Physical Explanation for Paradoxical Climate Change in Semi-Arid Inland Eurasia Based on a Remodeled Precipitation Recycling Ratio and Clausius–Clapeyron Equation
Abstract
1. Introduction
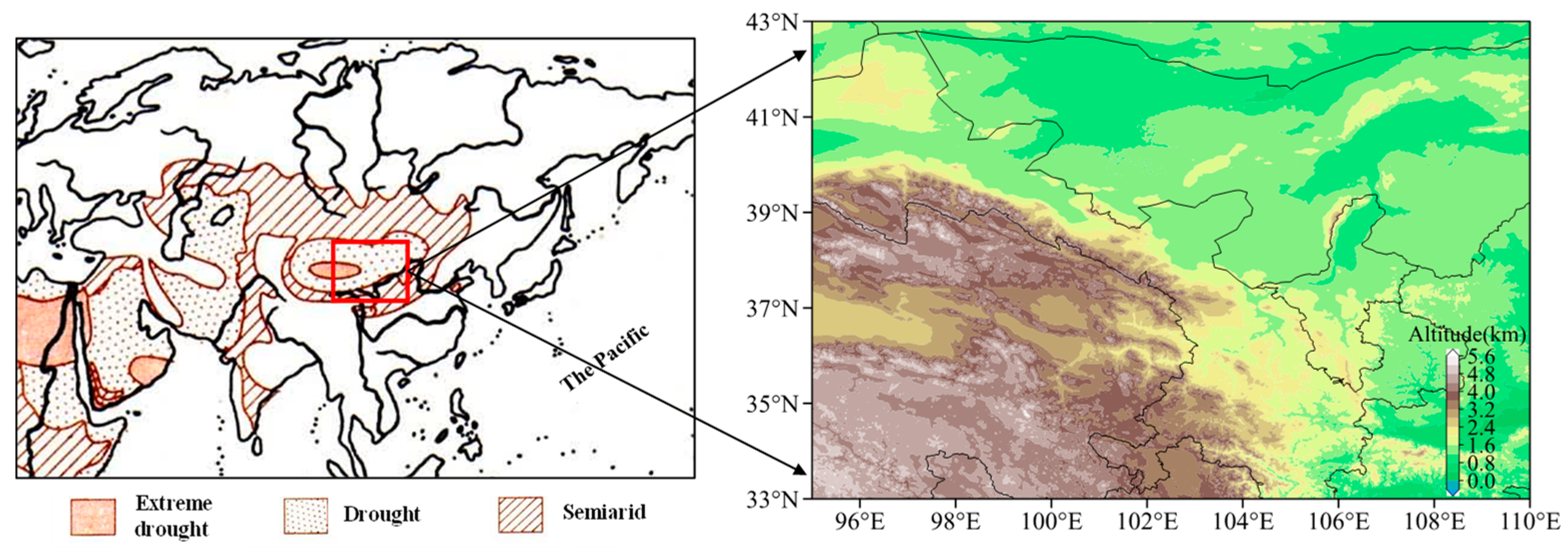
2. Data and Model Restructuring
2.1. Data
2.2. Restructuring of the PRR Model
3. Results
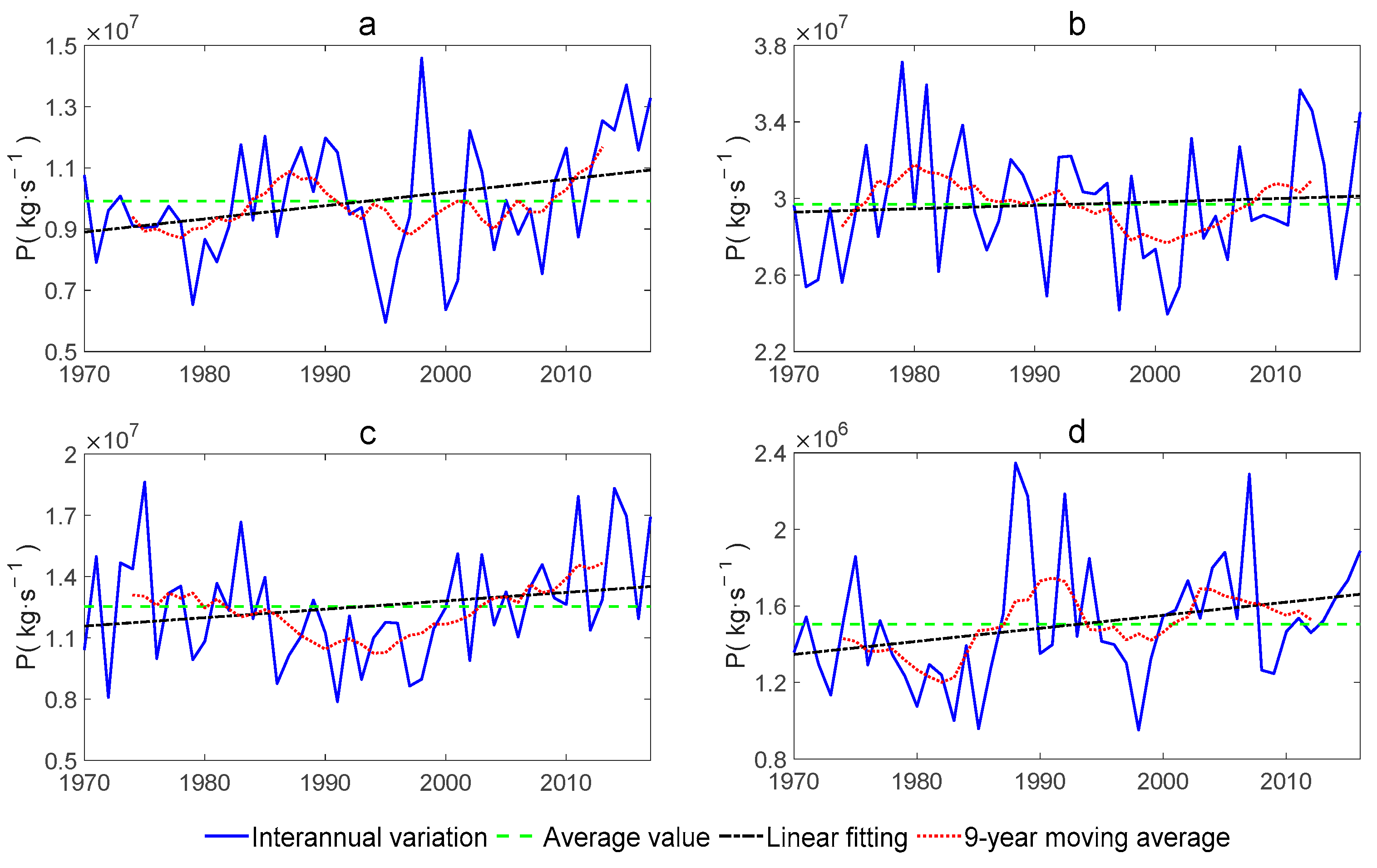
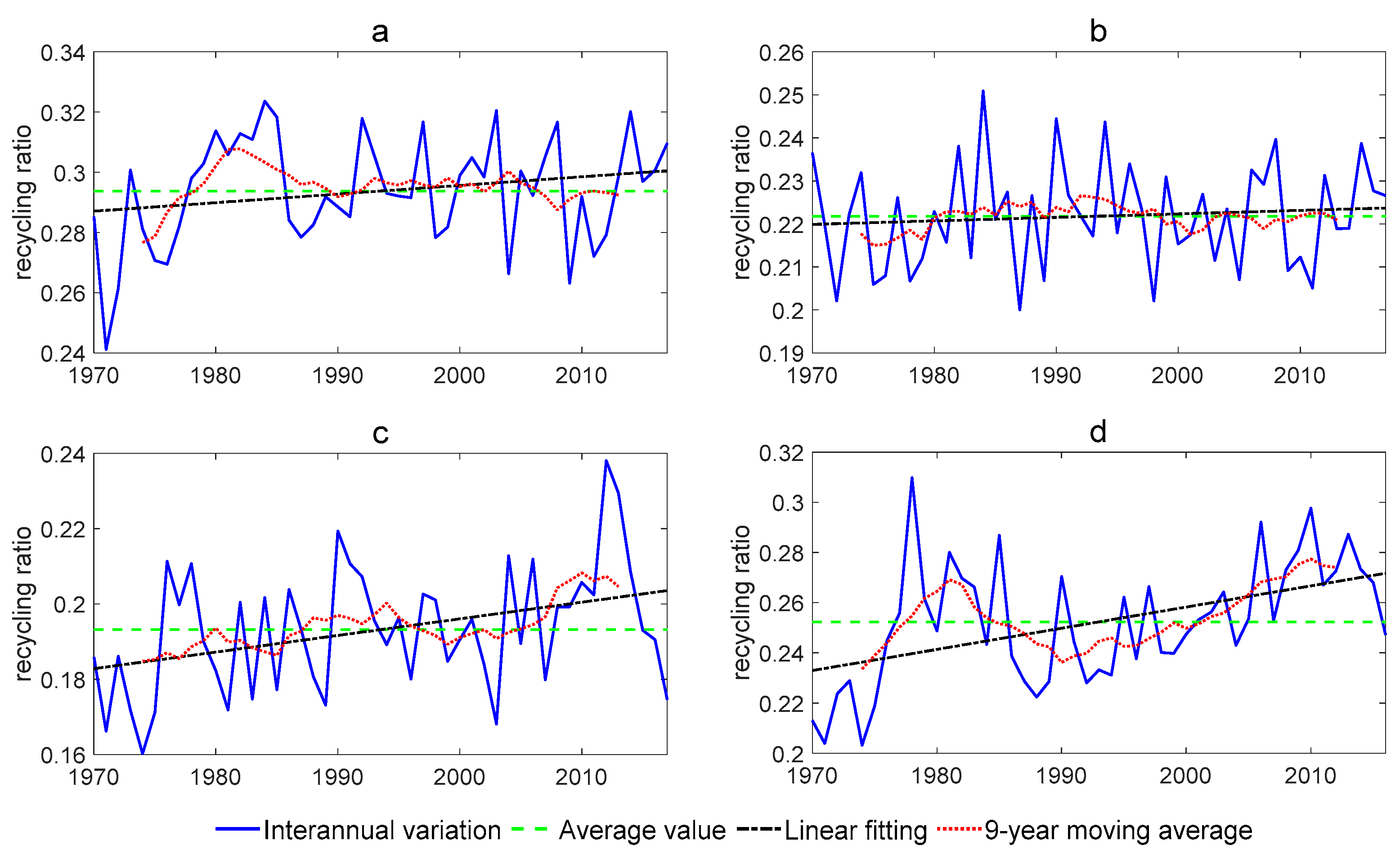
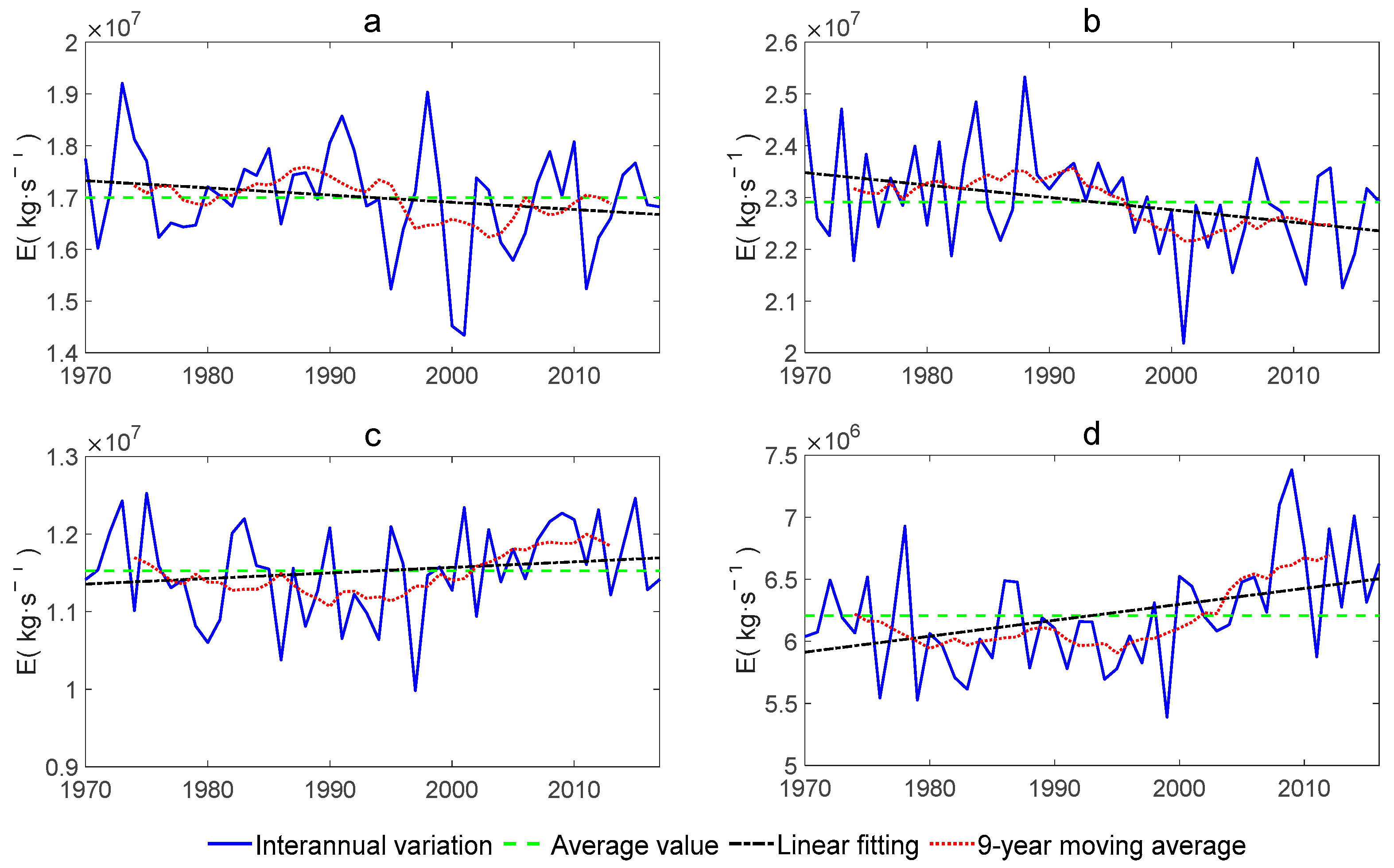
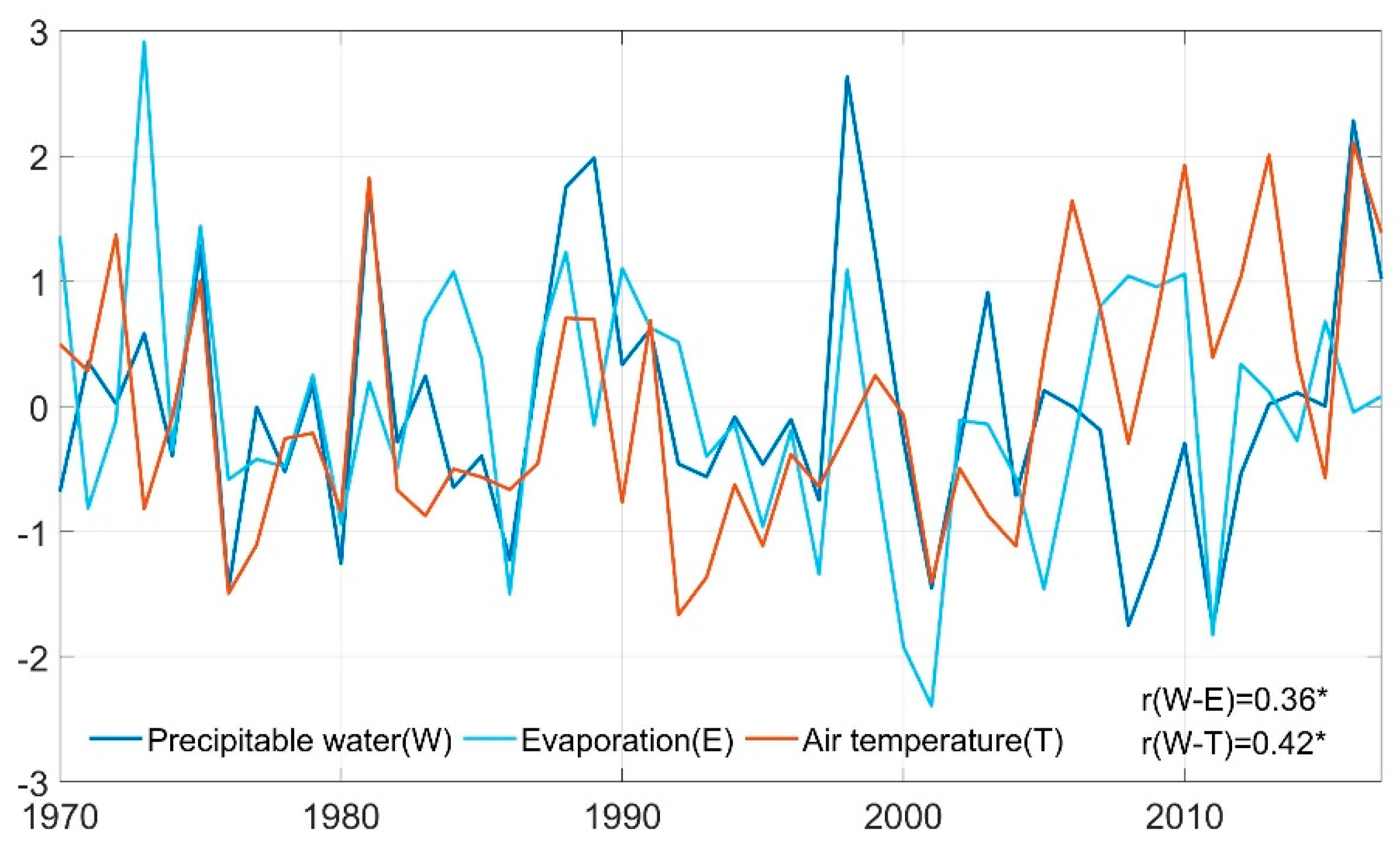
3.1. Paradoxical Changes among Different Branches of the Water Cycle in SAIE
3.2. Seasonal Contributions to the Paradox in SAIE
3.3. Physical Explanation for the Paradoxical Climate Change
4. Conclusions and Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Igel, M.R.; Biello, J.A. A reconstructed total precipitation framework. npj Clim. Atmos. Sci. 2019, 2, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, G.-Q.; Wang, C.-H.; Chang, L.-L.; Wu, Y.-P.; Li, L.; Jin, Z. Effects of feedback regulation on vegetation patterns in semi-arid environments. Appl. Math. Model. 2018, 61, 200–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- New, M.; Todd, M.; Hulme, M.; Jones, P. Precipitation measurements and trends in the twentieth century. Int. J. Climatol. 