Abstract
Different Light-Absorbing Snow Impurities (LASI) can deposit on snow- and ice-covered surfaces. These particles are able to decrease snow and ice albedo and trigger positive albedo feedback. The aim of this work was to develop a new method to quantify the carbonaceous fractions that are present in snow and ice samples that contribute significantly to their darkening. Currently, in the literature, there is an absence of a unified and accepted method to perform these studies. To set up the method proposed here, snow samples were collected at two Italian locations, Claviere and Val di Pejo (Northern Italy). The samples were analyzed using two main techniques, Total Organic Carbon analysis (TOC analysis) and Thermal Optical analysis in Transmittance mode (TOT), which enabled the speciation of the carbonaceous fraction into organic (OC), inorganic (IC), and elemental carbon (EC), and further into the soluble and insoluble parts. The results highlighted a correlation between the nature of the sample (i.e., location, age, and exposure of the snow) and the experimental results, giving validity to the method. For example, the abundant presence of terrigenous constituents was reflected in high amounts of insoluble IC. Moreover, due to the trend between insoluble IC and Elemental Carbon (EC), the role of IC in TOT analysis was investigated. Indeed, IC turned out to be an interfering agent, suggesting that the two techniques (TOC analysis and TOT) are complementary and therefore need to be used in parallel when performing these studies. Finally, the results obtained indicate that the newly proposed method is suitable for studying the carbonaceous fractions in snow samples.
1. Introduction
Nowadays, the problem of glacier shrinkage is well known, not only to scholars of the field, but also to many people not directly involved in the related scientific research [1,2]. In 2019, the special report ‘Ocean and Cryosphere in a Changing Climate’ [3], following the indications from the IPCC (Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change), reported that between 2006 and 2015, glaciers worldwide, outside Greenland and Antarctica, lost mass at an average rate of 220 ± 30 Gt per year, equivalent to a sea level rise of 0.61 ± 0.08 mm per year. The decline of glaciers, snow, and permafrost has altered the frequency, strength, and location of most related natural hazards, such as landslides, avalanches, floods, land subsidence, and forest fires. The impact of this phenomenon on the cryosphere can be traced back to the increase in average temperatures and to the darkening of ice and snow surfaces [4]. Indeed, the two effects are directly correlated: the increase in temperatures is responsible for accelerated melting, which, in turn, causes debris and rocks to rise to the surface of the snow. Another cause of darkening is the presence of impurities on the snow’s surface, such as biogenic formations, which include colorful algal blooms and the deposition of atmospheric aerosols (an increase in algal productivity is reported as the concentration of inorganic carbon increases, and this is referred to as bio-albedo [5]).
The darkening of a surface is measured by the reduction in its albedo. The albedo of a surface is the reflectance of the surface, when the incident radiation is solar radiation, integrated over all directions of solar view [6]. The albedo of pristine snow and ice is generally between 80 and 90%, depending on the grain size. An increase in temperature accelerates the melting process and modifies the grain size, altering the snow’s albedo. In addition, the deposition of light-absorbing impurities on the surface of snow reduces the ability of snow to reflect incoming visible radiation and decreases its albedo. Such an effect depends on the microphysical properties of the deposited material. These impurities are called Light-Absorbing Snow Impurities (LASI) and include Light-Absorbing Particles (LAPs) [7].
A concept related to albedo is radiative forcing, a measure of the influence of a factor, such as the concentration of a pollutant, on the balance between incoming and outgoing energy in the Earth–atmosphere system. Positive radiative forcing, expressed in W m−2, indicates an increase in absorbed radiation and a decrease in the albedo.
In the atmosphere, several substances are present, both as gases (i.e., volatile organic compounds [8]) and as particles, arising from various emission sources, including biomass combustion [9], which contributes to the emission of particles (in particular BrC, Brown Carbon) responsible for light absorption, as explained later in this text. Atmospheric particles contain 50–60% mineral compounds by mass, including light-absorbing oxides (e.g., hematite in Saharan Dust; it was reported that the mineral fraction strongly reduced the spectral reflectance of snow, particularly between 350 and 600 nm [10]); the remaining percentage is constituted by carbonaceous species. Estimates of global radiative forcing due to Black Carbon (BC) in snow alone range between +0.01 and +0.09 W m−2 [11]. Atmospheric aerosols also contain particles that are not strongly light-absorbing, yet it must be considered that induced radiative forcing is highly dependent on the surface underneath; the effect of the same aerosol over a dark and over a highly reflective surface can be the opposite [12]. Indeed, the overall effect of atmospheric particles deposited on snow and ice, highly reflective surfaces, is the reduction in their albedo [4]; therefore, they can be regarded as LASI.
The carbonaceous component of the atmospheric particles is usually described as Total Carbon (TC), according to Equation (1):
where TOC is the total organic content (Total Organic Carbon), IC is the inorganic content (Inorganic Carbon), and BC is Black Carbon. Moreover, TC can be further separated into its soluble and insoluble fractions. BC is entirely insoluble, whereas TOC and IC have soluble and insoluble fractions [13]. In the melting season and in the melting/refreezing cycles, the insoluble hydrophobic fractions remain at the water–air interface or emerge from the underlying layers, while the soluble fraction is dissolved and diffuses into the depths of the liquid. The result is an accumulation of the hydrophobic fraction on the surface with a further reduction in albedo (in addition to the effects of increased grain size due to heat) [14]. Similar effects are also noticed, to a much lesser extent, in the accumulation season due to melting or sublimation [15]. These post-deposition processes, which must be integrated with all possible chemical, photochemical, biochemical, and degradation reactions, especially of the organic fraction, account for the different concentrations observed in aged snow [13]. While IC is generally negligible in the atmosphere, aside from specific cases, such as sites in the proximity of known IC sources, such as marble quarries [16], in snow, it may not be. In fact, depending on the location, snow can be easily contaminated by dust and ground soil rich in carbonates.
TC = TOC + IC + BC
Light-Absorbing Carbon (LAC), which is a subgroup of LASI, includes different components of the previously defined carbonaceous fraction that are able to absorb visible light [17,18]. These include:
- BC: Black Carbon, carbonaceous material that displays the following five properties [18]. Continuous, wavelength-independent absorption of visible light; at 550 nm, BC shows a Mass Absorption Coefficient (MAC) of 5 m2 g−1 or more. It exhibits refractory properties at vaporization temperatures above 4000 K; gasification is possible only by oxidation above 340 °C. It has a graphitic structure and a fractal-like chain-aggregate morphology. It is insoluble in water and in most common organic solvents.
- BrC: Brown Carbon, which is a component of the TOC fraction. Its absorption depends on the light wavelength [19]. BrC is generally emitted by biomass combustion, but it is also produced by atmospheric oxidation reactions [20].
Despite these general definitions, all components of the carbonaceous fraction remain, to date, operationally defined. Regarding Black Carbon, there are no analytical techniques that are able to simultaneously identify all of the five properties that define BC [18]. It is worth noting that, in the text, BC will be used as a general term, i.e., when this component is not determined by a specific chemical method. Otherwise, when using Evolution Gas Analysis (EGA) techniques, the result will be referred to as Elemental Carbon (EC) [17].
In this work, a newly optimized method for the characterization and quantification of the carbonaceous fraction in snow is presented. Data from the literature were thoroughly evaluated in order to define the best possible operational details, from sampling to analysis. This work is, in fact, of high interest because it provides a global view on every aspect of the analysis. Thirteen snow samples from two Italian alpine locations (Claviere and Val di Pejo) were used to develop the method and analysis was performed using a combination of two techniques: Total Organic Carbon analysis (TOC analysis) and Thermal Optical analysis in the Transmittance mode (TOT). The results highlighted a complementarity of the two techniques, which is a crucial factor in achieving a complete characterization of the carbonaceous fractions.
2. Materials and Methods
There are many methods proposed in the literature for the analysis of the carbonaceous fractions in snow samples. Regarding the main steps of the methods (sampling, pre-treatment, melting, filtration, and analysis), many aspects are still debated. It appears that the method must be adapted to the specific sample, bearing in mind all possible sources of contamination and/or loss of analytes [7] (Section 2.1). Taking into consideration all the issues emerging from the data in the literature, the newly optimized method developed in this study is presented in Section 2.2.
2.1. Analytical Methods: State of the Art (S.A.)
2.1.1. S.A.—Sampling
The selection of the snow and ice containers to carry out the sampling procedure is not straightforward. Some authors recommend the use of sterile materials. Glass [13] or steel [7,21] palettes are commonly used, along with plastic. All the materials have strengths and weaknesses related to their use. For instance, glass is known to retain BC [21], while plastic can contaminate the sample with Water-Soluble Organic Carbon (WSOC) [22] and retain carbonaceous particles [23].
