Disturbances of Doppler Frequency Shift of Ionospheric Signal and of Telluric Current Caused by Atmospheric Waves from Explosive Eruption of Hunga Tonga Volcano on January 15, 2022
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Technique
2.1. Barometric Pressure
2.2. Doppler Frequency Shift of Ionospheric Signal on Inclined Radio Paths
2.3. Measurements of Telluric Current
3. Results and Discussion
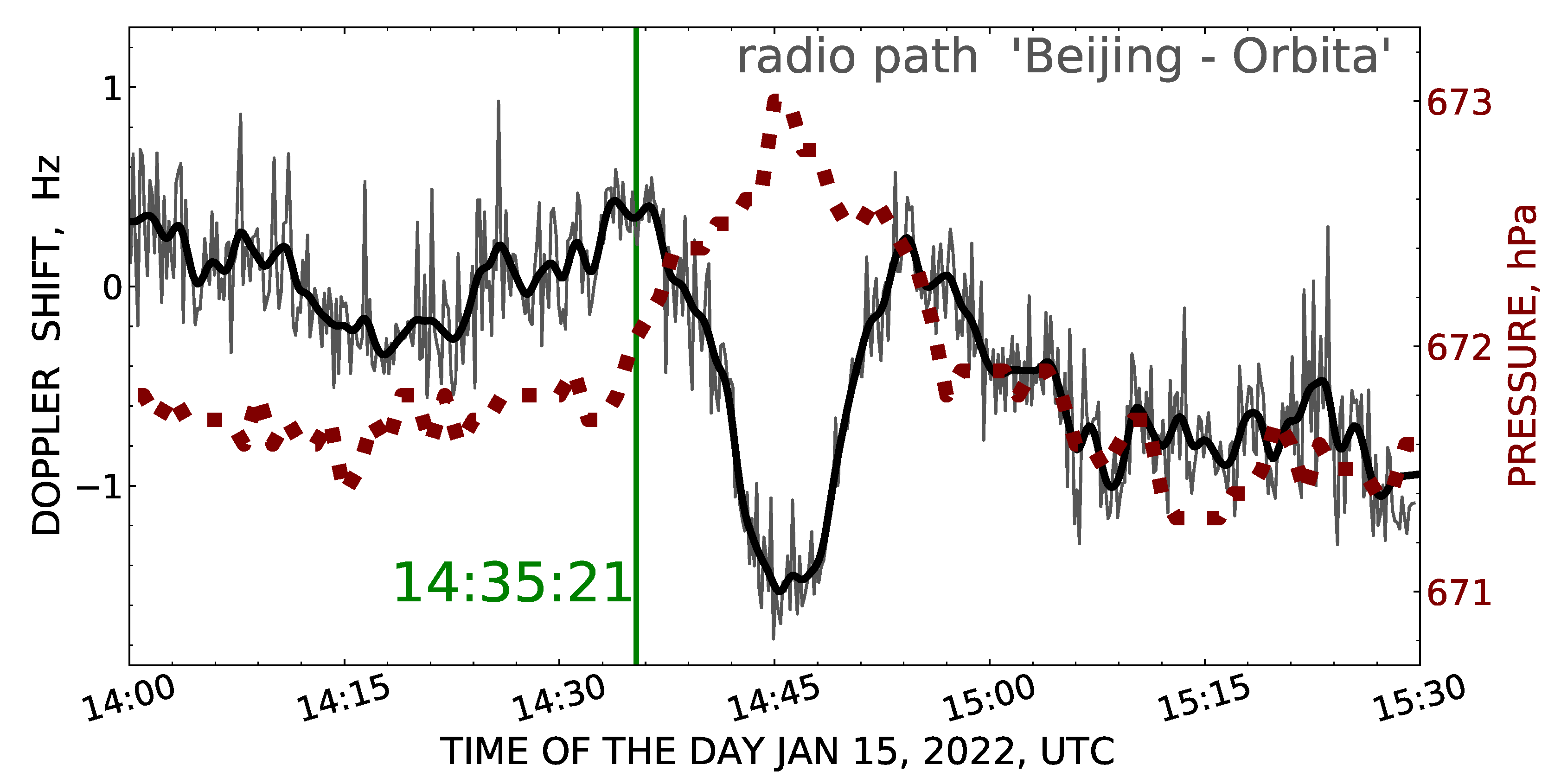
3.1. Anomaly of Atmospheric Pressure
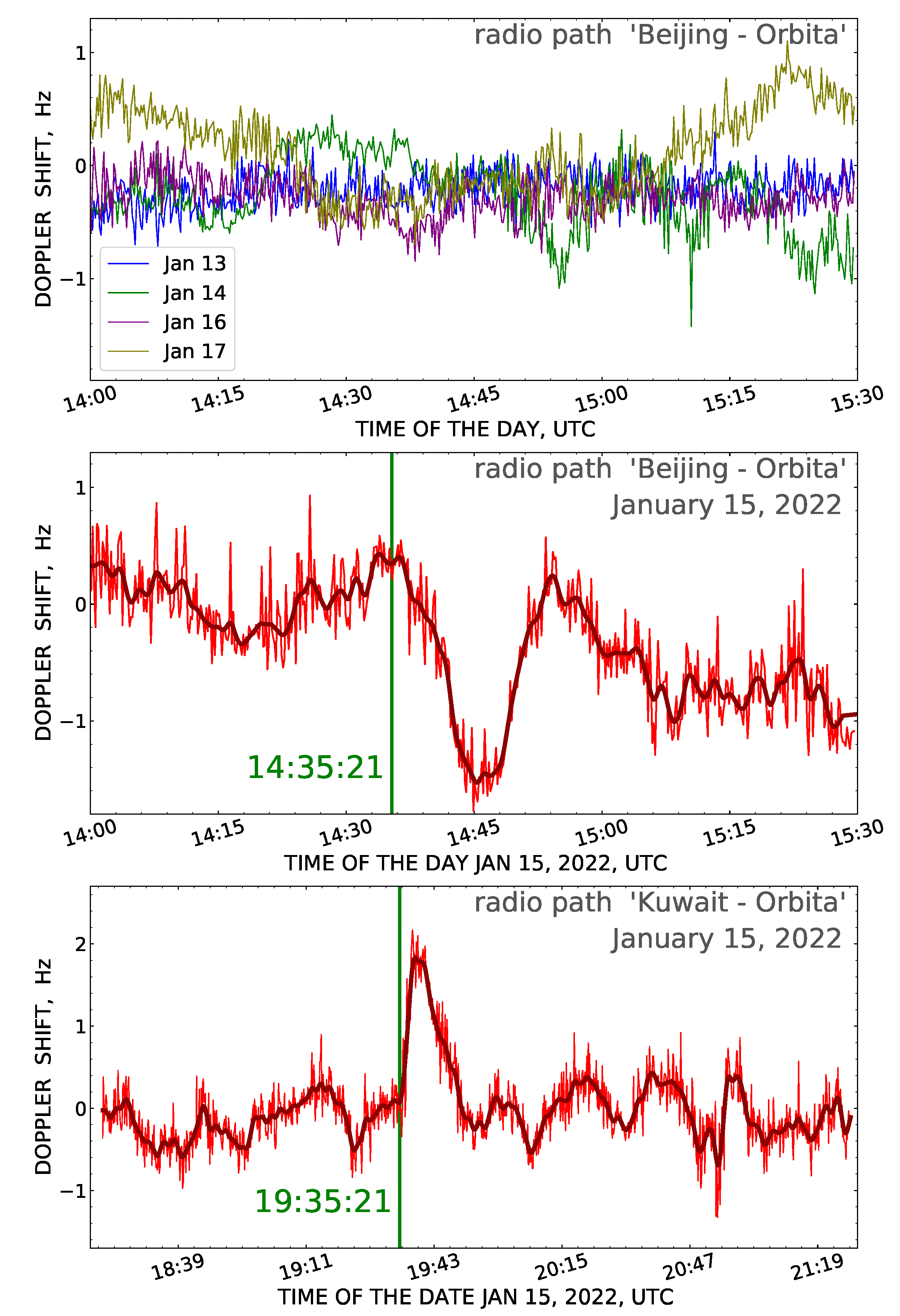
3.2. Doppler Frequency Shift of Ionospheric Signal
3.3. Measurements of Telluric Current
3.4. Evaluation of Energy Released into the Atmosphere upon Hunga Tonga Volcano Explosion
4. Conclusions
- On 15 January 2022, 11 h, 46 min, and 10 s after the volcano explosion, an anomalous short-time pulse of the atmospheric pressure was detected; it had an amplitude of 1.3 hPa and duration of about (25−30) min and propagated in the atmosphere at the velocity of Lamb waves, 0.3056 km·s, as it was registered by the barometer of the Tien Shan mountain station.
