Characteristics and Variations of Raindrop Size Distribution in Chengdu of the Western Sichuan Basin, China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Instrument, Data, and Methods
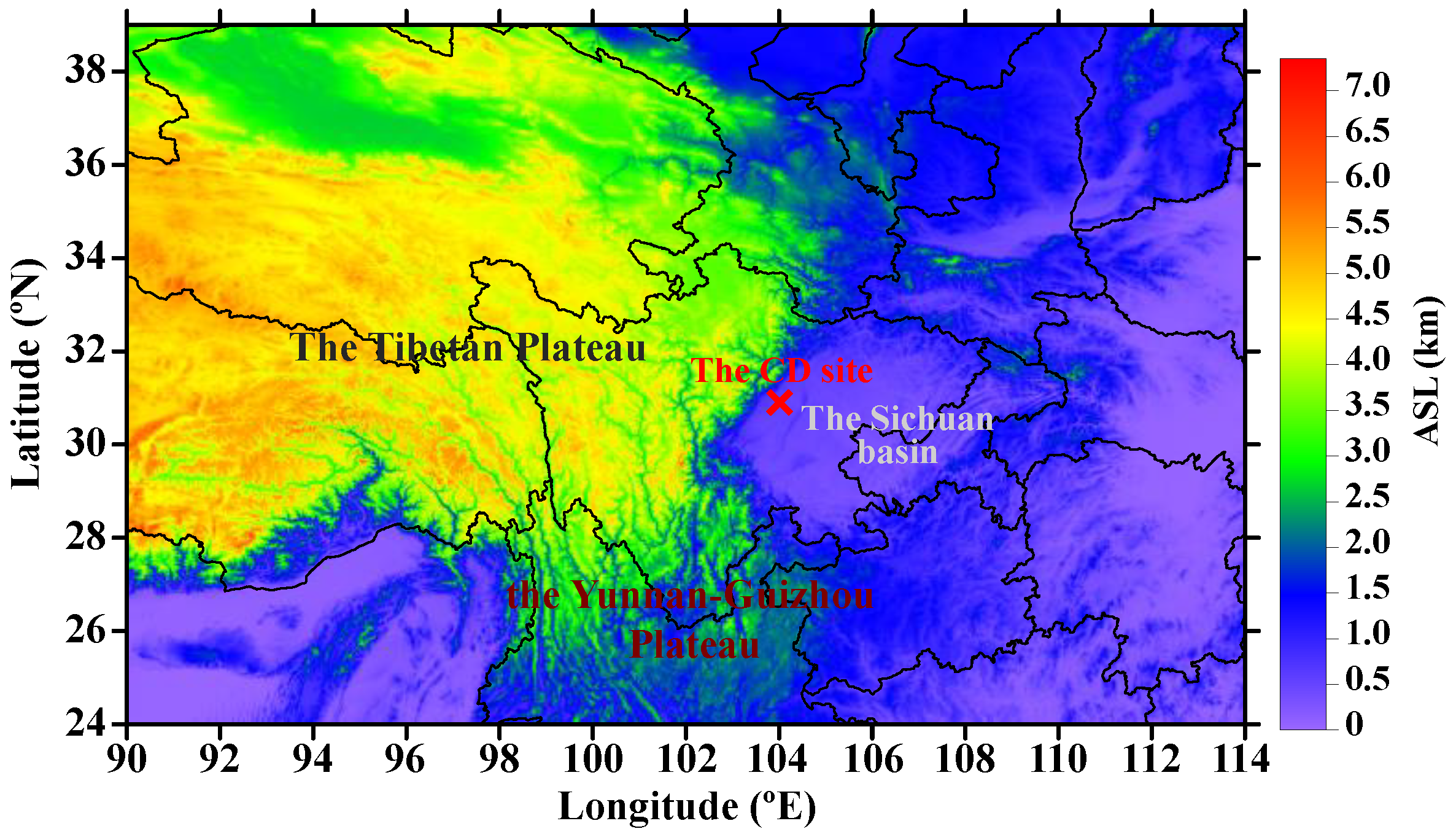
2.1. Observation Site, Instrument, and Measurements
2.2. RSD Data Quality Control and Postprocessing
3. Results
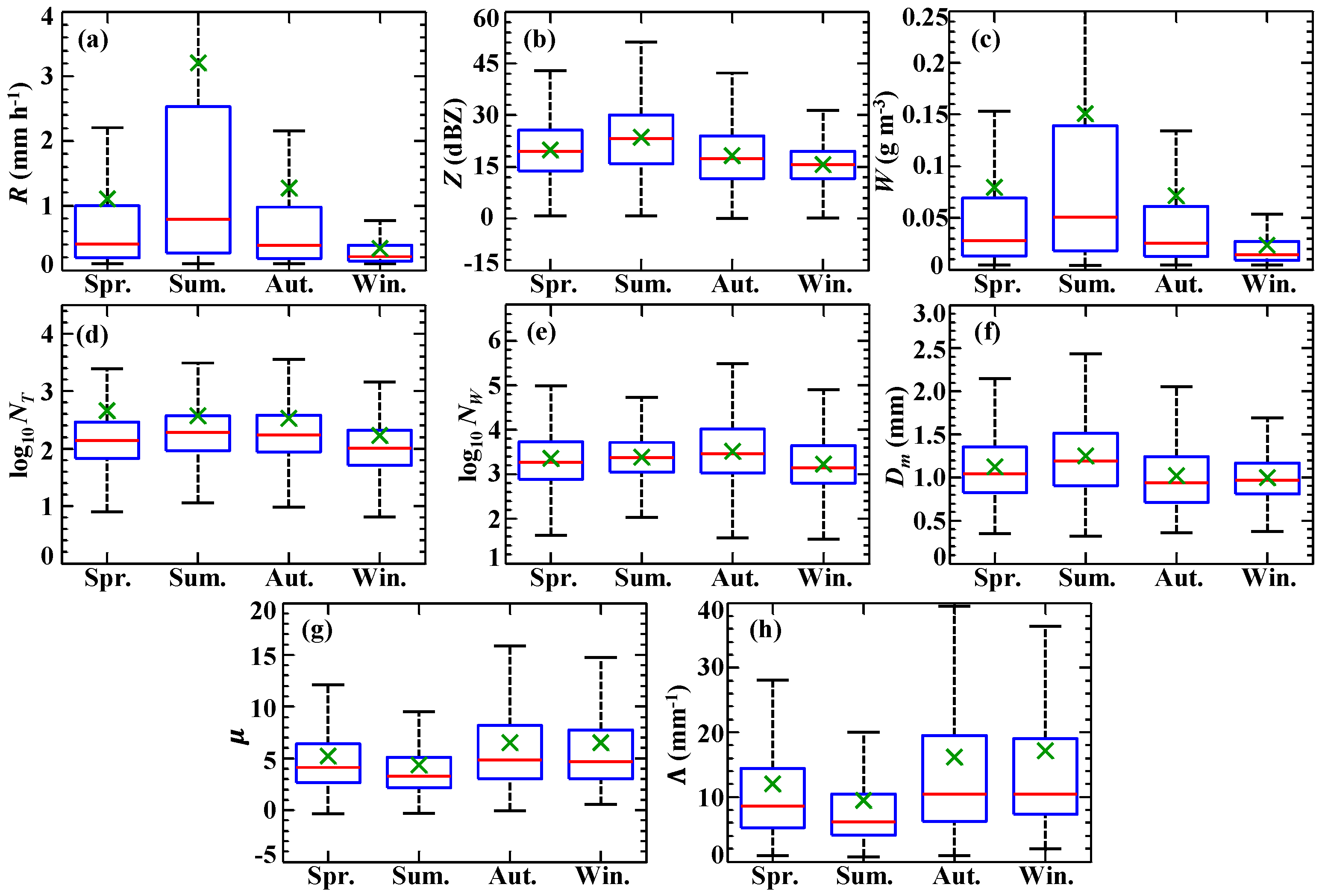
3.1. RSD Seasonal Variation
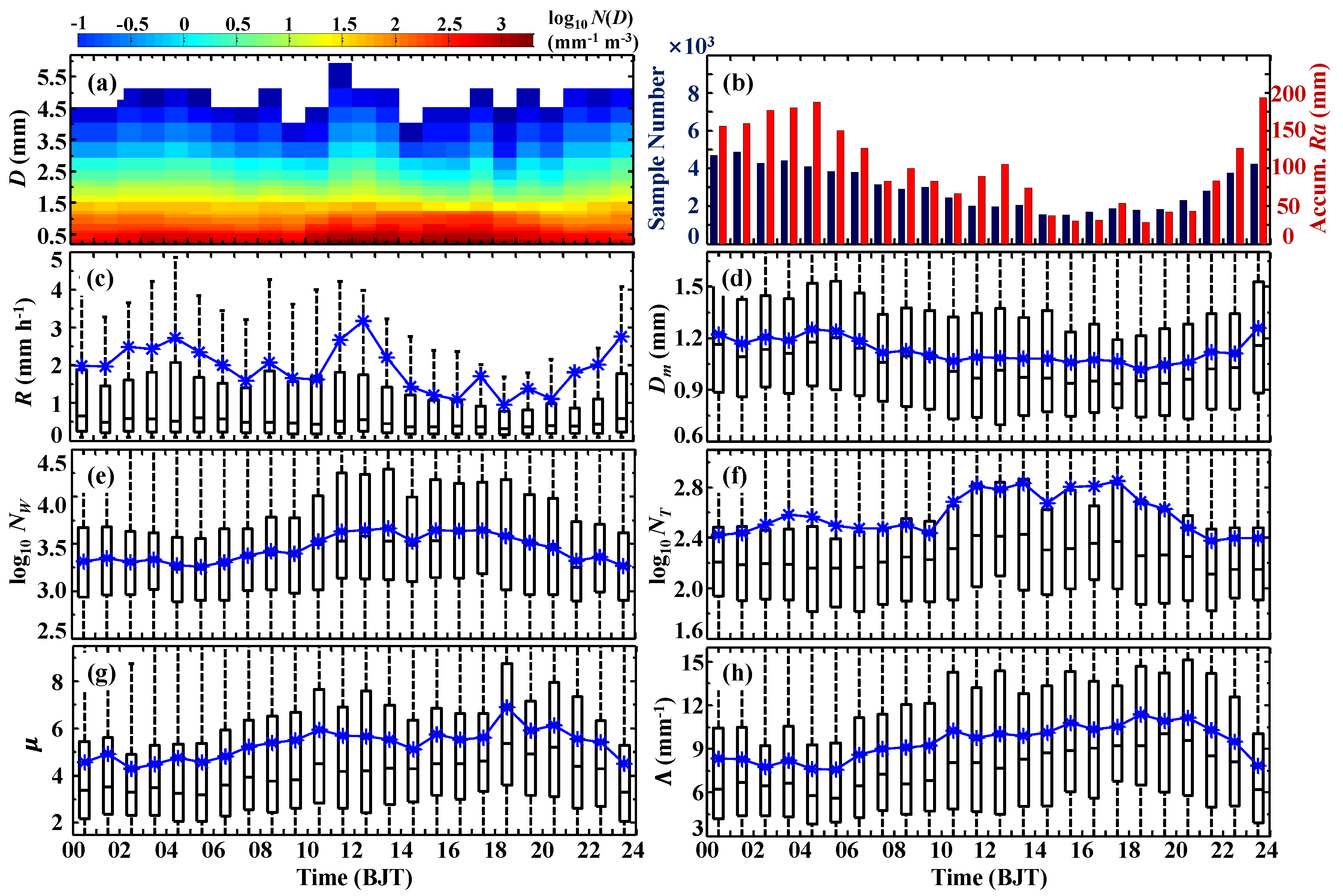
3.2. RSD Diurnal Variation
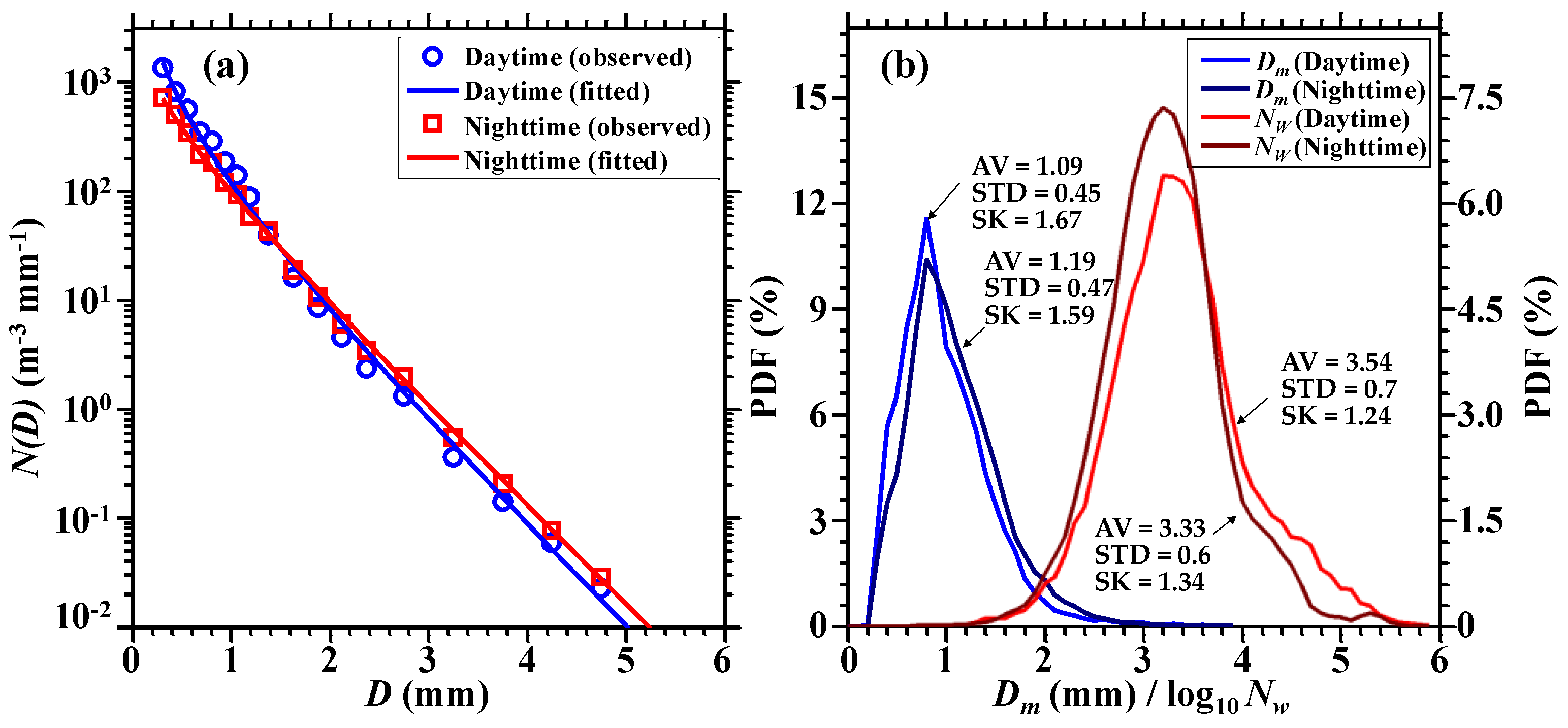
3.3. RSD Differences between Diverse Rain Types
3.4. Local Relationships of μ–Λ and Z–R
4. Discussion
4.1. Analysis of Temporal Variations in Atmospheric Conditions
4.2. Comparison of –
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Villermaux, E.; Bossa, B. Single-drop fragmentation determines size distribution of raindrops. Nat. Phys. 2009, 5, 697–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thurai, M.; Bringi, V.N. Application of the generalized gamma model to represent the full raindrop size distribution spectra. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2018, 57, 1197–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Testik, F.Y.; Gebremichael, M. Rainfall: State of the Science; American Geophysical Union: Washington, DC, USA, 2013; p. 287. [Google Scholar]
- Morrison, H.; van Lier-Walqui, M.; Fridlind, A.M.; Grabowski, W.W.; Harrington, J.Y.; Hoose, C.; Korolev, A.; Kumjian, M.R.; Milbrandt, J.A.; Pawlowska, H.; et al. Confronting the Challenge of Modeling Cloud and Precipitation Microphysics. J. Adv. Model. Earth Syst. 2020, 12, e2019MS001689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ulbrich, C.W. Natural variations in the analytical form of the raindrop size distribution. J. Clim. Appl. Meteor. 1983, 22, 1764–1775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Testud, J.; Oury, S.; Black, R.A.; Amayenc, P.; Dou, X.K. The Concept of ‘Normalized’ Distribution to Describe Raindrop Spectra: A Tool for Cloud Physics and Cloud Remote Sensing. J. Appl. Meteor. 