Regardless of the material, sampling bottles undergo cleaning prior to sampling. One of the options consists of a 24 h treatment with dilute solutions of hydrochloric or nitric acid (0.5–1 M) [24]. Alternatively, more aggressive substances, such as chromic solutions in sulfuric acid, are used [21]. This treatment is followed by cleaning with milli-Q water and a resting period in which the containers are filled with milli-Q water and left to rest for 24 h.
In order to limit contamination, wearing dustproof clothing, gloves, and head and face masks [21] is recommended when sampling. Moreover, it is useful to prepare blanks by exposing the empty containers upwind for the entire sampling period [24]. As sample contamination is not uncommon, especially bacterial contamination, some studies recommend the addition of an antibacterial substance (a small amount of HgCl2, an option not advisable in the case of concomitant ion analysis) and storing the melted samples in the refrigerator. Alternatively, in order to avoid melting, samples can be kept in the freezer, where the low temperatures significantly inhibit or slow down the rate constants of the bacterial degradation of OC [25].
In order to evaluate the impact of LASI on snow over time, samples are often collected at different depths with a resolution of 5–10 cm [21,24]. Another approach is based on the collection of the first 0–2 cm layer in the accumulation season or the 0–10 cm layer in the melting season [7], if the optical properties are to be investigated. Furthermore, for aged snow, there is an amplification of the concentrations in the first 2–4 cm due to melting or sublimation, even in the accumulation season [15].
2.1.2. S.A.—Sample Pre-Treatment
The sample must be homogenized if it needs to be portioned prior to melting. One possibility is mechanical homogenization, with a mixer, operating in a refrigerated chamber [11].
2.1.3. S.A.—Sample Melting
A wide variety of methods have been used and/or tested in the literature. These include the use of microwaves [26], water baths at various temperatures [8,21], and melting in air at 1 °C [11]. The selection of the melting temperature highly depends on the analytical technique used [27]. Some articles concluded that the melting method does not change the particle dimensional distribution [28], whereas others concluded otherwise [11].
Temperature and time are two parameters that should be controlled during melting, because both can lead to the adhesion of BC onto the walls of the container [8,27]. If one is interested in analyzing the liquids, when working with open vessels, low temperatures are recommended to avoid evaporation [29]. Moreover, in order to limit the degradation of the organic fraction, it is recommended to limit the duration of the melting process under 4 hours [21]. Based on these considerations, the best melting method appears to be fast melting conducted at low temperatures.
2.1.4. S.A.—Filtration
The use of pre-burned filters [21,29] is recommended in order to remove the carbonaceous matter that may be present on the filter. The side of the filter is another variable that can affect the results; indeed, differences in filtration efficiency can be observed when using the filter upside-down [29].
Regarding the material of the filter, quartz is typically preferred when TOT analyses are planned due to its ability to withstand the high temperatures (800 °C) reached by the oven. However, authors have pointed out some issues with the filtration efficiency of quartz. The filtration efficiency is the percentage of retained particles compared to the total present in suspension. Some have suggested that the use of a coagulant increases the filtration efficiency of BC from 30% to around 95% [7]; others claim that the efficiency is already as high as 95% for particles of 0.1 µm diameter due to the complex passages in the filter [15]. A coagulant is an inorganic salt that increases ionic strength in order to eliminate the electrostatic protection of the colloid inducing its coalescence. Filtration efficiency appears to increase with increasing BC concentration [27]. In the case of gravimetric analysis, quartz is known to lose fragments in proportion to the amount of liquid filtered [7]. For volumes above 300 mL, leakage occurs; hence, the filtration efficiency decreases [29].
Given that BC adsorbs on glass, the filtration time should be minimized or a steel filtration system should be used [27]. Some authors include a sonication step prior to filtration in order to detach BC from the walls [21]. The effect is often negligible, especially if the containers are made of plastic [29], although, as previously mentioned, opinions on this material vary from one author to the other [23]. Moreover, sonication is also in contrast with the use of coagulants, as this procedure may break down the aggregates. In this case, the coagulant could be added after sonication (author’s comment).
In a study where the authors suspected the presence of large soil debris, the sample was decanted prior to filtration. Samples that reasonably do not contain unwanted soil are shaken and then filtered in order to recover even the largest particles [23].
Not rinsing the bottles used for sampling leads to negligible differences in results [30].
Finally, following filtration, it is recommended to allow the filters to dry under a laminar flow hood [21].
2.1.5. S.A.—Analysis
Regardless of the method used for analysis, it is important to note that there is no widely accepted reference standard for BC [31]. Some authors have considered the dispersion of BC in snow [32] or the use of colloidal carbon solutions [27]; however, the differences between natural soot and laboratory-generated soot are evident, at least with regards to their optical properties [30].
For the measurement of the LASI, there are three common methods [7,24]: optical methods, Laser Incandescence methods (LII), and thermal–optical methods. Optical methods are based on the phenomenon of absorption of radiation, which is the closest to what occurs with solar radiation. They can quantify colored inorganics, BrC, and BC. The quantification of BC requires the BC mass absorption coefficients to be known; thus, optically defined BC is referred to as equivalent BC (or eBC) [18]. SP2 measurements, a kind of LII technique, simultaneously quantify the mass size distribution and total mass concentration data using scattered light to obtain information regarding the diameter (Mie theory) and blackbody emission (LII) to estimate the mass of BC present in the incoming aerosol [11]—this is referred to as refractory BC (rBC). The variance associated with measurements performed on snow samples with the aforementioned techniques is greater compared to other atmospheric measurements. This indicates the need for an in-depth study of nebulizer performance and calibration at large diameters for the proper characterization of snow samples [27].
The thermal–optical method is part of the Evolution Gas Analyses (EGAs). It is used to quantify OC, which is comprehensive of BrC, and EC, as mentioned before. The results depend primarily on the filtration efficiency of quartz and on the temperature/time protocol chosen [7]. It has been pointed out that the commonly used IMPROVE_A protocol can suffer from incomplete OC evolution [33] (due to lower temperatures in the inert phase), while NIOSH-like protocols potentially suffer from the premature evolution of EC [31] and/or incomplete evolution of Pyrolytic Carbon (PC) in the inert phase [34] (due to the higher temperatures of the inert phase and to the presence of a large amount of mineral dust in the samples, including inorganic oxides, which can decompose and release oxygen, which should be absent in the first inert phase [31]). The latter phenomena would not be a problem if PC evolved before EC or if these two components had the same optical properties. As these conditions are often not verified, a new method was needed [31]. In order to reduce charring (PC formation), thus eliminating the problem, and to ensure that any PC is evolved before the oxidizing phase so that PC and EC, which have different optical properties, are clearly separated, the temperature steps can be changed and the residence times can be extended at each temperature. The resulting protocol was EUSAAR2 (European Supersites for Atmospheric Aerosol Research 2). Table 1 compares this protocol with NIOSH870 (National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health 870) and IMPROVE_A (Interagency Monitoring of Protected Visual Environments).

Table 1.
Comparison of three TOT protocols; the maximum temperature is highlighted in bold.
Regarding Carbonatic Carbon (CC), this component is usually present in atmospheric particulate matter in negligible quantities. In snow, this may not be true due to the transfer and/or dissolution from the soil. Studies have shown that, with both NIOSH-like and EUSAAR2 protocols, carbonatic carbon evolves as the last peak of the inert phase, which is confirmed by the analysis of natural calcite samples [31]. While this is demonstrable for atmospheric particulate matter, the issue will be addressed further in Section 3. An acidification treatment can be employed to eliminate carbonates prior to analysis by exposure to gaseous HCl for a minimum of 1 h. This procedure may alter the appearance of the EC profile, but the EC result should not be affected significantly [35,36].
In snow, carbonates undergo many phenomena; for example, one study showed that, in aqueous suspensions, the concentration of mineral dust decreased over time in favor of an increase in the concentration of the calcium ion, a phenomenon attributable to the dissolution of carbonates [37]. Furthermore, one of the few studies quantifying IC in snow [38] reported concentrations between 2 and 83 ppb and stated that dissolution during melting causes the loss of up to 91% of the IC that is initially present as a solid. Finally, melting the snow in a CaCO3-saturated solution, on the other hand, seems to limit the loss during melting down to 24%.
2.2. The Analyzed Snow Samples and the Applied Method
2.2.1. Sampling Procedure and Description of the Samples
Snow samples were taken from two macro-zones: Claviere and Val di Pejo (Figure 1a). These samples were used to validate the method.
