Abstract
The research on regional aerosol optical properties is of great significance for exploring climate regulation mechanisms and controlling atmospheric pollution. Based on the solar radiation observation platform, a three-month optical observation of atmospheric aerosols was conducted in Wuhan, China. The daily and monthly variation characteristics of aerosol optical depth (AOD550), Angstrom parameter (α440–870), and turbidity coefficient (β) were revealed, and the interrelations between the three optical parameters were fitted. Then, the potential relationships between atmospheric particulate matter (PM2.5, PM10) with AOD550 and β were discussed. The results show that the average values of AOD550, α440–870, and β in this case study are 0.42, 1.32, and 0.20, respectively. The frequency distribution patterns of the three optical parameters are all unimodal. AOD550 has a good linear correlation system with β, and the Pearson correlation coefficient reaches 0.94, while its correlation with α440–870 is not significant. The daily variation in AOD550 and β both show an increasing trend, and their monthly increases are more than 50%. However, the daily variation in α440–870 is relatively stable, and the fitted line is a nearly horizontal line with no significant monthly variation. The fluctuation of particulate matter concentration affects the aerosol optical properties to some extent, among which β has a prominent effect on the response to the change in PM2.5 concentration with a linear correlation coefficient of 0.861. As the concentration of particulate matter increases, the proportion of fine particulate matter in the atmosphere increases monthly, and the ratio of PM10 to PM2.5 concentrations decreases from 1.8:1 to 1.2:1. Atmospheric pollution conditions are frequent during this observation period, mainly at mildly turbid levels. Atmospheric turbidity shows an increasing trend month by month, and the concentration of particulate matter increases rapidly. The response of atmospheric aerosol optical properties to the changes in fine particulate matter concentration is significant, and controlling the particulate matter content in the atmosphere is an effective means to mitigate aerosol pollution.
1. Introduction
Aerosols are multiphase systems of solid particles and liquid droplets suspended in the atmosphere, with diameters usually ranging from 0.001 to 100 μm. Aerosols change the regional climate environment by participating in the formation of clouds and rain in the atmosphere, and their absorption and scattering effects on solar radiation also affect the radiation balance of the Earth-atmosphere system [1,2]. Aerosols can be classified into various categories according to different classification bases, and multiple types of aerosols can exist simultaneously in the atmosphere [3,4]. Various types of aerosol particles participate together in the evolution of the atmosphere, and their interactions lead to the production of more aerosol particles, diversifying the composition of the atmosphere [5,6,7]. Aerosols are present in the human living environment all the time, and the occurrence of atmospheric pollution events such as acid rain, haze, and dust are closely related to aerosols [8,9]. Harmful substances such as viruses and bacteria carried in aerosols can cause respiratory damage and pose a serious threat to human health [10,11,12]. Some studies have shown that transmissible diseases such as COVID-19 can be transmitted through aerosols [13]. As an important component of the atmosphere, aerosols have an inescapable role in the regional climate environment, the energy balance of the Earth-atmosphere system, and human life [14,15]. Therefore, it is of great application and scientific significance to actively extend the research of aerosol optical properties of multi-regional and deeply analyze their response mechanisms to the atmospheric environment.
The more pronounced spatial and temporal variability of aerosols and their smaller amount in the atmosphere makes it difficult to obtain the optical properties of aerosols than other gases [16,17]. The current methods of aerosol observation are ground-based observations and satellite remote sensing [18,19]. The advantages of satellite remote sensing include wide spatial coverage, lengthy time series, high resolution, and regional projection imaging [20,21]. In recent years, a large number of observations and analyses of aerosol optical properties have been carried out by domestic and foreign scientists using satellite remote sensing [22,23,24,25]. Instruments such as Moderate-resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) and Multi-angle Imaging Spectrometer (MISR) have become common tools for satellite remote sensing observations [26,27]. Satellite remote sensing technology allows real-time aerosol observations in most regions of the world by combining different inversion algorithms. Therefore, it is a good solution to the challenge of aerosol research across regions [28,29]. However, the drawbacks of satellite remote sensing cannot be ignored, such as fewer aerosol product bands, longer intervals between remote sensing observations, and insufficient data accuracy [30,31].
Continuous long-term series of aerosol characterization is indispensable in resolving the response of the atmospheric environment to aerosol changes. In order to make up for the shortage of satellite remote sensing observations, ground-based observations are favored by many scientists because of their high accuracy and time continuity [32,33,34]. Gong W. et al. analyzed columnar aerosol volume size distributions from March 2012 to February 2013 in Wuhan, China [35]. Ground-based observation methods have also been used to verify the accuracy of satellite remote sensing data [36,37,38]. Wang W. et al. evaluated the AOD of VIIRS and MODIS in the Wuhan area using photometric measurements [39]. In fact, most ground-based observational studies rely on the global Aerosol Robotic Network (AERONET) established by NASA. However, there are few ground-based sites in China, and many of them are not publicly authorized for use. Therefore, in regions where AERONET stations are not located, self-established aerosol ground-based observation platforms are of significant importance for aerosol characterization research [40,41].
