Bioaerosol Identification by Wide Particle Size Range Single Particle Mass Spectrometry
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experiment
2.1. SPAMS
2.2. Sample Standards
2.3. TEST Methods
3. Results and Conclusions
3.1. Distribution of Bioaerosol Particle Size
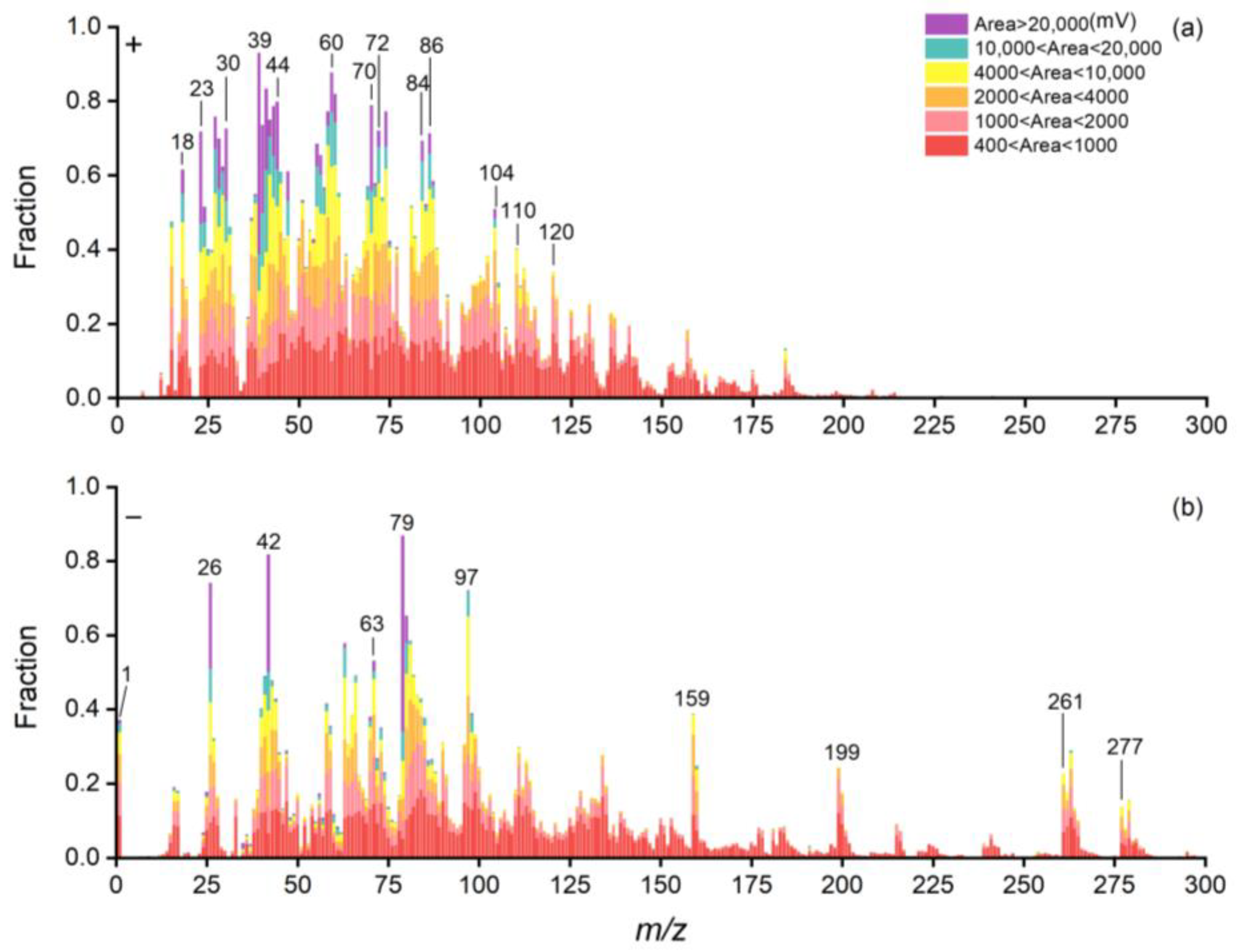
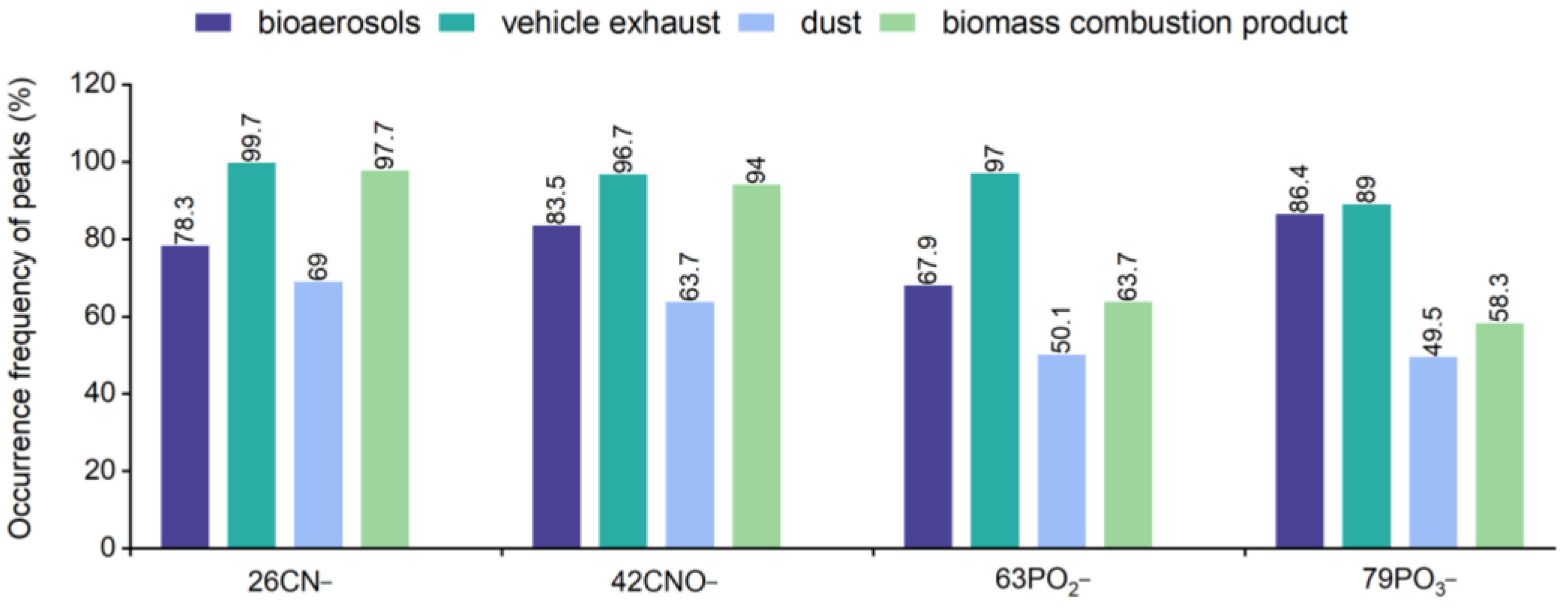
3.2. Characteristic Spectrum of Bioaerosols
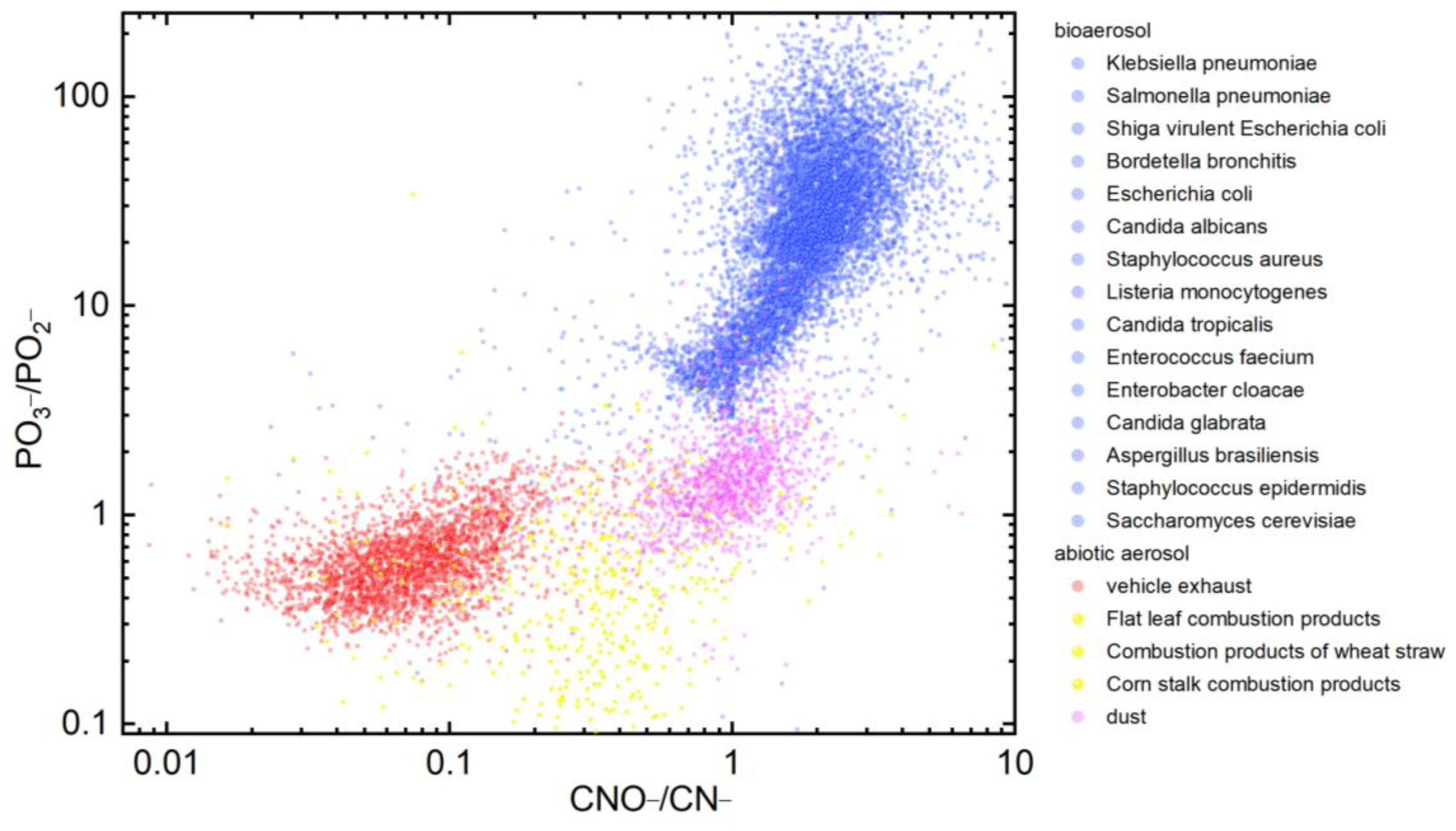
3.3. Bioaerosol Identification Based on Characteristic Peak Ratio
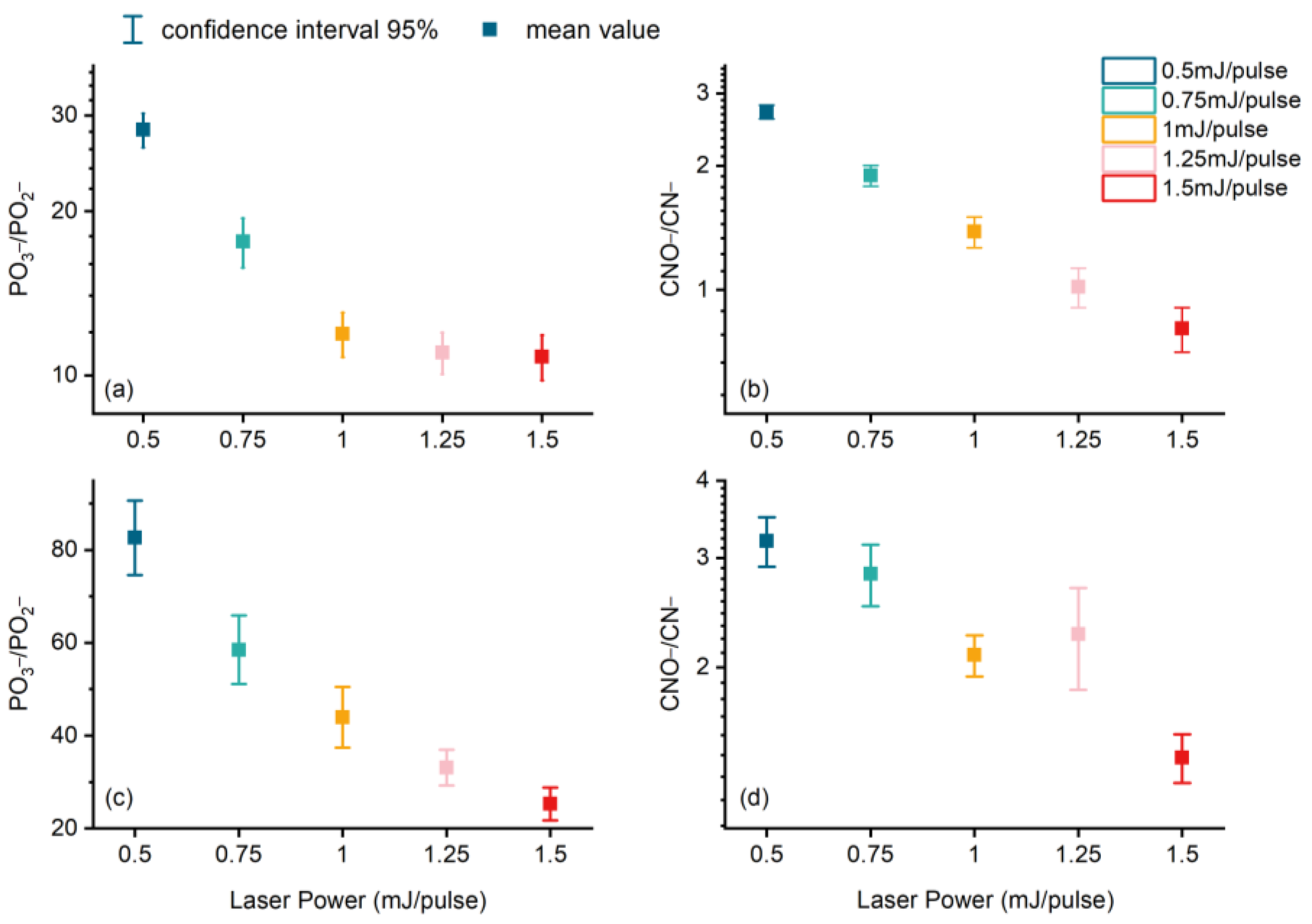
3.4. Influence Analysis of Laser Energy
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fröhlich-Nowoisky, J.; Kampf, C.-J.; Weber, B.; Huffman, J.-A.; Pöhlker, C.; Andreae, M.-O.; Lang-Yona, N.; Burrows, S.-M.; Gunthe, S.-S.; Elbert, W.; et al. Bioaerosols in the Earth system: Climate, health, and ecosystem interactions. Atmos. Res. 2016, 182, 346–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burrows, S.-M.; Elbert, W.; Lawrence, M.-G.; PoSchl, U. Bacteria in the global atmosphere -Part 1: Review and synthesis of literature data for different ecosystems. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2009, 9, 10777–10827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huffman, J.; Santarpia, J.-A. Online Techniques for Quantification and Characterization of Biological Aerosols. Microbiol. Aerosols 2017, 2017, 83–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Després, V.; Huffman, J.-A.; Burrows, S.-M.; Hoose, C.; Safatov, A.; Buryak, G.; Fröhlich-Nowoisky, J.; Elbert, W.; Andreae, M.; Pöschl, U.; et al. Primary biological aerosol particles in the atmosphere: A review. Tellus B Chem. Phys. Meteorol. 2012, 64, 15598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Ran, B.; Wu, W.; Wang, Q.; Tong, Z.; Zhang, X.; Li, Y. Progress in the application of fluorescence spectroscopy in biological aerosol monitoring. Mil. Med. 2018, 42, 464–470. [Google Scholar]
