Study of Haze Boundary Layer Features Based on Multi-Source Data in Shihezi, China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Detection Site and Equipment
2.2. Data
2.3. The Method for Determining Boundary Layer Height
3. Results
3.1. Meteorological Characteristics
3.1.1. Characteristics of Ground Observations
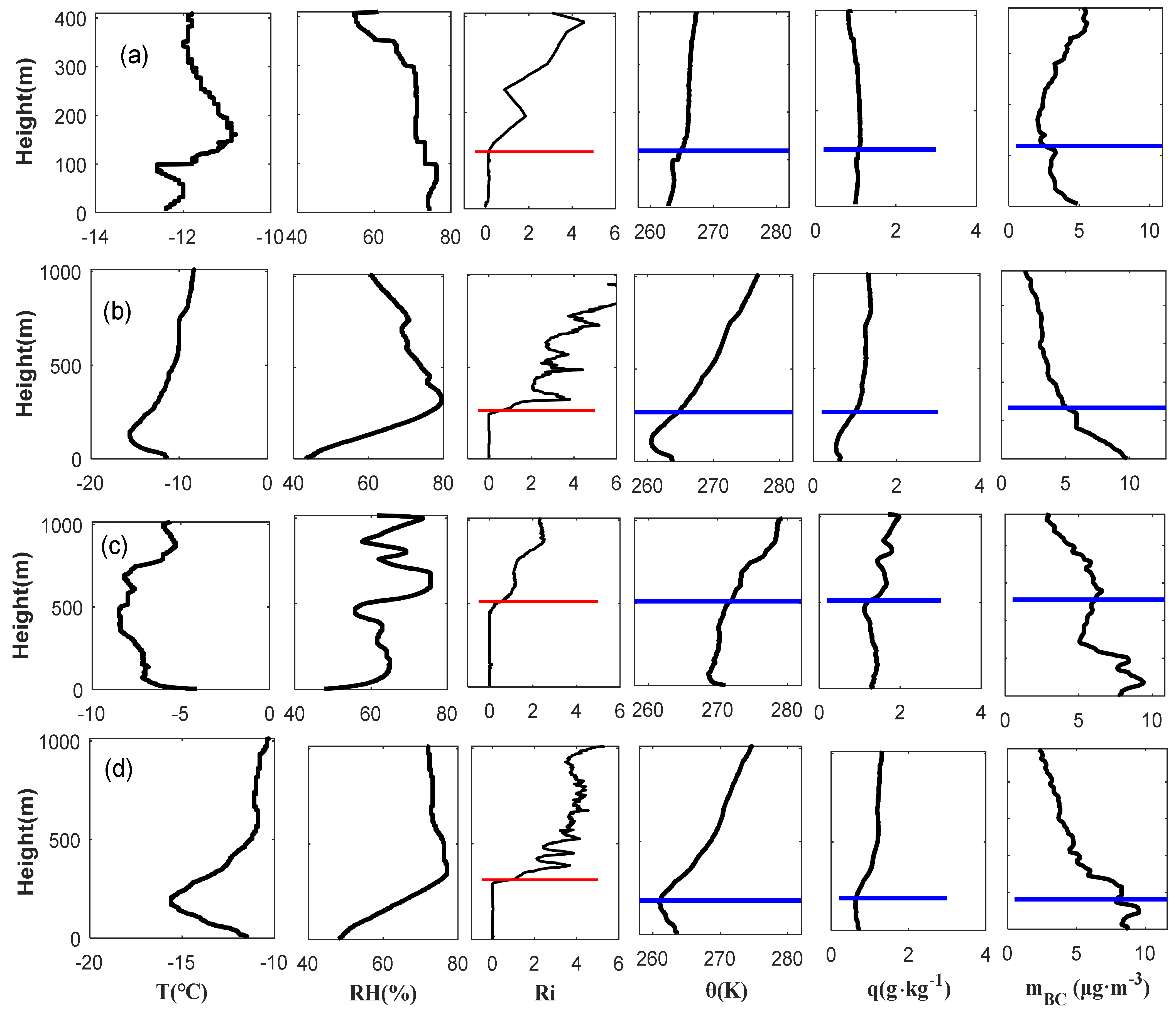
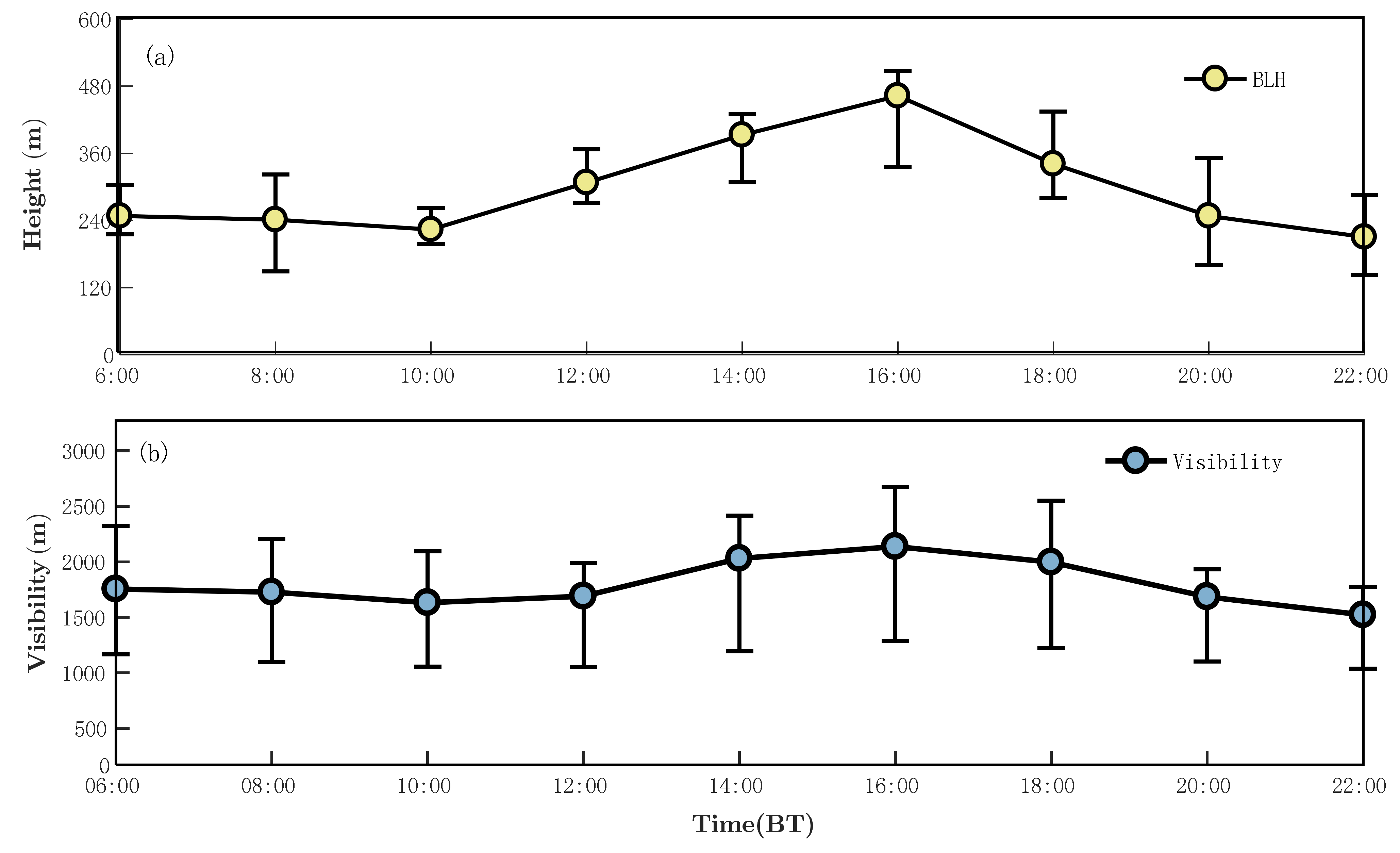
3.1.2. Characteristics of Boundary Layer Height
3.1.3. Temporal–Spatial Characteristics of Temperature
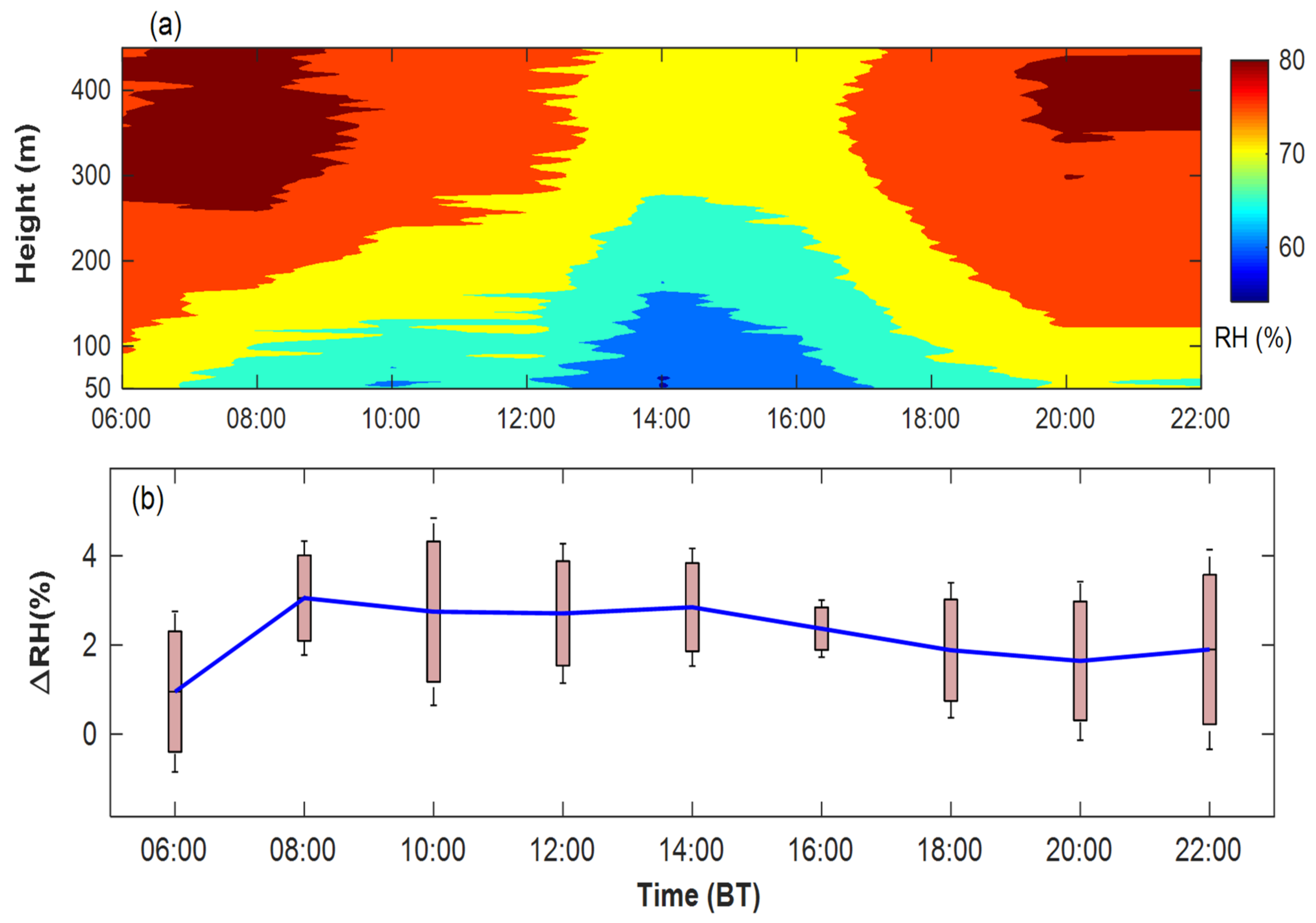
3.1.4. Temporal–Spatial Characteristics of Relative Humidity