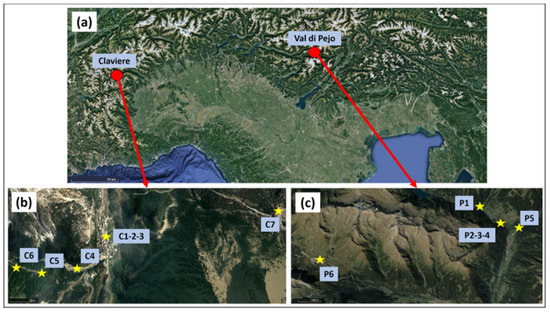
Figure 1.
(a) Sampling locations; (b) Claviere samples; (c) Val di Pejo samples.
Claviere (Figure 1b) is an Italian town located on the border with France (North-Western Italy). The greatest anthropic activity during the year is represented by the presence of tourism. The vehicular traffic that used to pass through the town has now been rerouted through a tunnel, largely protecting the town from pollution from this source. Claviere samples (Table 2) were collected in polyethylene (PE) bottles after being treated with 0.2 M nitric acid for 24 h, cleaned with milli-Q water, and left to rest for several hours in milli-Q water. No exposure blanks were sampled; therefore, two laboratory blanks were prepared by placing approximately 300 mL of milli-Q water in two PE bottles, which were refrigerated for the same time as the samples. The cold chain was not maintained; however, all samples were melted under the same conditions and stored in a refrigerator (+1 °C). The maximum volume of liquid sampled was 150 mL.

Table 2.
Sample descriptions.
Val di Pejo (Figure 1c), bordering Val di Sole, is a valley in Trentino Alto-Adige (North-Eastern Italy) immersed in the Parco dello Stelvio, a very popular site for tourism. One peculiarity of this location is that it is known for its mineral water, which is very rich in iron. Samples from Val di Pejo (Table 2) were taken using a stainless-steel spoon in PE food bags, which were then tied shut. The cold chain was maintained from the sampling point to the laboratory freezer (about −18 °C) using a thermal bag filled with additional snow. Two bags were also exposed to ambient air in the P5 and P6 areas.
No bactericides were added in this stage. It was assumed that the container material would not pollute the sample if it remained in the solid state. The sampling depth was not controlled accurately in this study, as the core of the work was focused on the development of the analytical method and not necessarily on the characteristics of the chosen samples.
2.2.2. Analytical Techniques
In order to identify the carbonaceous fractions, the analytical techniques employed were Total Organic Carbon analysis (TOC analysis) and Thermal Optical analysis in Transmittance mode (TOT). In addition, for a preliminary characterization of the mineral fraction, analyses were carried out with Attenuated Total Reflection Fourier-Transformed InfraRed spectroscopy (ATR-FTIR) and Scanning Electron Microscopy coupled with Energy Dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (SEM-EDX).
The instrumentation used was a TOC-V CPH analyzer (Shimadzu Corporation, Kyoto, Japan), a Laboratory OC-EC Aerosol TOT analyzer (Sunset Laboratory Inc., Model 5, Hillsborough, NC, USA), a Nicolet 380 ATR-FTIR spectrometer (Thermo Electron Corporation, Waltham, MA, USA), and a TM4000 PlusII scanning electron microscope (Hitachi, Tokyo, Japan).
TOC Analysis—This analysis was performed on the samples under stirring. The analysis consisted of the oxidation of the carbonaceous materials over a platinum oxide catalyst at high temperatures (680 °C). Carbonaceous organic and inorganic species were converted into carbon dioxide, which was then detected using a Non-Dispersive InfraRed (NDIR) detector. The following operationally defined fractions can be detected using TOC Analysis:
- TC analyzed by burning the entire injected aliquot. All carbonaceous species were converted into carbon dioxide;
- IC, which evolves into carbon dioxide after acidification (pH < 3) and sample purging;
- NPOC, which corresponds to TC determined after purging for IC quantification;
- POC, Purgeable Organic Carbon, which evolves together with IC and is not revealed directly.
Depending on their volatility, organic substances are distributed between the POC and NPOC fractions. IC consists mainly of carbonates, bicarbonates, and dissolved carbon dioxide; however, all carbon that evolves with carbonates after acidification and purging is quantified as IC.
Total Carbon (TC) and Total Organic Carbon (TOC) can be calculated using Equations (2) and (3):
TC = IC + TOC
TOC = NPOC + POC
TOC can be estimated as the difference between TC and IC or by measuring NPOC.
For the TOC determination, the TC–IC combination was chosen because preliminary analyses showed the IC to be around 30% and the TOC was better estimated with this method, rather than with the NPOC method, as suggested by the user manual, because NPOC method suffer from a more extensive sample treatment that also include the loss of POC.
TC calibration—In order to avoid interference by the carbon content in the water used by the instrument for the automatic dilutions, the calibration line was shifted to zero. This meant that the intercept value obtained without shifting the line to zero was subtracted from the areas of the standards. The non-zero-shifted line was fitted with the weighted least-squares model, whereas the zero-shifted line was fitted with the weighted least-squares model through the origin. In Figure 2, the regression model is reported (the confidence and prediction intervals for n = 3 are shown).
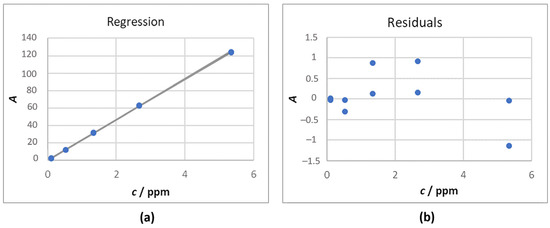
Figure 2.
Calibration for TC: (a) Regression line obtained; (b) Residuals graph.
The uncertainty associated with the corrected standard areas was calculated by the propagation of the uncertainty of repeatability and the uncertainty associated with the intercept. The instrument was used in high-resolution mode and the injection volume used was 300 µL.
The equation of the calibration curve obtained is reported in Equation (4).
y = (23.34 ± 0.08) x
The linearity of the calibration curve was evaluated using the lack-of-fit test (alpha 0.01, ISO 11095:1996), Mandel’s test (alpha 0.01, ISO 8466-1:2001), and the 5%-interval test (EN 15984:2022). The aforementioned tests yielded positive results. Moreover, the R2 value was 0.9999 and the cross-validated R2 was 0.9999.
Considering 3 independent determinations for the samples, the LOD (4s0) was 0.02 ppm and the LOQ (3LOD) was 0.05 ppm (ISO 13530:2009).
IC calibration—The same procedure followed for TC calibration was used. The instrument was used in the high-resolution mode and the injection volume used was 1000 µL. The IC purging time was set to 2 min.
In Figure 3, the regression model is reported.
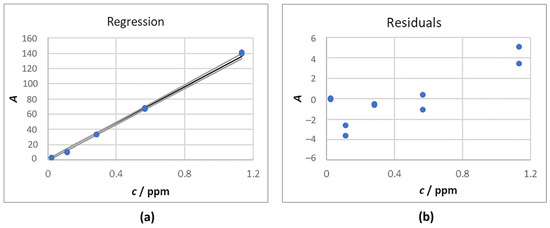
Figure 3.
Calibration for IC: (a) Regression line obtained; (b) Residuals graph.
The equation of the curve that was obtained is reported in Equation (5).
y = (120 ± 1) x
Following residual analysis, it was possible to attribute the failure of the linearity tests to factors other than a non order-one dependence of the dependent variable over the independent variable; thus, the use of a straight line as a calibration curve was confirmed. The R2 value was 0.999 and the cross-validated R2 was 0.999. The LOD was 0.02 ppm and the LOQ was 0.05 ppm.
TOT analysis—This technique involved the thermal desorption of the operational carbonaceous fractions induced by the application of a specific thermal protocol. The first step occurs in an inert atmosphere and causes OC to evolve. The second step instead occurs in an oxidizing atmosphere and causes the EC to evolve. If PC is formed in the inert phase, it will evolve in the second oxidizing step, and it may, therefore, be confused with EC. This potential error is corrected by measuring the transmittance of the sample during the whole course of the analysis. As charring takes place, the filter becomes darker and the transmittance decreases. When this parameter returns to its initial value, it is assumed that all the OC, pyrolyzed or not, has evolved and all of the remaining carbon can be assigned to EC.
TOT calibration—The instrument used was already calibrated and a calibration check with control standards was performed on the same day as sample analysis. The LOD was 0.5 µg of carbon and the LOQ was 1.5 µg of carbon.