Domestic and foreign scientists have conducted extensive studies worldwide through ground-based measurements and remote-sensing observations. However, regional research on aerosol optical properties, especially for regions without AERONET sites, still needs to be supplemented. Therefore, in this study, aerosol optical depth (AOD550), Angstrom parameter (α440–870), and turbidity coefficient (β) were measured for the period from November 2021 to January 2022 using a ground-based observation platform equipped with the TBS-4 solar spectrometer built in Wuhan. Its applicability as an aerosol observation instrument was verified by comparison with the aerosol products obtained from satellite remote sensing. The variation characteristics of aerosol optical parameters and their interrelationships were then analyzed from the perspective of daily and monthly variation, respectively. Finally, the effects of particulate matter (PM2.5, PM10) on aerosol optical properties were revealed based on air quality data.
2. Experimental Principles and Methods
2.1. Experimental Instruments and Data
The TBS-4 solar spectrometer used in this paper is manufactured by Jinzhou Sunshine Meteorological Technology Co., Ltd. (Jinzhou, China). It uses synchronous measurement technology and GPS satellite location tracking technology to simultaneously measure solar spectral radiation in 9 bands (340, 380, 440, 500, 675, 870, 936, 1020, and 1640 nm) with a measurement accuracy of less than 1%. The experimental site is located at Wuhan University of Science and Technology (114°26′ E, 30°44′ N), with an altitude of 40 m above sea level. There is no shade over the location of the solar spectrometer, and the instrument is powered by solar photovoltaic panels, with a power storage device that can meet the low light operation for 3 days. Figure 1 shows the location and physical presence of the TBS-4 sun photometer. The observation period is from November 2021 to January 2022, with spectral radiation collected every 5 min. Valid data selection criteria: Cumulative sunshine hours must be greater than 5 h, or the data for that day are rejected. Mean values were taken for each half-hour observation, excluding offsets greater than 20% and 550 band radiative values less than 10 W·m−2 from the observations. To take three adjacent data in chronological order, the intermediate moment data need not be smaller than the previous and next data values; otherwise, the data are not available. The remaining daily data amounts larger than 50 were used as the final radiation data. The data were filtered to leave 38 available observation days.
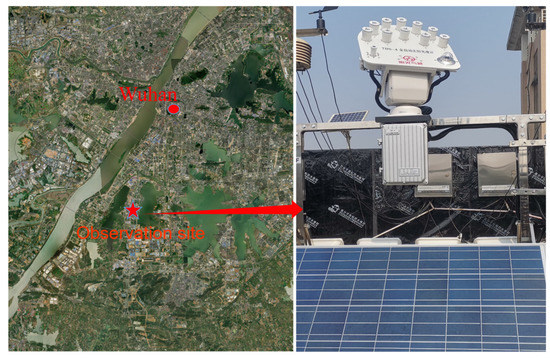
Figure 1.
The TBS-4 solar photometer and its location.
PM2.5 and PM10 are pollution concentration indicators that are divided based on the equivalent diameter of particles, and their values directly affect atmospheric quality. The concentration data of PM2.5 and PM10 are sourced from the Air Quality Online Monitoring and Analysis Platform (https://www.aqistudy.cn/ (accessed on 21 May 2023)). The daily and monthly average PM concentrations were calculated separately for use. The satellite remote sensing data used in this study were obtained from 3 km resolution AOD550 products provided by the Terra satellite of the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA). Remote sensing image processing and analysis of the study area were carried out by ENVI + IDL software.
2.2. Principles and Methods of Calculation
According to Bouguer–Lamber law, in the non-water vapor absorption channel, the direct solar radiation E(λ) of the surface incident on the earth with a wavelength of λ is:
E0(λ) is the solar spectral irradiance at the solar-terrestrial mean distance at the upper boundary of the atmosphere at a wavelength of λ. is the solar-terrestrial distance correction factor. Neglecting the absorption of solar radiation by the absorbing gas in the above bands, . is the atmospheric optical mass at a zenith angle of θ. τ(λ) is the total atmospheric optical depth of the spectrum.
where n is the number of day sequences, with January 1st as the first day, and h is the solar altitude angle.
Take the logarithm at both ends of Equation (1) to obtain the following formula:
A simple linear regression was performed with m as the independent variable and as the dependent variable. The total atmospheric optical depth is represented by the slope of the fit result in absolute terms, and the instrument calibration value is represented by the intercept .
In order to ensure calibration accuracy, clear weather is chosen for the calibration of the spectrometer. When the atmosphere is clear and cloudless, the aerosol state is stable, and the AOD changes slightly. In the linear regression fitting, the variation range of m should be larger than 3.5. The sample points with the largest fitting residuals should be excluded when the correlation coefficient is less than 0.99. The number of excluded samples should be less than 30%, and the remaining samples should be more than 15.
