The Climate Change Crisis: A Review of Its Causes and Possible Responses
Abstract
1. Introduction
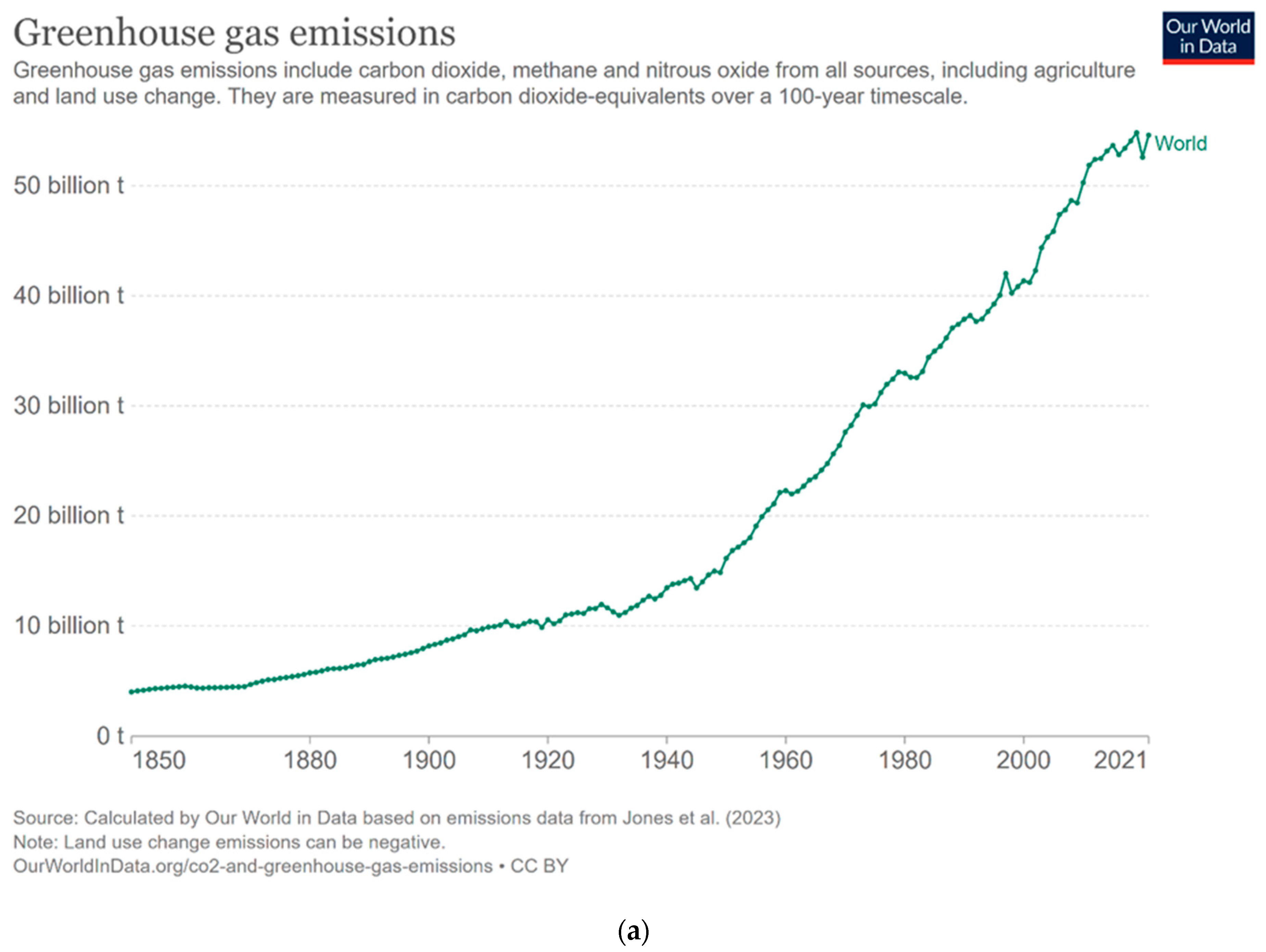
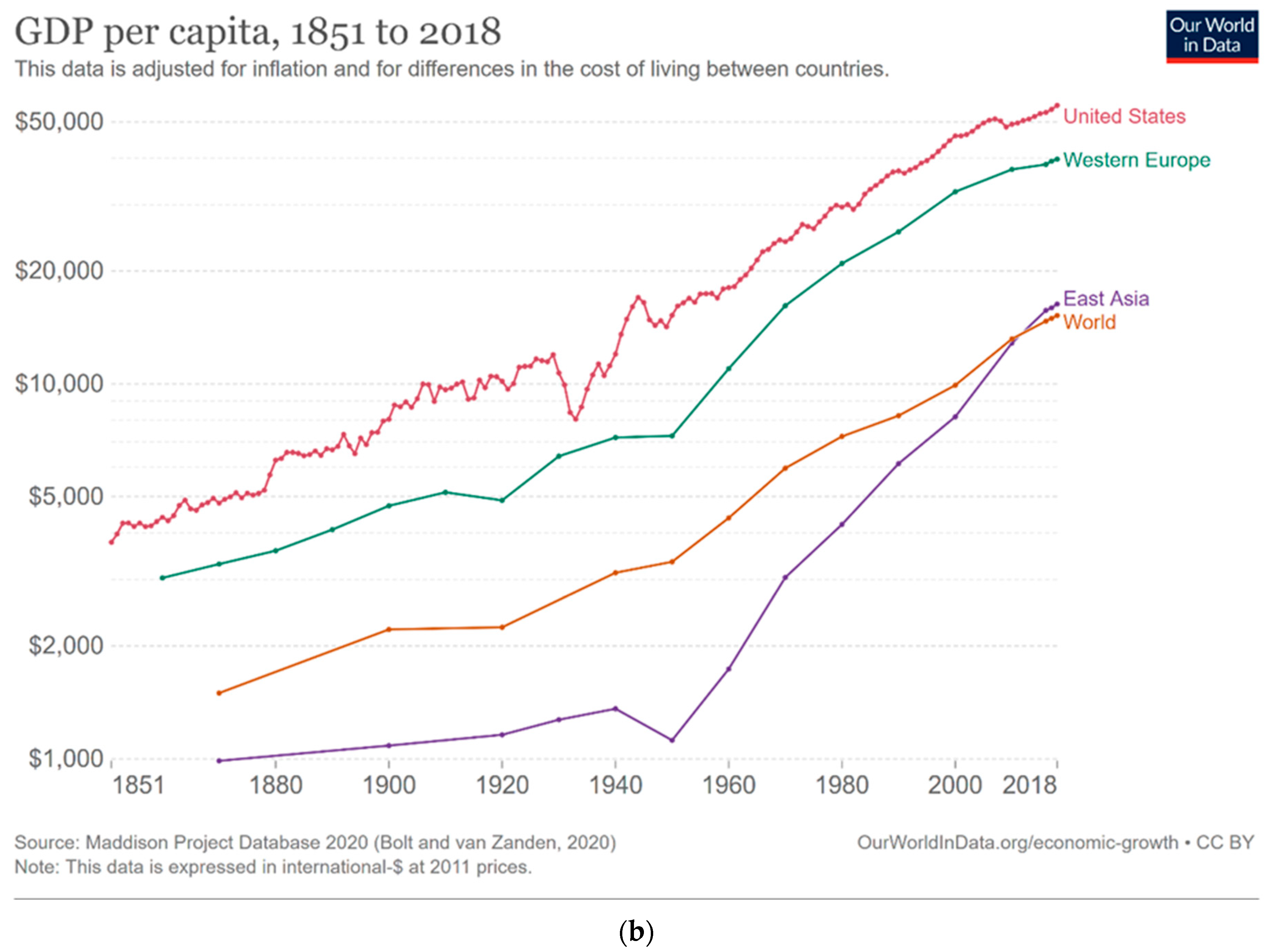
2. Mitigation Failure
3. Calls for Transformative Change
4. Nonlinearity in the Climate System
- -
- The possibility of the system undergoing sharp transitions, even in the presence of steady forcing;
- -
- A small change in some parameters can cause great qualitative differences in the resulting behavior (e.g., chaos);
- -
- The response of a nonlinear system to oscillatory external forcing usually exhibits frequencies not present in the external forcing.
