Numerical Investigation on Impact Erosion of Aeolian Sand Saltation in Gobi
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methodology
2.1. Particle Motion Governing Equations
2.2. Aerodynamic Governing Equations
2.3. Surface Process
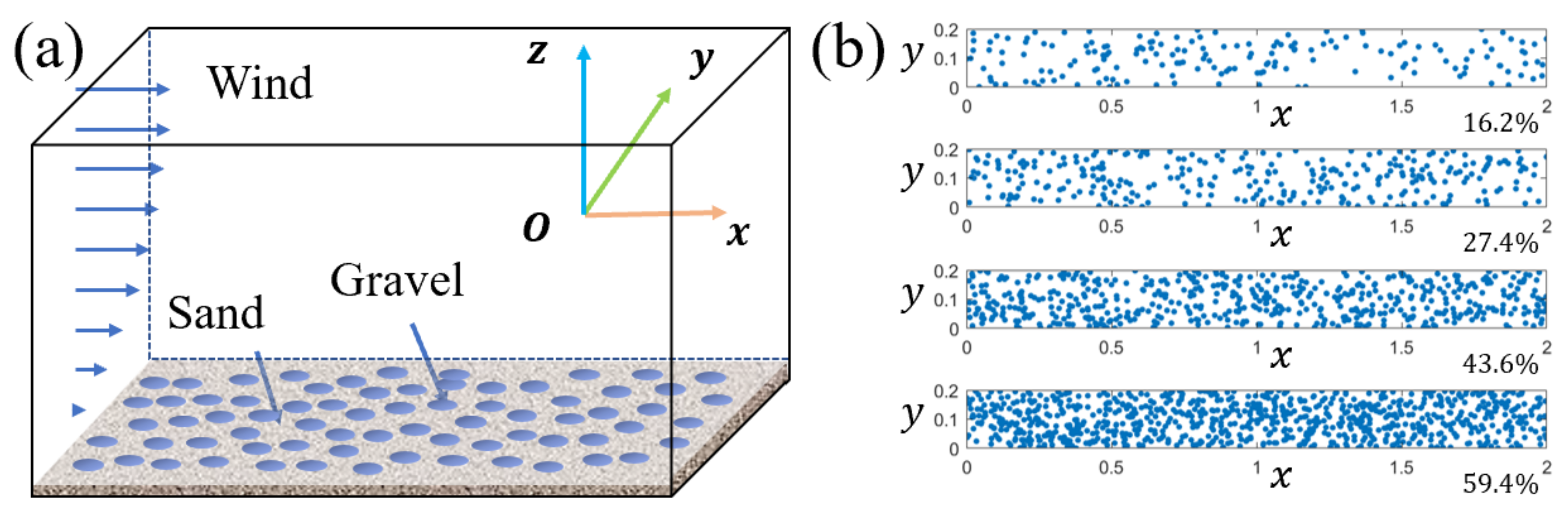
2.4. Realization Method of Gobi Bed
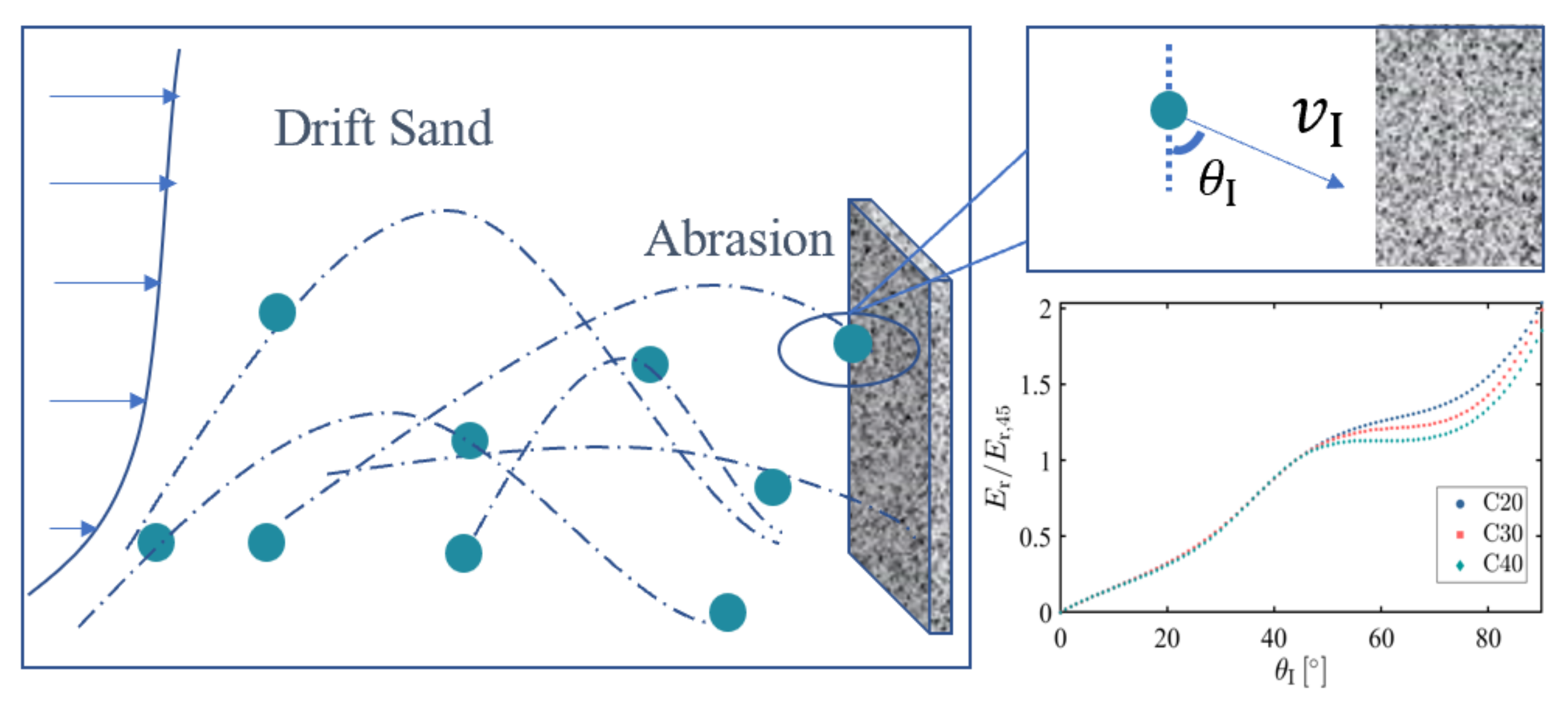
2.5. Calculation Method of Impact Erosion by Sand Drift
2.6. Calculation Procedure
- Search all particles and find out every collision pair. Renew the velocity of collision particles using Equation (5).
