Volatility of a Ship’s Emissions in the Baltic Sea Using Modelling and Measurements in Real-World Conditions
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
3. Results
3.1. Volatility Distribution of a Ship’s Emissions
3.2. Comparison to Existing Volatility Distributions
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BC | Black Carbon |
| CPC | Condensation Particle Counter |
| DMA | Differential Mobility Analyser |
| DBT | Dibenzothiophenes |
| eBC | Equivalent Black Carbon |
| FID | Flame Ionisation Detector |
| GC-MS | Gas Chromatography Mass Spectrometer |
| IVOC | Intermediate Volatile Organic Compound |
| LVOC | Low Volatile Organic Compound |
| MGO | Marine Gas Oil |
| NMHC | Non-Methane Hydrocarbon |
| OC | Organic Carbon |
| OM | Organic (Particulate) Matter |
| PAH | Polyaromatic Hydrocarbon |
| POA | Primary Organic Aerosol |
| PTD | Porous Tube Diluter |
| PTFE | Polytetrafluoroethylene |
| PTR-ToF-MS | Proton Transfer Reaction—Time of Flight—Mass Spectrometer |
| SCR | Selective Catalytic Reduction |
| SMPS | Scanning Mobility Particle Sizer |
| SOA | Secondary Organic Aerosol |
| SP-AMS | Soot Particle Aerosol Mass Spectrometer |
| STEAM | Ship Traffic Emission Assessment Model |
| SVOC | Semi-Volatile Organic Compound |
| THC | Total Hydrocarbons |
| VBS | Volatility Basis Set |
| VOC | Volatile Organic Compound |
References
- Pope, C.A.; Dockery, D.W. Health Effects of Fine Particulate Air Pollution: Lines that Connect. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2006, 56, 709–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caiazzo, F.; Ashok, A.; Waitz, I.A.; Yim, S.H.L.; Barrett, S.R.H. Air pollution and early deaths in the United States. Part I: Quantifying the impact of major sectors in 2005. Atmos. Environ. 2013, 79, 198–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pieters, N.; Koppen, G.; Van Poppel, M.; De Prins, S.; Cox, B.; Dons, E.; Nelen, V.; Panis, L.I.; Plusquin, M.; Schoeters, G.; et al. Blood Pressure and Same-Day Exposure to Air Pollution at School: Associations with Nano-Sized to Coarse PM in Children. Environ. Health Perspect. 2015, 123, 737–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lelieveld, J. Clean Air in the Anthropocene. Faraday Discuss. 2017, 200, 693–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramanathan, V.; Feng, Y. Air pollution, greenhouse gases and climate change: Global and regional perspectives. Atmos. Environ. 2009, 43, 37–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seinfeld, J.H.; Bretherton, C.; Carslaw, K.S.; Coe, H.; DeMott, P.J.; Dunlea, E.J.; Feingold, G.; Ghan, S.; Guenther, A.B.; Kahn, R.; et al. Improving Our Fundamental Understanding of the Role of Aerosol-cloud Interactions in the Climate System. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 5781–5790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bellouin, N.; Quaas, J.; Gryspeerdt, E.; Kinne, S.; Stier, P.; Watson-Parris, D.; Boucher, O.; Carslaw, K.S.; Christensen, M.; Daniau, A.-L.; et al. Bounding Global Aerosol Radiative Forcing of Climate Change. Rev. Geophys. 2016, 58, e2019RG000660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sofiev, M.; Winebrake, J.J.; Johansson, L.; Carr, E.W.; Prank, M.; Soares, J.; Vira, J.; Kouznetsov, R.; Jalkanen, J.-P.; Corbett, J.J. Cleaner fuels for ships provide public health benefits with climate tradeoffs. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becagli, S.; Anello, F.; Bommarito, C.; Cassola, F.; Calzolai, G.; Di Iorio, T.; di Sarra, A.; Gómez-Amo, J.-L.; Lucarelli, F.; Marconi, M.; et al. Constraining the ship contribution to the aerosol of the central Mediterranean. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2017, 17, 2067–2084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moldanová, J.; Fridell, E.; Winnes, H.; Holmin-Fridell, S.; Boman, J.; Jedynska, A.; Tishkova, V.; Demirdjian, B.; Joulie, S.; Bladt, H.; et al. Physical and chemical characterisation of PM emissions from two ships operating in European Emission Control Areas. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2013, 6, 3577–3596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Review of Maritime Transport 2022. United Nations Conference on Trade and Development. Available online: https://unctad.org/webflyer/reviewmaritime-transport-2021 (accessed on 5 April 2023).