ATR–FTIR—This technique allowed for the initial characterization of the mineral fraction. Data was acquired between 4000 and 400 cm−1 with a resolution of 4 cm−1.
SEM-EDX—This technique allowed for morphological analysis of the samples and semi-quantitative determination of the elements present.
2.2.3. Work Scheme
The work scheme set up and followed in this work (as represented in Figure 4) involved melting the solid samples without portioning them (no pre-treatment needed), an initial sieving necessary for TOC analysis, and filtration through a quartz filter, which was analyzed using TOT (the operations of melting, sieving, and filtration are described further in the following paragraphs).
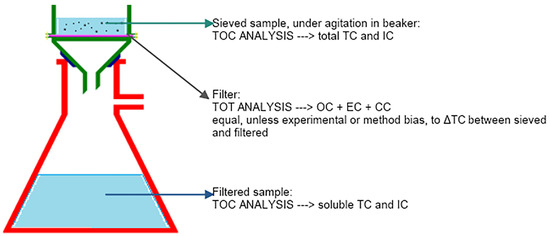
Figure 4.
The work scheme.
The sieved suspension (i.e., prior to filtration) and the filtered solution were analyzed, as well as the filter. By filtering, the content of the suspension was distributed between the filter and the solution. The insoluble fraction remained on the filter, whereas the soluble fraction passed through the filter and into the filtered solution.
The insoluble fraction was determined using two different procedures:
- directly by TOT analysis on the filter;
- using TOC analysis and calculating the difference between the concentrations found in the sieved suspension and the filtered solution.
In the absence of experimental and/or methodological errors, the two procedures should yield the same results. This is because OC and EC are part of the TOC fraction, and CC is part of the IC fraction.
The Milli-Q water used in all experimental tests was filtered through a 0.22 µm filter. The water TOC level was 2 ppb and the resistance equal to 18.2 mOhm. It could be classified as Reagent Water Type 1 according to ISO 3696:1987 and ASTM D1193-99.
2.2.4. Sample Melting
The samples from Claviere were liquid and analyzed once they reached room temperature. Samples from Val di Pejo, on the other hand, were melted in a water bath at 30 °C, by immersing the entire closed bag, thus sample contamination and loss of mass through evaporation were avoided. All samples melted completely within 20 min. Only one sample, P1, released a relatively large amount of gas during the melting process.
Regarding the blanks, the bags were opened, filled with approximately 300 mL of milli-Q water, resealed, and heated to 30 °C for the same time as the samples. Milli-Q water was not added earlier on the assumption that any contamination by PE would be insignificant in the solid state, with a low contact area, as the samples were composed mostly of ice grains. The melted samples were immediately analyzed to avoid contamination from prolonged contact with the plastic, which can be a source of WSOC contamination.
2.2.5. Sieving
The samples were then sieved (Figure 5) using a stainless-steel flour sieve with a mesh size of 0.5 mm. This step was necessary due to the instrumental limitations of the TOC analysis. Assuming that nothing was retained by the PE bags, the samples were not sonicated. In addition, no coagulant was added. This topic is still under debate in the literature [39].
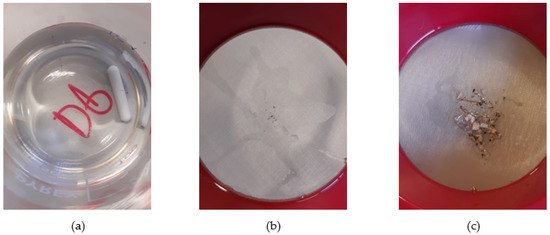
Figure 5.
(a) Visually clean sieved sample; (b) Residue from a visually clean sample; (c) Residue collected after sieving sample P4.
The Claviere samples were shaken, sieved, and poured into a glass beaker. Instead, in order to limit possible contamination, in the Val di Pejo samples, a corner of the bag was cut off (as if it was a sac a poche) after drying the area with absorbent paper. After each sample, the sieve was cleaned with a strong jet of milli-Q water and left to dry in the air.
2.2.6. Filtration
The amount of volume filtered was varied between the different samples in order to ensure that the particulate concentration on the filter was within the optimal range for TOT analysis. The filtered volume was 50 mL for most samples, except for P2, P4, and P5. Sample P4 had a particularly high concentration of particulates; therefore, only 5 mL was filtered. Additionally, 20 mL samples of P2 and P5 were filtered in order to avoid filter overload. Regardless of the volume used for TOT analysis, another 50 mL was filtered for all samples to perform ATR-FTIR analysis.
Before filtration, the sample was placed in a glass beaker under vigorous stirring (500 rpm).
Filtration was performed with quartz filters using a glass septum system. Blank filters underwent TOT analysis to verify the presence of any residual carbon. The response was negligible; therefore, the filters were not pre-burned prior to filtration. The diameter of the septum, which coincided with the diameter of the deposit on the filter, was measured, and corresponded to an area of (2.77 ± 0.07) cm2. To limit the contact with glass, filtration was performed under vacuum conditions. Fully emptying pipettes were employed in order to avoid any accumulation of particles in the tip during sample transfer.
In order to obtain depositions as homogenously dispersed as possible on the filters, the funnel was filled and then the vacuum was turned on (Figure 6). Moreover, care was taken to keep the filter in a horizontal position in order to avoid preferential loading of one side. In the case of diluted samples, this was the most effective method. In the more concentrated samples, the larger particles, probably mineral dust (see SEM-EDX analysis), were deposited preferentially around the borders of the filters.
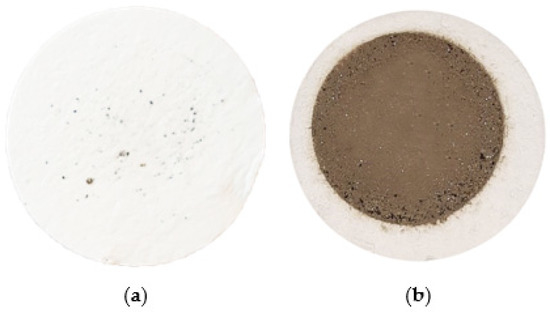
Figure 6.
(a) Filter after filtering 50 mL of a visually clean sample; (b) Filter after filtering 50 mL of sample P4—a ‘ring’ of large particles is evident.
The filtrate was stored in a glass flask sealed with parafilm until the analysis was performed. The adhesion of EC onto the glass was not a problem as this component was retained by the filter.
2.2.7. Analysis
The TC/IC (TOC analysis) blanks were the sieved and filtered blanks described above; the OC/EC (TOT) blanks were the filtered residues of the same.
The TOC analysis instrument was switched on at least half an hour beforehand in order to allow the detector signal to stabilize.
TOC analysis on the sieved sample was performed as soon as possible to minimize the residence time in the glass container. Continuous stirring was performed in order to retrieve the larger suspended particles. Three readings for each sample were performed when possible.
After sieving the sample, the filtrate was analyzed. The filtrate was not stirred due to the absence of suspended particles. A control standard was analyzed once a day.
The TC analysis lasted approximately 2–3 min, while the IC analysis lasted 5–6 min. Samples were analyzed at the injection volumes provided by the calibrations shown, except for sample P4, which was analyzed at lower injection volumes, and the blanks, which were analyzed at the maximum injection volume of 2000 µL to maximize sensitivity. These values were scaled to those obtained from the calibration line considering a constant CV% (please refer to Supplementary Materials). Detector signal integration was performed manually, as described in the Supplementary Materials.
As already mentioned, the TOC was calculated by subtracting TC–IC. Each measurement was carried out by performing blank subtraction. The insoluble part was then determined for each carbonaceous fraction by subtracting the filtered sample results from the sieved sample results. Differences whose confidence interval (95%) included zero were not considered relevant.
The filter, which was subjected to TOT analysis, was considered dry at the end of the TOC analysis of the sieved and filtered samples. TOT analysis was carried out after the stabilization of the transmittance signal using the EUSAAR2 protocol in order to avoid the underestimation of EC. To sample the largest possible portion of the filter and increase representativeness, 1.5 cm2 punches were used. A control standard was analyzed every 4–6 samples. The TOT results were obtained as follows (Equation (6)):
Conc. in suspension = Conc. (referred to 1 cm2) × Area (punch) × Area (filter) /
/Vol (filtered)
/Vol (filtered)
The blank was then subtracted from the results if it had a measurable response.
ATR analyses were performed without filter cut-out using 256 scans between 4000 and 400 cm−1. The most concentrated sample (P4) was analyzed using 1024 scans in order to obtain clearer signals.