- Find out particles below the surface and the coordinates of their impact location. The properties of bound particles and ejected particles can be inferred from the splash function in Table 1. If the rebound velocity of a particle after hitting the bed is not sufficient to move it to a height above one particle diameter, the particle is considered to have transformed into a static particle on the bed and is removed from the saltation system.
- Identify the particles that come into contact with the wall and the corresponding collision locations. Calculate the impact erosion based on Equation (15).
- Calculate and update the wind field with Equation (10).
- Return to step (2) and start the calculation of the next step.
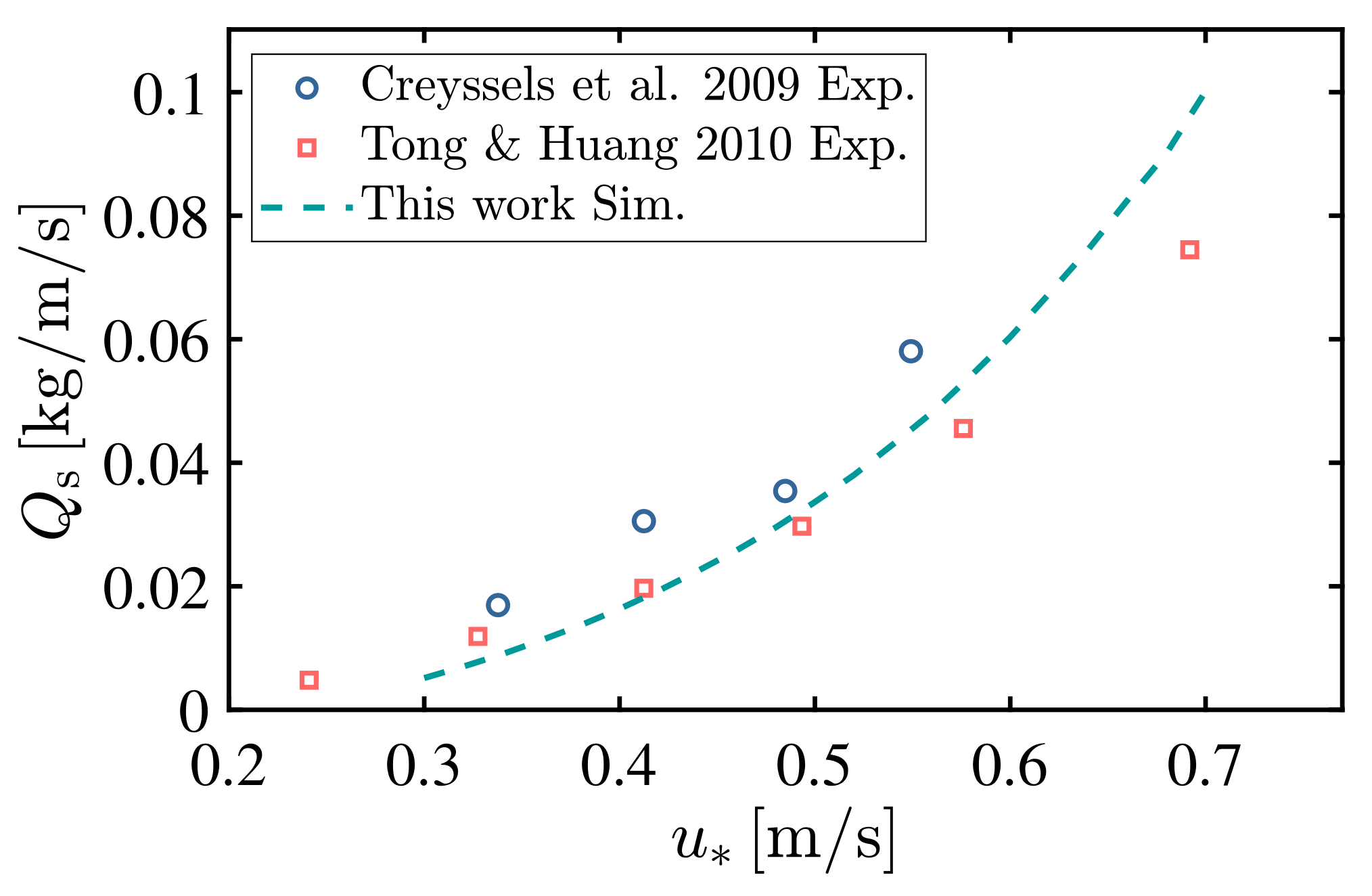
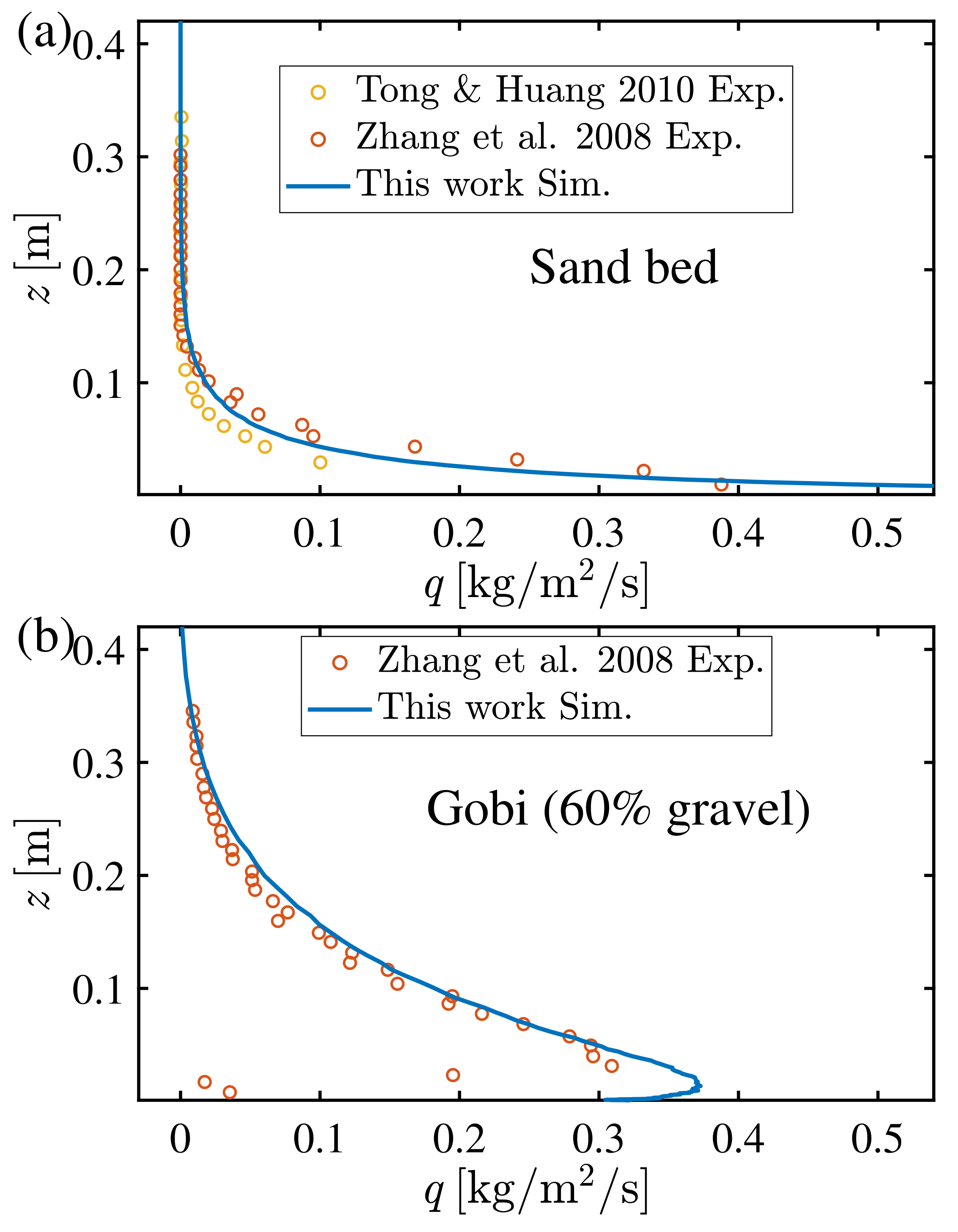
2.7. Model Verification
3. Results and Discussion
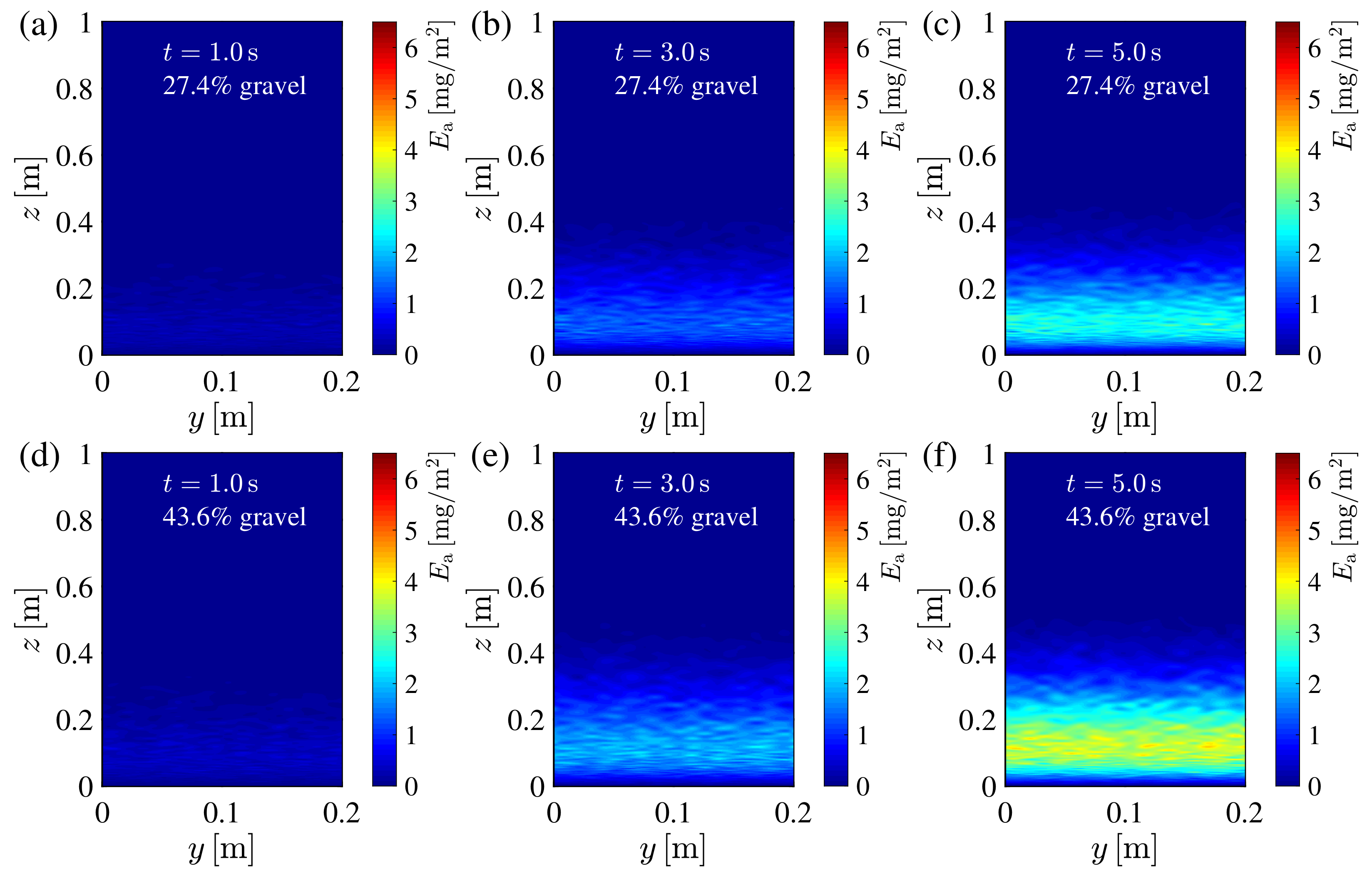
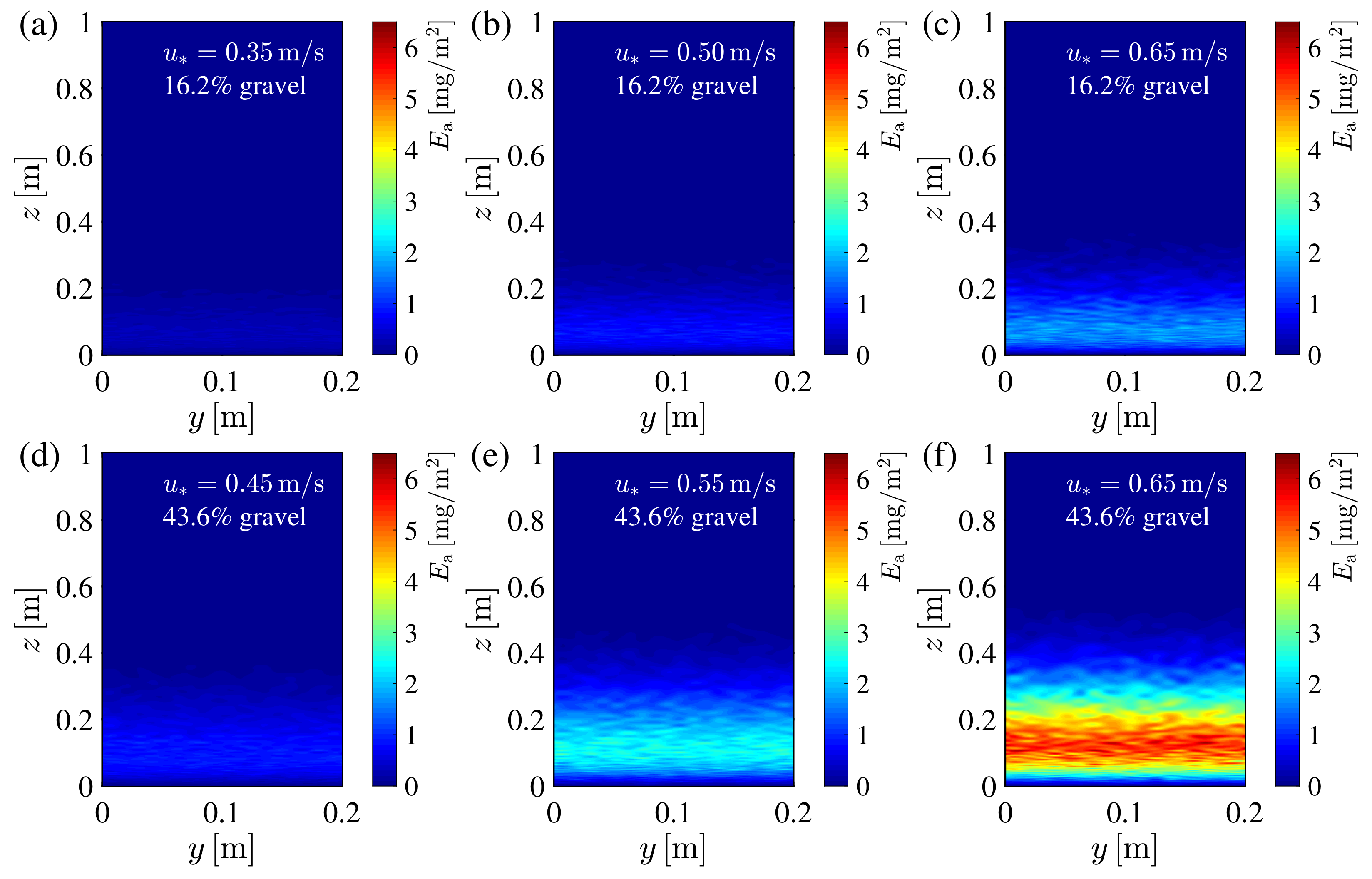
3.1. Spatial Distribution Image of Sand Drift Erosion
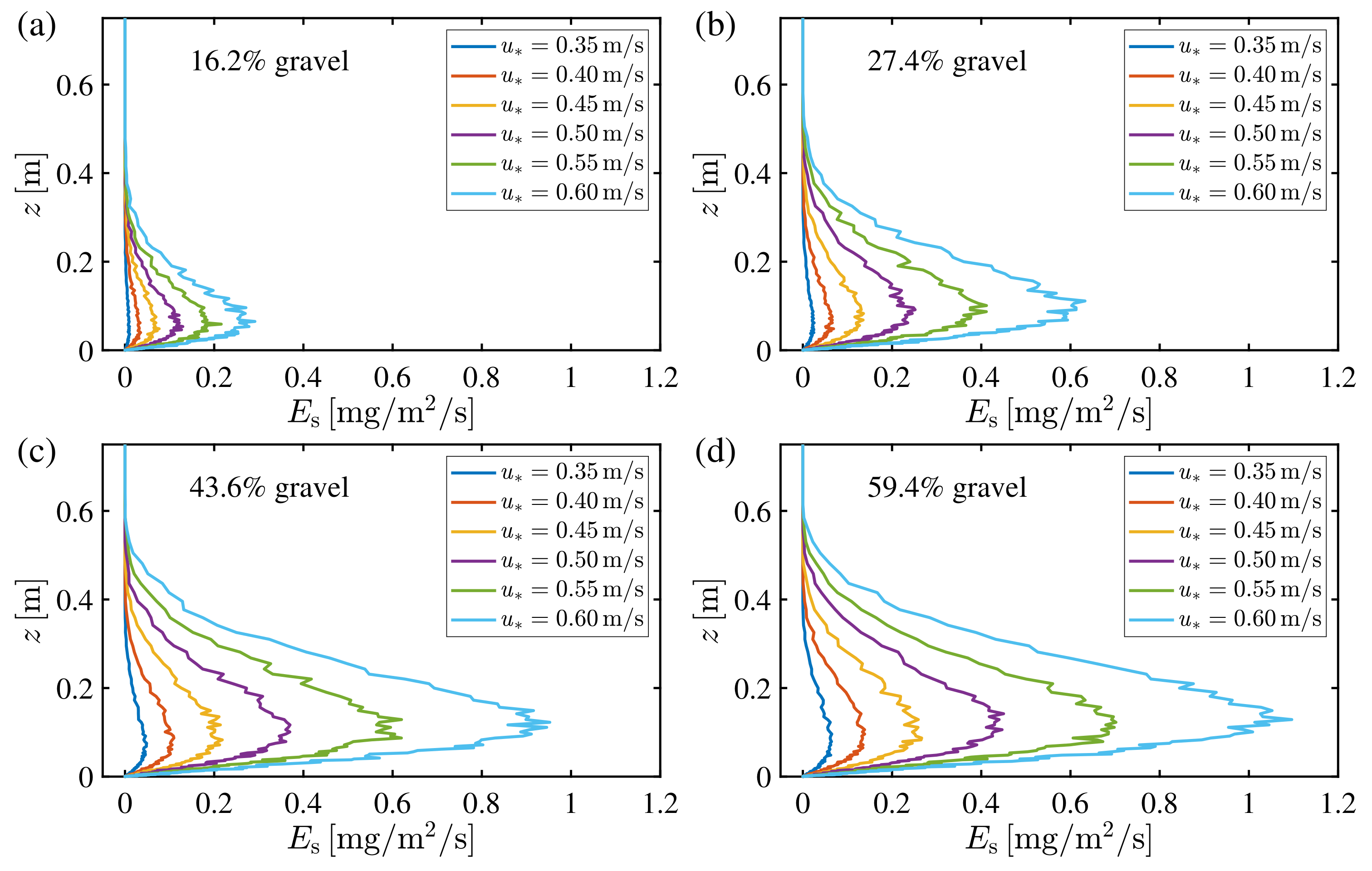
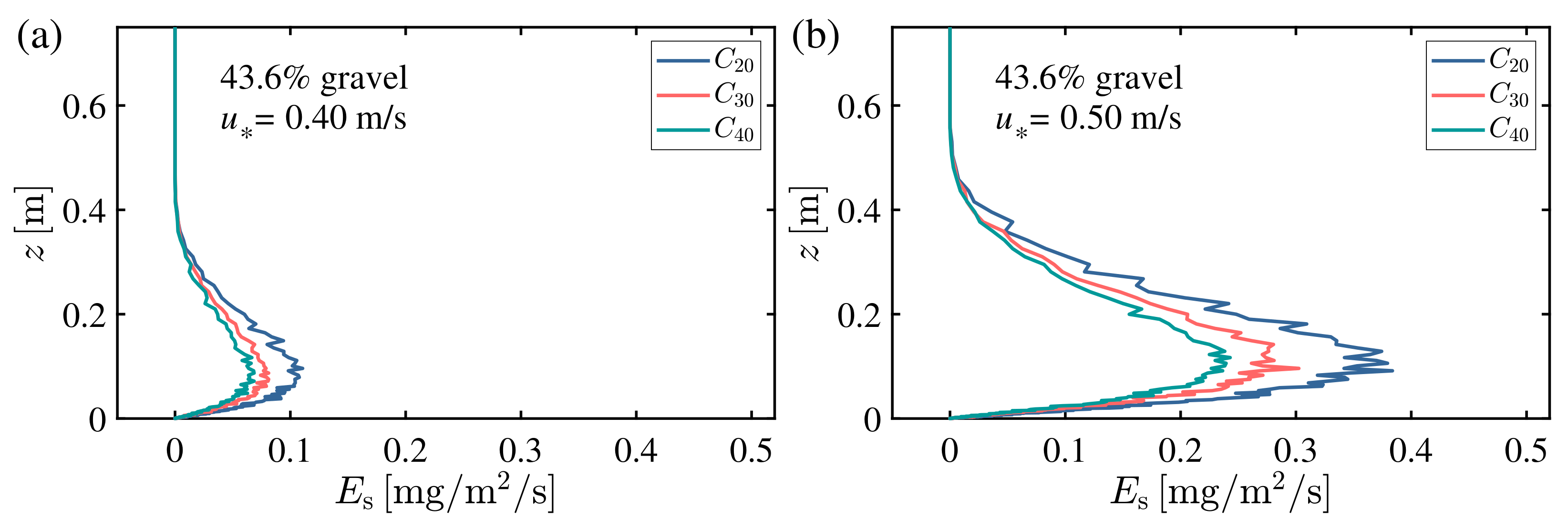
3.2. Vertical Structure of Saltation Erosion Rate
3.3. Scaling Rate of Saltation Erosion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Carr, M.H. The Geology of the Terrestrial Planets. Rev. Geophys. 1983, 21, 160–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Titus, T.N.; Lancaster, N.; Hayward, R.; Fenton, L.; Bourke, M. Priorities for Future Research on Planetary Dunes Planetary Dunes: Workshop: A Record of Climate Change; Alamogordo, New Mexico, 28 April to 2 May 2008. Eos Trans. Am. Geophys. Union 2008, 89, 447–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lancaster, N.; Nickling, W.G.; Gillies, J.A. Sand Transport by Wind on Complex Surfaces: Field Studies in the McMurdo Dry Valleys, Antarctica. J. Geophys. Res. Earth Surf. 2010, 115, F03027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagnold, R.A. The Physics of Blown Sand and Desert Dunes; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1941. [Google Scholar]
- Owen, P.R. Saltation of Uniform Grains in Air. J. Fluid Mech. 1964, 20, 225–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, G. Some aspects of the eolian saltation load. Sedimentology 1964, 3, 257–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barndorff-Nielsen, O.E.; Willetts, B.B. (Eds.) Aeolian Grain Transport 1; Acta Mechanica Supplementum; Springer: Vienna, Austria, 1991; Volume 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pye, K.; Tsoar, H. Aeolian Sand and Sand