Abstract
Intense rainfall (≥100 mm/24 h) constitutes the most frequent atmospheric hazard on Spain’s Mediterranean coast; this phenomenon causes serious damage to property and kills or injures inhabitants. The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, in its latest report in 2022, indicates that in the current climate change scenario, these episodes will become more frequent, hence the importance of analysing and characterising them. The present paper analysed intense rainfall episodes in the central sector of the Spanish Mediterranean coast (province of Alicante) in the 1981–2020 period. A total of 129 episodes were identified which have affected different areas of this province. The rainfall events were analysed by means of three synoptic classification methods subjective/manual and objective/automatic in order to assess the strengths and weaknesses of the two modalities. The main objective was to identify the most favourable atmospheric situations triggering intense rainfall in the study area. The period with the highest propensity for these episodes to develop was identified, as well as the geographical areas most affected in the study period. Autumn concentrates the biggest amount of intense rainfall episodes throughout the year. Herein, we attempt to demonstrate the relationship between atmospheric situation, accumulated rainfall volume, geographical area affected, and the most favourable period of the year for the development of these events. The main results of the synoptic analysis of extreme events show the coincidence, in the three classification methods used, that the existence of instability in the middle and upper layers of the atmosphere (DANA and troughs) and humid and warm E and NE surface flows are decisive. In addition, the warming recorded in the waters of the western Mediterranean in recent decades is related to extreme events.
1. Introduction
Analysing torrential rainfall events is a complex task due to the great inter-annual variability and the spatial distribution that these episodes present [1], particularly in the southeast of the Iberian Peninsula [2], an area that urgently needs to be studied in order to establish the hazards associated with extreme weather events. The Mediterranean area is characterised by a high concentration of daily rainfall, i.e., a high percentage of the annual total is recorded on a very limited number of days [3]; this gives rise to extreme events surpassing 100 mm/day and causing torrential rainfall events [4,5,6]. One of the main consequences of high-intensity hourly events involves recurring floods in the Western Mediterranean Basin [7,8,9,10]. In view of the intensity of these episodes, there is significant interest in establishing the characteristics of the synoptic situations that cause them. The present paper addresses the synoptic causes of torrential rainfall events in the Alicante province. To this end, a comparative analysis was applied to the different methods of synoptic classification for 129 days on which the 100 mm/day threshold was exceeded over a 40-year period; this method is widely used in studies characterising torrential events [5,11,12,13].
Since the 1950s and 1960s, many geographers have proposed methods for synoptic classification, influenced by the trends in German, French, and Swiss synoptic climatology [14]. Numerous methods for subjective or manual classification exist for the Mediterranean region, as well as objective or automatic methods.
Among the subjective classifications, one can find some catalogues created by meteorologists in the second half of the 20th century, as is the case of Linés Escardó [15] who established a catalogue of “Typical disturbances” affecting the Iberian Peninsula, and which made particular reference to synoptic situations. Font Tullot [16] created a synoptic catalogue addressing the climates of Spain and Portugal; therein he analyses the air masses affecting the Peninsula, defining three circulation types according to the degree of undulation of the circumpolar vortex—Zonal circulation, meridian circulation, and high-altitude cold depression. Based on this proposal he created a catalogue providing 23 weather types. For the Western Mediterranean Basin, it is of note that the studies conducted by Jansá Guardiola [17,18] and Florit Ameller and Jansá Clar [19]. Within the scope of Spanish geography, in the last few decades, we can highlight the contributions of Spanish geographers with regard to classifying the general synoptic situations affecting the Iberian Peninsula. These are based upon different approaches: Martín Vide [20] establishes 16 types of synoptic situations based on the surface and topographic maps at 500 hPa; the classification by Olcina Cantos [14] is mainly based on the configuration of the upper layers of the troposphere (300 and 500 hPa) and creates a catalogue based on the different air masses—subtropical, arctic, polar—displaced towards Iberian latitudes from their places of origin. The classifications are of great interest in the field of climatology, and are vital with regard to comprehending the climatic characteristics of the Western Mediterranean Basin; however, the great diversity and high degree of subjectivity can constitute a hindrance in this sense.
Among the most recent studies, applying manual (subjective) synoptic classification methods one can find those of Martín Vide et al. [21] who applied the method proposed by Martín Vide [20] for 68 rainfall episodes of over 200 mm/day in the SE of Spain (Alicante and Murcia) for the 1941–2017 period. For the area of the Balearic Isles Grimalt-Gilabert et al. [22] classify 53 episodes surpassing the threshold of 200 mm/day in the 1941–2010 period, according to the types established by Martín Vide [20] and combined with the automatic classification method of Jenkinson and Collison [23], hereinafter J&C. Likewise, Miró et al. [24] combined Martín Vide’s subjective classification [20] with the objective method of J&C. Other studies that have made use of subjective classifications, whether according to types of synoptic situations or types of climate for Spain and its regions, are those by Martín Vide [20], Gil Olcina and Olcina Cantos [25], Romero et al. [26], Capel-Molina [27], and Martín Vide and Olcina [2].
Automatic, or objective, classification methods, based upon quantitative criteria and on the computing by the software programmes, have the advantage of being reproducible, i.e., the same results are obtained whichever researcher employs the methods. Moreover, comparisons can be made between the manual methods and the automatic ones, such as that of J&C, proposed for the British Isles and based on surface atmospheric pressure. This method allows for detailed analyses intended to associate extreme rainfall episodes with the synoptic situation causing them; for the Iberian Peninsula and the Balearic Isles, the method was adapted by Spellman [28]. This methodology was subsequently employed by different authors in the south-east of the Peninsula; Martín Vide [29] applied the automatic classification by J&C to 25 dates in the 1975–1990 period, in which rainfall of over 200 mm/day was recorded in observatories of the Valencia Regional Autonomy. For the Western Mediterranean Basin, Grimalt-Gilabert et al. [30] established the climate types for 22,646 days of the 1948–2009 period.
Llop Garau and Alomar Garau [31] applied the classification of J&C, analysing 691 episodes with a threshold similar to, or higher than, 100 mm/day recorded in 272 observatories in Catalonia and the Balearic Isles. For the Isle of Majorca, the same authors classify 49 high-intensity episodes (200 mm/day) during the 1939–2001 period [32]. For the Catalonia region, Gilabert and Llasat [33] analysed 261 extreme events (1900–2010) in accordance with the method by J&C. In the province of Alicante, Azorín-Molina et al. [34] employed J&C’s method to establish the weather types favouring the development of sea breezes; to this end they analysed 19 stations in the province at high resolution over a six-year period (2000–2005), obtaining 475 sea breeze events, for which different parameters were measured (direction, speed, and wind duration).
The J&C method is part of the COST733 action (Harmonization and Applications of Weather Type Classifications for European Regions), a project, developed between 2005 and 2010, which involved 23 countries that evaluated and analysed multiple methods of automatic classifications to find the most suitable for European regions [35]. Other projects have addressed the classification of weather types in relation to intense rainfall in the Mediterranean, such as HyMeX [36,37] and MEDEX [38]. At the scale of the Western Mediterranean, the COST733 project developed a classification technique that is highly applicable to any European region. The region is divided into 11 domains and Iberian Peninsula is placed in domain nine (D09) [39]. This action compiles different analyses and perspectives, e.g., Cahynová and Huth [40] analysed the influence of atmospheric circulation types on trends in daily maximum and minimum temperatures and precipitation. Philipp et al. [41] carried out a comparison between methods of classification of circulation types to analyse possible links between them. In the Iberian Peninsula framework, Casado et al. [42] evaluated the discriminating ability of winter precipitation variability over Spain by using a large set of circulation types, while Casado and Pastor [43] focused on the classifications compiled in COST733 to evaluate circulation types and their characteristics as a function of the percentage of winter precipitation recorded on a particular day. Cortesi et al. [44] analysed how the weather types of the Lamb classification determine the spatial variability of monthly mean precipitation in the Iberian Peninsula at high spatial resolution. On the other hand, Rasilla Álvarez and García-Codrón [45] addressed the influence of local and regional atmospheric conditions on sea level variability in SW Europe (Spain).
In the study of extreme precipitation events, Khodayar et al. [46] analysed the atmospheric conditions associated with heavy rainfall in 5 subdomains (France, northern and southern Italy, Spain, and North Africa); they employed the topography at 950 hPa for events > 100 mm/day for the autumn period (SON) from 2011 and 2012. Fernández-Montes et al. [47] relates circulation types and the frequency of daily precipitation extremes in spring and autumn at 44 stations in Iberian Peninsula. In the review of published studies on intense rainfall events in the Mediterranean by Dayan et al. [48] they specifically distinguish the atmospheric conditions that induce extreme episodes in the Western Mediterranean. Alpert et al. [49] applied a semi-objective classification of the most frequent synoptic systems in the countries of the Eastern Mediterranean (1948–2000), defining six main synoptic groups to analyse the changes in distribution of the systems resulting from climate change.
The present paper is based upon one principal research question: do synoptic situations exist that are favourable for the development of torrential rainfall episodes (≥100 mm/day) in the province of Alicante? How frequent are they? In an attempt to answer these questions, the following objectives were established: (1) to select the extreme rainfall episodes equal to, or greater than, 100 mm/day in some of the 26 observatories in the province of Alicante for the 1981–2020 period; (2) to conduct a comparative analysis of different methods of synoptic classification of torrential events in the province of Alicante (1981–2020), making use of the subjective (manual) classifications proposed by Martín Vide [20] and Olcina Cantos [14], and the objective (automatic) classification of J&C [23]. To analyse the strengths and weaknesses of subjective/manual and objective/automatic classification methods for selecting situations presenting intense rainfall; (3) to establish the situations most likely to promote the development of intense rainfall events in the study area; (4) to locate the most favourable areas for the development of intense rainfall events in the study area; and (5) to establish the calendar of monthly frequencies of the development of intense rainfall events in the study area according to the different methods of synoptic classification.
2. Data and Methods
It was employed the data on daily rainfall recorded by the observatories of the province of Alicante provided by the Banco Nacional de Datos Climatológicos (BNDC—National Climatology Database) belonging to the Agencia Estatal de Meteorología (AEMET—State Meteorology Agency) available for the analysis period from 1 January 1981 to 31 December 2020, a forty-year period, which is more convenient for a study area, such as the southeast of the Peninsula, where rainfall is highly variable in relation to the rest of the Iberian Peninsula [50] (p. 13). In order to work with the most complete datasets possible, we only worked with the observatories containing a minimum of 95% of the complete series. A total of 26 observatories was selected following an RPI (real precision index) quality analysis [51], corresponding to the AEMET’s primary and secondary climatological networks [52]. Having obtained the days on which the threshold established is surpassed, we conducted an error detection process, identifying duplicated data, which we verified with those from nearby observatories and, subsequently, eliminated. Figure 1 shows the location of the study area and the observatories that have recorded rainfall equal to, or greater than, 100 mm/day in the province of Alicante.
