Temporal Variations and Spatial Distribution of Air Pollutants in Shaoxing, a City in Yangtze Delta, China Based on Mobile Monitoring Using a Sensor Package
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
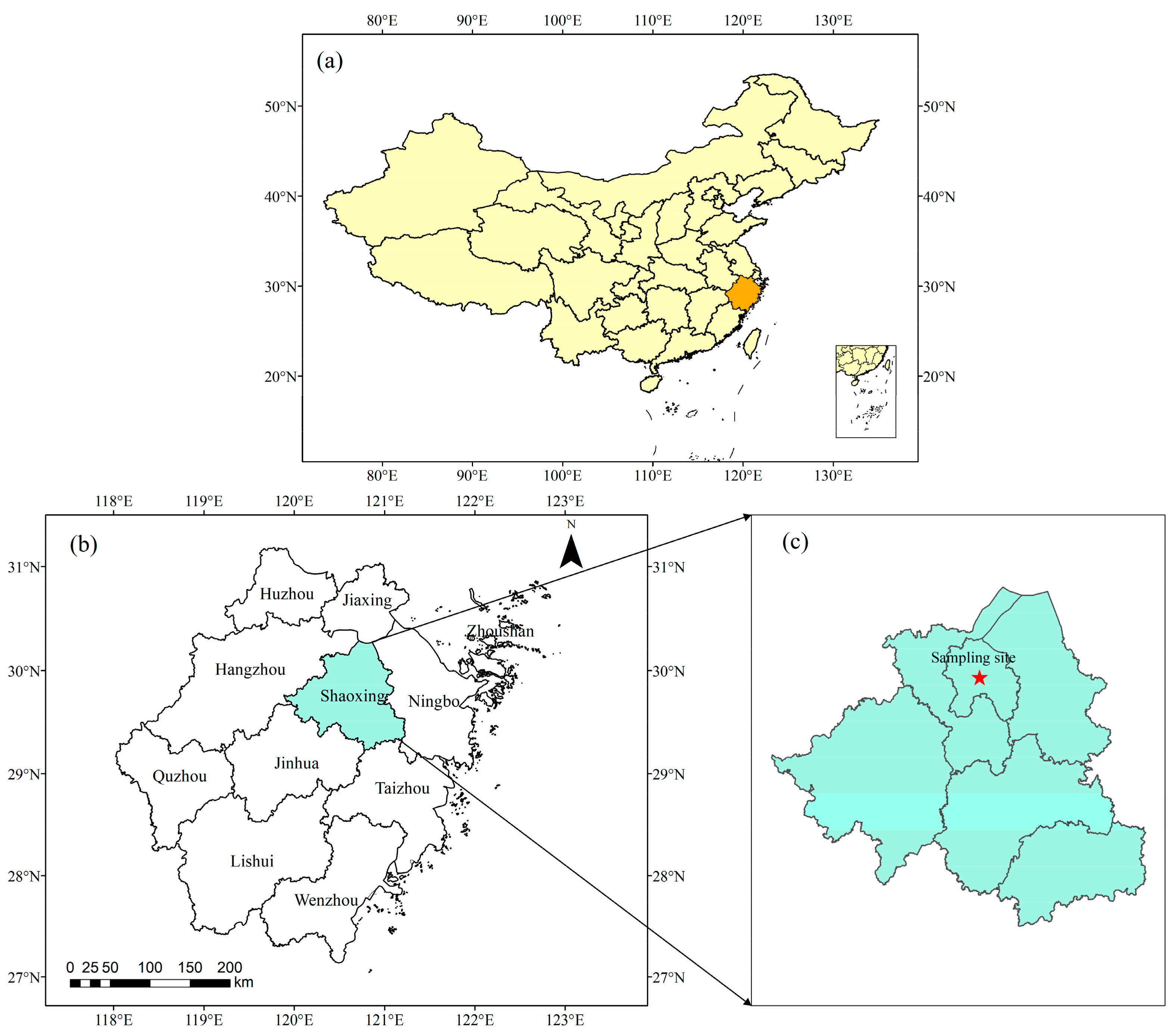
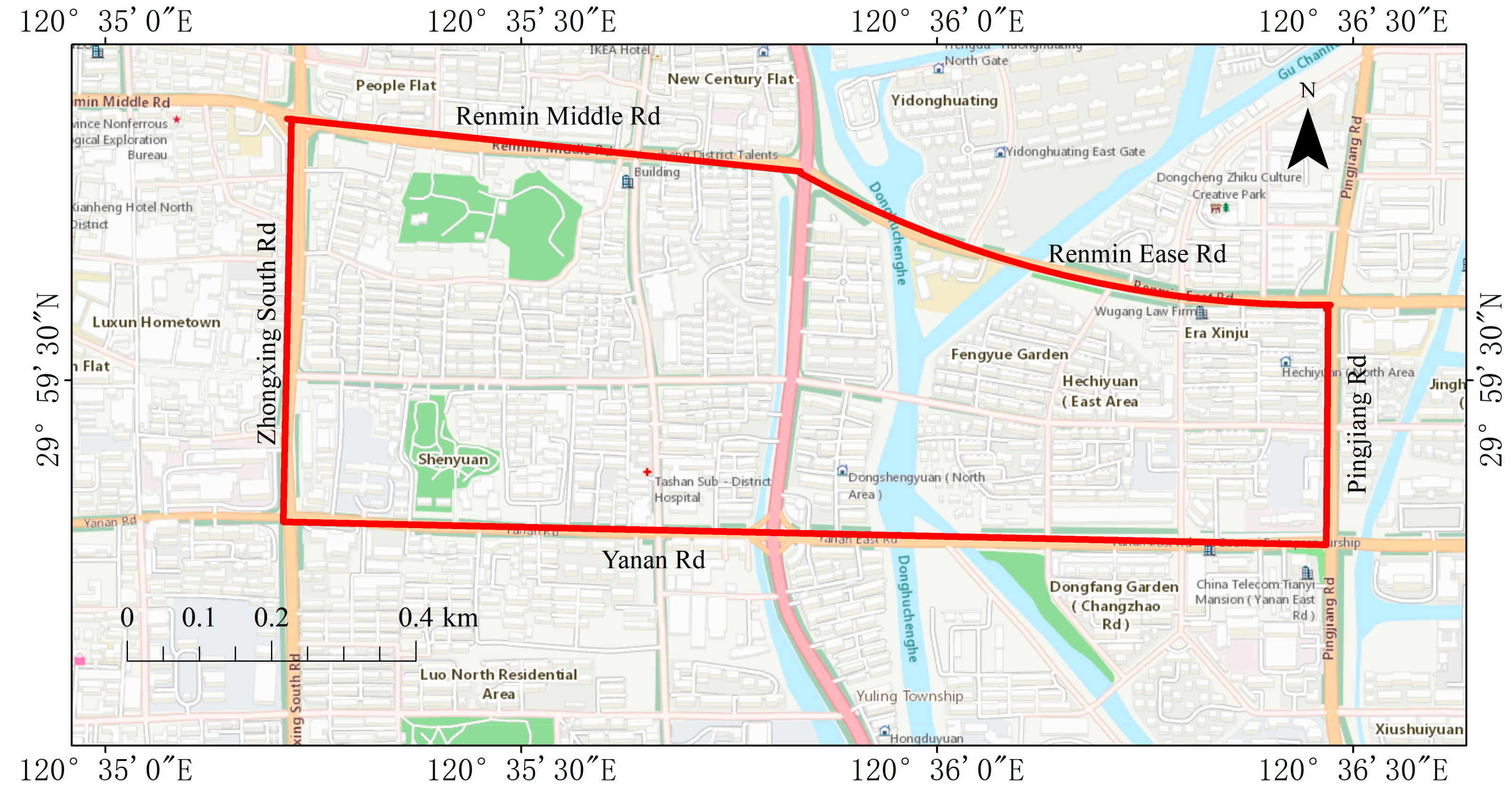
2.1. Sampling Site
2.2. Monitoring Time
2.3. Instrumentations
2.4. Data Quality Assurance
3. Results and Discussion
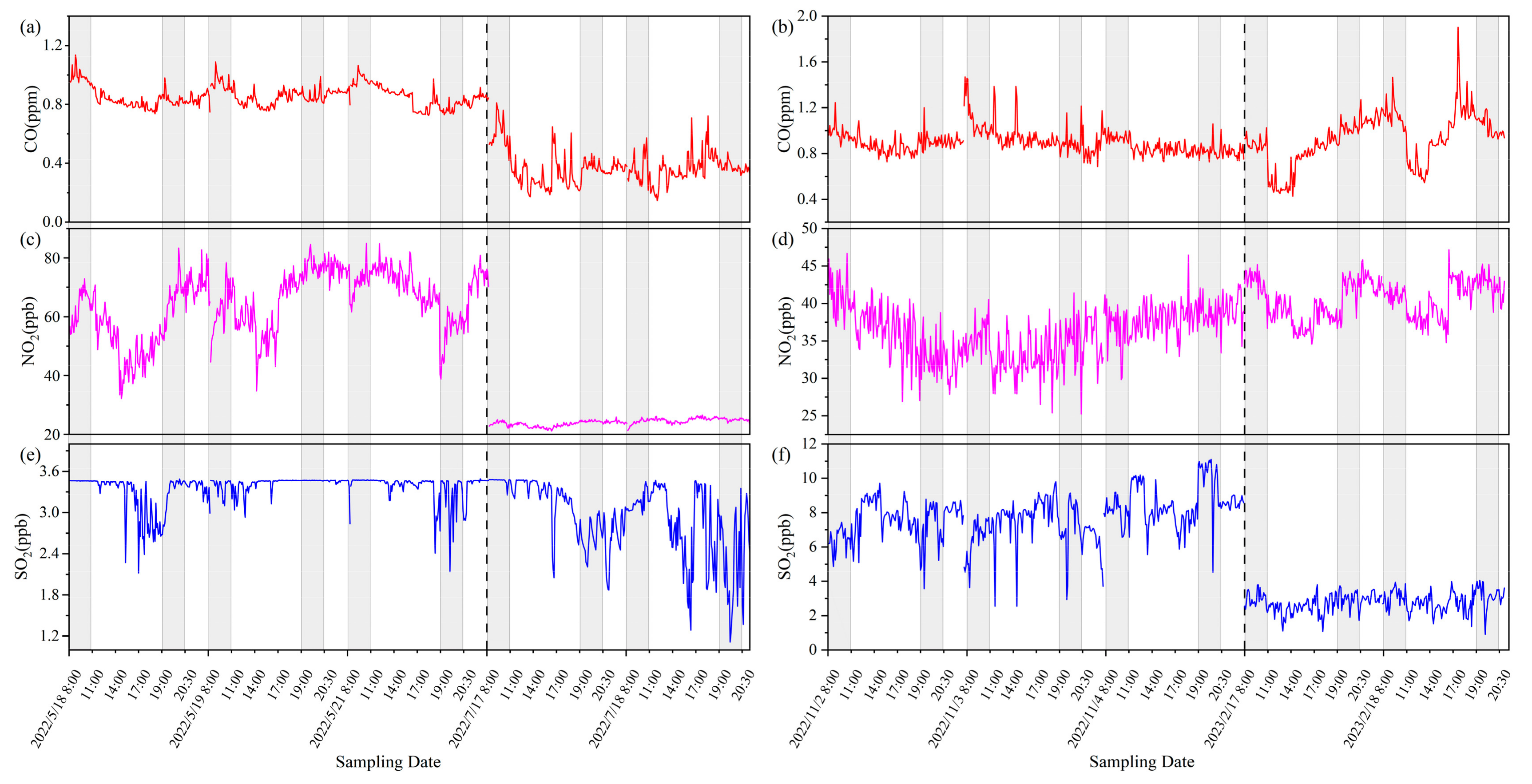
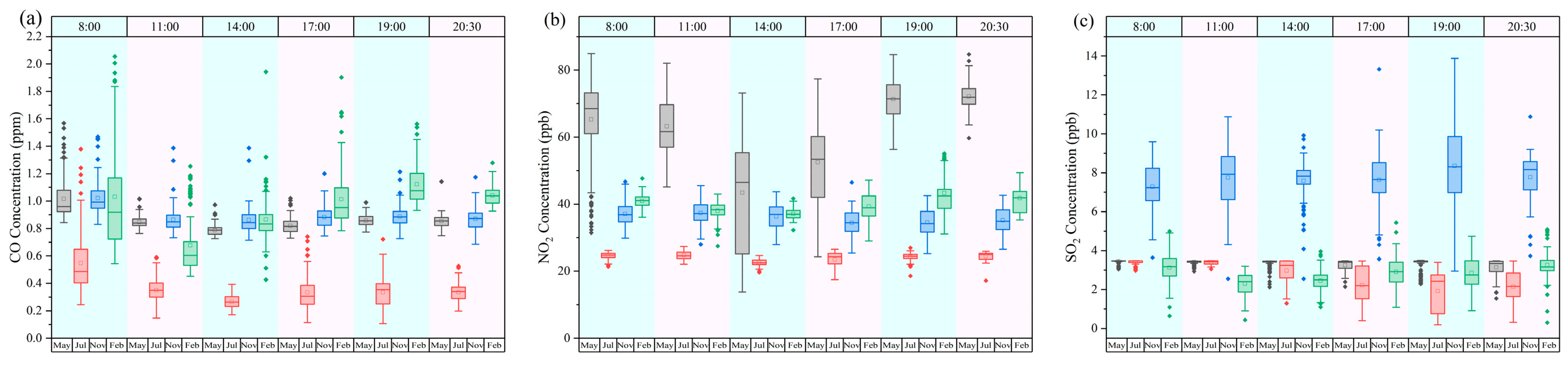
3.1. Temporal Variability of TRAPs
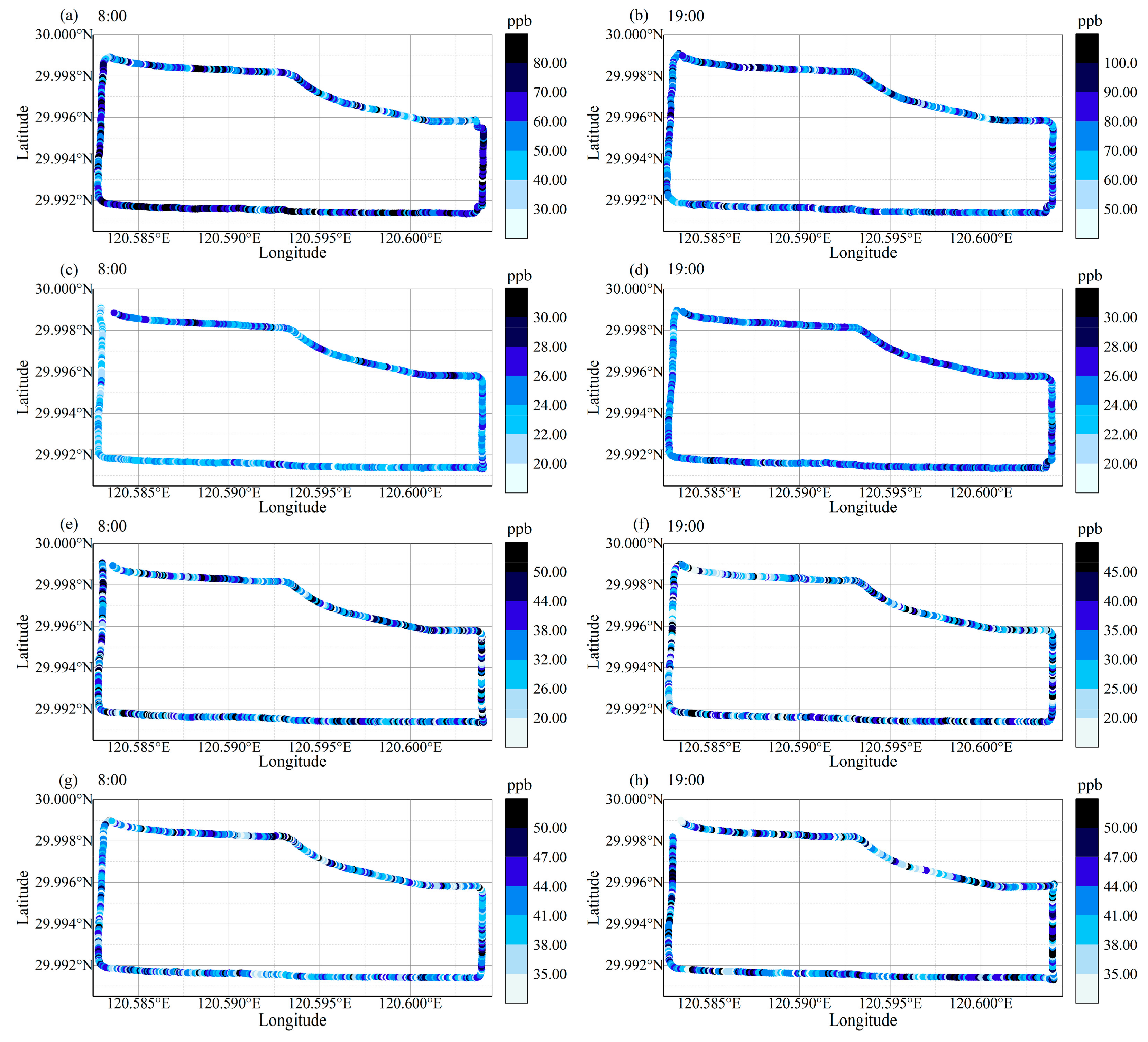
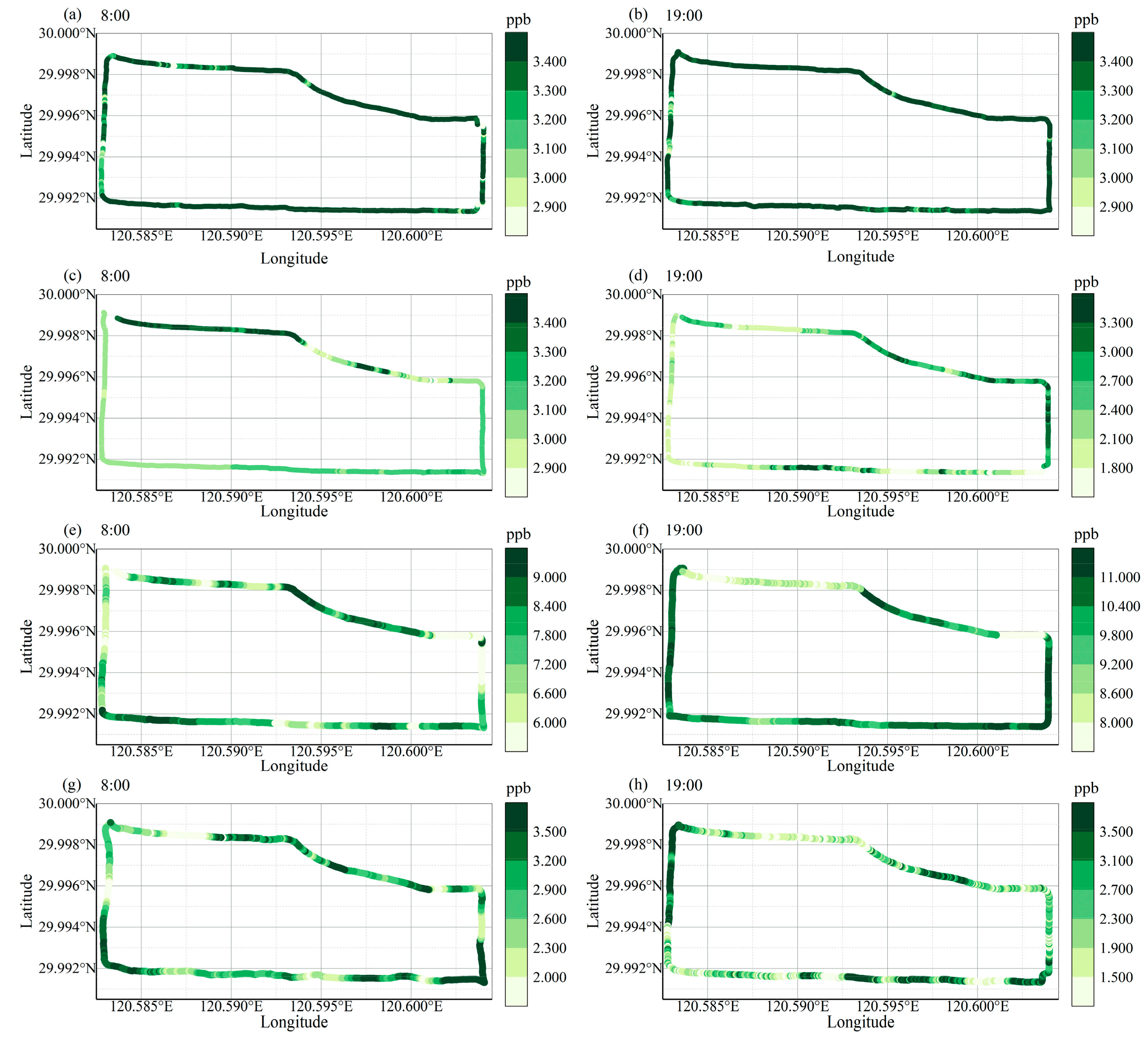
3.2. Spatial Variability of TRAPs
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Parajuli, R.P.; Shin, H.H.; Maquiling, A.; Smith-Doiron, M. Multi-pollutant urban study on acute respiratory hospitalization and mortality attributable to ambient air pollution in Canada for 2001–2012. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2021, 12, 101234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Villamizar, L.A.; Rojas-Roa, N.Y.; Fernández-Niño, J.A. Short-term joint effects of ambient air pollutants on emergency department visits for respiratory and circulatory diseases in Colombia, 2011–2014. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 248, 380–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dominski, F.H.; Lorenzetti Branco, J.H.; Buonanno, G.; Stabile, L.; Gameiro Da Silva, M.; Andrade, A. Effects of air pollution on health: A mapping review of systematic reviews and meta-analyses. Environ. Res. 2021, 201, 111487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Wang, Q.; Xu, B.; Xu, Y.; Ding, Z.; Sun, H. Air pollution and cardiovascular mortality in Nanjing, China: Evidence highlighting the roles of cumulative exposure and mortality displacement. Chemosphere 2021, 265, 129035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, C.-Y.; Fang, Y.; Li, F.-L.; Dong, B.; Hua, X.-G.; Jiang, W.; Zhang, H.; Lyu, Y.; Zhang, X.