Dunes; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kok, J.F.; Parteli, E.J.R.; Michaels, T.I.; Karam, D.B. The Physics of Wind-Blown Sand and Dust. Rep. Prog. Phys. 2012, 75, 106901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valance, A.; Rasmussen, K.R.; Ould El Moctar, A.; Dupont, P. The Physics of Aeolian Sand Transport. Comptes Rendus Phys. 2015, 16, 105–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodruff, N.P. Wind-Blown Soil Abrasive Injuries to Winter Wheat Plants. Agron. J. 1956, 48, 499–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armbrust, D.V. Recovery and Nutrient Content of Sandblasted Soybean Seedlings1. Agron. J. 1972, 64, 707–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heshmati, G.A.; Squires, V.R. Introduction to Deserts and Desertified Regions in China. In Combating Desertification in Asia, Africa and the Middle East: Proven Practices; Heshmati, G.A., Squires, V.R., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2013; pp. 3–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, J.; Huang, N.; Dong, G.; Zhang, W. The Role and Significance of the Gobi Desert Pavement in Controlling Sand Movement on the Cliff Top near the Dunhuang Magao Grottoes. J. Arid. Environ. 2001, 48, 357–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, L.; Qu, J.; Wang, T.; Zhang, K.; An, Z. Field Observation Evidence for Kink Points in the Vertical Kinetic Energy Flux Profiles of Wind-Blown Sand Over Gobi and Its Significance. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2021, 48, e2020GL091224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werner, B.T. A Steady-State Model of Wind-Blown Sand Transport. J. Geol. 1990, 98, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.J.; Luo, S.H.; He, L.H. The Characteristic of Streamwise Mass Flux of Windblown Sand Movement. Geomorphology 2012, 139–140, 188–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagnold, R.A.; Taylor, G.I. The Movement of Desert Sand. Proc. R. Soc. London. Ser. A-Math. Phys. Sci. 1936, 157, 594–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, B.R.; Schulz, J.C. Magnus Effect in Saltation. J. Fluid Mech. 1977, 81, 497–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rumpel, D.A. Successive Aeolian Saltation: Studies of Idealized Collisions. Sedimentology 1985, 32, 267–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Y.; Li, A. Numerical Modelling of Saltation in the Atmospheric Surface Layer. Bound.-Layer Meteorol. 