- Bozlee, B.-J.; Misra, A.-K.; Sharma, S.K.; Ingram, M. Remote Raman and fluorescence studies of mineral samples. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2005, 61, 2342–2348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabey, A.-M.; Gallagher, M.-W.; Whitehead, J.; Dorsey, J.-R.; Kaye, P.-H.; Stanley, W.-R. Measurements and comparison of primary biological aerosol above and below a tropical forest canopy using a dual channel fluorescence spectrometer. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2010, 10, 4453–4466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, S.-C.; Pinnick, R.-G.; Niles, S.; Pan, Y.; Holler, S.; Chang, R.; Bottiger, J.; Chen, B.; Orr, C.-S.; Feather, G. Real-time measurement of fluorescence spectra from single airborne biological particles. Field Anal. Chem. Technol. 1999, 3, 221–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- David, P.-F.; Maurice, E.-P.; Herbert, J.-T.; Paul, T.-S.; Gregg, A.-C.; Scott, C.-R.; Carlito, B.-L.; Joanne, M.-H.; Keith, R.-C.; Srivastava, A.; et al. Reagentless Detection and Classification of Individual Bioaerosol Particles in Seconds. Anal. Chem. 2004, 76, 373–378. [Google Scholar]
- Kleefsman, I.; Stowers, M.-A.; Verheijen, P.J.; Van Wuijckhuijse, A.L.; Kientz, C.E.; Marijnissen, J.C.M. Marijnissen Bioaerosol analysis by single particle mass spectrometry. Part. Part. Syst. Charact. 2007, 24, 85–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, M.; Xu, C.; Xu, X.; Zhu, C.; Li, J.; Lv, G. Size distribution of bioaerosols from biomass burning emissions: Characteristics of bacterial and fungal communities in submicron (PM1.0) and fine (PM2.5) particles. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 171, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, N.; Huang, B.; Li, M.; Cheng, P.; Li, L.; Huang, Z.; Gao, W.; Zhou, Z. Single particle mass spectrometry characteristics of atmospheric fine particulate dust sources. China Environ. Sci. 2017, 37, 1262–1268. [Google Scholar]