- The continuous monitoring of the Doppler frequency shift of the ionospheric signal on the inclined radio paths with lengths of 3212 km (7245 kHz) and 2969 km (5860 kHz) permitted us to reveal two different ionosphere disturbances on the day of the Hunga Tonga explosive eruption. The disturbance onset time corresponded to the arrival of the atmospheric waves moving at velocities of 0.3059 km·s and 0.2602 km·s at the reflection point of radio waves in the ionosphere. Judging by the velocity values, the observed disturbances of the Doppler frequency shift of the ionospheric signal arose as a result of the successive passage of the Lamb- and acoustic-gravity waves generated by the volcano explosion and their influence on the ionosphere.
- On the day of the volcano explosion, two consecutive disturbances of the variations in telluric current were found, with their appearance being consistent with the passage of the atmospheric waves at velocities of 0.3056 km·s and 0.2600 km·s. Both velocity estimates permitted us to connect the observed effects to the passage of the Lamb and acoustic-gravity waves from the volcano explosion at the point of the telluric current registration. Thus, the atmospheric waves, propagating across the whole thickness of the atmosphere, caused the modulation of the electric currents in the ionosphere, which induced an electromagnetic response of telluric current registered at the ground level.
- The energy transferred into the atmosphere upon the explosion of the Hunga Tonga volcano was roughly estimated using the parameters of the Lamb wave as 2000 Mt of TNT equivalent.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kulichkov, S.N.; Chunchuzov, I.P.; Popov, O.E.; Gorchakov, G.I.; Mishenin, A.A.; Perepelkin, V.G.; Bush, G.A.; Skorokhod, A.I.; Vinogradov, Y.A.; Semutnikova, E.G.; et al. Acoustic-gravity Lamb waves from the eruption of the Hunga-Tonga–Hunga-Hapai volcano, its energy release and impact on aerosol concentrations and tsunami. Pure Appl. Geophys. 2022, 179, 1533–1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matoza, R.S.; Fee, D.; Assink, J.D.; Iezzi, A.M.; Green, D.N.; Kim, K.; Toney, L.; Lecocq, T.; Krishnamoorthy, S.; Lalande, J.-M.; et al. Atmospheric waves and global seismoacoustic observations of the January 2022 Hunga eruption, Tonga. Science 2022, 377, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.-H.; Zhang, X.; Sun, Y.-Y.; Wang, F.; Liu, T.-C.; Lin, C.-Y.; Gao, Y.; Lyu, J.; Jin, X.; Zhao, X.; et al. Individual wave propagations in ionosphere and troposphere triggered by the Hunga Tonga–Hunga Ha´apai underwater volcano eruption on 15 January 2022. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 2179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubota, T.; Saito, T.; Nishida, K. Global fast-traveling tsunamis driven by atmospheric Lamb waves on the 2022 Tonga eruption. Science 2022, 377, 91–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wright, C.J.; Hindley, N.P.; Alexander, M.J.; Barlow, M.; Hoffmann, L.; Mitchell, C.N.; Prata, F.; Bouillon, M.; Carstens, J.; Clerbaux, C.; et al. Surface-to-space atmospheric waves from Hunga Tonga–Hunga Ha´apai eruption. Nature 2022, 609, 741–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heki, K. Ionospheric signatures of repeated passages of atmospheric waves by the 2022 Jan. 15 Hunga Tonga–Hunga Ha´apai eruption detected by QZSS–TEC observations in Japan. Earth Planets Space 2022, 74, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Themens, D.R.; Watson, C.; Žagar, N.; Vasylkevych, S.; Elvidge, S.; McCaffrey, A.; Prikryl, P.; Reid, B.; Wood, A.; Jayachandran, P.T. Global propagation of ionospheric disturbances associated with the 2022 Tonga volcanic eruption. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2022, 49, e2022GL0981582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.