2001, 21, 1889–1922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, M.; Qiao, S.; Feng, T.; Wu, Y.; Feng, G. The inter-decadal change in anomalous summertime water vapour transport modes over the tropical Indian Ocean-western Pacific in the mid-1980s. Int. J. Clim. 2018, 38, 2672–2685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Li, Z.; Zhang, F.; Lu, Y.; Duan, C.; Xu, Y. Seasonal dynamics of carbon dioxide and water fluxes in a rice-wheat rotation system in the Yangtze-Huaihe region of China. Agric. Water Manag. 2023, 275, 107992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Wu, Y.; Wang, R.; Liu, B.; Qian, Z.; Li, C. Assessment of climatic impact on vegetation spring phenology in northern China. Atmosphere 2023, 14, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, G.L.; Yang, J.; Zhi, R.; Zhao, J.H.; Gong, Z.Q.; Zheng, Z.H.; Xiong, K.G.; Qiao, S.B.; Yan, Z.; Wu, Y.P.; et al. Improved prediction model for flood-season rainfall based on a nonlinear dynamics-statistic combined method. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2020, 140, 110160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, H.; Chen, Y.; Shi, X.; Li, W.; Wang, H.; Zhang, S.; Fang, G. Dynamics of temperature and precipitation extremes and their spatial variation in the arid region of northwest China. Atmos. Res. 2013, 138, 346–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Shen, Y.; Kang, E.; Li, D.; Ding, Y.; Zhang, G.; Hu, R. Recent and Future Climate Change in Northwest China. Clim. Chang. 