- Sodeman, D.-A.; Toner, S.-M.; Prather, K.-A. Determination of single particle mass spectral signatures from light-duty vehicle emissions. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 4569–4580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, J.P.; Carlin, R.A.; Prather, K.A. Single particle analysis of suspended soil dust from Southern California. Atmos. Environ. 2000, 34, 1811–1820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zawadowicz, M.-A.; Froyd, K.-D.; Murphy, D.-M.; Cziczo, D.-J. Improved identification of primary biological aerosol particles using single-particle mass spectrometry. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2017, 17, 7193–7212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smets, W.; Moretti, S.; Denys, S.; Lebeer, S. Airborne bacteria in the atmosphere: Presence, purpose, and potential. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 139, 214–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leone, N.; Descroix, D.; Mohammed, S. Bioaerosol Detection with Atomic Emission Spectroscopy. Bioaerosol Detect. Technol. 2014, 2014, 143–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, L.-R.; Gonzalez, L.-A.; Peck, J.; Trimborn, D.; McInnis, J.; Farrar, M.-R.; Moore, K.-D.; Jayne, J.-T.; Robinson, W.-A.; Lewis, D.-K.; et al. Characterization of an aerodynamic lens for transmitting particles greater than 1 micrometer in diameter into the Aerodyne aerosol mass spectrometer. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2013, 6, 3271–3280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cahill, J.-F.; Darlington, T.-K.; Wang, X.; Mayer, J.; Spencer, M.-T.; Holecek, J.-C.; Reed, B.-E.; Prather, K.-A. Development of a High-Pressure Aerodynamic Lens for Focusing Large Particles (4–10 μm) into the Aerosol Time-of-Flight Mass Spectrometer. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 948–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cahill, J.-F.; Darlington, T.-K.; Fitzgerald, C.; Schoepp, N.-G.; Beld, J.; Burkart, M.-D.; Prather, K.