-R.; Vierinen, J.; Aa, E.; Goncharenko, L.P.; Erickson, P.J.; Rideout, W.; Coster, A.J.; Spicher, A. 2022 Tonga volcanic eruption induced global propagation of ionospheric disturbances via Lamb waves. Front. Astron. Space Sci. 2022, 9, 871275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aa, E.; Zhang, S.; Wang, W.; Erickson, P.J.; Qian, L.; Eastes, R.; Harding, B.J.; Immel, T.J.; Karan, D.K.; Daniell, R.E.; et al. Pronounced suppression and X-pattern merging of equatorial ionization anomalies after the 2022 Tonga volcano eruption. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2022, 127, e2022JA030527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cahyadi, M.N.; Handoko, E.Y.; Rahayu, R.W.; Heki, K. Comparison of volcanic explosions in Japan using impulsive ionospheric disturbances. Earth Planets Space 2021, 73, 228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heki, K.; Fujimoto, T. Atmospheric modes excited by the 2021 August eruption of the Fukutoku–Okanoba volcano, Izu–Bonin Arc, observed as harmonic TEC oscillations by QZSS. Earth Planets Space 2022, 74, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shepetov, A.; Kryakunova, O.; Mamina, S.; Ryabov, V.; Saduyev, N.; Sadykov, T.; Salikhov, N.; Vildanova, L.; Zhukov, V. Geophysical Aspect of Cosmic Ray Studies at the Tien Shan Mountain Station: Monitoring of Radiation Background, Investigation of Atmospheric Electricity Phenomena in Thunderclouds, and the Search for the Earthquake Precursor Effects. Phys. At. Nucl. 2021, 84, 1128–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salikhov, N.M.; Argynova, K.A.; Vildanova, L.I.; Zhukov, V.V.; Idrisova, T.K.; Iskakov, B.M.; Mamina, S.A.; Pak, G.D.; Ryabov, V.A.; Saduyev, N.O.; et al. Multichannel monitoring of the radiation background and a search for precursor signals of the seismic activity at the Tien Shan Mountain Station. Bull. Lebedev Phys. Inst. 2022, 49, 317–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salikhov, N.M.; Somsikov, V.M. The program- and hardware complex for registration of the Doppler frequency shift of ionosphere radio-signal over earthquake epicenters. Bull. Nat. Acad. Sci. Kazakhstan Repub. 2014, 296, 115–121. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Salikhov, N.M. New registration method of the dynamic of ionosphere ionization bursts by the program- and hardware complex of Doppler measurements on a slanted radio-track. Bull. Nat. Acad. Sci. Kazakhstan Repub. 2016, 308, 27–33. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Drobzhev, V.I.; Krasnov, V.M.; Salikhov, N.M. Ionospheric disturbances accompanying earthquakes and explosions. Radiophys. Quant. Electr. 1978, 21, 1295–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drobzhev, V.I.; Zheleznyakov, E.V.; Idrisov, I.K.; Kaliev, M.Z.; Kazakov, V.V.; Krasnov, V.M.; Pelenitsyn, G.M.; Savel’Ev, V.L.; Salikov, N.M.; Shingarkin, A.D. Ionospheric effects of the acoustic wave above the epicenter of an industrial explosion. Radiophys. Quant. Electr. 1987, 30, 1047–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laštovička, J.; Chum, J. A review of results of the international ionospheric Doppler sounder network. Adv. Space Res. 2017, 60, 1629–1643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krasnov, V.M.; Drobzheva, Y.V.; Chum, J. Far-field coseismic ionospheric disturbances of Tohoku earthquake. J. Atmos. Sol. Terr. Phys. 2015, 135, 12–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salikhov, N.; Shepetov, A.; Pak, G.; Nurakynov, S.; Ryabov, V.; Saduyev, N.; Sadykov, T.; Zhantayev, Z.; Zhukov, V. Monitoring of gamma radiation prior to earthquakes in a study of lithosphere-atmosphere-ionosphere coupling in Northern Tien Shan. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salikhov, N.M.; Pak, G.D. Ionospheric effects of solar flares and earthquake according to Doppler frequency shift on an inclined radio path. Bull. Nat. Acad. Sci. Kazakhstan Repub. 2020, 331, 108–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Tien-Shan Mountain Station’s Database. Available online: http://www.tien-shan.org (accessed on 1 December 2022).
- SHORT-WAVE.INFO. Available online: https://www.short-wave.info (accessed on 1 December 2022).
