Remote Detection of Different Marine Fuels in Exhaust Plumes by Onboard Measurements in the Baltic Sea Using Single-Particle Mass Spectrometry
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Single-Particle Mass Spectrometer
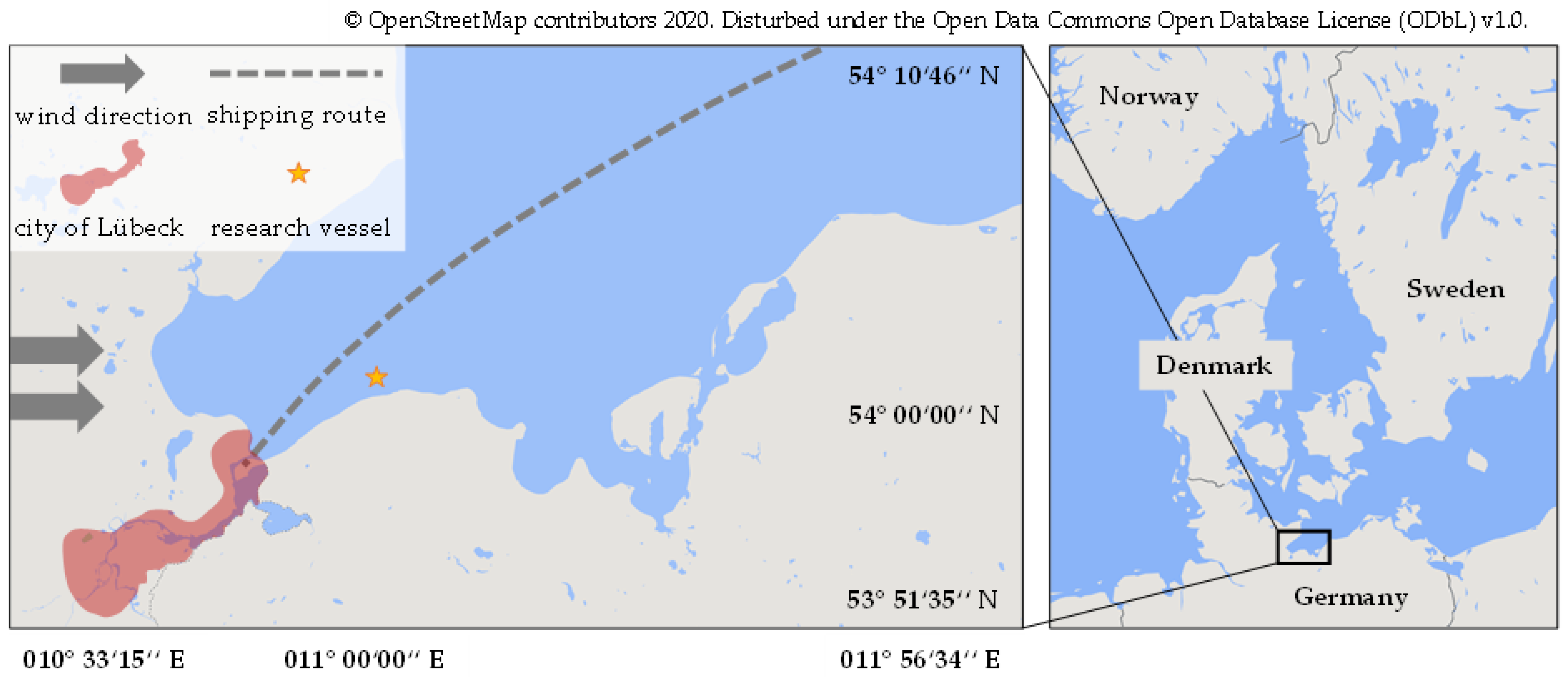
2.2. Measurement Site and Aerosol Sampling
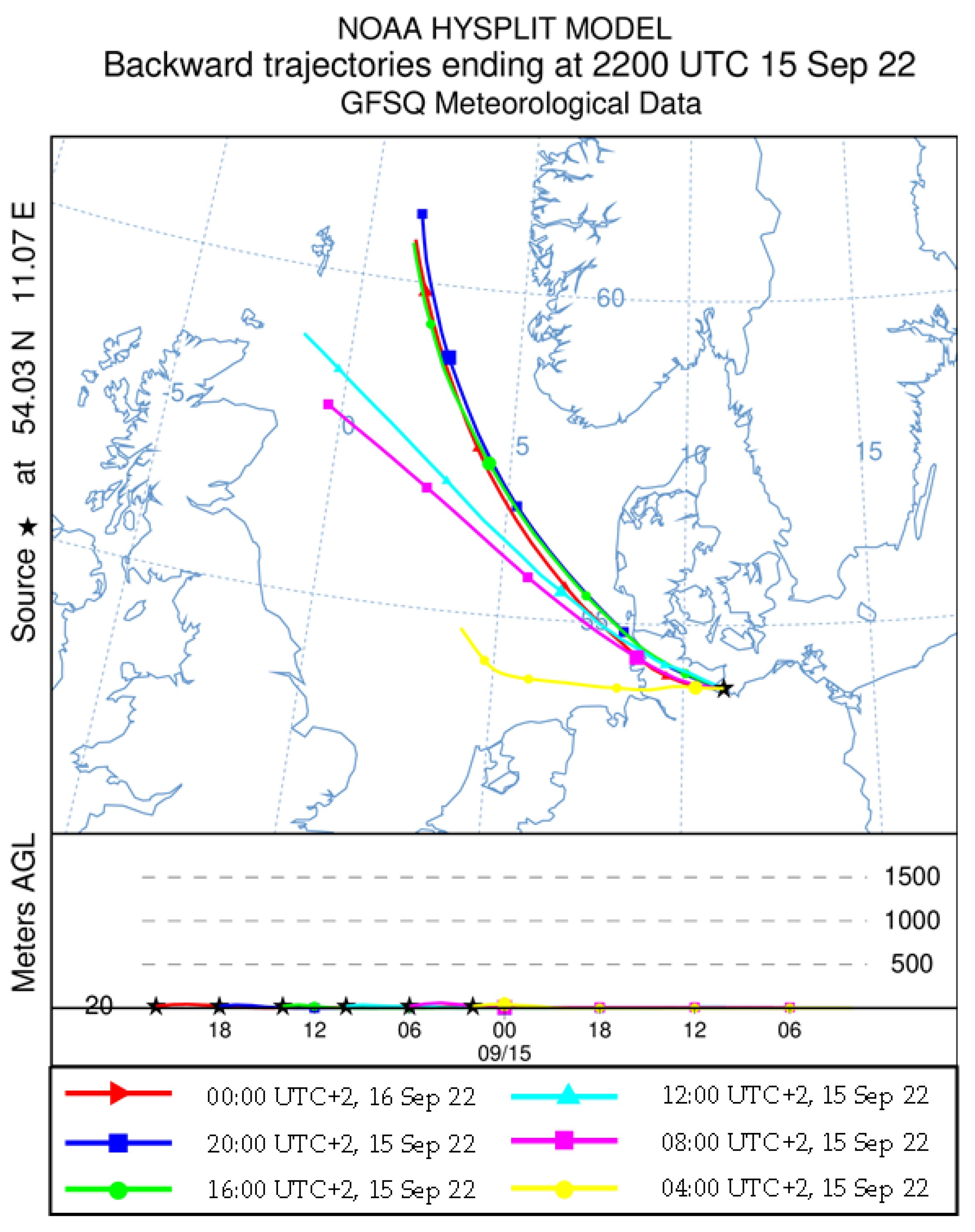
2.3. Meteorological Data
2.4. Data Analysis
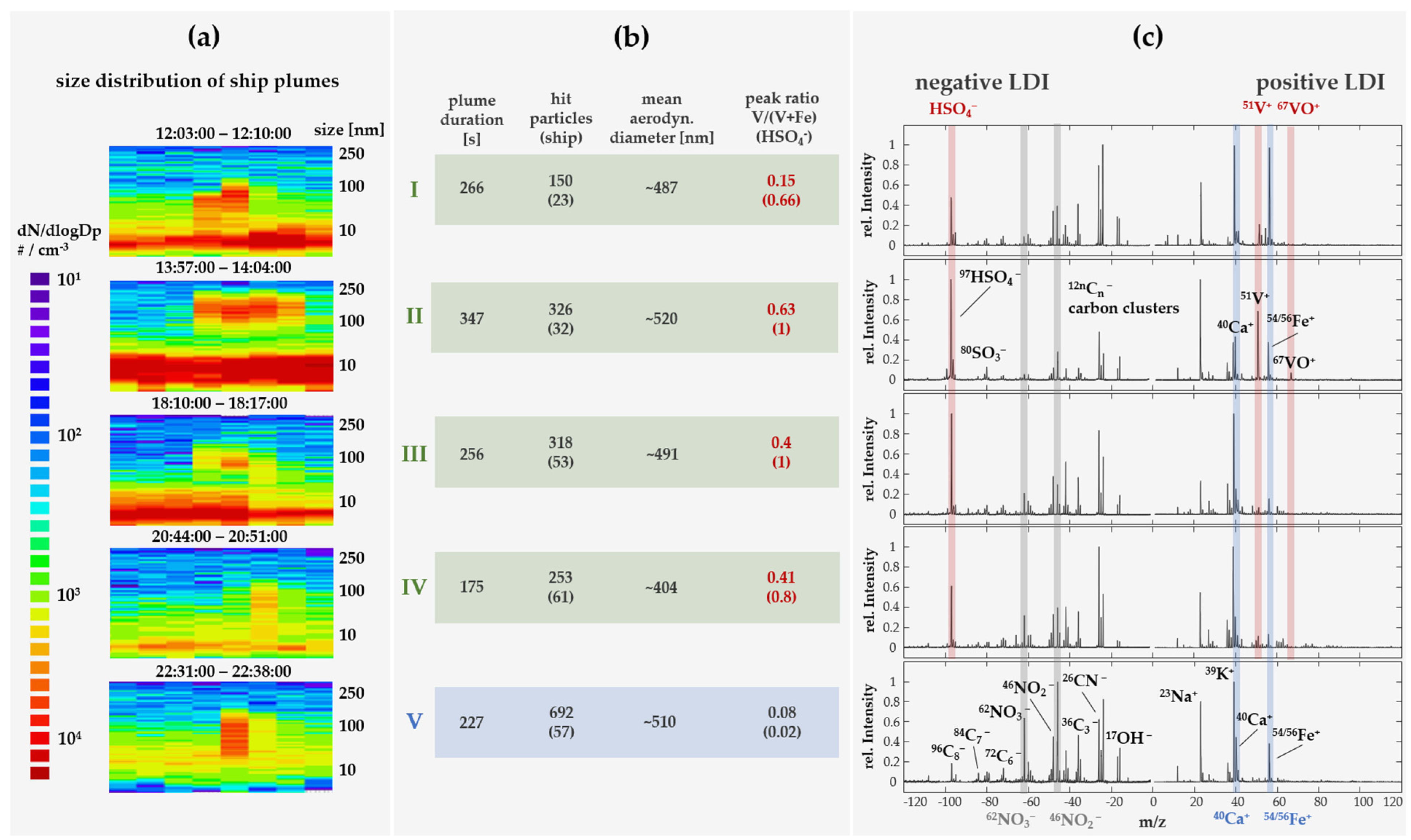
3. Results
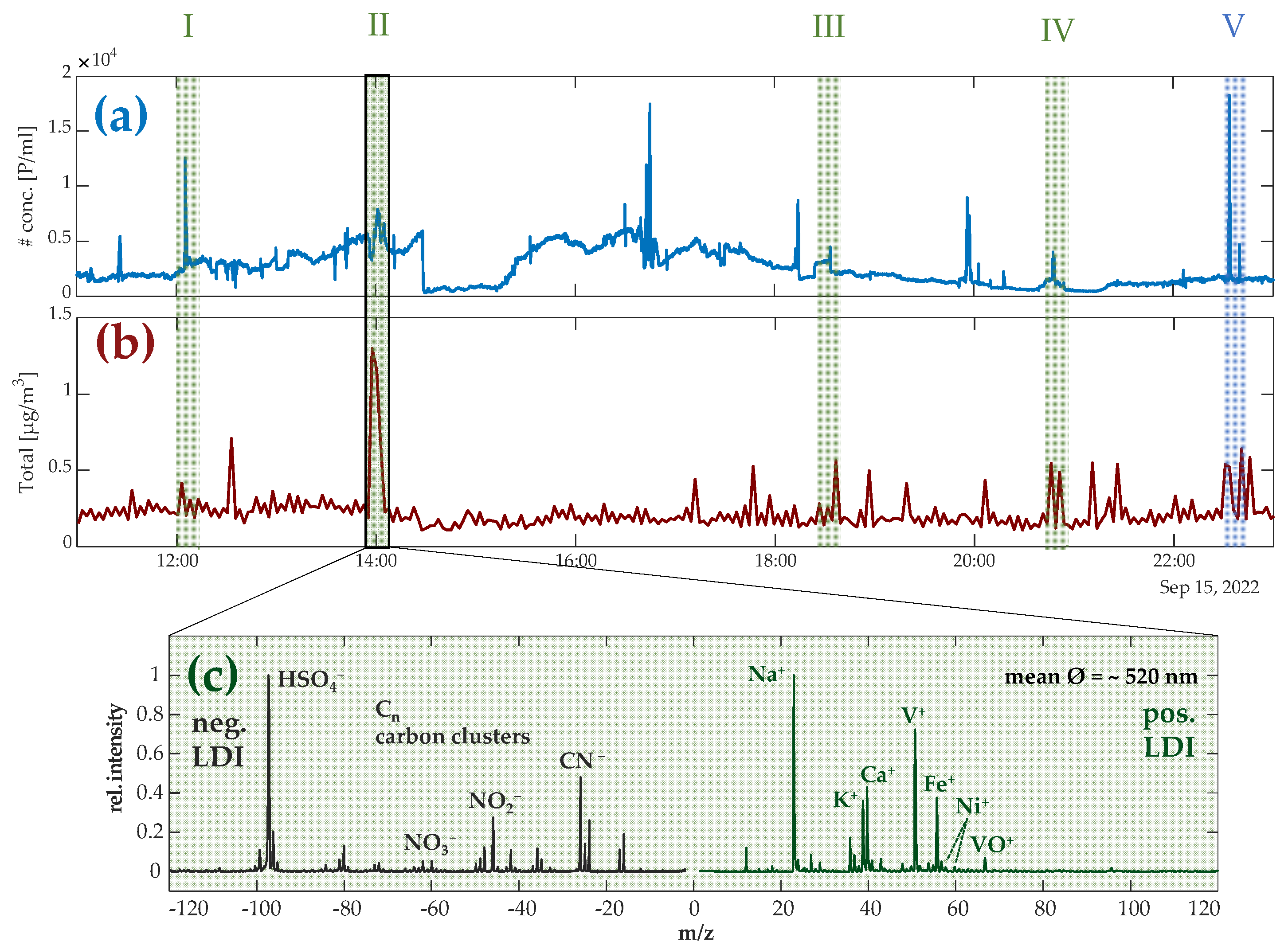
3.1. Temporal Profile of Airborne Particles
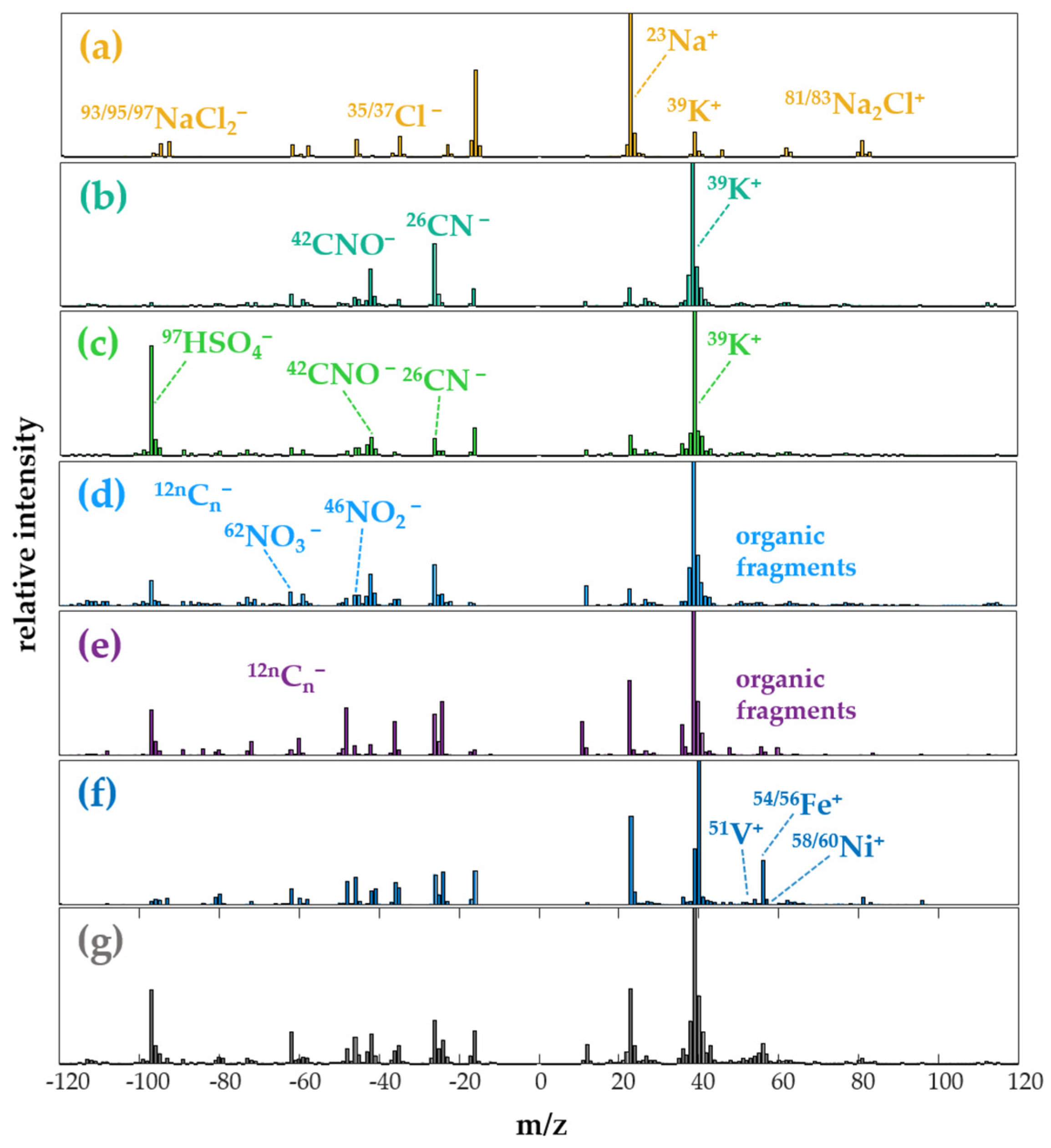
3.2. Chemical Profile of Ship Emission Particles
4. Discussion
4.1. Ship Plume Detection
4.2. Ship Particle Characterization
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Time | Wind Direction | Wind Speed [m/s] | Air Pressure [hPa] | Temperature [°C] | Humidity [%] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 11:00 | 259° ± 5° | 10.1 ± 1.5 | 1001 ± 0.1 | 15.8 ± 0.2 | 65.7 ± 2.1 |
| 12:00 | 267.5° ± 13.4° | 11.5 ± 2.6 | 1001.4 ± 0.3 | 14.7 ± 1.3 | 69.7 ± 5.5 |
| 13:00 | 264.7° ± 5.3° | 9.1 ± 1.5 | 1001.4 ± 0.2 | 15 ± 0.5 | 69 ± 1.7 |
| 14:00 | 274.5° ± 12.8° | 11.3 ± 1.5 | 1001 ± 0.1 | 15.9 ± 0.3 | 65.2 ± 3.5 |
| 15:00 | 271.6° ± 12.7° | 11.4 ± 1.7 | 1001 ± 0.1 | 15.8 ± 0.3 | 63.9 ± 2.8 |
| 16:00 | 281.7° ± 7.2° | 11.3 ± 1.6 | 1001.1 ± 0.1 | 15.7 ± 0.1 | 62.9 ± 4.4 |
| 17:00 | 282.7° ± 8.3° | 10.9 ± 1.6 | 1001.2 ± 0.1 | 15.3 ± 0.1 | 63.4 ± 3 |
| 18:00 | 280.4° ± 6.2° | 11.2 ± 1.4 | 1001.4 ± 0.2 | 14.9 ± 0.2 | 61 ± 2.5 |
| 19:00 | 271.4° ± 9.3° | 10.8 ± 1.3 | 1001.8 ± 0.1 | 14.3 ± 0.3 | 66.7 ± 3 |
| 20:00 | 267.3° ± 5.5° | 10.7 ± 1.1 | 1001.9 ± 0.1 | 13.8 ± 0.2 | 71.8 ± 1.9 |
| 21:00 | 262.1° ± 6.4° | 11 ± 1.2 | 1002 ± 0.1 | 13.4 ± 0.2 | 75.4 ± 1.7 |
| 22:00 | 267.4° ± 6.1° | 11.1 ± 1.5 | 1002.1 ± 0.1 | 13.1 ± 0.2 | 75.6 ± 1.6 |
References
- Corbett, J.J.; Winebrake, J.J.; Green, E.H.; Kasibhatla, P.; Eyring, V.; Lauer, A. Mortality from ship emissions: A global assessment. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 8512–8518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eyring, V.; Isaksen, I.S.; Berntsen, T.; Collins, W.J.; Corbett, J.J.; Endresen, O.; Grainger, R.G.; Moldanova, J.; Schlager, H.; Stevenson, D.S. Transport impacts on atmosphere and climate: Shipping. Atmos. Environ. 2010, 44, 4735–4771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viana, M.; Hammingh, P.; Colette, A.; Querol, X.; Degraeuwe, B.; de Vlieger, I.; van Aardenne, J. Impact of maritime transport emissions on coastal air quality in Europe. Atmos. Environ. 2014, 90, 96–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonson, J.E.; Gauss, M.; Schulz, M.; Jalkanen, J.-P.; Fagerli, H. Effects of global ship emissions on European air pollution levels. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2020, 20, 11399–11422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, S.; Bendl, J.; Saraji-Bozorgzad, M.; Käfer, U.; Etzien, U.; Schade, J.; Bauer, M.; Jakobi, G.; Orasche, J.; Fisch, K.; et al. Aerosol emissions from a marine diesel engine running on different fuels and effects of exhaust gas cleaning measures. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 316, 120526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ausmeel, S.; Eriksson, A.; Ahlberg, E.; Sporre, M.K.; Spanne, M.; Kristensson, A. Ship plumes in the Baltic Sea Sulfur Emission Control Area: Chemical characterization and contribution to coastal aerosol concentrations. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2020, 20, 9135–9151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuittinen, N.; Jalkanen, J.-P.; Alanen, J.; Ntziachristos, L.; Hannuniemi, H.; Johansson, L.; Karjalainen, P.; Saukko, E.; Isotalo, M.; Aakko-Saksa, P.; et al. Shipping Remains a Globally Significant Source of Anthropogenic PN Emissions Even after 2020 Sulfur Regulation. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 129–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sofiev, M.; Winebrake, J.J.; Johansson, L.; Carr, E.W.; Prank, M.; Soares, J.; Vira, J.; Kouznetsov, R.; Jalkanen, J.-P.; Corbett, J.J. Cleaner fuels for ships provide public health benefits with climate tradeoffs. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IMO. Annex VI of MARPOL 73/78, Regulations for the Prevention of Air Pollution from Ships Reg. 14. Available online: https://www.imo.org/en/OurWork/Environment/Pages/Pollution-Prevention.aspx (accessed on 7 March 2023).
- Lähteenmäki-Uutela, A.; Yliskylä-Peuralahti, J.; Repka, S.; Mellqvist, J. What explains SECA compliance: Rational calculation or moral judgment? WMU J. Marit. Aff. 2019, 18, 61–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winnes, H.; Fridell, E.; Moldanová, J. Effects of Marine Exhaust Gas Scrubbers on Gas and Particle Emissions. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2020, 8, 299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehtoranta, K.; Aakko-Saksa, P.; Murtonen, T.; Vesala, H.; Ntziachristos, L.; Rönkkö, T.; Karjalainen, P.; Kuittinen, N.; Timonen, H. Particulate Mass and Nonvolatile Particle Number Emissions from Marine Engines Using Low-Sulfur Fuels, Natural Gas, or Scrubbers. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 3315–3322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jonson, J.E.; Gauss, M.; Jalkanen, J.-P.; Johansson, L. Effects of strengthening the Baltic Sea ECA regulations. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2019, 19, 13469–13487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.; Pasternak, D.; Lee, J.; Yang, M.; Bell, T.; Bower, K.; Wu, H.; Liu, D.; Reed, C.; Bauguitte, S.; et al. Characterizing the Particle Composition and Cloud Condensation Nuclei from Shipping Emission in Western Europe. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 15604–15612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fridell, E.; Salo, K. Measurements of abatement of particles and exhaust gases in a marine gas scrubber. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part M J. Eng. Marit. Environ. 2016, 230, 154–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lunde Hermansson, A.; Hassellöv, I.-M.; Moldanová, J.; Ytreberg, E. Comparing emissions of polyaromatic hydrocarbons and metals from marine fuels and scrubbers. Transp. Res. Part D Transp. Environ. 