-A. Online analysis of single cyanobacteria and algae cells under nitrogen-limited conditions using aerosol time-of-flight mass spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 8039–8046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuo, Z.; Su, B.; Xie, Q.; Li, L.; Huang, Z.; Zhou, Z.; Mai, Z.; Tan, G. Simulation design and experimental study of aerodynamics particle concentrator for single particle mass spectrometry. Vac. Sci. Technol. 2021, 41, 441–447. [Google Scholar]
- Ronningen, T.-J.; Schuetter, J.-M.; Wightman, J.-L.; Murdock, A.; Bartko, A.-P. Raman spectroscopy for biological identification. Biol. Identif. 2014, 2014, 313–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, C.W.; Schwab, M.; Hill, S.; Santarpia, J.; Pan, Y.-L. Raman scattering and red fluorescence in the photochemical transformation of dry tryptophan particles. Opt. Express 2016, 24, 11654–11667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steele, P.T.; Tobias, H.J.; Fergenson, D.P. Laser Power Dependence of Mass Spectral Signatures from Individual Bacterial Spores in Bioaerosol Mass Spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 2003, 75, 5480–5487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornwell, G.-C.; Sultana, C.-M.; Petters, M.-D.; Al-Mashat, H.; Rothfuss, N.-E.; Mhler, O.; Demott, P.-J.; Martin, A.-C.; Prather, K.-A. Discrimination between individual dust and bioparticles using aerosol time-of-flight mass spectrometry. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2022, 56, 592–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Huang, Z.; Dong, J.; Li, M.; Gao, W.; Nian, H.; Fu, Z.; Zhang, G.; Bi, X.; Cheng, P.; et al. Real time bipolar time-of-flight mass spectrometer for analyzing single aerosol particles. Int. J. Mass Spectrom. 2011, 303, 118–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Liu, L.; Li, X.; Li, M.; Li, X.; Gao, W.; Huang, Z.; Cheng, P. Improvement in the Mass Resolution of Single Particle Mass Spectrometry Using Delayed Ion Extraction. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 2018, 29, 2105–2109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, W.; Dai, X.; Huang, Z.; Hou, Z.; Cai, W.; Du, X.; Zhou, Z.; Li, M.; Li, L. Improvement of the dynamic range of data acquisition system in single particle mass spectrometry. Chin. Cine 2018, 39, 331–336. [Google Scholar]