-J. Association between ambient air pollution and Parkinson’s disease: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Environ. Res. 2019, 168, 448–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hales, S.; Atkinson, J.; Metcalfe, J.; Kuschel, G.; Woodward, A. Long term exposure to air pollution, mortality and morbidity in New Zealand: Cohort study. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 801, 149660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knibbs, L.D.; Cortés De Waterman, A.M.; Toelle, B.G.; Guo, Y.; Denison, L.; Jalaludin, B.; Marks, G.B.; Williams, G.M. The Australian Child Health and Air Pollution Study (ACHAPS): A national population-based cross-sectional study of long-term exposure to outdoor air pollution, asthma, and lung function. Environ. Int. 2018, 120, 394–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ju, K.; Lu, L.; Chen, T.; Duan, Z.; Chen, D.; Liao, W.; Zhou, Q.; Xu, Z.; Wang, W. Does long-term exposure to air pollution impair physical and mental health in the middle-aged and older adults?—A causal empirical analysis based on a longitudinal nationwide cohort in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 827, 154312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strak, M.; Weinmayr, G.; Rodopoulou, S.; Chen, J.; De Hoogh, K.; Andersen, Z.J.; Atkinson, R.; Bauwelinck, M.; Bekkevold, T.; Bellander, T.; et al. Long term exposure to low level air pollution and mortality in eight European cohorts within the ELAPSE project: Pooled analysis. Brit. Med. J. 2021, 374, n1904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stafoggia, M.; Oftedal, B.; Chen, J.; Rodopoulou, S.; Renzi, M.; Atkinson, R.W.; Bauwelinck, M.; Klompmaker, J.O.; Mehta, A.; Vienneau, D.; et al. Long-term exposure to low ambient air pollution concentrations and mortality among 28 million people: Results from seven large European cohorts within the ELAPSE project. Lancet Planet. Health 2022, 6, e9–e18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marquart, H.; Stark, K.; Jarass, J. How are air pollution and noise perceived en route? Investigating cyclists’ and pedestrians’ personal exposure, wellbeing and practices during commute. J. Transp. Health 2022, 24, 101325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bala, G.P.; Rajnoveanu, R.M.; Tudorache, E.; Motisan, R.; Oancea, C. Air pollution exposure-the (in)visible risk factor for respiratory diseases. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 19615–19628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raysoni, A.U.; Sarnat, J.A.; Sarnat, S.E.; Garcia, J.H.; Holguin, F.; Luevano, S.F.; Li, W.W. Binational school-based monitoring of traffic-related air pollutants in El Paso, Texas (USA) and Ciudad Juarez, Chihuahua (Mexico). Environ. Pollut. 2011, 159, 2476–2486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Den Bossche, J.; Peters, J.; Verwaeren, J.; Botteldooren, D.; Theunis, J.; De Baets, B. Mobile monitoring for mapping spatial variation in urban air quality: Development and validation of a methodology based on an extensive dataset. Atmos. Environ. 2015, 105, 148–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivas, I.; Kumar, P.; Hagen-Zanker, A.; Andrade, M.D.F.; Slovic, A.D.; Pritchard, J.P.; Geurs, K.T. Determinants of black carbon, particle mass and number concentrations in London transport microenvironments. Atmos. Environ. 2017, 161, 247–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zwack, L.M.; Paciorek, C.J.; Spengler, J.D.; Levy, J.I. Characterizing local traffic contributions to particulate air pollution in street canyons using mobile monitoring techniques. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 45, 2507–2514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, P.; Brimblecombe, P.; Yang, F.; Anand, A.; Xing, Y.; Sun, L.; Sun, Y.; Chu, M.; Ning, Z. Determination of local traffic emission and non-local background source contribution to on-road air pollution using fixed-route mobile air sensor network. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 290, 118055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Y.T.; Xiang, S.; Li, R.