The total atmospheric optical depth is mainly composed of Rayleigh scattering optical depth , aerosol optical depth and absorbing gas optical depth .
where the main components of the absorbing gas are ozone, water vapor, carbon dioxide, and oxygen, among others. For the 440 nm and 870 nm bands chosen for the calculations in this paper, only the absorption effect of ozone needs to be taken into account; P and P0 are the atmospheric pressure and standard atmospheric pressure (1013.25 mbar) at the observation site, respectively; λ is the wavelength of the spectrum, calculated in µm; is the absorption coefficient of ozone; and U is the ozone content.
The formula for calculating the ozone content is as follows:
where ξ and φ are the longitude and latitude of the observation location.
The relationship between aerosol optical depth and the Angstrom parameter α and turbidity coefficient β is expressed as:
AOD, α, and β are three basic dimensionless parameters to characterize the atmospheric aerosol optical properties, which are key factors used to assess aerosol content, determine the types of aerosols and measure the degree of atmospheric pollution [42,43,44]. AOD is defined as the integral of the atmospheric extinction coefficient in the vertical direction, which reflects the extinction characteristics of aerosols. α reflects the particle size of aerosol particles, and its value generally ranges from 0 to 2. The closer the value of α is to 2, the smaller the particle size of the main particles of aerosols, and vice versa. β is numerically equal to the aerosol optical depth at a wavelength of 1 µm and can be used to indicate the degree of atmospheric turbidity. According to the common classification basis, the atmosphere is generally classified into four classes: clean atmosphere (β ≤ 0.1), mildly turbid atmosphere (0.1 < β ≤ 0.2), turbid atmosphere (0.2 < β ≤ 0.4), and heavily turbid atmosphere (β > 0.4) [45,46].
To match the 550 nm band aerosol products provided by MODIS, the AOD550 are obtained by substituting α440–870 and β values into Equation (10) using the interpolation method.
2.3. Accuracy Verification of the Measured AOD550
In order to verify the feasibility of observing aerosol optical properties by this model of the spectrometer, the accuracy of ground-based measurement of AOD550 was verified using AOD550 of MOD04_3K. The average value of ground-based observations before and after the satellite transit for half an hour is calculated as the measured value. The image element of the remote sensing image where the ground-based site is located, its surroundings are selected as the study area, and its mean value is used as the satellite remote sensing value. The ground-based measurement values and the satellite remote sensing values were spatially and temporally matched according to the above method and then presented as data points in Figure 2, with linear regression processing. The linear fit of data points results in , which shows a small angle with the 1:1 reference line. In the low-value region of AOD550, the ground-based measurements are somewhat underestimated compared with the satellite remote sensing values. The experimentally measured AOD550 was calculated to have a good linear correlation with the remotely sensed observed AOD550. Their Pearson correlation coefficients reached 0.96, and the root mean square error was 0.076. It is evident that the inversion of AOD550 using the TBS-4 model solar spectrometer is workable.
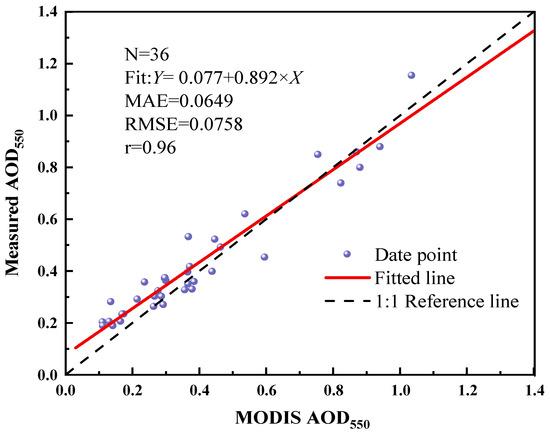
Figure 2.
Accuracy verification of ground-based measured AOD550.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Aerosol Optical Properties
3.1.1. General Characteristics of Aerosol Optical Parameters
The daily average values of the three optical parameters (AOD550, α440–870, and β) were calculated daily, and their daily variations were presented as dotted line plots in Figure 3. As seen in the figure, the AOD550 on November 30, 2021, is 0.19, and the β coefficient is only 0.09, which is the lowest value during the observation period. According to the criteria for classifying atmospheric turbidity levels by beta coefficients, the atmosphere was in the best clean state on that day. The AOD550 values on 9 December 2021 and 19 January 2022 showed anomalously high values of 1.16 and 1.26, respectively, which far exceeded the values of other observed days. Moreover, the turbidity coefficients exceed 0.4, and the atmosphere is in a heavily turbid state on these two days due to severe aerosol pollution events. The daily mean values of the optical parameters are fitted linearly, as shown by the dashed lines in Figure 3. AOD550 and β show an increasing trend, and the slope of the fitted line is 0.0067 and 0.0029, respectively, which indicates that the atmospheric pollution condition is worsening. As a whole, when the AOD550 value increases or decreases, the β value also produces a certain magnitude of isotropic fluctuations. The trends of AOD550 and β are consistent, but the growth rate of AOD550 is higher than that of β, and the linear fit of α440–870 results in an approximate horizontal straight line. The data points show irregular and limited fluctuations above and below the fitted line, indicating that the particle size of the main atmospheric aerosol particles changes steadily during the observation period.