- Salikhov, N.; Pak, G.; Shepetov, A.; Zhukov, V.; Seifullina, B. Hardware-Software Complex for the telluric current investigation in a seismically hazardous region of Zailiysky Alatau. News Nat. Acad. Sci. Kazakhstan Repub. Ser. Geol. Tech. Sci. 2021, 5, 94–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SENSOR.COMMUNITY. Available online: https://archive.sensor.community (accessed on 1 December 2022).
- Kanamori, H.; Mori, J.; Harkrider, D.G. Excitation of atmospheric oscillations by volcanic eruptions. J. Geophys. Res. 1994, 99, 21947–21961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harding, B.J.; Wu, Y.J.; Alken, P.; Yamazaki, Y.; Triplett, C.C.; Immel, T.J.; Gasque, L.C.; Mende, S.B.; Xiong, C. Impacts of the January 2022 Tonga volcanic eruption on the ionospheric dynamo: ICON-MIGHTI and Swarm observations of extreme neutral winds and currents. J. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2022, 49, e2022GL098577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drobzhev, V.I.; Krasnov, V.M.; Salikhov, N.M. Simultaneous spectral analysis of wave perturbations in the ionospheric D-layer and F-layer. Radiophys. Quant. Electr. 1979, 22, 168–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
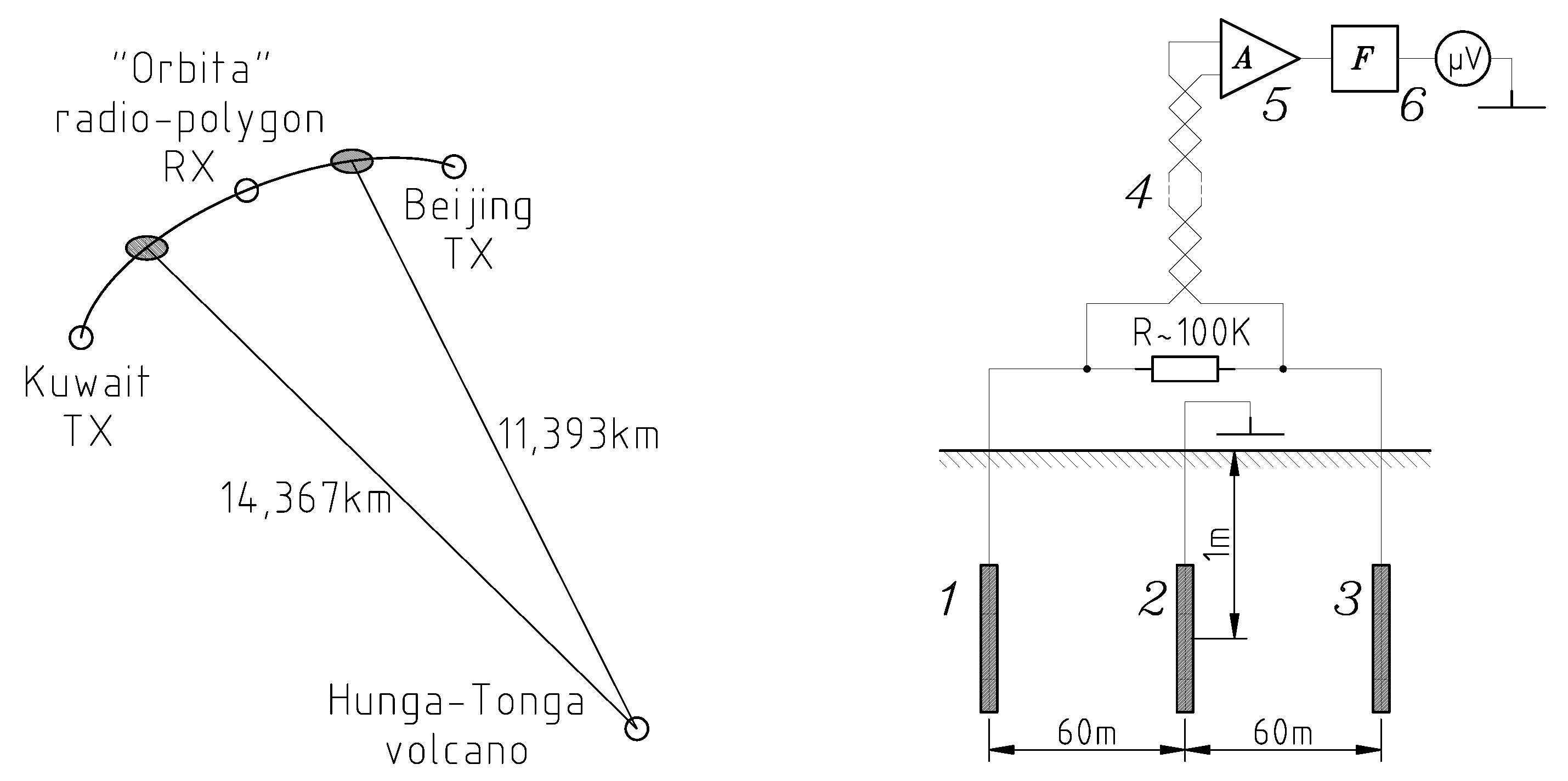



| Observation Point | Geographical Coordinates | Distance, km | Arrival of Pressure Pulse, UTC | Propagation Time, s | Propagation Speed, km·s |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Auckland | S36.83970 E174.82843 | 2040 | 05:56:44 | 6119 | 0.3334 |
| Brisbane | S27.46778 E153.02806 | 3291 | 07:03:24 | 10,119 | 0.3252 |
| Tokyo | N36.23000 E140.18000 | 7850 | 11:10:47 | 24,962 | 0.3145 |
| Seattle | N47.64236 W122.33348 | 9226 | 12:11:57 | 28,632 | 0.3222 |
| Santiago | S33.31831 W70.68514 | 10,056 | 12:57:55 | 31,390 | 0.3241 |
| Irkutsk | N52.27000 E104.45000 | 11,152 | 14:22:37 | 36,472 | 0.3058 |
| Tien Shan Station | N43.04361 E76.94139 | 12,948 | 16:00:55 | 42,370 | 0.3056 |
| Yekaterinburg | N56.85400 E60.64400 | 13,943 | 16:54:00 | 45,555 | 0.3061 |
