Estimating Precipitation Using LSTM-Based Raindrop Spectrum in Guizhou
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Data and Quality Control
2.1. Data Sources
2.1.1. Weather Radar Data
2.1.2. Raindrop Spectrometer and Rain Gauge Data
2.2. Data Quality Control
2.2.1. Data Quality Control of Raindrop Spectrometer
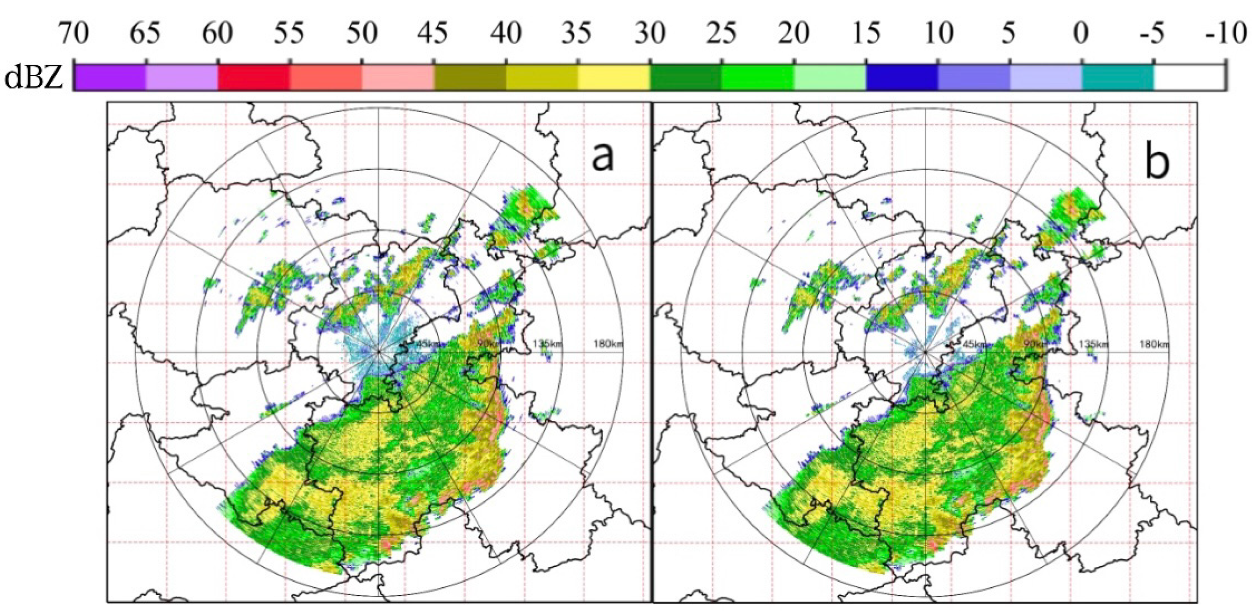
2.2.2. Weather Radar Data Quality Control
3. Calculation and Characteristic Analysis of Raindrop Spectrum Parameters
3.1. Calculation of Raindrop Spectrum Parameters
3.1.1. Number Density
3.1.2. Precipitation Intensity
3.1.3. Mean Diameter
3.1.4. Mass-Weighted Average Diameter
3.1.5. VMD
3.1.6. M-P Distribution and GAMMA Distribution
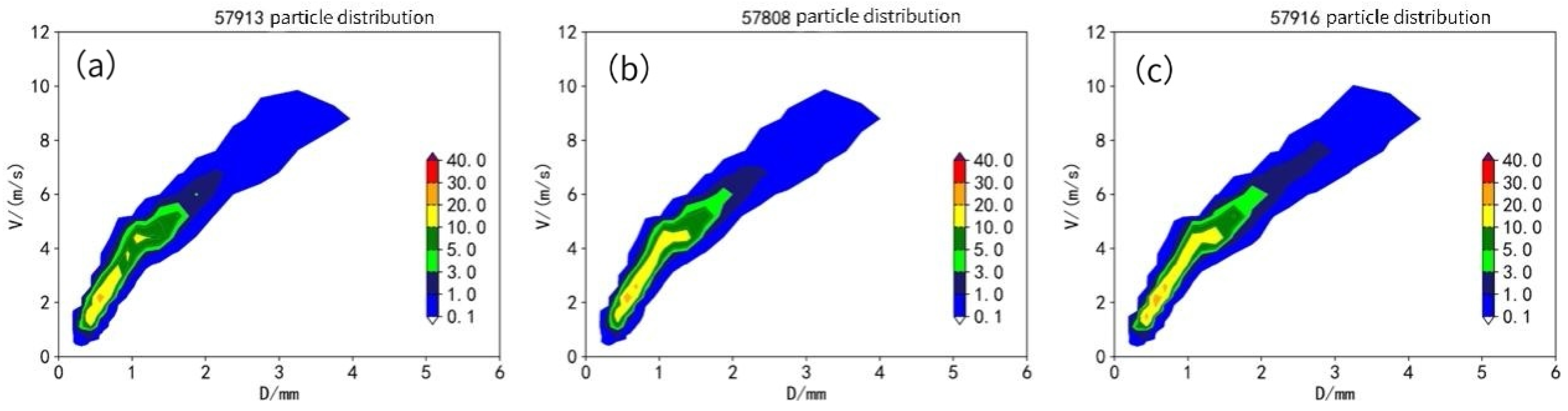
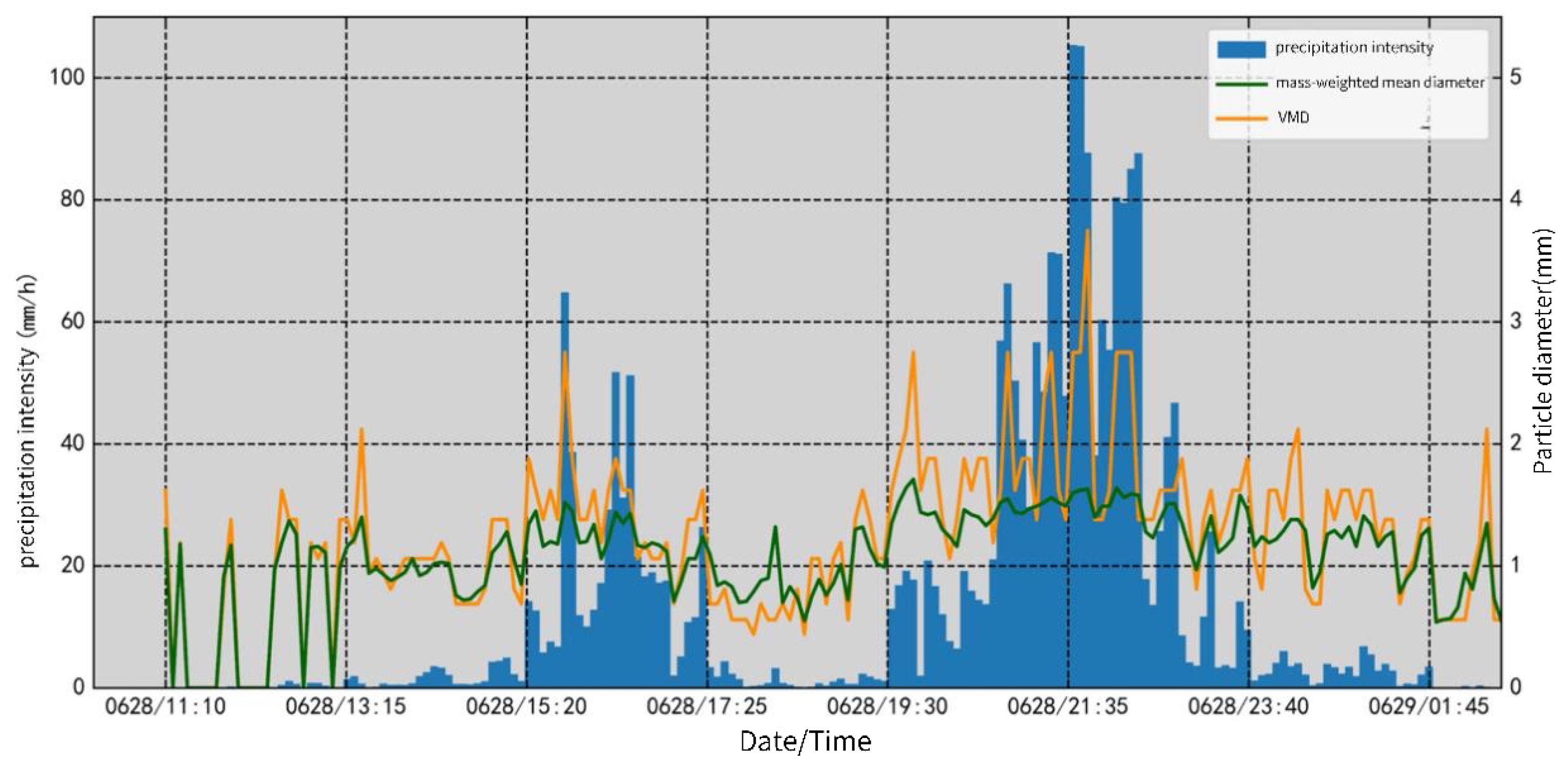
3.2. Analysis of Raindrop Spectrum Characteristics
4. Precipitation Estimation Method and Result Analysis
4.1. Precipitation Estimation Method
4.1.1. Dynamic Z-I Relationships
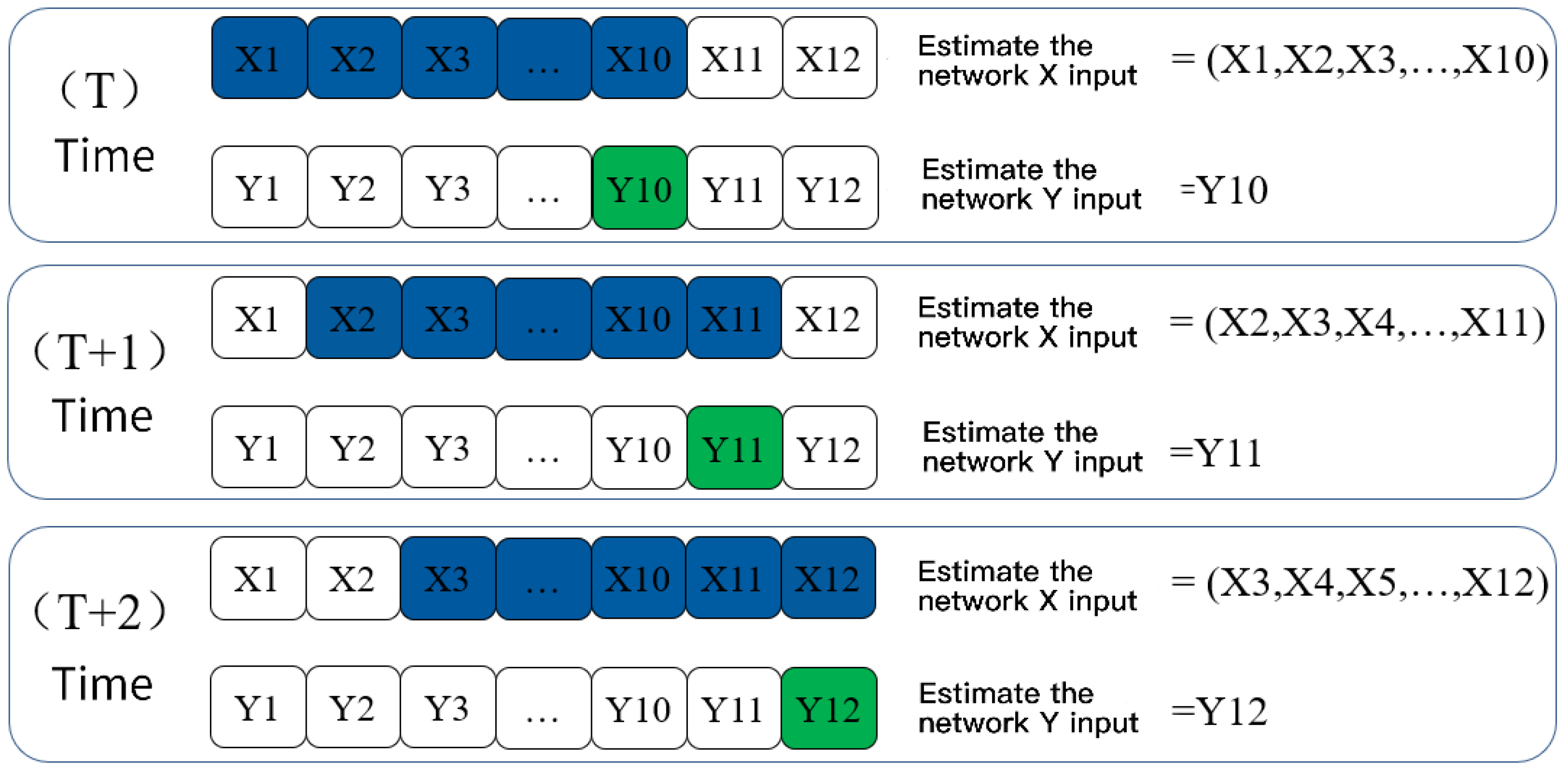
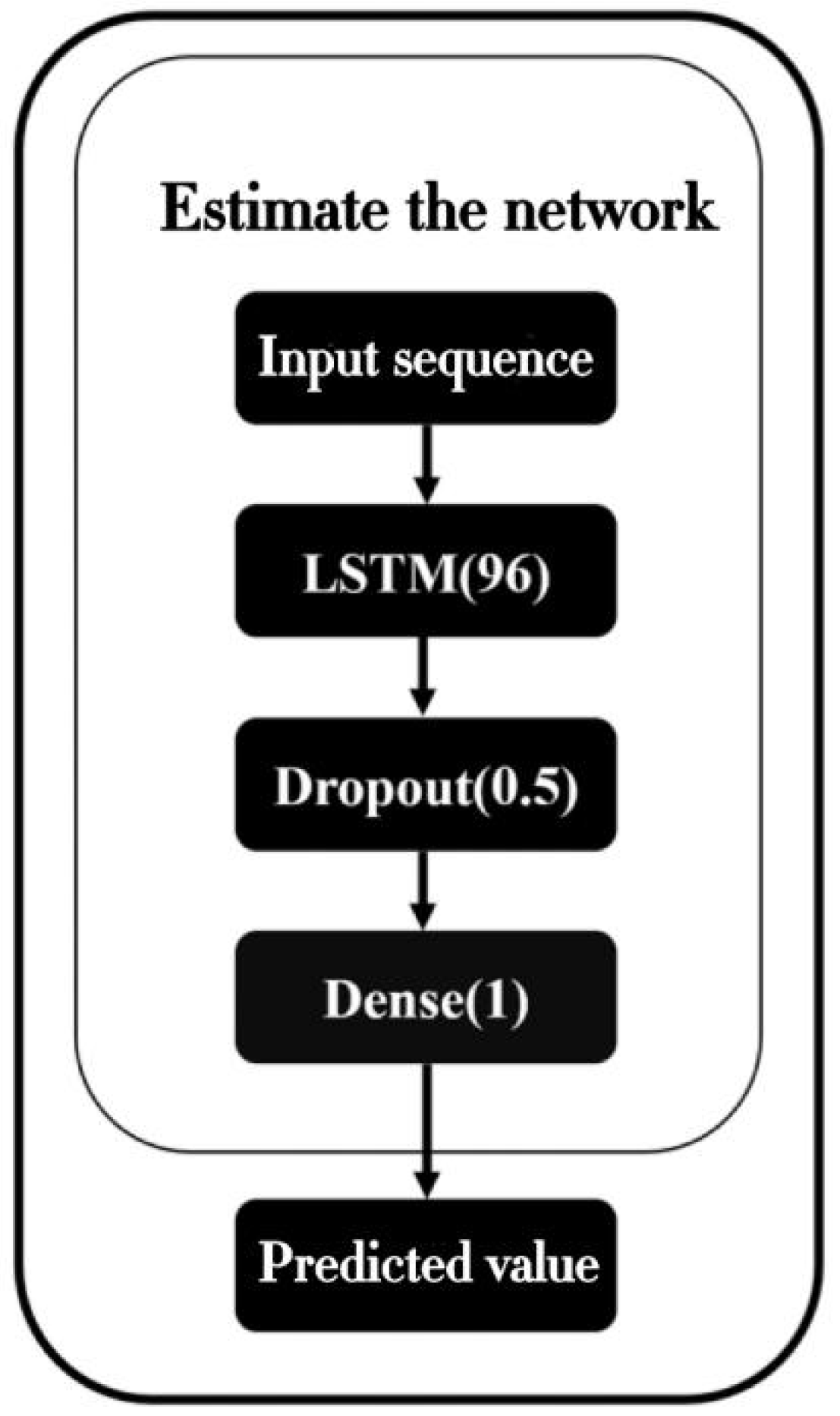
4.1.2. Neural Network Method
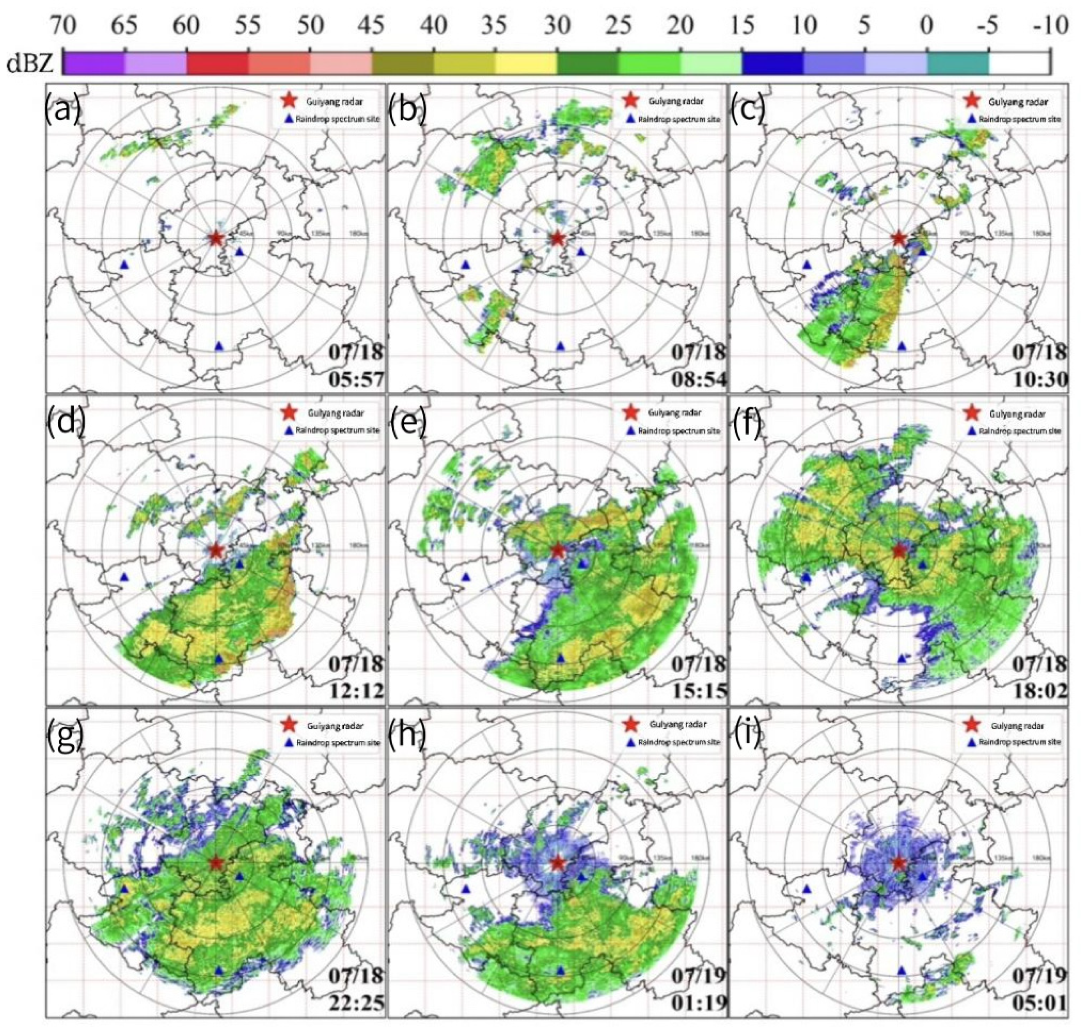
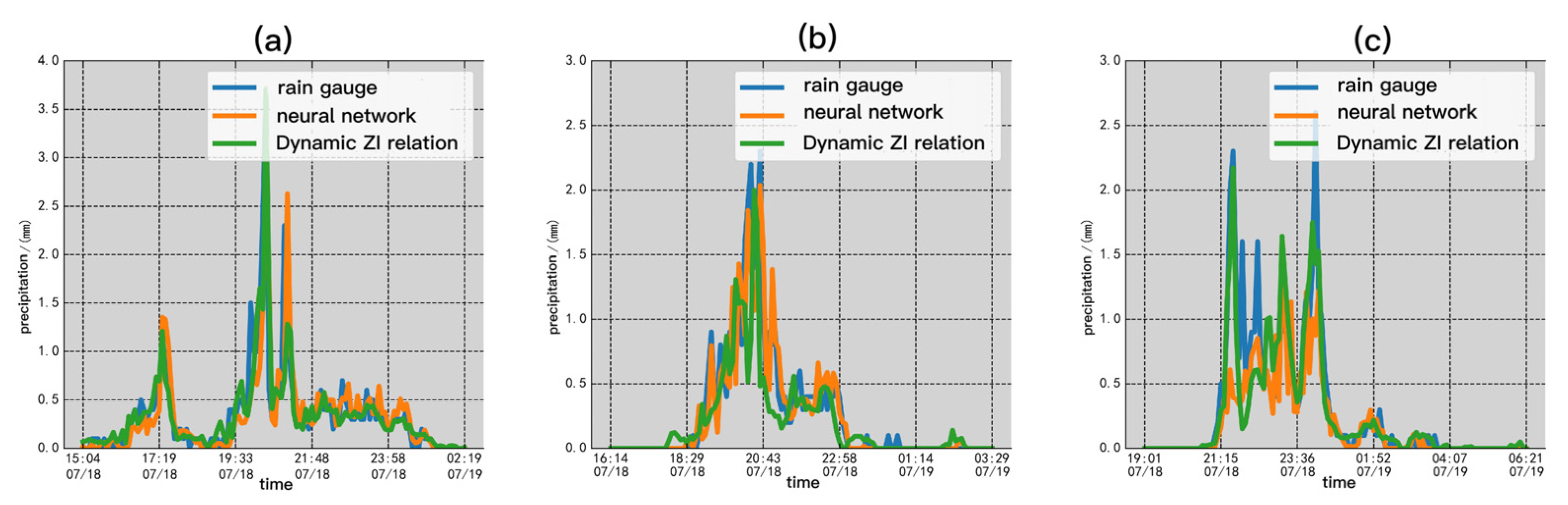
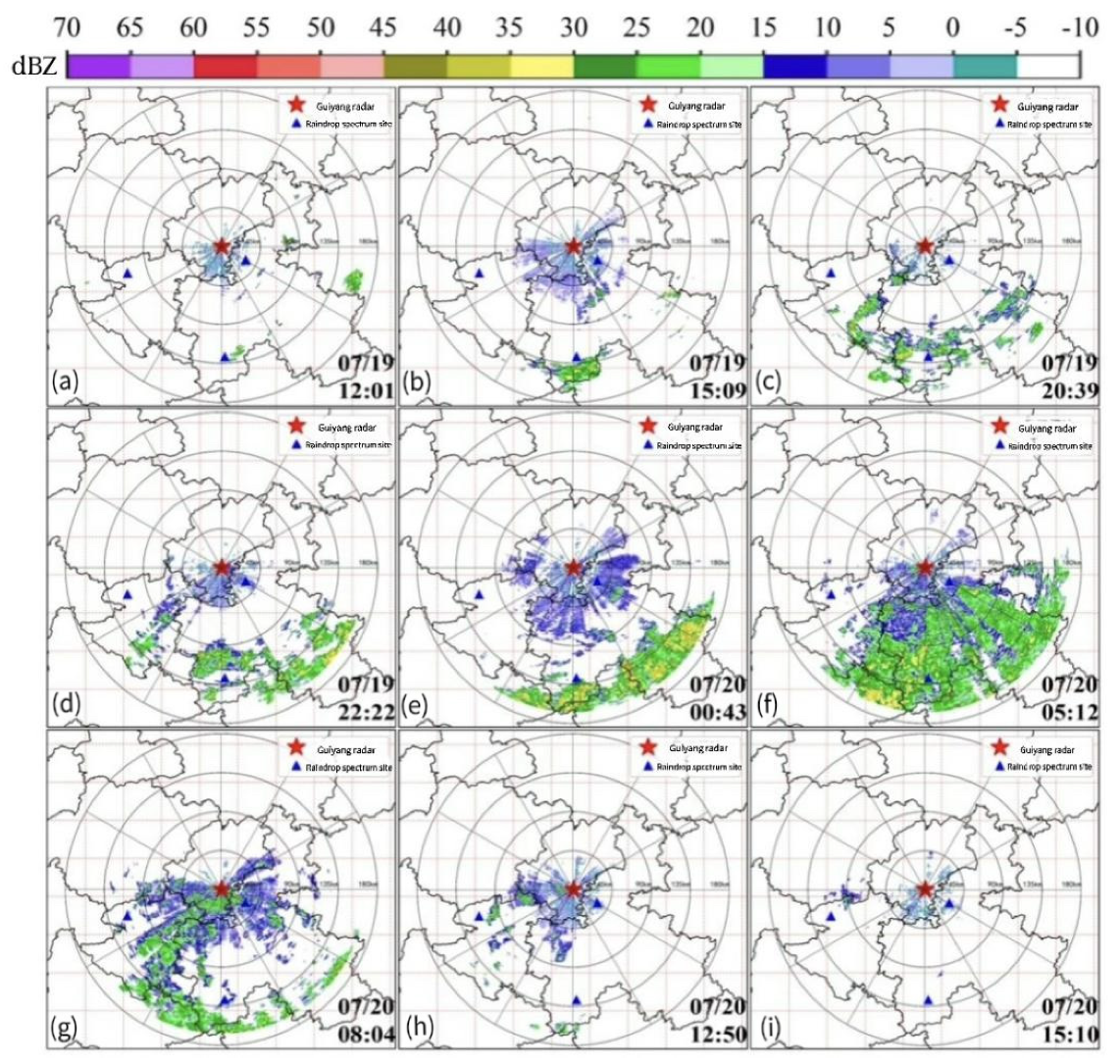
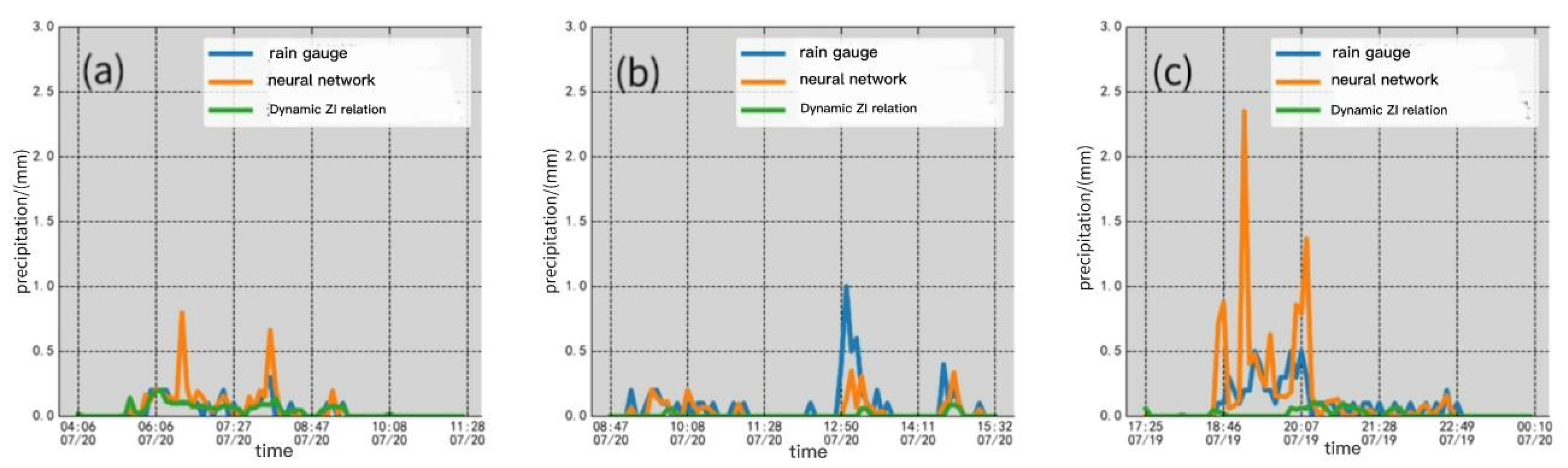
4.2. Analysis of Precipitation Estimation Results