2006, 80, 379–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.; Xue, H.; Zhao, C.; Lu, D. The roles of convective and stratiform precipitation in the observed precipitation trends in Northwest China during 1961–2000. Atmos. Res. 2016, 169, 139–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Shen, Y.; Hu, R. Preliminary study on signal, impact and foreground of climatic shift from warm-dry to warm-humid in northwest China. J. Glaciol. Geocryol. 2002, 24, 219–226. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Chen, F.; Gou, X. The temporal and spatial distribution of seasonal dry-wet changes over the northwestern China: Based on PDSI. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2007, 62, 1142–1152. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.J. The weakening of the Asian monsoon circulation after the end of 1970’s. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2001, 18, 376–386. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, P.L.; Yang, J.H.; Lu, G.Y.; Zhu, B.; Liu, W. The transitional change of climate in the east of Northwest China. Plateau Meteorol. 2020, 39, 840–850. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Trenberth, K.E. Atmospheric moisture recycling: Role of advection and local evaporation. J. Clim. 1999, 12, 1368–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burde, G.I.; Zangvil, A. The estimation of regional precipitation recycling. Part I: Review of recycling models. J. Clim. 2001, 14, 2497–2508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hai, H.E.; Guihua, L.U. Precipitation Recycling in Tarim River Basin. J. Hydrol. Eng. 2013, 18, 1549–1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budyko, M.I.; Drozdov, O.A. Zakonomernosti vlagooborota v atmosfere (Regularities of the hydrologic cycle in the atmosphere). Izv. Akad. Nauk SSSR Ser. Geogr. 1953, 4, 5–14. [Google Scholar]
- Salati, E.; Dall’Olio, A.; Matsui, E.; Gat, J.R. Recycling of water in the Amazon Basin: An isotopic study. Water Resour. Res. 1979, 15, 1250–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brubaker, K.L.; Entekahabi, D.; Eagleson, P.S. Estimation of continental precipitation recycling. J. Clim. 1993, 6, 1077–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eltahir, E.A.B.; Bras, R.L. Precipitation recycling. Rev. Geophys. 1996, 34, 367–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schär, C.; Lüthi, D.; Beyerle, U.; Heise, E. The Soil–Precipitation Feedback: A Process Study with a Regional Climate Model. J. Clim. 1999, 12, 722–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Ent, R.J.; Savenije, H.H.G.; Schaefli, B.; Steele-Dunne, S.C. Origin and fate of atmospheric moisture over continents. Water Resour. Res. 2010, 46, W09525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, P.; Ding, Y.; Liu, Y.; Li, X. The characteristics of moisture recycling and its impact on regional precipitation against the background of climate warming over Northwest China. Int. J. Clim. 2019, 39, 5241–5255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, H.W.; Gu, X.Q.; Fu, X.; Xu, X. Precipitation recycling over the Northern China. J. Appl. Meteorol. Sci. 2005, 16, 139–147. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Fu, X.; Xu, X.D.; Kang, H.W. Research on precipitation recycling during Meiyu season over Middle-Lower Reaches of Changjiang River in 1998. Meteorol. Sci. Technol. 2006, 34, 394–399. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Li, R.; Wang, C.; Wu, D. Changes in precipitation recycling over arid regions in the Northern Hemisphere. Theor. Appl. Clim. 2016, 131, 489–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Gao, X.; Shen, Y.; Xu, C.; Shi, Y.; Giorgi, F.S. A daily temperature dataset over China and its application in validating a RCM simulation. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2009, 26, 763–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Gao, X.J. A gridded daily observation dataset over China region and comparison with the other datasets. Chin. J. Geophys. 2013, 56, 1102–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, T.; Feng, T.; Feng, G. Evaporation variability under climate warming in five reanalyses and its association with pan evaporation over China. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2015, 120, 8080–8098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.-P.; Shen, Y.-P.; Li, B.L. Possible physical mechanism of water vapor transport over Tarim River Basin. Ecol. Complex. 2012, 9, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, B.; Su, T.; Wu, Y.; Feng, G. The Interdecadal Reverse of the Relationship and Feedback Mechanism between Sea Surface Temperature and Evaporation over the Indian Ocean during Boreal Autumn. J. Clim. 2020, 33, 10205–10219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, F.; Li, K.; Yang, K. On the increase of precipitation in the Northwestern China under the global warming. Adv. Earth Sci. 2021, 36, 980–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huntington, T.G. Evidence for intensification of the global water cycle: Review and synthesis. J. Hydrol. 2006, 319, 83–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karl, T.R.; Trenberth, K.E. Modern Global Climate Change. Science 2003, 302, 1719–1723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalnay, E.; Kanamitsu, M.; Kistler, R.; Collins, W.; Deaven, D.; Gandin, L. The NCEP/NCAR 40-year reanalysis project. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 1996, 77, 437–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Zhang, H.; Zuo, J.; Yang, L.; Yang, J.; Xiong, K.; Feng, G.; Dong, W. Oceanic drivers and empirical prediction of interannual rainfall variability in late summer over Northeast China. Clim. Dyn. 2021, 58, 861–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, X.-Y.; Bao, X.