5. Enhancing Natural Carbon Sinks
6. Geoengineering of Climate
6.1. Solar Radiation Management (SRM)
6.2. Marine Cloud Brightening (MCB)
7. Conclusions
8. Dedication
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ripple, W.J.; Wolf, C.; Gregg, J.W.; Levin, K.; Rockström, J.; Newsome, T.M.; Betts, M.G.; Huq, S.; Law, B.E.; Kemp, L.; et al. World Scientists’ Warning of a Climate Emergency 2022. BioScience 2022, 72, 1149–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kemp, L.; Xu, C.; Depledge, J.; Ebi, K.L.; Gibbins, G.; Kohler, T.A.; Rockström, J.; Scheffer, M.; Schellnhuber, H.J.; Steffen, W.; et al. Climate Endgame: Exploring catastrophic climate change scenarios. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2022, 119, e2108146119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stoddard, I.; Anderson, K.; Capstick, S.; Carton, W.; Depledge, J.; Facer, K.; Gough, C.; Hache, F.; Hoolohan, C.; Hultman, M. Three decades of climate mitigation: Why haven’t we bent the global emissions curve? Annu. Rev. Environ. Resour. 2021, 46, 653–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keeling, C.D.; Bacastow, R.B.; Bainbridge, A.E.; Ekdahl, C.A., Jr.; Guenther, P.R.; Waterman, L.S.; Chin, J.F.S. Atmospheric carbon dioxide variations at Mauna Loa Observatory, Hawaii. Tellus 1976, 28, 538–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.R.; Raftery, A.E. Country-based rate of emissions reductions should increase by 80% beyond nationally determined contributions to meet the 2 C target. Commun. Earth Environ. 2021, 2, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- BP. The Energy Institute Statistical Review of World Energy. Available online: https://www.bp.com/en/global/corporate/energy-economics/statistical-review-of-world-energy.html (accessed on 22 May 2023).
- Parmesan, C.; Hanley, M.E. Plants and climate change: Complexities and surprises. Ann. Bot. 2015, 116, 849–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halsch, C.A.; Shapiro, A.M.; Fordyce, J.A.; Nice, C.C.; Thorne, J.H.; Waetjen, D.P.; Forister, M.L. Insects and recent climate change. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2002543117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doney, S.C.; Busch, D.S.; Cooley, S.R.; Kroeker, K.J. The Impacts of Ocean Acidification on Marine Ecosystems and Reliant Human Communities. Annu. Rev. Environ. Resour. 2020, 45, 83–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poloczanska, E.S.; Brown, C.J.; Sydeman, W.J.; Kiessling, W.; Schoeman, D.S.; Moore, P.J.; Brander, K.; Bruno, J.F.; Buckley, L.B.; Burrows, M.T.; et al. Global imprint of climate change on marine life. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2013, 3, 919–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, T.P.; Baird, A.H.; Bellwood, D.R.; Card, M.; Connolly, S.R.; Folke, C.; Grosberg, R.; Hoegh-Guldberg, O.; Jackson, J.B.C.; Kleypas, J.; et al. Climate Change, Human Impacts, and the Resilience of Coral Reefs. Science 2003, 301, 929–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahl, K.; Licker, R.; Abatzoglou, J.T.; Declet-Barreto, J. Increased frequency of and population exposure to extreme heat index days in the United States during the 21st century. Environ. Res. Commun. 2019, 1, 075002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fowler, H.J.; Lenderink, G.; Prein, A.F.; Westra, S.; Allan, R.P.; Ban, N.; Barbero, R.; Berg, P.; Blenkinsop, S.; Do, H.X.; et al. Anthropogenic intensification of short-duration rainfall extremes. Nat. Rev. Earth Environ. 2021, 2, 107–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vicedo-Cabrera, A.M.; Scovronick, N.; Sera, F.; Royé, D.; Schneider, R.; Tobias, A.; Astrom, C.; Guo, Y.; Honda, Y.; Hondula, D.M.; et al. The burden of heat-related mortality attributable to recent human-induced climate change. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2021, 11, 492–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patz, J.A.; Campbell-Lendrum, D.; Holloway, T.; Foley, J.A. Impact of regional climate change on human health. Nature 2005, 438, 310–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berchin, I.I.; Valduga, I.B.; Garcia, J.; de Andrade Guerra, J.B.S.O. Climate change and forced migrations: An effort towards recognizing climate refugees. Geoforum 2017, 84, 147–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coronese, M.; Lamperti, F.; Keller, K.; Chiaromonte, F.; Roventini, A. Evidence for sharp increase in the economic damages of extreme natural disasters. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 21450–21455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Academies of Sciences, Engineering and Medicine. Attribution of Extreme Weather Events in the Context of Climate Change; National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Stott, P. How climate change affects extreme weather events. Science 2016, 352, 1517–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Oldenborgh, G.J.; van der Wiel, K.; Kew, S.; Philip, S.; Otto, F.; Vautard, R.; King, A.; Lott, F.; Arrighi, J.; Singh, R.; et al. Pathways and pitfalls in extreme event attribution. Clim. Chang. 2021, 166, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simpson, N.P.; Mach, K.J.; Constable, A.; Hess, J.; Hogarth, R.; Howden, M.; Lawrence, J.; Lempert, R.J.; Muccione, V.; Mackey, B. A framework for complex climate change risk assessment. One Earth 2021, 4, 489–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pörtner, H.-O.; Roberts, D.; Tignor, M.; Poloczanska, E.; Mintenbeck, K.; Alegría, A.; Craig, M.; Langsdorf, S.; Löschke, S.; Möller, V.; et al. Climate Change 2022: Impacts, Adaptation and Vulnerability Working Group II Contribution to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; IPCC: Geneva, Switzerland, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Head, M.J.; Steffen, W.; Fagerlind, D.; Waters, C.N.; Poirier, C.; Syvitski, J.; Zalasiewicz, J.A.; Barnosky, A.D.; Cearreta, A.; Jeandel, C.; et al. The Great Acceleration is real and provides a quantitative basis for the proposed Anthropocene Series/Epoch. Int. Union Geol. Sci. 2022, 45, 359–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UN. World Population Prospects 2022. Available online: https://population.un.org/wpp/Download/Standard/Population/ (accessed on 11 May 2023).
- Zhou, P.; Wang, M. Carbon dioxide emissions allocation: A review. Ecol. Econ. 2016, 125, 47–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williges, K.; Meyer, L.H.; Steininger, K.W.; Kirchengast, G. Fairness critically conditions the carbon budget allocation across countries. Glob. Environ. Chang. 2022, 74, 102481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritchie, H.; Roser, M.; Rosado, P. CO2 and Greenhouse Gas Emissions [Online Resource]. Available online: https://ourworldindata.org/co2-and-greenhouse-gas-emissions (accessed on 2 May 2023).
- Jones, M.W.; Peters, G.P.; Gasser, T.; Andrew, R.M.; Schwingshackl, C.; Gütschow, J.; Houghton, R.A.; Friedlingstein, P.; Pongratz, J.; Le Quéré, C. National contributions to climate change due to historical emissions of carbon dioxide, methane, and nitrous oxide since 1850. Sci. Data 2023, 10, 155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolt, J.; Van Zanden, J.L. Maddison style estimates of the evolution of the world economy. A new 2020 update. In Maddison-Project Working Paper WP-15; University of Groningen: Groningen, The Netherlands, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Oreskes, N. The scientific consensus on climate change. Science 2004, 306, 1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewandowsky, S.; Oreskes, N.; Risbey, J.S.; Newell, B.R.; Smithson, M. Seepage: Climate change denial and its effect on the scientific community. Glob. Environ. Chang. 2015, 33, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamb, W.F.; Mattioli, G.; Levi, S.; Roberts, J.T.; Capstick, S.; Creutzig, F.; Minx, J.C.; Müller-Hansen, F.; Culhane, T.; Steinberger, J.K. Discourses of climate delay. Glob. Sustain. 2020, 3, e17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballew, M.T.; Leiserowitz, A.; Roser-Renouf, C.; Rosenthal, S.A.; Kotcher, J.E.; Marlon, J.R.; Lyon, E.; Goldberg, M.H.; Maibach, E.W. Climate Change in the American Mind: Data, Tools, and Trends. Environ. Sci. Policy Sustain. Dev. 2019, 61, 4–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyhan, B.; Porter, E.; Wood, T.J. Time and skeptical opinion content erode the effects of science coverage on climate beliefs and attitudes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2022, 119, e2122069119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, R.; Muttarak, R.; Peisker, J.; Stanig, P. Climate change experiences raise environmental concerns and promote Green voting. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2022, 12, 148–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hornsey, M.J.; Chapman, C.M.; Humphrey, J.E. Climate skepticism decreases when the planet gets hotter and conservative support wanes. Glob. Environ. Chang. 2022, 74, 102492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glavovic, B.C.; Smith, T.F.; White, I. The tragedy of climate change science. Clim. Dev. 2022, 14, 829–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, G.P.; Marland, G.; Le Quéré, C.; Boden, T.; Canadell, J.G.; Raupach, M.R. Rapid growth in CO2 emissions after the 2008–2009 global financial crisis. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2012, 2, 2–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rittel, H.W.; Webber, M.M. Wicked problems. Man-Made Futur. 1974, 26, 272–280. [Google Scholar]
- Scott, V.; Gilfillan, S.; Markusson, N.; Chalmers, H.; RS, H. Last chance for carbon capture and storage. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2013, 3, 105–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Cohen, F.; Smith, S.M.; Pfeiffer, A. Plant conversions and abatement technologies cannot prevent stranding of power plant assets in 2 °C scenarios. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin-Roberts, E.; Scott, V.; Flude, S.; Johnson, G.; Haszeldine, R.S.; Gilfillan, S. Carbon capture and storage at the end of a lost decade. One Earth 2021, 4, 1569–1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oreskes, N. Carbon-reduction plans rely on tech that doesn’t exist. Sci. Am. 2022, 327, 90. [Google Scholar]
- Díaz, S.; Settele, J.; Brondízio, E.S.; Ngo, H.T.; Agard, J.; Arneth, A.; Balvanera, P.; Brauman, K.A.; Butchart, S.H.M.; Chan, K.M.A.; et al. Pervasive human-driven decline of life on Earth points to the need for transformative change. Science 2019, 366, eaax3100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francis, P. Praise Be to You: Laudato Si’: On Care for Our Common Home; Ignatius Press: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Raymond, C.; Horton, R.M.; Zscheischler, J.; Martius, O.; AghaKouchak, A.; Balch, J.; Bowen, S.G.; Camargo, S.J.; Hess, J.; Kornhuber, K.; et al. Understanding and managing connected extreme events. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2020, 10, 611–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz, S.; Settele, J.; Brondizio, E.; Ngo, H.; Guèze, M.; Agard, J.; Arneth, A.; Balvanera, P.; Brauman, K.; Butchart, S. Summary for Policymakers of the Global Assessment Report on Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services–Unedited Advance Version; Intergovernmental Science-Policy Platform on Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services (IPBES): Bonn, Germany, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Kates, R.W.; Travis, W.R.; Wilbanks, T.J. Transformational adaptation when incremental adaptations to climate change are insufficient. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 7156–7161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heikkinen, M.; Ylä-Anttila, T.; Juhola, S. Incremental, reformistic or transformational: What kind of change do C40 cities advocate to deal with climate change? J. Environ. Policy Plan. 2019, 21, 90–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linnér, B.-O.; Wibeck, V. Conceptualising variations in societal transformations towards sustainability. Environ. Sci. Policy 2020, 106, 221–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scoones, I.; Stirling, A.; Abrol, D.; Atela, J.; Charli-Joseph, L.; Eakin, H.; Ely, A.; Olsson, P.; Pereira, L.; Priya, R.; et al. Transformations to sustainability: Combining structural, systemic and enabling approaches. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sustain. 2020, 42, 65–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.; Moser, S. Transformative climate adaptation in the United States: Trends and prospects. Science 2021, 372, eabc8054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sachs, J.D.; Schmidt-Traub, G.; Mazzucato, M.; Messner, D.; Nakicenovic, N.; Rockström, J. Six transformations to achieve the sustainable development goals. Nat. Sustain. 2019, 2, 805–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jewell, J.; Cherp, A. On the political feasibility of climate change mitigation pathways: Is it too late to keep warming below 1.5 °C? WIREs Clim. Chang. 