Emission Characteristics of Tyre Wear Particles from Light-Duty Vehicles
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Apparatus and Methodology
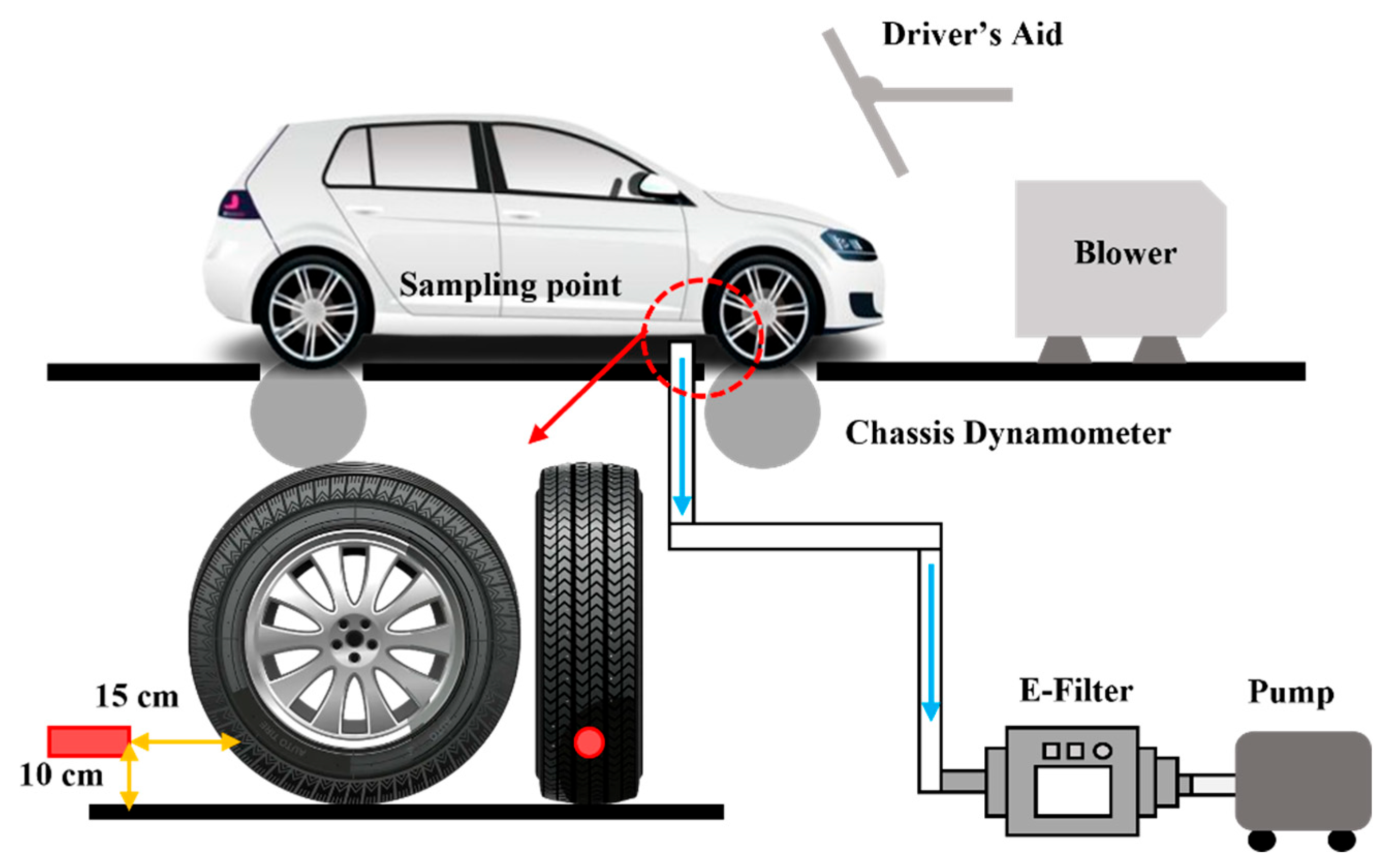
2.1. Experiment System and Sampling Method
2.2. Test Vehicles
2.3. ICP-OES Analysis Method
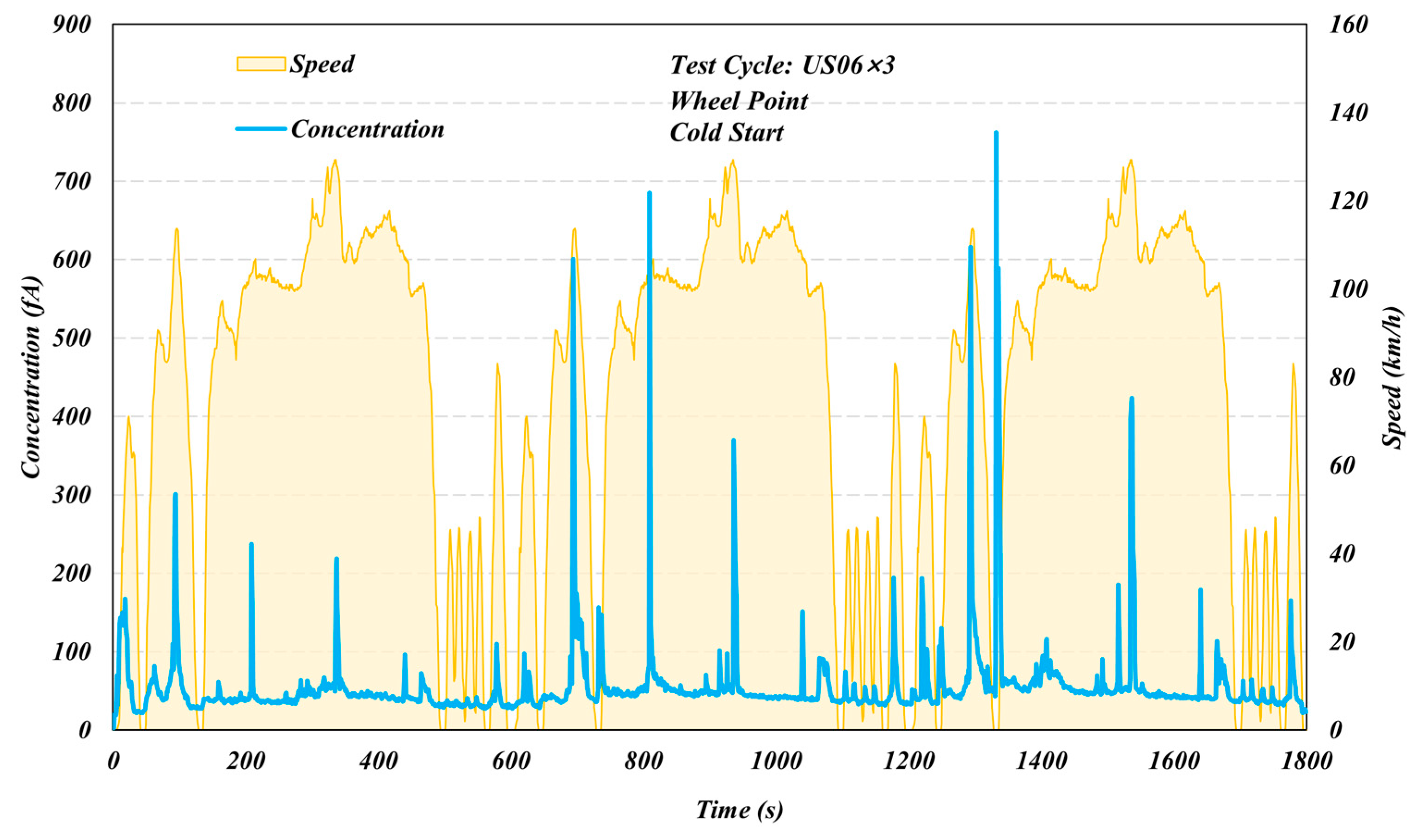
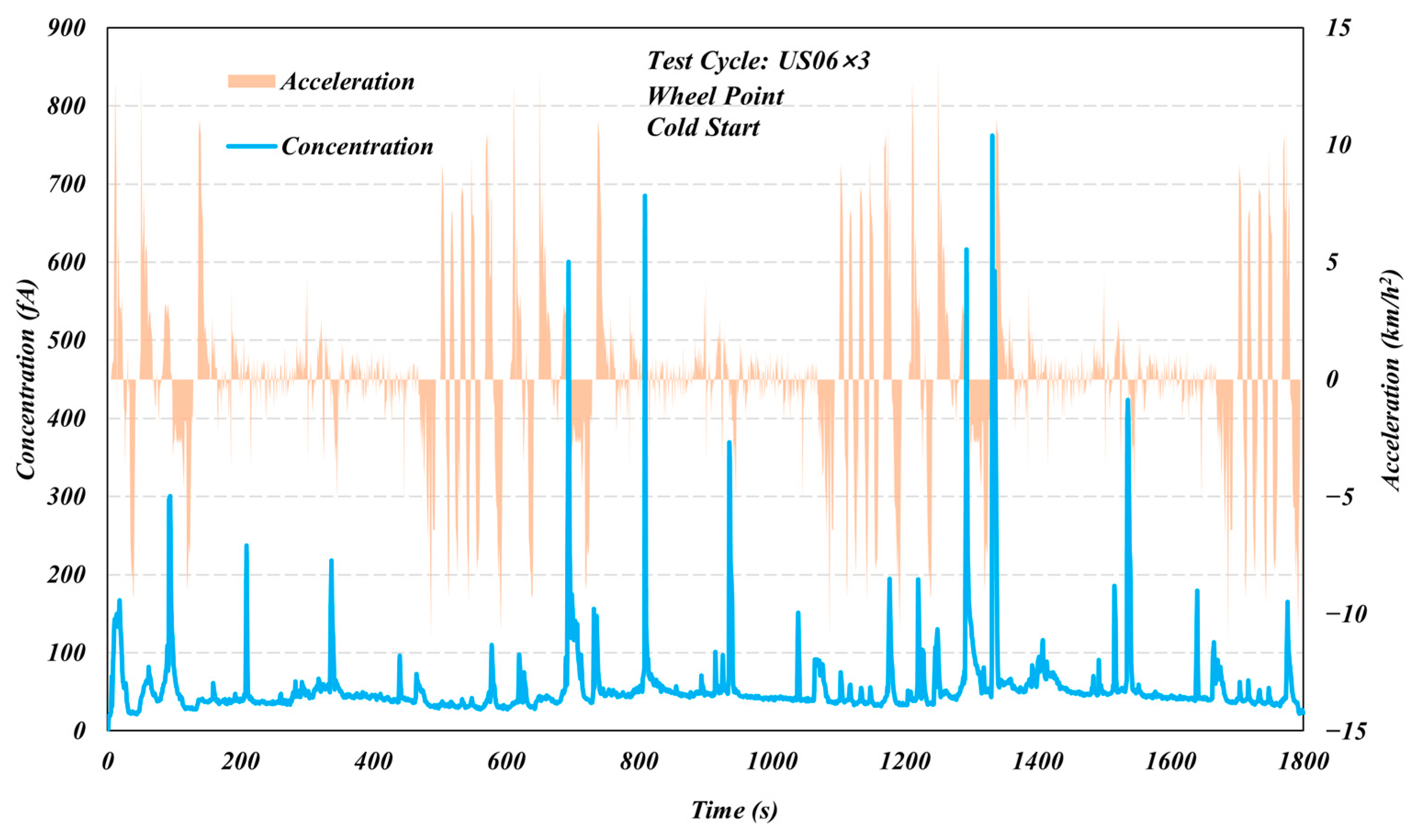
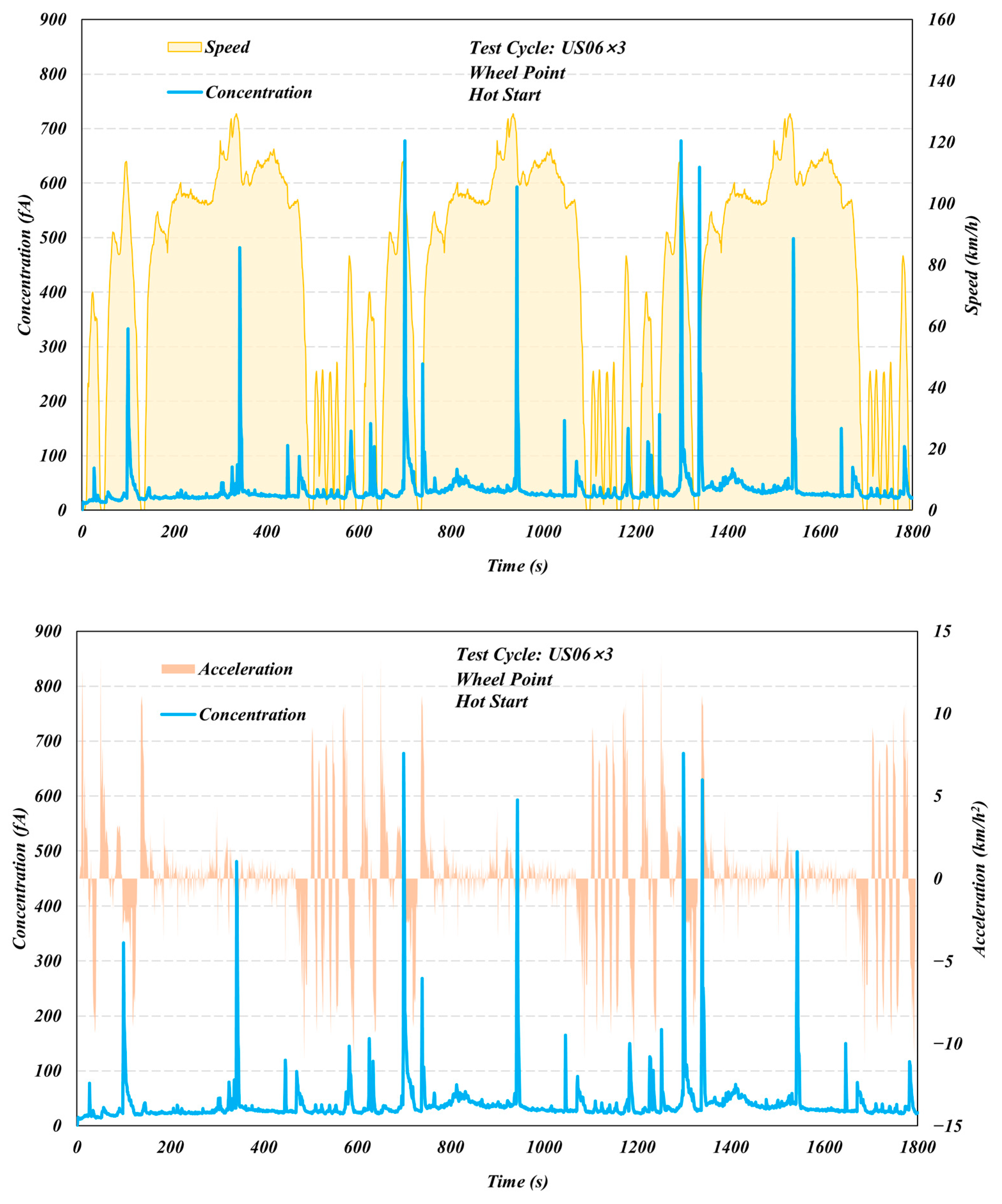
3. Results and Discussion
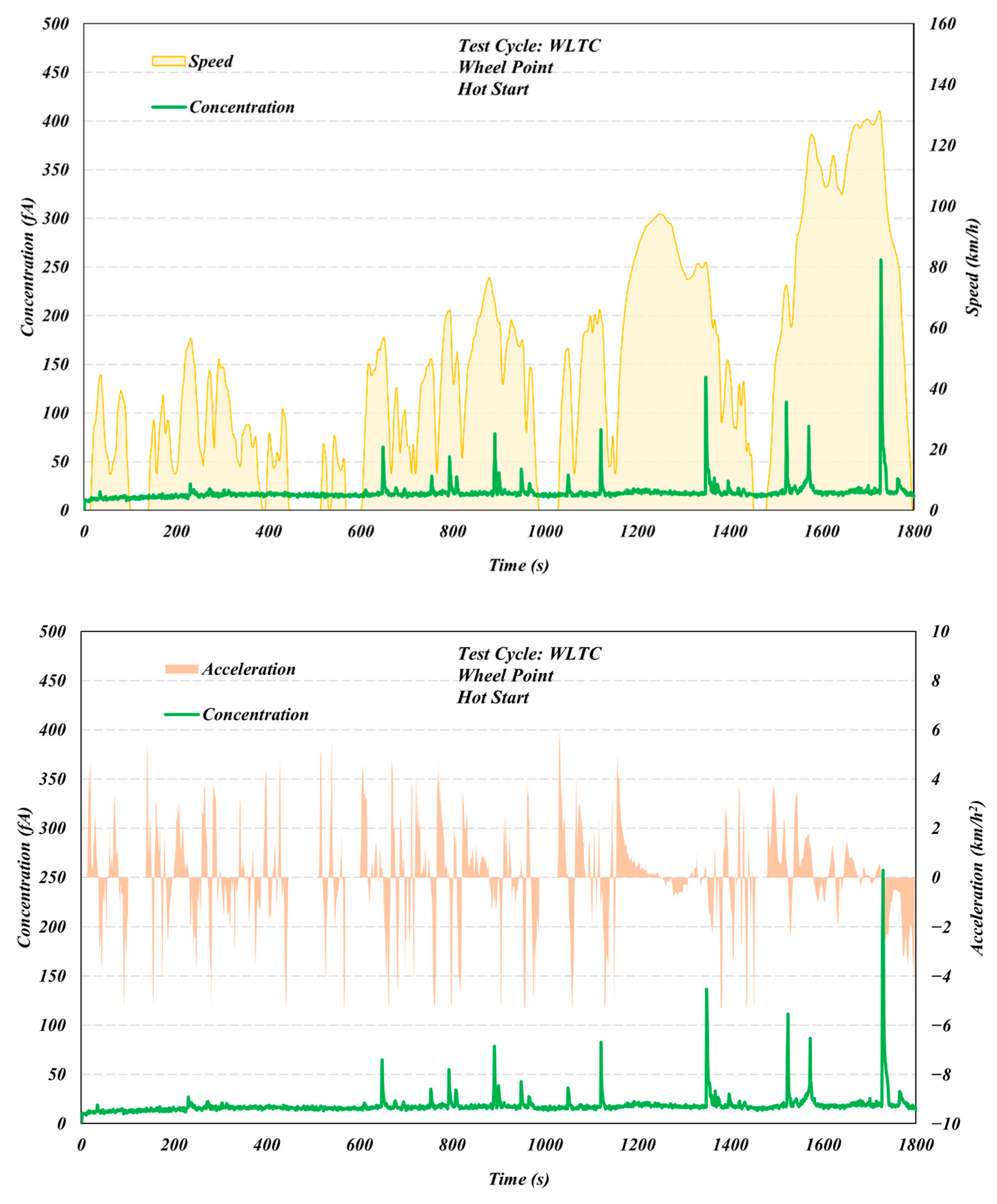
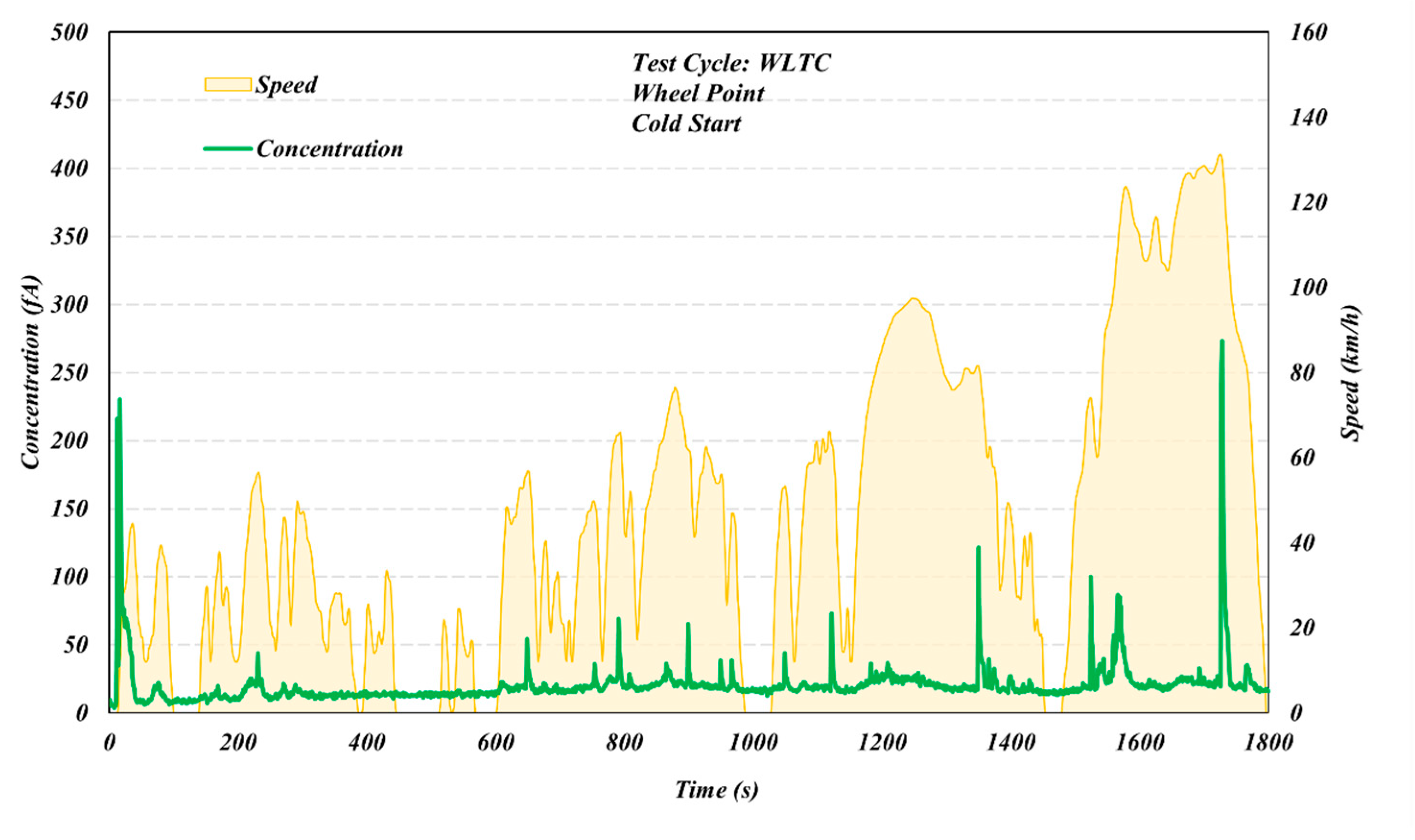
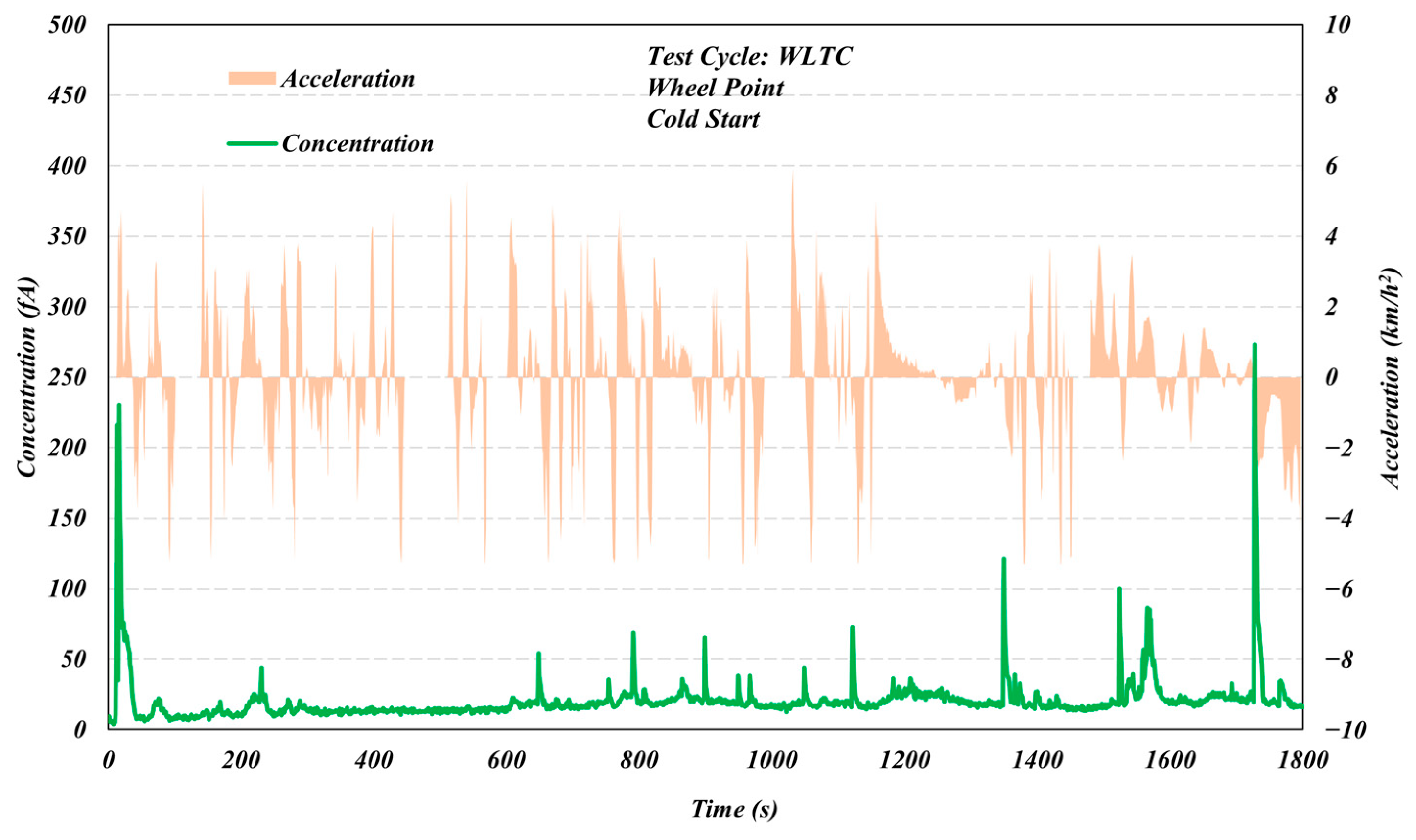
3.1. Comparison of Different Test Cycles
3.2. Start Temperature Effects
3.3. Element Distributions
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, T.; Li, B.; Zou, X.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; Xu, Y.; Mao, L.; Zhang, C.; Yu, W. Emission of primary microplastics in mainland China: Invisible but not negligible. Water Res. 2019, 162, 214–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baensch-Baltruschat, B.; Kocher, B.; Stock, F.; Reifferscheid, G. Tyre and road wear particles (TRWP)—A review of generation, properties, emissions, human health risk, ecotoxicity, and fate in the environment. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 733, 137823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stojanovic, N.; Abdullah, O.I.; Grujic, I.; Boskovic, B. Particles formation due to the wear of tires and measures for the wear reduction: A review. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part D J. Automob. Eng. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wik, A.; Dave, G. Occurrence and effects of tire wear particles in the environment—A critical review and an initial risk assessment. Environ. Pollut. 