-Y.; Huang, Y.; Li, Z.-W.; Yong, J.-H.; Wu, Y.-P.; Feng, G.-L.; Sun, G.-Q. Physical Explanation for Paradoxical Climate Change in Semi-Arid Inland Eurasia Based on a Remodeled Precipitation Recycling Ratio and Clausius–Clapeyron Equation. Atmosphere 2023, 14, 376. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14020376
Wang X-Y, Bao X-Y, Huang Y, Li Z-W, Yong J-H, Wu Y-P, Feng G-L, Sun G-Q. Physical Explanation for Paradoxical Climate Change in Semi-Arid Inland Eurasia Based on a Remodeled Precipitation Recycling Ratio and Clausius–Clapeyron Equation. Atmosphere. 2023; 14(2):376. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14020376
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Xi-Yu, Xin-Yue Bao, Yu Huang, Zhong-Wai Li, Jia-Hua Yong, Yong-Ping Wu, Guo-Lin Feng, and Gui-Quan Sun. 2023. "Physical Explanation for Paradoxical Climate Change in Semi-Arid Inland Eurasia Based on a Remodeled Precipitation Recycling Ratio and Clausius–Clapeyron Equation" Atmosphere 14, no. 2: 376. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14020376
APA StyleWang, X.-Y., Bao, X.-Y., Huang, Y., Li, Z.-W., Yong, J.-H., Wu, Y.-P., Feng, G.-L., & Sun, G.-Q. (2023). Physical Explanation for Paradoxical Climate Change in Semi-Arid Inland Eurasia Based on a Remodeled Precipitation Recycling Ratio and Clausius–Clapeyron Equation. Atmosphere, 14(2), 376. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14020376