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Huang, Z.W.; Peng, S.Y.; Zhang, H.R.; Zheng, J.F.; Zeng, Z.M.; Wang, Y.Y. Characteristics of raindrop size distribution in Anxi, Fujian. J. Appl. Meteorol. Sci. 2022, 33, 205–217. [Google Scholar]
- Chakravarty, K.; Raj, P.E. Raindrop size distributions and their association with characteristics of clouds and precipitation during monsoon and post-monsoon periods over a tropical Indian station. Atmos. Res. 2013, 124, 181–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.C.; Zhang, L.J.; Liang, H.H.; Li, L.; Liu, Y.L. Analysis of summer raindrop spectrum characteristics in Beijing mountainous and plain areas. Meteorol. Mon. 2021, 47, 830–842. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.X.; Han, H.B.; Guo, S.Y.; Tian, J.B.; Tang, W.T. Characteristics of raindrop size distribution and Z-R relationship of different precipitation clouds in summer at the southern foot of Qilian Mountains. Arid Zone Res. 2021, 38, 1048–1057. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, S. Research on Precipitation Phenomenon Recognition Technology Based on Raindrop Spectrum and Machine Learning; Nanjing University of Information Science and Technology: Nanjing, China, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Jing, G.F.; Luo, L.; Guo, J.; Cui, X.L. Application of raindrop spectrometer in weather radar precipitation estimation. Foreign Electron. Meas. Technol. 