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, K.M.; Si, S.; Wu, X.; Wu, Y. Characterizing spatial variations of city-wide elevated PM10 and PM2.5 concentrations using taxi-based mobile monitoring. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 829, 154478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deshmukh, P.; Kimbrough, S.; Krabbe, S.; Logan, R.; Isakov, V.; Baldauf, R. Identifying air pollution source impacts in urban communities using mobile monitoring. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 715, 136979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Poppel, M.; Peters, J.; Bleux, N. Methodology for setup and data processing of mobile air quality measurements to assess the spatial variability of concentrations in urban environments. Environ. Pollut. 2013, 183, 224–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apte, J.S.; Messier, K.P.; Gani, S.; Brauer, M.; Kirchstetter, T.W.; Lunden, M.M.; Marshall, J.D.; Portier, C.J.; Vermeulen, R.C.H.; Hamburg, S.P. High-Resolution Air Pollution Mapping with Google Street View Cars: Exploiting Big Data. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 6999–7008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samad, A.; Vogt, U. Mobile air quality measurements using bicycle to obtain spatial distribution and high temporal resolution in and around the city center of Stuttgart. Atmos. Environ. 2021, 244, 117915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Lei, X.-N.; Xiu, G.-L.; Gao, C.-Y.; Gao, S.; Qian, N.-S. Personal exposure to black carbon during commuting in peak and off-peak hours in Shanghai. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 524–525, 237–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; He, Z.; Zhang, K.; Zeng, L.; De Nazelle, A. Investigation into Beijing commuters’ exposure to ultrafine particles in four transportation modes: Bus, car, bicycle and subway. Atmos. Environ. 2021, 266, 118734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Y.; Lipsky, E.M.; Saleh, R.; Robinson, A.L.; Presto, A.A. Characterizing the Spatial Variation of Air Pollutants and the Contributions of High Emitting Vehicles in Pittsburgh, PA. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 14186–14194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, C.H.; Fan, Z.; Lioy, P.J.; Baptista, A.; Greenberg, M.; Laumbach, R.J. A novel mobile monitoring approach to characterize spatial and temporal variation in traffic-related air pollutants in an urban community. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 141, 161–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crocchianti, S.; Del Sarto, S.; Ranalli, M.G.; Moroni, B.; Castellini, S.; Petroselli, C.; Cappelletti, D. Spatiotemporal correlation of urban pollutants by long-term measurements on a mobile observation platform. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 268, 115645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desouza, P.; Lu, R.; Kinney, P.; Zheng, S. Exposures to multiple air pollutants while commuting: Evidence from Zhengzhou, China. Atmos. Environ. 2021, 247, 118168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Gu, P.; Schulte, N.; Zhou, X.; Mara, S.; Croes, B.E.; Herner, J.D.; Vijayan, A. A new mobile monitoring approach to characterize community-scale air pollution patterns and identify local high pollution zones. Atmos. Environ. 2022, 272, 118936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, X.B.; Chen, L.; Shi, K.L.; Wu, F.; Chen, J.M.; Fang, S.X.; Wang, J.L.; Xu, M. A lightweight low-cost and multipollutant sensor package for aerial observations of air pollutants in atmospheric boundary layer. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 764, 142828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Pang, X.; Wu, Z.; Wang, B. Measurement of Fine Particulate Matter Emission from Chimneys in Textile Printing and Dyeing Industrial Area by UAV. Ecol. Environ. Monit. Three Gorges. Available online: http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/50.1214.x.20221125.1034.002.html (accessed on 26 June 2023).