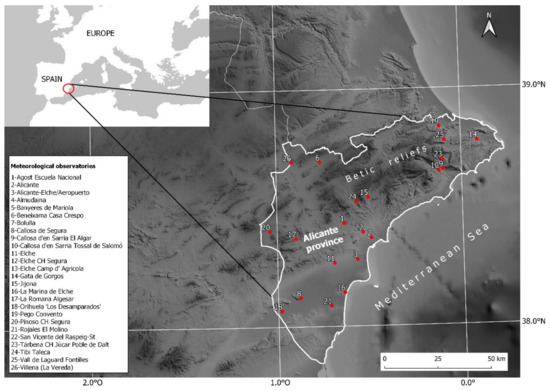
Figure 1.
Geographic location of meteorological observatories that have recorded rainfall equal to, or greater than, 100 mm/day in the province of Alicante.
In order to study the atmospheric situations selected, it was consulted synoptic reanalysis maps included in the archive of the Climate Forecast System (CFS), available on the website wetterzentrale.de (archive). These maps show the atmospheric situation on the surface and at 500 hPa.
In the methodological process of drafting the present paper (Table 1), the first step involved identifying the dates on which at least one weather station of those considered in the analysis recorded rainfall equal to, or greater than, 100 mm/day during the 1981–2020 period. The sample obtained involved 129 days with rainfall surpassing the established threshold; this is a statistically large enough sample to determine the most frequent synoptic situations that give rise to this kind of rainfall.

Table 1.
Steps of the general methodology.
Secondly, it was established the synoptic classifications for each date, in accordance with the proposal for a manual and subjective classification by Martín Vide [20] (pp. 66–67) and Olcina Cantos [14], and the automatic and objective classification of J&C [23]. The first one establishes 16 types of synoptic classifications based upon the surface map and the topography map at 500 hPa. This classification has been subjected to modifications—new types have been considered: “North-easterly advection with DANA” as well as the differentiation between “deep trough”, when this is perfectly defined over the Iberian Peninsula, and “weak trough”, with a gentle flow from the east, when this is not perfectly defined, but one can detect the undulation of the isobars presenting a westerly component and when there is weak easterly advection on the surface.
The second classification, proposed by Olcina Cantos [14], is based upon the configurations that develop in the upper layers of the troposphere (300 and 500 hPa) over the Iberian Peninsula and the adjacent sea surfaces and the principal direction of the surface winds within the study area. Based upon the trajectory of displacement of the main air masses existing in the Atlantic–European area and in north Africa (mA, cP, mP, cT, mT), five main configurations were established which can exhibit a certain degree of variation according to the central axis of anticyclone troughs and crests at high altitude in relation to the geographical position of the Iberian Peninsula (Figure 2). This aspect is important with regard to determining the geographic areas presenting the greater vortex advection (atmospheric instability), fundamental for the development of intense rainfall. This classification has been employed in different studies on synoptic climatology in Spain [14,28,53,54].
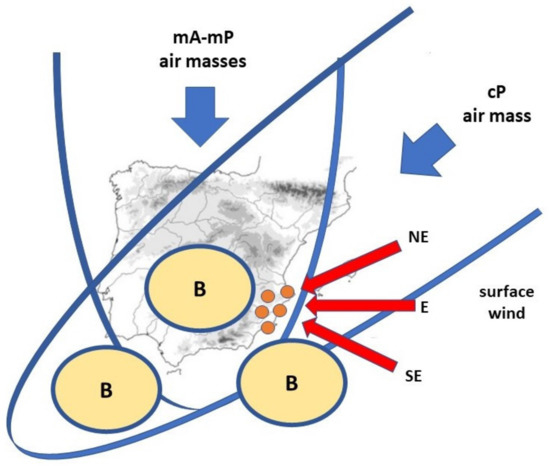
Figure 2.
Diagram of the unstable atmospheric situations most favourable for the development of intense rainfall in the study area. Source: Olcina Cantos [14].
In these two subjective methods the term DANA (High-Altitude Isolated Depression) has been used; it was proposed by the AEMET [55] as the equivalent to the cut-off low mechanism, thus replacing the popular term ‘gota fría’ (‘cold drop’).
The third one corresponds to the automatic synoptic classification of J&C [23]; it was obtained by means of the “synoptReg” R Package [56]. This classification contains 27 types that are obtained with the use of an algorithm with certain pre-defined rules. To this end, the surface atmospheric pressure is obtained on a grid, in this case with 16 points encompassing the study area. In the present study, we employed the 16-point octagonal grid between the parallels 30° N and 50° N and the meridians 20° W and 20° E (Figure 3).
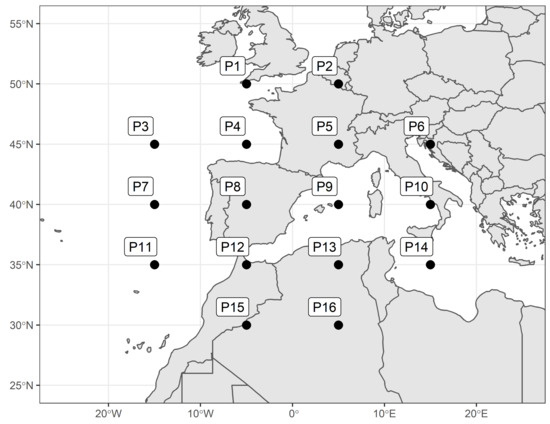
Figure 3.
The 16-point grid used in the J&C method.
Likewise, it was considered that other synoptic features are relevant at continental scale and which are significant in the observations column (Appendix A). For this analysis it was availed of the daily values of the Western Mediterranean Oscillation (WeMOi) [57] for each synoptic situation. The daily database with the WeMOi values from 1981 to 2020 was provided by the Climatology Group of Barcelona University. The WeMO is the teleconnection pattern that best explains the occurrence of torrential rainfall from the northeast to the south of the Iberian Peninsula [58]. It is, therefore, of great interest to establish its values for the 129 dates which are subsequently analysed in relation to torrentiality.
3. Results
Appendix A shows the 129 dates presenting episodes equal to, or greater than, 100 mm/day. The first two columns correspond to the observatory and the date of the extreme event. It should be kept in mind that for one date several observatories can register ≥ 100 mm, and we, therefore, selected the one presenting the maximum value for each date. The third column corresponds to the amounts recorded. The fourth, fifth, and sixth columns show the classifications according to the different methods employed. The seventh column indicates the value of the WeMOi and the eighth provides the observations (details) of the synoptic situation at continental scale. Appearing in the last place is the number of observatories recording equal to, or greater than, 100 mm on the date in question.
Using the synoptic classification of Martín Vide [20], the following situations (Figure 4) and absolute frequencies (Table 2) were obtained. The most relevant result involves the high frequency of the easterly surface Advection with DANA at high altitudes at 500 hPa, which is represented in almost half of the events studied (48.84%). The group displaying the second-highest frequency, albeit far behind the first one, involves the deep Trough type (16.28%) and the north-easterly Advection with DANA (11.63%). The latter type has been included in the classification of the 16 types of situations expounded by Martín Vide [20], because for the province of Alicante it is considered relevant to differentiate according to the easterly or north-easterly origin of the surface air masses, due to the influence of the relief of the Betic Ranges to the north of the Alicante province; these act as an orographic barrier against the wet gregal winds (NE), which characterise the wet pole of the province [59] (p. 77). These three weather types combined represent 76.7% of the total (99 dates of the 129 analysed). A third group is represented by situations involving Cold-core lows (9.30%) and a weak Trough with a weak easterly flow (6.98%). Lastly, the least represented weather types in relation to torrential events are easterly Advection (2.33%), northerly Advection (1.5%), north-easterly Advection (1.5%), and DANA to the southwest (1.5%).
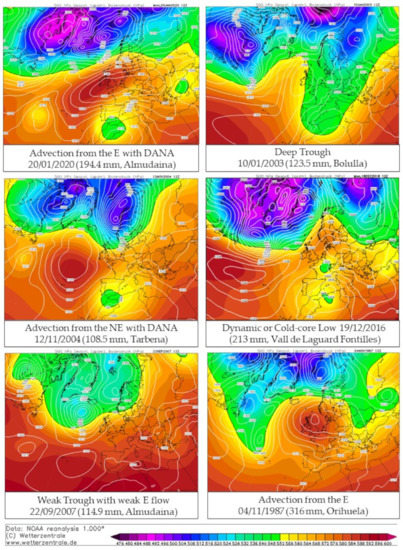
Figure 4.
Examples representing the different synoptic situations for the classification by Martín Vide [20] on days presenting ≥ 100 mm of rainfall. Source: www.wetterzentrale.de (consulted 24 March 2022).

Table 2.
Atmospheric situations causing intense rainfall episodes analysed in the study according to Martín Vide [20].
The results obtained with the classification proposed by Olcina Cantos [14] for the 129 situations of intense rainfall in the present study are shown in Figure 5; their absolute frequencies appear in Table 3.
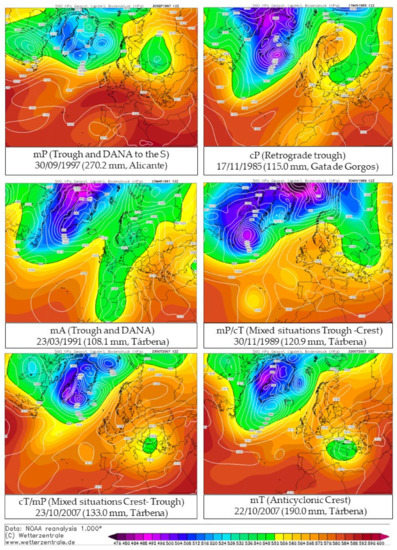
Figure 5.
Representative examples of different synoptic situations for the classification by Olcina Cantos [14] on days presenting ≥ 100 mm rainfall. Source: www.wetterzentrale.de (consulted 24 March 2022).

Table 3.
Atmospheric situations causing intense rainfall episodes analysed in the study according to Olcina Cantos [14].
