Impact of Thermal Forcing over the Southeast of the Tibetan Plateau on Frequency of Tropical Cyclones Affecting Guangxi during Boreal Summer
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
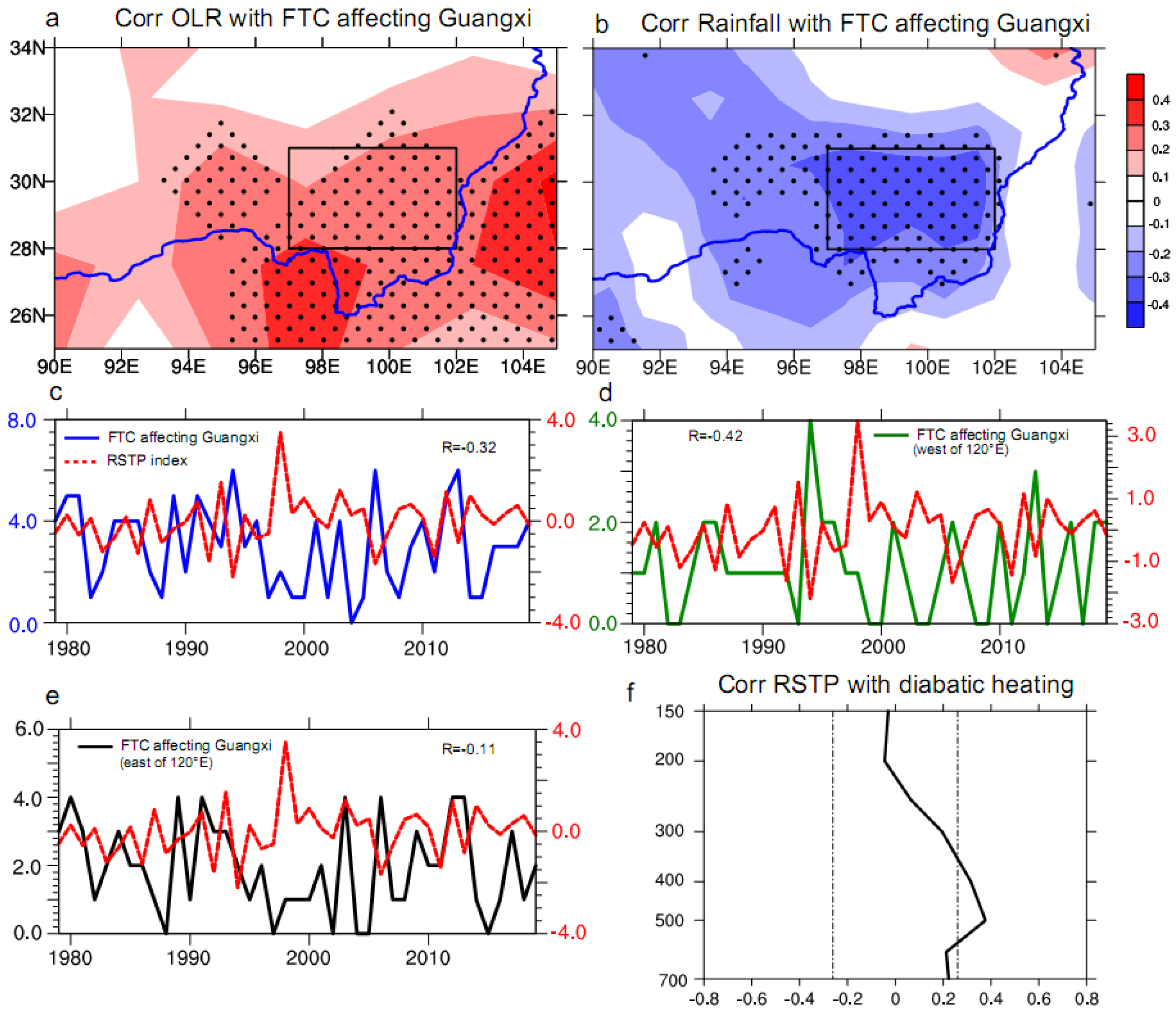
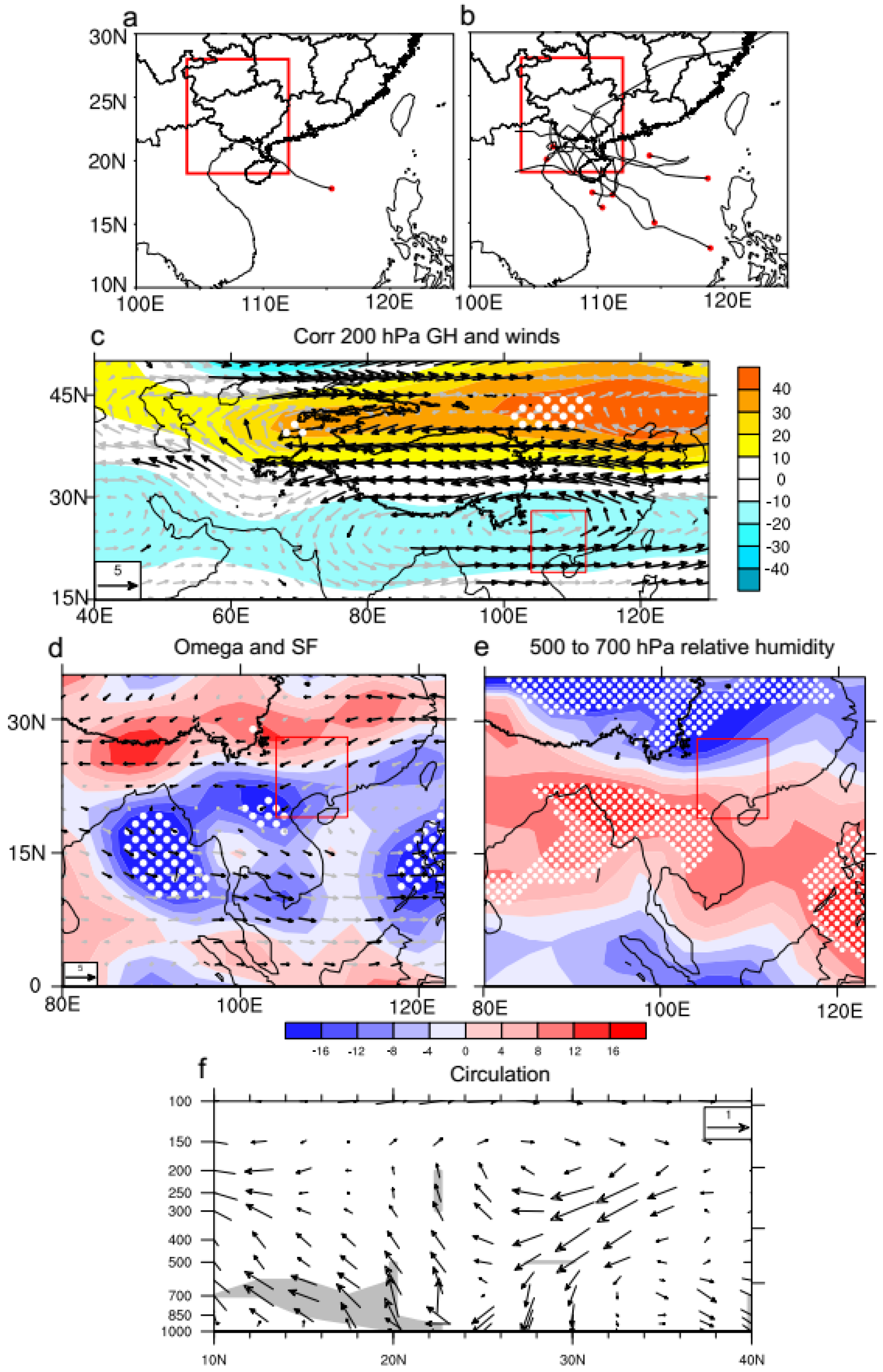
3.1. Relationship between Thermal Forcing over the Southeast of the TP and the FTC Affecting Guangxi
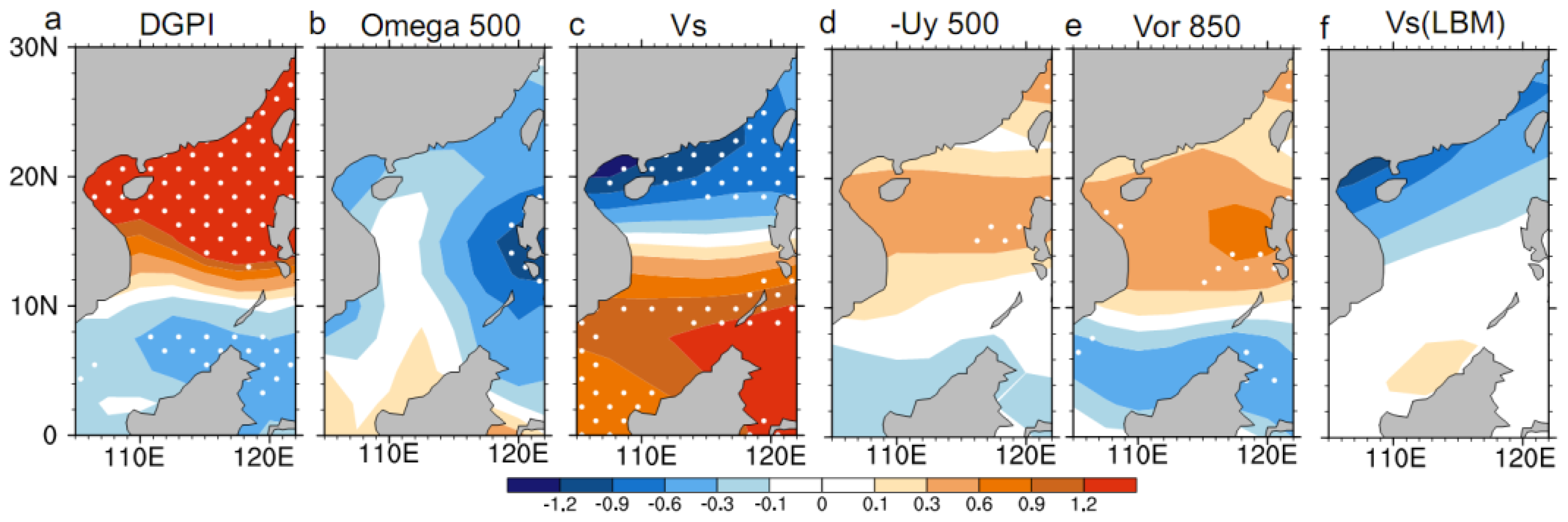
3.2. Results from LBM Experiments
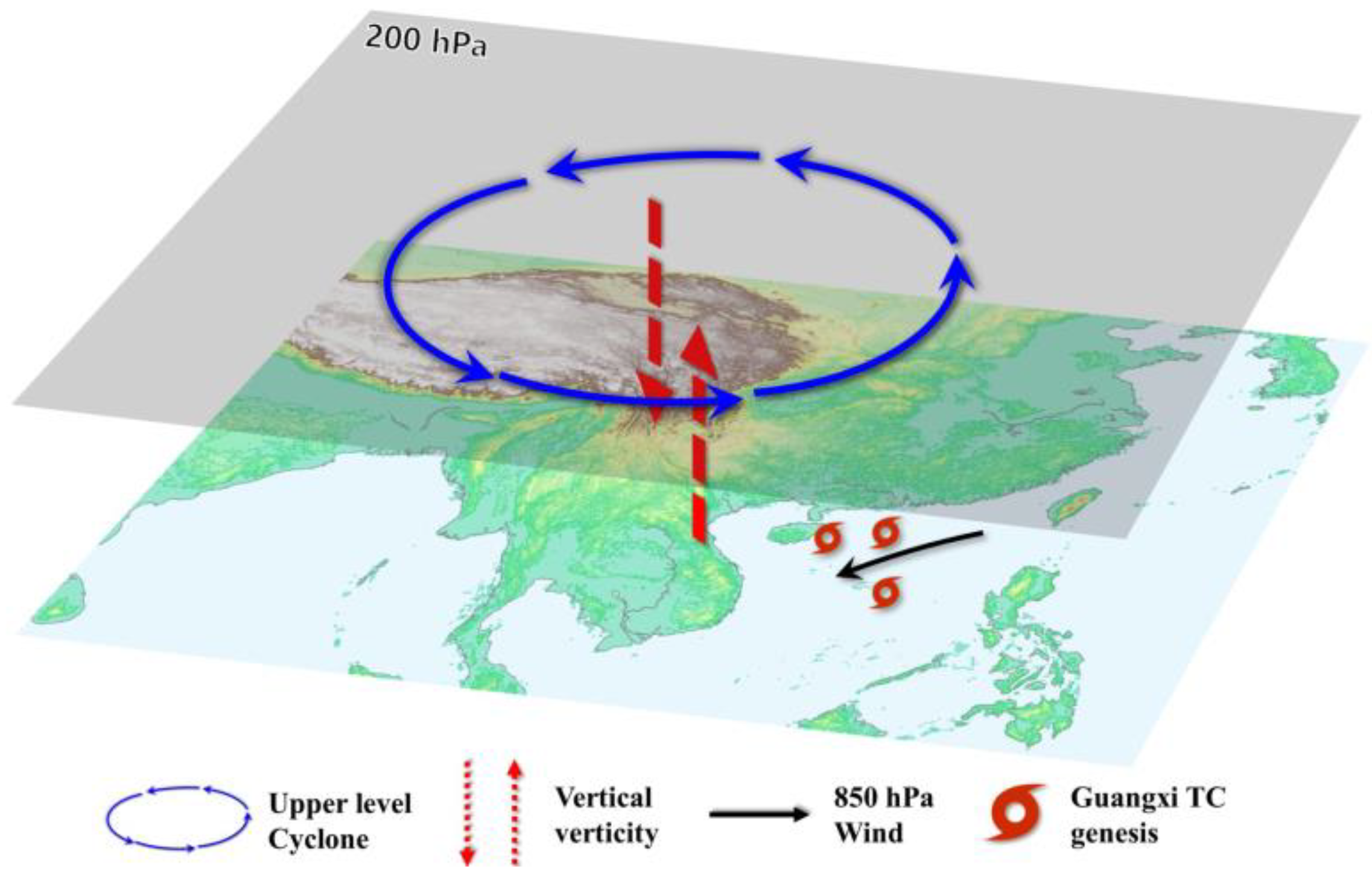
4. Conclusions and Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Woodruff, J.D.; Irish, J.L.; Camargo, S.J. Coastal flooding by tropical cyclones and sea-level rise. Nature 2013, 504, 44–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, H.; Jiang, X.; Wu, L. Modulation of Northwest Pacific tropical cyclone genesis by the intraseasonal variability. J. Meteorol. Soc. Jpn. 2015, 93, 81–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peduzzi, P.B.; Chatenoux, B.; Dao, H.; De Bono, A.; Herold, C.; Kossin, J.; Mouton, F.; Nordbeck, O. Global trends in tropical cyclone risk. Nat. Clim. Change 2012, 2, 289–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, K.; Zhao, H.; Raga, G.B.; Yoshida, R.; Wang, W.; Klotzbach, P.J. Changes in extended boreal summer tropical cyclogenesis associated with large-scale flow patterns over the western North Pacific in response to the global warming hiatus. Clim. Dyn. 2021, 56, 515–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Hu, C.; Huang, G.; Yao, C.; Zheng, Z.; Wang, T.; Wu, Z.; Yang, S.; Chen, D. Perspective on landfalling frequency and genesis location variations of southern China typhoon during peak summer. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2019, 46, 6830–6838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Yang, S.; Wu, Z.; Cai, F. Large-scale atmospheric features favoring the tropical cyclone activity affecting the Guangdong–Hong Kong–Macao Greater Bay Area of China. Environ. Res. Lett. 2022, 17, 104057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Zheng, Y.; Liu, C.; Huang, Z.; Weng, H.; Xu, J.; Tu, S. Climatology of Different Classifications of Tropical Cyclones Landfalling in Guangdong Province of China during 1951–2020. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.S.; Chan, J.C.L. Recent increase in extreme intensity of tropical cyclones making landfall in South China. Clim. Dyn. 2020, 55, 1059–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, K.; Yu, X. Variability of tropical cyclone landfalls in China. J. Clim. 2021, 34, 9235–9247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, C.; Xiao, Z.; Yang, S.; Luo, X. Increased severe landfall typhoons in China since 2004. Int. J. Climatol. 2021, 41, E1018–E1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Wang, L.; Dai, Y.; Chen, H. Relationships between the Southwest Monsoon Surge and the Heavy Rainfall Associated with Landfalling Super Typhoon Rammasun. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoarau, K.; Lander, M.; De Guzman, R.; Guard, C.; Barba, R. Did Typhoon Haiyan have a new record-minimum pressure? Weather 2017, 72, 291–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choy, C.-W.; Wu, M.-C.; Lee, T.-C. Assessment of the damages and direct economic loss in Hong Kong due to Super Typhoon Mangkhut in 2018. Trop. Cyclone Res. Rev. 2017, 9, 193–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, L.; Fang, W.; Duan, X. On the Driving Forces of Historical Changes in the Fatalities of Tropical Cyclone Disasters in China from 1951~2014. Nat. Hazards 2019, 98, 507–533. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, G.; Huang, D.P.; Zhao, S.S. Annual and monthly risk assessment of typhoon disasters in China based on the information diffusion method. Meteor. Mon. 2019, 45, 1600–1610. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Lu, Y.; Zhao, H.k.; Zhao, D.; Li, Q. Spatial-temporal characteristic of tropical cyclone disasters in China during 1984–2017. Haiyang Xuebao 2021, 43, 45–61. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Y.; Jin, L.; Zhao, H.S.; Huang, X.Y. Fuzzy neural network and LLE Algorithm for forecasting precipitation in tropical cyclones: Comparisons with interpolation method by ECMWF and stepwise regression method. Nat. Hazards 2018, 91, 201–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, A.; Wu, G.; Liu, Y.; Ma, Y.; Zhao, P. Weather and climate effects of the Tibetan Plateau. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2012, 29, 978–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Duan, A.; Wang, T.; Wan, R.; Liu, X.; Li, W.