2.2.8. Quality Control
Please refer to the Supplementary Material for a comprehensive description of data and uncertainty handling. In particular, the procedures for the determination of LOD and LOQ are reported.
The TOC analysis results were comprehensive of calibration uncertainty while the TOT results were not, yet its contribution could be reasonably considered negligible.
All uncertainties are presented in this paper as the 95% confidence interval (Equation (7)), unless stated otherwise.
In Equation (7) ‘dof’ stands for degrees of freedom.
3. Results
3.1. TOC Analysis Results
The analysis of the blanks was useful to assert that washing the beaker only with water, after analysis of the sieved samples, was not sufficient to clean it. In fact, a blank that was analyzed after the most concentrated sample showed a TC concentration of about 0.9 ppm and an IC concentration of about 0.2 ppm, whereas, in the other blanks, being both from bottles or bags, the concentrations were 0.3 and 0.1 ppm. It was noted that the beaker must be wiped with paper and then washed vigorously.
Table 3 reports the results of the TOC analysis.

Table 3.
TOC Analysis results; averages of 3 determinations unless stated otherwise, with blank subtraction. Referring to Figure 4, the sieved sample is the ‘upper’ suspension while the filtered sample is the ‘lower’ solution.
The results were processed as described in the Analysis section to determine the TOC fraction and the distribution of each fraction in the soluble and insoluble parts. The results are shown in Figure 7.
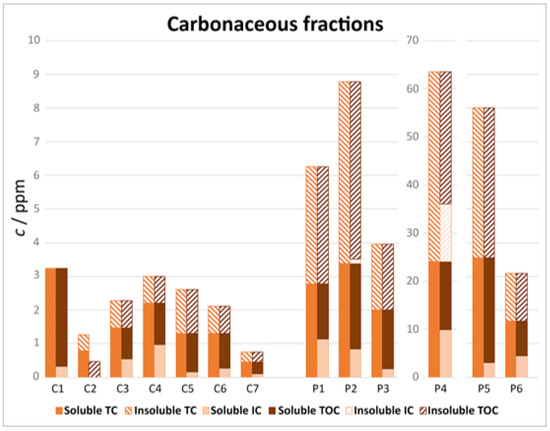
The insoluble fraction of sample C1 was not reported due to high uncertainties in the results. Regarding sample C2, the analysis was not carried out due to the limited amount of sample.
The TC concentrations of samples C4, C5, C6, and C7 decreased with increasing distance from the ‘Rio Secco’ site. Indeed, a 30% decrease was observed from sample C4 to sample C6, which corresponded to around 700 meters.
Samples P2, P3, and P4 were collected in close proximity to one another. Regarding the TC content, the highest concentrations were observed for sample P4, followed by P2 and finally P3. These results can be explained by the sampling locations; indeed, sample P4 was collected at the side of the road, whereas samples P2 and P3 were collected on the top of a table. The contribution of soil dust and dirt particles deriving from the passage of vehicles was significant for sample P4 (note the sieved sample shown in Figure 5c). Despite it showing the highest TC concentration, the IC/TC ratio was comparable to those of the other samples. Instead, sample P4 had the highest percentage of insoluble IC.
After the exclusion of samples C1, C2, and P4 (that, as discussed before, were different from each other), an ANOVA test was conducted for the two groups Claviere and Val di Pejo, and no differences in relative composition were evidenced (p ≥ 0.05 ANOVA). For this reason, on the remaining 10 samples (5 from Claviere and 5 from Val di Pejo), the average composition, reported in Figure 8, was calculated.
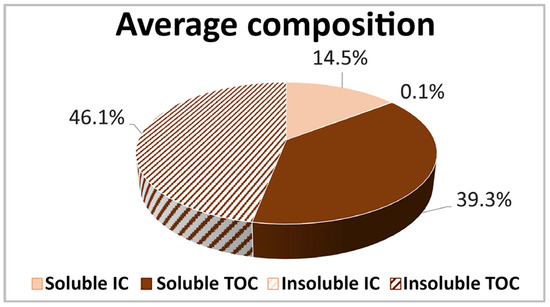
Figure 8.
Relative composition of the samples. The soluble and insoluble carbonaceous fractions were in a ratio of about 1:1.
3.2. TOT Analysis Results
The blank filters did not show significant amounts of carbon—the amount, in the few cases detected, was below the LOD. The only blank that showed signs of contamination was excluded from the averages.
Single analyses were performed on the Claviere samples, whereas the Val di Pejo filters were measured in triplicate. Based on the average CV% of the replicated measurements (please refer to Supplementary Material), a 30% uncertainty value was assigned to the samples for which no replicates were available. Figure 9 shows the results obtained.
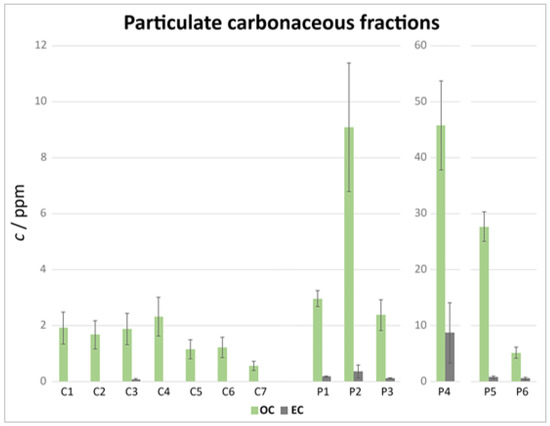
Figure 9.
Elaborated TOT results (OC and EC).
In general, for the samples from Claviere, EC was lower than the LOD. The samples from Val di Pejo, on the other hand, showed a higher amount of EC. With the exception of the roadside sample P4, the average EC contribution to the carbonaceous fraction was (6 ± 2) % (mean and pooled standard deviation of the mean). Considering that, in urban environments, EC can account for up to 15% of the total carbon in particulate matter (PM), this value is in line with the rural areas sampled in this study. The greatest EC concentrations were observed for sample P4 (>10%).
Only two samples showed a statistically significant amount of insoluble IC: P2 and P4. The insoluble IC over insoluble TC ratio was (2 ± 1) % for P2 and (30 ± 5) % for P4. While the amount of insoluble IC, probably carbonates, was negligible compared with the total carbon in P2, this was not the case for P4.
As reported in the literature, IC can interfere with OC and EC quantification using TOT. Therefore, reference standards of carbonates and bicarbonates (sodium and calcium) were subjected to TOT analyses following the NIOSH870 and EUSAAR2 protocols in order to investigate their possible interference in EC quantification. The results are reported in Figure 10 and Figure 11. Analyses with the IMPROVE_A protocol were not carried out but, as they had a maximum temperature in the inert phase that was lower than that in EUSAAR2, the behavior of carbonates was expected to be like that with EUSAAR2.
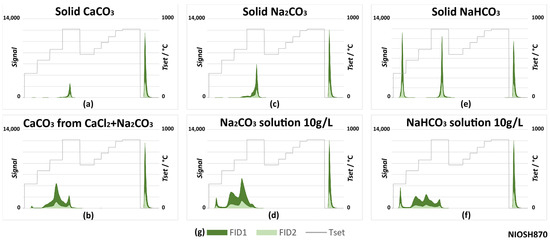
Figure 10.
Carbonates’ behaviors with the NIOSH870 TOT protocol: thermograms (a) for calcium carbonate; (b) for calcium carbonate obtained by precipitation from aqueous solution; (c) for solid sodium carbonate; (d) for sodium carbonate by deposition from solution; (e) for sodium bicarbonate; (f) for sodium bicarbonate by deposition from solution; (g) legend for all graphs.
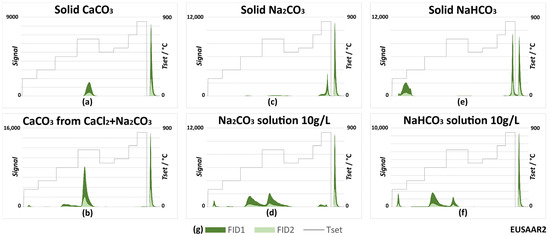
Figure 11.
Carbonates’ behaviors with the EUSAAR2 TOT protocol (the protocol applied to the snow samples): thermograms (a) for calcium carbonate; (b) for calcium carbonate obtained by precipitation from aqueous solution; (c) for solid sodium carbonate; (d) for sodium carbonate by deposition from solution; (e) for sodium bicarbonate; (f) for sodium bicarbonate by deposition from solution; (g) legend for all graphs.