2009, 157, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Power, M.C.; Adar, S.D.; Yanosky, J.D.; Weuve, J. Exposure to air pollution as a potential contributor to cognitive function, cognitive decline, brain imaging, and dementia: A systematic review of epidemiologic research. Neurotoxicology 2016, 56, 235–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, Y.; Deng, S.; Qiu, Z.; Lu, Z.; Song, H.; Yang, N. Chemical characterization of PM2.5 emitted from China IV and China V light-duty vehicles in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 783, 147101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostenidou, E.; Martinez-Valiente, A.; R’Mili, B.; Marques, B.; Temime-Roussel, B.; Durand, A.; André, M.; Liu, Y.; Louis, C.; Vansevenant, B.; et al. Technical note: Emission factors, chemical composition, and morphology of particles emitted from Euro 5 diesel and gasoline light-duty vehicles during transient cycles. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2021, 21, 4779–4796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raza, M.; Chen, L.; Leach, F.; Ding, S. A Review of Particulate Number (PN) Emissions from Gasoline Direct Injection (GDI) Engines and Their Control Techniques. Energies 2018, 11, 1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.; Lee, J.; Jang, J.; Park, S. Effects of fuel-injection systems on particle emission characteristics of gasoline vehicles. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 217, 116941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, R.-H.; Peng, X.; Lin, W.; He, L.-Y.; Wei, F.-H.; Tang, M.-X.; Huang, X.-F. Trends and Challenges Regarding the Source-Specific Health Risk of PM2.5-Bound Metals in a Chinese Megacity from 2014 to 2020. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 56, 6996–7005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Chen, H.; Wu, S.; Gao, J.; Li, Y.; An, Z.; Mao, B.; Tu, R.; Li, T. Impact of vehicle type, tyre feature and driving behaviour on tyre wear under real-world driving conditions. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 842, 156950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Yin, H.; Tan, J.; Wang, X.; Yang, Z.; Hao, L.; Du, T.; Niu, Z.; Ge, Y. A comprehensive review of tyre wear particles: Formation, measurements, properties, and influencing factors. Atmos. Environ. 2023, 297, 119597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Peng, J.; Song, C.; Ma, C.; Men, Z.; Wu, J.; Wu, L.; Wang, T.; Zhang, X.; Tao, S.; et al. Vehicular non-exhaust particulate emissions in Chinese megacities: Source profiles, real-world emission factors, and inventories. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 266, 115268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matthaios, V.N.; Lawrence, J.; Martins, M.A.; Ferguson, S.T.; Wolfson, J.M.; Harrison, R.M.; Koutrakis, P. Quantifying factors affecting contributions of roadway exhaust and non-exhaust emissions to ambient PM10–2.5 and PM2.5–0.2 particles. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 835, 155368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yin, H.; Yang, Z.; Su, S.; Hao, L.; Tan, J.; Wang, X.; Niu, Z.; Ge, Y. Assessing the brake particle emissions for sustainable transport: A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2022, 167, 112737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussein, T.; Johansson, C.; Karlsson, H.; Hansson, H.-C. Factors affecting non-tailpipe aerosol particle emissions from paved roads: On-road measurements in Stockholm, Sweden. Atmos. Environ. 