1999, 91, 199–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kok, J.F.; Renno, N.O. A Comprehensive Numerical Model of Steady State Saltation (COMSALT). J. Geophys. Res. 2009, 114, D17204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ungar, J.E.; Haff, P.K. Steady State Saltation in Air. Sedimentology 1987, 34, 289–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, R.S.; Sørensen, M.; Willetts, B.B. A Review of Recent Progress in Our Understanding of Aeolian Sediment Transport. In Aeolian Grain Transport 1; Barndorff-Nielsen, O.E., Willetts, B.B., Eds.; Springer: Vienna, Austria, 1991; Volume 1, pp. 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, N.; Ren, S.; Zheng, X. Effects of the Mid-Air Collision on Sand Saltation. Sci. China Ser. Phys. Mech. Astron. 2008, 51, 1416–1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, N.; Wang, C.; Pan, X. Simulation of Aeolian Sand Saltation with Rotational Motion. J. Geophys. Res. 2010, 115, D22211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durán, O.; Andreotti, B.; Claudin, P. Numerical Simulation of Turbulent Sediment Transport, from Bed Load to Saltation. Phys. Fluids 2012, 24, 103306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; He, L.; Wu, J. Vertical Profiles of Mass Flux for Windblown Sand Movement at Steady State. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2004, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, D.; Huang, N. Numerical Simulation of Saltating Particles in Atmospheric Boundary Layer over Flat Bed and Sand Ripples. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2012, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dupont, S.; Bergametti, G.; Marticorena, B.; Simoëns, S. Modeling Saltation Intermittency. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2013, 118, 7109–7128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zhang, J.; Huang, N.; Xu, B. An Experimental Study on Splash Functions of Natural Sand-Bed Collision. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2019, 124, 7226–7235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Huang, N.; Dun, H.C. Experimental Study on Sand/Bed Collision Over the Gobi Surface. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2022, 127, e2021JD035766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Liu, L.; Li, X.; Zhao, L. An Experimental Method for Analyzing Environmental Effects of Blowing Sands on Glass Abrasion. Procedia Environ. Sci. 2010, 2, 207–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molinari, J.F.; Ortiz, M. A Study of Solid-Particle Erosion of Metallic Targets. Int. J. Impact Eng. 2002, 27, 347–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López, D.; Congote, J.P.; Cano, J.R.; Toro, A.; Tschiptschin, A.P. Effect of Particle Velocity and Impact Angle on the Corrosion–Erosion of AISI 304 and AISI 420 Stainless Steels. Wear 2005, 259, 118–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bousser, E.; Martinu, L.; Klemberg-Sapieha, J.E. Solid Particle Erosion Mechanisms of Protective Coatings for Aerospace Applications. Surf. Coatings Technol. 