2020, 39, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.N.; Wang, G.L. The influence of DSD parameters on precipitation estimation by dual-frequency radar. Plateau Meteorol. 2020, 39, 570–580. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, L.P.; He, J.X.; Wen, H. Application of raindrop spectrometer network data in radar quantitative precipitation estimation. Torrential Rain Disasters 2016, 35, 173–181. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, L.M.; Zhang, H.S.; Wang, J.; Wang, Q.; Chen, X.L. Characteristics of raindrop spectrum of a typical stratocumulus mixed cloud precipitation process. Meteorol. Sci. Technol. 2010, 22, 73–77. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, Y.Z.; Wang, Q.; Yuan, C.A.; Lin, K.P. Application of data mining technology in meteorological forecast research. J. Drought Meteorol. 2015, 33, 19–27. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, J.L.; Wang, H.M.; Yuan, F.F.; Wang, Z.P.; Huang, J.; Qiu, T. Prediction of Precipitation Basedon Recurrent Neural Networks in Jingdezhen, Jiangxi Province, China. Atmosphere 2020, 11, 246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, H.J.; Luo, Y.; Zhao, Z.C.; Wang, H.J. Research on summer precipitation prediction in China based on LSTM network. Clim. Chang. Res. 2020, 16, 263–275. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, W.; Ma, S.C.; Chen, R. The early warning method of rainfall-induced debris flow in northwestern Sichuan based on LSTM. J. Guilin Univ. Technol. 