2008, 42, 688–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klöckner, P.; Reemtsma, T.; Eisentraut, P.; Braun, U.; Ruhl, A.S.; Wagner, S. Tire and road wear particles in road environment—Quantification and assessment of particle dynamics by Zn determination after density separation. Chemosphere 2019, 222, 714–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwak, J.; Lee, S.; Lee, S. On-road and laboratory investigations on non-exhaust ultrafine particles from the interaction between the tire and road pavement under braking conditions. Atmos. Environ. 2014, 97, 195–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreider, M.L.; Panko, J.M.; McAtee, B.L.; Sweet, L.I.; Finley, B.L. Physical and chemical characterization of tire-related particles: Comparison of particles generated using different methodologies. Sci. Total Environ. 2010, 408, 652–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirjola, L.; Kupiainen, K.; Perhoniemi, P.; Tervahattu, H.; Vesala, H. Non-exhaust emission measurement system of the mobile laboratory SNIFFER. Atmos. Environ. 2009, 43, 4703–4713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathissen, M.; Scheer, V.; Vogt, R.; Benter, T. Investigation on the potential generation of ultrafine particles from the tire–road interface. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 45, 6172–6179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aatmeeyata; Sharma, M. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, elemental and organic carbon emissions from tire-wear. Sci. Total Environ. 2010, 408, 4563–4568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dall’Osto, M.; Beddows, D.C.; Gietl, J.K.; Olatunbosun, O.A.; Yang, X.; Harrison, R.M. Characteristics of tyre dust in polluted air: Studies by single particle mass spectrometry (ATOFMS). Atmos. Environ. 2014, 94, 224–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, I.; Kim, H.; Lee, S. Characteristics of tire wear particles generated in a laboratory simulation of tire/road contact conditions. J. Aerosol Sci. 2018, 124, 30–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foitzik, M.