Figure 10 and Figure 11 show that solid standards evolved in a rather narrow time range. With both the NIOSH870 and EUSAAR2 protocols, calcium carbonate (Figure 10a and Figure 11a) evolved as part of the OC4 fraction (870 or 650 °C, depending on the protocol), as is the usual case for the atmospheric PM samples. The same occurred for sodium carbonate analyzed using NIOSH870 (Figure 10c). However, with the EUSAAR2 protocol, sodium carbonate evolved during the second oxidizing phase (Figure 11c), interfering with the determination of EC. This is because EUSAAR2 reaches a lower maximum temperature in the inert atmosphere. Finally, tests on bicarbonates (Figure 10e and Figure 11e) showed an additional peak in the OC1 fraction and no signals in the second phase.
Differences in thermograms can be observed by changing the state of the species, from solid to solution (note the differences between Figure 10/Figure 11a and Figure 10/Figure 11b, Figure 10/Figure 11c and Figure 10/Figure 11d, Figure 10/Figure 11e and Figure 10/Figure 11f). Overall, several peaks were present in the first phase, especially with NIOSH870. Instead, peaks in the second phase, interfering with EC, could be observed using EUSAAR 2. Sodium and calcium carbonate solutions were associated with the typical peaks of bicarbonates in the inert phase. The effect was more pronounced when calcium carbonate was precipitated directly on the filter (Figure 10b and Figure 11b). In these experiments, 40 µL of Na2CO3 (10 g/L) was deposited on the filter and 60 µL of CaCl2 (10 g/L) was added. Initially, the intent was to deposit a known quantity of CaCO3 on the filter, but this option was later discarded since weighing was not feasible and depositing aliquots of saturated solution was also not possible due to the fact that the solubility of calcium carbonate is greatly affected by the partial pressure of CO2 in air [40]. These results can be explained by the equilibrium existing between the carbonate and bicarbonate species.
Regarding snow samples, according to the results of TOC analysis, inorganic carbon was absent from all samples except for P2 and P4. The presence of EC may have been due to the nature of the sample (roadside); however, possible interference caused by the presence of carbonates and bicarbonates evolving together with EC using the EUSAAR 2 protocol was possible. As will be highlighted in the following section, the high percentage of insoluble IC could also account for the disagreement between TOC analysis and TOT for sample P4 due to the overestimation of OC.
3.3. TOC and TOT Comparison
A deeper cross-reference of the data was conducted (Figure 12), comparing the results obtained from both techniques. The insoluble TOC was calculated as the difference between the sieved suspension and the filtered solution TOC and was then compared with the OC from TOT analysis. The TC detected with the two techniques was not used for the comparisons because of the considerations made regarding IC, CC, and EC in the previous sections.
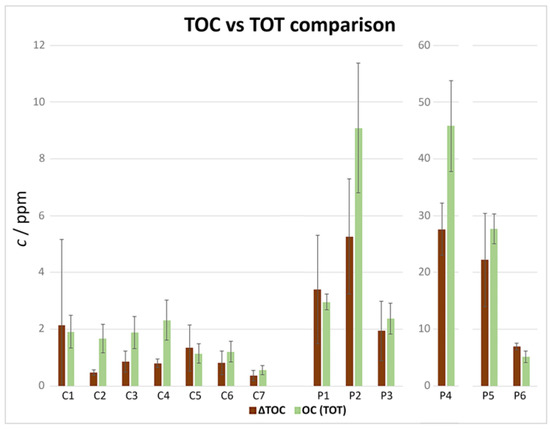
Figure 12.
Comparison of TOC and TOT results.
The results obtained with the two techniques were in agreement, suggesting the accuracy of the measurements. When the confidence intervals were not overlapping, the TOT (OC) measurements were slightly higher. Greater differences were observed for sample P4 and should be studied on a dataset with a higher number of replicates to lower the uncertainty, as well as improve the calibration, not in terms of range, but in terms of replicates over time.
3.4. ATR-FTIR Results
FTIR spectra were acquired in different points on the same filter. A certain variability in the relative intensity of the bands of the various constituents was noted. Therefore, the results were only qualitative. The results are shown for sample P4 (Figure 13), the sample with the most material deposited on the filter.
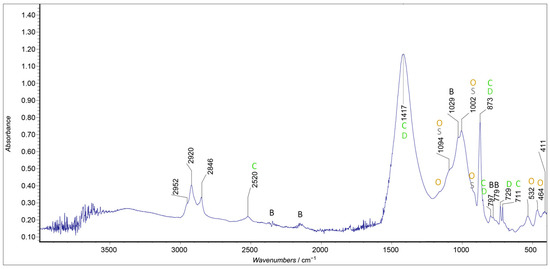
Figure 13.
ATR-IR spectra for sample P4, ATR-corrected.
The most intense signal corresponds to quartz, which was due to the nature of the filter [41]. This precluded the possibility of investigating the presence of silicates in the deposited particles.
The typical peaks of calcite were also present [42]. The weak band at 729 cm−1 indicated the presence of the mineral dolomite, chemically a carbonate of calcium and magnesium [43]. The bands at about 1420 and 873 cm−1 were also common to calcite and dolomite. Instead, the peaks at 532 and 464 cm−1 [37], together with the small shoulder present at 913 cm−1, were ascribed to the presence of ochre, a mixture of iron oxides. The shoulders at 1110 and 1165 cm−1 could also be ascribable to the presence of ochre. The very broad peak present at around 3300 cm−1 was due to the stretching of the hydroxyl group, probably due to the presence of liquid water, even if the contribution of hydration molecules, rather than an alcohol or carbohydrate component, could not be distinguished, given the presence of the peaks at about 2900 cm−1, corresponding to the symmetric and asymmetric stretching of -CH groups.
3.5. SEM-EDX Analysis Results
The coarse fraction deposited on the filter of sample P4 was also investigated by SEM-EDX analyses (Figure 14 and Figure 15).
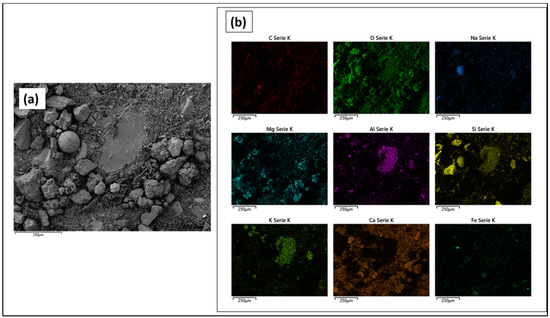
Figure 14.
(a) P4 SEM image, mix of secondary and backscattered detection; (b) Elemental EDX maps.

Figure 15.
(a) Sample P4 SEM-EDX composite image; (b) another part of sample P4.
From the maps, it can be observed that the larger particles mainly consisted of silicates, due to the co-presence of silicon, oxygen, aluminum, sodium, potassium, calcium, and magnesium in the same area.
The simultaneous presence of all these elements in the same area can be ascribed to clays and ochres.
4. Discussion
4.1. Blank Analysis
Regarding TOC analysis, the measurements of the blanks proved to be crucial in highlighting certain strengths and weaknesses of the method. Indeed, the analysis of four blanks led to the conclusion that the residence time required for TOC analysis in the glass beaker was too long. The analysis of a blank processed in the same beaker used for sample P4 and rinsed in milli-Q resulted in the fouling of the blank. A jet of milli-Q water was not sufficient to remove all the EC particles attached to the walls; therefore, mechanical removal with paper followed by further washing was required. Given the low concentrations of EC in the other analyzed samples (the EC analysis was considered reliable—the residence time in glass for filtration was minimal), we assumed that the use of glass did not affect these results significantly. A more in-depth study needs to be performed to obtain reliable conclusions on the matter, considering that some authors reported that plastic can also retain particles [23].
4.2. Comments on the Snow Sample Composition
First, it is important to underline that the purpose of this work was the development of a new method for the analysis of the carbonaceous fraction, and all other considerations regarding the results of the study are secondary.
Both TOC analysis and TOT agreed on the fact that Claviere samples were less polluted than those from Val di Pejo. Higher urbanization and vehicular traffic were the two driving factors behind this difference. Another explanation could be related to the age of the snow; indeed, fresh snow samples were collected in Claviere, whereas aged snow (from a few days to a couple of weeks) was sampled in Val di Pejo, except for samples P3 and P6, which were fresh. The absolute concentrations in these two samples were, in fact, comparable to those of the samples from Claviere. These results may indicate that, in addition to the co-deposition of particulate matter during snowfall, the concentrations of the carbonaceous fractions may increase as the surface layer remains exposed to the atmosphere for more time.