2021, 97, 102912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, D.R.; Hassellöv, I.-M.; Ytreberg, E.; Rutgersson, A. Shipping and the environment: Smokestack emissions, scrubbers and unregulated oceanic consequences. Elem. Sci. Anthr. 2017, 5, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thor, P.; Granberg, M.E.; Winnes, H.; Magnusson, K. Severe Toxic Effects on Pelagic Copepods from Maritime Exhaust Gas Scrubber Effluents. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 5826–5835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moldanová, J.; Fridell, E.; Winnes, H.; Holmin-Fridell, S.; Boman, J.; Jedynska, A.; Tishkova, V.; Demirdjian, B.; Joulie, S.; Bladt, H.; et al. Physical and chemical characterisation of PM emissions from two ships operating in European Emission Control Areas. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2013, 6, 3577–3596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Streibel, T.; Schnelle-Kreis, J.; Czech, H.; Harndorf, H.; Jakobi, G.; Jokiniemi, J.; Karg, E.; Lintelmann, J.; Matuschek, G.; Michalke, B.; et al. Aerosol emissions of a ship diesel engine operated with diesel fuel or heavy fuel oil. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2017, 24, 10976–10991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Li, Q.; Ding, X.; Sun, J.; Li, D.; Fu, H.; Teich, M.; Ye, X.; Chen, J. Primary Particulate Matter Emitted from Heavy Fuel and Diesel Oil Combustion in a Typical Container Ship: Characteristics and Toxicity. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 12943–12951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corbin, J.C.; Czech, H.; Massabò, D.; de Mongeot, F.B.; Jakobi, G.; Liu, F.; Lobo, P.; Mennucci, C.; Mensah, A.A.; Orasche, J.; et al. Infrared-absorbing carbonaceous tar can dominate light absorption by marine-engine exhaust. NPJ Clim. Atmos. Sci. 2019, 2, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winebrake, J.J.; Corbett, J.J.; Green, E.H.; Lauer, A.; Eyring, V. Mitigating the health impacts of pollution from oceangoing shipping: An assessment of low-sulfur fuel mandates. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 4776–4782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oeder, S.; Kanashova, T.; Sippula, O.; Sapcariu, S.C.; Streibel, T.; Arteaga-Salas, J.M.; Passig, J.; Dilger, M.; Paur, H.-R.; Schlager, C.; et al. Particulate matter from both heavy fuel oil and diesel fuel shipping emissions show strong biological effects on human lung cells at realistic and comparable in vitro exposure conditions. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0126536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kattner, L.; Mathieu-Üffing, B.; Burrows, J.P.; Richter, A.; Schmolke, S.; Seyler, A.; Wittrock, F. Monitoring compliance with sulfur content regulations of shipping fuel by in situ measurements of ship emissions. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2015, 15, 10087–10092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Deng, F.; Man, H.; Fu, M.; Lv, Z.; Xiao, Q.; Jin, X.; Liu, S.; He, K.; Liu, H. Compliance and port air quality features with respect to ship fuel switching regulation: A field observation campaign, SEISO-Bohai. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2019, 19, 4899–4916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, F.; Hou, L.; Zhong, R.; Chen, W.; Ni, X.; Pan, S.; Zhao, M.; An, B. Monitoring the compliance of sailing ships with fuel sulfur content regulations using unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) measurements of ship emissions in open water. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2020, 13, 4899–4909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beecken, J.; Mellqvist, J.; Salo, K.; Ekholm, J.; Jalkanen, J.-P. Airborne emission measurements of SO2, NOx and particles from individual ships using a sniffer technique. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2014, 7, 1957–1968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Huey, L.G.; Trainer, M.; Nicks, D.; Corbett, J.; Ryerson, T.; Parrish, D.; Neuman, J.A.; Nowak, J.; Tanner, D.; et al. An investigation of the chemistry of ship emission plumes during ITCT 2002. J. Geophys. Res. 2005, 110, D10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lack, D.A.; Corbett, J.J.; Onasch, T.; Lerner, B.; Massoli, P.; Quinn, P.K.; Bates, T.S.; Covert, D.S.; Coffman, D.; Sierau, B.; et al. Particulate emissions from commercial shipping: Chemical, physical, and optical properties. J. Geophys. Res. 2009, 114, D7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petzold, A.; Hasselbach, J.; Lauer, P.; Baumann, R.; Franke, K.; Gurk, C.; Schlager, H.; Weingartner, E. Experimental studies on particle emissions from cruising ship, their characteristic properties, transformation and atmospheric lifetime in the marine boundary layer. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2008, 8, 2387–2403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berg, N.; Mellqvist, J.; Jalkanen, J.-P.; Balzani, J. Ship emissions of SO2 and NO2: DOAS measurements from airborne platforms. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2012, 5, 1085–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diesch, J.-M.; Drewnick, F.; Klimach, T.; Borrmann, S. Investigation of gaseous and particulate emissions from various marine vessel types measured on the banks of the Elbe in Northern Germany. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2013, 13, 3603–3618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ausmeel, S.; Eriksson, A.; Ahlberg, E.; Kristensson, A. Methods for identifying aged ship plumes and estimating contribution to aerosol exposure downwind of shipping lanes. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2019, 12, 4479–4493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celik, S.; Drewnick, F.; Fachinger, F.; Brooks, J.; Darbyshire, E.; Coe, H.; Paris, J.-D.; Eger, P.G.; Schuladen, J.; Tadic, I.; et al. Influence of vessel characteristics and atmospheric processes on the gas and particle phase of ship emission plumes: In situ measurements in the Mediterranean Sea and around the Arabian Peninsula. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2020, 20, 4713–4734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celo, V.; Dabek-Zlotorzynska, E.; McCurdy, M. Chemical characterization of exhaust emissions from selected canadian marine vessels: The case of trace metals and lanthanoids. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 5220–5226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Chen, Y.; Tian, C.; Wang, X.; Huang, G.; Fang, Y.; Zong, Z. Identification and quantification of shipping emissions in Bohai Rim, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 497–498, 570–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pratt, K.A.; Prather, K.A. Mass spectrometry of atmospheric aerosols--recent developments and applications. Part II: On-line mass spectrometry techniques. Mass Spectrom. Rev. 2012, 31, 17–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passig, J.; Zimmermann, R. Laser Ionization in Single-Particle Mass Spectrometry. In Photoionization and Photo-Induced Processes in Mass Spectrometry; Zimmermann, R., Hanley, L., Eds.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2021; pp. 359–411. ISBN 9783527682201. [Google Scholar]
- Reinard, M.S.; Adou, K.; Martini, J.M.; Johnston, M.V. Source characterization and identification by real-time single particle mass spectrometry. Atmos. Environ. 2007, 41, 9397–9409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arndt, J.; Sciare, J.; Mallet, M.; Roberts, G.C.; Marchand, N.; Sartelet, K.; Sellegri, K.; Dulac, F.; Healy, R.M.; Wenger, J.C. Sources and mixing state of summertime background aerosol in the north-western Mediterranean basin. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2017, 17, 6975–7001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Shen, Y.; Lin, Y.; Pan, J.; Zhang, Y.; Louie, P.K.K.; Li, M.; Fu, Q. Atmospheric pollution from ships and its impact on local air quality at a port site in Shanghai. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2019, 19, 6315–6330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Healy, R.M.; O’Connor, I.P.; Hellebust, S.; Allanic, A.; Sodeau, J.R.; Wenger, J.C. Characterisation of single particles from in-port ship emissions. Atmos. Environ. 2009, 43, 6408–6414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ault, A.P.; Gaston, C.I.; Wang, Y.; Dominguez, G.; Thiemens, M.H.; Prather, K.A. Characterization of the single particle mixing state of individual ship plume events measured at the Port of Los Angeles. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 1954–1961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, Q.; Li, M.; Liu, H.; Deng, F.; Fu, M.; Man, H.; Jin, X.; Liu, S.; Lv, Z.; He, K. Characteristics of Marine Shipping Emissions at Berth: Profiles for PM and VOCs. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 18, 9527–9545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passig, J.; Schade, J.; Irsig, R.; Li, L.; Li, X.; Zhou, Z.; Adam, T.; Zimmermann, R. Detection of ship plumes from residual fuel operation in emission control areas using single-particle mass spectrometry. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2021, 14, 4171–4185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Huang, Z.; Dong, J.; Li, M.; Gao, W.; Nian, H.; Fu, Z.; Zhang, G.; Bi, X.; Cheng, P.; et al. Real time bipolar time-of-flight mass spectrometer for analyzing single aerosol particles. Int. J. Mass Spectrom. 2011, 303, 118–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Huang, X.H.; Griffith, S.M.; Li, M.; Li, L.; Zhou, Z.; Wu, C.; Meng, J.; Chan, C.K.; Louie, P.K.; et al. A field measurement based scaling approach for quantification of major ions, organic carbon, and elemental carbon using a single particle aerosol mass spectrometer. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 143, 300–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.; Sipin, M.F.; Furutani, H.; Prather, K.A. Development and characterization of an aerosol time-of-flight mass spectrometer with increased detection efficiency. Anal. Chem. 2004, 76, 712–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pratt, K.A.; Mayer, J.E.; Holecek, J.C.; Moffet, R.C.; Sanchez, R.O.; Rebotier, T.P.; Furutani, H.; Gonin, M.; Fuhrer, K.; Su, Y.; et al. Development and characterization of an aircraft aerosol time-of-flight mass spectrometer. Anal. Chem. 2009, 81, 1792–1800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passig, J.; Schade, J.; Rosewig, E.I.; Irsig, R.; Kröger-Badge, T.; Czech, H.; Sklorz, M.; Streibel, T.; Li, L.; Li, X.; et al. Resonance-enhanced detection of metals in aerosols using single-particle mass spectrometry. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2020, 20, 7139–7152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schade, J.; Passig, J.; Irsig, R.; Ehlert, S.; Sklorz, M.; Adam, T.; Li, C.; Rudich, Y.; Zimmermann, R. Spatially Shaped Laser Pulses for the Simultaneous Detection of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons as well as Positive and Negative Inorganic Ions in Single Particle Mass Spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 2019, 91, 10282–10288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romay, F.J.; Roberts, D.L.; Marple, V.A.; Liu, B.Y.H.; Olson, B.A. A High-Performance Aerosol Concentrator for Biological Agent Detection. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2002, 36, 217–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Su, B.; Xie, Q.; Li, L.; Huang, Z.; Zhou, Z.; Mai, Z.; Tan, G. Imroved Aerodynamic Particle Concentrator for Single Particle Aerosol Mass Spectrometry: A Simulation and Characterization Study. Chin. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. 2021, 443–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passig, J.; Schade, J.; Irsig, R.; Kröger-Badge, T.; Czech, H.; Adam, T.; Fallgren, H.; Moldanova, J.; Sklorz, M.; Streibel, T.; et al. Single-particle characterization of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in background air in northern Europe. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2022, 22, 1495–1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zelenyuk, A.; Yang, J.; Choi, E.; Imre, D. SPLAT II: An Aircraft Compatible, Ultra-Sensitive, High Precision Instrument for In-Situ Characterization of the Size and Composition of Fine and Ultrafine Particles. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 411–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stein, A.F.; Draxler, R.R.; Rolph, G.D.; Stunder, B.J.B.; Cohen, M.D.; Ngan, F. NOAA’s HYSPLIT Atmospheric Transport and Dispersion Modeling System. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2015, 96, 2059–2077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furutani, H.; Jung, J.; Miura, K.; Takami, A.; Kato, S.; Kajii, Y.; Uematsu, M. Single-particle chemical characterization and source apportionment of iron-containing atmospheric aerosols in Asian outflow. J. Geophys. Res. 2011, 116, D18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.-H.; Hopke, P.K.; Fergenson, D.P.; Prather, K.A. Classification of Single Particles Analyzed by ATOFMS Using an Artificial Neural Network, ART-2A. Anal. Chem. 1999, 71, 860–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sultana, C.M.; Cornwell, G.C.; Rodriguez, P.; Prather, K.A. FATES: A flexible analysis toolkit for the exploration of single-particle mass spectrometer data. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2017, 10, 1323–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spencer, M.T.; Shields, L.G.; Sodeman, D.A.; Toner, S.M.; Prather, K.A. Comparison of oil and fuel particle chemical signatures with particle emissions from heavy and light duty vehicles. Atmos. Environ. 2006, 40, 5224–5235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toner, S.M.; Sodeman, D.A.; Prather, K.A. Single particle characterization of ultrafine and accumulation mode particles from heavy duty diesel vehicles using aerosol time-of-flight mass spectrometry. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2006, 40, 3912–3921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerminen, V.-M.; Chen, X.; Vakkari, V.; Petäjä, T.; Kulmala, M.; Bianchi, F. Atmospheric new particle formation and growth: Review of field observations. Environ. Res. Lett. 2018, 13, 103003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merikanto, J.; Spracklen, D.V.; Mann, G.W.; Pickering, S.J.; Carslaw, K.S. Impact of nucleation on global CCN. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2009, 9, 8601–8616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spracklen, D.V.; Carslaw, K.S.; Kulmala, M.; Kerminen, V.-M.; Mann, G.W.; Sihto, S.-L. The contribution of boundary layer nucleation events to total particle concentrations on regional and global scales. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2006, 6, 5631–5648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winnes, H.; Granberg, M.E.; Magnusson, K.; Malmaeus, K.; Mellin, A.; Stripple, H.; Yaramenka, K.; Zhang, Y. Scrubbers: Closing the Loop; Activity 3. Task 2; Risk Assessment of Marine Exhaust Gas Scrubber Water. Available online: https://www.ivl.se/english/ivl/publications/publications/scrubbers-closing-the-loop-activity-3.-task-2-risk-assessment-of-marine-exhaust-gas-scrubber-water.html (accessed on 2 March 2023).