- Streibel, T.; Schnelle-Kreis, J.; Czech, H.; Harndorf, H.; Jakobi, G.; Jokiniemi, J.; Karg, E.; Lintelmann, J.; Matuschek, G.; Michalke, B.; et al. Aerosol emissions of a ship diesel engine operated with diesel fuel or heavy fuel oil. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 10976–10991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, F.; Feng, Y.; Zheng, M.; Li, Q.; Chen, J. Emission Characteristics and Formation Pathways of Intermediate Volatile Organic Compounds from Ocean-Going Vessels: Comparison of Engine Conditions and Fuel Types. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 56, 12917–12925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehtoranta, K.; Vesala, H.; Koponen, P.; Korhonen, S. Selective Catalytic Reduction Operation with Heavy Fuel Oil: NOx, NH3, and Particle Emissions. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 4735–4741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robinson, A.L.; Donahue, N.M.; Shrivastava, M.K.; Weitkamp, E.A.; Sage, A.M.; Grieshop, A.P.; Lane, T.E.; Pierce, J.R.; Pandis, S.N. Rethinking Organic Aerosols: Semivolatile Emissions and Photochemical Aging. Science 2007, 315, 1259–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, P.K.; Khlystov, A.; Grieshop, A.P. Downwind evolution of the volatility and mixing state of near-road aerosols near a US interstate highway. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 18, 2139–2154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Hu, Q.; Li, Y.; Tian, J.; Ma, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Feng, J.; An, J.; Qiao, L.; Wang, H.; et al. Intermediate Volatility Organic Compound Emissions from a Large Cargo Vessel Operated under Real-World Conditions. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 12934–12942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Ling, Z.; Liu, H.; Shao, M.; Lu, S.; Wu, L.; Wang, X. A Gridded Emission Inventory of Semi-Volatile and Intermediate Volatility Organic Compounds in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 761, 106546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Hennigan, C.J.; May, A.A.; Tkacik, D.S.; de Gouw, J.A.; Gilman, J.B.; Kuster, W.C.; Borbon, A.; Robinson, A.L. Intermediate-Volatility Organic Compounds: A Large Source of Secondary Organic Aerosol. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 13743–13750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortega, A.M.; Hayes, P.L.; Peng, Z.; Palm, B.B.; Hu, W.; Day, D.A.; Li, R.; Cubison, M.J.; Brune, W.H.; Graus, M.; et al. Real-Time Measurements of Secondary Organic Aerosol Formation and Aging from Ambient Air in an Oxidation Flow Reactor in the Los Angeles Area. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 16, 7411–7433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, Z.; Wu, L.; Wang, Y.; Shao, M.; Wang, X.; Huang, W. Roles of Semivolatile and Intermediate-Volatility Organic Compounds in Secondary Organic Aerosol Formation and Its Implication: A Review. J. Environ. Sci. 2022, 114, 259–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donahue, N.M.; Robinson, A.L.; Stanier, C.O.; Pandis, S.N. Coupled Partitioning, Dilution, and Chemical Aging of Semivolatile Organics. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2006, 40, 2635–2643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, Z.; Xie, Z.; Wang, G.; Zhang, R.; Tao, J. Modeling Organic Aerosols over East China Using a Volatility Basis-Set Approach with Aging Mechanism in a Regional Air Quality Model. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 124, 186–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciarelli, G.; Aksoyoglu, S.; Crippa, M.; Jimenez, J.-L.; Nemitz, E.; Sellegri, K.; Äijälä, M.; Carbone, S.; Mohr, C.; O’Dowd, C.; et al. Evaluation of European Air Quality Modelled by CAMx Including the Volatility Basis Set Scheme. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 16, 10313–10332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riipinen, I.; Pierce, J.R.; Donahue, N.M.; Pandis, S.N. Equilibration time scales of organic aerosol inside thermodenuders: Evaporation kinetics versus thermodynamics. Atmos. Environ. 2010, 44, 597–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donahue, N.M.; Epstein, S.A.; Pandis, S.N.; Robinson, A.L. A Two-Dimensional Volatility Basis Set: 1. Organic-Aerosol Mixing Thermodynamics. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2011, 11, 3303–3318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Epstein, S.A.; Riipinen, I.; Donahue, N.M. A Semiempirical Correlation between Enthalpy of Vaporization and Saturation Concentration for Organic Aerosol. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 743–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tikkanen, O.-P.; Hämäläinen, V.; Rovelli, G.; Lipponen, A.; Shiraiwa, M.; Reid, J.P.; Lehtinen, K.E.J.; Yli-Juuti, T. Optimization of process models for determining volatility distribution and viscosity of organic aerosols from isothermal particle evaporation data. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2019, 19, 9333–9350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yli-Juuti, T.; Pajunoja, A.; Tikkanen, O.-P.; Buchholz, A.; Faiola, C.; Väisänen, O.; Hao, L.; Kari, E.; Peräkylä, O.; Garmash, O.; et al. Factors controlling the evaporation of secondary organic aerosol from α-pinene ozonolysis. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2017, 44, 2562–2570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Aksoyoglu, S.; El-Haddad, I.; Ciarelli, G.; Denier van der Gon, H.A.C.; Canonaco, F.; Gilardoni, S.; Paglione, M.; Minguillón, M.C.; Favez, O.; et al. Sources of Organic Aerosols in Europe: A Modeling Study Using CAMx with Modified Volatility Basis Set Scheme. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2019, 19, 15247–15270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Yang, W.; Wang, Z.; Li, J.; Hu, M.; An, J.; Wu, Q.; Wang, Z.; Chen, H.; Wei, Y.; et al. Improving New Particle Formation Simulation by Coupling a Volatility-Basis Set (VBS) Organic Aerosol Module in NAQPMS+APM. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 204, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Nguyen, N.T.; Presto, A.A.; Hennigan, C.J.; May, A.A.; Robinson, A.L. Intermediate Volatility Organic Compound Emissions from On-Road Gasoline Vehicles and Small Off-Road Gasoline Engines. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 4554–4563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alam, M.S.; Zeraati-Rezaei, S.; Xu, H.; Harrison, R.M. Characterization of Gas and Particulate Phase Organic Emissions (C9–C37) from a Diesel Engine and the Effect of Abatement Devices. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 11345–11352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Q.; Zhao, Y.; Robinson, A.L. Comprehensive Organic Emission Profiles for Gasoline, Diesel, and Gas-Turbine Engines Including Intermediate and Semi-Volatile Organic Compound Emissions. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 18, 17637–17654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, M.; Salo, K.; Hallquist, Å.M.; Fridell, E. Characterization of Particles from a Marine Engine Operating at Low Loads. Atmos. Environ. 2015, 101, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alanen, J.; Isotalo, M.; Kuittinen, N.; Simonen, P.; Martikainen, S.; Kuuluvainen, H.; Honkanen, M.; Lehtoranta, K.; Nyyssönen, S.; Vesala, H.; et al. Physical Characteristics of Particle Emissions from a Medium Speed Ship Engine Fueled with Natural Gas and Low-Sulfur Liquid Fuels. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 5376–5384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alanen, J.; Simonen, P.; Saarikoski, S.; Timonen, H.; Kangasniemi, O.; Saukko, E.; Hillamo, R.; Lehtoranta, K.; Murtonen, T.; Vesala, H.; et al. Comparison of Primary and Secondary Particle Formation from Natural Gas Engine Exhaust and of Their Volatility Characteristics. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2017, 17, 8739–8755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onasch, T.B.; Trimborn, A.; Fortner, E.C.; Jayne, J.T.; Kok, G.L.; Williams, L.R.; Davidovits, P.; Worsnop, D.R. Soot Particle Aerosol Mass Spectrometer: Development, Validation, and Initial Application. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 804–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petzold, A.; Hasselbach, J.; Lauer, P.; Baumann, R.; Franke, K.; Gurk, C.; Schlager, H.; Weingartner, E. Experimental Studies on Particle Emissions from Cruising Ship, Their Characteristic Properties, Transformation and Atmospheric Lifetime in the Marine Boundary Layer. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2008, 8, 2387–2403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timonen, H.; Teinilä, K.; Barreira, L.; Saarikoski, S.; Simonen, P.; Dal Maso, M.; Keskinen, J.; Kalliokoski, J.; Moldonova, J.; Salberg, H.; et al. SCIPPER Project Deliverable D3.3 Ship on-Board Emissions Characterisation; EU: Maastricht, The Netherlands, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Kautzman, K.E.; Surratt, J.D.; Chan, M.N.; Chan, A.W.H.; Hersey, S.P.; Chhabra, P.S.; Dalleska, N.F.; Wennberg, P.O.; Flagan, R.C.; Seinfeld, J.H. Chemical Composition of Gas- and Aerosol-Phase Products from the Photooxidation of Naphthalene. J. Phys. Chem. A 2010, 114, 913–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalkanen, J.-P.; Brink, A.; Kalli, J.; Pettersson, H.; Kukkonen, J.; Stipa, T. A Modelling System for the Exhaust Emissions of Marine Traffic and Its Application in the Baltic Sea Area. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2009, 9, 9209–9223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalkanen, J.-P.; Johansson, L.; Kukkonen, J.; Brink, A.; Kalli, J.; Stipa, T. Extension of an Assessment Model of Ship Traffic Exhaust Emissions for Particulate Matter and Carbon Monoxide. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2012, 12, 2641–2659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, H.; Welch, W.A.; Miller, J.W.; Cocker, D.R. Emission Measurements from a Crude Oil Tanker at Sea. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 7098–7103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sippula, O.; Stengel, B.; Sklorz, M.; Streibel, T.; Rabe, R.; Orasche, J.; Lintelmann, J.; Michalke, B.; Abbaszade, G.; Radischat, C.; et al. Particle Emissions from a Marine Engine: Chemical Composition and Aromatic Emission Profiles under Various Operating Conditions. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 11721–11729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reichle, L.J.; Cook, R.; Yanca, C.A.; Sonntag, D.B. Development of Organic Gas Exhaust Speciation Profiles for Nonroad Spark-Ignition and Compression-Ignition Engines and Equipment. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2015, 65, 1185–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grigoriadis, A.; Mamarikas, S.; Ntziachristos, L.; Majamäki, E.; Jalkanen, J.-P. SCIPPER Project Deliverable D4.1 New Set of Emission Factors and Activity Information; EU: Maastricht, The Netherlands, 2021. [Google Scholar]

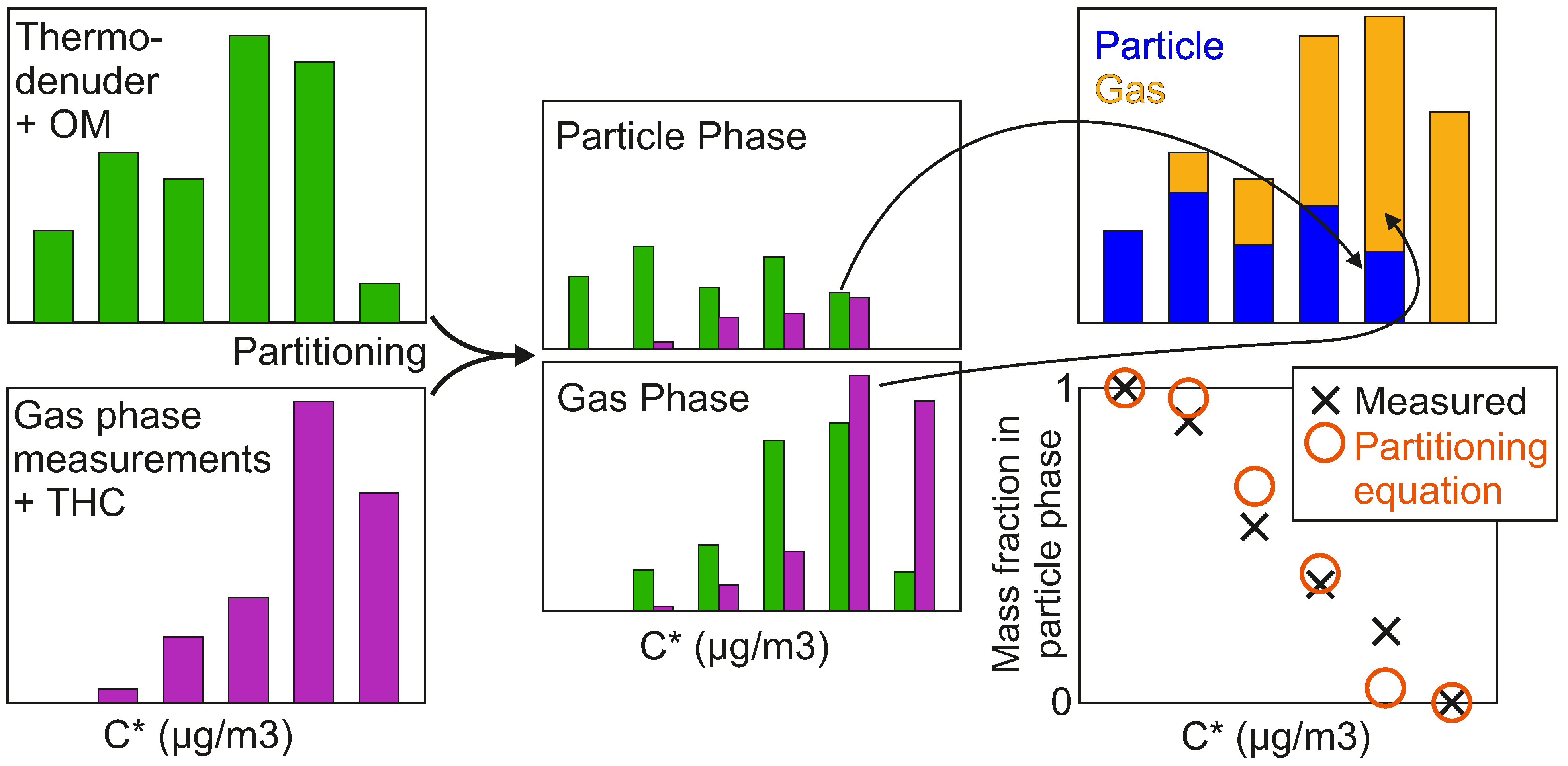







| Fuel | Engine Load | After-Treatment |
|---|---|---|
| Marine gas oil | 70% | SCR without urea |
| Marine gas oil | 70% | SCR with urea |
| Marine gas oil | 50% | SCR without urea |
| Marine gas oil | 50% | SCR with urea |
| Methanol | 50% | SCR without urea |
| MGO, 70% Load, Urea Off | MGO, 70% Load, Urea On | MGO, 50% Load, Urea Off | MGO, 50% Load, Urea On | Methanol, 50% Load, Urea Off | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total concentration in the exhaust (mg/m) | 13.9 | 12.8 | 7.7 | 9.0 | 73.2 |
| Particle phase emission (mg/kg fuel) | 208.4 | 174.7 | 77.0 | 101.3 | 248.1 |
| Gas phase emission (mg CHeq./kg fuel) | 284.7 | 327.1 | 276.2 | 268.2 | 1349.5 |
| Particle phase emission (mg/kg fuel) (DR = 1000) | 127.2 | 124.3 | 58.6 | 78.2 | 32.6 |
| Gas phase emission (mg CHeq./kg fuel) (DR = 1000) | 416.4 | 411.4 | 297.4 | 302.9 | 1700.9 |
| LogC* | MGO with 50% Engine Load, Urea Off | Huang et al. [17], Low Sulfur Fuel |
|---|---|---|
| Nonvolatile (<−1) | 3 | |
| −1 | ||
| 0 | ||
| 1 | ||
| 2 | ||
| 3 | ||
| 4 | ||
| 5 | ||
| 6 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kangasniemi, O.; Simonen, P.; Moldanová, J.; Timonen, H.; Barreira, L.M.F.; Hellén, H.; Jalkanen, J.-P.; Majamäki, E.; D’Anna, B.; Lanzafame, G.; et al. Volatility of a Ship’s Emissions in the Baltic Sea Using Modelling and Measurements in Real-World Conditions. Atmosphere 2023, 14, 1175. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14071175
Kangasniemi O, Simonen P, Moldanová J, Timonen H, Barreira LMF, Hellén H, Jalkanen J-P, Majamäki E, D’Anna B, Lanzafame G, et al. Volatility of a Ship’s Emissions in the Baltic Sea Using Modelling and Measurements in Real-World Conditions. Atmosphere. 2023; 14(7):1175. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14071175
Chicago/Turabian StyleKangasniemi, Oskari, Pauli Simonen, Jana Moldanová, Hilkka Timonen, Luis M. F. Barreira, Heidi Hellén, Jukka-Pekka Jalkanen, Elisa Majamäki, Barbara D’Anna, Grazia Lanzafame, and et al. 2023. "Volatility of a Ship’s Emissions in the Baltic Sea Using Modelling and Measurements in Real-World Conditions" Atmosphere 14, no. 7: 1175. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14071175
APA StyleKangasniemi, O., Simonen, P., Moldanová, J., Timonen, H., Barreira, L. M. F., Hellén, H., Jalkanen, J.-P., Majamäki, E., D’Anna, B., Lanzafame, G., Temime-Roussel, B., Mellqvist, J., Keskinen, J., & Dal Maso, M. (2023). Volatility of a Ship’s Emissions in the Baltic Sea Using Modelling and Measurements in Real-World Conditions. Atmosphere, 14(7), 1175. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14071175







