A Numerical Study of Critical Variables on Artificial Cold Cloud Precipitation Enhancement in the Qilian Mountains, China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methodology
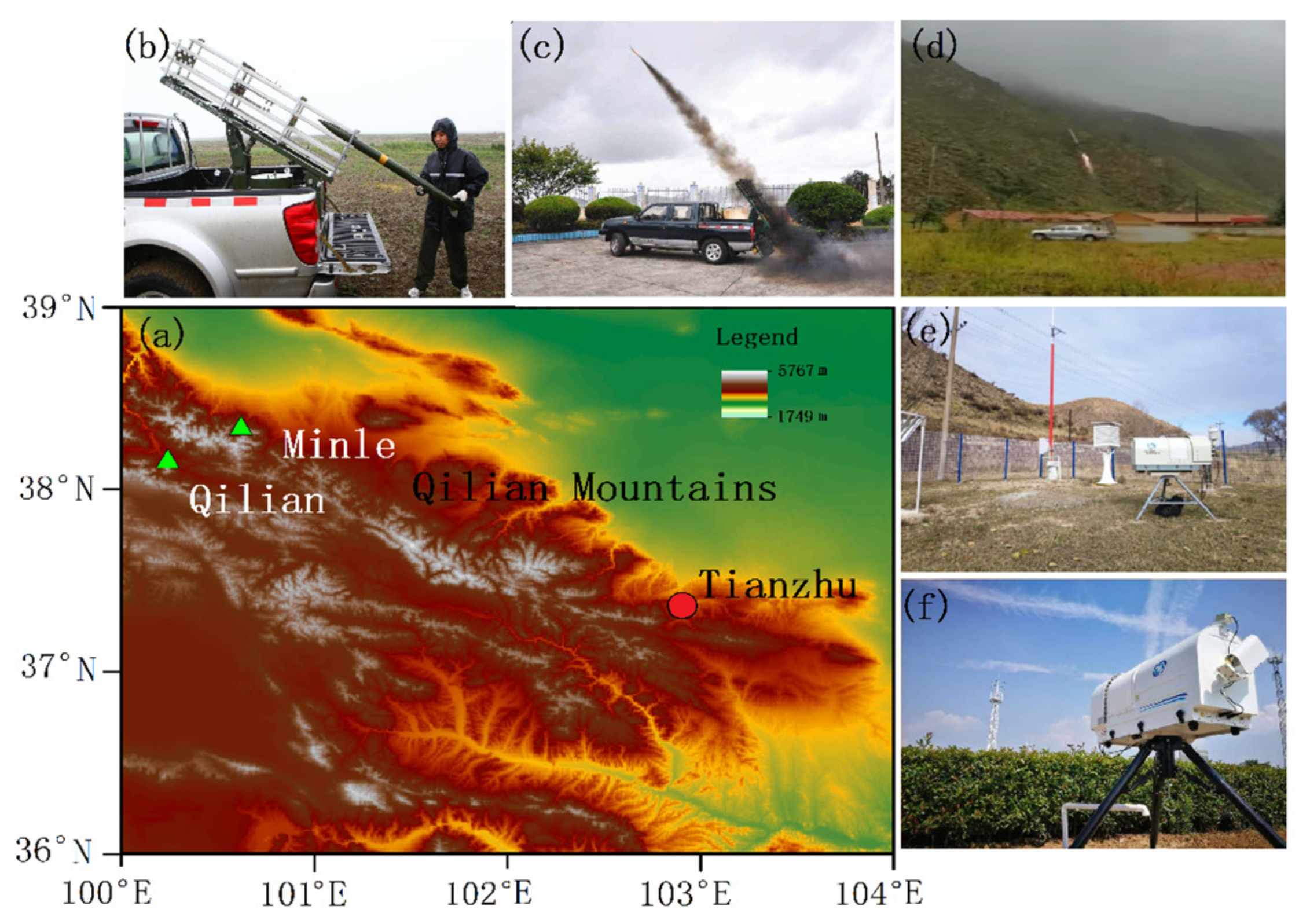
2.1. Artificial Precipitation Enhancements
2.2. Model Optimization and Numerical Experiments
2.2.1. Catalytic Processing
- Freezing and nucleation of cloud and rain drops in contact with silver iodide particles:
- ii.
- Condensation and nucleation of water vapor on an artificial ice core:
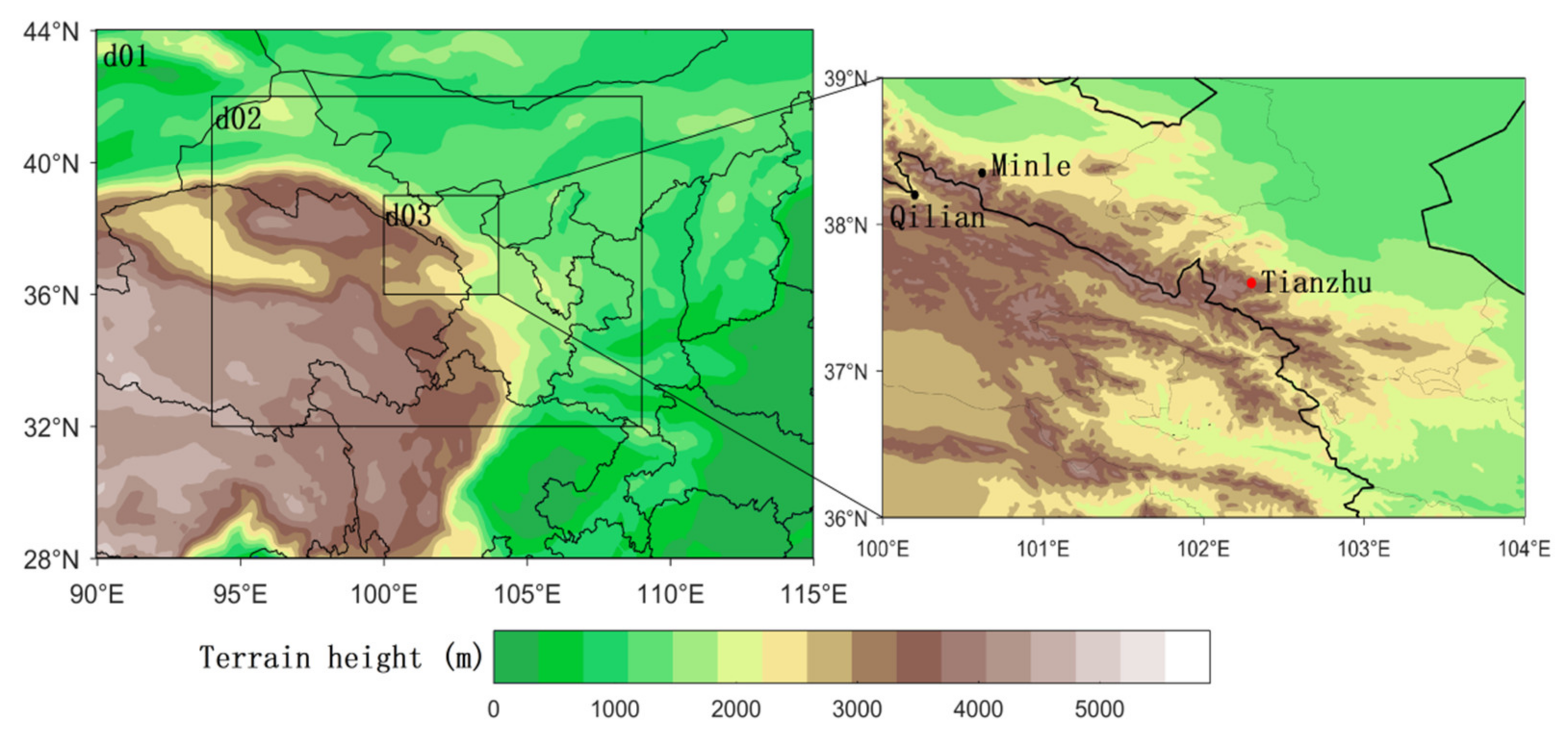
2.2.2. Numerical Experiments
2.3. Data Used for Validating Simulations
Microwave Radiometer Observations
3. Results
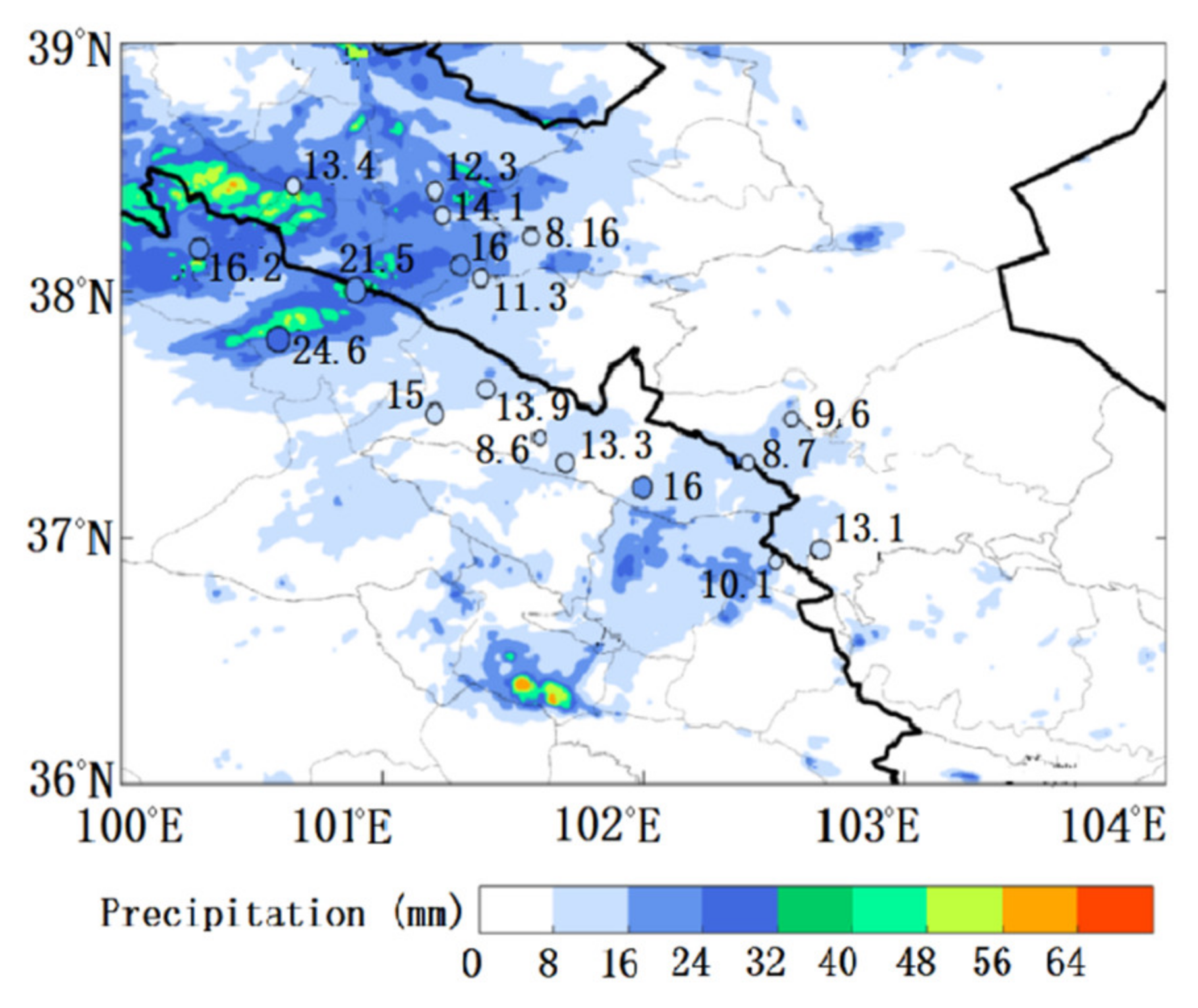
3.1. Comparison of Measured and Simulated Results
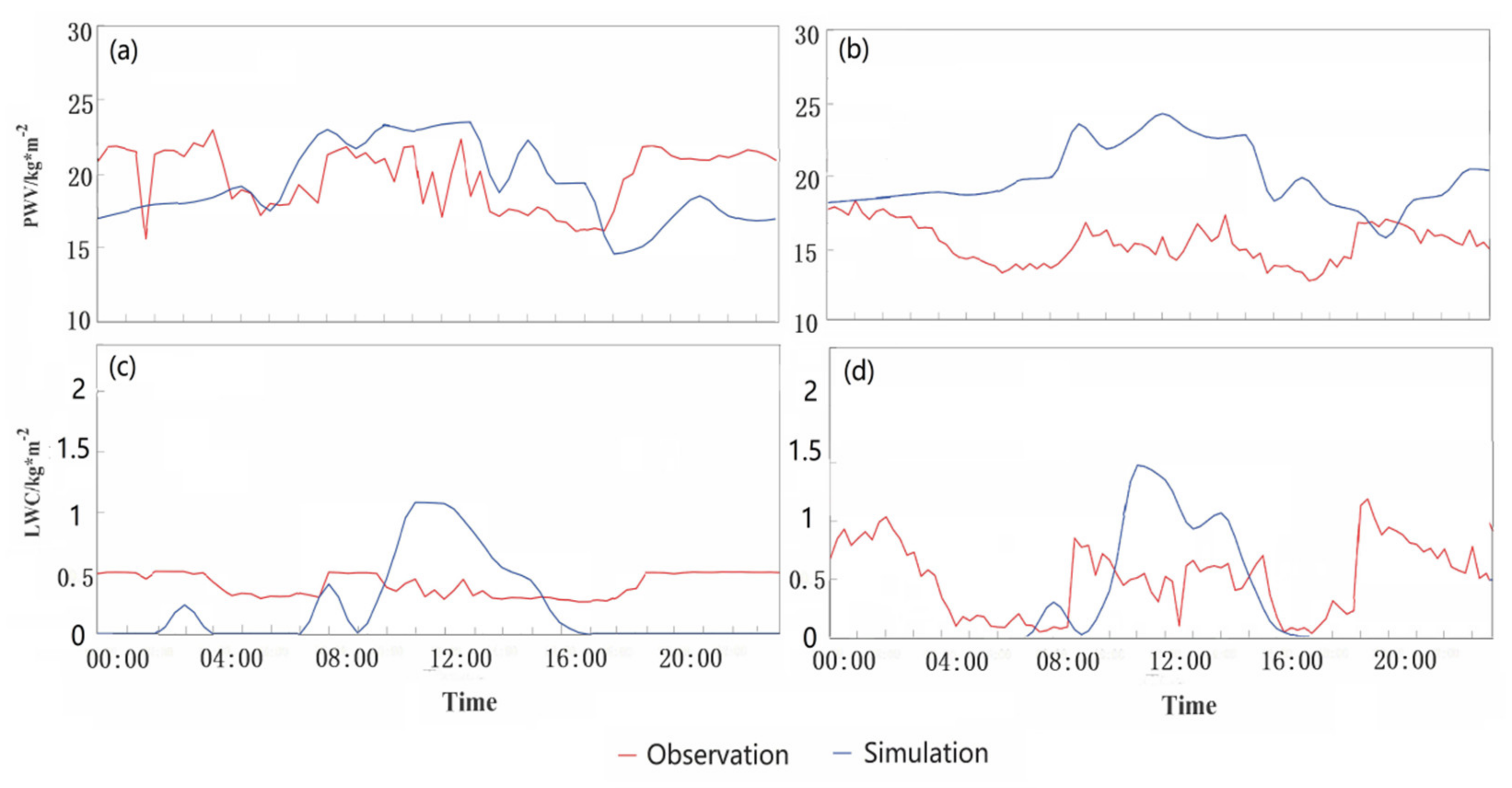
3.1.1. Comparison of Measured and Simulated Precipitation, Water Vapor and Liquid Water Content
3.1.2. Movement and Diffusion of Silver Iodide
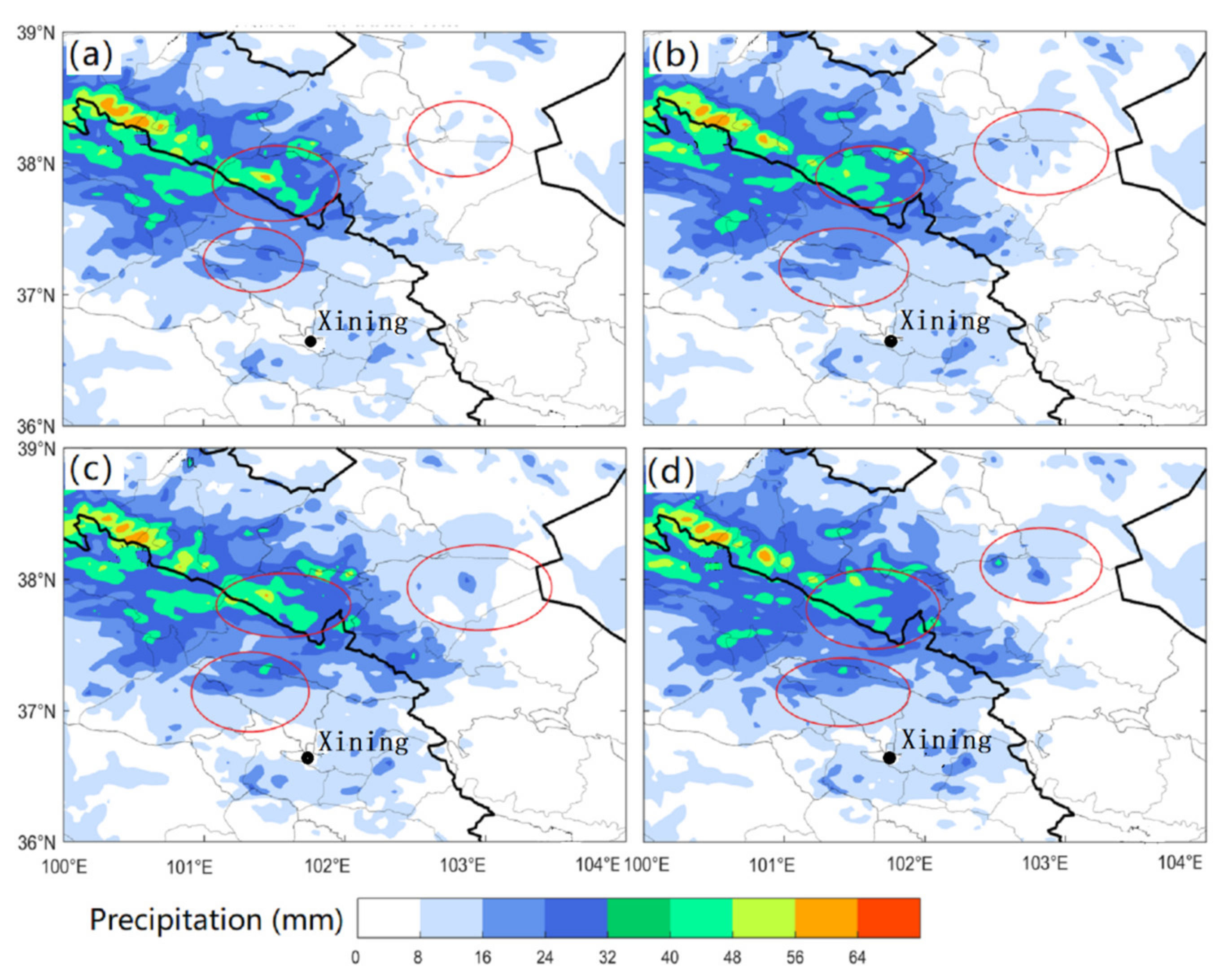
3.1.3. Evolution of Precipitation after Catalysis
3.1.4. Analysis of Precipitation Enhancement Mechanism
3.2. Catalytic Tests at Different Heights and Rate
3.2.1. Catalytic Tests for Heights
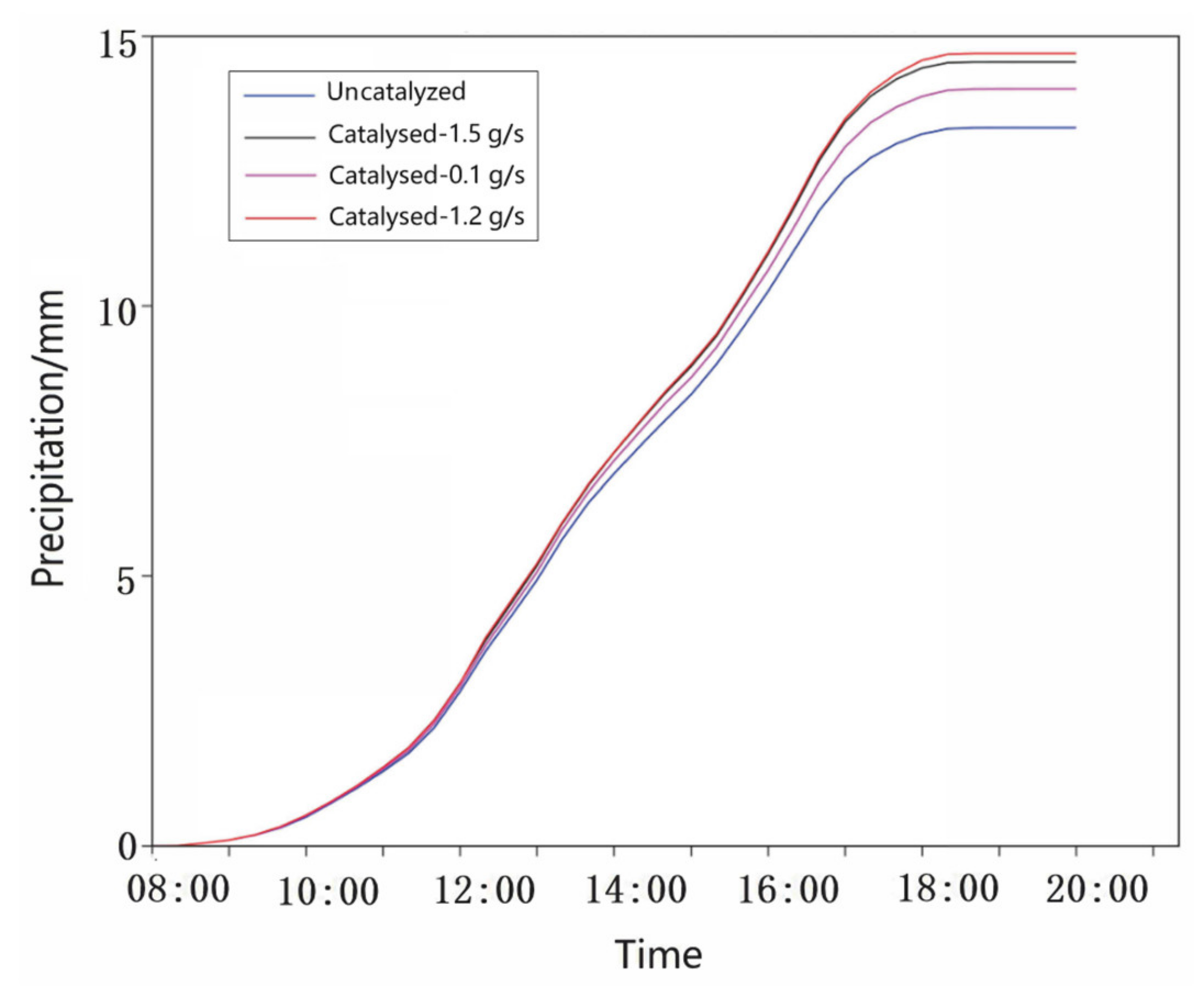
3.2.2. Catalytic Test for Rate
4. Conclusions and Outlooks
