Direct Electrical Sensing of Iodine Gas by a Covalent Organic Framework-Based Sensor
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Characterization
2.3. Synthesis of the AQ-COF
2.4. Sensor Fabrication
2.5. Iodine Gas Exposure
2.6. Selectivity Test
3. Results and Discussion
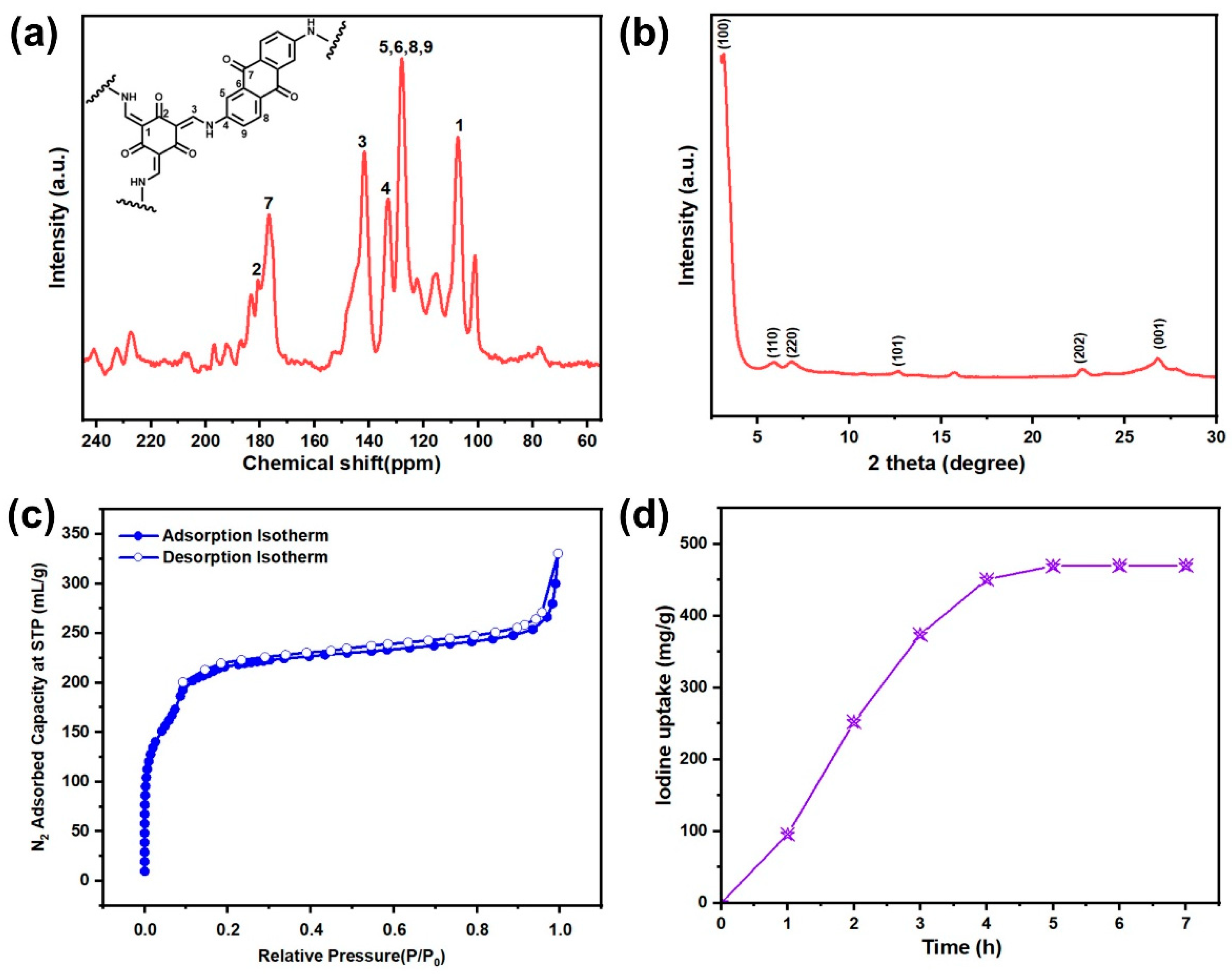
3.1. Materials Synthesis and Characterization
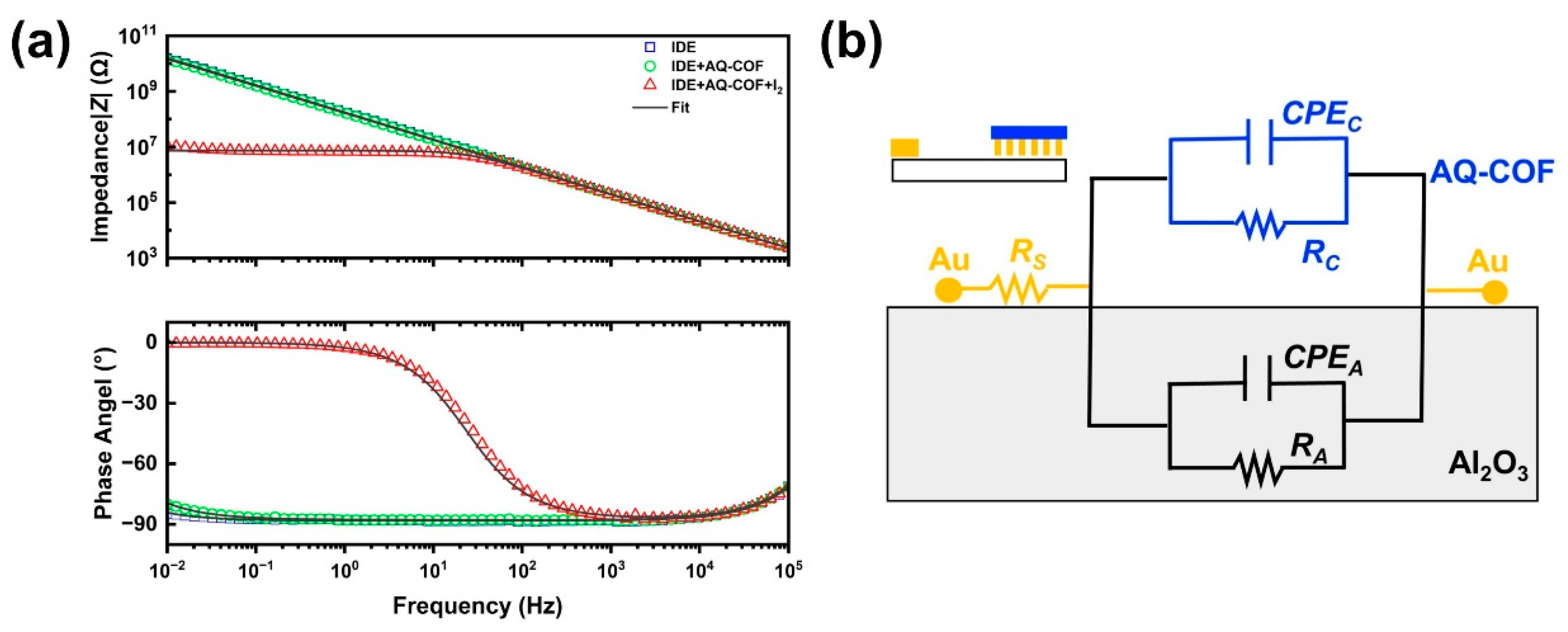
3.2. Sensor Fabrication and the Iodine Vapor Impedance Sensing
3.3. Time-Dependent Sensor Response
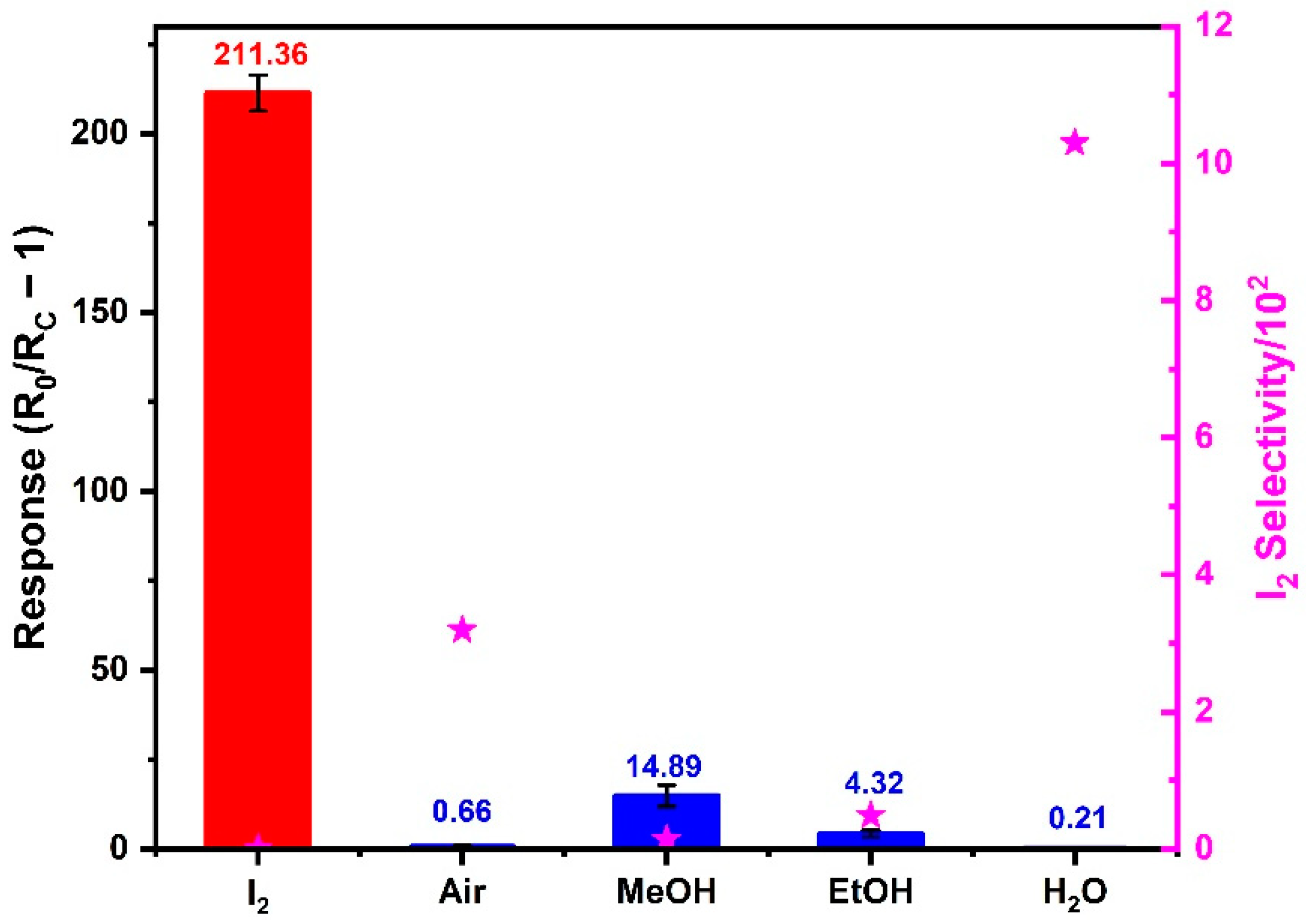
3.4. Selectivity
3.5. Mechanism Study
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Guo, X.; Li, Y.; Zhang, M.; Cao, K.; Tian, Y.; Qi, Y.; Li, S.; Li, K.; Yu, X.; Ma, L. Colyliform Crystalline 2D Covalent Organic Frameworks (COFs) with Quasi-3D Topologies for Rapid I2 Adsorption. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 22697–22705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ten Hoeve, J.E.; Jacobson, M.Z. Worldwide health effects of the Fukushima Daiichi nuclear accident. Energy Environ. Sci. 2012, 5, 8743–8757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; da Silva, I.; Godfrey, H.G.W.; Callear, S.K.; Sapchenko, S.A.; Cheng, Y.; Vitorica-Yrezabal, I.; Frogley, M.D.; Cinque, G.; Tang, C.C.; et al. Confinement of Iodine Molecules into Triple-Helical Chains within Robust Metal-Organic Frameworks. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 16289–16296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kupper, F.C.; Feiters, M.C.; Olofsson, B.; Kaiho, T.; Yanagida, S.; Zimmermann, M.B.; Carpenter, L.J.; Luther, G.W., 3rd; Lu, Z.; Jonsson, M.; et al. Commemorating two centuries of iodine research: An interdisciplinary overview of current research. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 11598–11620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sava, D.F.; Rodriguez, M.A.; Chapman, K.W.; Chupas, P.J.; Greathouse, J.A.; Crozier, P.S.; Nenoff, T.M. Capture of volatile iodine, a gaseous fission product, by zeolitic imidazolate framework-8. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 12398–12401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ewing, R.C.; von Hippel, F.N. Nuclear Waste Management in the United States-Starting Over. Science 2009, 325, 151–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koenig, T.K.; Baidar, S.; Campuzano-Jost, P.; Cuevas, C.A.; Dix, B.; Fernandez, R.P.; Guo, H.; Hall, S.R.; Kinnison, D.; Nault, B.A.; et al. Quantitative detection of iodine in the stratosphere. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 1860–1866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Yang, P.; Li, Y.; Gu, J. AgNPs-Containing Metal–Organic Frameworks for the Effective Adsorption and Immobilization of Radioactive Iodine. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2020, 65, 1986–1992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, G.; Zhu, L.; Duan, T.; Zhang, L.; Liu, B.; Lei, J. Efficient capture of iodine by a polysulfide-inserted inorganic NiTi-layered double hydroxides. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 378, 1986–1992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.B.; Yu, C.; Guo, H.; Cheng, Y.Q.; Li, Y.W.; Zheng, D.Y.; Feng, S.S.; Lin, Y.X. Robust fluorescent detection of iodine vapor by a film sensor based on a polymer of intrinsic microporosity. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 438, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Yu, C.; Wang, X. Fast and Quantitative Electrical Detection of Iodine Based on a Polymer of Intrinsic Microporosity. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2022, 4, 9151–9159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz-Ramirez, M.L.; Vargas, B.; Raziel Alvarez, J.; Landeros-Rivera, B.; Rivera-Almazo, M.; Ramos, C.; Gabriel Flores, J.; Morales, E.; Vargas, R.; Garza, J.; et al. Fluorometric detection of iodine by MIL-53(Al)-TDC. Dalton Trans. 2020, 49, 6572–6577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Small, L.J.; Hill, R.C.; Krumhansl, J.L.; Schindelholz, M.E.; Chen, Z.; Chapman, K.W.; Zhang, X.; Yang, S.; Schroder, M.; Nenoff, T.M. Reversible MOF-Based Sensors for the Electrical Detection of Iodine Gas. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 27982–27988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Small, L.J.; Nenoff, T.M. Direct Electrical Detection of Iodine Gas by a Novel Metal-Organic-Framework-Based Sensor. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 44649–44655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, J.; Namuangruk, S.; Kong, W.; Kungwan, N.; Guo, J.; Wang, C. Manipulation of Amorphous-to-Crystalline Transformation: Towards the Construction of Covalent Organic Framework Hybrid Microspheres with NIR Photothermal Conversion Ability. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 13979–13984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uribe-Romo, F.J.; Hunt, J.R.; Furukawa, H.; Klock, C.; O’Keeffe, M.; Yaghi, O.M. A Crystalline Imine-Linked 3-D Porous Covalent Organic Framework. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 4570–4571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kandambeth, S.; Mallick, A.; Lukose, B.; Mane, M.V.; Heine, T.; Banerjee, R. Construction of crystalline 2D covalent organic frameworks with remarkable chemical (acid/base) stability via a combined reversible and irreversible route. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 19524–19527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, S.-Y.; Gao, J.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Song, W.-G.; Su, C.-Y.; Wang, W. Construction of Covalent Organic Framework for Catalysis: Pd/COF-LZU1 in Suzuki-Miyaura Coupling Reaction. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 19816–19822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Gao, J.; Jiang, D. Stable, crystalline, porous, covalent organic frameworks as a platform for chiral organocatalysts. Nat. Chem. 2015, 7, 905–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Han, X.; Zhang, J.; Wu, X.; Liu, Y.; Cui, Y. Homochiral 2D Porous Covalent Organic Frameworks for Heterogeneous Asymmetric Catalysis. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 12332–12335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Combarieu, G.; Morcrette, M.; Millange, F.; Guillou, N.; Cabana, J.; Grey, C.P.; Margiolaki, I.; Férey, G.; Tarascon, J.M. Influence of the Benzoquinone Sorption on the Structure and Electrochemical Performance of the MIL-53(Fe) Hybrid Porous Material in a Lithium-Ion Battery. Chem. Mater. 2009, 21, 1602–1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chmiola, J.; Yushin, G.; Gogotsi, Y.; Portet, C.; Simon, P.; Taberna, P.L. Anomalous Increase in Carbon Capacitance at Pore Sizes Less Than 1 Nanometer. Science 2006, 313, 1760–1763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandra, S.; Kundu, T.; Kandambeth, S.; BabaRao, R.; Marathe, Y.; Kunjir, S.M.; Banerjee, R. Phosphoric Acid Loaded Azo (−N=N−) Based Covalent Organic Framework for Proton Conduction. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 6570–6573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, S.-Y.; Dong, M.; Wang, Y.-W.; Chen, Y.-T.; Wang, H.-Z.; Su, C.-Y.; Wang, W. Thioether-Based Fluorescent Covalent Organic Framework for Selective Detection and Facile Removal of Mercury(II). J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 3031–3037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, H.; Li, N.; Linghu, J.; Dong, J.; Wang, Y.; Karmakar, A.; Yuan, J.; Li, M.; Buenconsejo, P.J.S.; Liu, G.; et al. Chip-Level Integration of Covalent Organic Frameworks for Trace Benzene Sensing. ACS Sens. 2020, 5, 1474–1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, S.S.; Li, X.; Zhu, J.Y.; Zhang, G.; Van Puyvelde, P.; Van der Bruggen, B. Covalent organic frameworks for membrane separation. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2019, 48, 2665–2681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.X.; Liu, X.; Li, Y.P.; Xia, M.; Xia, T.; Sun, H.C.; Sui, Z.Y.; Hu, X.M.; Chen, Q. Ultra-stable fluorescent 2D covalent organic framework for rapid adsorption and selective detection of radioiodine. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2021, 319, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, J.; Li, H.; Zhao, J.; Guan, X.; Li, C.; Yu, G.; Valtchev, V.; Yan, Y.; Qiu, S.; Fang, Q. Tetrathiafulvalene-based covalent organic frameworks for ultrahigh iodine capture. Chem. Sci. 2021, 12, 8452–8457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Y.; Pan, T.; Lei, Q.; Chen, C.; Dong, X.; Yuan, Y.; Maksoud, W.A.; Zhao, L.; Cavallo, L.; Pinnau, I.; et al. Efficient and simultaneous capture of iodine and methyl iodide achieved by a covalent organic framework. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 2878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Q.; Li, X.; Ning, G.H.; Leng, K.; Tian, B.B.; Liu, C.B.; Tang, W.; Xu, H.S.; Loh, K.P. Highly photoluminescent two-dimensional imine-based covalent organic frameworks for chemical sensing. Chem. Commun. 