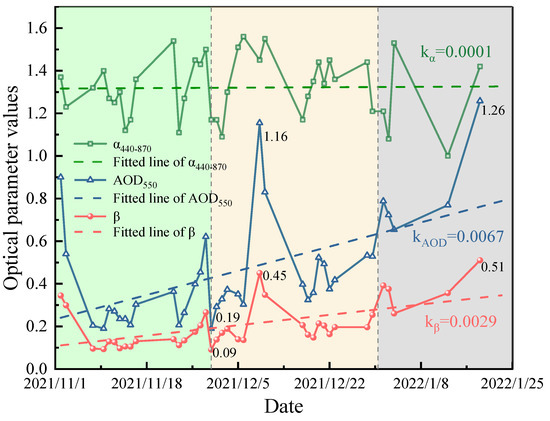
Figure 3.
Daily variation in the atmospheric aerosol optical properties.
The experimental AOD550, α440–870, and β were numerically counted, and their means and standard deviations were calculated for the whole experimental period. The detailed values are shown in Table 1. The intervals of AOD550, α440–870, and β were divided by 0.1 steps, and the frequency ratios of each interval were counted, and the results are shown in Figure 4. The frequency ratios for all three optical parameters show unimodal distribution. The percentage of frequencies of AOD550 in the low-value range (AOD550 < 0.4) reached 55.7%. Its peak occurs in the interval of 0.3–0.4, and the frequency in this interval reaches 23.0%. The mean value of AOD550 is 0.42, and the standard deviation is 0.24, which shows that the attenuation effect of aerosols on solar radiation is not significant. The mean value of α440–870 is 1.32 with a standard deviation of 0.20. Its frequency proportion in the peak interval of 1.3–1.4 reaches 23.4%, indicating that the atmosphere is mainly composed of fine size aerosol particles. The mean value of β is 0.20 with a standard deviation of 0.09. According to the distribution of the frequency proportion of β in each interval, it can be seen that the frequency proportion of clean atmosphere is only 12.9%, while the frequency in the interval of 0.1–0.2 is as high as 52.6%. Based on the criteria for classifying atmospheric turbidity levels based on β values, the atmospheric pollution conditions in the Wuhan area during this observation period were frequent, mainly at mild turbidity degrees, and some states reached heavy turbidity levels.

Table 1.
Mean value and standard deviation of aerosol optical parameters.
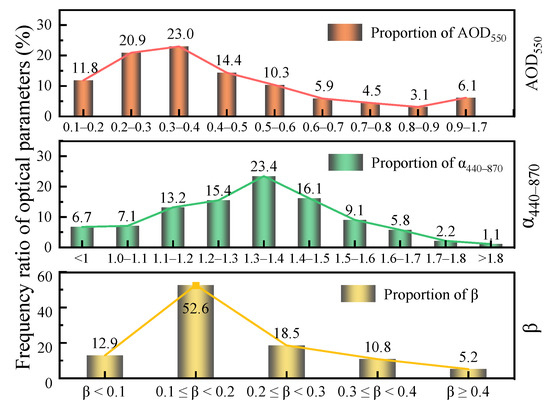
Figure 4.
Frequency distribution of atmospheric aerosol optical properties.
3.1.2. Correlation of Aerosol Optical Parameters
Figure 5 shows the scatter plot of AOD550 with α440–870 and β, respectively, using density mapping to show the data distribution. The solid line in the figures is the result of the linear fit. The red color represents the high degree of sample aggregation, while the blue color represents the small sample size and low aggregation. AOD550 and β show a regular linear distribution, and their fitting equation is . With the increase in atmospheric turbidity, the attenuation effect of aerosol particles on radiation is enhanced, which makes AOD550 increase. Their linear correlation was extremely high, with a positive correlation coefficient of 0.94. In the low-value region where AOD550 was less than 0.4 and β was less than 0.2, the proportion of samples reached 57.6%, while in the high-value region, it was relatively scattered. Once again, it shows that the main state of atmospheric aerosols during this observation period was mildly turbid degree with low aerosol content. The sample distribution of AOD550 and α440–870 was relatively scattered, and the linear fit correlation coefficient was only 0.36. The scattered distribution results of AOD550 and α440–870 showed that they were mainly gathered in the region of AOD550 less than 0.6 but did not show an obvious linear correlation. With the increase in AOD550, α440–870 and β mainly showed increasing trends, among which the increasing trend of α440–870 was relatively slight. This phenomenon indicated that the particle size of the main aerosol particles showed a small decrease when the atmospheric turbidity increased.
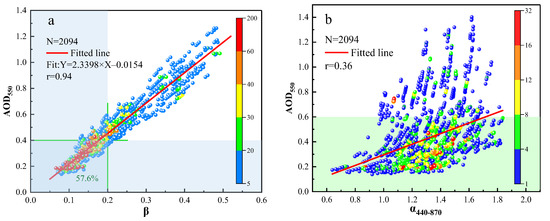
Figure 5.