In terms of the relative concentrations, a significant difference between the two sites was not observed, indicating similar sources of pollution. In order to further investigate the impact of the different sources, future work will entail the study of levoglucosan, a known marker of biomass combustion produced by the pyrolysis of cellulose, which is present in the soluble TOC fraction [44].
Moving on, ATR-FTIR analysis confirmed the abundant presence of carbonates in sample P4 (due to terrigenous constituents), together with ochres, as was suggested by the pale red color of the filter following TOT analysis.
4.3. Inorganic Carbon
Inorganic carbon is usually negligible in atmospheric PM, but this was not the case for the analyzed snow samples. TOC analysis revealed that sample P4 was the only one in which insoluble IC was detected, which was probably related to the fact that this sample was also associated with the abundant presence of terrigenous constituents. This component was negligible in all the other samples, probably because P4 was the only one in direct contact with the soil. In order to confirm the relationship between insoluble IC and terrigenous constituents, further studies will be necessary to investigate the relationship between the soluble and insoluble fractions. In fact, some authors in the literature [38] state that a large percentage of the inorganic carbon, which is insoluble in snow, passes into the soluble fraction during melting.
Regarding TOT, being the different components operationally defined carbonaceous fraction, the results are strictly dependent on the temperature protocol used. In the case of CC, also taking into consideration the chemical nature of the species, these will evolve at different points during analysis. The only one that evolved, as expected, in the OC4 fraction was anhydrous calcium carbonate. However, this may not be the only species evolving in this time frame, as peaks were also observed for samples in which insoluble IC was not detected via TOC analysis. Changing the state of the substances (solid vs. solution) had a significant impact on the results, as the carbonate–bicarbonate equilibrium is established in solution. For these reasons, in the analysis of snow samples that have melted, carbonate carbon should be eliminated a priori by exposure to gaseous HCl [38].
These conclusions further emphasize the importance of the complementarity of the two analytical techniques (TOC analysis and TOT). The main example was sample P4, in which the contamination due to carbonates could explain both the unusually high presence of EC and the large difference in the results of the two techniques for this sample, as both OC and EC could have been overestimated because of the presence of insoluble IC.
4.4. Larger Particles
The uncertainties associated with OC and EC measurements are representative of the reproducibility of the various steps of the method (stirring, filtration, …). Taking larger particles from the stirred solution depends on the efficiency of the stirring in keeping the suspension homogeneous. The most critical step, mainly for larger particles, is filtration, particularly in depositing the material homogeneously.
However, in accordance with the SEM-EDX analysis (Figure 14), the largest particles were not those with the highest carbon content. This certainly reduces the potential impact of the problem without indicating that it should be completely overlooked.
5. Conclusions
In order to optimize all the steps of the method, samples from two Northern Italian locations were analyzed. Both visually clean and contaminated samples were chosen in order to evaluate the effect of high pollutant concentrations. Depending on the nature of the sample, the different steps of the method were optimized. Melting was carried out at 30 °C and achieved in a very short time. Sieved samples were kept under stirring for TOC analysis in order to maximize their homogeneity. Filtration was conducted by taking 5 to 50 mL from the samples, kept under stirring. Glass containers proved not to be optimal for highly contaminated samples. The samples were analyzed mainly using Total Organic Carbon analysis (attention was paid to choosing the right injection volumes in order to maximize sensitivity) and Thermal Optical analysis in the Transmittance mode (EUSAAR2 protocol was chosen due to the potentially high presence of minerals). The proposed method allowed the analysis of the operational carbonaceous fractions TC, TOC, IC, OC, and EC, categorizing them as soluble and insoluble. Blank analysis proved to be effective in highlighting possible issues. Regarding the samples, it was found that fresh snow and snow sheltered from atmospheric deposition showed similar levels of contamination. About 50% of the carbonaceous content was part of the insoluble fraction. The insoluble IC content was significant only for the one sample contaminated with large soil debris.
The main source of uncertainty was found to be the inhomogeneity of the samples, which affected the repeatability of several of the method’s steps (sampling for filtration, sampling for TOC analysis, sampling for TOT). This situation also affected the choices regarding data treatment (see Supplementary Material).
Attention was drawn to the use of the TOT technique, which is routinely used for the analysis of atmospheric particulate matter. The presence of insoluble carbonate and bicarbonate species in snow samples represented, in fact, an interference in the OC and EC measurements by TOT; the combined use of both TOT and TOC techniques is, therefore, necessary. Indeed, various carbonates and bicarbonates were tested with the EUSAAR2 protocol, and they evolved both in the OC and EC regions of the thermogram.
Samples were further analyzed by ATR-FTIR and SEM-EDX. IR analysis confirmed the presence of calcite and dolomite in the most contaminated sample, while SEM-EDX analysis was useful to assert that the larger particles in suspension contained a lower percentage of carbon, being composed of aluminum silicates.
Correlations between the characteristics of the samples (i.e., location, age, and exposure of the snow) and the experimental results were found. This work carried out on snow samples thus made it possible to confirm the validity of the proposed method, which was intended to find homogeneity in the fragmentary literature; the method is applicable in the context of studying the darkening of snow and ice surfaces with regards to the carbonaceous components. The developed analytical method, based on TOC and TOT analyses, will be used in the quantification of the carbonaceous fractions of snow and ice samples from different Italian sites.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/atmos14020371/s1. Supplementary QA QC.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, P.F. and S.G.; methodology, M.B. and P.F.; validation, P.F., S.G., M.L. and M.B.; formal analysis, V.G.; investigation, M.B.; data curation, V.C., A.B. and C.A.L.; writing—original draft preparation, M.B. and P.F.; writing—review and editing, A.B., V.C., S.G., B.D.M. and M.B.; supervision, P.F.; project administration, P.F. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Wang, X.; Wei, H.; Liu, J.; Xu, B.; Wang, M.; Ji, M.; Jin, H. Quantifying the Light Absorption and Source Attribution of Insoluble Light-Absorbing Particles on Tibetan Plateau Glaciers between 2013 and 2015. Cryosphere 2019, 13, 309–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skiles, S.M.K.; Flanner, M.; Cook, J.M.; Dumont, M.; Painter, T.H. Radiative Forcing by Light-Absorbing Particles in Snow. Nat. Clim. Change 2018, 8, 964–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IPCC Special Report: The Ocean and Cryosphere in a Changing Climate. 2019. Available online: https://www.ipcc.ch/report/srocc/ (accessed on 10 December 2022).
- di Mauro, B. A Darker Cryosphere in a Warming World. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2020, 10, 979–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamilton, T.L.; Havig, J.R. Inorganic Carbon Addition Stimulates Snow Algae Primary Productivity. ISME J. 2020, 14, 857–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- John Maurer Retrieval of Surface Albedo from Space. Available online: http://www2.hawaii.edu/~jmaurer/albedo/ (accessed on 20 December 2022).