Some noteworthy atmospheric situations are those related to the establishment of troughs and DANA associated with the displacement in the upper layers of masses of polar sea air (Troughs and DANA with a centred axis (27.7%), a Trough and DANA to the south of the Peninsula (35.4%), Zonal circulation (0.78%), and polar continental (Retrograde trough, 27.7%) from eastern Europe towards the Mediterranean Basin. These situations represent 91% of the days with intense rainfall in the study area, corresponding to 118 dates of the 129 analysed.
Days with hot air masses (mT) over the Iberian Peninsula which, a priori do not tend to generate rainfall, are only present on two of the days analysed (1.6%) and are included in one unstable episode (22 and 23 October 2007), such as instability in the higher layers over the Western Mediterranean, a fact that favoured the genesis of storms in the study area.
Surface winds are of a maritime origin in all cases, and are NE-E and S components are predominant, transporting wet air from the Mediterranean Sea to the coast.
The classification, conducted according to the method of J&C (Table 4), provided the synoptic patterns (Figure 6) of the atmospheric situations which gave rise to rainfall events equal to, or greater than, the threshold of 100 mm/day. There is an unequivocal predominance of the pure advection types from the E (24.03%) and NE (22.48%). If all the resulting types of pure advection are considered, such as SE (10.08%) and N (2.33%), they represent over half (58.92%) of the total number of episodes. As for the pure cyclonic type (12.4%) and cyclonic hybrid advection—CNE (11.3%), CE (9.3%), CSE (2.33%), and CS (0.78%)—together these represent 36.44% of the total number of events. Each of the pure anti-cyclonic weather types A (1.55%) anti-cyclonic hybrid advections—ASE, ANE, and AN—are present in the classification on only one day, and only one case is considered to constitute an undetermined situation (U).

Table 4.
Atmospheric situations causing intense rainfall events analysed in the study according to J&C [23].

Figure 6.
Synoptic patterns obtained from the J&C classification types representing days with equal to, or greater than, 100 mm of rainfall. The synoptic type is displayed on each map.
Notably, in most situations, events presenting a pure or hybrid advection (110 days) involve an easterly component (105 days); in these situations, the advection originates in the north—N, AN—(4 days) and only in the south on one occasion. Surprisingly, pure anti-cyclonic situations are classified as A (2 days) or hybrid—ASE, ANE, AN—and that they generate torrential rainfall, although in two of them (ASE, ANE) with an easterly component. On the contrary, in this classification no case involving an easterly component can be found.
The WeMOi was negative on 122 dates (94.57%) of the 129 events scrutinised in the study; it was positive on 4 dates (3.10%) (Figure 7) and no record exists on three days (2.33%) for the index (Appendix A). The mean value is −1.5. The lowest one was −3.93 on 20 January 2020. In 34 events (27.87% of the 94.57%) the index was equal to, or below −2.0, an extremely negative value [60]. On the dates on which the WeMOi is positive, north-easterly or northerly advection is seen to exist, as occurred on 22 October 2007.
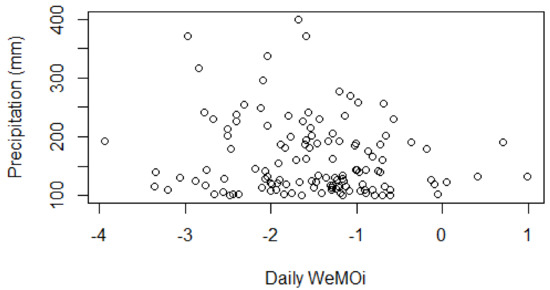
Figure 7.
Statistical distribution of the daily values of the WeMOi for days with intense rainfall in the 1981–2020 period in the province of Alicante.
We tested the correlation between the WeMOi and maximum rainfall values by means of Pearson’s r test −0.1507, and, although the correlation is negative, it is not significant at the 95% confidence level (p value < 0.09).
The manual synoptic classification methods have an advantage with regard to conducting studies on extreme events. Therein, the experience of the investigator is vital because the subjectivity involved provides different results when the method is applied repeatedly to one singular classification method. The advantage of the method proposed by Martín Vide [20] lies in the comparison of the situations at two levels. He focuses the analysis upon the principal flow generated in the atmosphere (advection), and the general direction of the main flow both at high altitudes and on the surface, interrelating the influence of the surface flows upon the atmospheric situation in the mid-level layers. With regard to the method employed by Olcina Cantos [14] its main advantage is that the classification entails analysing the circulation in the medium and upper layers of the troposphere; thus, the displacement of the air mass towards the Iberian Peninsula, and the synoptic figure this process produces will determine the areas of greatest instability (vortex advection). In addition, the method takes into consideration the energy transfer between the atmospheric fringe of the medium latitudes, which is where the calorific balance of the planetary system takes place. The general application of the classification by J&C to the Iberian Peninsula can present shortcomings, as it is located in an intermediate zone between the medium and low latitudes where the differentiation of the cyclonic type involves analysing the situation at 500 hPa. This setback is attenuated when this classification is applied to a series of dates exhibiting certain specific meteorological conditions, such as the torrential rainfall in the southeast of the Peninsula.
The different classification methodologies [14,20,23] indicate that the situations most conducive to torrential rainfall are: advections from the E with DANA (63 out of 129 episodes); mP Trough and DANA with a centred axis or one to the south (82 out of 129 episodes); and E and NE (60 of 129 episodes). On determining these rainfall patterns, there is one that repeats in the different classification methods: flows from the E or NE and the presence of DANA over the southeast of the Peninsula or the Mediterranean.
Considering the 129 dates on which extreme events were recorded for the series analysed, the stations making up the 95th percentile of the rainiest days are Vall de Laguard-Fontilles, Pego, Tárbena, and Orihuela; the first three are located to the north of the province of Alicante.
If one takes into account the distribution of the absolute frequencies of the different classification methods in the annual calendar, the highest absolute frequencies are seen to be recorded in the autumn, with November as the month with the most frequent events.
We now analyse the absolute frequencies of the types of synoptic situation that caused extreme events (200 mm/day). In total, this threshold was exceeded in 30 days during the whole study period. Of the absolute frequencies shown in Table 5, 10 out of the 30 days that surpassed the established threshold correspond to a situation of advection from the E with DANA during autumn. As for the results presented in Table 6, 14 out of the 30 days that surpassed the established threshold correspond to a situation of mP in autumn. Table 7 highlights the absolute frequency of type E, with 7 of the 30 days exceeding the established threshold during autumn.

Table 5.
Monthly absolute frequencies according to the classification by Martín Vide [20].

Table 6.
Monthly absolute frequencies according to the classification by Olcina Cantos [14].

Table 7.
Monthly absolute frequencies according to the classification by J&C [23].
4. Discussion and Conclusions
In the current context of climate change, studies such as the one presented here may be of interest to understand the influence of atmospheric dynamics in the Mediterranean region, where extreme weather phenomena are becoming more and more recurrent. Therefore, knowing the intensity of the events and their frequency, as well as the synoptic patterns that trigger them, can be crucial for understanding how the future climate will evolve.
According to the results obtained, the research questions can be answered. It has been identified that the most favourable situations for the development of torrential rainfall (≥100 mm) in Alicante are related to the existence of configurations that favour instability in the medium and upper layers of the atmosphere (DANA and troughs), and on the surface, flows presenting a wet and warm E and NE component. Both the isolated depression and the troughs containing cold air in their core favour the development of intense rainfall, with serious economic and social consequences. According to the frequency revealed by the study with each classification method used, the highest frequencies are related to the aforementioned configurations. Specifically, the weather type advection from the E with DANA (49%) is the most frequent in the first classification method; in the second method Trough and DANA to the S of the Peninsula (36%); the third, advection from the E (24%). Therefore, Figure 8 shows the proposed most frequent synoptic pattern model that causes torrential rainfall events in the province.
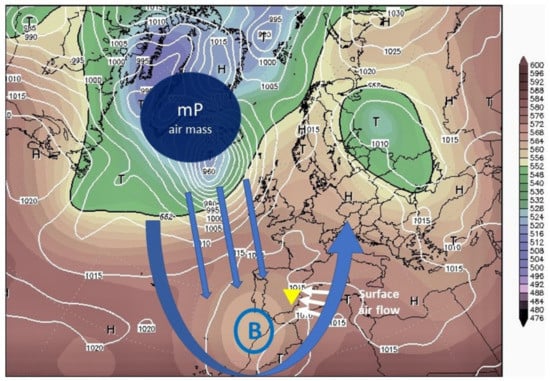
Figure 8.
Standard synoptic model most frequently causing torrential rainfall episodes in the province of Alicante. Source: www.wetterzentrale.de (accessed on 22 March 2022). Own design.
The most relevant result is, first, the high frequency of advection from the E with DANA (48.84%) and the advection from the NE with DANA (11.63%), differentiated in the present study by the degree of influence of the winds from the E in the north of the province of Alicante; second, the deep Troughs (16.28%) and, lastly, Cold-core lows (9.38%).
In a study similar to the one presented herein, Martín Vide et al. [21], concluded that the specific synoptic situation involving advection from the E with DANA is the most frequent configuration in the occurrence of torrential rainfall in the SE of the Iberian Peninsula. Their results widely coincide with those obtained in the present investigation, where the application of the first classification method determines that advection from the E with a DANA is the most frequent synoptic pattern in the 129 days analysed.
In the SE of Spain, for the dates on which over 200 mm rainfall was recorded (1941–2017), Martín Vide et al. [21] also obtained a higher frequency of Advection from the E with DANA (52.9%), in second place the Trough type (17.6%), and, lastly, the Cold-core low (16.2%). Grimalt-Gilabert et al. [22], however, for episodes with a threshold higher than 200 mm/day, for the Balearic Isles, obtained the highest frequencies in the dynamic Low type (26.4%), Troughs (24.5%), advections from the E with DANA (24.5%), and advections from the NE with DANA (11.3%). In another study for the coastal provinces of Catalonia, in the NE of the Iberian Peninsula, 304 days were analysed that presents a threshold similar to, or greater than, 100 mm/day (1950–2005), and the 7 most frequent patterns were identified by means of PCA analysis, among which can be highlighted the weak Cold-core low to the E, a blocking situation to the SE and advection from the SE, with differences in relation to the southeast [13]. For the same region, Pino et al. [61] analysed 24 catastrophic flood events, where the most frequent synoptic patterns were cut-off low (38%), trough (29%), high-altitude low (21%), flash trigger (4%) and 2 (8%) unclassified events.