- Du, X.; Zhuo, Z.; Li, X.; Li, X.; Li, M.; Yang, J.; Zhou, Z.; Gao, W.; Huang, Z.; Li, L. Design and Simulation of Aerosol Inlet System for Particulate Matter with a Wide Size Range. Atmosphere 2023, 14, 664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, B.; Zhang, G.; Zhuo, Z. Different characteristics of individual particles from light-duty diesel vehicle at the launching and idling state by AAC-SPAMS. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 418, 126304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, J.-H.; Lee, J.-E. In situ real-time measurement of physical characteristics of airborne bacterial particles. Atmos. Environ. 2013, 81, 609–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Liu, L.; Xu, L.; Zhang, J.; Yuan, Q.; Ding, X.; Hu, W.; Fu, P.; Zhang, D. Overview of primary biological aerosol particles from a Chinese boreal forest: Insight into morphology, size, and mixing state at microscopic scale. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 719, 137520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czerwieniec, G.-A.; Russell, S.-C.; Tobias, H.-J.; Pitesky, M.-E.; David, P.-S.; Fergenson, P.; Srivastava, A.; Horn, J.-M.; Frank, M.; Gard, E.-E. Stable Isotope Labeling of Entire Bacillus atrophaeus Spores and Vegetative Cells Using Bioaerosol Mass Spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 2005, 77, 1081–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abneesh, S.; Pitesky, M.-E.; Steele, P.-T.; Tobias, H.-J.; Fergenson, D.-P.; Horn, J.-M.; Russell, S.-C.; Czerwieniec, G.-A.; Lebrilla, C.-B.; Gard, E.-E.; et al. Comprehensive Assignment of Mass Spectral Signatures from Individual Bacillus atrophaeus Spores in Matrix-Free Laser Desorption/Ionization Bioaerosol Mass Spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 2005, 77, 3315–3323. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, Z.; Yu, J.; Liu, P.; Huang, F.; Chen, Y.; Huang, Z.; Gao, W.; Li, M.; Zhou, Z.; Li, L. Analysis of bacterial aerosol particle aerosol mass spectrometer. Anal. Chem. 2019, 47, 1344–1351. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Kozlovskiy, V.; Du, X.; Lv, J.; Nikiforov, S.; Yu, J.; Kolosov, A.; Gao, W.; Zhou, Z.; Huang, Z.; et al. Increase of the particle hit rate in a laser single-particle mass spectrometer by pulse delayed extraction technology. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2020, 13, 941–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Li, B.; Liu, C.; Li, M.; Zhou, Z. Analysis of single-cell microbial mass spectra profiles from single-particle aerosol mass spectrometry. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2021, 35, 9069–9078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.-L.; Kalume, A.; Wang, C.; Santarpia, J. Atmospheric aging processes of bioaerosols under laboratory-controlled conditions: A review—ScienceDirect. J. Aerosol Sci. 2021, 155, 105767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Number. | Name | Type | Hit Rate |
|---|---|---|---|
| #01 | Klebsiella pneumoniae | Gram-negative bacillus | 25.17% |
| #02 | Salmonella pneumoniae | Gram-negative bacteria | 33.77% |
| #03 | Shiga virulent Escherichia coli | Gram-negative bacillus | 45.77% |
| #04 | Bordetella bronchitis | Gram-negative bacillus | 21.62% |
| #05 | Escherichia coli | Gram-negative bacillus | 24.71% |
| #06 | Staphylococcus aureus | Gram-positive cocci | 62.85% |
| #07 | Listeria monocytogenes | Gram-positive bacteria | 32.38% |
| #08 | Enterococcus faecium | Gram-positive cocci | 54.11% |
| #09 | Enterobacter cloacae | Gram-negative bacillus | 40.83% |
| #10 | Staphylococcus epidermidis | Gram-positive cocci | 17.73% |
| #11 | Candida albicans | Eukaryotic fungi | 54.26% |
| #12 | Candida tropicalis | Eukaryotic fungi | 13.25% |
| #13 | Candida glabrata | Eukaryotic fungi | 32.37% |
| #14 | Aspergillus brasiliensis | Multicellular fungi | 15.87% |
| #15 | Saccharomyces cerevisiae | Eukaryotic fungi | 40.57% |