3.2. The Characteristics of Pollutants
3.2.1. Temporal–Spatial Characteristics of BC
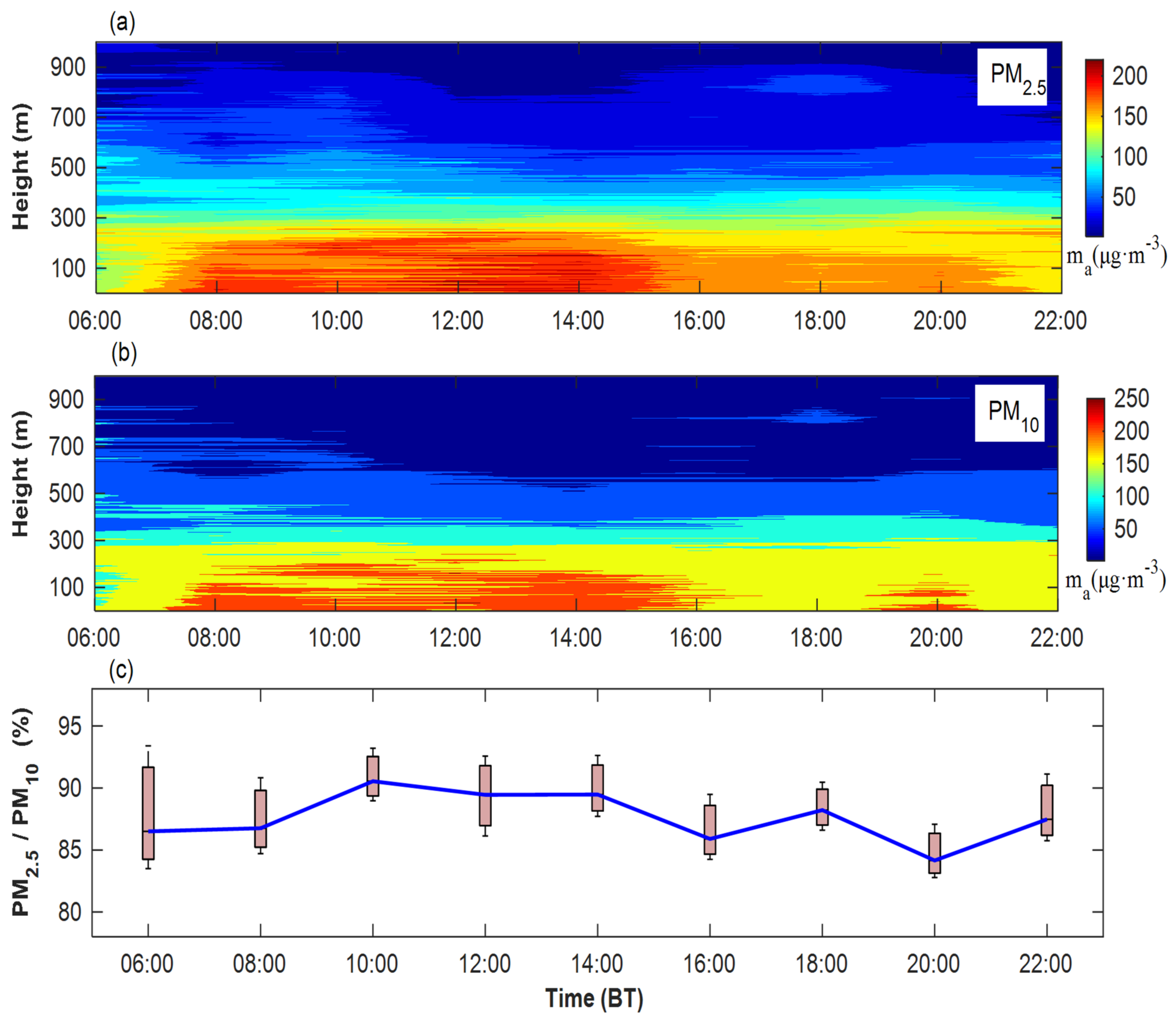
3.2.2. Temporal–Spatial Characteristics of PM2.5 and PM10
3.2.3. Temporal–Spatial Characteristics of the Extinction Coefficient
3.2.4. Temporal Characteristics of CO, NO2, and SO2
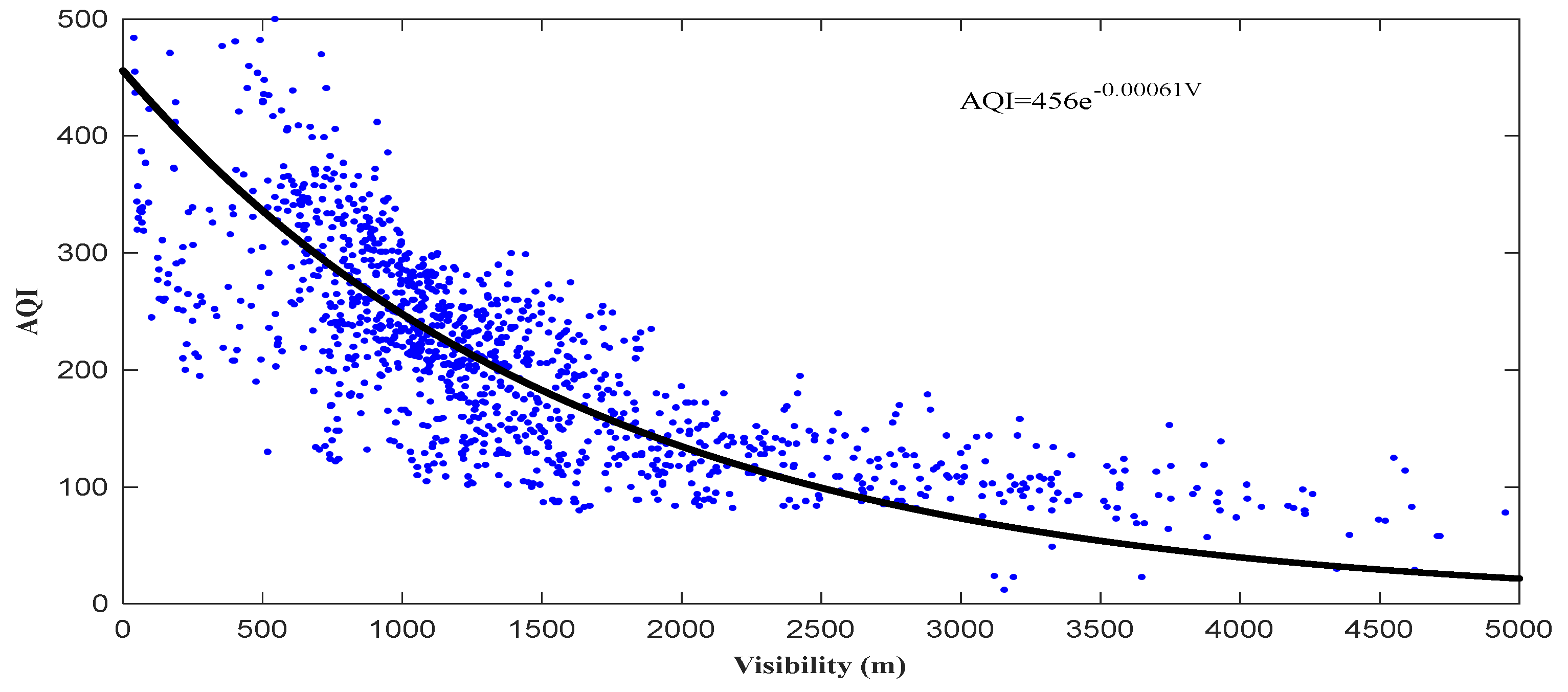
3.2.5. The Relationship between V and AQI during Haze Events
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- The BLH of haze events in Shihezi is relatively low and has a positive correlation with visibility. Moreover, the BLH is mainly distributed in 200–450 m, with the maximum BLH occurring at 15:30–16:30.
- (2)
- The temperature within the BLH is mainly between −5 °C and −15 °C with the vertical temperature difference basically greater than 0 except 15:00–17:00, which indicates that there is a temperature inversion layer in the low-level atmosphere and that the atmospheric structure is very stable.
- (3)
- The RH within the BLH is between 60 and 75%. When the time period is 6:00–8:00 and after 20:00, the average RH is > 70% with a little ∆RH, and the vapor flux is very small; however, it is mostly hazy with RH < 70% at 10:00 to 14:00 with a large ∆RH, and the vapor flux is relatively large.
- (4)
- During haze events, the PM2.5 and PM10 within the BLH are mainly concentrated at and , respectively. PM2.5 and PM10 increase to the maximum ( and ), and PM2.5/PM10 are generally greater than 85% at 11:00–14:00.
- (5)
- BC is mainly distributed in 6–8 and concentrated within the BL, and BC decreases obviously around the BLH. Moreover, the EC is inversely correlated with visibility and mainly concentrated at 4–9 km−1.
- (6)
- During winter haze events, the relationship between V and AQI (air quality index) is constructed as .
