Spatial Distribution and Trends of Wind Energy at Various Time Scales over the South China Sea
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Data and Methods
2.1. Data
2.2. Method
2.2.1. Mean Wind
2.2.2. Mean Wind Power Density
2.2.3. Linear Regression Method
2.2.4. Student’s t-Test
2.3. Workflow
3. Spatial Distribution of Wind Energy over the SCS
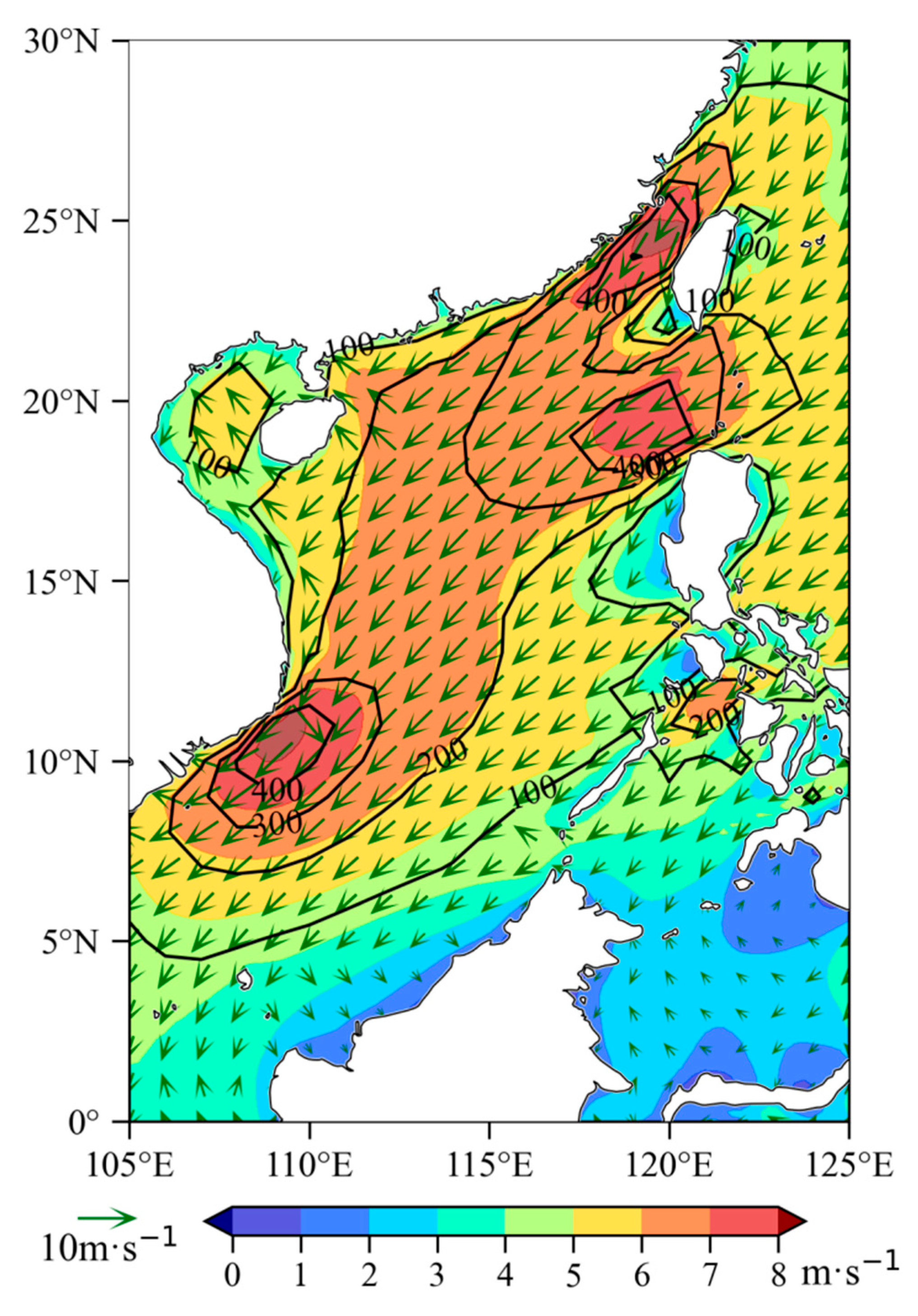
3.1. Annual Mean Distribution
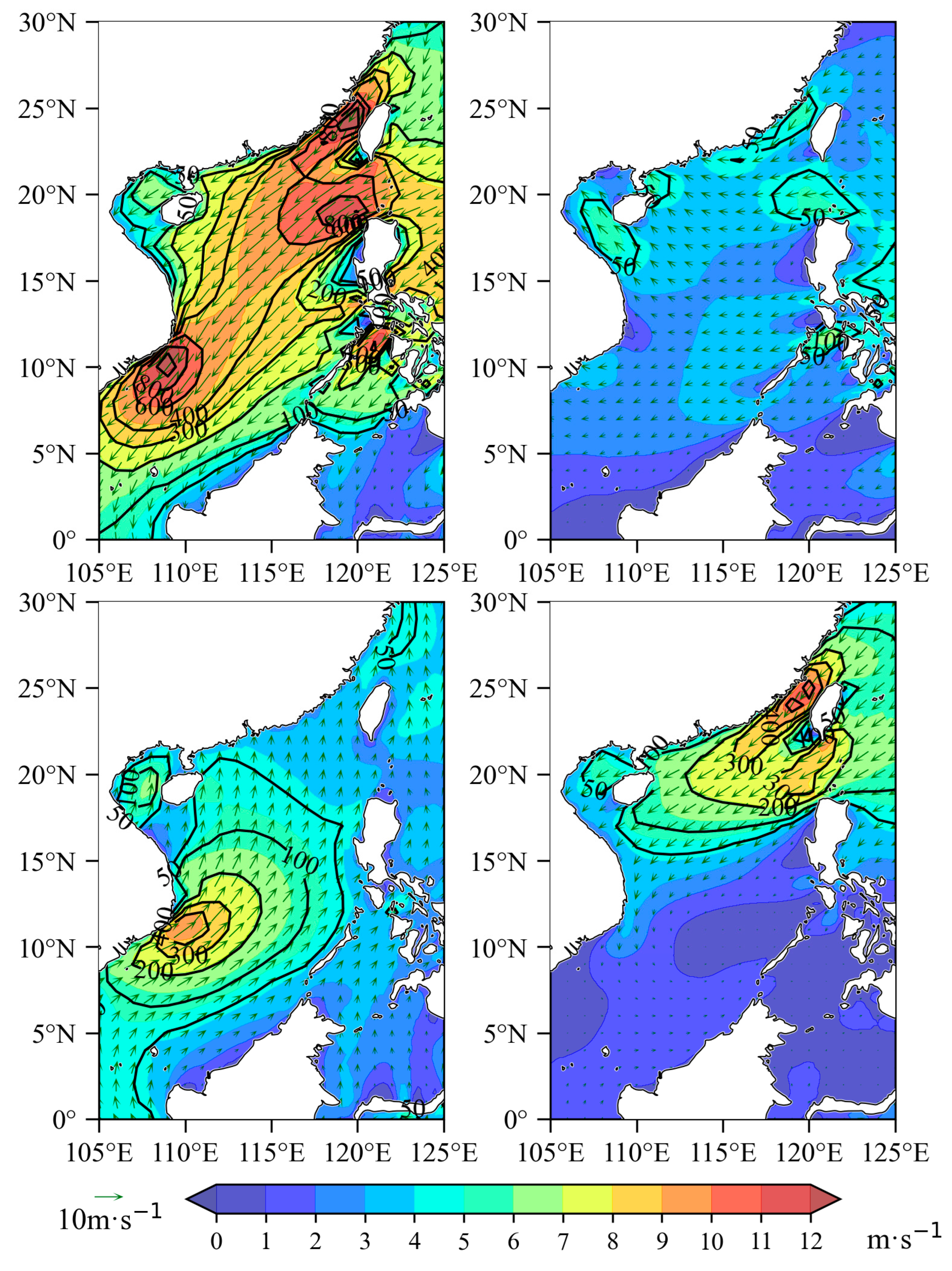
3.2. Seasonal Mean Distribution
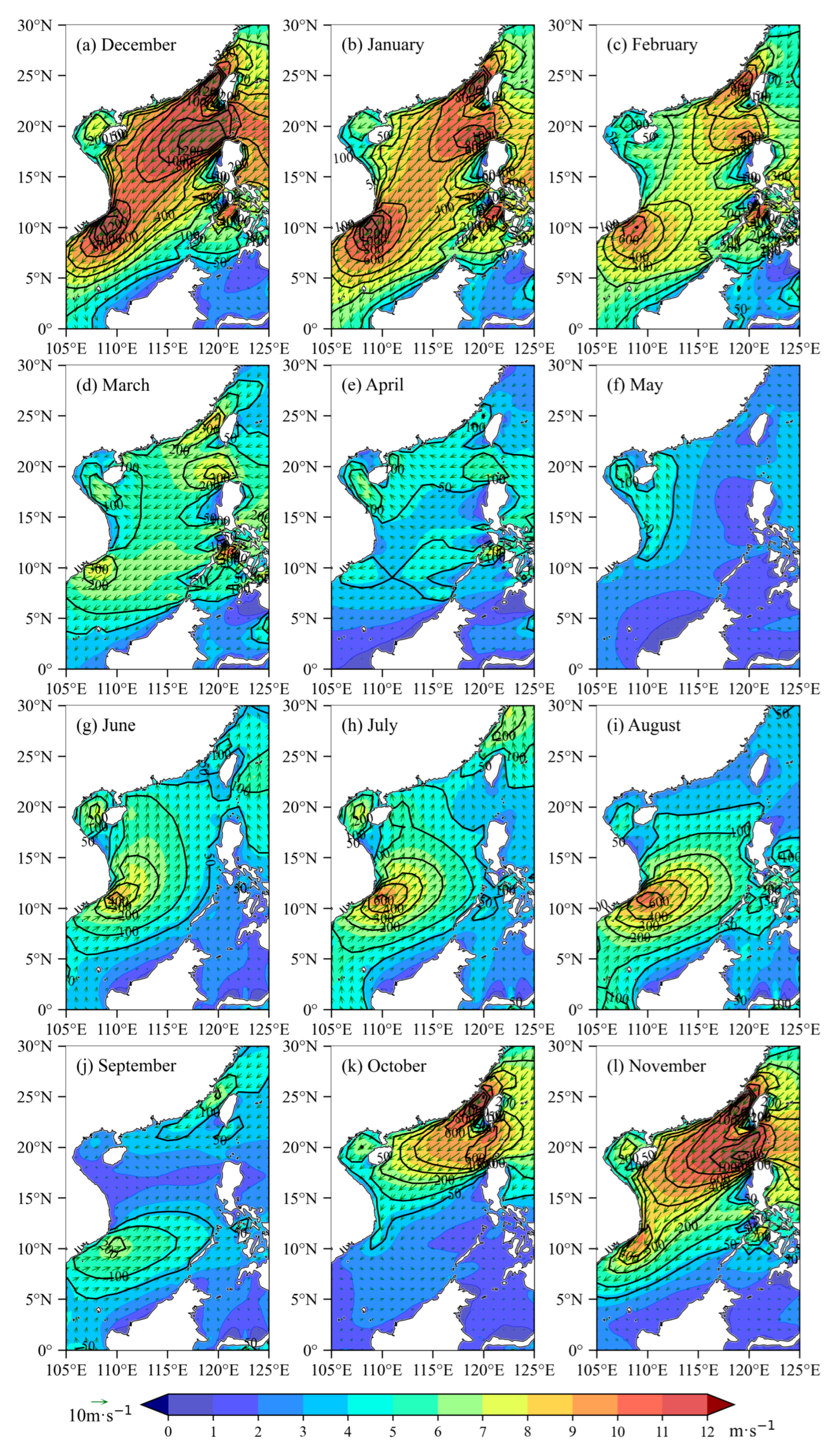
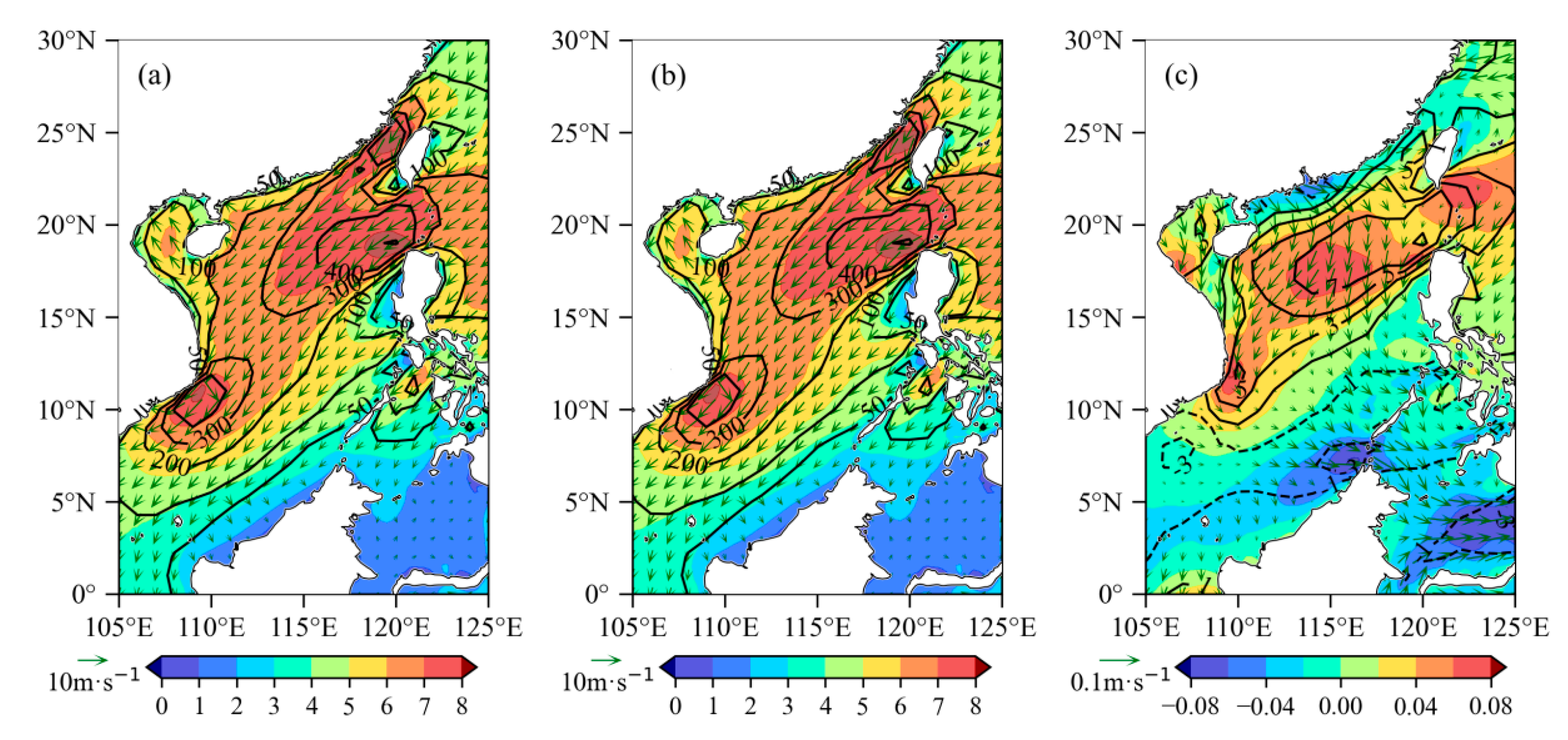
3.3. Monthly Mean Distribution
4. Trends of Wind Energy
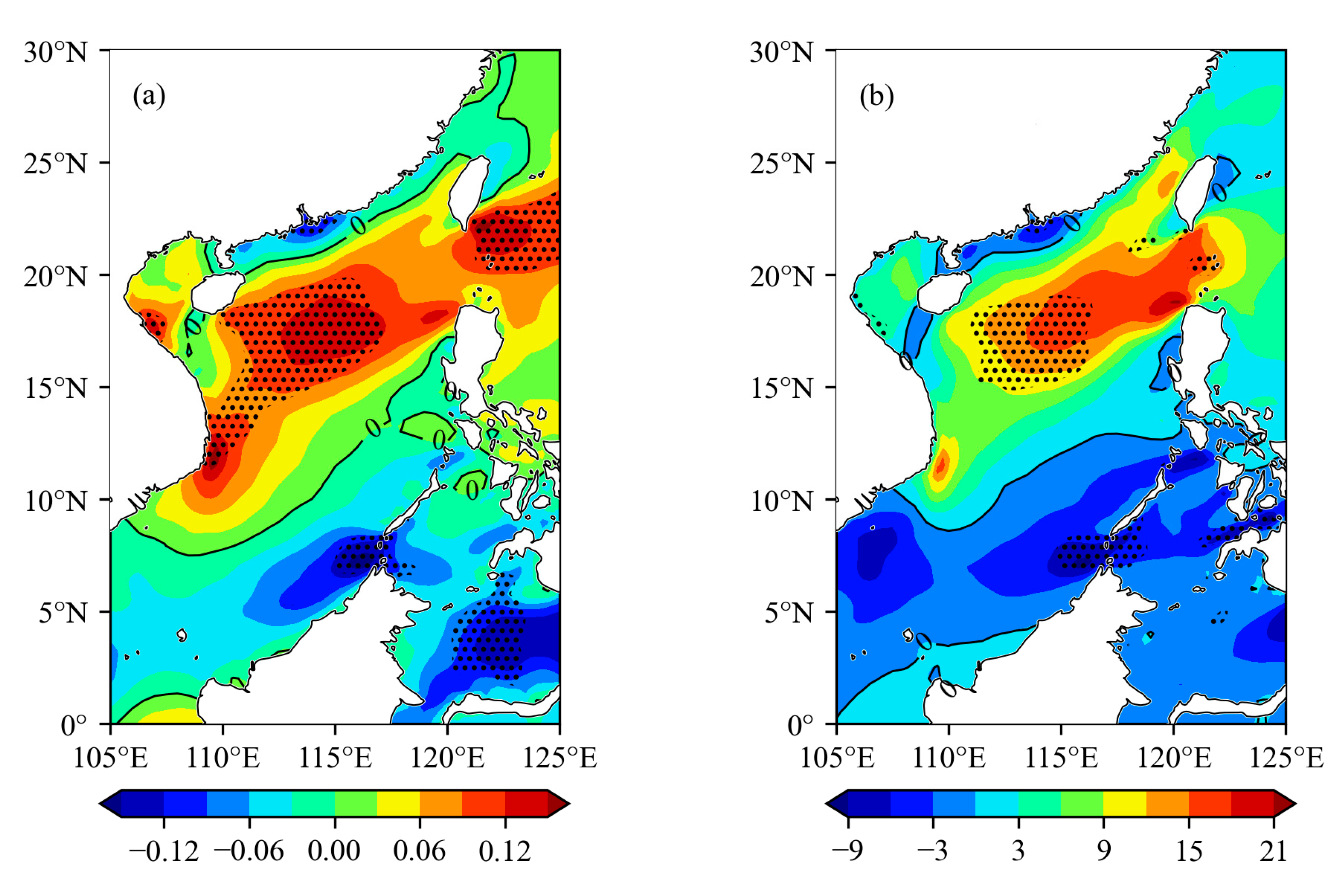
4.1. Trends of Annual Mean Wind Energy
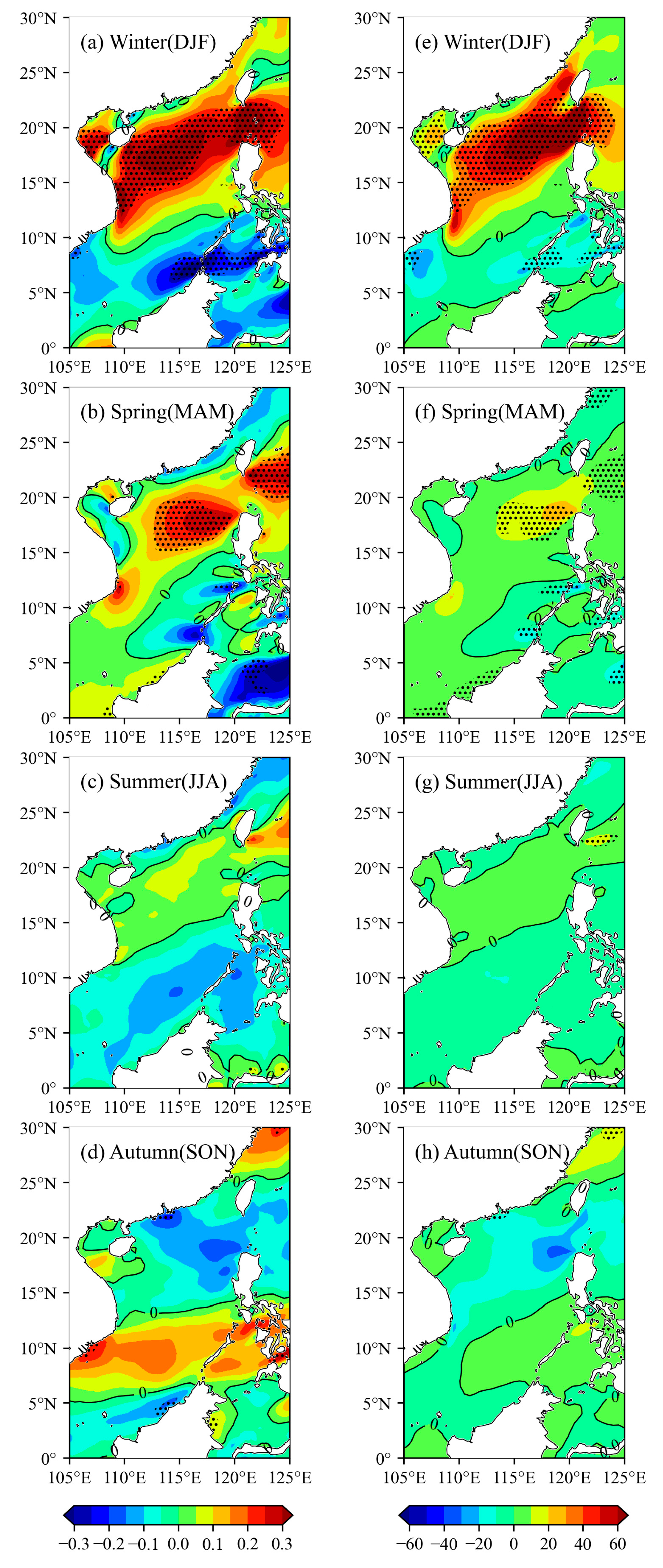
4.2. Trends of Seasonal Mean Wind Energy
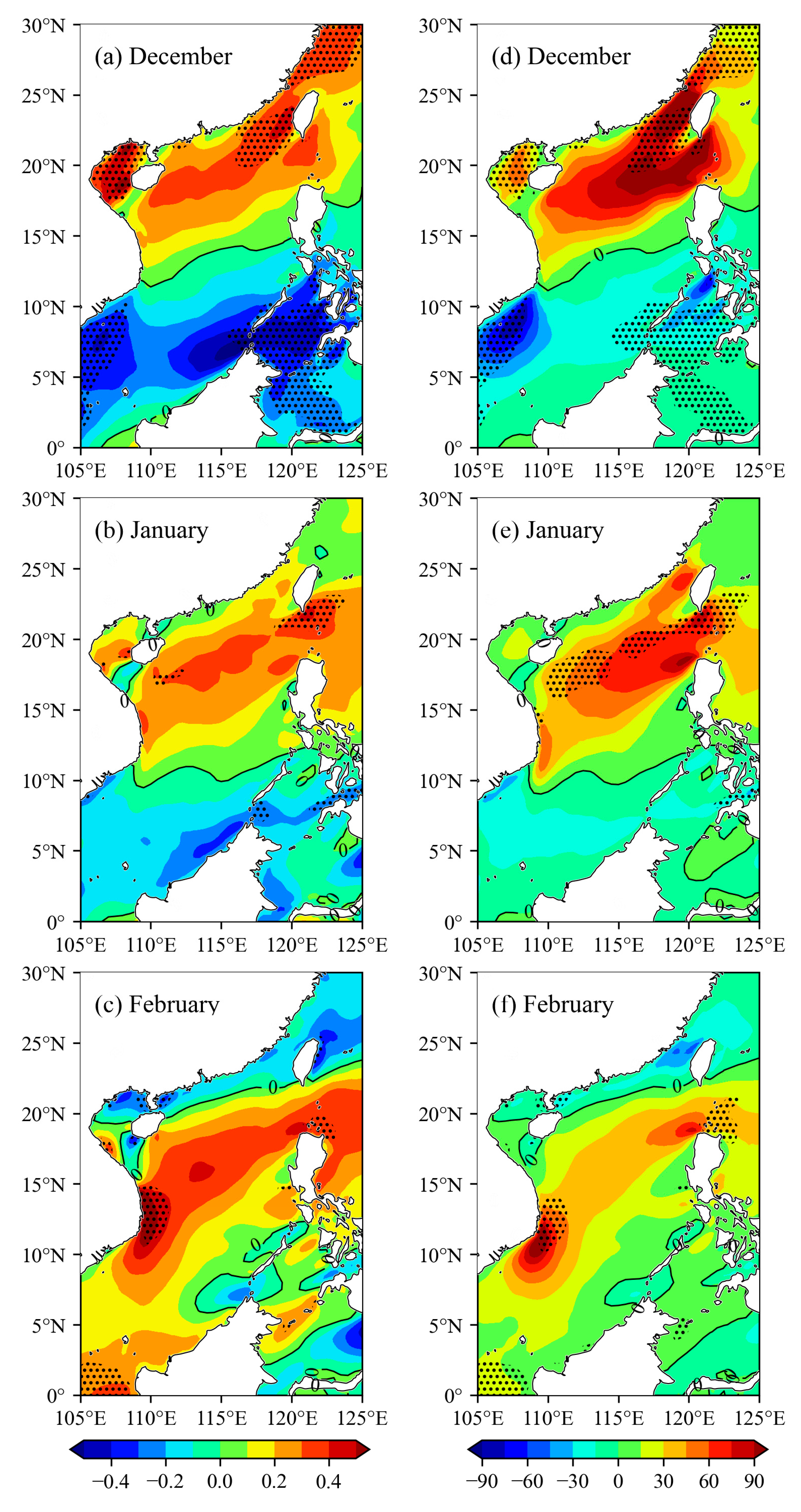
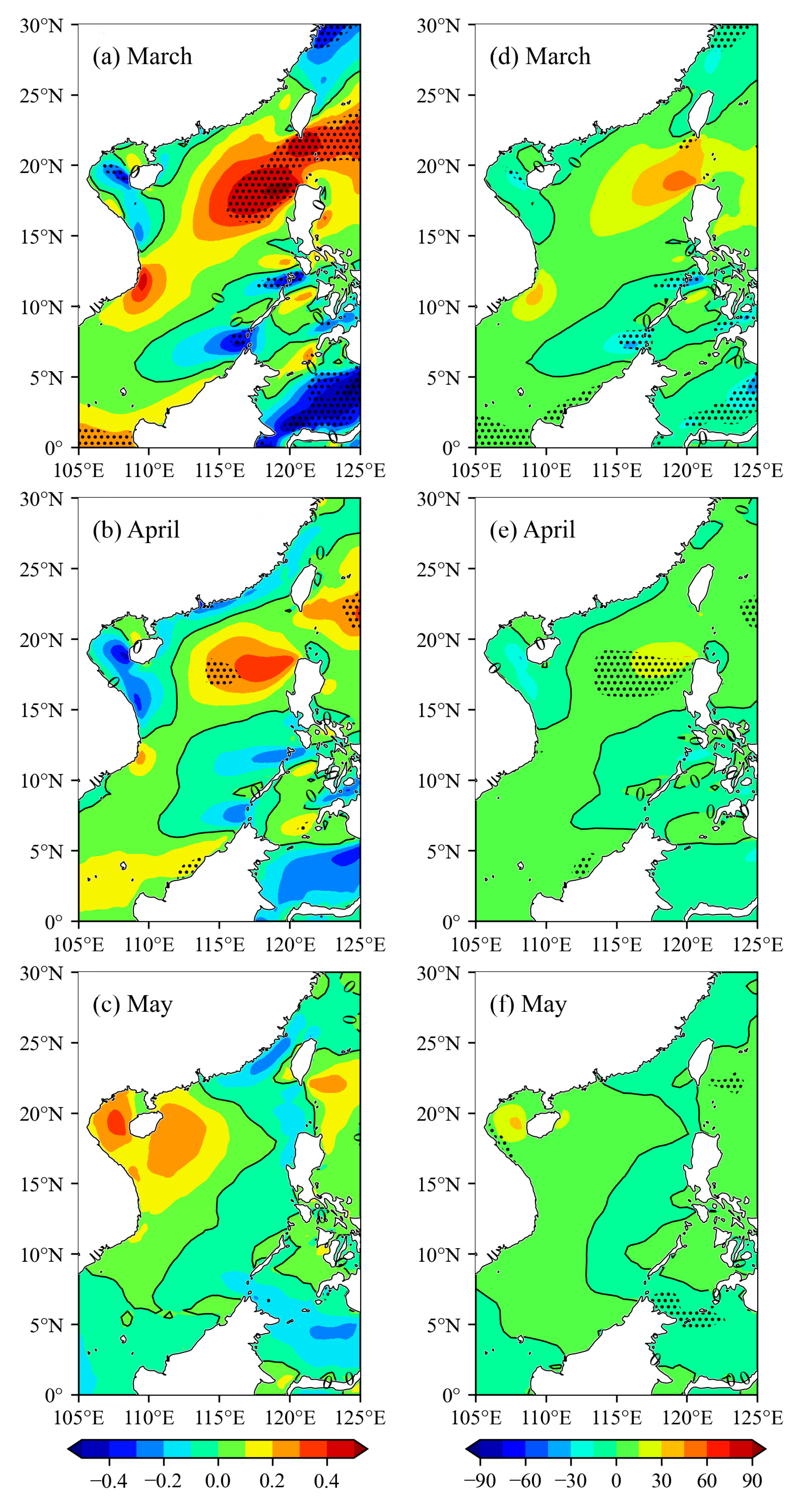
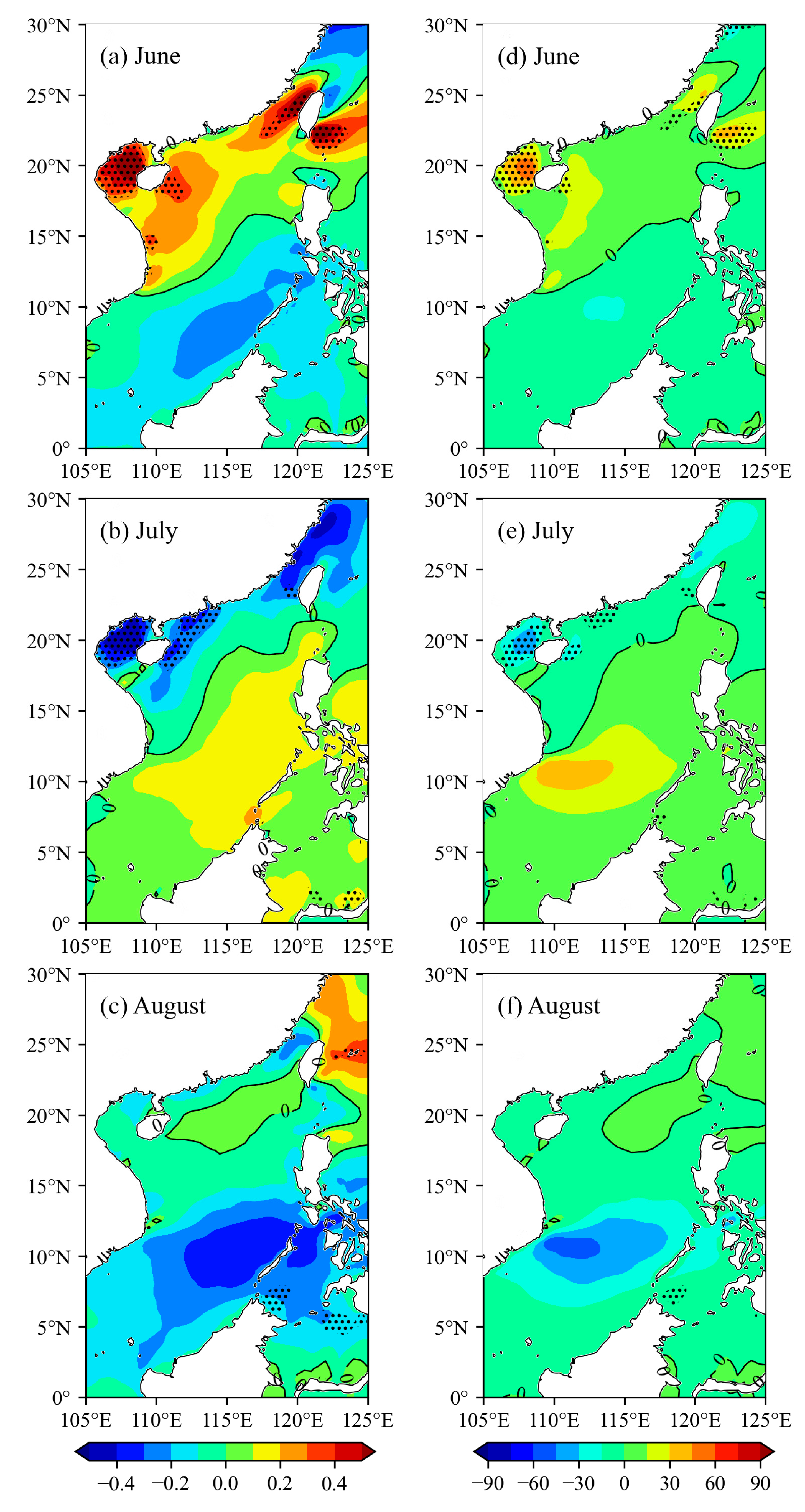
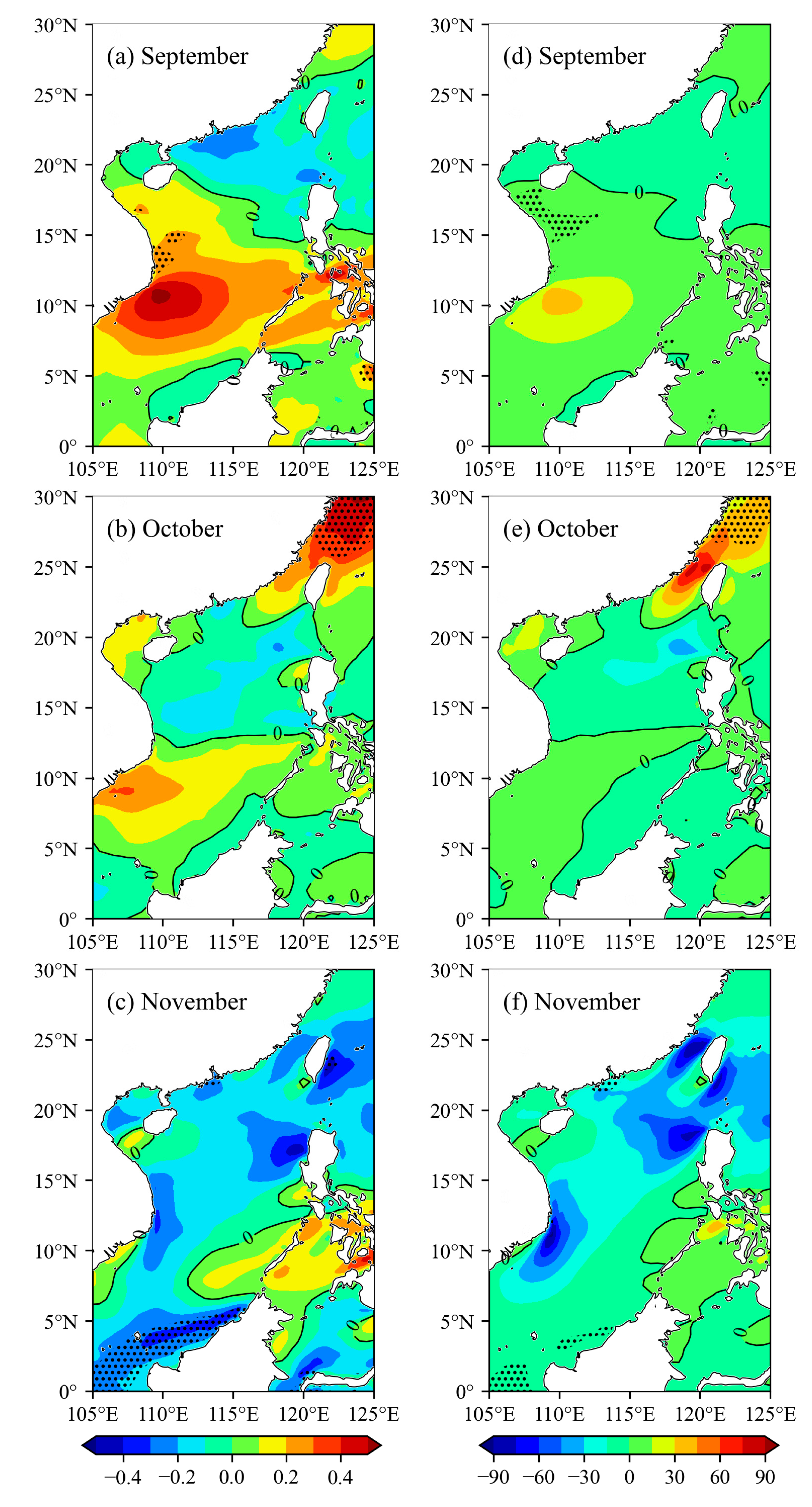
4.3. Trends of Monthly Mean Wind Energy
4.4. Prediction of Spatial Distribution of Wind Energy over the SCS
5. Conclusion and Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Díaz, C.H. Guedes Soares. Review of the current status, technology and future trends of offshore wind farms. Ocean Eng. 2020, 209, 107381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renewables Consulting Group. GWEC 2020. Glob. Offshore Wind Rep. 2020, 2020, 130. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.; Zhao, F. GWEC global wind report 2019. Wind Energy Technol. 2020, 78. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.P.; Wang, K.M.; Zhang, Z.H.; Zeng, Y.D.; Zhang, Y.; O’Driscoll, K. An assessment of wind and wave climate as potential sources of renewable energy in the nearshore Shenzhen coastal zone of the South China Sea. Energy 2017, 134, 789–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, K.J. Calculation and Analysis of Wind Energy Resources in Guangdong Province. Trop. Weather 1989, 1, 79–84. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.Z.; Xu, J.W. China Offshore Wind Energy Resources Assessment. Wind Energy 2009, 3, 44–47. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.Q. Research on Wind Farm Site Selection Based on Wind Resource Assessment. Strateg. Emerg. Ind. China 2018, 40, 16. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Srensen, B. A New Method for Estimating Off-shore Wind Potentials. Int. J. Green Energy 2008, 5, 139–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheridan, B.; Baker, S.D.; Pearre, N.S.; Firestone, J.; Kempton, W. Calculating the Offshore Wind Power Resource. Robust Assessment Methods Applied to the US Atlantic Coast. Renew. Energy 2012, 43, 224–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.W.; Luo, Y.; Zhang, X.Z.; Zhu, R. China Offshore Wind Energy Resources Assessment with the QuikSCAT Data. Soc. Photo-Opt. Instrum. Eng. 2008, 7105, 80–89. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, Q.Y.; Huang, R.; Zhuang, L.W.; Zhang, K.Y.; Huang, J.F. Assessment of China’s Offshore Wind Resources Based on the Integration of Multiple Satellite Data and Meteorological Data. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruun Christiansen, M.; Koch, W.; Horstmann, J.; Hasager, C.B.; Nielsen, M. Wind resource assessment from C-band SAR. Remote Sens. Environ. 2006, 105, 68–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.S.; Cheng, Y.C.; Li, Y.Z. Variability of Wind Energy in the South China Sea. In Proceedings of the 2022 Photonics & Electromagnetics Research Symposium (PIERS), Hangzhou, China, 25–29 April 2022; pp. 456–459. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, R.; Zhu, R.; Merete Badger Charlotte Bay Hasager Xing, X.H.; Jiang, Y.R. Offshore Wind Resources Assessment from Multiple Satellite Data and WRF Modeling over South China Sea. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 467–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Chan, P.W.; Li, Q.; Lee, C.W. Spatiotemporal analysis of offshore wind field characteristics and energy potential in Hong Kong. Energy 2020, 201, 117622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, S.; Gong, Y.J.; Wang, Z.F.; Incecik, A. Wind and wave energy resources assessment around the Yangtze River Delta. Ocean Eng. 2019, 182, 75–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.F.; Li, P.L.; Zhai, F.G.; Gu, Y.Z.; Liu, Z.Z. Evaluation of different wind resources in simulating wave height for the Bohai, Yellow, and East China Seas (BYES) with SWAN model. Continent. Shelf Res. 2020, 207, 104217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Guo, J.H.; Li, W.; Zhang, F.; Xiao, C.; Pan, Z.R. Changes in wind energy potential over China using a regional climate model ensemble. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2022, 159, 112219. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.F.; Duan, C.L.; Dong, S. Long-term wind and wave energy resource assessment in the South China sea based on 30-year hindcast data. Ocean Eng. 2018, 163, 58–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, R.; Zhang, D.; Wang, Y.D.; Xing, X.H.; Li, Z.C. Assessment of wind energy potential in China. Eng. Sci. 2009, 7, 18–26. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, S.L.; Feng, S.L.; Wang, B.; Hu, J.; Ma, Z.Q.; Song, Z.P. Assessment of offshore wind resource in China using CFSR data. Adv. Mater. Res. 2014, 1070–1072, 303–308. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, S.M.; Liu, J.L.; Zhang, G.; Han, B.; Wu, R.H.; Chen, D. Evaluation of NCEP-CFSv2, ERA5, and CCMP wind datasets against buoy observations over Zhejiang nearshore waters. Ocean Eng. 2022, 259, 111832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, B.; Zhang, J. Long-Term Trends of Sea Surface Wind in the Northern South China Sea under the Background of Climate Change. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2021, 9, 752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olauson, J. ERA5: The new champion of wind power modelling? Renew. Energy 2018, 126, 322–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groisman, P.Y.; Knight, R.W.; Karl, T.R.; Easterling, D.R.; Sun, B.; Lawrimore, J.H. Contemporary Changes of the Hydrological Cycle over the Contiguous United States: Trends Derived from In Situ Observations. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2004, 5, 64–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pryor, S.C.; Barthelmie, R.J.; Kjellström, E. Potential climate change impact on wind energy resources in northern Europe: Analyses using a regional climate model. Clim. Dyn. 2005, 25, 815–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pryor, S.C.; Schoof, J.T.; Barthelmie, R.J. Climate change impacts on wind speeds and wind energy density in northern Europe: Empirical downscaling of multiple AOGCMs. Clim. Res. 2005, 29, 183–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sailor, D.J.; Smith, M.; Hart, M. Climate change implications for wind power resources in the Northwest United States. Renew. Energy 2008, 33, 2393–2406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Bustamante, E.; González-Rouco, J.F.; Jiménez, P.A.; Navarro, J.; Montávez, J.P. A comparison of methodologies for monthly wind energy estimation. Wind Energy 2009, 12, 640–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McVicar, T.R.; Roderick, M.L.; Donohue, R.J.; Li, L.T.; Van Niel, T.G.; Thomas, A.; Grieser, J.; Jhajharia, D.; Himri, Y.; Mahowald, N.M.; et al. Global review and synthesis of trends in observed terrestrial near-surface wind speeds: Implications for evaporation. J. Hydrol. 2012, 416–417, 182–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soldatenko, S.; Karlin, L. The Climate Change Impact on Russia’s Wind Energy Resource: Current Areas of Research. Energy Power Eng. 2014, 6, 371–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Li, X.; Han, X.; Zhang, Y.F.; Wang, C.Q. Analysis of the spatial and temporal distribution characteristics of offshore wind energy resources in China. Ocean Forecast 2022, 39, 55–61. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wen, Y.; Kamranzad, B.; Lin, P.Z. Assessment of long-term offshore wind energy potential in the south and southeast coasts of China based on a 55-year dataset. Energy 2021, 224, 120225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vautard, R.; Cattiaux, J.; Yiou, P.; Thépaut, J.-N.; Ciais, P. Northern Hemisphere atmospheric stilling partly attributed to an increase in surface roughness. Nat. Geosci. 2010, 3, 756–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Xu, M.; Hu, Q. Changes in near-surface wind speed in China: 1969-2005. Int. J. Climatol. A J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2011, 31, 349–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Luo, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Tao, S. Changes in wind speed over China during 1956-2004. Theor. Appl. Cfimatol. 2009, 99, 421–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zha, J.L.; Wu, J.; Zhao, D.M.; Tang, J.P. A possible recovery of the near-surface wind speed in Eastern China during winter after 2000 and the potential causes. Theor. Appl. Cfimatol. 2019, 136, 119–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Chang, C.