2001, 40, 1118–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallet, C.; Barthes, L. Estimation of Gamma Raindrop Size Distribution Parameters: Statistical Fluctuations and Estimation Errors. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2009, 26, 1572–1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryzhkov, A.V.; Giangrande, S.E.; Schuur, T.J. Rainfall Estimation with a Polarimetric Prototype of WSR-88D. J. Appl. Meteor. 2005, 44, 502–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, M.M.; Sharma, A.; Johnson, F.; Mariethoz, G.; Seed, A. Correcting bias in radar Z-R relationships due to uncertainty in point rain gauge networks. J. Hydrol. 2014, 519, 1668–1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozu, T.; Iguchi, T.; Shimomai, T.; Kashiwagi, N. Raindrop size distribution modeling from a statistical rain parameter relation and its application to the TRMM precipitation radar rain retrieval algorithm. J. Appl. Meteorol. Clim. 2009, 48, 716–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.F.; Sun, J.Z.; Brandes, E.A. Improving Parameterization of Rain Microphysics with Disdrometer and Radar Observations. J. Atmos. Sci. 2006, 63, 1273–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, Y.; Wilcox, E.M.; Gao, L.; Lin, L.; Mitchell, D.L.; Yin, Y.; Zhao, T.; Zhang, L.; Shi, H.; Gao, M. Evaluating Errors in Gamma-Function Representations of the Raindrop Size Distribution: A Method for Determining the Optimal Parameter Set for Use in Bulk Microphysics Schemes. J. Atmos. Sci. 2020, 77, 513–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.J.; Zheng, J.F.; Cheng, Z.G.; Wang, B.Y. Characteristics of Raindrop Size Distribution on the Eastern Slope of the Tibetan Plateau in Summer. Atmosphere 2020, 11, 562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seela, B.K.; Janapati, J.; Lin, P.L.; Reddy, K.K.; Shirooka, R.; Wang, P.K. A comparison study of summer season raindrop size distribution between Palau and Taiwan, two Islands in Western Pacific: RSD characteristics of Taiwan and Palau. J. Geophys. Res.-Atmos. 