-J.; Unrau, H.-J.; Gauterin, F.; Dörnhöfer, J.; Koch, T. Investigation of ultra fine particulate matter emission of rubber tires. Wear 2018, 394, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gustafsson, M.; Blomqvist, G.; Gudmundsson, A.; Dahl, A.; Swietlicki, E.; Bohgard, M.; Lindbom, J.; Ljungman, A. Properties and toxicological effects of particles from the interaction between tyres, road pavement and winter traction material. Sci. Total Environ. 2008, 393, 226–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, G.; Lee, S. Characteristics of Tire Wear Particles Generated by a Tire Simulator under Various Driving Conditions. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 12153–12161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tonegawa, Y.; Sasaki, S. Development of Tire-Wear Particle Emission Measurements for Passenger Vehicles. Emiss. Control. Sci. Technol. 2021, 7, 56–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwak, J.-H.; Kim, H.; Lee, J.; Lee, S. Characterization of non-exhaust coarse and fine particles from on-road driving and laboratory measurements. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 458, 273–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sommer, F.; Dietze, V.; Baum, A.; Sauer, J.; Gilge, S.; Maschowski, C.; Gieré, R. Tire Abrasion as a Major Source of Microplastics in the Environment. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2018, 18, 2014–2028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knight, L.J.; Parker-Jurd, F.N.F.; Al-Sid-Cheikh, M.; Thompson, R.C. Tyre wear particles: An abundant yet widely unreported microplastic? Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 18345–18354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.; Zhang, L.; Liu, L.; Wen, S. Investigation of the external conditions and material compositions affecting the formation mechanism and size distribution of tire wear particles. Atmos. Environ. 