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, Q. The influence of mechanical and thermal forcing by the Tibetan Plateau on Asian climate. J. Hydrometeorol. 2007, 8, 770–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Z.; Duan, A.; Wang, Z. Atmospheric heat sinks over the western Tibetan Plateau associated with snow depth in late spring. Int. J. Climatol. 2019, 39, 5170–5180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Ma, L.; Ma, M.; Zhang, H.; Yuan, W. Spatial–temporal variability of snow cover and depth in the Qinghai–Tibetan Plateau. J. Clim. 2017, 30, 1521–1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, P.; Chen, L. Climatic features of atmospheric heat source/sink over the Qinghai-Xizang Plateau in 35 years and its relation to rainfall in China. Sci. China 2001, 44, 858–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Guo, X.; He, J.; Qin, J.; Koike, T. On the climatology and trend of the atmospheric heat source over the Tibetan Plateau: An experiments-supported revisit. J. Clim. 2011, 24, 1525–1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Li, Y.; Yang, S. Interannual variation of summer atmospheric heat source over the Tibetan Plateau and the role of convection around the western Maritime Continent. J. Clim. 2016, 29, 121–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Y.; Ji, L. The numerical experiment of the medium-range change of the subtropical high I: The influence of the heat source over Tibetan Plateau. J. Trop. Meteorol. 1998, 14, 106–112. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, X.; Ting, M. A Dipole Pattern of Summertime Rainfall across the Indian Subcontinent and the Tibetan Plateau. J. Clim. 2017, 30, 9607–9620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Yang, S.; Duan, A.; Hua, W.; Ullah, K.; Liu, S. Tibetan Plateau heating as a driver of monsoon rainfall variability in Pakistan. Clim. Dyn. 2019, 52, 6121–6130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Yang, S.; Lau, N.-C.; Duan, A. Teleconnection between Summer NAO and East China Rainfall Variations: A Bridge Effect of the Tibetan Plateau. J. Clim. 2018, 31, 6433–6444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalnay, E.; Kanamitsu, M.; Kistler, R.; Collins, W.; Deaven, D.; Gandin, L.; Iredell, M.; Saha, S.; White, G.; Woollen, J.; et al. The NCEP/NCAR 40-Year Reanalysis Project. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 1996, 77, 437–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liebmann, B.; Smith, C.A. Description of a complete (interpolated) outgoing longwave radiation dataset. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 1996, 77, 1275–1277. [Google Scholar]
- Ying, M.; Zhang, W.; Yu, H.; Lu, X.; Feng, J.; Fan, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Chen, D. An overview of the China Meteorological Administration tropical cyclone database. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2014, 31, 287–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanai, M.; Esbensen, S.; Chu, J.H. Determination of bulk properties of tropical cloud clusters from large-Scale heat and moisture budgets. J. Atmos. Sci. 1973, 30, 611–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Murakami, H. Dynamic genesis potential index for diagnosing present-day and future global tropical cyclone genesis. Environ. Res. Lett. 2020, 15, 114008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, M.; Kimoto, M. Atmosphere-ocean thermal coupling in the North Atlantic: A positive feedback. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2000, 126, 3343–3369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goh, A.; Chan, J.C.L. An improved statistical scheme for the prediction of tropical cyclones making landfall in South China. Weather Forecast. 2010, 25, 587–593. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.; Graf, H.-F.; Leung, Y.; Herzog, M. Different El Nino types and tropical cyclone landfall in East Asia. J. Clim. 2012, 24, 6510–6523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Du, Y.; Wang, D.; Wang, C.; Wang, X. Impact of intraseasonal oscillation on the tropical cyclone track in the South China Sea. Clim. Dyn. 2015, 44, 1505–1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Wang, B. Impacts of the South Asian high on tropical cyclone genesis in the South China Sea. Clim. Dyn. 2021, 56, 2279–2288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.C.Y.; Zhou, W.; Shun, C.M.; Lee, T.C. Change in destructiveness of Landfalling tropical cyclones over China in recent decades. J. Clim. 2017, 30, 3367–3379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, J.; Chen, J. Large-scale indices for assessing typhoon activity around Taiwan. Int. J. Climatol. 