2017, 122, 11787–11805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozu, T.; Reddy, K.; Mori, S.; Thurai, M.; Ong, J.T.; Rao, D.N.; Shimomai, T. Seasonal and diurnal variations of raindrop size distribution in Asian monsoon region. J. Meteor. Res. Jpn. Ser. II 2006, 84A, 195–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radhakrishna, B.; Rao, T.N.; Rao, D.N.; Rao, N.P.; Nakamura, K.; Sharma, A.K. Spatial and seasonal variability of raindrop size distributions in southeast India. J. Geophys. Res. 2009, 114, D04203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakravarty, K.; Raj, P.E.; Bhattacharya, A.; Maitra, A. Microphysical characteristics of clouds and precipitation during pre-monsoon and monsoon period over a tropical Indian station. J. Atmos. Sol-Terr. Phys. 2013, 94, 28–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ushiyama, T.; Reddy, K.K.; Kubota, H.; Yasunaga, K.; Shirooka, R. Diurnal to interannual variation in the raindrop size distribution over Palau in the western tropical Pacific. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2009, 36, L02810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seela, B.K.; Janapati, J.; Lin, P.L.; Wang, P.K.; Lee, M.T. Raindrop size distribution characteristics of summer and winter season rainfall over north Taiwan. J. Geophys. Res.-Atmos. 2018, 123, 11–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, L.; Zhao, K.; Wang, M.Y.; Zhang, G.F. Seasonal Variations of Observed Raindrop Size Distribution in East China. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2019, 36, 346–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suh, S.H.; You, C.H.; Lee, D.I. Climatological characteristics of raindrop size distributions in Busan, Republic of Korea. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2016, 20, 193–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Hu, Z.; Liu, L.; Zhang, G. Raindrop size distribution measurements at 4,500 m on the Tibetan Plateau during TIPEX-III. J. Geophys. Res.-Atmos. 2017, 122, 11092–11106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.; Guo, X.L. Characteristics of convective cloud and precipitation during summer time at Naqu over Tibetan Plateau. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2016, 61, 1706–1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waldvogel, A. The N0 jump of raindrop spectra. J. Atmos. Sci. 1974, 31, 1067–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, H.W.; Pan, P.C.; Shi, H.Y.; Chen, J.; Wang, J.Z. Observed microphysical characteristics of stratiform and convective precipitation over an inland arid region of Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Water 2020, 12, 2300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokay, A.; Short, D.A. Evidence from tropical raindrop spectra of the origin of rain from stratiform versus convective clouds. J. Appl. Meteor. 1996, 35, 355–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bringi, V.; Chandrasekar, V.; Hubbert, J.; Gorgucci, E.; Randeu, W.L.; Schoenhuber, M. Raindrop Size Distribution in Different Climatic Regimes from Disdrometer and Dual-Polarized Radar Analysis. J. Atmos. Sci. 2003, 60, 354–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, L.; Zhao, K.; Chen, G.; Wang, M.; Zhou, B.; Huang, H.; Hu, D.; Lee, W.C.; Hu, H. Drop size distribution characteristics of seven typhoons in China. J. Geophys. Res.-Atmos. 2018, 123, 6529–6548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, R.C.; Yuan, W.H.; Li, J.; Fu, Y.F. Diurnal phase of late-night against late-afternoon of stratiform and convective precipitation in summer southern contiguous China. Clim. Dyn. 2009, 35, 567–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, R.C.; Zhou, T.J.; Xiong, A.Y.; Zhu, Y.J.; Li, J.M. Diurnal variations of summer precipitation over contiguous China. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2007, 34, L01704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, X.; Liu, X.F. Onset-withdrawal dates of autumn persistent rains over West China and the associated autumn to winter evolution of the atmospheric circulation. Acta Meteorol. Sin. 2013, 71, 913–924. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokay, A.; Wolff, D.B.; Petersen, W. Evaluation of the new version of the laser-optical disdrometer, OTT parsivel2. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2014, 31, 1276–1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, L.; Zhao, K.; Zhang, G.F.; Liu, S.; Chen, G. Impacts of instrument limitations on estimated raindrop size distribution, radar parameters and model microphysics during mei-yu season in east china. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2017, 34, 1021–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battaglia, A.; Rustemeier, E.; Tokay, A.; Blahak, U.; Simmer, C. PARSIVEL snow observations: A critical assessment. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2010, 27, 333–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Q.; Yuan, Y.; Liu, H.J.; Shi, C.E.; Li, J.B. Analysis of microphysical characteristics of the raindrop spectrum over the area between the Yangtze River and the Huaihe River during summer. Acta Meteorol. Sin. 2015, 73, 778–788. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuter, S.E.; Kingsmill, D.E.; Nance, L.B.; Löffler-Mang, M. Observations of precipitation size and fall speed characteristics within coexisting rain and wet snow. J. Appl. Meteorol. Clim. 2006, 45, 1450–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaffrain, J.; Berne, A. Experimental quantification of the sampling uncertainty associated with measurements from PARSIVEL disdrometers. J. Hydrometeorol. 2011, 12, 352–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Guo, J.P.; Yun, Y.X.; Li, J.; Guo, X.R.; Lv, Y.M.; Wang, D.; Li, L.; Zhang, Y. Regional variability of summertime raindrop size distribution from a network of disdrometers in Beijing. Atmos. Res. 2021, 257, 105591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atlas, D.; Srivastava, R.C.; Sekhon, R.S. Doppler radar characteristics of precipitation at vertical incidence. Rev. Geophys. Space Phys. 1973, 11, 1–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulbrich, C.W.; Atlas, D. Rainfall microphysics and radar properties: Analysis methods for drop size spectra. J. Appl. Meteor. 1998, 37, 912–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.F.; Vivekanandan, J.; Brandes, E.A.; Meneghini, R.; Kozu, T. The shape–slope relation in observed gamma raindrop size distributions: Statistical error or useful information. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2003, 20, 1106–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, P.L.; Kliche, D.V.; Johnson, R.W. The Bias and Error in Moment Estimators for Parameters of Drop Size Distribution Functions: Sampling from Gamma Distributions. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2009, 48, 2118–2126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.J.; Yang, J.; Pu, J.P. Statistical characteristics of raindrop size distribution in the Meiyu season observed in eastern China. J. Meteor. Soc. Jpn. 2013, 91, 215–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vivekanandan, J.; Zhang, G.F.; Brandes, E. Polarimetric radar estimators based on a constrained gamma drop size distribution model. J. Appl. Meteor. 2004, 43, 217–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandes, E.A.; Zhang, G.F.; Vivekanandan, J. An evaluation of a drop distribution–based polarimetric radar rainfall estimator. J. Appl. Meteor. 2003, 42, 652–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.C.; Xue, L.L.; Chen, B.J.; Zhang, Y.X. Characteristics of raindrop size distributions in Chongqing observed by a dense network of disdrometers. J. Geophys. Res.-Atmos. 2021, 126, e2021JD035172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenfeld, D.; Ulbrich, C.W. Cloud microphysical properties, processes, and rainfall estimation opportunities. Meteor. Monogr. 2003, 30, 237–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fulton, R.A.; Breidenbach, J.P.; Seo, D.-J.; Miller, D.A. The WSR-88D rainfall algorithm. Weather Forecast. 1998, 13, 377–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marshall, J.S.; Palmer, W.M.K. The distribution of raindrops with size. J. Meteor. 1948, 5, 165–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenfeld, D.; Wolff, D.B.; Atlas, D. General probability-matched relations between radar reflectivity and rain rate. J. Appl. Meteorol. Clim. 1993, 32, 50–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrasekar, V.; Meneghini, R.; Zawadzki, I. Global and Local Precipitation Measurements by Radar. Meteor. Monogr. 