2020, 40, 719–725. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Zhao, N.; Guo, J.Y.; Guo, B. Prediction of monthly precipitation over the Tibetan Plateau based on LSTM neural network. J. Earth Inf. Sci. 2020, 22, 1617–1629. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, H.; Qi, Z.F. Monthly precipitation prediction in eastern Sichuan based on LSTM network. Water Resouces Power 2021, 39, 14–17+13. [Google Scholar]
- Yashon, O.O.; Rodrick, C.; Alice, N.W. Rainfall and Runoff Time-Series Trend Analysis Using LSTM Recurrent Neural Network and Wavelet Neural Network with Satellite-Based Meteorological Data: Case Study of Nzoia Hydrologic Basin. Complex Intell. Syst. 2021, 8, 213–236. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Q.; Qin, L.; Gao, P.; Zhang, R.B. Based on the EEMD-LSTM model, the annual precipitation prediction of the economic belt on the northern slope of the Tianshan Mountains. Arid Zone Res. 2021, 38, 1235–1243. [Google Scholar]
- Atlas, D.; Srivastava, R.C.; Sekhon, R.S. Doppler characteristics of precipitation at vertical incidence. Rev. Geophys. Space Phys. 1973, 11, 1–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruger, A.; Krajewski, W.F. Two-dimensional video disdrometer: A description. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2002, 19, 602–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pruppacher, H.R.; Klett, J.D.; Wang, P.K. Microphysics of Clouds and Precipitation; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Marshall, J.S.; Palmer, W.M. The distribution of raindrops with size. J. Atmos. Sci. 1948, 5, 165–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulbrich, C.W. Natural variations in the analytical form of the raindrop size distribution. J. Clim. Appl. Meteorol. 1983, 22, 1764–1775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Feng, Y.R.; Cai, J.H.; Hu, S. Z-I relationship estimation method of radar quantitative precipitation dynamic classification. J. Trop. Meteorol. 2011, 27, 601–608. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, P.C.; Du, B.Y.; Dai, T.P. Radar Meteorology; Meteorological Press: Beijing, China, 2001; pp. 181–187. [Google Scholar]
- Tokay, A.; Petersen, W.A.; Gatlin, P.; Matthew, W. Comparison of Raindrop Size Distribution Measurements by Collocated Disdrometers. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2013, 30, 1672–1690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Station Number | Station Name | Geographical Coordinates | Distance from Radar |
|---|---|---|---|
| 57913 | Longli | 106.98° E, 26.45° N | 30.21 km |
| 57808 | Puding | 105.74° E, 26.31° N | 99.95 km |
| 57916 | Luodian | 106.76° E, 25.43° N | 129.03 km |
| Station Name Station Number | N0 | λ | Correlation Coefficient |