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Elahi, E.; Khalid, Z.; Tauni, M.Z.; Zhang, H.; Lirong, X. Extreme weather events risk to crop-production and the adaptation of innovative management strategies to mitigate the risk: A retrospective survey of rural Punjab, Pakistan. Technovation 2023, 117, 102255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elahi, E.; Khalid, Z.; Zhang, Z. Understanding farmers’ intention and willingness to install renewable energy technology: A solution to reduce the environmental emissions of agriculture. Appl. Energy 2022, 309, 118459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zipori, A.; Rosenfeld, D.; Shpund, J.; Steinberg, D.M.; Erel, Y. Targeting and impacts of AgI cloud seeding based on rainchemical composition and cloud top phase characterization. Atmos. Res. 2012, 114, 119–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, A.; Waseem, M.; Ullah, W.; Zhao, C.; Zhu, J. Spatiotemporal Analysis of Meteorological and Hydrological Droughts and Their Propagations. Water 2021, 13, 2237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waseem, M.; Khursheed, T.; Abbas, A.; Ahmad, I.; Javed, Z. Impact of meteorological drought on agriculture production at different scales in Punjab, Pakistan. J. Water Clim. Change 2021, 13, 113–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, L.; Chu, X.; Rasmussen, R.; Breed, D. Radar observations and WRF LES simulations of the impact of ground-based glaciogenic seeding effect on orographic clouds and precipitation: Part II: AgI dispersion and seeding signals simulated by WRF. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2016, 55, 445–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Guo, X.; Chang, Y. A Numerical Investigation on Microphysical Properties of Clouds and Precipitation over the Tibetan Plateau in Summer 2014. J. Meteorol. Res. 2019, 33, 463–477. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.Y.; Huang, Y.; Yin, X.Z. Observations and Research Progress of Cloud-Seeding (Snow) Project in Qilian Mountains. Adv. Meteorol. Sci. Technol. 2021, 11, 102–116. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Xue, L.; Chu, X.; Rasmussen, R.; Breed, D.; Boe, B.; Geerts, B. The dispersion of silver iodide particles from ground-based generators over complex terrain. Part II: WRF large-eddy simulations versus Observations. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2014, 53, 1342–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.B. Coauthors The operational mesogammascale analysis and forecast system of the U.S. Army Test and Evaluation Command. Part I: Overview of the modeling system, the forecast products, and how the products are used. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2008, 47, 1077–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boe, B.; Heimbach, J.A., Jr.; Krauss, T.W.; Xue, L.; Chu, X.; McPartland, J.T. The dispersion of silver iodide particles from ground-based generators over complex terrain. Part 1: Observations by acoustic ice nucleus counters. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2014, 53, 1325–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.E.; Gao, Q.; He, H.; Ji, L. Numerical Simulation Research on Silver Iodide Cold Cloud Seeding. Meteorol. Mon. 2016, 42, 347–355. [Google Scholar]