2003, 30, 215–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.H.; Liu, L.P. Statistical characteristics of raindrop size distribution in the Tibetan Plateau and southern China. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2017, 34, 727–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, G.C.; Wang, S.G.; Yim, S.H.L.; Li, J.X.; Hu, Y.L.; Shang, Z.W.; Wang, J.Y.; Wang, J.X. Impact of low-pressure systems on winter heavy air pollution in the northwest Sichuan Basin, China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 18, 13601–13615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, T.; Gui, K.; Jiang, W.; Wang, S.; Wang, B.; Zeng, Z.; Che, H.; Wang, Y.; Sun, Y. Air stagnation and its impact on air quality during winter in sichuan and chongqing, southwestern China. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 635, 576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.H.; Xue, M.; Zhu, K.F.; Zhou, B.W. What is the main cause of diurnal variation and nocturnal peak of summer precipitation in Sichuan Basin, China? The key role of boundary layer low-level jet inertial oscillations. J. Geophys. Res.-Atmos. 2019, 124, 2643–2664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.; Wu, T.W.; LI, L. The quasi-stationary feature of nocturnal precipitation in the Sichuan Basin and the role of the Tibetan Plateau. Clim. Dyn. 2012, 41, 977–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, A.; Hu, J.; Chen, S.; Hu, D.; Liang, Z.; Huang, C.; Xiao, L.; Min, C.; Li, H. Statistical Characteristics of Raindrop Size Distribution in the Monsoon Season Observed in Southern China. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

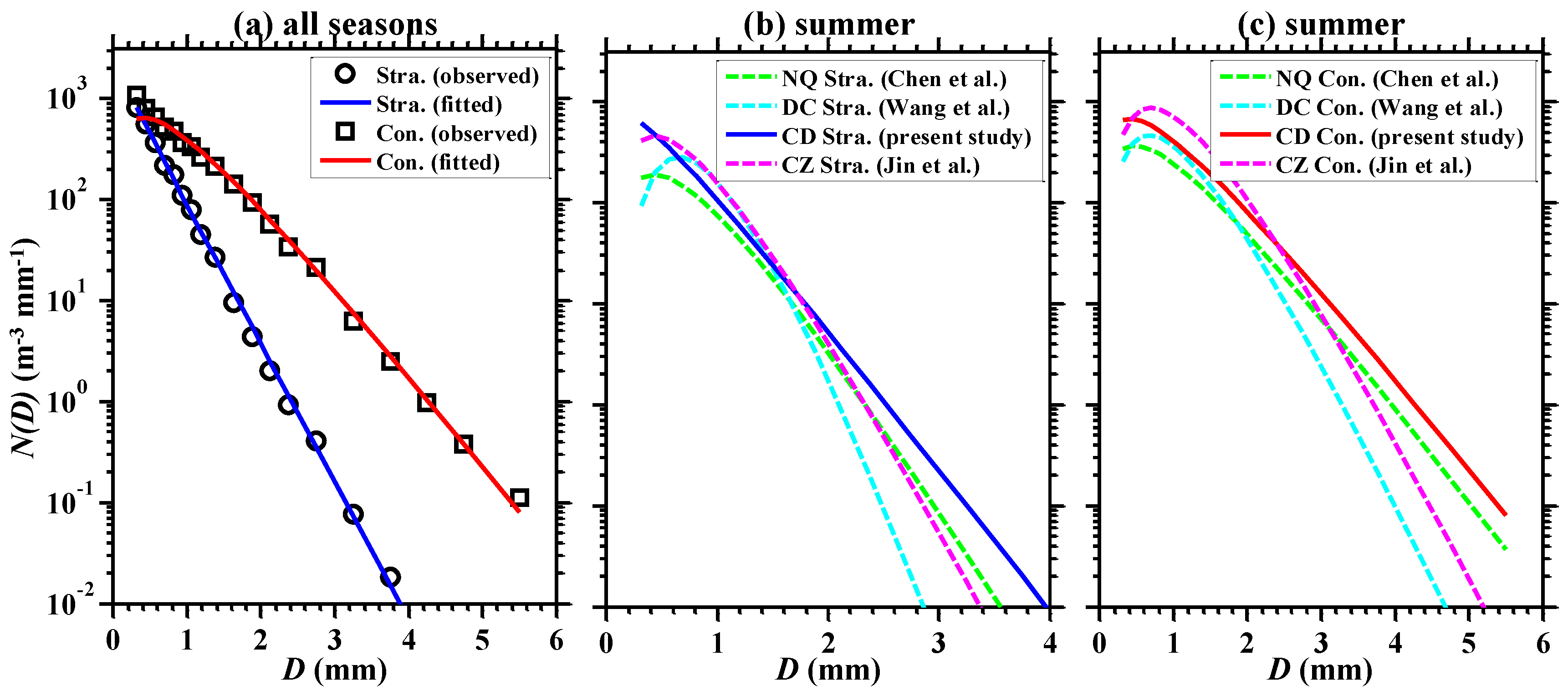
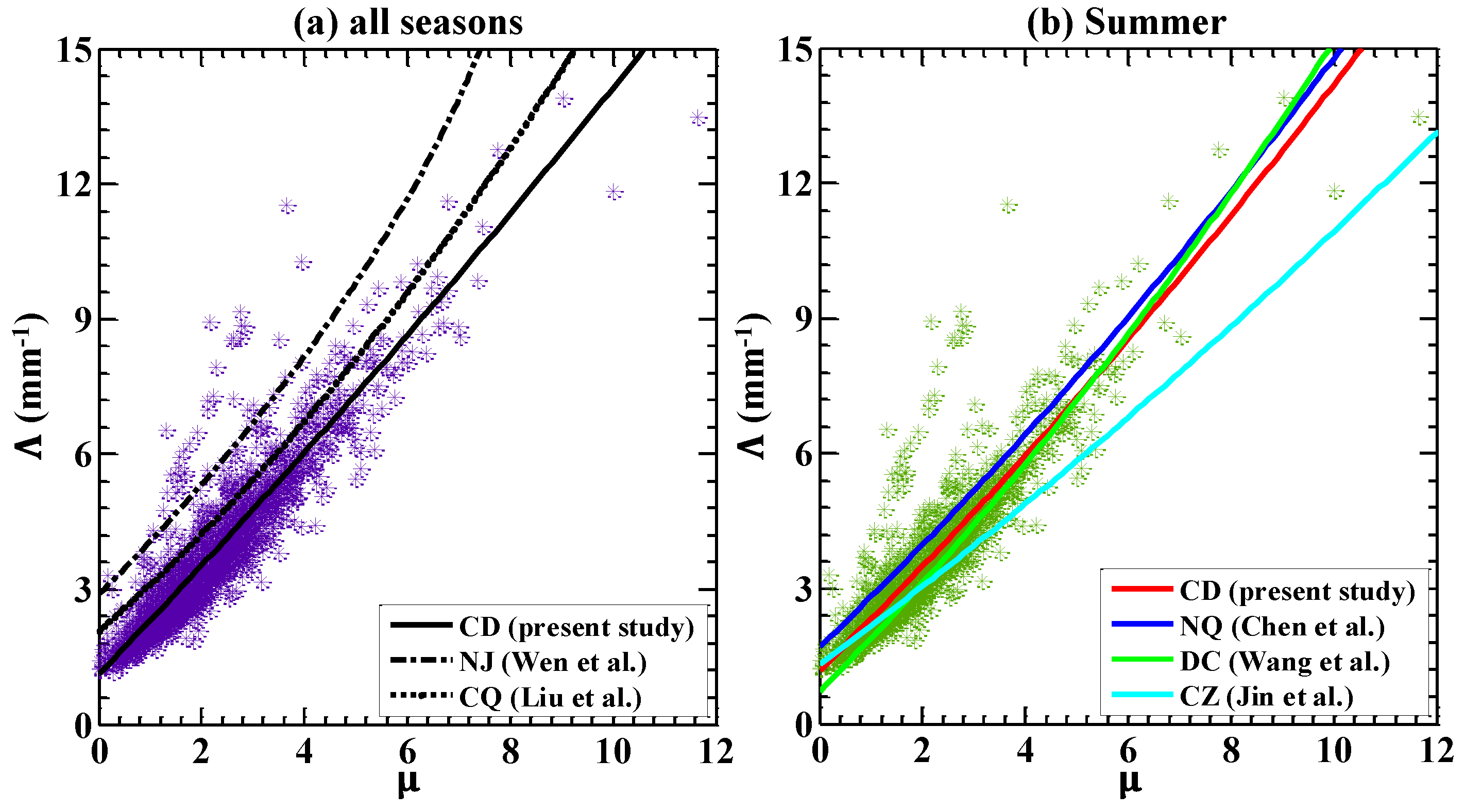
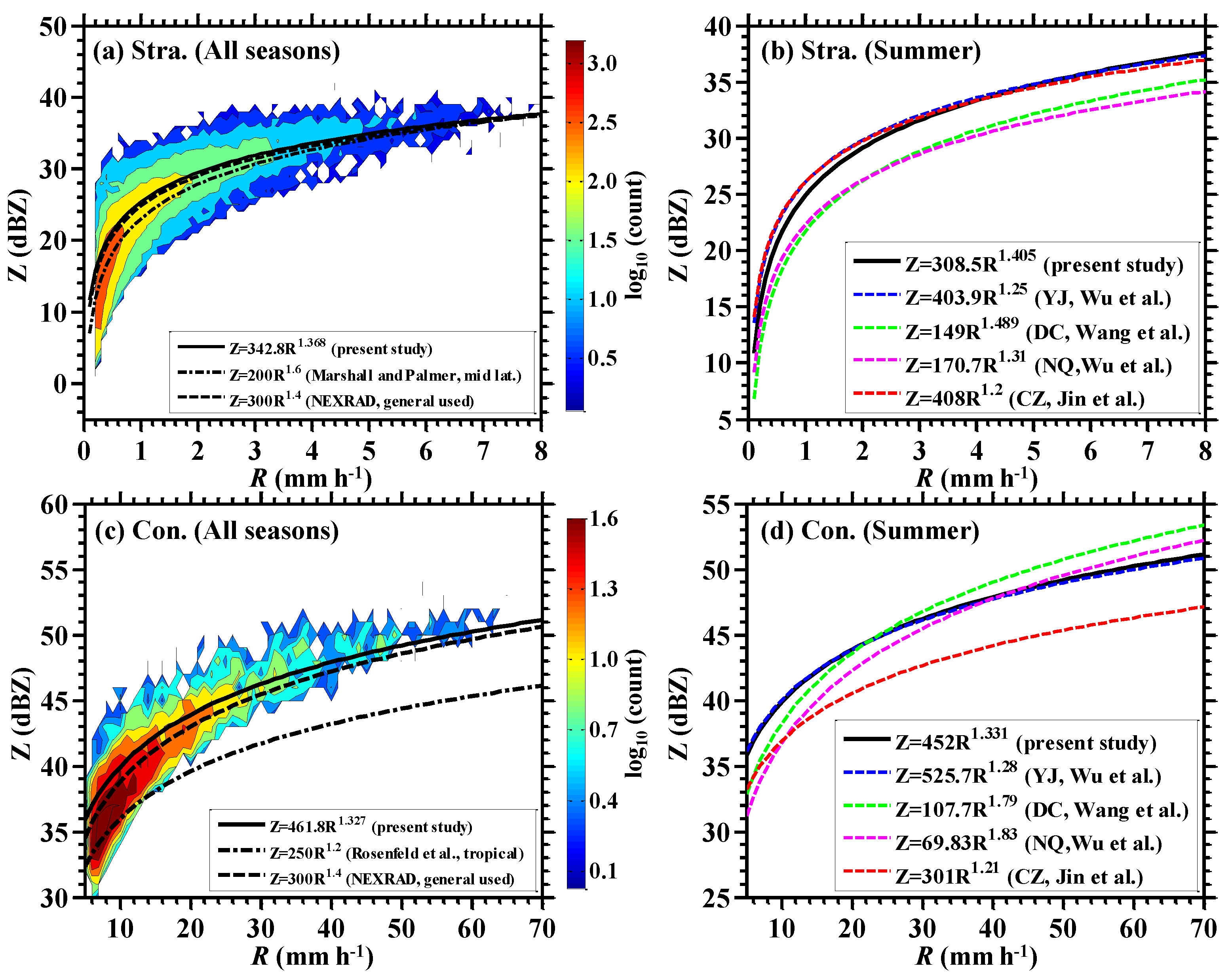
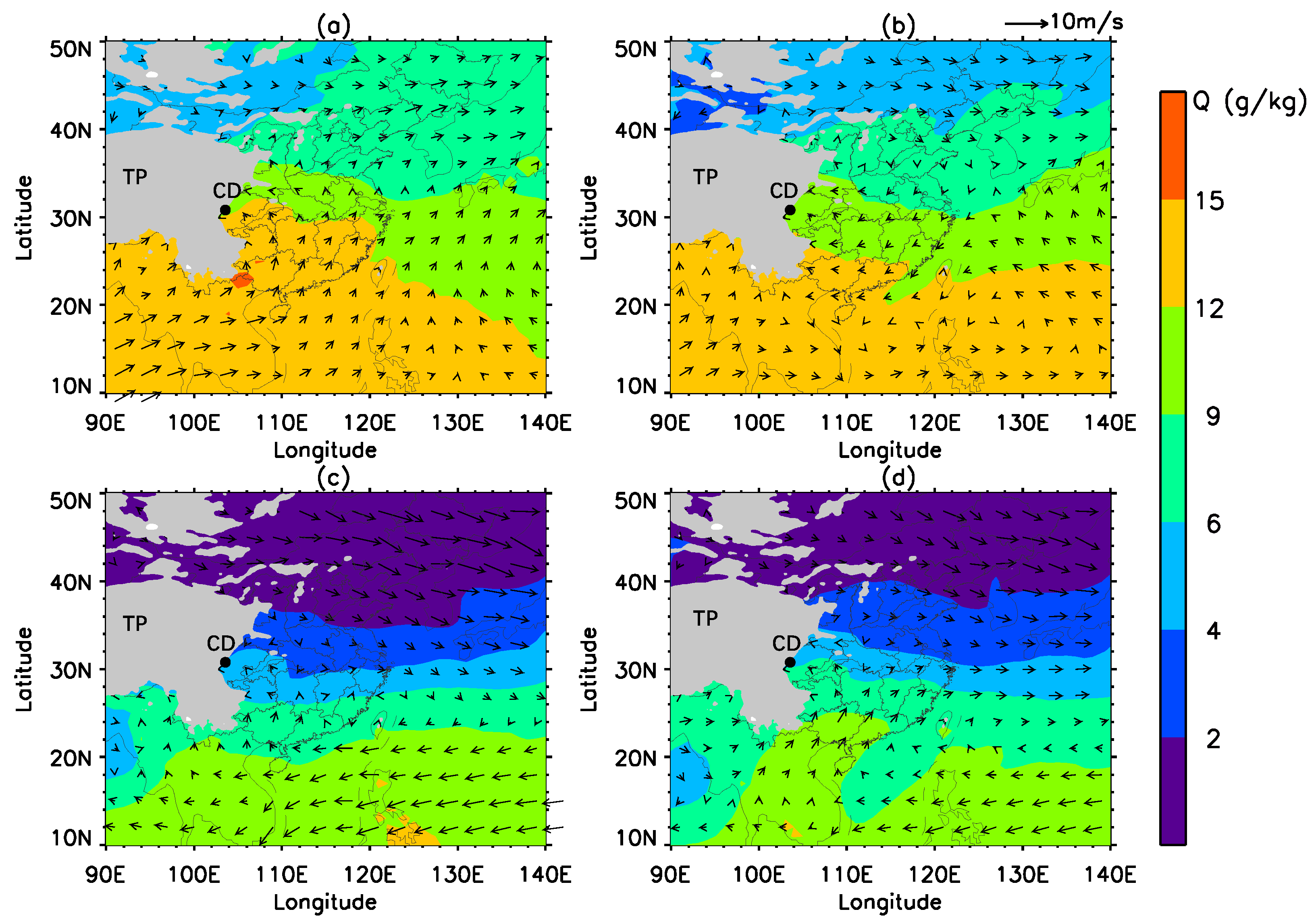
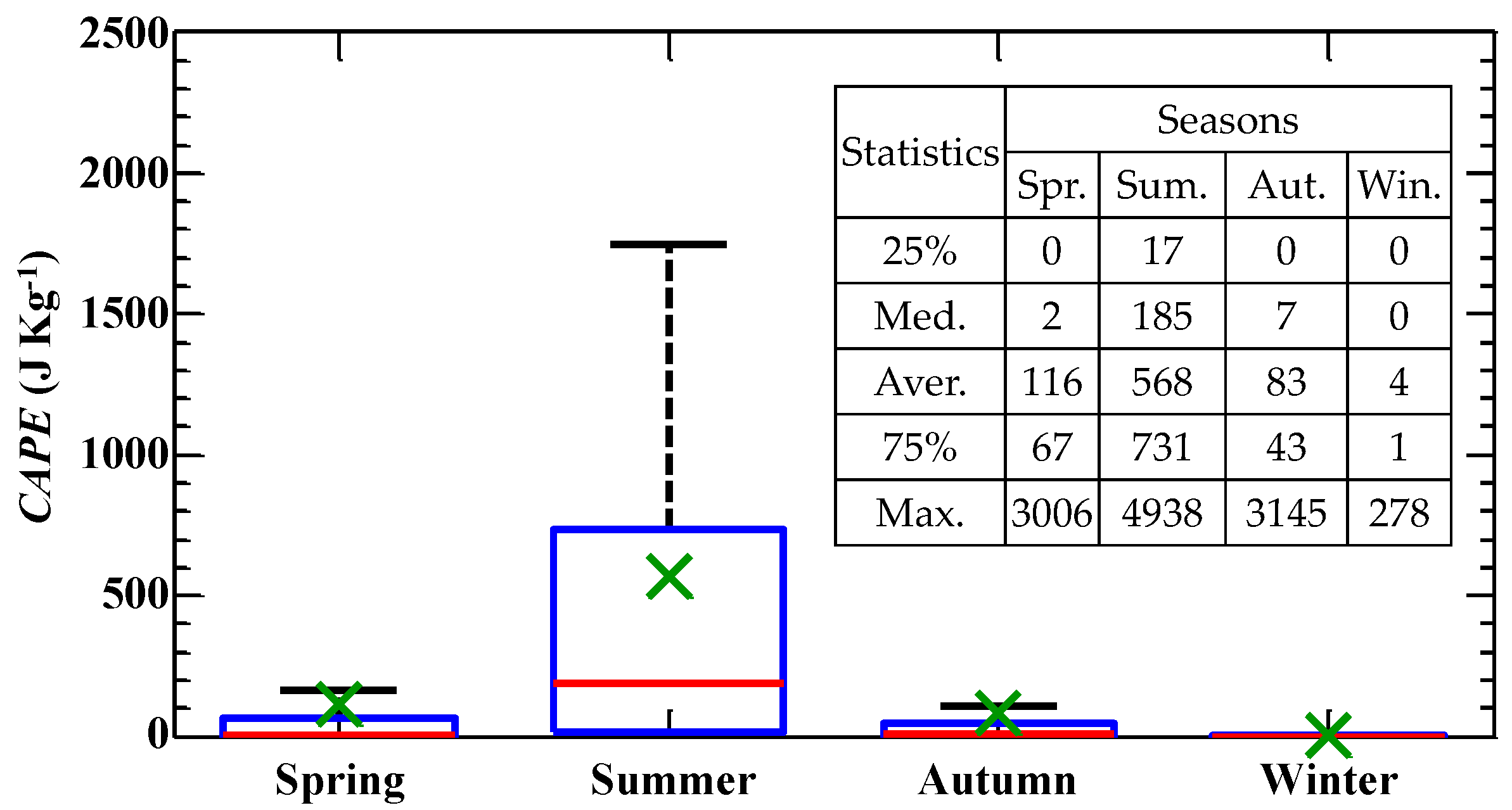

| Season | Accumulated RSD Sample Number | Accumulated Rain Amount (mm) | Averaged Rain Rate (mm h−1) | Rain Rate Range (mm h−1, 5th–95th Percentiles) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Spring | 18,258 (25.7%) | 336 (13.9%) | 1.10 | 0.11–3.70 |