- Kuchiki, K.; Aoki, T.; Niwano, M.; Matoba, S.; Kodama, Y.; Adachi, K. Elemental Carbon, Organic Carbon, and Dust Concentrations in Snow Measured with Thermal Optical and Gravimetric Methods: Variations during the 2007-2013 Winters at Sapporo, Japan. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2015, 120, 868–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ielpo, P.; Mangia, C.; de Gennaro, G.; di Gilio, A.; Palmisani, J.; Dinoi, A.; Bergomi, A.; Comite, V.; Fermo, P. Air Quality Assessment of a School in an Industrialized Area of Southern Italy. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 8870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergomi, A.; Morreale, C.; Fermo, P.; Migliavacca, G. Determination of Pollutant Emissions from Wood-Fired Pizza Ovens. Chem. Eng. Trans. 2022, 92, 499–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- di Mauro, B.; Fava, F.; Ferrero, L.; Garzonio, R.; Baccolo, G.; Delmonte, B.; Colombo, R. Mineral Dust Impact on Snow Radiative Properties in the European Alps Combining Ground, UAV, and Satellite Observations. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2015, 120, 6080–6097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinase, T.; Kita, K.; Tsukagawa-Ogawa, Y.; Goto-Azuma, K.; Kawashima, H. Influence of the Melting Temperature on the Measurement of the Mass Concentration and Size Distribution of Black Carbon in Snow. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2016, 9, 1939–1945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keil, A.; Haywood, J.M. Solar Radiative Forcing by Biomass Burning Aerosol Particles during SAFARI 2000: A Case Study Based on Measured Aerosol and Cloud Properties. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2003, 108, SAF3-1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doherty, S.J.; Grenfell, T.C.; Forsström, S.; Hegg, D.L.; Brandt, R.E.; Warren, S.G. Observed Vertical Redistribution of Black Carbon and Other Insoluble Light-Absorbing Particles in Melting Snow. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2013, 118, 5553–5569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aamaas, B.; Bøggild, C.E.; Stordal, F.; Berntsen, T.; Holmén, K.; Ström, J. Elemental Carbon Deposition to Svalbard Snow from Norwegian Settlements and Long-Range Transport. Tellus B Chem. Phys. Meteorol. 2011, 63, 340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagler, G.S.W.; Bergin, M.H.; Smith, E.A.; Dibb, J.E.; Anderson, C.; Steig, E.J. Particulate and Water-Soluble Carbon Measured in Recent Snow at Summit, Greenland. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2007, 34, L16505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuccia, E.; Gianelle, V.; Dal Santo, U.; Colombi, C. Campagna Di Misura Della Qualità Dell’Aria—Relazione Finale—Comune Di Rezzato; ARPA Lombardia: Milan, Italy, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Lack, D.A.; Moosmüller, H.; McMeeking, G.R.; Chakrabarty, R.K.; Baumgardner, D. Characterizing Elemental, Equivalent Black, and Refractory Black Carbon Aerosol Particles: A Review of Techniques, Their Limitations and Uncertainties. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2013, 406, 99–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petzold, A.; Ogren, J.A.; Fiebig, M.; Laj, P.; Li, S.M.; Baltensperger, U.; Holzer-Popp, T.; Kinne, S.; Pappalardo, G.; Sugimoto, N.; et al. Recommendations for Reporting Black Carbon Measurements. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2013, 13, 8365–8379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beres, N.D.; Sengupta, D.; Samburova, V.; Khlystov, A.Y.; Moosmüller, H. Deposition of Brown Carbon onto Snow: Changes in Snow Optical and Radiative Properties. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2020, 20, 6095–6114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, P.; Liu, J.; Shilling, J.E.; Kathmann, S.M.; Laskin, J.; Laskin, A. Molecular Characterization of Brown Carbon (BrC) Chromophores in Secondary Organic Aerosol Generated from Photo-Oxidation of Toluene. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2015, 17, 23312–23325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ming, J.; Xiao, C.; Cachier, H.; Qin, D.; Qin, X.; Li, Z.; Pu, J. Black Carbon (BC) in the Snow of Glaciers in West China and Its Potential Effects on Albedos. Atmos. Res. 2009, 92, 114–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legrand, M.; Preunkert, S.; Jourdain, B.; Guilhermet, J.; Faïn, X.; Alekhina, I.; Petit, J.R. Water-Soluble Organic Carbon in Snow and Ice Deposited at Alpine, Greenland, and Antarctic Sites: A Critical Review of Available Data and Their Atmospheric Relevance. Clim. Past 2013, 9, 2195–2211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Doherty, S.J.; Huang, J. Black Carbon and Other Light-Absorbing Impurities in Snow across Northern China. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2013, 118, 1471–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Kang, S.; Gao, T.; Schmale, J.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, W.; Guo, J.; Du, W.; Hu, Z.; Cui, X.; et al. Dissolved Organic Carbon in Snow Cover of the Chinese Altai Mountains, Central Asia: Concentrations, Sources and Light-Absorption Properties. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 647, 1385–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawamura, K.; Matsumoto, K.; Tachibana, E.; Aoki, K. Low Molecular Weight (C 1-C 10) Monocarboxylic Acids, Dissolved Organic Carbon and Major Inorganic Ions in Alpine Snow Pit Sequence from a High Mountain Site, Central Japan. Atmos. Environ. 2012, 62, 272–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doherty, S.J.; Dang, C.; Hegg, D.A.; Zhang, R.; Warren, S.G. Black Carbon and Other Light-Absorbing Particles in Snow of Central North America. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2014, 119, 12–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, S.; Faïn, X.; Zanatta, M.; Cozic, J.; Jaffrezo, J.L.; Ginot, P.; Laj, P. Refractory Black Carbon Mass Concentrations in Snow and Ice: Method Evaluation and Inter-Comparison with Elemental Carbon Measurement. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2014, 7, 3307–3324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarz, J.P.; Gao, R.S.; Perring, A.E.; Spackman, J.R.; Fahey, D.W. Black Carbon Aerosol Size in Snow. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meinander, O.; Heikkinen, E.; Aurela, M.; Hyvärinen, A. Sampling, Filtering, and Analysis Protocols to Detect Black Carbon, Organic Carbon, and Total Carbon in Seasonal Surface Snow in an Urban Background and Arctic Finland (>60° N). Atmosphere 2020, 11, 923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svensson, J.; Ström, J.; Kivekäs, N.; Dkhar, N.B.; Tayal, S.; Sharma, V.P.; Jutila, A.; Backman, J.; Virkkula, A.; Ruppel, M.; et al. Light-Absorption of Dust and Elemental Carbon in Snow in the Indian Himalayas and the Finnish Arctic. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2018, 11, 1403–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavalli, F.; Viana, M.; Yttri, K.E.; Genberg, J.; Putaud, J.P. Toward a Standardised Thermal-Optical Protocol for Measuring Atmospheric Organic and Elemental Carbon: The EUSAAR Protocol. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2010, 3, 79–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.; Takano, Y.; Liou, K.N.; Yang, P.; Li, Q.; Chen, F. Impact of Snow Grain Shape and Black Carbon-Snow Internal Mixing on Snow Optical Properties: Parameterizations for Climate Models. J. Clim. 2017, 30, 10019–10036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bautista, A.T.; Pabroa, P.C.B.; Santos, F.L.; Quirit, L.L.; Asis, J.L.B.; Dy, M.A.K.; Martinez, J.P.G. Intercomparison between NIOSH, IMPROVE_A, and EUSAAR_2 Protocols: Finding an Optimal Thermal-Optical Protocol for Philippines OC/EC Samples. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2015, 6, 334–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannoni, M.; Calzolai, G.; Chiari, M.; Cincinelli, A.; Lucarelli, F.; Martellini, T.; Nava, S. A Comparison between Thermal-Optical Transmittance Elemental Carbon Measured by Different Protocols in PM2.5 Samples. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 571, 195–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashley, K.; O’Connor, P.F. NIOSH Manual of Analytical Methods (NMAM), 5th ed.; Cdc, 2017. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/niosh/nmam/pdfs/nmam_5thed_ebook.pdf (accessed on 17 May 2022).
- Kuchiki, K.; Aoki, T.; Niwano, M. Possible Causes of Error in Measurement of Mass Concentration of Snow Impurities –Effects of a Filter and Carbonate Carbon. In Proceedings of the Summaries of JSSI and JSSE Joint Conference on Snow and Ice Research; 2010; Volume 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sala, M.; Delmonte, B.; Frezzotti, M.; Proposito, M.; Scarchilli, C.; Maggi, V.; Artioli, G.; Dapiaggi, M.; Marino, F.; Ricci, P.C.; et al. Evidence of Calcium Carbonates in Coastal (Talos Dome and Ross Sea Area) East Antarctica Snow and Firn: Environmental and Climatic Implications. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2008, 271, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clow, D.W.; Ingersoll, G.P. Particulate Carbonate Matter in Snow from Selected Sites in the South-Central Rocky Mountains. Atmos. Environ. 1994, 28, 575–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellinzona, C. Ottimizzazione Di Una Metodologia Analitica Tramite Metodi Termici e Termo-Ottici per Lo Studio Della Composizione e Origine Delle Particelle Assorbenti Nella Neve. Master’s degree Thesis, Università degli Studi di Milano-Bicocca, Milan, Italy, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Coto, B.; Martos, C.; Peña, J.L.; Rodríguez, R.; Pastor, G. Effects in the Solubility of CaCO3: Experimental Study and Model Description. Fluid Phase Equilib 2012, 324, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ATR-IR Spectrum of Quartz. Available online: https://spectra.chem.ut.ee/paint/fillers/quartz/ (accessed on 20 December 2022).
- ATR-IR Spectrum of Calcite. Available online: https://spectra.chem.ut.ee/paint/fillers/calcite/ (accessed on 20 December 2022).
- ATR-IR Spectrum of Dolomite. Available online: https://spectra.chem.ut.ee/paint/fillers/dolomite/ (accessed on 20 December 2022).
- Pietrogrande, M.C.; Bacco, D.; Visentin, M.; Ferrari, S.; Poluzzi, V. Polar Organic Marker Compounds in Atmospheric Aerosol in the Po Valley during the Supersito Campaigns-Part 1: Low Molecular Weight Carboxylic Acids in Cold Seasons. Atmos. Environ. 2014, 86, 164–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).