2020, 11, e621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenner, D.; Heede, R. White knights, or horsemen of the apocalypse? Prospects for Big Oil to align emissions with a 1.5° C pathway. Energy Res. Soc. Sci. 2021, 79, 102049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pörtner, H.-O.; Roberts, D.C.; Adams, H.; Adler, C.; Aldunce, P.; Ali, E.; Begum, R.A.; Betts, R.; Kerr, R.B.; Biesbroek, R. Climate Change 2022: Impacts, Adaptation and Vulnerability; IPCC: Geneva, Switzerland, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Shukla, P.R.; Skea, J.; Slade, R.; Al Khourdajie, A.; van Diemen, R.; McCollum, D.; Pathak, M.; Some, S.; Vyas, P.; Fradera, R. Climate Change 2022: Mitigation of Climate Change; Contribution of working group III to the sixth assessment report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Maslin, M.; Lang, J.; Harvey, F. A short history of the successes and failures of the international climate change negotiations. UCL Open Environ. 2022, Preprint. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tracker, C.A. Warming Projections Global Update November 2022. Available online: https://policycommons.net/artifacts/3153102/cat_2022-11-10_globalupdate_cop27/3950927/ (accessed on 11 May 2023).
- Rial, J.A.; Pielke, R.A.; Beniston, M.; Claussen, M.; Canadell, J.; Cox, P.; Held, H.; de Noblet-Ducoudré, N.; Prinn, R.; Reynolds, J.F. Nonlinearities, feedbacks and critical thresholds within the Earth’s climate system. Clim. Chang. 2004, 65, 11–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rial, J.A. Abrupt climate change: Chaos and order at orbital and millennial scales. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2004, 41, 95–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnamurthy, V. Predictability of Weather and Climate. Earth Space Sci. 2019, 6, 1043–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dansgaard, W.; Johnsen, S.J.; Clausen, H.B.; Dahl-Jensen, D.; Gundestrup, N.S.; Hammer, C.U.; Hvidberg, C.S.; Steffensen, J.P.; Sveinbjörnsdottir, A.E.; Jouzel, J.; et al. Evidence for general instability of past climate from a 250-kyr ice-core record. Nature 1993, 364, 218–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alley, R.B.; Ágústsdóttir, A.M. The 8k event: Cause and consequences of a major Holocene abrupt climate change. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2005, 24, 1123–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenton, T.M.; Held, H.; Kriegler, E.; Hall, J.W.; Lucht, W.; Rahmstorf, S.; Schellnhuber, H.J. Tipping elements in the Earth’s climate system. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 1786–1793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lenton, T.M.; Rockström, J.; Gaffney, O.; Rahmstorf, S.; Richardson, K.; Steffen, W.; Schellnhuber, H.J. Climate tipping points—Too risky to bet against. Nature 2019, 575, 592–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kriegler, E.; Hall, J.W.; Held, H.; Dawson, R.; Schellnhuber, H.J. Imprecise probability assessment of tipping points in the climate system. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 5041–5046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armstrong McKay, D.I.; Staal, A.; Abrams, J.F.; Winkelmann, R.; Sakschewski, B.; Loriani, S.; Fetzer, I.; Cornell, S.E.; Rockström, J.; Lenton, T.M. Exceeding 1.5C global warming could trigger multiple climate tipping points. Science 2022, 377, eabn7950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steffen, W.; Rockström, J.; Richardson, K.; Lenton, T.M.; Folke, C.; Liverman, D.; Summerhayes, C.P.; Barnosky, A.D.; Cornell, S.E.; Crucifix, M.; et al. Trajectories of the Earth System in the Anthropocene. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 8252–8259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vermeulen, S.J.; Campbell, B.M.; Ingram, J.S. Climate change and food systems. Annu. Rev. Environ. Resour. 2012, 37, 195–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibbs, H.K.; Salmon, J.M. Mapping the world’s degraded lands. Appl. Geogr. 2015, 57, 12–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanderman, J.; Hengl, T.; Fiske, G.J. Soil carbon debt of 12,000 years of human land use. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 9575–9580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friedlingstein, P.; Jones, M.W.; O’Sullivan, M.; Andrew, R.M.; Bakker, D.C.; Hauck, J.; Le Quéré, C.; Peters, G.P.; Peters, W.; Pongratz, J. Global carbon budget 2021. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2022, 14, 1917–2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuss, S.; Lamb, W.F.; Callaghan, M.W.; Hilaire, J.; Creutzig, F.; Amann, T.; Beringer, T.; de Oliveira Garcia, W.; Hartmann, J.; Khanna, T.; et al. Negative emissions—Part 2: Costs, potentials and side effects. Environ. Res. Lett. 2018, 13, 063002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griscom, B.W.; Adams, J.; Ellis, P.W.; Houghton, R.A.; Lomax, G.; Miteva, D.A.; Schlesinger, W.H.; Shoch, D.; Siikamäki, J.V.; Smith, P.; et al. Natural climate solutions. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 11645–11650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amelung, W.; Bossio, D.; de Vries, W.; Kögel-Knabner, I.; Lehmann, J.; Amundson, R.; Bol, R.; Collins, C.; Lal, R.; Leifeld, J.; et al. Towards a global-scale soil climate mitigation strategy. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 5427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lal, R.; Bouma, J.; Brevik, E.; Dawson, L.; Field, D.J.; Glaser, B.; Hatano, R.; Hartemink, A.E.; Kosaki, T.; Lascelles, B.; et al. Soils and sustainable development goals of the United Nations: An International Union of Soil Sciences perspective. Geoderma Reg. 2021, 25, e00398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fyson, C.L.; Jeffery, M.L. Ambiguity in the Land Use Component of Mitigation Contributions Toward the Paris Agreement Goals. Earth’s Future 2019, 7, 873–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthews, H.D.; Wynes, S. Current global efforts are insufficient to limit warming to 1.5 °C. Science 2022, 376, 1404–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keith, D.W. Geoengineering the climate: History and prospect. Annu. Rev. Energy Environ. 2000, 25, 245–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gattuso, J.-P.; Williamson, P.; Duarte, C.M.; Magnan, A.K. The Potential for Ocean-Based Climate Action: Negative Emissions Technologies and Beyond. Front. Clim. 2021, 2, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lampitt, R.S.; Achterberg, E.P.; Anderson, T.R.; Hughes, J.A.; Iglesias-Rodriguez, M.D.; Kelly-Gerreyn, B.A.; Lucas, M.; Popova, E.E.; Sanders, R.; Shepherd, J.G.; et al. Ocean fertilization: A potential means of geoengineering? Philos. Trans. R. Soc. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2008, 366, 3919–3945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lawrence, M.G.; Crutzen, P.J. Was breaking the taboo on research on climate engineering via albedo modification a moral hazard, or a moral imperative? Earth’s Future 2017, 5, 136–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, J.H. Glacial-interglacial CO2 change: The Iron Hypothesis. Paleoceanography 1990, 5, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strong, A.L.; Cullen, J.J.; Chisholm, S.W. Ocean Fertilization Science, Policy, and Commerce. Oceanography 2009, 22, 236–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charlson, R.J.; Schwartz, S.E.; Hales, J.M.; Cess, R.D.; Coakley, J.A.; Hansen, J.E.; Hofmann, D.J. Climate Forcing by Anthropogenic Aerosols. Science 1992, 255, 423–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charlson, R.J.; Lovelock, J.E.; Andreae, M.O.; Warren, S.G. Oceanic phytoplankton, atmospheric sulphur, cloud albedo and climate. Nature 1987, 326, 655–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penner, J.E.; Hegg, D.; Leaitch, R. Unravelling the role of aerosols in climate change. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2001, 35, 332A–340A. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabric, A.; Matrai, P.; Jones, G.; Middleton, J. The nexus between sea ice and polar emissions of marine biogenic aerosols. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2018, 99, 61–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kristiansen, N.; Stohl, A.; Wotawa, G. Atmospheric removal times of the aerosol-bound radionuclides 137 Cs and 131 I during the months after the Fukushima Dai-ichi nuclear power plant accident--a constraint for air quality and climate models. Atmos. Chem. Phys. Discuss. 2012, 12, 10759–10769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rotstayn, L.D.; Collier, M.A.; Chrastansky, A.; Jeffrey, S.J.; Luo, J.J. Projected effects of declining aerosols in RCP4.5: Unmasking global warming? Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2013, 13, 10883–10905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreae, M.O. Atmospheric aerosols versus greenhouse gases in the twenty-first century. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2007, 365, 1915–1923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glantz, P.; Fawole, O.G.; Ström, J.; Wild, M.; Noone, K.J. Unmasking the Effects of Aerosols on Greenhouse Warming Over Europe. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2022, 127, e2021JD035889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philipona, R.; Behrens, K.; Ruckstuhl, C. How declining aerosols and rising greenhouse gases forced rapid warming in Europe since the 1980s. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2009, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robock, A. Volcanic eruptions and climate. Rev. Geophys. 2000, 38, 191–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toohey, M.; Jia, Y.; Tegetmeier, S. Stratospheric residence time and the lifetime of volcanic aerosol. In Proceedings of the EGU General Assembly Conference Abstracts, online, 19–30 April 2021; p. EGU21-12131. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Bi, J.; Hu, Z.; Ma, J.; Li, B. Regional transportation and influence of atmospheric aerosols triggered by Tonga volcanic eruption. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 325, 121429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Wang, F.; Li, J.; Duan, Y.; Zhu, C.; He, J. Potential Impact of Tonga Volcano Eruption on Global Mean Surface Air Temperature. J. Meteorol. Res. 2022, 36, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pope, F.D.; Braesicke, P.; Grainger, R.G.; Kalberer, M.; Watson, I.M.; Davidson, P.J.; Cox, R.A. Stratospheric aerosol particles and solar-radiation management. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2012, 2, 713–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasch, P.J.; Tilmes, S.; Turco, R.P.; Robock, A.; Oman, L.; Chen, C.-C.; Stenchikov, G.L.; Garcia, R.R. An overview of geoengineering of climate using stratospheric sulphate aerosols. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2008, 366, 4007–4037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Church, J.A.; White, N.J.; Arblaster, J.M. Significant decadal-scale impact of volcanic eruptions on sea level and ocean heat content. Nature 2005, 438, 74–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trenberth, K.E.; Dai, A. Effects of Mount Pinatubo volcanic eruption on the hydrological cycle as an analog of geoengineering. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2007, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paik, S.; Min, S.-K.; An, S.-I. How explosive volcanic eruptions reshape daily precipitation distributions. Weather Clim. Extrem. 2022, 37, 100489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latham, J. Amelioration of global warming by controlled enhancement of the albedo and longevity of low-level maritime clouds. Atmos. Sci. Lett. 2002, 3, 52–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, F.; Feingold, G. What can Possibly go Wrong? Cloud Microphysical Implications for Marine Cloud Brightening. In Proceedings of the AGU Fall Meeting Abstracts, online, 1–17 December 2020; pp. A200–A207. [Google Scholar]
- Diamond, M.S.; Gettelman, A.; Lebsock, M.D.; McComiskey, A.; Russell, L.M.; Wood, R.; Feingold, G. To assess marine cloud brightening’s technical feasibility, we need to know what to study—and when to stop. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2022, 119, e2118379119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gabric, A.J. The Climate Change Crisis: A Review of Its Causes and Possible Responses. Atmosphere 2023, 14, 1081. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14071081
Gabric AJ. The Climate Change Crisis: A Review of Its Causes and Possible Responses. Atmosphere. 2023; 14(7):1081. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14071081
Chicago/Turabian StyleGabric, Albert J. 2023. "The Climate Change Crisis: A Review of Its Causes and Possible Responses" Atmosphere 14, no. 7: 1081. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14071081
APA StyleGabric, A. J. (2023). The Climate Change Crisis: A Review of Its Causes and Possible Responses. Atmosphere, 14(7), 1081. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14071081