| Summer | 31,482 (44.4%) | 1,682 (69.8%) | 3.21 | 0.12–14.26 |
| Autumn | 17,451 (24.6%) | 369 (15.3%) | 1.27 | 0.11–3.91 |
| Winter | 3,739 (5.3%) | 22 (1.0%) | 0.34 | 0.11–9.23 |
| All seasons | 70,957 | 2,409 | 2.04 | 0.12–7.6 |
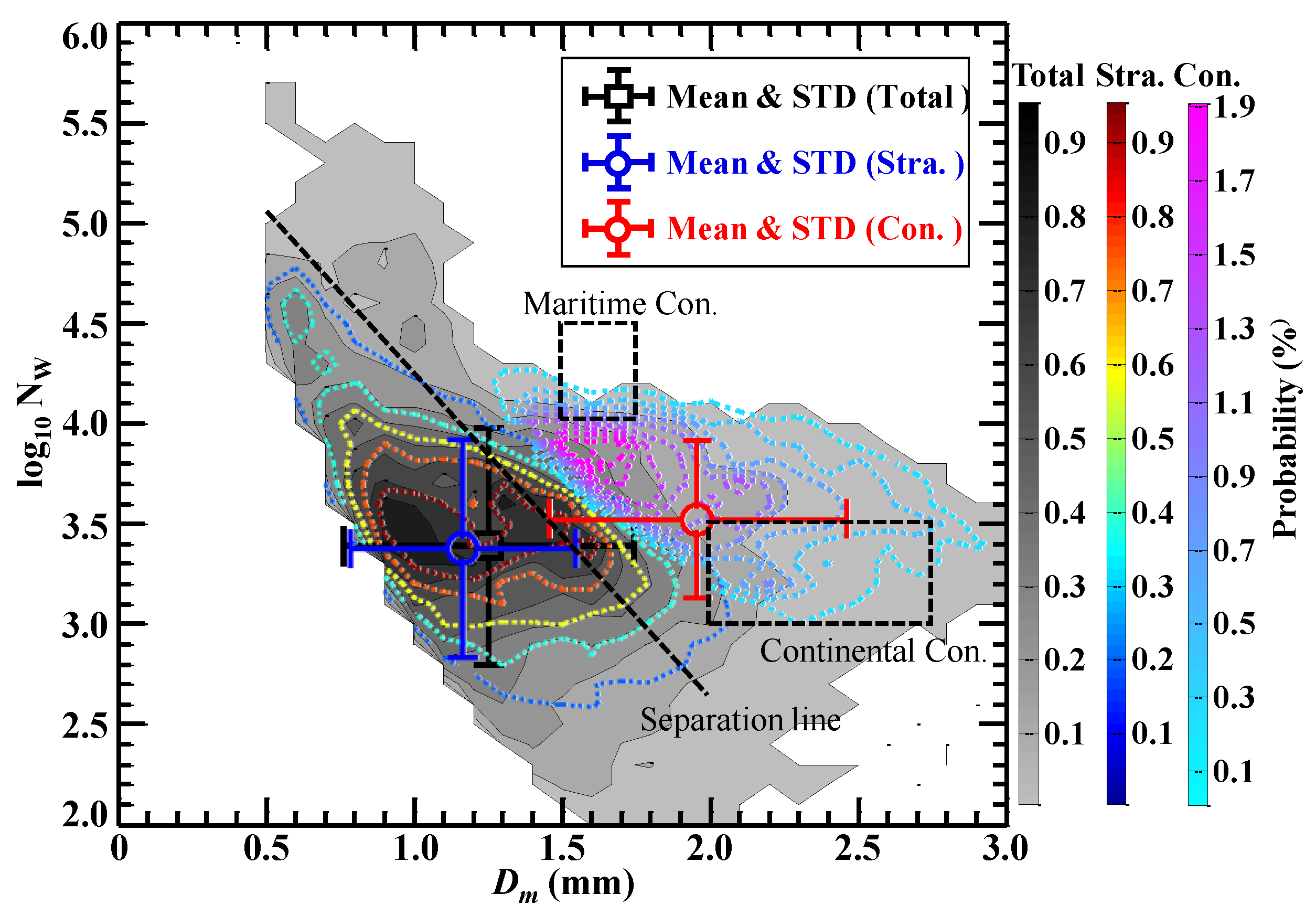
| Location | Chengdu (WSB) | Naqu (Mid-TP) | Daocheng (East TP) | Chongqing (Eastern Sichuan Basin) | Nanjing (East China) | Beijing (North China) | Zhuhai (South China) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Str. (mm) | 1.166 | 1.084 | 0.932 | 1.13 | 1.3 | 1.02 | 1.53 |
| Str. (m−3 mm−1) | 3.376 | 3.6 | 3.467 | 3.83 | 3.45 | 3.71 | 3.87 |
| Con. (mm) | 1.958 | 1.830 | 1.496 | 1.67 | 1.71 | 1.30 | 2.21 |
| Con. (m−3 mm−1) | 3.524 | 3.5 | 3.437 | 3.92 | 3.8 | 4.16 | 4.36 |
| All (mm) | 1.252 | 1.3 | ― | 1.13 | 1.4 | ― | 1.47 |
| All (m−3 mm−1) | 3.389 | 3.39 | ― | 3.76 | 3.55 | ― | 3.86 |
| Reference | Present study | Chen et al. 2017 [22] | Wang et al. 2020 [13] | Liu et al. 2021 [46] | Chen et al. 2013 [43] | Han et al. 2021 [38] | Zhang et al. 2019 [57] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, T.; Wei, W.; Zheng, L.; Chen, Y. Characteristics and Variations of Raindrop Size Distribution in Chengdu of the Western Sichuan Basin, China. Atmosphere 2023, 14, 76. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14010076
Zhang T, Wei W, Zheng L, Chen Y. Characteristics and Variations of Raindrop Size Distribution in Chengdu of the Western Sichuan Basin, China. Atmosphere. 2023; 14(1):76. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14010076
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Tao, Wei Wei, Liying Zheng, and Yangruixue Chen. 2023. "Characteristics and Variations of Raindrop Size Distribution in Chengdu of the Western Sichuan Basin, China" Atmosphere 14, no. 1: 76. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14010076
APA StyleZhang, T., Wei, W., Zheng, L., & Chen, Y. (2023). Characteristics and Variations of Raindrop Size Distribution in Chengdu of the Western Sichuan Basin, China. Atmosphere, 14(1), 76. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14010076