If one compares the results obtained with regard to the origin of the air masses that most frequently give rise to torrential events, the mP stands out, whether it takes the shape of a Trough or DANA. In this respect, the layout of the axes of the trough in the synoptic configuration will determine the location of the highest rainfall events recorded, especially when the ascending branch or “leading edge” is situated above the study area [20]. Nonetheless, a study conducted in the Mediterranean region analyses the influence of the transfer of tropical air to the medium latitudes in relation to the development of extreme rainfall events. The result provided by the analysis of different case studies (Italy, south-eastern Spain, Israel, and southern Turkey) indicates that the influence of wet tropical air in the development of heavy rainfall in the region [62].
In the specific case of the Valencia Regional Autonomy (provinces of Alicante, Valencia, and Castellón), a study by Martín Vide [29] analysed 25 days with rainfall greater than, or equal to, 200 mm/day (1975–1990), employing the J&C classification. The author concludes that 56% of the episodes are of the pure cyclonic type (C) or present an easterly component (CNE, CE and CSE) and 36% are advective with an easterly component (NE, E and SE); this latter percentage is more closely related to the results obtained in the present paper for the province of Alicante, where 56.6% of the 129 dates correspond to the NE, E, and SE types.
In the region of Catalonia, the study by Gilabert and Llasat [33] analyses 261 flood episodes in the period 1900–2010. The authors differentiate between extreme (EXT, ∼100 mm) and catastrophic (CAT, ∼250 mm) episodes, to which they apply the J&C classification. In total they identified 22 synoptic types. 45.6% of the total episodes are of the pure cyclonic type (C), the most repeated type, as well as in the two subcategories (EXT, 42.4%; CAT, 57.1%). These results are in line with those presented by Llop and Alomar [31] in a join study for Catalonia and the Balearic Islands, where the pure cyclonic type (C) was also the most represented in 56.9% of the 691 events analysed. As for the EXT events, the second most frequent type is indeterminate, which accounted for 20%. In the case of CAT events, the second most frequent type is the SE advective (10.7%); this would be more in line with the frequencies obtained for the province of Alicante, where 10.08% of the 129 episodes correspond to the SE type.
The differences are much greater on comparing the results of the classification by J&C for the Peninsula and for the islands. According to the J&C classification, in Alicante the days with torrential rainfall present the circulation type from the E and NE (46.5%), whereas in the Balearic Isles, they are associated with pure cyclonic situations (C) (75.5%) [22]. In Alicante, however, this type of situation is only represented in 12.2% of the days analysed. The results obtained by Martín Vide [29] partially coincided with those obtained by Grimalt-Gilabert et al. [22] for the Balearic Isles, where the pure cyclonic type (C) stands out with 75.5%, while advection or hybrid advection (CE, E, NE, ASE) represents 20.7% of the 53 dates analysed in that study.
In this sense, the conditions of insularity made the difference, because the wet flows might be coming from different directions [22]. A study conducted for the island of Majorca indicated the predominance of situations coming from the E and, above all, the N, due to the influence the Tramuntana mountain range has upon the flows presenting a N component [32], similar to the influence of the orography in the north of Alicante, although in this case with the wet flows from the E and NE. In the general area of the province of Alicante situations presenting an easterly component (NE, E, and SE) prevail, because, in the Western Mediterranean Basin, the influence of the wet winds from the east is fundamental with regard to the development of episodes of high hourly intensity. The existence of wet flows from the E and NE will to a great degree mean that the area most affected by torrential rains is the north of the province of Alicante, due to the orography of the Betic relief and the orientation of the coastline, which acts as a barrier to the arrival of warm and wet winds presenting an E and NE component, from the Mediterranean Sea, these penetrate inland of the Peninsula, and, on ascending, they generate high rainfall values. This fact is also ratified by Khodayar et al. [46], who conclude that the south–north layout of the mountain ranges in eastern Spain have an influence upon rainfall distribution in this area, which is mainly affected by storms and connective rainfall; these authors highlight the importance of humidity in the low and medium, level atmosphere with regard to identifying conditions existing prior to extreme events.
The results obtained on seasonal frequencies can be compared with those of Martín Vide et al. [21] for the SE of the Peninsula. A slight difference was observed with regard to the seasonal distribution of the episodes, although in both cases the highest percentage is to be found in autumn (50% in Alicante, and 69.1% in the SE of the Peninsula). In the case of the Balearic Isles, autumn is the most noteworthy season in relation to the seasonal distribution of torrential episodes (62.3%) [22], a pattern similar to that of the SE of the Peninsula (69.1%) [21]. Insua-Costa et al. [63] in their study of the western sector of the Mediterranean Basin indicated that the Valencia autonomous region is one of the sub-regions exhibiting the highest number of extreme events (analysis period 1980–2015), with the notable seasonal character in autumn representing 75% (SON). Gilabert and Llasat [33] for Catalonia obtained a higher frequency of events in autumn attributed to SE air masses, due to a corridor of warm and humid air from the south. Llop and Alomar [31] for Catalonia and Balearic Isles extracted the absolute frequencies with the highest percentage in autumn, being 45.07% and 51.42%, respectively.
The seasonal distribution according to the types of atmospheric circulation (according to J&C) at different spatial scales, shows differences between the province of Alicante and the Iberian Peninsula. For the results obtained in this research, where heavy rainfall events are analysed, the highest frequency of events occurs in autumn (SON), where the most frequent circulation types are E and NE. On the scale of the western Mediterranean Grimalt et al. [30] determined that the highest monthly frequency in the autumn stage (1948–2009) is the indeterminate type (U), followed by type A, C, and ADV. For the Iberian Peninsula as a whole, Cortesi et al. [44] obtain the mean monthly frequency of circulation types that follows the same atmospheric pattern, with type A being the most frequent during the SON months, but followed by types E and NE, just like the province of Alicante. These frequencies are repeated in the results shown by Ramos et al. [64]. Following a relational approach between circulation types and their contribution to monthly precipitation [44,64], the greatest contribution in autumn is associated with types W and C, due to the predominant westerly flow and the greater influence of Atlantic cyclones.
The results presented here come from the comparison of subjective and objective automatic classification methods, necessary for a good interpretation in the synoptic-climatological study [40]. Regarding the former, their value in establishing relationships between air masses and synoptic configurations linked to their movements is highlighted, as well as the ease of understanding the synoptic types defined. However, it is true that, compared to the objective and automatic methods, they are less precise in the exact location of the atmospheric effects of the synoptic types, the latter being more precise geographically. Moreover, the automatic classifications allow comparison for different regional entities within the same general atmospheric circulation band. All methods can be used descriptively, without expecting some classification methods to be more justified than others, as each synoptic classification method reports different results [41].
The effect of the WeMO pattern upon torrential rainfall in the south-east of the Iberian Peninsula, intended to account for the variability of the NAO, was not observed in the east of the Iberian Peninsula [57,60], and the results obtained by means of the WeMOi are coherent with the nature of this Mediterranean pattern. The value of the WeMOi was negative in 94.57% of the events studied. The mean value is −1.5. On 27.87% of the 94.57% of the days, the index was equal to, or lower than, −2.0, an extremely negative value [60]. The lowest value was −3.93 on 20 January 2020, presenting a DANA to the south of the Iberian Peninsula and a powerful European anticyclone, which channel the flows with an easterly component, which are wet for the eastern façade of the Iberian Peninsula. These results tally with those of Martín Vide et al. [21] for the SE of the Iberian Peninsula, where the values of the WeMOi were negative for all the events studied, and extremely negative in 31% of the cases. Furthermore, over 60% of the events exhibited wet surface flows with an easterly component. In this sense it should be pointed out that the increase in the surface temperature of the Mediterranean Sea (MSST, in Spanish TSM—sea surface temperature in the Mediterranean) might give rise to high-intensity daily and hourly rainfall on Spain’s Mediterranean coast. Indeed, the sea surface temperature in the Mediterranean in the sectors close to the Iberian Peninsula and the Balearic Isles has risen by an average of 1.29° C from 1982 to 2022; however, some sectors—the Balearic Sea—present an increase of approximately 1.4° C for this time period [65,66]. Evidently, a warmer sea involves a sea-atmosphere heat transfer of greater intensity, which causes the formation of a more intense convective cloudiness, with rainfall more concentrated in time and in space. This is especially obvious during the autumn, when the Mediterranean presents a higher heat energy, and, therefore, a high degree of evaporation [46], which promotes instability when it comes into contact with cold air in the medium layers of the troposphere. Olcina Cantos [8] analysed the increase in intense rainfall events of a lesser range (less than 50 mm/24 h) recorded in the city of Alicante as from 2000; concluding that this was a process related to the higher water temperature of the Mediterranean Sea. In addition, Ferreira [67] associated the effect of the temperature increase in the Mediterranean with a higher number of DANA in the east of the Iberian Peninsula, concluding that the simulations conducted with the WRF model predict a 50% increase in DANA on the eastern façade of the Iberian Peninsula [67].
Thus, this is a highly interesting future line of study with regard to verifying whether the above-mentioned temperature increase in the air and in the sea water gives rise to alterations in the synoptic configurations favouring the development of intense rainfall episodes, as a result of changes in the temperature and pressure fields in the atmospheric column, and owing to the higher energy concentration in the advection processes.
This research represents an advance in the knowledge of heavy rainfall events in the selected study area by statistically characterising the synoptic types most prone to the development of such events. It also provides a method for the comparison of subjective and objective synoptic analysis methods, which can be applied to other mid-latitude study areas. On the other hand, trends in the evolution of synoptic situations causing heavy rainfall are related to the current process of climate warming. Finally, the relationship between seawater temperatures and the location of higher amounts of precipitation in subregional-scale geographical areas, in connection with the circulation of flows determined by the synoptic types analysed, is suggested as a line of future work.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, methodology, E.S.-A., J.M.-V., J.O.-C. and M.L.-C.; software, M.L.-C. and E.S.-A.; validation, E.S.-A., J.M.-V., J.O.-C. and M.L.-C.; formal analysis, E.S.-A. and J.O.-C.; investigation, E.S.-A., J.M.-V., J.O.-C. and M.L.-C.; writing—original draft preparation, E.S.-A. and J.O.-C.; writing—review and editing, E.S.-A., J.M.-V., J.O.-C. and M.L.-C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Vice-Rectorate for Research of the University of Alicante (predoctoral fellowship to E.S.-A., reference FPUA2019-54), the Interuniversity Institute of Geography of the University of Alicante (Research Groups Water and Territory; Climate and Spatial Planning) and Proyecto EXE (PID2020-116860RB-C21) financiado por el Ministerio de Ciencia e Innovación y Fondos FEDER (IP: J.Martin-Vide).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
This research is the result of a research stay at the Climatology Group of the University of Barcelona, under the supervision of Professor Javier Martin Vide. We would also acknowledge AEMET for the daily precipitation dataset provided for this study.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Appendix A

Table A1.