2014, 257, 165–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarodiya, R.; Levy, A. Surface Erosion Due to Particle-Surface Interactions—A Review. Powder Technol. 2021, 387, 527–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Y.; Feng, Y.; Fan, J. Experimental Study into Erosion Damage Mechanism of Concrete Materials in a Wind-Blown Sand Environment. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 111, 662–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goretta, K.C.; Burdt, M.L.; Cuber, M.M.; Perry, L.A.; Singh, D.; Wagh, A.S.; Routbort, J.L.; Weber, W.J. Solid-Particle Erosion of Portland Cement and Concrete. Wear 1999, 224, 106–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieira, R.E.; Mansouri, A.; McLaury, B.S.; Shirazi, S.A. Experimental and Computational Study of Erosion in Elbows Due to Sand Particles in Air Flow. Powder Technol. 2016, 288, 339–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mbabazi, J.G.; Sheer, T.J. Computational Prediction of Erosion of Air Heater Elements by Fly Ash Particles. Wear 2006, 261, 1322–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Reuterfors, E.P.; McLaury, B.S.; Shirazi, S.A.; Rybicki, E.F. Comparison of Computed and Measured Particle Velocities and Erosion in Water and Air Flows. Wear 2007, 263, 330–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greeley, R.; Leach, R.N.; Williams, S.H.; White, B.R.; Pollack, J.B.; Krinsley, D.H.; Marshall, J.R. Rate of Wind Abrasion on Mars. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 1982, 87, 10009–10024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lancaster, N. Characteristics and Occurrence of Wind Erosion Features in the Namib Desert. Earth Surf. Process. Landforms 1984, 9, 469–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ta, W. Study of the Energy Abrasion Rates of Five Soil Types Subject to Oblique Impacts. Geoderma 2007, 140, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raffaele, L.; Bruno, L. Windblown Sand Action on Civil Structures: Definition and Probabilistic Modelling. Eng. Struct. 