|---|---|---|---|
| Longli (57913) | 85.5219 | −1.1507 | 83.52% |
| Puding (57808) | 84.5301 | −1.0243 | 85.25% |
| Luodian (57916) | 69.1213 | −0.9158 | 81.69% |
| Station Name Station Number | N0 | µ | λ | Correlation Coefficient |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Longli(57913) | 1,177,999.13 | 6.0209 | 11.1092 | 95.65% |
| Puding(57808) | 154,920.62 | 5.1694 | 8.6301 | 95.84% |
| Luodian(57916) | 62,872.31 | 4.3027 | 7.7396 | 94.82% |
| Station Name Station Number | Correlation Coefficient between Average Diameter and Rainfall Intensity | Correlation Coefficient between Mass Weighted Average Diameter and Rainfall Intensity | Correlation Coefficient between Average Volume Diameter and Rainfall Intensity |
|---|---|---|---|
| Longli (57913) | 25.04% | 46.89% | 67.80% |
| Puding (57808) | 28.45% | 49.51% | 71.28% |
| Luodian (57916) | 18.13% | 47.03% | 71.46% |
| Data | State | Start Time | Deadline | Sample Size |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Raindrop spectrometer, weather radar, automatic rain gauge | train | 15 April 2019 0:00 3 March 2020 0:04 | 17 July 2019 23:58 30 June 2020 23:57 | 49,297 |
| inspection | 1 July 2020 0:03 | 16 August 2020 06:05 | 12,126 |
| Eigenvalue | Estimated Value |
|---|---|
| Radar reflectivity intensity (1–3 layers) | A rain gauge measures precipitation |
