eng. 2016, 42, 314–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kim, H. Subway PM10 measurement and development of correction equation using the light scattering method. J. Odor Indoor Environ. 2018, 17, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, W.; Hagler, G.; Williams, R.; Sharpe, R.; Brown, R.; Garver, D.; Judge, R.; Caudill, M.; Rickard, J.; Davis, M.; et al. Community Air Sensor Network (CAIRSENSE) project: Evaluation of low-cost sensor performance in a suburban environment in the southeastern United States. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2016, 9, 5281–5292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, H.; Choi, I.; Jeon, H.; Kim, Y.; Lee, J.; Park, C.H.; Kim, H.S. An air pollutants prediction method integrating numerical models and artificial intelligence models targeting the area around Busan port in Korea. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Instrument | Pollutant | Equipment | Measurement Method | Measurement Range |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FEM meter | Particulate matter 2.5 (PM2.5) | Thermo Scientific (FH 62 C14) | Beta-ray absorption method (ISO 10473 equivalent method) | 0–500 μg/m3 |
| Low-cost sensor | PM2.5 | Plantower PMS 7003 | OPC laser | 0–500 μg/m3 |
| Sensor PM2.5 | FEM PM2.5 | Temperature | Humidity | CO2 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Count | 2203 | 1960 | 2208 | 2208 | 2171 |
| Mean | 41.9 | 28.9 | 15.9 | 47.1 | 403.2 |
| Standard deviation | 26.0 | 18.2 | 3.2 | 19.4 | 77.2 |
| Minimum | 3.5 | 1.8 | 5.9 | 14.9 | 302.0 |
| 25% | 20.2 | 15.1 | 14.0 | 33.7 | 346.7 |
| 50% | 36.0 | 24.2 | 16.0 | 42.8 | 385.0 |
| 75% | 60.2 | 38.2 | 18.3 | 57.0 | 444.0 |
| Maximum | 153.0 | 94.2 | 26.6 | 99.7 | 862.3 |
| Classifier | Coefficients | Standard Deviation | t | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Intercept | −7.783 | 3.123 | −2.492 | 0.013 |
| PM2.5 | 0.564 | 0.012 | 48.561 | 0.001 |
| Temperature | 1.363 | 0.101 | 13.480 | 0.001 |
| Humidity | −0.228 | 0.021 | −10.906 | 0.001 |
| CO2 | 0.033 | 0.006 | 5.309 | 0.001 |
| Weekday | −7.369 | 0.677 | −10.889 | 0.001 |
| Hyperparameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Learning rate | 0.001 |
| Batch size | 128 |
| Number of iterations | 2000 |
| Model Parameters | Root Mean Squared Error (RMSE) | R-Squared | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Layer | 2_Layer | 5.198 | 0.930 |
| 3_Layer | 3.569 | 0.962 | |
| 4_Layer | 3.626 | 0.958 | |
| Optimizer | Adam | 5.198 | 0.930 |
| Adamax | 5.408 | 0.900 | |
| RMSprop | 4.529 | 0.933 | |
| Node | 32_Node | 5.198 | 0.930 |
| 64_Node | 3.827 | 0.950 | |
| 128_Node | 3.574 | 0.962 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jeon, H.; Ryu, J.; Kim, K.M.; An, J. The Development of a Low-Cost Particulate Matter 2.5 Sensor Calibration Model in Daycare Centers Using Long Short-Term Memory Algorithms. Atmosphere 2023, 14, 1228. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14081228
Jeon H, Ryu J, Kim KM, An J. The Development of a Low-Cost Particulate Matter 2.5 Sensor Calibration Model in Daycare Centers Using Long Short-Term Memory Algorithms. Atmosphere. 2023; 14(8):1228. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14081228
Chicago/Turabian StyleJeon, Hyungjin, Jewan Ryu, Kyoung Min Kim, and Junyeong An. 2023. "The Development of a Low-Cost Particulate Matter 2.5 Sensor Calibration Model in Daycare Centers Using Long Short-Term Memory Algorithms" Atmosphere 14, no. 8: 1228. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14081228
APA StyleJeon, H., Ryu, J., Kim, K. M., & An, J. (2023). The Development of a Low-Cost Particulate Matter 2.5 Sensor Calibration Model in Daycare Centers Using Long Short-Term Memory Algorithms. Atmosphere, 14(8), 1228. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14081228