- Ault, A.P.; Moore, M.J.; Furutani, H.; Prather, K.A. Impact of emissions from the Los Angeles port region on San Diego air quality during regional transport events. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 3500–3506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viana, M.; Amato, F.; Alastuey, A.; Querol, X.; Moreno, T.; Dos Santos, S.G.; Herce, M.D.; Fernández-Patier, R. Chemical tracers of particulate emissions from commercial shipping. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 7472–7477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shields, L.G.; Suess, D.T.; Prather, K.A. Determination of single particle mass spectral signatures from heavy-duty diesel vehicle emissions for PM2.5 source apportionment. Atmos. Environ. 2007, 41, 3841–3852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toner, S.M.; Shields, L.G.; Sodeman, D.A.; Prather, K.A. Using mass spectral source signatures to apportion exhaust particles from gasoline and diesel powered vehicles in a freeway study using UF-ATOFMS. Atmos. Environ. 2008, 42, 568–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moldanová, J.; Fridell, E.; Popovicheva, O.; Demirdjian, B.; Tishkova, V.; Faccinetto, A.; Focsa, C. Characterisation of particulate matter and gaseous emissions from a large ship diesel engine. Atmos. Environ. 2009, 43, 2632–2641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, S.M.; Agrawal, H.; Sorooshian, A.; Padró, L.T.; Gates, H.; Hersey, S.; Welch, W.A.; Lung, H.; Miller, J.W.; Cocker, D.R.; et al. Comprehensive simultaneous shipboard and airborne characterization of exhaust from a modern container ship at sea. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 4626–4640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaie-Levrel, F.; Perrier, S.; Perraudin, E.; Stoll, C.; Grand, N.; Schwell, M. Development and characterization of a single particle laser ablation mass spectrometer (SPLAM) for organic aerosol studies. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2012, 5, 225–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seinfeld, J.H.; Pandis, S.N. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics: From Air Pollution to Climate Change, 3rd ed.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2016; ISBN 978-1-118-94740-1. [Google Scholar]
- Dall’Osto, M.; Beddows, D.C.S.; Kinnersley, R.P.; Harrison, R.M.; Donovan, R.J.; Heal, M.R. Characterization of individual airborne particles by using aerosol time-of-flight mass spectrometry at Mace Head, Ireland. J. Geophys. Res. 2004, 109, D21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dallosto, M.; Harrison, R. Chemical characterisation of single airborne particles in Athens (Greece) by ATOFMS. Atmos. Environ. 2006, 40, 7614–7631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dall’Osto, M.; Beddows, D.C.S.; McGillicuddy, E.J.; Esser-Gietl, J.K.; Harrison, R.M.; Wenger, J.C. On the simultaneous deployment of two single-particle mass spectrometers at an urban background and a roadside site during SAPUSS. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 16, 9693–9710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badeke, R.; Matthias, V.; Grawe, D. Parameterizing the vertical downward dispersion of ship exhaust gas in the near field. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2021, 21, 5935–5951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthias, V.; Arndt, J.A.; Aulinger, A.; Bieser, J.; van der Denier Gon, H.; Kranenburg, R.; Kuenen, J.; Neumann, D.; Pouliot, G.; Quante, M. Modeling emissions for three-dimensional atmospheric chemistry transport models. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2018, 68, 763–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rosewig, E.I.; Schade, J.; Passig, J.; Osterholz, H.; Irsig, R.; Smok, D.; Gawlitta, N.; Schnelle-Kreis, J.; Hovorka, J.; Schulz-Bull, D.; et al. Remote Detection of Different Marine Fuels in Exhaust Plumes by Onboard Measurements in the Baltic Sea Using Single-Particle Mass Spectrometry. Atmosphere 2023, 14, 849. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14050849
Rosewig EI, Schade J, Passig J, Osterholz H, Irsig R, Smok D, Gawlitta N, Schnelle-Kreis J, Hovorka J, Schulz-Bull D, et al. Remote Detection of Different Marine Fuels in Exhaust Plumes by Onboard Measurements in the Baltic Sea Using Single-Particle Mass Spectrometry. Atmosphere. 2023; 14(5):849. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14050849
Chicago/Turabian StyleRosewig, Ellen Iva, Julian Schade, Johannes Passig, Helena Osterholz, Robert Irsig, Dominik Smok, Nadine Gawlitta, Jürgen Schnelle-Kreis, Jan Hovorka, Detlef Schulz-Bull, and et al. 2023. "Remote Detection of Different Marine Fuels in Exhaust Plumes by Onboard Measurements in the Baltic Sea Using Single-Particle Mass Spectrometry" Atmosphere 14, no. 5: 849. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14050849
APA StyleRosewig, E. I., Schade, J., Passig, J., Osterholz, H., Irsig, R., Smok, D., Gawlitta, N., Schnelle-Kreis, J., Hovorka, J., Schulz-Bull, D., Zimmermann, R., & Adam, T. W. (2023). Remote Detection of Different Marine Fuels in Exhaust Plumes by Onboard Measurements in the Baltic Sea Using Single-Particle Mass Spectrometry. Atmosphere, 14(5), 849. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14050849