| Inversion of particle number density with raindrop spectrometer | |
| Average particle velocity inversion with raindrop spectrometer | |
| Raindrop spectrometer inversion average volume diameter |
| Site | Estimating Method | Real-Time Correlation Coefficient | MRE | MAE | RMSE |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Longli (57913) | Dynamic Z-I | 0.8432 | 0.5046 | 0.1462 | 0.2745 |
| Neural network | 0.8745 | 0.4646 | 0.1228 | 0.2454 | |
| Puding (57808) | Dynamic Z-I | 0.7763 | 0.8039 | 0.1324 | 0.2962 |
| Neural network | 0.9125 | 0.7628 | 0.0935 | 0.1884 | |
| Luodian (57916) | Dynamic Z-I | 0.8658 | 0.7799 | 0.1357 | 0.3379 |
| Neural network | 0.8676 | 0.7986 | 0.1372 | 0.3412 |
| Site | Estimating Method | Real-Time Correlation Coefficient | MRE | MAE | RMSE |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Longli (57913) | Dynamic Z-I | 0.6933 | 0.8068 | 0.0267 | 0.0479 |
| Neural network | 0.7114 | 0.8008 | 0.0401 | 0.1047 | |
| Puding (57808) | Dynamic Z-I | 0.0902 | 0.9794 | 0.0704 | 0.1721 |
| Neural network | 0.4984 | 0.8771 | 0.0564 | 0.1416 | |
| Luodian (57916) | Dynamic Z-I | 0.1409 | 0.9396 | 0.0880 | 0.1445 |
| Neural network | 0.4902 | 0.8409 | 0.1183 | 0.3211 |
| Site | Estimating Method | Correlation Coefficient | MRE | MAE | RMSE | Relative Error |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Longli (57913) | Dynamic Z-I | 0.9951 | 0.0816 | 19.4211 | 22.0374 | −2.68% |