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, H.; Liu, A.; Zhen, Z.; Yin, Y.; Li, B.; Li, Y.; Chen, K.; Xu, J. Vertical structures of meteorological elements and black carbon at Mt. Tianshan using an unmanned aerial vehicle system. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Ming, H. Study on radar detection of one stratiform cloud precipitation process in the central part of the Tianshan Mountains in China. Asia-Pac. J. Atmos. Sci. 2018, 54, 511–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, X.; Talifu, D.; Ding, X.; Wang, X.; Abulizi, A.; Zhao, Q.; Liu, B. Secondary formation and influencing factors of WSOC in PM2.5 over Urumqi, NW China. Atmos. Environ. 2023, 293, 119450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhao, H.; Ma, Y.; Yang, H.; Wang, Y.; Wang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Zou, X.; Wang, H.; Wen, R. Characteristics of particulate matter and meteorological conditions of a typical air-pollution episode in Shenyang, northeastern China, in winter 2017. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2021, 12, 316–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molepo, K.M.; Abiodun, B.J.; Magoba, R.N. The transport of PM10 over Cape Town during high pollution episodes. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 213, 116–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ming, H.; Wei, M.; Wang, M.; Gao, L.; Chen, L.; Wang, X. Analysis of fog at Xianyang Airport based on multi-source ground-based detection data. Atmos. Res. 2019, 220, 34–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salmond, J.; Dirks, K.; Fiddes, S.; Pezza, A.; Talbot, N.; Scarfe, J.; Renwick, J.; Petersen, J. A climatological analysis of the incidence of brown haze in Auckland, New Zealand. Int. J. Climatol. 2016, 36, 2516–2526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crawford, J.; Chambers, S.; Cohen, D.; Williams, A.; Griffiths, A.; Stelcer, E. Assessing the impact of atmospheric stability on locally and remotely sourced aerosols at Richmond, Australia, using Radon-222. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 127, 107–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Ye, J.; Xin, J.; Zhang, W.; Vilà-Guerau de Arellano, J.; Wang, S.; Zhao, D.; Dai, L.; Ma, Y.; Wu, X. The stove, dome, and umbrella effects of atmospheric aerosol on the development of the planetary boundary layer in hazy regions. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2020, 47, e2020GL087373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Kwong, J.C.; Copes, R.; Tu, K.; Villeneuve, P.J.; Van Donkelaar, A.; Hystad, P.; Martin, R.V.; Murray, B.J.; Jessiman, B. Living near major roads and the incidence of dementia, Parkinson’s disease, and multiple sclerosis: A population-based cohort study. Lancet 2017, 389, 718–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Jia, L.; Zhang, F.; Hu, M.; Shi, Y.; Chen, X. Characteristics of haze weather in Chongqing, China and its determinants analysis based on automatic monitoring stations. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2016, 7, 638–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, C.K.; Yao, X. Air pollution in mega cities in China. Atmos. Environ. 2008, 42, 1–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marley, H.G.; Dirks, K.N.; Neverman, A.J.; McKendry, I.; Salmond, J.A. The relationship between Brown haze, atmospheric boundary layer structure, and air pollution in an urban area of complex coastal terrain. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2021, 12, 101057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.; Zhou, S.; Liu, C.; Guo, J. Synoptic circulation pattern and boundary layer structure associated with PM2.5 during wintertime haze pollution episodes in Shanghai. Atmos. Res. 2019, 228, 186–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, H.; Qi, B.; Zhao, H.; Xia, X.; Eck, T.F.; Goloub, P.; Dubovik, O.; Estelles, V.; Cuevas-Agulló, E.; Blarel, L. Aerosol optical properties and direct radiative forcing based on measurements from the China Aerosol Remote Sensing Network (CARSNET) in eastern China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 18, 405–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.J.; Kim, K.W.; Kim, S.D.; Lee, B.K.; Han, J.S. Fine particulate matter characteristics and its impact on visibility impairment at two urban sites in Korea: Seoul and Incheon. Atmos. Environ. 2006, 40, 593–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, X.; Wu, B.; Cai, X.; Song, Y.; Zhu, T. Coupled-decoupled turbulence structures of stable boundary layer during heavy haze pollution events. Atmos. Res. 2023, 281, 106465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, N.; Solanki, R.; Ojha, N.; Janssen, R.H.; Pozzer, A.; Dhaka, S.K. Boundary layer evolution over the central Himalayas from radio wind profiler and model simulations. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 16, 10559–10572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shikhovtsev, A.Y. A Method of Determining Optical Turbulence Characteristics by the Line of Sight of an Astronomical Telescope. Atmos. Ocean. Opt. 2022, 35, 303–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovadlo, P.G.; Shikhovtsev, A.Y.; Kopylov, E.A.; Kiselev, A.V.; Russkikh, I.V. Study of the Optical Atmospheric Distortions using Wavefront Sensor Data. Russ. Phys. J. 2021, 63, 1952–1958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ming, H.; Wang, M.; Gao, L.; Qian, Y.; Gao, M.; Chehri, A. Study on the Boundary Layer of the Haze at Xianyang Airport Based on Multi-Source Detection Data. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Zhao, P.; Xu, J.; Meng, W.; Pu, W.; Dong, F.; He, D.; Shi, Q. Analysis of a winter regional haze event and its formation mechanism in the North China Plain. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2013, 13, 5685–5696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, Y.; Hu, X.M.; Liu, S.; Qian, T.; Xue, M.; Zheng, Y.; Wang, S. Seasonal variation of local atmospheric circulations and boundary layer structure in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region and implications for air quality. J. Adv. Model. Earth Syst. 2015, 7, 1602–1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, E.; Han, J.; Lee, M.; Lee, G.; Kim, J.C. Chemical characteristics of size-resolved aerosols from Asian dust and haze episode in Seoul Metropolitan City. Atmos. Res. 2013, 127, 34–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Huang, K.; Zhuang, G.; Fu, J.S.; Wang, Q.; Liu, T.; Deng, C.; Fu, Q. A multi-year evolution of aerosol chemistry impacting visibility and haze formation over an Eastern Asia megacity, Shanghai. Atmos. Environ. 2014, 92, 76–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norela, S.; Saidah, M.; Mahmud, M. Chemical composition of the haze in Malaysia 2005. Atmos. Environ. 2013, 77, 1005–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Yan, L.; Huang, Y.; Wang, Q.; Morawska, L.; Zhaolin, G.; Cao, J.; Zhang, L.; Li, B.; Wang, Y. Characterization of particle size distributions during winter haze episodes in urban air. Atmos. Res. 2019, 228, 55–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Liu, L.; Wang, Y.; Ren, Y.; Wang, X.; Shi, Z.; Zhang, D.; Che, H.; Zhao, H.; Liu, Y. Chemical composition, source, and process of urban aerosols during winter haze formation in Northeast China. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 231, 357–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Wang, Z.; Ding, A. Impact of aerosol-PBL interaction on haze pollution: Multiyear observational evidences in North China. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2018, 45, 8596–8603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, L.; Zhang, X.; Che, Y.; Liu, X.; Zhao, T.; Song, M. Vertical profile and radiative forcing of black carbon in a winter pollution period over Chengdu, China. Atmos. Res. 2022, 265, 105896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Huang, M.; Tian, P.; He, H.; Lowe, D.; Zhou, W.; Sheng, J.; Wang, F.; Bi, K.; Kong, S. Vertical characteristics of black carbon physical properties over Beijing region in warm and cold seasons. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 213, 296–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Z.; Wang, C.; Wang, X.; Chen, Y.; Li, H. Simultaneous removal of SO2 and NOx from coal-fired flue gas using steel slag slurry. Energy Fuels 2018, 32, 2028–2036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, J.-H.; Duan, J.-C.; Ma, Y.-L.; Yang, F.-M.; Cheng, Y.; He, K.-B.; Yu, Y.-C.; Wang, J.-W. Source of atmospheric heavy metals in winter in Foshan, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 493, 262–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiang, P.; Zhou, X.; Duan, J.; Tan, J.; He, K.; Yuan, C.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, Y. Chemical characteristics of water-soluble organic compounds (WSOC) in PM2. 5 in Beijing, China: 2011–2012. Atmos. Res. 2017, 183, 104–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, J.; Zhang, L.; Zhou, X.; Duan, J.; Li, Y.; Hu, J.; He, K. Chemical characteristics and source apportionment of PM2.5 in Lanzhou, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 601, 1743–1752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, P.; Liu, D.; Huang, M.; Liu, Q.; Zhao, D.; Ran, L.; Deng, Z.; Wu, Y.; Fu, S.; Bi, K. The evolution of an aerosol event observed from aircraft in Beijing: An insight into regional pollution transport. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 206, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Li, P.; Ren, G.; Yuan, L.; Li, Y.; Yang, J. Aircraft measurements of aerosol distribution, warm cloud microphysical properties, and their relationship over the Eastern Loess Plateau in China. Tellus B Chem. Phys. Meteorol. 2019, 71, 1663994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, T.; Wu, C.; Wu, D.; Liu, B.; Sun, J.Y.; Mao, X.; Yang, H.; Deng, T.; Song, L.; Li, M. Time-resolved black carbon aerosol vertical distribution measurements using a 356-m meteorological tower in Shenzhen. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2020, 140, 1263–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ran, L.; Deng, Z.; Xu, X.; Yan, P.; Lin, W.; Wang, Y.; Tian, P.; Wang, P.; Pan, W.; Lu, D. Vertical profiles of black carbon measured by a micro-aethalometer in summer in the North China Plain. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 16, 10441–10454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Gao, Z.; Li, D.; Li, Y.; Zhang, N.; Zhao, X.; Chen, J. On the computation of planetary boundary-layer height using the bulk Richardson number method. Geosci. Model. Dev. 2014, 7, 2599–2611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Tian, Y.; Wei, N.; Ho, S.-p.; Li, J. Rising planetary boundary layer height over the Sahara Desert and Arabian Peninsula in a warming climate. J. Clim. 2021, 34, 4043–4068. [Google Scholar]
- Ryoo, J.-M.; Pfister, L.; Ueyama, R.; Zuidema, P.; Wood, R.; Chang, I.; Redemann, J. A meteorological overview of the ORACLES (ObseRvations of Aerosols above CLouds and their intEractionS) campaign over the southeastern Atlantic during 2016–2018: Part 2—Daily and synoptic characteristics. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2022, 22, 14209–14241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, J.; Bai, Y.; Zhao, T.; Zhou, Y.; Sun, X.; Xu, J.; Zhang, W.; Leng, L.; Xu, G. Synergistic Effect of Atmospheric Boundary Layer and Regional Transport on Aggravating Air Pollution in the Twain-Hu Basin: A Case Study. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 5166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zeng, X.; Xu, X.; Xie, F.; Zhao, Y. Improving the estimate of summer daytime planetary boundary layer height over land from GPS radio occultation data. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2022, 49, e2021GL096304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.L.; Wang, Y.F.; Shen, L.; Zhang, H.; Zhao, H.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, Y. Characteristics of boundary layer structure during a persistent haze event in the central Liaoning city cluster, Northeast China. J. Meteorol. Res. 2018, 32, 302–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, T.; Wu, D.; Deng, X.J.; Tan, H.; Li, F.; Liao, B. A vertical sounding of severe haze process in Guangzhou area. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2014, 44, 2307–2314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, S.; Zheng, Y. Analysis of a Severe Pollution Episode in December 2017 in Sichuan Province. Atmosphere 2019, 10, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Che, H.; Derimian, Y.; Dubovik, O.; Schuster, G.L.; Chen, C.; Li, Q.; Wang, Y.; Guo, B.; Zhang, X. Retrievals of fine mode light-absorbing carbonaceous aerosols from POLDER/PARASOL observations over East and South Asia. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 247, 111913. [Google Scholar]
- Duan, J.; Hu, J.; Tan, J.; Chen, H. Design of Characteristic Radar Chart and Its Application in Air Pollution Analysis. Res. Environ. Sci. 2018, 31, 1329–1336. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obolkin, V.; Molozhnikova, E.; Shikhovtsev, M.; Netsvetaeva, O.; Khodzher, T. Sulfur and Nitrogen Oxides in the Atmosphere of Lake Baikal: Sources, Automatic Monitoring, and Environmental Risks. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 1348. [Google Scholar]
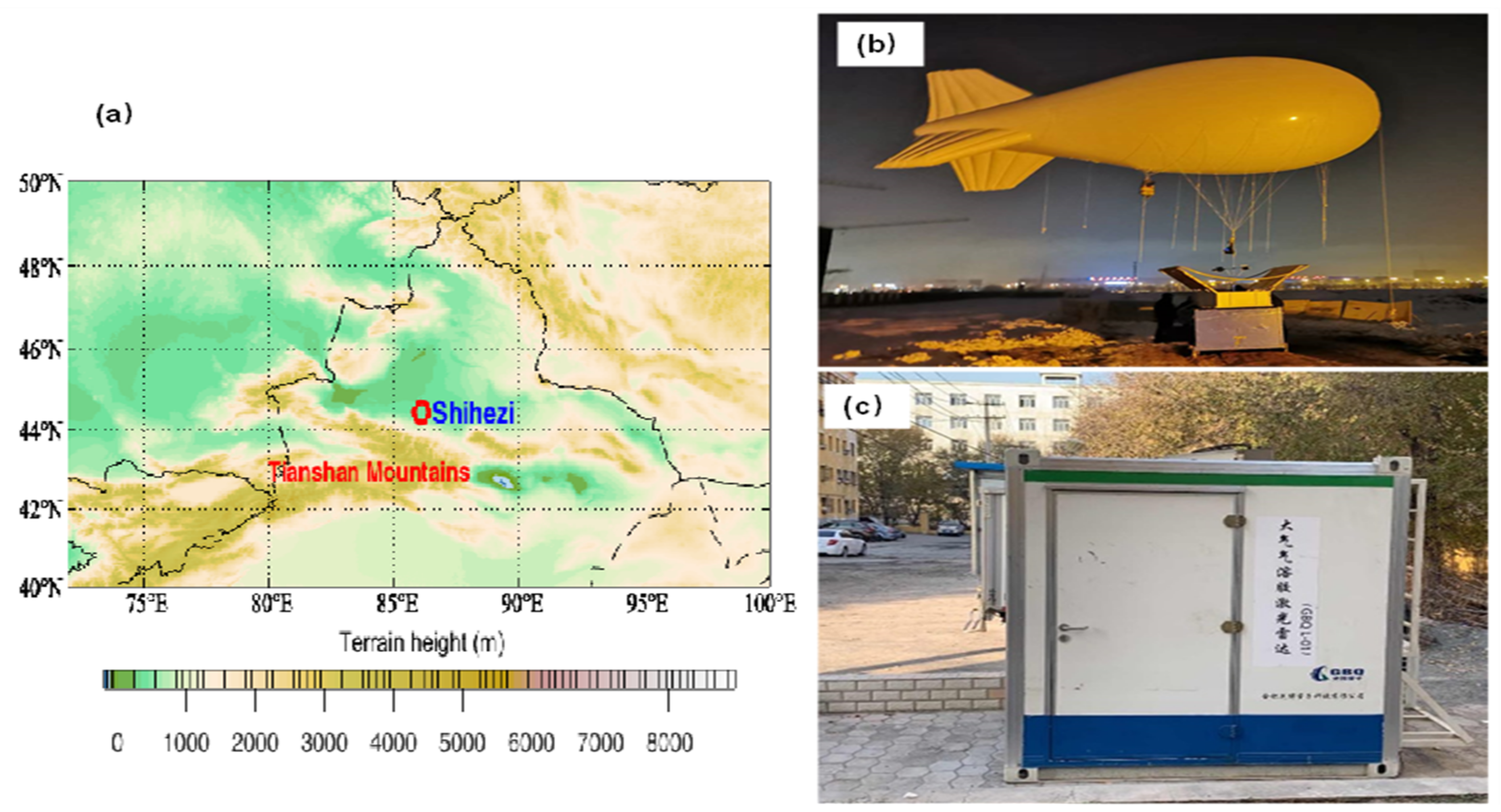





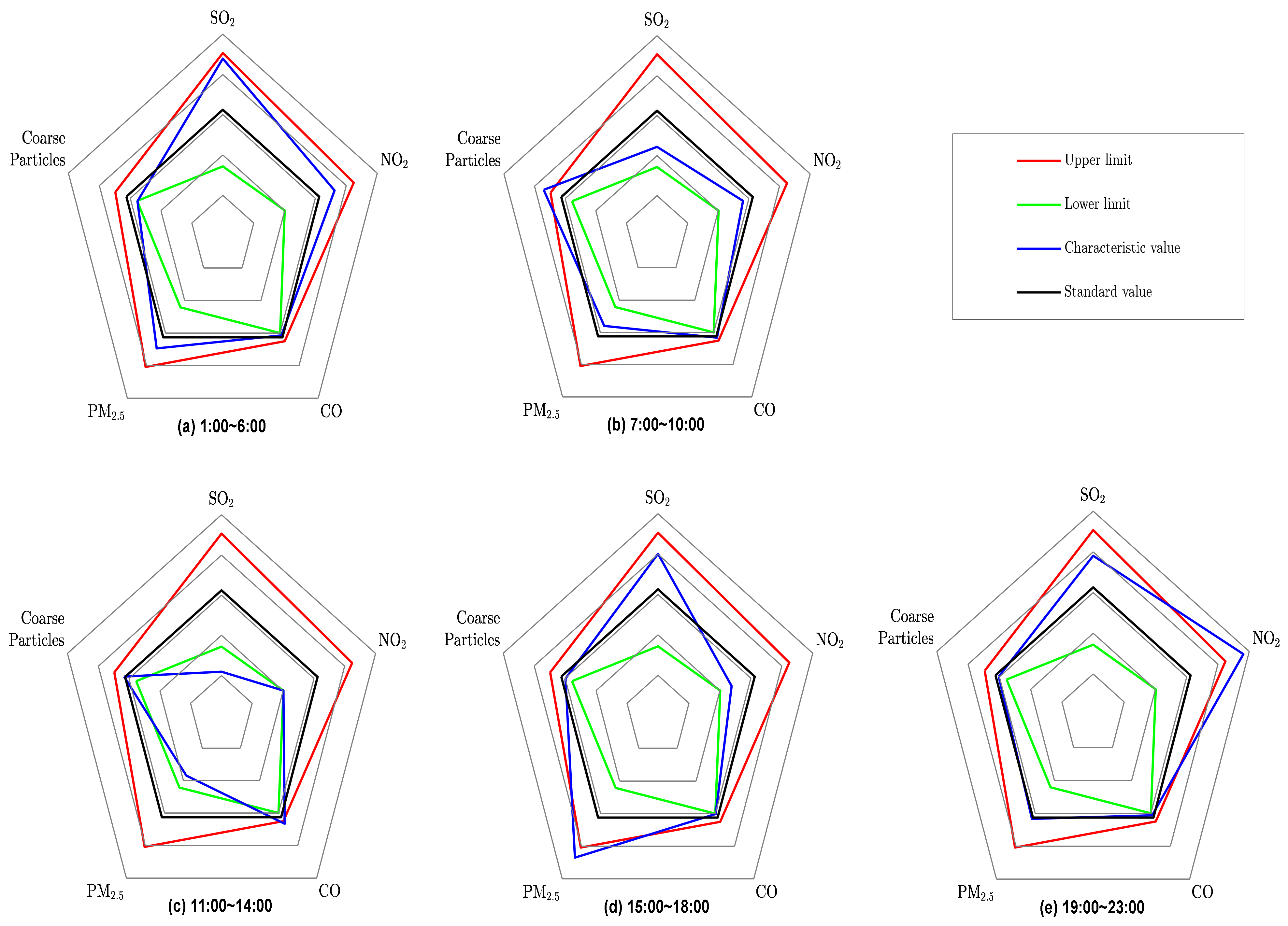
| Pollutant | Pollution Sources | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| CO | Incomplete combustion of coal and industrial production | Li et al. [11] |
| SO2 | Coal burning | Meng et al. [32] |
| SO2 | Motor vehicles and coal combustion | Tan et al. [33] |
| PM2.5 | Primary and secondary sources | Xiang et al. [34] |
| Coarse particles | Blowing sand | Tan et al. [35] |
| Time | Frequency | Time | Frequency | Time | Frequency |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 06:00–08:00 | 7 | 12:00–14:00 | 6 | 18:00–20:00 | 9 |
| 08:00–10:00 | 10 | 14:00–16:00 | 6 | 20:00–22:00 | 7 |
| 10:00–12:00 | 7 | 16:00–18:00 | 8 | 22:00–23:00 | 10 |
| Parameter Name | Parameter | Parameter Name | Parameter |
|---|---|---|---|
| Transmit power | ≥1 mJ | Measurement channel | 532 nm |
| Wavelength | 532 nm | Pulse frequency | ≥3 kHz |
| Time resolution | 1 min | Vertical resolution | 7.5 m |
| Sampling frequency | 20 MHz | Effective detection height | 15 km |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ren, G.; Ming, H.; Wang, J.; Wang, W.; An, D.; Lei, W.; Zhang, Q. Study of Haze Boundary Layer Features Based on Multi-Source Data in Shihezi, China. Atmosphere 2023, 14, 1587. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14101587
Ren G, Ming H, Wang J, Wang W, An D, Lei W, Zhang Q. Study of Haze Boundary Layer Features Based on Multi-Source Data in Shihezi, China. Atmosphere. 2023; 14(10):1587. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14101587
Chicago/Turabian StyleRen, Gang, Hu Ming, Jin Wang, Wenxiao Wang, Dongliang An, Wei Lei, and Qing Zhang. 2023. "Study of Haze Boundary Layer Features Based on Multi-Source Data in Shihezi, China" Atmosphere 14, no. 10: 1587. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14101587
APA StyleRen, G., Ming, H., Wang, J., Wang, W., An, D., Lei, W., & Zhang, Q. (2023). Study of Haze Boundary Layer Features Based on Multi-Source Data in Shihezi, China. Atmosphere, 14(10), 1587. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14101587