| Moscow | N55.76660 E37.57324 | 15,235 | 18:04:09 | 49,755 | 0.3061 |
| Barcelona | N41.65060 E2.44564 | 17,658 | 20:12:08 | 57,443 | 0.3074 |
| Radio Path | Geographical Coordinates of the Radio Wave Reflection Point | Distance from the Reflection Point, km | Time Moment of the Ionospheric Anomaly, UTC | Propagation Time, s | Propagation Speed, km·s |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Beijing “Orbita” | N43.66260 E96.75869 | 11,393 | 14:35:21 | 37,236 | 0.3059 |
| Kuwait “Orbita” | N36.89300 E60.39300 | 14,367 | 19:35:21 | 55,241 | 0.2602 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Salikhov, N.; Shepetov, A.; Pak, G.; Saveliev, V.; Nurakynov, S.; Ryabov, V.; Zhukov, V. Disturbances of Doppler Frequency Shift of Ionospheric Signal and of Telluric Current Caused by Atmospheric Waves from Explosive Eruption of Hunga Tonga Volcano on January 15, 2022. Atmosphere 2023, 14, 245. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14020245
Salikhov N, Shepetov A, Pak G, Saveliev V, Nurakynov S, Ryabov V, Zhukov V. Disturbances of Doppler Frequency Shift of Ionospheric Signal and of Telluric Current Caused by Atmospheric Waves from Explosive Eruption of Hunga Tonga Volcano on January 15, 2022. Atmosphere. 2023; 14(2):245. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14020245
Chicago/Turabian StyleSalikhov, Nazyf, Alexander Shepetov, Galina Pak, Vladimir Saveliev, Serik Nurakynov, Vladimir Ryabov, and Valery Zhukov. 2023. "Disturbances of Doppler Frequency Shift of Ionospheric Signal and of Telluric Current Caused by Atmospheric Waves from Explosive Eruption of Hunga Tonga Volcano on January 15, 2022" Atmosphere 14, no. 2: 245. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14020245
APA StyleSalikhov, N., Shepetov, A., Pak, G., Saveliev, V., Nurakynov, S., Ryabov, V., & Zhukov, V. (2023). Disturbances of Doppler Frequency Shift of Ionospheric Signal and of Telluric Current Caused by Atmospheric Waves from Explosive Eruption of Hunga Tonga Volcano on January 15, 2022. Atmosphere, 14(2), 245. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14020245