| Sample | Description | Study |
|---|---|---|
| Road dust | Guangzhou Accelerator Industrial Park road dust | Reported for the first time |
| Vehicle exhaust | Fresh exhaust collected from a light-duty diesel vehicle with the engine started and at steady state | Su et al., 2021, Journal of Hazardous Materials [30]. |
| Wheat stalk combustion products | Stems and leaves of mature wheat in East China | Reported for the first time |
| Corn stalk combustion products | Stems and leaves of mature corn in East China | Reported for the first time |
| Oblate leaf combustion products | Dried oblate leaves of eastern China | Reported for the first time |
| Species | CN− | CNO− | PO2− | PO3− |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bacteria | 92.9 ± 1.8% | 96.5 ± 1.1% | 82.9 ± 5.0% | 97.6 ± 2.5% |
| Fungi | 63.8 ± 21.1% | 70.4 ± 21.3% | 52.8 ± 18.5% | 75.3 ± 26.6% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, X.; Li, L.; Zhuo, Z.; Zhang, G.; Du, X.; Li, X.; Huang, Z.; Zhou, Z.; Cheng, Z. Bioaerosol Identification by Wide Particle Size Range Single Particle Mass Spectrometry. Atmosphere 2023, 14, 1017. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14061017
Li X, Li L, Zhuo Z, Zhang G, Du X, Li X, Huang Z, Zhou Z, Cheng Z. Bioaerosol Identification by Wide Particle Size Range Single Particle Mass Spectrometry. Atmosphere. 2023; 14(6):1017. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14061017
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Xuan, Lei Li, Zeming Zhuo, Guohua Zhang, Xubing Du, Xue Li, Zhengxu Huang, Zhen Zhou, and Zhi Cheng. 2023. "Bioaerosol Identification by Wide Particle Size Range Single Particle Mass Spectrometry" Atmosphere 14, no. 6: 1017. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14061017
APA StyleLi, X., Li, L., Zhuo, Z., Zhang, G., Du, X., Li, X., Huang, Z., Zhou, Z., & Cheng, Z. (2023). Bioaerosol Identification by Wide Particle Size Range Single Particle Mass Spectrometry. Atmosphere, 14(6), 1017. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14061017