2020, 244, 118018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kupiainen, K.J.; Tervahattu, H.; Räisänen, M.; Mäkelä, T.; Aurela, M.; Hillamo, R. Size and Composition of Airborne Particles from Pavement Wear, Tires, and Traction Sanding. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 699–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Wang, J.; Gheni, A.; ElGawady, M.A. Reduced zinc leaching from scrap tire during pavement applications. Waste Manag. 2018, 81, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, I.; Lee, J.; Lee, S. Laboratory study of the generation of nanoparticles from tire tread. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 188–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, X.-D.; Huang, H.-B.; Jiao, R.-N.; Liu, J.-P. Experimental investigation on the characteristics of tire wear particles under different non-vehicle operating parameters. Tribol. Int. 2020, 150, 106354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panko, J.M.; Chu, J.; Kreider, M.L.; Unice, K.M. Measurement of airborne concentrations of tire and road wear particles in urban and rural areas of France, Japan, and the United States. Atmos. Environ. 2013, 72, 192–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timmers, V.R.; Achten, P.A. Non-exhaust PM emissions from electric vehicles. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 134, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grigoratos, T.; Gustafsson, M.; Eriksson, O.; Martini, G. Experimental investigation of tread wear and particle emission from tyres with different treadwear marking. Atmos. Environ. 