2018, 54, 2349–2352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.J.; Liu, D.Q.; Wang, G.T. Covalent Organic Frameworks for Chemical and Biological Sensing. Molecules 2022, 27, 2586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.D.; Yuan, B.Q.; Liu, G.; Zhang, D.J. Electrochemical Sensors Based on Covalent Organic Frameworks: A Critical Review. Front. Chem. 2020, 8, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Lan, X.; An, G.; Ricardez-Sandoval, L.; Wang, Z.; Bai, G. Visible-Light-Responsive Anthraquinone Functionalized Covalent Organic Frameworks for Metal-Free Selective Oxidation of Sulfides: Effects of Morphology and Structure. ACS Catal. 2020, 10, 6664–6675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, Q.; Wang, H.; Wu, Y.; Lv, L.P.; Chen, S.; Sun, W.; Wang, Y. Covalent-Induced Heterostructure of Covalent-Organic Frameworks and MXene as Advanced Electrodes with Motivated Pseudocapacitance Performance. ChemElectroChem 2022, 9, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeBlase, C.R.; Silberstein, K.E.; Truong, T.T.; Abruna, H.D.; Dichtel, W.R. beta-Ketoenamine-linked covalent organic frameworks capable of pseudocapacitive energy storage. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 16821–16824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Yan, D.; Zhang, Z.; Matsushita, M.M.; Awaga, K. Electron Highways into Nanochannels of Covalent Organic Frameworks for High Electrical Conductivity and Energy Storage. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 7661–7665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, X.; He, Q.; Li, M.; Wang, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, W. Fluorescence and electrochemical detection of iodine vapor in the presence of high humidity using Ln-based MOFs. Dalton Trans. 2021, 50, 15567–15575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Geng, T.M.; Tang, K.B. The cyclotriphosphazene-based covalent organic frameworks constructed entirely by flexible building blocks for adsorping and fluorescence sensing iodine. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2022, 343, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, L.P.; Han, D.D.; Dong, J.H.; Jiang, W.Q.; Nie, R.M.; Yang, X.B.; Luo, X.L.; Li, Z.P. Constructing Stable and Porous Covalent Organic Frameworks for Efficient Iodine Vapor Capture. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2021, 42, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.N.; Wei, W.; Ma, J.G.; Luo, J.Q.; Zhou, Y.M.; Zhou, Z.Y.; Liu, S.J. Adsorption of Iodine on Adamantane-Based Covalent Organic Frameworks. ChemistrySelect 2021, 6, 10141–10148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.