- Chen, L.; Li, J.; Pang, X.; Shi, K.; Chen, J.; Wang, J.; Xu, M. Impact of COVID-19 Lockdown on Air Pollutants in a Coastal Area of the Yangtze River Delta, China, Measured by a Low-Cost Sensor Package. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patton, A.P.; Perkins, J.; Zamore, W.; Levy, J.I.; Brugge, D.; Durant, J.L. Spatial and temporal differences in traffic-related air pollution in three urban neighborhoods near an interstate highway. Atmos. Environ. 2014, 99, 309–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.Y.; Lu, Q.C.; He, H.D.; Wang, D.S.; Gao, Y.; Peng, Z.R. Investigation of the spatiotemporal variation and influencing factors on fine particulate matter and carbon monoxide concentrations near a road intersection. Front. Earth Sci. 2017, 11, 63–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pattinson, W.; Longley, I.; Kingham, S. Using mobile monitoring to visualise diurnal variation of traffic pollutants across two near-highway neighbourhoods. Atmos. Environ. 2014, 94, 782–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.D.; Helfter, C.; Purvis, R.M.; Beevers, S.D.; Carslaw, D.C.; Lewis, A.C.; Moller, S.J.; Tremper, A.; Vaughan, A.R.; Nemitz, E. Measurement of NO(x) fluxes from a tall tower in Central London, UK and comparison with emissions inventories. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 1025–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Yin, S.; Zhang, R.-Q.; Yuan, M.; Ying, Q. Assessment of summertime O3 formation and the O3-NOX-VOC sensitivity in Zhengzhou, China using an observation-based model. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 813, 152449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.M.; Jeong, C.-H.; Zimmerman, N.; Healy, R.M.; Evans, G.J. Real world vehicle fleet emission factors: Seasonal and diurnal variations in traffic related air pollutants. Atmos. Environ. 2018, 184, 77–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Pang, X.; Lyu, Y.; Li, J.; Xing, B.; Chen, J.; Mao, Y.; Shang, Q.; Wu, H. Characteristics and sources analysis of ambient volatile organic compounds in a typical industrial park: Implications for ozone formation in 2022 Asian Games. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 848, 157746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Wang, Y.; Hu, J.; Ying, Q.; Hu, X.M. Relationships between meteorological parameters and criteria air pollutants in three megacities in China. Environ. Res. 2015, 140, 242–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Pang, X.; Li, J.; Lyu, Y.; Zhang, B.; Wang, J. Variation Characteristics of Air Pollutants in Hangzhou During the 13th Five-Year Plan Period. Ecol. Environ. Monit. Three Gorges 2022, 7, 23–34. [Google Scholar]
- Kovács, K.D. Determination of the human impact on the drop in NO2 air pollution due to total COVID-19 lockdown using Human-Influenced Air Pollution Decrease Index (HIAPDI). Environ. Pollut. 2022, 306, 119441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Alli, A.S.; Clark, S.; Hughes, A.; Ezzati, M.; Beddows, A.; Vallarino, J.; Nimo, J.; Bedford-Moses, J.; Baah, S.; et al. Nitrogen oxides (NO and NO2) pollution in the Accra metropolis: Spatiotemporal patterns and the role of meteorology. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 803, 149931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aneja, V.P.; Agarwal, A.; Roelle, P.A.; Phillips, S.B.; Tong, Q.; Watkins, N.; Yablonsky, R. Measurements and analysis of criteria pollutants in New Delhi, India. Environ. Int. 2001, 27, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Yuan, Y.; Wang, Q.; Liu, C.; Zhi, Q.; Cao, J. Changes in air quality related to the control of coronavirus in China: Implications for traffic and industrial emissions. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 731, 139133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Ali, M.A.; Bilal, M.; Qiu, Z.F.; Mhawish, A.; Almazroui, M.; Shahid, S.; Islam, M.N.; Zhang, Y.Z.; Haque, M.N. Identification of NO2 and SO2 Pollution Hotspots and Sources in Jiangsu Province of China. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 3742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