| Neural network | 0.9998 | 0.0526 | 10.3156 | 10.5963 | −4.25% | |
| Puding (57808) | Dynamic Z-I | 0.9938 | 0.0986 | 9.3672 | 11.4746 | −7.41% |
| Neural network | 0.9992 | 0.0911 | 14.3672 | 16.8846 | −11.35% | |
| Luodian (57916) | Dynamic Z-I | 0.9862 | 0.1542 | 26.6712 | 32.5039 | −21.23% |
| Neural network | 0.9996 | 0.1122 | 16.4154 | 17.3465 | −8.68% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, F.; Cao, Y.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, T.; Su, D. Estimating Precipitation Using LSTM-Based Raindrop Spectrum in Guizhou. Atmosphere 2023, 14, 1031. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14061031
Wang F, Cao Y, Wang Q, Zhang T, Su D. Estimating Precipitation Using LSTM-Based Raindrop Spectrum in Guizhou. Atmosphere. 2023; 14(6):1031. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14061031
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Fuzeng, Yaxi Cao, Qiusong Wang, Tong Zhang, and Debin Su. 2023. "Estimating Precipitation Using LSTM-Based Raindrop Spectrum in Guizhou" Atmosphere 14, no. 6: 1031. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14061031
APA StyleWang, F., Cao, Y., Wang, Q., Zhang, T., & Su, D. (2023). Estimating Precipitation Using LSTM-Based Raindrop Spectrum in Guizhou. Atmosphere, 14(6), 1031. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14061031