Study events—Dates on which precipitation equal to or greater than 100 mm/day occurred at any observatory in Alicante, synoptic situation, classification methods, WeMOi value (1981–2020), other synoptic characteristics and numbers of observatories where the event is recorded.
Table A1.
Study events—Dates on which precipitation equal to or greater than 100 mm/day occurred at any observatory in Alicante, synoptic situation, classification methods, WeMOi value (1981–2020), other synoptic characteristics and numbers of observatories where the event is recorded.
| Observatory | Date | mm/day | Synoptic Situation Martín Vide (1984) | Synoptic Situation Olcina Cantos (1994) | Synoptic Situation J&C (1977) | WeMOi | Other Synoptic Features | Nº Obs. Recorded the Event |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PEGO CONVENTO | 21/04/81 | 108.2 | Advection from the E with DANA | cP (Retrograde trough) | CNE | −2.00 | Retrograde trough. DANA over IP, B in North Africa | 4 |
| LA ROMANA ALGESAR | 29/05/82 | 110.0 | Advection from the E with DANA | mP centred | CSE | −0.61 | British Isles-Central Europe A. DANA over Portugal. B in North Africa | 3 |
| ALICANTE-ELCHE/AEROPUERTO | 19/10/82 | 235.0 | Advection from the E with DANA | mP centred | NE | −1.13 | Azores A. B in Algeria, DANA in the S of the IP and N of the Morocco | 9 |
| ALMUDAINA | 31/10/82 | 124.2 | Advection from the E with DANA | cP (Retrograde trough) | A | −1.15 | Retrograde trough, Central Europe A, DANA over Algeria | 7 |
| ALMUDAINA | 01/11/82 | 130.5 | Advection from the E with DANA | mP to the south | A | −1.26 | Retrograde trough, Central Europe A, DANA over Algeria | 5 |
| BANYERES DE MARIOLA | 10/11/84 | 129.0 | Dynamic or Cold- core Low | mP to the south | C | −2.55 | Algeria low, Scandinavian A | 8 |
| ROJALES EL MOLINO | 21/02/85 | 133.0 | Deep Trough | mP centred | SE | 0.99 | Azores A with bridge with British Isles-Scandinavian-Russian A. B in North Africa | 4 |
| CALLOSA D’EN SARRIA EL ALGAR | 28/10/85 | 195.0 | Advection from the NE with DANA | cP (Retrograde trough) | CNE | −1.59 | A Islas Británicas, B in North Africa, DANA over Balearic Isles | 6 |
| PEGO CONVENTO | 15/11/85 | 249.0 | Deep Trough | mP centred | E | −2.12 | Azores A with bridge with Scandinavian A. Trough over Portugal | 15 |
| GATA DE GORGOS | 16/11/85 | 200.0 | Advection from the NE with DANA | mP to the south | CNE | −1.76 | Azores A with bridge with Scandinavian A. DANA over Morocco | 2 |
| GATA DE GORGOS | 17/11/85 | 115.0 | Advection from the NE with DANA | cP (Retrograde trough) | NE | −1.12 | Azores A with bridge with Scandinavian A. DANA over Morocco | 1 |
| ALMUDAINA | 29/12/85 | 105.0 | Deep Trough | mP centred | C | −1.41 | Low in the Strait of Gibraltar | 2 |
| TARBENA CH JUCAR POBLE DE DALT | 29/09/86 | 241.1 | Advection from the E with DANA | cP (Retrograde trough) | E | −1.56 | British Isles A. DANA over Ibiza | 9 |
| TARBENA CH JUCAR POBLE DE DALT | 30/09/86 | 218.2 | Advection from the E with DANA | mP to the south | E | −2.04 | British Isles A | 3 |
| ALMUDAINA | 16/11/86 | 128.0 | Advection from the E with DANA | mP to the south | NE | −1.16 | A to the W of the IP, low over Algeria | 3 |
| CALLOSA D’EN SARRIA EL ALGAR | 17/11/86 | 160.0 | Advection from the NE with DANA | mP to the south | NE | −0.70 | Azores A. DANA over Algeria | 5 |
| PEGO CONVENTO | 03/11/87 | 371.5 | Dynamic or Cold- core Low | mP to the south | CSE | −2.97 | British Isles A, rhombus pattern. B to the Cape of San Vicente | 6 |
| ORIHUELA ‘LOS DESAMPARADOS’ | 04/11/87 | 316.00 | Advection from the E | mP to the south | SE | −2.84 | British Isles A | 7 |
| GATA DE GORGOS | 30/09/88 | 206.0 | Deep Trough | mP centred | CE | −1.29 | British Isles A, Trough to the N of the IP | 4 |
| LA ROMANA ALGESAR | 14/10/88 | 118.0 | Advection from the E with DANA | mP centred | CS | −2.77 | Azores A with bridge with Central Europe A. B over Galicia | 2 |
| VALL DE LAGUARD FONTILLES | 04/11/88 | 110.0 | Advection from the E | mP to the south | SE | −3.20 | Central Europe A | 1 |
| GATA DE GORGOS | 17/03/89 | 187.0 | Deep Trough | mP centred | C | −0.72 | Azores A. Trough to the E of the IP | 4 |
| TARBENA CH JUCAR POBLE DE DALT | 18/03/89 | 143.6 | Advection from the E with DANA | mP centred | NE | −1.00 | Azores A, B over Algeria. DANA to the S of the IP and Morocco | 4 |
| TARBENA CH JUCAR POBLE DE DALT | 04/09/89 | 255.6 | Deep Trough | mP centred | E | −0.69 | Azores A, B in North Africa | 3 |
| GATA DE GORGOS | 05/09/89 | 201.0 | Deep Trough | mP centred | E | −1.53 | A Azores, retrograde trough, B in North Africa | 5 |
| TIBI TALECA | 07/09/89 | 113.6 | Advection from the E with DANA | mP centred | CE | −2.10 | North-Atlantic A. B to the Gulf of Cadiz | 8 |
| TARBENA CH JUCAR POBLE DE DALT | 30/11/89 | 120.9 | Advection from the E | mP/cT | SE | −1.92 | Central Europe powerful A | 3 |
| ALICANTE | 01/12/89 | 119.8 | Advection from the E with DANA | cP (Retrograde trough) | SE | −1.82 | Central Europe A | 6 |
| CALLOSA D’EN SARRIA EL ALGAR | 01/05/90 | 126.0 | Weak trough with gentle flow from the E | cP (Retrograde trough) | E | −1.23 | Central Europe A | 1 |
| VALL DE LAGUARD FONTILLES | 19/12/90 | 128.0 | Advection from the E with DANA | cP (Retrograde trough) | E | −2.07 | Retrograde trough, Azores A. B in the Morocco coast | 6 |
| TARBENA CH JUCAR POBLE DE DALT | 23/03/91 | 108.1 | Deep Trough | mA (Trough) | C | - | Azores A, Algeria low | 1 |
| TARBENA CH JUCAR POBLE DE DALT | 23/10/91 | 143.5 | Advection from the E with DANA | mP centred | E | - | Retrograde trough, British Isles A. DANA to the E of the IP | 7 |
| PEGO CONVENTO | 24/10/91 | 128.9 | Advection from the E with DANA | mP centred | E | - | Retrograde trough, British Isles A. DANA in front of Portugal | 7 |
| CALLOSA D’EN SARRIA TOSSAL DE SALOMÓ | 19/02/92 | 124.3 | Deep Trough | cP (Retrograde trough) | CSE | −2.88 | British Isles A, retrograde trough. B in the Gulf of Cadiz | 6 |
| CALLOSA D’EN SARRIA EL ALGAR | 20/02/92 | 145.0 | Advection from the E with DANA | cP (Retrograde trough) | E | −2.19 | Retrograde trough, Azores A | 6 |
| TARBENA CH JUCAR POBLE DE DALT | 02/03/92 | 122.9 | Advection from the E with DANA | mP to the south | SE | −1.47 | Retrograde trough | 4 |
| TARBENA CH JUCAR POBLE DE DALT | 02/05/92 | 176.5 | Deep Trough | mP centred | NE | −0.87 | Azores A, B in North Africa, DANA over Sicilia | 2 |
| CALLOSA D’EN SARRIA EL ALGAR | 03/05/92 | 201.0 | Advection from the NE with DANA | mP to the south | NE | −0.66 | Azores A- British Isles A, B in North Africa, DANA over Oran | 5 |
| GATA DE GORGOS | 13/06/92 | 105.0 | Advection from the E with DANA | cP (Retrograde trough) | CE | −0.89 | Azores A | 10 |
| PEGO CONVENTO | 08/10/92 | 123.0 | Advection from the E with DANA | mP to the south | CE | −1.67 | British Isles A | 4 |
| ALMUDAINA | 01/02/93 | 240.5 | Advection from the E with DANA | mP to the south | SE | −2.78 | Central Europe A | 5 |
| ALMUDAINA | 02/02/93 | 102.6 | Advection from the E with DANA | mP to the south | E | −1.84 | Central Europe A | 2 |
| PEGO CONVENTO | 25/10/93 | 117.0 | Deep Trough | cP (Retrograde trough) | E | −1.28 | British Isles A, Trough to the E of the PI | 3 |
| PEGO CONVENTO | 26/10/93 | 118.5 | Advection from the E with DANA | cP (Retrograde trough) | E | −1.99 | British Isles A | 2 |
| PEGO CONVENTO | 08/11/93 | 118.7 | DANA to the SW | mP to the south | C | −0.09 | Azores A. DANA S Portugal, B in North Africa. | 1 |
| TARBENA CH JUCAR POBLE DE DALT | 24/11/93 | 141.7 | Advection from the E with DANA | mP to the south | E | −2.07 | Azores A with bridge with Russian A | 6 |
| TARBENA CH JUCAR POBLE DE DALT | 25/11/93 | 162.4 | Advection from the E with DANA | cP (Retrograde trough) | NE | −1.29 | Russian - Central Europe A | 5 |
| GATA DE GORGOS | 15/04/94 | 125.0 | Deep Trough | mA (Trough) | NE | −1.52 | British Isles A, Algeria Low | 4 |
| GATA DE GORGOS | 15/04/95 | 100.0 | Advection from the NE | cP (Retrograde trough) | ANE | −0.61 | A to the W British Isles. B in North Africa. DANA in Italy and central Europe | 1 |
| PEGO CONVENTO | 10/09/96 | 186.0 | Advection from the E with DANA | mP to the south | E | −1.88 | A to the W British Isles | 5 |
| PEGO CONVENTO | 11/09/96 | 160.1 | Advection from the E with DANA | mP centred | CE | −1.71 | A to the W British Isles | 1 |
| CALLOSA D’EN SARRIA EL ALGAR | 08/04/97 | 230.0 | Advection from the E with DANA | mP to the south | SE | −2.68 | Azores A with bridge with central Europe- Scandinavian- Arctic A | 5 |
| VILLENA (LA VEREDA) | 18/06/97 | 192.0 | Weak trough with gentle flow from the E | mP centred | NE | −1.33 | Azores A. Trough to the E of IP | 2 |
| ALICANTE | 30/09/97 | 270.2 | Advection from the E with DANA | mP to the south | E | −1.07 | - | 3 |
| TARBENA CH JUCAR POBLE DE DALT | 28/10/97 | 162.3 | Deep Trough | mP | C | −1.58 | Central Europe powerful A | 2 |
| VALL DE LAGUARD FONTILLES | 04/12/97 | 400.0 | Deep Trough | cP (Retrograde trough) | CE | −1.68 | British Isles A, B in the Strait | 3 |
| TARBENA CH JUCAR POBLE DE DALT | 05/12/97 | 180.3 | Dynamic or Cold- core Low | mP to the south | NE | −1.84 | France A. B over Algeria. DANA to the E in the IP- Balearic Isles- North Africa. | 7 |