Scatter distribution of the combination of AOD550 with β (a) and α440–870 (b), respectively.
3.1.3. Monthly Variation in Aerosol Optical Parameters
The mean values of AOD550, α440–870, and β by month are counted, and the results are shown in Table 2. Moreover, Figure 6 shows the numerical variations in the three optical parameters in the form of a boxplot. Compared with November 2021, the mean value of α440–870 in December 2021 increased by 0.1, indicating a small decrease in the aerosol particle size. The standard deviation of α440–870 in each month was close, among which the standard deviation of α440–870 in December 2021 was the smallest at 0.19, and the best concentration of particle size can be found in that month combined with the boxplot. The mean value of α440–870 fell back to 1.26 in January 2022. However, the particle size distribution of aerosols was more dispersed in that month, with a maximum standard deviation of 0.25. The aerosols in each month of the observation period mainly consisted of fine-sized particles with a more concentrated particle size distribution. The mean value of β showed an increasing trend monthly, from 0.14 in November 2021 to 0.22 in December 2021, reflecting the increase in the atmospheric from mild turbidity level to turbidity level. The mean value of β increased again to 0.36 in January 2022, which was 63.64% higher compared to the previous month, and the degree of atmospheric pollution further increased. The standard deviation of β for all months was less than 0.1, indicating the high degree of aggregation of β distribution. AOD550 increased rapidly at a rate of more than 0.20 per month. Its average value was 0.30 in November 2021, and by January 2022, the average AOD550 value reached 0.76, an increase of 153.33%. It revealed that the atmospheric turbidity in the Wuhan region gradually increased during the study period, and the attenuation of solar radiation by atmospheric aerosol particles also gradually increased.

Table 2.
Monthly means and standard deviations of aerosol optical parameters.
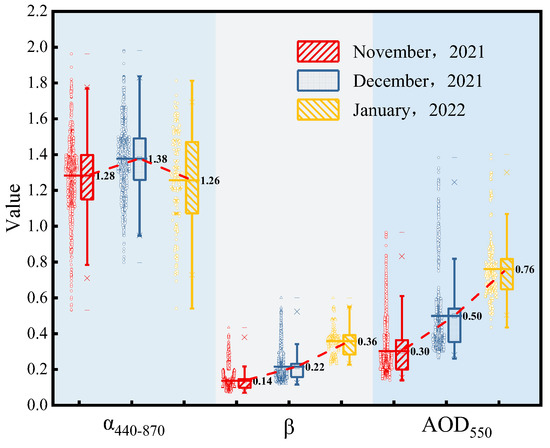
Figure 6.
Boxplot of monthly variation in AOD550, α440–870, and β.
3.2. Atmospheric Particulate Matter
The mean values of particulate matter concentrations (PM2.5, PM10) during the observation period were calculated by month and shown in Figure 7, along with the monthly variations in aerosol optical depth and turbidity coefficient. By comparing with the aerosol optical parameters, it can be found that the concentration of particulate matter rises rapidly with the aggravation of atmospheric turbidity, showing an increasing trend from month to month. The monthly relative increases in PM2.5, AOD550, and β all exceeded 50%, while the monthly relative increase in PM10 was near 30%. The monthly increase in fine particulate matter content far exceeded the increase in coarse particulate matter over the same period, as detailed in Table 3. Regarding the closest monthly relative increase in PM2.5 and β, the increase in PM2.5 content from November 2021 to December 2021 was 52%, and the increase in β during the same period was 57%. By January 2022, the monthly increase in PM2.5 increased to 76%, and the increase in β value in that period was 64%. This indicates that there was a relatively strong correlation between the fine particulate matter content and the degree of atmospheric turbidity. In November 2021, the PM10 and PM2.5 concentrations were 74.47 μg·m−3 and 41.82 μg·m−3, respectively, with a ratio of 1.8:1, and in January 2022, the ratio decreased to 1.2:1. As atmospheric turbidity increases during the observation period, the particulate matter content increases significantly, with fine particulate matter playing a major role in this process.
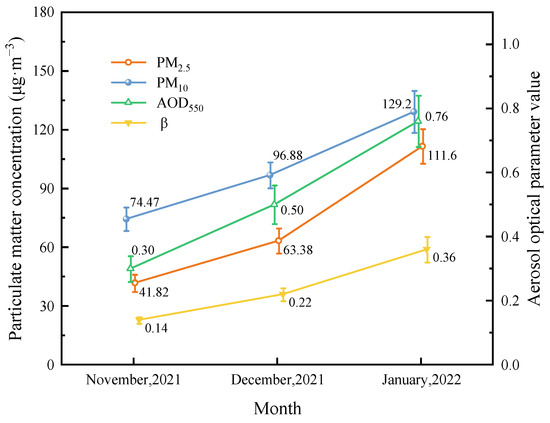
Figure 7.
