Abstract
With the development of industrialization and the increase in the number of motor vehicles in megacities in China, ozone pollution has become a prominent problem. Although different models have been used on ozone concentration simulation, the accuracy of different models still varies. In this study, the performance of two models including a linear stepwise regression (SR) model and a non-linear artificial neural network (ANN) model on the simulation of ozone concentration were analyzed in the Jing-Jin-Ji region, which is one of the most polluted areas in China. Results showed that the performance of the ANN model (adjusted R2 = 0.8299, RMSE = 22.87, MAE = 16.92) was better than the SR model (adjusted R2 = 0.7324, RMSE = 28.61, MAE = 22.30). The performance of the ANN on simulating an ozone pollution event was better than the SR model since a higher probability of detection (POD) and threat score (TS) values were obtained by the ANN model. The model performance for spring, autumn and winter was generally higher than that for summer, which may because the weights of factors on simulating high and low ozone concentrations were different. The method proposed by this study can be used in ozone concentration estimation.
1. Introduction
With the development of industrialization in megacities in China and the increase in the number of motor vehicles, ozone pollution has become a growing prominent problem [1]. Ozone in the troposphere is mainly produced by photochemical reactions of gaseous pollutants such as volatile organic compounds (VOCs), NO2 and CO, which are emitted by motor vehicle exhaust and factories [2,3]. In addition, vegetation is also one of the most important sources of VOCs in urban environments [2]. VOCs react photochemically with nitrogen oxides (NOx) and generate ozone in the presence of ultraviolet radiation [4,5]. Studies show that the increase in ozone concentration is harmful to human health, such as by means of inflammation of the respiratory system and dysfunction of the cardiovascular system [6]. However, the spatial resolution of air quality monitoring sites is relatively low in China. Thus, it is important to forecast ozone concentration accurately to protect human health.
Plenty of studies have shown that ozone precursors and meteorological conditions were important factors affecting ozone concentration [7,8,9,10]. The photochemical reaction rate of precursors will be strengthened under the condition of strong solar radiation and high temperature, thus increasing the ozone concentration [8,9,10]. On the contrary, rainfall and higher relative humidity always leads to a decrease in ozone concentration due to a decrease in photochemical production efficiency and an increase in wet deposition [7]. In addition, wind speed is another factor that affects ozone concentration. Normally, the increase in wind speed reduces O3 concentration because high wind speeds are generally not conductive to local ozone concentration accumulation.
Due to the relatively low spatial accuracy of the ozone concentration monitoring network in China, researchers have explored different models to simulate ozone concentration. In previous studies, multiple linear regression model has been used to analyze the relationship between ozone and its affecting factors, including precursors and meteorological factors [11,12]. However, the simulation accuracy of this method is relatively low because the linear regression cannot fully explain the nonlinear reactions process of ozone formation in the air. Researchers have introduced the technique of machine learning into the ozone concentration prediction. Machine learning is one of the most commonly used artificial intelligence (AI) technologies to solve air pollution problems [13,14,15,16]. As one of the commonly used models of machine leaning, the artificial neural network (ANN) model solves complex nonlinear problems by imitating the structure and function of the human brain [17]. ANNs have good approximation performance and fast convergence speed, and can approximate any multivariable nonlinear function [18]. Compared with the linear regression model, ANNs have better simulation effects on the relationship of nonlinearity between air pollution concentration and different influencing factors [19,20]. Bandyopadhyay et al. used single hidden layer ANN models and multiple linear regression (MLR) models, respectively, to predict the average monthly total ozone concentration in Arosa, Switzerland. They found the ANN model overperformed the MLR model by using the method of error estimation and least squares to evaluate [21]. AlOmar et al. applied the wavelet transform (WT) approach to the ANN model; they compared the hybrid model (W-ANN) with classical ANN in predicting 1 h ahead ozone concentrations and found the W-ANN performed better than the ANN model [22]. ANN modeling combined with principal component analysis (PCA) was used to forecast ozone concentration by Al-Alawi et al. in the lower atmosphere [15]. They found that the R2 between the real and predicted ozone values for the ANN, PCA, and the combined model were 0.986, 0.965, and 0.995, respectively. The combined model improves the prediction of ozone concentration. Gao et al. estimated O3_8h in Hebei province, China, by ANN using factors of NO2, CO, SO2, wind speed, temperature, pressure, visibility, precipitation, sunlight duration and boundary layer height. Results showed that ANN has good ozone estimation performance with R2 of 0.80 [16].