2019, 178, 88–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharp, R.P. Wind-Driven Sand in Coachella Valley, California. GSA Bull. 1964, 75, 785–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.Y.; Gao, S.Y.; Shi, P.J.; Li, X.Y.; Dong, Z.B. Wind Tunnel Measurements of Adobe Abrasion by Blown Sand: Profile Characteristics in Relation to Wind Velocity and Sand Flux. J. Arid. Environ. 2003, 53, 351–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Shi, X. Numerical Prediction on Erosion Damage Caused by Wind-Blown Sand Movement. Eur. J. Environ. Civ. Eng. 2014, 18, 550–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, X.; Dun, H.; Huang, N.; Zhang, J. 3D Direct Numerical Simulation on the Emergence and Development of Aeolian Sand Ripples. Front. Phys. 2021, 9, 662389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, X.; Huang, N.; Zhang, J. A Numerical Research on the Relationship between Aeolian Sand Ripples and the Sand Flux. Processes 2022, 10, 354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Y. Physics and Modelling of Wind Erosion; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Anderson, R.S.; Haff, P.K. Wind Modification and Bed Response during Saltation of Sand in Air. In Aeolian Grain Transport 1; Barndorff-Nielsen, O.E., Willetts, B.B., Eds.; Springer: Vienna, Austria, 1991; Volume 1, pp. 21–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, L.; Zhang, X. Chapter 8—Numerical Methods. In Modeling and Analysis of Modern Fluid Problems; Mathematics in Science and Engineering; Zheng, L., Zhang, X., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2017; pp. 361–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brilliantov, N.V.; Poschel, T. Kinetic Theory of Granular Gases, Illustrated Edition; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Schwager, T.; Becker, V.; Pöschel, T. Coefficient of Tangential Restitution for Viscoelastic Spheres. Eur. Phys. J. E 2008, 27, 107–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fohanno, S.; Oesterlé, B. Analysis of the Effect of Collisions on the Gravitational Motion of Large Particles in a Vertical Duct. Int. J. Multiph. Flow 2000, 26, 267–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Versteeg, H.K.; Malalasekera, W. An Introduction to Computational Fluid Dynamics: The Finite Volume Method, 2nd ed.; Pearson Education Ltd: Harlow, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Mitha, S.; Tran, M.Q.; Werner, B.T.; Haff, P.K. The Grain-Bed Impact Process in Aeolian Saltation. Acta Mech. 1986, 63, 267–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McEWAN, I.K.; Willetts, B.B.; Rice, M.A. The Grain/Bed Collision in Sand Transport by Wind. Sedimentology 