Variation in monthly mean and standard error of particulate matter, AOD550, and β.

Table 3.
Statistics of monthly average growth of particulate matter and optical parameters.
The interrelation between atmospheric particulate matter and aerosol optical properties was further investigated. Firstly, the daily average concentration values of particulate matter were calculated. Then scatter plots were drawn with AOD550 and β as horizontal coordinates and particulate matter concentrations as vertical coordinates, respectively. The results of the linear fit based on scatter plots are shown in Figure 8. The fitting results of PM concentration and AOD550 were similar to those of PM concentration and β, and their scatter distribution had some similarity, which was caused by the high linear correlation between AOD550 and β. With the increase in AOD550 or β, the PM concentration showed an obvious positive correlation trend. Among them, PM2.5 concentration showed the strongest linear correlation with β, and the Pearson correlation coefficient reached 0.861. When the concentration of particulate matter suspended in the atmosphere increases, the attenuation effect of aerosols on solar radiation is enhanced, leading to an increase in aerosol optical depth, along with an increase in atmospheric turbidity. During the fluctuation of aerosol optical properties caused by the change in particulate matter concentration, the response effect of AOD550 and β to the change in fine particulate matter concentration is more prominent. From the above analysis, it can be seen that reducing the particulate matter content in the atmosphere is an effective way to reduce atmospheric turbidity, of which controlling the fine particulate matter content is the most important.
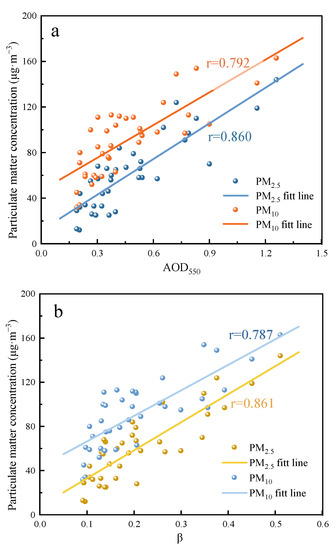
Figure 8.
The correlation between particulate matter concentration with AOD550 (a) and β (b).
4. Conclusions
Experimental observations of aerosols were carried out in Wuhan from January 2021 to January 2022 using the TBS-4 solar spectrometer, and the variation characteristics of aerosol optical properties are analyzed in detail. By monitoring the air quality during the observation period, the influence of atmospheric particulate matter content on the aerosol optical properties is revealed to some extent. The main conclusions are as follows:
(1) During this case study, the mean value of AOD550 was 0.42, and the atmospheric aerosol content was at a low level; the mean value of β was 0.20, and the atmosphere was lightly turbid. Their daily variations show an increasing trend. The mean value of α440–870 was 1.32, and the fitting result of its daily variation indicates that the fluctuation of aerosol particle size is more stable, which is mainly fine particle size aerosol. The frequency ratios of AOD550, α440–870, and β are unimodal distributions. The results of the frequency distribution of the aerosol optical parameters show the frequency of atmospheric pollution conditions. The atmosphere was mainly in mild turbidity degree. The linear correlation coefficient between AOD550 and β reached 0.94. With the increase in atmospheric turbidity, the attenuation effect of aerosol particles on solar radiation was enhanced, resulting in an increase in AOD550. The data points consisting of AOD550 and α440–870 presented a weak positive correlation growth trend, and their linear fit correlation was poor.
(2) Atmospheric turbidity increased on a monthly basis, from a mild turbidity level in November 2021 to a high turbidity level in December 2021. β increased again in January 2022, and atmospheric turbidity increased further. Along with the increase in β, AOD550 rapidly increased, and the monthly increase in both exceeded 50%. The monthly variation in α440–870 was relatively small, and its value had a small proportional increase in December 2021 and decreased in January 2022. The mean value of α440–870 in December 2021 was higher than the remaining two months, the standard deviation of α440–870 in that month was the smallest, and the aerosol particle size distribution was the most concentrated.
(3) Particulate matter concentrations show a good linear correlation with both AOD550 and β. A sharp increase in the concentration of particulate matter was observed when the aerosol content increased, and the turbidity level increased. Among them, the response of β to the change in fine particulate matter concentration is most effective, with their linear correlation coefficient reaching 0.861 and their monthly relative increases being close. The monthly relative increase in PM2.5 exceeds 50%, while the monthly relative increase in PM10 is near 30%. As atmospheric turbidity increases month by month, the ratio of PM10 to PM2.5 concentration shrinks from 1.8:1 in November 2021 to 1.2:1 in January 2022, with the proportion of fine particulate matter in the atmosphere increasing.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Q.M. and G.H.; methodology and validation, G.H.; writing—original draft preparation, G.H.; editing and review, Q.M. and X.N.; funding acquisition, Q.M. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 51876147).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data not available due to privacy restrictions.