2018, 182, 200–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahl, A.; Gharibi, A.; Swietlicki, E.; Gudmundsson, A.; Bohgard, M.; Ljungman, A.; Blomqvist, G.; Gustafsson, M. Traffic-generated emissions of ultrafine particles from pavement–tire interface. Atmos. Environ. 2006, 40, 1314–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, C.; Vicente, A.; Calvo, A.; Baumgardner, D.; Amato, F.; Querol, X.; Pio, C.; Gustafsson, M. Physical and chemical properties of non-exhaust particles generated from wear between pavements and tyres. Atmos. Environ. 2020, 224, 117252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, S.; Ward, M.; Lin, R.; Brydson, R.; Dall’Osto, M.; Harrison, R.M. Comparative study of single particle characterisation by Transmission Electron Microscopy and time-of-flight aerosol mass spectrometry in the London atmosphere. Atmos. Environ. 2012, 62, 400–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beji, A.; Deboudt, K.; Khardi, S.; Muresan, B.; Flament, P.; Fourmentin, M.; Lumière, L. Non-exhaust particle emissions under various driving conditions: Implications for sustainable mobility. Transp. Res. Part D Transp. Environ. 2020, 81, 102290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, C.E.; Choi, S.-S. Preparation and Characterization of Model Tire–Road Wear Particles. Polymers 2022, 14, 1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorpe, A.; Harrison, R.M. Sources and properties of non-exhaust particulate matter from road traffic: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2008, 400, 270–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Dimensions (mm) | 90 × 85 × 225 |
| Sample temperature (°C) | 10–50 |
| Sensitivity (fA) | 3 |
| Maximum concentration (fA) | 250,000 |
| Minimum particle size (nm) | 5 |
| Saving interval (s) | 1 |
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Engine displacement (mL) | 1300 |
| Rotational Mass (kg) | 1389 |
| Resistance coefficient A (N) | 116.10 |