1992, 39, 971–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oger, L.; Ammi, M.; Valance, A.; Beladjine, D. Study of the Collision of One Rapid Sphere on 3D Packings: Experimental and Numerical Results. Comput. Math. Appl. 2008, 55, 132–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ammi, M.; Oger, L.; Beladjine, D.; Valance, A. Three-Dimensional Analysis of the Collision Process of a Bead on a Granular Packing. Phys. Rev. E 2009, 79, 021305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lämmel, M.; Dzikowski, K.; Kroy, K.; Oger, L.; Valance, A. Grain-Scale Modeling and Splash Parametrization for Aeolian Sand Transport. Phys. Rev. E 2017, 95, 022902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, M.; He, C. 3D Ejection Behavior of Different Sized Particles in the Grain-Bed Collision Process. Geomorphology 2013, 187, 94–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, L.; Guo, L.; Liu, D. Reconstructing the Vertical Distribution of the Aeolian Saltation Mass Flux Based on the Probability Distribution of Lift-off Velocity. Geomorphology 2008, 96, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Z.; Wang, H.; Liu, X.; Wang, X. A Wind Tunnel Investigation of the Influences of Fetch Length on the Flux Profile of a Sand Cloud Blowing over a Gravel Surface. Earth Surf. Process. Landforms 2004, 29, 1613–1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Tan, L.; Zhang, G.; Qiu, F.; Zhan, H. Aeolian Processes over Gravel Beds: Field Wind Tunnel Simulation and Its Application atop the Mogao Grottoes, China. Aeolian Res. 2014, 15, 335–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zou, X.; Zhang, C.; Kang, L.; Cheng, H.; Liu, B.; Liu, W.; Fang, Y.; Yang, D.; Wu, X. Effects of Gravel Cover on the Near-Surface Airflow Field and Soil Wind Erosion. Soil Tillage Res. 2021, 214, 105133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Z.; Liu, X.; Wang, X. Aerodynamic Roughness of Gravel Surfaces. Geomorphology 2002, 43, 17–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Zhang, W.; Tan, L.; An, Z.; Zhang, H. Effects of Gravel Mulch on Aeolian Transport: A Field Wind Tunnel Simulation. J. Arid. Land 2015, 7, 296–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oka, Y.I.; Okamura, K.; Yoshida, T. Practical Estimation of Erosion Damage Caused by Solid Particle Impact: Part 1: Effects of Impact Parameters on a Predictive Equation. Wear 2005, 259, 95–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Creyssels, M.; Dupont, P.; El Moctar, A.O.; Valance, A.; Cantat, I.; Jenkins, J.T.; Pasini, J.M.; Rasmussen, K.R. Saltating