Acknowledgments
A very special acknowledgment is made to the editors and referees who make important comments to improve this paper.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Allen, R.J.; Landuyt, W.; Rumbold, S.T. An increase in aerosol burden and radiative effects in a warmer world. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2015, 6, 269–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.; Dong, C.; Liang, D.; Mao, J. A weighted-sum-of-gray soot-fractal-aggregates model for nongray heat radiation in the high temperature gas-soot mixture. J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transf. 2021, 260, 107431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, J.; Gong, C.; Wang, S.; Wang, Y. Aerosol direct radiative forcing in desert and semi-desert regions of northwestern China. Atmos. Res. 2016, 171, 56–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Kumar, K.R.; Lu, R.; Ma, J. Changes in column aerosol optical properties during extreme haze-fog episodes in January 2013 over urban Beijing. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 210, 217–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, Q.; Cheng, F.; Chen, M. Experimental Study on the Chemical Characterization of Atmospheric Aerosols in Wuhan, China. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, D.; Li, L.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Cheng, M.; Sun, Y.; Liu, Z.; Wang, L.; Tang, G.; Hu, B.; et al. The heaviest particulate air-pollution episodes occurred in northern China in January, 2013: Insights gained from observation. Atmos. Environ. 2014, 92, 546–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Che, H.; Zhang, X.; Ma, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, H.; Wang, Y. Characteristics of visibility and particulate matter (PM) in an urban area of Northeast China. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2013, 4, 427–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Che, H.; Xia, X.; Wang, Y.; Yang, L.; Chen, J.; Wang, H.; Zhao, H.; Li, L.; Zhang, L.; et al. Aerosol optical properties and its type classification based on multiyear joint observation campaign in north China plain megalopolis. Chemosphere 2020, 273, 128560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Tan, H.; Fan, S.; Cai, M.; Xu, H.; Li, F.; Chan, P. Influence of aerosol hygroscopicity and mixing state on aerosol optical properties in the Pearl River Delta region, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 627, 1560–1571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kampa, M.; Castanas, E. Human health effects of air pollution. Environ. Pollut. 2008, 151, 362–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lelieveld, J.; Klingmuller, K.; Pozzer, A.; Burnett, R.T.; Haines, A.; Ramanathan, V. Effects of fossil fuel and total anthropogenic emission removal on public health and climate. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 7192–7197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alam, K.; Trautmann, T.; Blaschke, T.; Majid, H. Aerosol optical and radiative properties during summer and winter seasons over Lahore and Karachi. Atmos. Environ. 2012, 50, 234–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Miao, Q.; Shen, L.; Yang, Q.; Wu, Y.; Wei, H. Air pollutant variations in Suzhou during the 2019 novel coronavirus (COVID-19) lockdown of 2020: High time-resolution measurements of aerosol chemical compositions and source apportionment. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 271, 116298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reddington, C.L.; Butt, E.W.; Ridley, D.A.; Artaxo, P.; Morgan, W.T.; Coe, H.; Spracklen, D.V. Air quality and human health improvements from reductions in deforestation-related fire in Brazil. Nat. Geosci. 2015, 8, 768–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Logan, T.; Xi, B.; Dong, X.; Li, Z.; Cribb, M. Classification and investigation of Asian aerosol absorptive properties. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2013, 13, 2253–2265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, P.N.; Dumka, U.C.; Babu, K.N.; Mathur, A.K. Aerosol characterization and radiative properties over Kavaratti, a remote island in southern Arabian Sea from the period of observations. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 599–600, 165–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaik, D.S.; Kant, Y.; Mitra, D.; Babu, S.S. Assessment of Aerosol Characteristics and Radiative Forcing Over Northwest Himalayan Region. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2017, 10, 5314–5321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, R.C.; Remer, L.A.; Dubovik, O. Global aerosol optical properties and application to Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer aerosol retrieval over land. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2007, 112, 7815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, Q.; Huang, C.; Zhang, H.; Chen, Q.; Yuan, Y. Performance of MODIS aerosol products at various timescales and in different pollution conditions over eastern Asia. Sci. China Technol. Sci. 2020, 64, 774–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Peng, Y.; Guo, J.; Sun, L. Performance of MODIS Collection 6.1 Level 3 aerosol products in spatial-temporal variations over land. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 206, 30–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gui, K.; Che, H.; Wang, Y.; Xia, X.; Holben, B.N.; Goloub, P.; Cuevas-Agulló, E.; Yao, W.; Zheng, Y.; Zhao, H.; et al. A global-scale analysis of the MISR Level-3 aerosol optical depth (AOD) product: Comparison with multi-platform AOD data sources. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2021, 12, 101238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jose, S.; Mishra, A.K.; Singh, S. A correlational study on size differentiated aerosols on monsoonal and pre-monsoonal cloud properties over the Indo Gangetic Basin. Atmos. Res. 2021, 262, 105796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabetghadam, S.; Alizadeh, O.; Khoshsima, M.; Pierleoni, A. Aerosol properties, trends and classification of key types over the Middle East from satellite-derived atmospheric optical data. Atmos. Environ. 