2019, 39, 921–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Zhu, C.; Yuan, Y. Two interannual dominant modes of the South Asian High in May and their linkage to the tropical SST anomalies. Clim. Dyn. 2017, 49, 2705–2720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Duan, A.; Wu, G.; Yang, S. Mechanism for occurrence of precipitation over the southern slope of the Tibetan Plateau without local surface heating. Int. J. Climatol. 2016, 36, 4164–4171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webster, P.; Yang, S. Monsoon and ENSO: Selectively interactive systems. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 1992, 118, 877–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, F.; Liang, J.; Wu, G.; Dong, W.; Yang, X. Reliability Analysis of Climate Change of Tropical Cyclone Activity over the Western North Pacific. J. Clim. 2011, 24, 5887–5898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Klotzbach, P.J.; Zhao, H.; Duan, Y. Slowdown in the decay of western North Pacific tropical cyclones making landfall on the Asian continent. Front. Earth Sci. 2021, 9, 749287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Chakraborty, P. Slower decay of landfalling hurricanes in a warming world. Nature 2020, 587, 230–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Couhert, A.T.; Schneider, J.; Li, D.; Waliser, E.; Tompkins, A.M. The maintenance of the relative humidity of the subtropical free troposphere. J. Clim. 2010, 23, 390–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Qiao, S.; Chen, D.; Wang, B.; Cheung, H.-N.; Liu, F.; Cheng, J.; Tang, S.; Zhang, Z.; Feng, G.; Dong, W. The longest 2020 Meiyu season over the past 60 years: Subseasonal perspective and its predictions. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2021, 48, e2021GL093596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Duan, A. Relative contributions of the Tibetan Plateau thermal forcing and the Indian Ocean sea surface temperature basin mode to the interannual variability of the East Asian summer monsoon. Clim. Dyn. 2015, 45, 2697–2711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, J.; You, Q.; Zhang, Y. The influence of the Asian summer monsoon onset on the northward movement of the South Asian high towards the Tibetan Plateau and its thermodynamic mechanism. Int. J. Climatol. 