Particles in a Turbulent Boundary Layer: Experiment and Theory. J. Fluid Mech. 2009, 625, 47–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Qu, J.; Zu, R.; Ta, W. Characteristics of Wind-Blown Sand on Gobi/Mobile Sand Surface. Environ. Geol. 2008, 54, 411–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Wang, T.; Wang, W.; Liu, B. Wind Tunnel Experiments on Vertical Distribution of Wind-Blown Sand Flux and Change of the Quantity of Sand Erosion and Deposition above Gravel Beds under Different Sand Supplies. Environ. Earth Sci. 2011, 64, 1031–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, L.; Zhang, W.; Qu, J.; Zhang, K.; An, Z.; Wang, X. Aeolian Sand Transport over Gobi with Different Gravel Coverages under Limited Sand Supply: A Mobile Wind Tunnel Investigation. Aeolian Res. 2013, 11, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Kimura, R.; Wu, J. Vertical Profiles of Wind-Blown Sand Flux over Fine Gravel Surfaces and Their Implications for Field Observation in Arid Regions. Atmosphere 2020, 11, 1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Distribution | Mean | Std. | References | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rebound on Gravel | ||||
| Normal | Chen et al. [31] | |||
| Lognormal | Chen et al. [31] | |||
| Rebound on Sand Bed | ||||
| Lognormal | Zhang et al. [32] | |||
| Lognormal | Zhang et al. [32] | |||
| Splash | ||||
| Lognormal | Chen et al. [31] | |||
| Lognormal | Chen et al. [31] | |||
| Lognormal | Chen et al. [31] | |||
| Normal | 0 | 15 | Xing and He [64] |
| Material | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Gravel Coverage | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Dun, H.; Huang, N. Numerical Investigation on Impact Erosion of Aeolian Sand Saltation in Gobi. Atmosphere 2023, 14, 349. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14020349
Wang Y, Zhang J, Dun H, Huang N. Numerical Investigation on Impact Erosion of Aeolian Sand Saltation in Gobi. Atmosphere. 2023; 14(2):349. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14020349
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Yong, Jie Zhang, Hongchao Dun, and Ning Huang. 2023. "Numerical Investigation on Impact Erosion of Aeolian Sand Saltation in Gobi" Atmosphere 14, no. 2: 349. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14020349
APA StyleWang, Y., Zhang, J., Dun, H., & Huang, N. (2023). Numerical Investigation on Impact Erosion of Aeolian Sand Saltation in Gobi. Atmosphere, 14(2), 349. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14020349