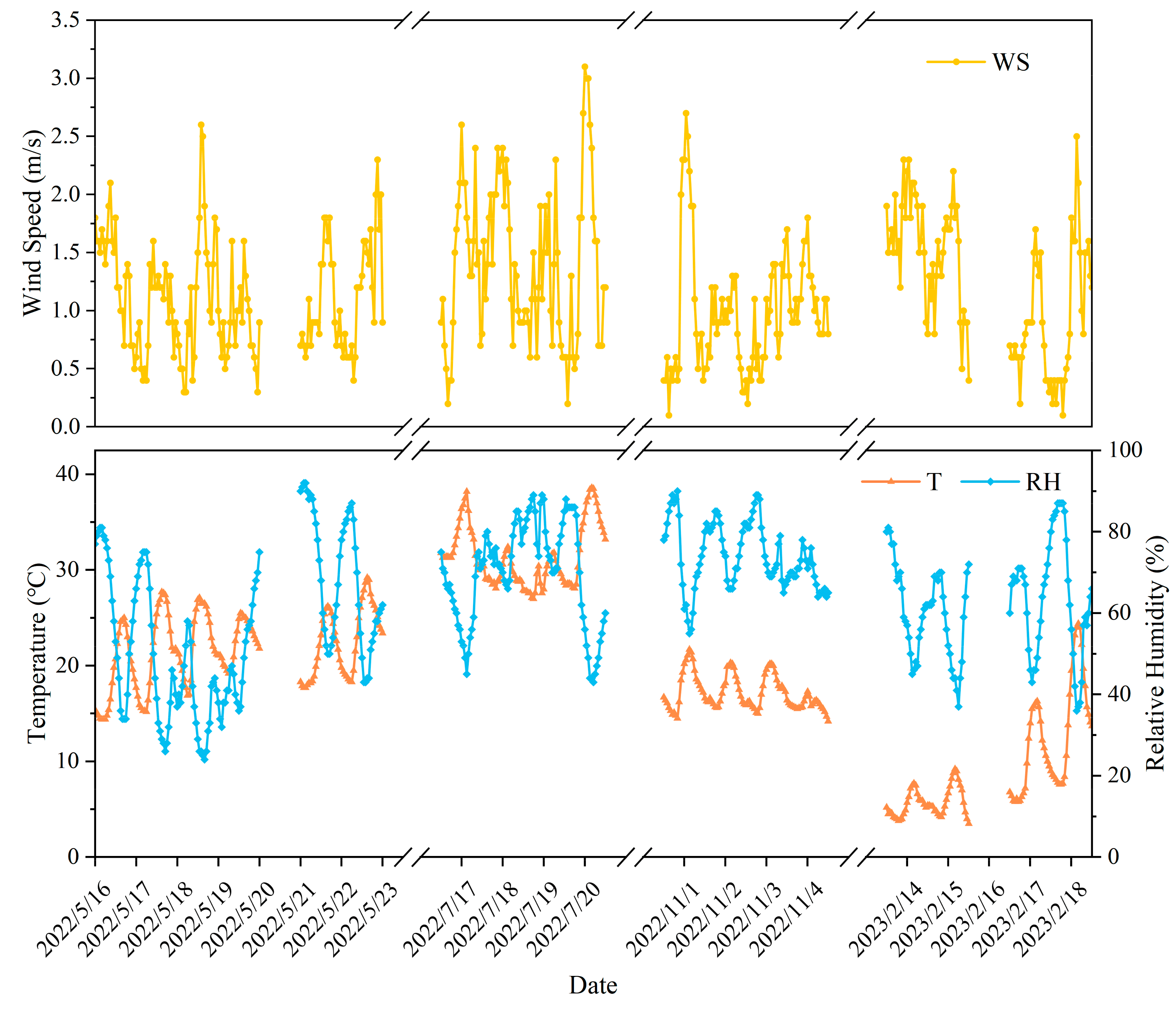

| Date | Weather | Temperature (°C) | Relative Humidity (%) | Wind Scale |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 16 May 2022 | Clear | 19 | 58 | Level II |
| 17 May 2022 | Cloudy | 21 | 51 | Level I |
| 18 May 2022 | Cloudy | 22 | 38 | Level I |
| 19 May 2022 | Cloudy | 22 | 50 | Level I |
| 21 May 2022 | Overcast | 22 | 72 | Level I |
| 22 May 2022 | Cloudy | 24 | 64 | Level I |
| 17 July 2022 | Cloudy | 33 | 61 | Level I |
| 18 July 2022 | Overcast | 29 | 74 | Level I |
| 19 July 2022 | Overcast | 29 | 79 | Level I |
| 20 July 2022 | Clear | 33 | 63 | Level II |
| 1 November 2022 | Cloudy | 17 | 79 | Level I |
| 2 November 2022 | Cloudy | 16 | 82 | Level I |
| 3 November 2022 | Cloudy | 17 | 80 | Level I |
| 4 November 2022 | Cloudy | 15 | 72 | Level II |
| 14 February 2023 | Cloudy | 5 | 64 | Level II |
| 15 February 2023 | Clear | 5 | 62 | Level I |
| 17 February 2023 | Clear | 9 | 68 | Level I |
| 18 February 2023 | Cloudy | 14 | 69 | Level I |
| Measuring | Manufacturer | Weight/g | EC/W | Range | LOD | TR/s |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CO | Alphasense | 12 | 0.5 | 0–20 ppm | 1 ppb | 1 |
| NO2 | Alphasense | 10 | 0.5 | 0–20 ppm | 0.5 ppb | 1 |
| SO2 | Alphasense | 12 | 0.5 | 0–200 ppm | 5 ppb | 1 |
| Temperature | Texas Instru. | 5 | 0.1 | −10–100 °C | 0.3 °C | 1 |
| Humidity | Honeywell | 5 | 0.1 | 0–100% | 2% | 1 |
| Pressure | NXP | 5 | 0.2 | 0–700 kPa | 150 Pa | 1 |
| Parameter | Temperature | Relative Humidity | Wind Speed |
|---|---|---|---|
| CO | −0.424 ** | 0.432 ** | −0.221 ** |
| NO2 | −0.644 ** | 0.401 ** | −0.426 ** |
| SO2 | 0.107 ** | −0.084 ** | −0.050 * |
| Number | Date | CO (ppm) | NO2 (ppb) | SO2 (ppb) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 16 May 2022 | 0.84 ± 0.07 (n = 3874) | 44.07 ± 23.78 (n = 3874) | 3.44 ± 0.06 (n = 3874) |
| 2 | 17 May 2022 | 0.86 ± 0.06 (n = 4683) | 62.23 ± 18.17 (n = 4683) | 3.14 ± 0.45 (n = 4683) |
| 3 | 18 May 2022 | 0.86 ± 0.11 (n = 5181) | 58.55 ± 19.03 (n = 5181) | 3.28 ± 0.33 (n = 5181) |
| 4 | 19 May 2022 | 0.87 ± 0.08 (n = 5155) | 66.62 ± 18.28 (n = 5155) | 3.42 ± 0.11 (n = 5155) |
| 5 | 21 May 2022 | 0.86 ± 0.11 (n = 5956) | 69.07 ± 16.60 (n = 5956) | 3.34 ± 0.28 (n = 5956) |
| 6 | 22 May 2022 | 0.92 ± 0.34 (n = 4538) | 59.84 ± 23.70 (n = 4538) | 3.40 ± 0.17 (n = 4538) |
| 7 | 17 July 2022 | 0.40 ± 0.21 (n = 5087) | 23.56 ± 2.02 (n = 5087) | 3.08 ± 0.42 (n = 5087) |
| 8 | 18 July 2022 | 0.37 ± 0.12 (n = 4588) | 24.85 ± 1.90 (n = 4588) | 2.76 ± 0.64 (n = 4588) |
| 9 | 19 July 2022 | 0.36 ± 0.15 (n = 4723) | 24.97 ± 2.09 (n = 4723) | 2.52 ± 1.15 (n = 4723) |
| 10 | 20 July 2022 | 0.30 ± 0.22 (n = 4373) | 22.70 ± 2.57 (n = 4373) | 2.10 ± 1.29 (n = 4373) |
| 11 | 1 November 2022 | 0.94 ± 0.21 (n = 5061) | 34.99 ± 12.57 (n = 5061) | 7.37 ± 2.17 (n = 5061) |
| 12 | 2 November 2022 | 0.89 ± 0.19 (n = 4572) | 36.04 ± 12.63 (n = 4572) | 7.50 ± 1.25 (n = 4572) |
| 13 | 3 November 2022 | 0.93 ± 0.24 (n = 4817) | 35.33 ± 12.68 (n = 4817) | 7.36 ± 2.01 (n = 4817) |
| 14 | 4 November 2022 | 0.85 ± 0.21 (n = 5362) | 37.90 ± 11.91 (n = 5362) | 8.52 ± 1.32 (n = 5362) |
| 15 | 14 February 2023 | 0.84 ± 0.20 (n = 5793) | 37.84 ± 5.98 (n = 5793) | 2.78 ± 1.35 (n = 5793) |
| 16 | 15 February 2023 | 0.87 ± 0.26 (n = 4686) | 40.26 ± 6.32 (n = 4686) | 2.73 ± 0.67 (n = 4686) |
| 17 | 17 February 2023 | 1.00 ± 0.23 (n = 4119) | 40.80 ± 5.89 (n = 4119) | 2.86 ± 0.71 (n = 4119) |