- Warburton, J.A.; Chai, S.K.; Young, L.G. A new method of assessing snowfall enhancement with silver iodide seeding using physical and chemical techniques. J. Appl. Microbiol. 1996, 35, 1569–1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsie, E.Y.; Farley, R.D.; Orville, H.D. Numerical Simulation of Ice-Phase Convective Cloud Seeding. J. Appl. Meteorol. 1980, 19, 950–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.M.; Liu, Q.J.; Zhang, J.C. A Numerical Simulation Study on Microphysical Structure and Cloud Seeding in Cloud System of Qilian Mountain Region. Meteorol. Mon. 2007, 7, 33–43. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Fang, C.G.; Guo, X.L.; Wang, P.X. The physical and precipitation response to AgI seeding from a mesoscale WRF-based seeding model. Chin. J. Atmos. Sci. 2009, 33, 621–633. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Qi, P.; Guo, X.; Chang, Y.; Tang, J.; Li, S. Cloud water path, precipitation amount, and precipitation efficiency derived from multiple datasets on the Qilian Mountains, Northeastern Tibetan Plateau. Atmos. Res. 2022, 274, 798–818. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, L.; Tessendorf, S.A.; Nelson, E.; Rasmussen, R.M.; Breed, D.; Parkinson, S.; Holbrook, P.; Blestrud, D. Implementation of a silver iodide cloud-seeding parameterization in WRF. Part II: 3D simulations of actual seeding events and sensitivity tests. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2013, 52, 1458–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Chen, Y.W. The mesoscale numerical simulation of the effectiveness of an artificial precipitation enhancement operation. J. Meteorol. Sci. 2011, 31, 613–620. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Guo, X.; Fu, D.; Zheng, G. Modeling study on optimal convective cloud seeding in rain augmentation. J. Korean Meteorol. Soc. 2007, 43, 273–284. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.E.; He, H.; Gao, Q. Research on application of the mesoscale silver iodide seeding numerical model. Acta Meteorol. Sin. 2021, 79, 359–368. [Google Scholar]
- Xin, J.; Bao, D.; Ma, Y.; Ma, Y.; Gong, C.; Qiao, S.; Jiang, Y.; Ren, X.; Pang, T.; Yan, P. Forecasting and Optimization of Wind Speed over the Gobi Grassland Wind Farm in Western Inner Mongolia. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 1943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Xin, J.; Yin, Y.; Wang, Z.; Wang, D.; Ma, Y.; Jia, D.; Jiang, Y.; Wu, L.; Pan, X. Adaptability evaluation of boundary layer schemes for simulation of sea and land breeze circulation in the west coast of the Yellow Sea. Atmos. Res. 2022, 178, 106354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Xin, J.; Yin, Y.; Chang, W.; Xue, M.; Jia, D.; Ma, Y. Understanding the Major Impact of Planetary Boundary Layer Schemes on Simulation of Vertical Wind Structure. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, M.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, J.; Tan, C.; Tang, Y.; Ma, Q.; Li, Q.; Mao, J.; Hu, Z. Quantifying the cloud water resource: Methods based on observational diagnosis and cloud model simulation. J. Meteorol. Res. 2020, 34, 1256–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geerts, B.; Miao, Q.; Yang, Y.; Rasmussen, R.; Breed, D. An airborne profiling radar study of the impact of glaciogenic cloud seeding on snowfall from winter orographic clouds. J. Atmos. Sci. 2010, 67, 3286–3302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geresdi, I.; Xue, L.; Rasmussen, R. Evaluation of orographic cloud seeding using bin microphysics scheme. Part I: Two-dimensional approach. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2016, 55, 1443–1462. [Google Scholar]
- Mirocha, J.; Kosović, B.; Kirkil, G. Resolved turbulence characteristics in large-eddy simulations nested within mesoscale simulations using the weather research and forecasting model. Mon. Weather Rev. 2014, 142, 806–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shuangxi, F.; Hongfen, Z.; Lijie, Y. Comparative analysis of different types of precipitation characteristics in the northern foot of Qilian Mountain under the influence of topography. Arid. Zone Res. 2021, 38, 1226–1234. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Thompson, G.; Rasmussen, R.M.; Manning, K. Explicit forecasts of winter precipitation using an improved bulk microphysics scheme. Part I: Description and sensitivity analysis. Mon. Weather Rev. 2004, 132, 519–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

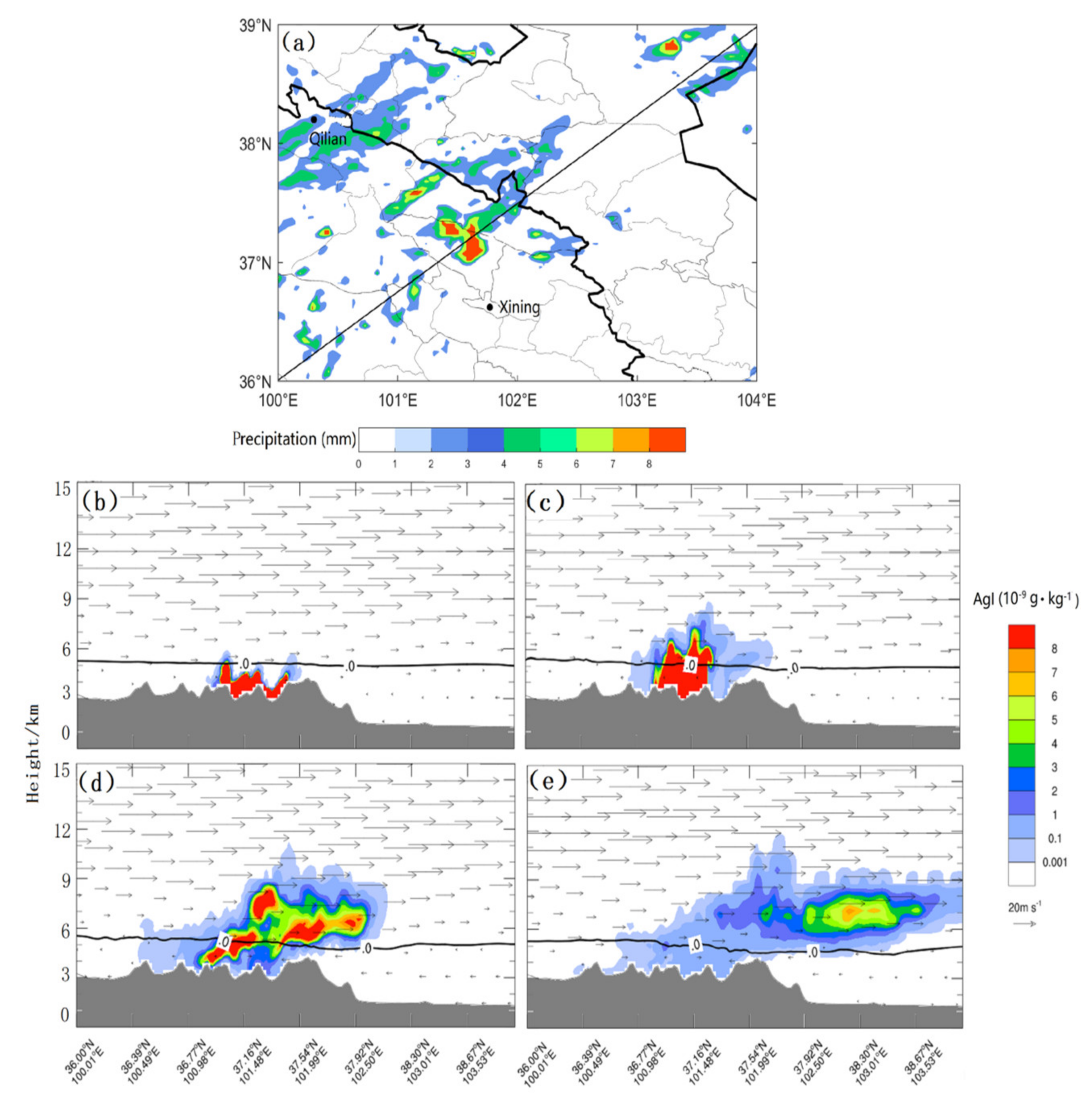
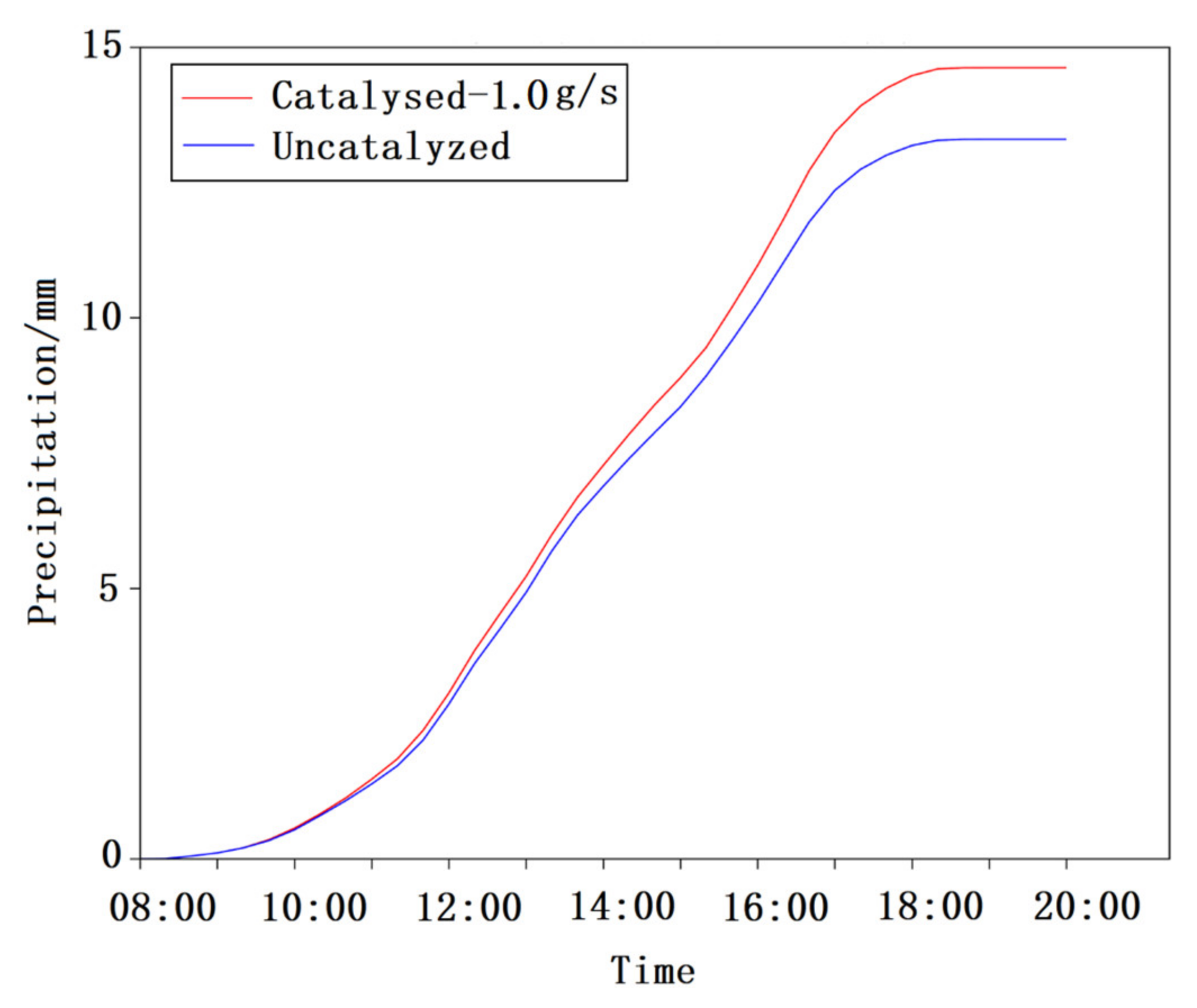
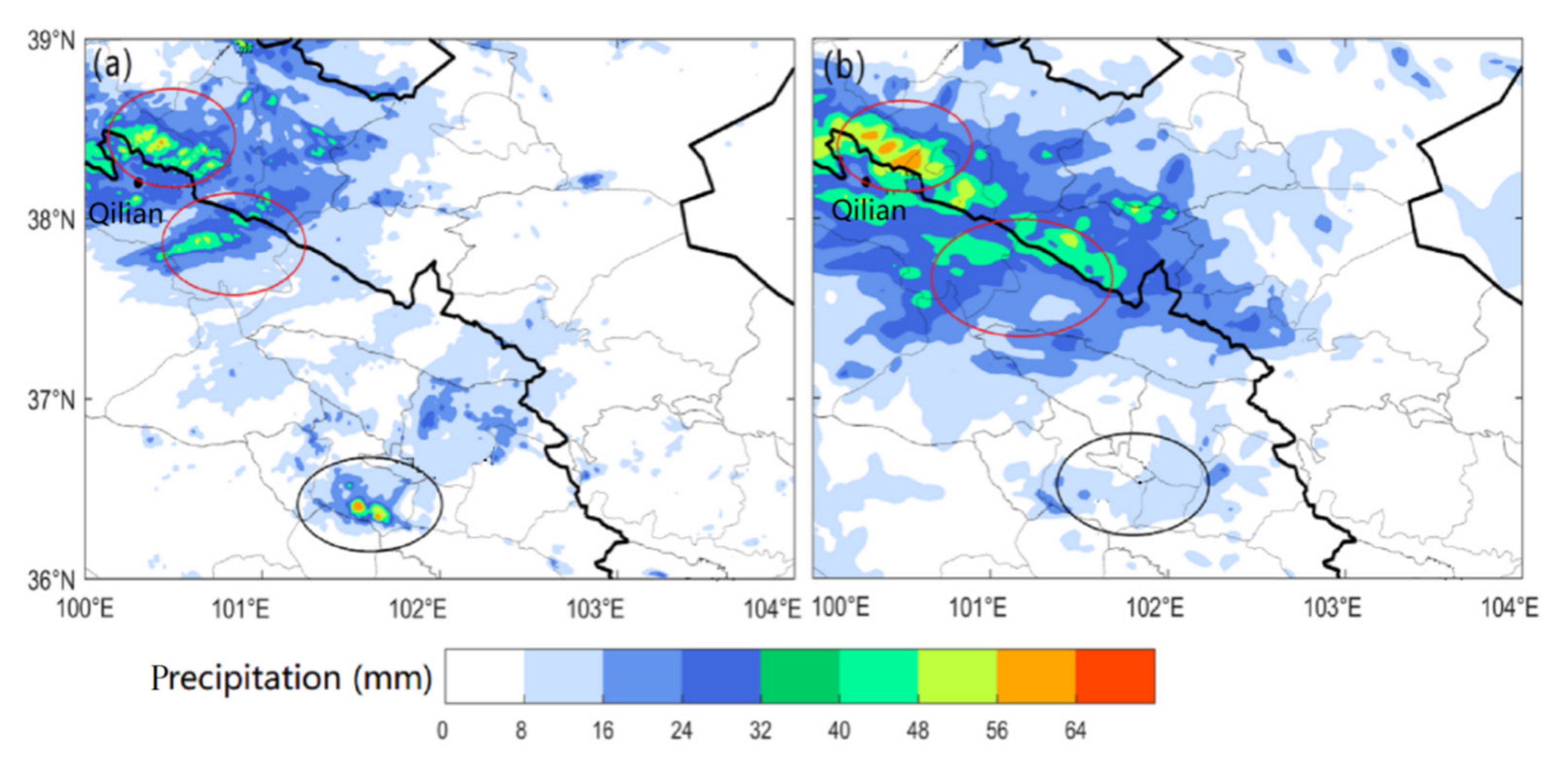
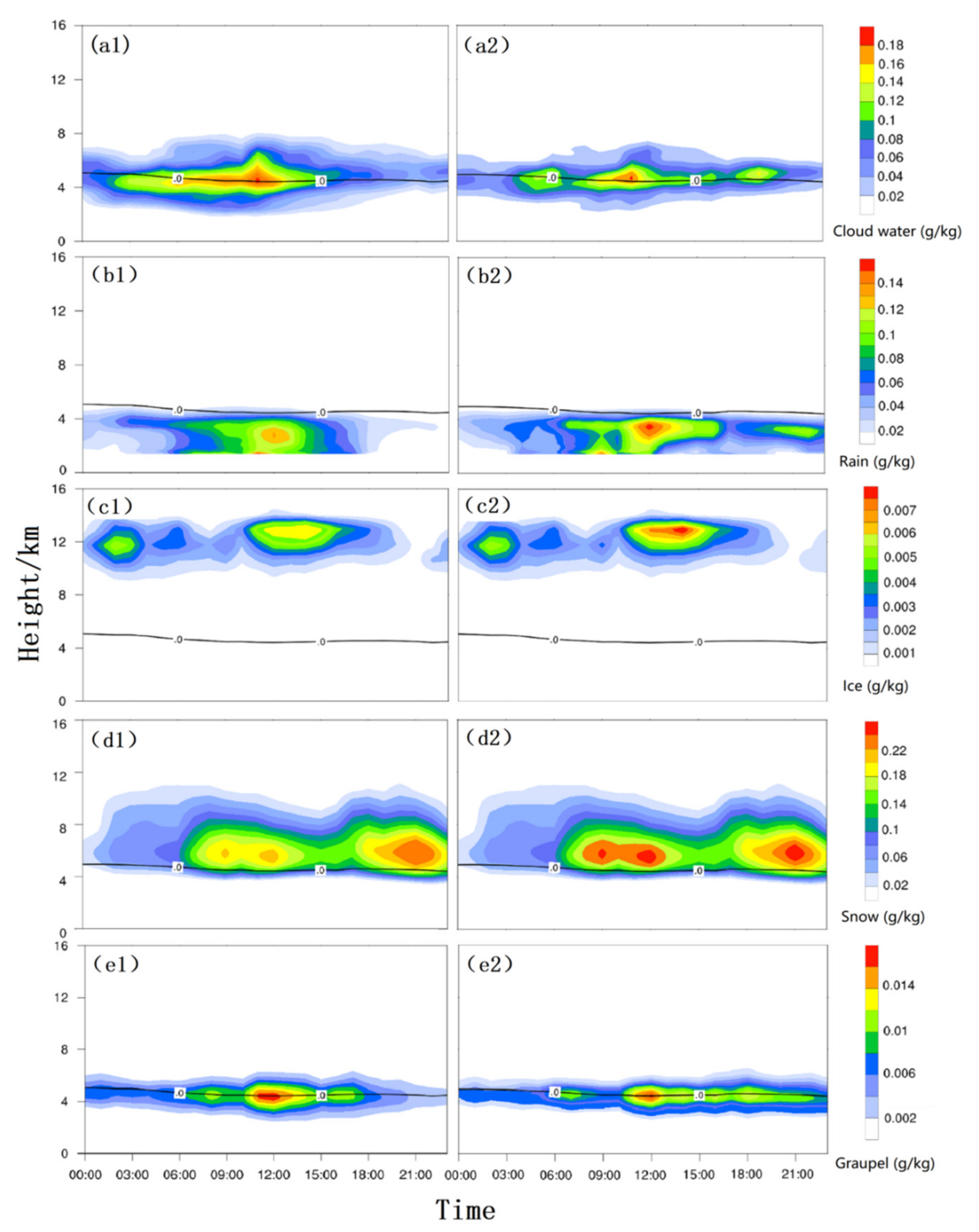

| Domain 1 | Domain 2 | Domain 3 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Grid spacing | 27 km | 9 km | 3 km |
| Lattice number | 115 × 91 | 154 × 124 | 154 × 124 |
| Vertical layer | 34 | 34 | 34 |
| Model top height | 50 hPa | 50 hPa | 50 hPa |
| Cumulus parameterization scheme | Grell-Devenyi | Grell-Devenyi | - |
| Boundary layer scheme | BMJ | BMJ | BMJ |
| Land surface process scheme | RUC | RUC | RUC |
| Long wave radiation scheme | RRTM | RRTM | RRTM |
| Cloud microphysics solution | Thompson | Thompson | Thompson |
| Surface layer scheme | Eta | Eta | Eta |
| Short wave radiation scheme | Goddard | Goddard | Goddard |
| Vertical Layer | Cloud Water (g·kg−1) | Ice Crystal (g·kg−1) | Vertical Velocity (m·s−1) | Temperature (°C) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3 | 0.110 | 0.250 | 0.050 | 15 |
| 4 | 0.080 | 0.210 | 0.065 | −3 |
| 5 | 0.025 | 0.090 | 0.061 | −21 |
| 6 | 0.001 | 0.003 | 0.027 | −39 |