2018, 38, 543–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Yang, S.; Luo, H.; Li, J. Drying tendency over the southern slope of the Tibetan Plateau in recent decades: Role of a CGT-like atmospheric change. Clim. Dyn. 2022, 59, 2801–2813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, M.; Yang, S.; Zhu, C.; Wang, J.; Lin, S.; Wei, W.; Fan, H. Thermal Impact of the Southern Tibetan Plateau on the Southeast Asian Summer Monsoon and Modulation by the Tropical Atlantic SST. J. Clim. 2022; in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, W.; Zhou, M.; Xu, S. Causality analysis of more tropical cyclones affecting Guangxi in 2013. Meteorol. Mon. 2015, 42, 709–715. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, C.; Lai, S.; Zheng, F.; He, L.; Luo, X.; Huang, C.; Zhou, X.; He, H. Impact of Thermal Forcing over the Southeast of the Tibetan Plateau on Frequency of Tropical Cyclones Affecting Guangxi during Boreal Summer. Atmosphere 2023, 14, 18. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14010018
Zhang C, Lai S, Zheng F, He L, Luo X, Huang C, Zhou X, He H. Impact of Thermal Forcing over the Southeast of the Tibetan Plateau on Frequency of Tropical Cyclones Affecting Guangxi during Boreal Summer. Atmosphere. 2023; 14(1):18. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14010018
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Chengyang, Sheng Lai, Fengqin Zheng, Liyang He, Xiaoli Luo, Cuiyin Huang, Xiuhua Zhou, and Hui He. 2023. "Impact of Thermal Forcing over the Southeast of the Tibetan Plateau on Frequency of Tropical Cyclones Affecting Guangxi during Boreal Summer" Atmosphere 14, no. 1: 18. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14010018
APA StyleZhang, C., Lai, S., Zheng, F., He, L., Luo, X., Huang, C., Zhou, X., & He, H. (2023). Impact of Thermal Forcing over the Southeast of the Tibetan Plateau on Frequency of Tropical Cyclones Affecting Guangxi during Boreal Summer. Atmosphere, 14(1), 18. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14010018