| PEGO CONVENTO | 11/11/99 | 237.7 | Advection from the E with DANA | cP (Retrograde trough) | CE | −2.41 | Omega blocking, retrograde trough, British Isles A | 1 |
| VALL DE LAGUARD FONTILLES | 13/03/00 | 180.0 | Advection from the E with DANA | cP (Retrograde trough) | CNE | −0.18 | Surface low to the SE of the IP | 4 |
| VALL DE LAGUARD FONTILLES | 23/10/00 | 226.0 | Advection from the E with DANA | mP to the south | SE | −2.41 | Azores A with bridge with Central Europe A | 2 |
| VALL DE LAGUARD FONTILLES | 24/10/00 | 110.0 | Advection from the E with DANA | mP to the south | SE | −1.94 | Azores A | 2 |
| VALL DE LAGUARD FONTILLES | 14/02/01 | 100.0 | Advection from the E with DANA | cP (Retrograde trough) | C | −0.79 | Omega blocking, retrograde trough, British Isles A | 1 |
| TARBENA CH JUCAR POBLE DE DALT | 19/09/01 | 110.0 | Weak trough with gentle flow from the E | mP centred | ASE | −0.91 | Russian A, Netherlands-Azores B, B in North Africa | 1 |
| GATA DE GORGOS | 28/03/02 | 140.0 | Advection from the E with DANA | cP (Retrograde trough) | SE | −3.35 | Central Europe A | 1 |
| GATA DE GORGOS | 02/04/02 | 113.0 | Deep Trough | mP centred | C | −1.29 | Algeria low | 2 |
| PEGO CONVENTO | 06/05/02 | 295.1 | Advection from the E with DANA | mP centred | E | −2.10 | Azores A with bridge with Scandinavian A | 2 |
| PEGO CONVENTO | 07/05/02 | 180.0 | Advection from the E with DANA | mP to the south | CNE | −2.47 | A to the W of British Isles with bridge with Scandinavian A | 1 |
| BOLULLA | 10/01/03 | 123.5 | Deep Trough | mA (Trough) | NE | 0.05 | Azores - British Isles – Scandinavian A, B in Algeria. | 1 |
| TARBENA CH JUCAR POBLE DE DALT | 15/02/03 | 144.3 | Deep Trough | cP (Retrograde trough) | NE | −0.90 | Scandinavian A | 1 |
| VALL DE LAGUARD FONTILLES | 15/04/03 | 202.5 | Advection from the E with DANA | mP centred | CE | −2.51 | Russian - Scandinavian A | 3 |
| ALMUDAINA | 17/11/03 | 114.3 | Advection from the E with DANA | mP to the south | NE | −1.20 | Azores A, Algeria low | 2 |
| PEGO CONVENTO | 28/03/04 | 115.7 | Advection from the E with DANA | mP centred | CE | −3.36 | Azores A, Retrograde trough | 2 |
| ROJALES EL MOLINO | 15/04/04 | 130.2 | Weak trough with gentle flow from the E | mP centred | SE | −3.06 | Azores A with bridge with Central Europe A, Morocco low | 1 |
| TARBENA CH JUCAR POBLE DE DALT | 11/05/04 | 116.1 | Advection from the E with DANA | mP to the south | C | −1.21 | Azores A | 1 |
| ALMUDAINA | 05/11/04 | 185.2 | Advection from the NE with DANA | mP to the south | E | −1.02 | British Isles A. DANA in the Gulf of Cadiz | 1 |
| TARBENA CH JUCAR POBLE DE DALT | 12/11/04 | 108.5 | Advection from the NE with DANA | mP to the south | NE | −1.09 | Azores A to the W of British Isles. B in North Africa. DANA to the S of IP and to the N of Morocco | 1 |
| ALMUDAINA | 04/12/04 | 181.6 | Advection from the NE with DANA | mP to the south | CNE | −1.56 | Retrograde trough. DANA to the SW of IP | 2 |
| ALMUDAINA | 05/12/04 | 142.9 | Advection from the NE with DANA | mP to the south | NE | −1.01 | Central Europe A. DANA in the N of Morocco | 2 |
| TARBENA CH JUCAR POBLE DE DALT | 07/12/04 | 133.6 | Advection from the NE with DANA | mP to the south | NE | −1.16 | Central Europe A. DANA to the SE of IP- N of Morocco and Balearic Isles | 2 |
| TARBENA CH JUCAR POBLE DE DALT | 30/01/06 | 154.2 | Advection from the NE with DANA | mP to the south | CNE | −1.92 | British Isles - Central Europe A. Western Mediterranean B. DANA to the S of IP, Morocco and Algeria | 2 |
| TARBENA CH JUCAR POBLE DE DALT | 20/12/06 | 140.0 | Advection from the NE with DANA | cP (Retrograde trough) | NE | −0.72 | British Isles A. DANA to the E of IP | 4 |
| TARBENA CH JUCAR POBLE DE DALT | 29/03/07 | 126.0 | Advection from the NE with DANA | mA (Trough) | N | −0.13 | Azores A. B in North Africa, DANA on the coast of Algeria | 1 |
| ALMUDAINA | 22/09/07 | 114.9 | Weak trough with gentle flow from the E | mP centred | U | −0.68 | Azores A | 1 |
| VALL DE LAGUARD FONTILLES | 11/10/07 | 371.2 | Advection from the E with DANA | cP (Retrograde trough) | NE | −1.59 | A over European mid-latitudes | 1 |
| GATA DE GORGOS | 12/10/07 | 258.9 | Advection from the E with DANA | cP (Retrograde trough) | NE | −0.98 | British Isles A, rhombus pattern | 1 |
| TARBENA CH JUCAR POBLE DE DALT | 17/10/07 | 104.0 | Weak trough with gentle flow from the E | mP centred | E | −1.19 | Europe A | 1 |
| PEGO CONVENTO | 18/10/07 | 100.4 | Advection from the NE | cP (Retrograde trough) | NE | −0.70 | British Isles A | 1 |
| TARBENA CH JUCAR POBLE DE DALT | 22/10/07 | 190.0 | Advection from the N | mT | AN | 0.70 | Russian- Scandinavian - British Isles A. DANA in Italy. B in the Adriatic | 3 |
| TARBENA CH JUCAR POBLE DE DALT | 23/10/07 | 133.0 | Advection from the N | cT/mP | N | 0.42 | Russian- Scandinavian - British Isles A. DANA to the S of Italy and Balkans | 2 |
| ALMUDAINA | 09/10/08 | 133.3 | Advection from the E with DANA | mP to the south | NE | −1.45 | A over European mid-latitudes | 1 |
| PEGO CONVENTO | 22/10/08 | 131.0 | Advection from the NE with DANA | mP centred | CNE | −1.36 | Azores A. DANA over Portugal | 2 |
| GATA DE GORGOS | 15/09/09 | 110.4 | Advection from the E with DANA | mP centred | C | −1.29 | A over European mid-latitudes | 3 |
| VALL DE LAGUARD FONTILLES | 22/09/09 | 109.0 | Advection from the E with DANA | cP (Retrograde trough) | NE | −0.81 | A over European mid-latitudes | 3 |
| GATA DE GORGOS | 27/09/09 | 111.0 | Advection from the E with DANA | cP (Retrograde trough) | E | −1.24 | A over European mid-latitudes | 1 |
| ROJALES EL MOLINO | 28/09/09 | 192.0 | Advection from the E with DANA | mP centred | E | −1.20 | A over European mid-latitudes | 1 |
| LA MARINA DE ELCHE | 29/09/09 | 119.3 | Weak trough with gentle flow from the E | mP to the south | E | −0.93 | Azores low, British Isles A | 1 |
| GATA DE GORGOS | 13/12/09 | 190.0 | Deep Trough | cP (Retrograde trough) | CNE | −0.36 | Algeria low, British Isles A | 1 |
| TARBENA CH JUCAR POBLE DE DALT | 14/12/09 | 188.0 | Deep Trough | cP (Retrograde trough) | CNE | −1.02 | Omega blocking, retrograde trough, Iceland A. Western Mediterranean B | 2 |
| TARBENA CH JUCAR POBLE DE DALT | 25/01/10 | 236.0 | Advection from the E with DANA | mA (Trough) | NE | −1.80 | A over European mid-latitudes | 1 |
| GATA DE GORGOS | 13/08/10 | 139.7 | Weak trough with gentle flow from the E | mP centred | CE | −0.97 | Atlantic A, North Sea low | 1 |
| ALMUDAINA | 12/10/10 | 132.1 | Dynamic or Cold- core Low | mP centred | C | −2.04 | DANA over IP, Balearic Isles B | 6 |
| TIBI TALECA | 11/03/11 | 102.5 | DANA to the SW | mP to the south | SE | −2.66 | Atlantic A - Mediterranean A. B in the N of Canary Isles | 1 |
| VALL DE LAGUARD FONTILLES | 28/10/11 | 189.0 | Advection from the E with DANA | mP/cT | CNE | −1.46 | Azores A with bridge with Central Europe A, Algeria low | 1 |
| ALMUDAINA | 29/10/11 | 100.5 | Advection from the E with DANA | mP to the south | NE | −1.16 | Central Europe A | 1 |
| PEGO CONVENTO | 21/11/11 | 121.7 | Dynamic or Cold- core Low | mP to the south | C | −2.00 | Azores A, Central Europe A. Algeria low | 4 |
| VALL DE LAGUARD FONTILLES | 22/11/11 | 107.0 | Dynamic or Cold- core Low | mP centred | C | −0.96 | Azores A with bridge with Central Europe – Scandinavian A. B in the Mediterranean, DANA over Portugal. | 1 |
| GATA DE GORGOS | 20/03/12 | 117.0 | Advection from the E with DANA | mP centred | E | −1.31 | A over European mid-latitudes | 1 |
| VALL DE LAGUARD FONTILLES | 11/11/12 | 230.0 | Advection from the NE with DANA | mP centred | C | −0.57 | Azores A- Russian A. Western Mediterranean B. DANA over IP | 3 |
| PEGO CONVENTO | 13/11/12 | 187.5 | Advection from the E with DANA | mP to the south | NE | −1.60 | Central Europe A, Algeria low | 1 |
| VALL DE LAGUARD FONTILLES | 24/04/13 | 105.0 | Advection from the E with DANA | mP to the south | E | −1.76 | Central Europe A | 2 |
| ALMUDAINA | 25/04/13 | 127.1 | Advection from the E with DANA | mP to the south | CE | −1.90 | Algeria low | 1 |
| BOLULLA | 30/11/13 | 103.0 | Deep Trough | mA (Trough) | N | −0.06 | A to the W British Isles | 2 |
| TIBI TALECA | 16/12/16 | 105.1 | Advection from the E with DANA | mP centred | C | −2.55 | Azores A with bridge with Central Europe A | 1 |
| TIBI TALECA | 17/12/16 | 102.6 | Advection from the E with DANA | mP to the south | E | −2.38 | A over European mid-latitudes | 1 |
| ALMUDAINA | 18/12/16 | 255.0 | Advection from the E with DANA | cP (Retrograde trough) | E | −2.31 | British Isles-France-Central Europe A | 2 |
| VALL DE LAGUARD FONTILLES | 19/12/16 | 213.0 | Dynamic or Cold- core Low | mP centred | C | −2.50 | Azores A with bridge with Central Europe A, DANA over France | 6 |
| TARBENA CH JUCAR POBLE DE DALT | 18/01/17 | 100.0 | Deep Trough | cP (Retrograde trough) | NE | −1.64 | Central Europe A. B to the S of Italy and Sicily | 1 |
| ALMUDAINA | 19/01/17 | 101.4 | Advection from the E with DANA | cP (Retrograde trough) | E | −2.44 | Central Europe A | 1 |
| TARBENA CH JUCAR POBLE DE DALT | 21/01/17 | 338.0 | Dynamic or Cold- core Low | mP to the south | CNE | −2.04 | Azores A with bridge with Central Europe A, DANA to the W of France, Balearic Isles low | 2 |