2021, 246, 118100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, Q.; Huang, C.; Chen, Q.; Zhang, H.; Yuan, Y. Satellite-based identification of aerosol particle species using a 2D-space aerosol classification model. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 219, 117057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Y.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, Z. Assessing spatiotemporal variations of AOD in Japan based on Himawari-8 L3 V31 aerosol products: Validations and applications. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2022, 13, 101439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Liu, B.; Gong, W.; Shi, Y.; Jin, S. Impact of environmental pollution on the retrieval of AOD products from Visible Infrared Imaging Radiometer Suite (VIIRS) over wuhan. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2019, 10, 2063–2071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Q.; Sun, Q. Monitoring the Spatial Variation of Aerosol Optical Depth and Its Correlation with Land Use/Land Cover in Wuhan, China: A Perspective of Urban Planning. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayer, A.M.; Munchak, L.A.; Hsu, N.C.; Levy, R.C.; Bettenhausen, C.; Jeong, M.J. MODIS Collection 6 aerosol products: Comparison between Aqua’s e-Deep Blue, Dark Target, and “merged” data sets, and usage recommendations. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2014, 119, 13965–913989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, R.C.; Mattoo, S.; Munchak, L.A.; Remer, L.A.; Sayer, A.M.; Patadia, F.; Hsu, N.C. The Collection 6 MODIS aerosol products over land and ocean. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2013, 6, 2989–3034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, M.; Wang, Z.; Tao, J.; Chen, L.; Wang, J.; Hou, C.; Wang, L.; Xu, X.; Zhu, H. How Do Aerosol Properties Affect the Temporal Variation of MODIS AOD Bias in Eastern China? Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Xia, X.; Wang, J.; Che, H.; Chen, H.; Zhang, J.; Xu, X.; Levy, R.; Oo, M.; Holz, R.; et al. Evaluation of aerosol optical depth and aerosol models from VIIRS retrieval algorithms over North China Plain. Remote Sens 2017, 9, 432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Che, H.; Zhang, X.; Ma, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, X.; Liu, C.; Hou, B.; Che, H. Aerosol optical properties over urban and industrial region of Northeast China by using ground-based sun-photometer measurement. Atmos. Environ. 2013, 75, 270–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullah, N.A.; Latif, M.T.; Juneng, L.; Uning, R.; Hassan, H.; Azhari, A.; Tuch, T.; Wiedensohler, A. Aerosol particle properties at a remote tropical rainforest in Borneo. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2022, 13, 101383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vicente-Luis, A.; Tremblay, S.; Dionne, J.; Chang, R.Y.W.; Fogal, P.F.; Leaitch, W.R.; Sharma, S.; Kolonjari, F.; Hayes, P.L. In situ optical and microphysical properties of tropospheric aerosols in the Canadian High Arctic from 2016 to 2019. Atmos. Environ. 2021, 250, 118254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, W.; Zhang, S.; Ma, Y. Aerosol Optical Properties and Determination of Aerosol Size Distribution in Wuhan, China. Atmosphere 2014, 5, 81–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bibi, S.; Alam, K.; Chishtie, F.; Bibi, H. Characterization of absorbing aerosol types using ground and satellites based observations over an urban environment. Atmos. Environ. 2017, 150, 126–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boiyo, R.; Kumar, K.R.; Zhao, T. Statistical intercomparison and validation of multisensory aerosol optical depth retrievals over three AERONET sites in Kenya, East Africa. Atmos. Res. 2017, 197, 277–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Ma, Y.; Gong, W.; Zhang, M.; Wang, W.; Shi, Y. Comparison of AOD from CALIPSO, MODIS, and Sun Photometer under Different Conditions over Central China. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 10066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Mao, F.; Pan, Z.; Du, L.; Gong, W. Validation of VIIRS AOD through a Comparison with a Sun Photometer and MODIS AODs over Wuhan. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.-X.; Shen, W.-X.; Yuan, Y.; Tan, H.-P. Verification of aerosol classification methods through satellite and ground-based measurements over Harbin, Northeast China. Atmos. Res. 2019, 216, 167–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, S.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, M.; Gong, W.; Lei, L.; Ma, X. Comparation of aerosol optical properties and associated radiative effects of air pollution events between summer and winter: A case study in January and July 2014 over Wuhan, Central China. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 218, 117004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ångström, A. On the Atmospheric Transmission of Sun Radiation and on Dust in the Air. Geogr. Ann. 2017, 11, 156–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Xie, L.; Yang, X.; Wu, H.; Cai, L.; Qi, P. Aerosol optical properties at seven AERONET sites over Middle East and Eastern Mediterranean Sea. Atmos. Environ. 2020, 243, 117884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breon, F.M.; Tanre, D.; Generoso, S. Aerosol effect on cloud droplet size monitored from satellite. Science 2002, 295, 834–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ångström, A. The parameters of atmospheric turbidity. Tellus 2016, 16, 64–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakey, A.S.; Abdelwahab, M.M.; Makar, P.A. Atmospheric turbidity over Egypt. Atmos. Environ. 2004, 38, 1579–1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).