| Resistance coefficient B (N/(km/h)) | 1.0670 |
| Resistance coefficient C (N/(km/h)2) | 0.0248 |
| Tyre size | 205/55 R17 |
| Tyre max load (kg) | 615 |
| Plies tread | 2 polyester + 2 steel + 1 polyamide |
| Sidewall | 2 polyester |
| Tyre pressure (kPa) | 260 |
| Elements | US06 × 3 (μg/g) | WLTC (μg/g) |
|---|---|---|
| Ca | 3756.69 | 2683.60 |
| Al | 2243.48 | 1496.02 |
| Mg | 695.80 | 481.76 |
| Fe | 852.10 | 362.48 |
| Pb | 662.25 | 215.42 |
| Zn | 429.15 | 149.96 |
| K | 124.70 | 51.47 |
| Ti | 86.77 | 57.53 |
| Sr | 60.31 | 39.71 |
| P | 5.49 | 3.93 |
| Cu | 0.95 | 0.58 |
| Cr | 3.24 | 2.14 |
| Mn | 2.95 | 1.79 |
| Sn | 3.27 | 1.61 |
| Ba | 0.85 | 0.61 |
| Ni | 0.46 | 0.34 |
| Sb | 0.20 | 0.11 |
| Te | 0.04 | 0.04 |
| Bi | N.D. | N.D. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, J.; Zhang, M.; Ge, Y.; Wen, Y.; Luo, J.; Yin, D.; Wang, C.; Wang, C. Emission Characteristics of Tyre Wear Particles from Light-Duty Vehicles. Atmosphere 2023, 14, 724. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14040724
Li J, Zhang M, Ge Y, Wen Y, Luo J, Yin D, Wang C, Wang C. Emission Characteristics of Tyre Wear Particles from Light-Duty Vehicles. Atmosphere. 2023; 14(4):724. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14040724
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Jiachen, Mengzhu Zhang, Yunshan Ge, Yi Wen, Jiaxin Luo, Dailin Yin, Chongyao Wang, and Changyu Wang. 2023. "Emission Characteristics of Tyre Wear Particles from Light-Duty Vehicles" Atmosphere 14, no. 4: 724. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14040724
APA StyleLi, J., Zhang, M., Ge, Y., Wen, Y., Luo, J., Yin, D., Wang, C., & Wang, C. (2023). Emission Characteristics of Tyre Wear Particles from Light-Duty Vehicles. Atmosphere, 14(4), 724. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14040724