| TARBENA CH JUCAR POBLE DE DALT | 22/01/17 | 114.0 | Dynamic or Cold- core Low | mP centred | CNE | −1.50 | Central Europe A. Balearic Isles low | 2 |
| AGOST ESCUELA NACIONAL | 13/03/17 | 167.0 | Advection from the E with DANA | cP (Retrograde trough) | NE | −0.82 | Azores A | 1 |
| ELCHE CH SEGURA | 19/04/19 | 100.0 | Advection from the E with DANA | mP to the south | CE | −2.47 | Scandinavian A | 1 |
| GATA DE GORGOS | 21/04/19 | 226.0 | Dynamic or Cold- core Low | mP to the south | CNE | −1.62 | Azores A with bridge with Central Europe A. Algeria low. DANA over Oran | 2 |
| PEGO CONVENTO | 20/08/19 | 141.0 | Weak trough with gentle flow from the E | mP/cT | E | −0.76 | A in the North Azores. Maritime flow | 1 |
| VALL DE LAGUARD FONTILLES | 11/09/19 | 215.0 | Advection from the E with DANA | mP to the south | NE | −1.53 | Azores A with bridge with Scandinavian A | 1 |
| ORIHUELA ‘LOS DESAMPARADOS’ | 12/09/19 | 230.8 | Advection from the E with DANA | mP to the south | E | −1.44 | A over European mid-latitudes | 1 |
| TARBENA CH JUCAR POBLE DE DALT | 03/12/19 | 143.0 | Dynamic or Cold- core Low | mP to the south | E | −2.75 | Azores A with bridge with Central Europe A. Orán low | 1 |
| TARBENA CH JUCAR POBLE DE DALT | 19/01/20 | 277.0 | Dynamic or Cold- core Low | cP (Retrograde trough) | CNE | −1.20 | British Isles A. DANA to the SE of IP | 2 |
| ALMUDAINA | 20/01/20 | 192.4 | Advection from the E with DANA | cP (Retrograde trough) | E | −3.93 | Central Europe powerful A | 1 |
References
- Lopez-Bustins, J.A.; Lemus-Canovas, M. The influence of the Western Mediterranean Oscillation upon the spatio-temporal variability of precipitation over Catalonia (northeastern of the Iberian Peninsula). Atmos. Res. 2020, 236, 104819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín Vide, J.; Olcina Cantos, J. Climas y Tiempos de España; Alianza Editorial: Madrid, Spain, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Martín-Vide, J. Spatial distribution of a daily precipitation concentration index in peninsular Spain. Int. J. Climatol. 2004, 24, 959–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estrela, M.J.; Peñarrocha, D.; Pastor, F.; Millán, M. Torrential rain events on the Spanish Mediterranean coast: Relationship between spatial precipitation patterns and synoptic conditions. In Mediterranean Storms; Editoriale Bios: Cosenza, Italy, 2000; pp. 97–110. [Google Scholar]
- Lopez-Bustins, J.A.; Arbiol-Roca, L.; Martin-Vide, J.; Barrera-Escoda, A.; Prohom, M. Intra-annual variability of the Western Mediterranean Oscillation (WeMO) and occurrence of extreme torrential precipitation in Catalonia (NE Iberia). Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2020, 20, 2483–2501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peñarrocha, D.; Estrela, M.J.; Millán, M. Classification of daily rainfall patterns in a Mediterranean area with extreme intensity levels: The Valencia region. Int. J. Climatol. 2002, 22, 677–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil-Guirado, S.; Pérez-Morales, A.; López-Martínez, F. SMC-Flood database: A high-resolution press database on flood cases for the Spanish Mediterranean coast (1960–2015). Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2019, 19, 1955–1971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olcina Cantos, J. Incremento de episodios de inundación por lluvias de intensidad horaria en el sector central del litoral mediterráneo español: Análisis de tendencias en Alicante. Sémata Cienc. Sociais E Humanid. 2017, 29, 143–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribas Palom, A.M.; Olcina Cantos, J.; Sauri Pujol, D. More exposed but also more vulnerable? Climate change, high intensity precipitation events and flooding in Mediterranean Spain. Disaster Prev. Manag. Int. J. 2020, 29, 229–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tapiador, F.J.; Marcos, C.; Sancho, J.M.; Santos, C.; Núñez, J.Á.; Navarro, A.; Kummerow, C.; Adler, R.F. The September 2019 floods in Spain: An example of the utility of satellite data for the analysis of extreme hydrometeorological events. Atmos. Res. 2021, 257, 105588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemus-Canovas, M.; Lopez-Bustins, J.A.; Martín-Vide, J.; Halifa-Marin, A.; Insua-Costa, D.; Martinez-Artigas, J.; Trapero, L.; Serrano-Notivoli, R.; Cuadrat, J.M. Characterisation of extreme precipitation events in the Pyrenees: From the local to the synoptic scale. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llasat, M.C. An objective classification of rainfall events on the basis of their convective features: Application to rainfall intensity in the Northeast of Spain. Int. J. Climatol. 2001, 21, 1385–1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin-Vide, J.; Sanchez-Lorenzo, A.; Lopez-Bustins, J.A.; Cordobilla, M.J.; Garcia-Manuel, A.; Raso, J.M. Torrential rainfall in northeast of the Iberian Peninsula: Synoptic patterns and WeMO influence. Adv. Sci. Res. 2008, 2, 99–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olcina Cantos, J. Métodos de clasificación sinóptica en España. Revisión y propuesta. Estud. Geogr. 1994, 55, 357–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linés Escardó, A. Perturbaciones Típicas que Descienden a la Península Ibérica y Precipitaciones Asociadas; Ministerio de Transportes, Turismo y Comunicaciones, Instituto Nacional de Meteorología, Sección de Publicaciones: Madrid, Spain, 1981. [Google Scholar]
- Font Tullot, I. Climatología de España y Portugal; Instituto Nacional de Meteorología, Sección de publicaciones: Madrid, Spain, 1983. [Google Scholar]
- Jansá Guardiola, J.M. La masa de aire mediterránea. Rev. Geofís. 1959, 18, 35–50. [Google Scholar]
- Jansá Guardiola, J.M. El frente mediterráneo. Rev. Geofís. 1962, 21, 249–259. [Google Scholar]
- Florit Ameller, J.; Jansa Clar, A. Situaciones de presión en el Mediterráneo Occidental repercusiones sobre el tiempo en Menorca y en el resto de España. Treb. De Geogr. 1978, 35, 57–84. [Google Scholar]
- Martín Vide, J. Interpretación de los Mapas del Tiempo; Ketres Editorial: Barcelona, Spain, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Martín-Vide, J.; Moreno-García, M.C.; López-Bustins, J.A. Synoptic causes of torrential rainfall in south-eastern spain (1941–2017). Geogr. Res. Lett. 2021, 47, 143–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimalt-Gelabert, M.; Alomar-Garau, G.; Martin-Vide, J. Synoptic Causes of Torrential Rainfall in the Balearic Islands (1941–2010). Atmosphere 2021, 12, 1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenkinson, A.F.; Collison, P. An Initial Climatology of GalesWales over the North Sea. Synoptic Climatology Branch Memorandum; Meteorological Office, Braknell: London, UK, 1977. [Google Scholar]
- Miró, J.R.; Pepin, N.; Peña, J.C.; Martin-Vide, J. Daily atmospheric circulation patterns for Catalonia (northeast Iberian Peninsula) using a modified version of Jenkinson and Collison method. Atmos. Res. 2020, 231, 104674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil Olcina, A.; Olcina Cantos, J. Tratado de Climatología; Servicio de Publicaciones, Universidad de Alicante: Sant Vicent del Raspeig, Spain, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Romero, R.; Sumner, G.; Ramis, C.; Genovés, A. A classification of the atmospheric circulation patterns producing significant daily rainfall in the Spanish Mediterranean area. Int. J. Climatol. 1999, 19, 765–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capel Molina, J.J. El Clima de la Península Ibérica; Ariel Geografía: Barcelona, Spain, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Spellman, G. The application of an objective weather-typing system to the Iberian peninsula. Weather 2000, 55, 375–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín Vide, J. Aplicación de la clasificación sinóptica automática de Jenkinson y Collison a días de precipitación torrencial en el este de España. In La Información Climática Como Herramienta de Gestión Ambiental; Cuadrat, J.M., Vicente, S., Saz, M.A., Eds.; Grupo de Climatología Asociación Española de Climatología: Albarracín, Spain, 2002; pp. 123–127. [Google Scholar]
- Grimalt, M.; Tomàs, M.; Alomar, G.; Martin-Vide, J.; Moreno-García, M.C. Determination of the Jenkinson and Collison’s weather types for the western Mediterranean basin over the 1948–2009 period. Temporal analysis. Atmósfera 2013, 26, 75–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llop Garau, J.; Alomar Garau, G. Clasificación sinóptica automática de Jenkinson y Collison para los días de precipitación mayor o igual a 100 mm en la franja litoral catalana e Islas Baleares. In Cambio Climático. Extremos e Impactos; Rodríguez, C., Ceballos, A., González, N., Morán, E., Hernández, A., Eds.; Asociación Española de Climatología: Salamanca, Spain, 2012; pp. 449–458. [Google Scholar]
- Llop Garau, J.; Alomar Garau, G. Clasificación sinóptica automática de Jenkinson y Collison para los días de precipitación mayor o igual a 200 mm en la isla de Mallorca. Territoris 2012, 8, 143–152. Available online: https://raco.cat/index.php/Territoris/article/view/259933 (accessed on 4 July 2022).