-X.; Tang, X.-H.; Wu, J.-L.; Dong, Z.-Y.; Yan, Y.-L.; Zheng, S.-R.; Fan, J.; Li, X.; Cai, S.; Zhang, W.-G. Transformation of a Hydrazone-Linked Covalent Organic Framework into a Highly Stable Hydrazide-Linked One. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2022, 4, 4624–4631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Dong, X.; Yin, J.; Li, Z.G.; Li, X.; Zhang, D.; Pan, T.; Lei, Q.; Liu, X.; Xie, Y.; et al. Chemically Stable Guanidinium Covalent Organic Framework for the Efficient Capture of Low-Concentration Iodine at High Temperatures. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2022, 144, 6821–6829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holzapfel, M.; Martinent, A.; Alloin, F.; Le Gorrec, B.; Yazami, R.; Montella, C. First lithiation and charge/discharge cycles of graphite materials, investigated by electrochemical impedance spectroscopy. J. Electr. Chem. 2003, 546, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Lu, L.H.; Chang, Y.Y.; Liu, M. Gas sensing based on metal-organic frameworks: Concepts, functions, and developments. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 429, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhou, W.; Kang, C.; Yu, C.; Cui, Z.; Wang, X. Direct Electrical Sensing of Iodine Gas by a Covalent Organic Framework-Based Sensor. Atmosphere 2023, 14, 181. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14010181
Zhou W, Kang C, Yu C, Cui Z, Wang X. Direct Electrical Sensing of Iodine Gas by a Covalent Organic Framework-Based Sensor. Atmosphere. 2023; 14(1):181. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14010181
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhou, Wanshuang, Chun Kang, Cong Yu, Zhaojie Cui, and Xinbo Wang. 2023. "Direct Electrical Sensing of Iodine Gas by a Covalent Organic Framework-Based Sensor" Atmosphere 14, no. 1: 181. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14010181
APA StyleZhou, W., Kang, C., Yu, C., Cui, Z., & Wang, X. (2023). Direct Electrical Sensing of Iodine Gas by a Covalent Organic Framework-Based Sensor. Atmosphere, 14(1), 181. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14010181