| 18 | 18 February 2023 | 1.22 ± 0.32 (n = 3606) | 41.92 ± 10.87 (n = 3606) | 2.92 ± 0.84 (n = 3606) |
| Sampling Time | 8:00 | 11:00 | 14:00 | 17:00 | 19:00 | 20:30 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CO (ppm) | May | 1.05 ± 0.30 (n = 5112) | 0.85 ± 0.05 (n = 5044) | 0.79 ± 0.04 (n = 4810) | 0.82 ± 0.06 (n = 5528) | 0.86 ± 0.05 (n = 4252) | 0.86 ± 0.05 (n = 3346) |
| July | 0.55 ± 0.24 (n = 2930) | 0.37 ± 0.23 (n = 3025) | 0.26 ± 0.06 (n = 3083) | 0.33 ± 0.14 (n = 2943) | 0.33 ± 0.11 (n = 4456) | 0.33 ± 0.08 (n = 2337) | |
| November | 1.02 ± 0.23 (n = 4095) | 0.86 ± 0.19 (n = 3178) | 0.84 ± 0.21 (n = 2983) | 0.88 ± 0.18 (n = 3563) | 0.89 ± 0.21 (n = 3080) | 0.87 ± 0.22 (n = 2921) | |
| February | 1.03 ± 0.39 (n = 3209) | 0.68 ± 0.22 (n = 3053) | 0.88 ± 0.28 (n = 2925) | 1.01 ± 0.22 (n = 3732) | 1.12 ± 0.16 (n = 2724) | 1.04 ± 0.08 (n = 2564) | |
| NO2 (ppb) | May | 65.22 ± 19.34 (n = 5112) | 63.21 ± 17.22 (n = 5044) | 43.39 ± 23.15 (n = 4810) | 52.58 ± 19.05 (n = 5528) | 71.24 ± 15.95 (n = 4252) | 72.15 ± 15.57 (n = 3346) |
| July | 24.63 ± 2.03 (n = 2930) | 24.73 ± 2.17 (n = 3025) | 22.57 ± 2.06 (n = 3083) | 23.52 ± 2.81 (n = 2943) | 24.24 ± 2.15 (n = 4456) | 24.56 ± 1.93 (n = 2337) | |
| November | 38.22 ± 12.50 (n = 4095) | 37.37 ± 12.30 (n = 3178) | 36.68 ± 12.50 (n = 2983) | 34.23 ± 12.46 (n = 3563) | 34.42 ± 12.42 (n = 3080) | 35.20 ± 12.33 (n = 2921) | |
| February | 40.88 ± 6.42 (n = 3209) | 37.97 ± 6.37 (n = 3053) | 37.10 ± 7.35 (n = 2925) | 39.32 ± 6.84 (n = 3732) | 42.23 ± 8.36 (n = 2724) | 41.75 ± 7.64 (n = 2564) | |
| SO2 (ppb) | May | 3.45 ± 0.08 (n = 5112) | 3.41 ± 0.11 (n = 5044) | 3.38 ± 0.24 (n = 4810) | 3.25 ± 0.32 (n = 5528) | 3.32 ± 0.33 (n = 4252) | 3.14 ± 0.47 (n = 3346) |
| July | 3.39 ± 0.16 (n = 2930) | 3.39 ± 0.13 (n = 3025) | 2.96 ± 0.63 (n = 3083) | 2.23 ± 1.00 (n = 2943) | 1.91 ± 1.06 (n = 4456) | 2.15 ± 0.99 (n = 2337) | |
| November | 7.27 ± 1.33 (n = 4095) | 7.63 ± 2.32 (n = 3178) | 7.80 ± 1.23 (n = 2983) | 7.61 ± 1.83 (n = 3563) | 8.33 ± 2.28 (n = 3080) | 7.76 ± 1.41 (n = 2921) | |
| February | 3.13 ± 0.90 (n = 3209) | 2.30 ± 0.75 (n = 3053) | 2.46 ± 0.71 (n = 2925) | 2.90 ± 1.06 (n = 3732) | 2.85 ± 0.98 (n = 2724) | 3.26 ± 1.03 (n = 2564) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, G.; Pang, X.; Li, J.; Xing, B.; Sun, S.; Chen, L.; Lu, Y.; Sun, Q.; Shang, Q.; Wu, Z.; et al. Temporal Variations and Spatial Distribution of Air Pollutants in Shaoxing, a City in Yangtze Delta, China Based on Mobile Monitoring Using a Sensor Package. Atmosphere 2023, 14, 1093. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14071093
Zhao G, Pang X, Li J, Xing B, Sun S, Chen L, Lu Y, Sun Q, Shang Q, Wu Z, et al. Temporal Variations and Spatial Distribution of Air Pollutants in Shaoxing, a City in Yangtze Delta, China Based on Mobile Monitoring Using a Sensor Package. Atmosphere. 2023; 14(7):1093. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14071093
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Gaohan, Xiaobing Pang, Jingjing Li, Bo Xing, Songhua Sun, Lang Chen, Youhao Lu, Qianqian Sun, Qianqian Shang, Zhentao Wu, and et al. 2023. "Temporal Variations and Spatial Distribution of Air Pollutants in Shaoxing, a City in Yangtze Delta, China Based on Mobile Monitoring Using a Sensor Package" Atmosphere 14, no. 7: 1093. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14071093
APA StyleZhao, G., Pang, X., Li, J., Xing, B., Sun, S., Chen, L., Lu, Y., Sun, Q., Shang, Q., Wu, Z., Yuan, K., Wu, H., Ding, S., Li, H., & Liu, Y. (2023). Temporal Variations and Spatial Distribution of Air Pollutants in Shaoxing, a City in Yangtze Delta, China Based on Mobile Monitoring Using a Sensor Package. Atmosphere, 14(7), 1093. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14071093