- Gilabert, J.; Llasat, M.C. Circulation weather types associated with extreme flood events in Northwestern Mediterranean. Int. J. Climatol. 2018, 38, 1864–1876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azorin-Molina, C.; Chen, D.; Tijm, S.; Baldi, M. A multi-year study of sea breezes in a Mediterranean coastal site: Alicante (Spain). Int. J. Climatol. 2011, 31, 468–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huth, R.; Beck, C.; Philipp, A.; Demuzere, M.; Ustrnul, Z.; Cahynová, M.; Kyselý, J.; Tveito, O.E. Classifications of Atmospheric Circulation Patterns. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2008, 1146, 105–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drobinski, P.; Ducrocq, V.; Alpert, P.; Anagnostou, E.; Béranger, K.; Borga, M.; Braud, I.; Chanzy, A.; Davolio, S.; Delrieu, G.; et al. HyMeX: A 10-Year Multidisciplinary Program on the Mediterranean Water Cycle. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2014, 95, 1063–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llasat, M.C.; Llasat-Botija, M.; Petrucci, O.; Pasqua, A.A.; Rosselló, J.; Vinet, F.; Boissier, L. Towards a database on societal impact of Mediterranean floods within the framework of the HYMEX project. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2013, 13, 1337–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jansa, A.; Alpert, P.; Arbogast, P.; Buzzi, A.; Ivancan-Picek, B.; Kotroni, V.; Llasat, M.C.; Ramis, C.; Richard, E.; Romero, R.; et al. MEDEX: A general overview. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2014, 14, 1965–1984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tveito, O.E.; Huth, R. Circulation-type classifications in Europe: Results of the COST 733 Action. Int. J. Climatol. 2016, 36, 2671–2672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cahynová, M.; Huth, R. Atmospheric circulation influence on climatic trends in Europe: An analysis of circulation type classifications from the COST733 catalogue. Int. J. Climatol. 2016, 36, 2743–2760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philipp, A.; Beck, C.; Huth, R.; Jacobeit, J. Development and comparison of circulation type classifications using the COST 733 dataset and software. Int. J. Climatol. 2016, 36, 2673–2691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casado, M.J.; Pastor, M.A.; Doblas-Reyes, F.J. Links between circulation types and precipitation over Spain. Phys. Chem. Earth 2010, 35, 437–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casado, M.J.; Pastor, M.A. Circulation types and winter precipitation in Spain. Int. J. Climatol. 2016, 36, 2727–2742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortesi, N.; Gonzalez-Hidalgo, J.C.; Trigo, R.M.; Ramos, A.M. Weather types and spatial variability of precipitation in the Iberian Peninsula. Int. J. Climatol. 2014, 34, 2661–2677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasilla Álvarez, D.F.; García-Codrón, J.C. Regional and local scale atmospheric forcing upon sea level along the coast of SW Europe. Int. J. Climatol. 2016, 36, 2792–2809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khodayar, S.; Kalthoff, N.; Kottmeier, C. Atmospheric conditions associated with heavy precipitation events in comparison to seasonal means in the western mediterranean region. Clim. Dyn. 2018, 51, 951–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Montes, S.; Seubert, S.; Rodrigo, F.S.; Rasilla Álvarez, D.F.; Hertig, E.; Esteban, P.; Philipp, A. Circulation types and extreme precipitation days in the Iberian Peninsula in the transition seasons: Spatial links and temporal changes. Atmos. Res. 2014, 138, 41–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dayan, U.; Nissen, K.; Ulbrich, U. Review Article: Atmospheric conditions inducing extreme precipitation over the eastern and western Mediterranean. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2015, 15, 2525–2544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alpert, P.; Osetinsky, I.; Ziv, B.; Shafir, H. Semi-objective classification for daily synoptic systems: Application to the eastern Mediterranean climate change. Int. J. Climatol. 2004, 24, 1001–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín Vide, J. El Tiempo y el Clima; Rubens Editorial: Barcelona, Spain, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Petrovic, P. Measurement Precision as a Cause of Inhomogeneity in Weather Data Time Series Measurement Precision as a cause of Inhomogeneity in Weather Data Time Series. In Proceedings of the 2nd Seminar on Homogenization of Surface Climatological Data, Budapest, Hungary, 9–13 November 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Rodríguez Ballesteros, C. Las Estaciones Termopluviométricas de la Red Climatológica de AEMET. Available online: www.divulgameteo.es (accessed on 25 March 2022).
- de Burriel Orueta, E.L.; Olcina Cantos, J. Un período fundamental para la climatología española: El “descubrimiento” de la circulación atmosférica en altitud, 1950–1980. Scr. Nova. Rev. Electrónica Geogr. Cienc. Soc. 2016, 20, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García Fernández, J. El Clima en Castilla y León; Ámbito: Valladolid, Spain, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Martín León, F. Las Gotas Frías/Danas: Ideas y Conceptos Básicos. 2003. Available online: https://www.aemet.es/documentos/es/conocermas/recursos_en_linea/publicaciones_y_estudios/estudios/dana_ext.pdf (accessed on 31 March 2022).
- Lemus-Canovas, M.; Lopez-Bustins, J.A.; Martin-Vide, J.; Royé, D. SynoptReg: An R package for computing a synoptic climate classification and a spatial regionalization of environmental data. Environ. Model. Softw. 2019, 118, 114–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín-Vide, J.; López-Bustins, J.A. The Western Mediterranean Oscillation and rainfall in the Iberian Peninsula. Int. J. Climatol. 2006, 26, 1455–1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín Vide, J. La Oscilación del Mediterráneo Occidental: Un patrón de teleconexión ad hoc para el este de la Península Ibérica. In Libro Jubilar en Homenaje al Profesor Antonio Gil Olcina; Olcina, J., Rico Amorós, A.M., Eds.; Publicaciones de la Universidad de Alicante, Servicio de Publicaciones: San Vicente del Raspeig, Spain, 2016; pp. 145–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quereda Sala, J.; Montón Chiva, E. Los elementos del clima: Distribución territorial de temperaturas y precipitaciones. In Climas y Tiempos del País Valenciano; Olcina Cantos, J., Moltó Mantero, E., Eds.; Publicaciones de la Universitat d’Alacant: San Vicente del Raspeig, Spain, 2019; pp. 72–77. [Google Scholar]
- López Bustins, J.A. L’ Oscil·Lació de la Mediterrània Occidental i la Precipitació als Països Catalans; Universitat de Barcelona: Barcelona, Spain, 2007; Available online: http://hdl.handle.net/10803/1953 (accessed on 4 April 2022).
- Pino, D.; Ruiz-Bellet, J.L.; Balasch, J.C.; Romero-León, L.; Tuset, J.; Barriendos, M.; Mazon, J.; Castelltort, X. Meteorological and hydrological analysis of major floods in NE Iberian Peninsula. J. Hydrol. 2016, 541, 63–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Krichak, S.O.; Barkan, J.; Breitgand, J.S.; Gualdi, S.; Feldstein, S.B. The role of the export of tropical moisture into midlatitudes for extreme precipitation events in the Mediterranean region. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2015, 121, 499–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Insua-Costa, D.; Lemus-Cánovas, M.; Miguez-Macho, G.; Llasat, M.C. Climatology and ranking of hazardous precipitation events in the western Mediterranean area. Atmos. Res. 2021, 255, 105521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, A.M.; Cortesi, N.; Trigo, R.M.; Nieto, R.; Kumar Jaswal, A. Circulation weather types and spatial variability of daily precipitation in the Iberian Peninsula. Front. Earth Sci. 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CEAM (Centro de Estudios Ambientales del Mediterráneo). Informe TSM Mediterráneo. Invierno 2022; CEAM: Valencia, Spain, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Pastor, F.; Valiente, J.A.; Palau, J.L. Sea Surface Temperature in the Mediterranean: Trends and Spatial Patterns (1982–2016). Pure Appl. Geophys. 2018, 175, 4017–4029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, R.N. Cut-off lows and extreme precipitation in Eastern Spain: Current and future climate. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).