| Test Name | Sowing Range (km) | Seeding Rate (g·s−1) | Duration (min) | Increase Precipitation Percentage (%) | Increase Precipitation (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CTL-1 | null | null | null | null | null |
| S1-1 | 54 × 54 × 15 | 0.1 | 10 | 5.4 | 0.72 |
| S1-2 | 54 × 54 × 15 | 1.2 | 10 | 10.4 | 1.38 |
| S1-3 | 54 × 54 × 15 | 1.5 | 10 | 10.0 | 1.32 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ren, J.; Zhang, W.; Kou, M.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, X. A Numerical Study of Critical Variables on Artificial Cold Cloud Precipitation Enhancement in the Qilian Mountains, China. Atmosphere 2023, 14, 1086. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14071086
Ren J, Zhang W, Kou M, Ma Y, Zhang X. A Numerical Study of Critical Variables on Artificial Cold Cloud Precipitation Enhancement in the Qilian Mountains, China. Atmosphere. 2023; 14(7):1086. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14071086
Chicago/Turabian StyleRen, Jing, Wenyu Zhang, Menggang Kou, Yongjing Ma, and Xinyu Zhang. 2023. "A Numerical Study of Critical Variables on Artificial Cold Cloud Precipitation Enhancement in the Qilian Mountains, China" Atmosphere 14, no. 7: 1086. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14071086
APA StyleRen, J., Zhang, W., Kou, M., Ma, Y., & Zhang, X. (2023). A Numerical Study of Critical Variables on Artificial Cold Cloud Precipitation Enhancement in the Qilian Mountains, China. Atmosphere, 14(7), 1086. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14071086