-P.; Fu, C.; Qi, Y.; Robock, A.; Robinson, D.; Zhang, H.-m. Steady decline of east Asian monsoon winds, 1969–2000: Evidence from direct ground measurements of wind speed. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2006, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Shen, Y.; Yan, Z.; Liu, C. Trend in pan evaporation and its attribution over the past 50 years in China. J. Geogr. Sci. 2010, 20, 557–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Xu, Z.; Yao, Z.; Huang, H. Comparison of surface variables from ERA and NCEP reanalysis with station data over eastern China. Theor. Appl. Cfimatol. 2011, 107, 611–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, P.J.; Zhang, G.F.; Kong, F.; Ye, Q. Wind Speed Change Zoning of China from 1961-2012. Prog. Clim. Chang. Res. 2015, 11, 387–394. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Adekunle, O.; Lin, X.P.; Zhao, D.L.; Wang, Z.F. Wind Energy Potentials and Its Trend in the South China Sea. Energy Environ. Res. 2016, 6, 36. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.Y.; Zhang, D.Y.; Zhang, Y.Z.; Wang, G.Q. Analysis of the spatial and temporal change characteristics and influencing factors of wind energy resources in Hexi Corridor from 1958 to 2012. Agric. Resour. Reg. China 2016, 37, 188–195. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, K.; Jiang, Y.; Li, C.B.; Wu, J.; Huang, F.X. Study on Long-term Change Characteristics of Wind Energy in 3 Typical Regions of China. Renew. Energy 2015, 33, 1853–1860. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- de Sousa Gomes, M.S.; de Paiva, J.M.F.; da Silva Moris, V.A.; Nunes, A.O. Proposal of a methodology to use offshore wind energy on the southeast coast of Brazil. Energy 2019, 185, 327–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, B.; Wei, Y.L.; Ding, J.; Zhang, R.; Liu, Y.X.; Wang, X.Y.; Fang, Y.Z. Trends of sea surface wind energy over the South China Sea. J. Oceanol. Limnol. 2019, 37, 1510–1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, S.; Yang, X.; Weng, H.; Zhang, T.; Tang, R.; Wang, H.; Su, J. Spatial Distribution and Trends of Wind Energy at Various Time Scales over the South China Sea. Atmosphere 2023, 14, 362. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14020362
Zhang S, Yang X, Weng H, Zhang T, Tang R, Wang H, Su J. Spatial Distribution and Trends of Wind Energy at Various Time Scales over the South China Sea. Atmosphere. 2023; 14(2):362. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14020362
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Shuqin, Xiaoqi Yang, Hanwei Weng, Tianyu Zhang, Ruoying Tang, Hao Wang, and Jinglei Su. 2023. "Spatial Distribution and Trends of Wind Energy at Various Time Scales over the South China Sea" Atmosphere 14, no. 2: 362. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14020362
APA StyleZhang, S., Yang, X., Weng, H., Zhang, T., Tang, R., Wang, H., & Su, J. (2023). Spatial Distribution and Trends of Wind Energy at Various Time Scales over the South China Sea. Atmosphere, 14(2), 362. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14020362