In order to establish a model that simulates ozone concentration more accurately, the performance of two models including a linear stepwise regression (SR) model and nonlinear ANN model on simulating the daily average of the maximum 8 h moving average of O3 concentration (O3_8h) in Jing-Jin-Ji region were compared using the concentrations of ozone precursors and meteorological factors. The result can provide a reference for making ozone pollution prevention and control measures, and is beneficial to the environment and public health.
2. Methods
2.1. Study Area
As shown in Figure 1, the research area of Jing-Jin-Ji region is located in the North China Plain and bordered by the Bohai Sea. The topography of Jing-Jin-Ji region is high in the northwest and low in the southeast. The region belongs to temperate monsoon climate. Summer is hot and humid, and winter is cold and dry. Rainfall is concentrated in the summer. The Jing-Jin-Ji region has an area of approximately 21,800 km2, which contains 13 major cities including Beijing, Tianjin, Shijiazhuang, Tangshan, Qinhuangdao, Handan, Baoding, Zhangjiakou, Chengde, Langfang, Cangzhou, Hengshui and Xingtai. Eleven cities expect Beijing and Tianjin belong to Hebei Province. As one of the world’s fastest-developing economic zones, Jing-Jin-Ji region is mainly engaged in heavy industry and manufacturing. Along with economic development, air pollution has increased mainly due to emissions from automobile exhausts and industry.
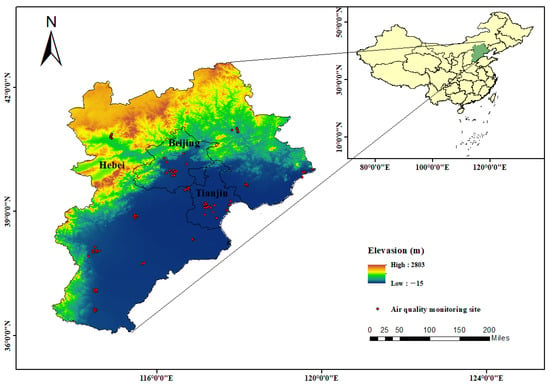
Figure 1.
Geographical location of study area and distribution of air quality monitoring sites.
2.2. Data Collection
The concentrations of air pollutants including the maximum 8 h moving average of O3 concentration (O3_8h), NO2, CO, PM10 and PM2.5 were collected from China National Environmental Monitoring Centre [23]. The data were collected from a total of 76 monitoring sites in the cities in Jing-Jin-Ji region (see Figure 1). The study period was from 1 January 2018 to 31 December 2020. In order to evaluate the effects of meteorological factors on ozone variance, factors including 2 m temperature (T2m, K), surface net solar radiation (SSR, J/m2), total precipitation (TP, m), surface pressure (SP, Pa), boundary layer height (BLH, m), 10 m u-component of wind (U10, m/s) and 10 m v-component of wind (U10, m/s) were downloaded from European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts (ECMWF) [24]. The spatial resolution of the hourly meteorological data was 0.25° × 0.25°. When the monitoring site of air pollutants was located in a specific grid cell, we assigned the air pollution data to the cell and matched them with the corresponding meteorological data. Wind direction (WD, m/s) and wind speed (WS, m/s) were not provided by ECMWF and they were calculated by the Formulas (1) and (2):
where, U10 and V10 are the u-component and v-component of wind at 10 m height.
2.3. Models
2.3.1. Stepwise Regression Model
The model of SR is a type of multiple linear regression model, which can select the most appropriate combination of independent variables for dependent variable prediction. In this study, we established a SR model with the O3_8h concentration as the dependent variable and the factors of NO2 concentration, CO concentration, PM10 and PM2.5 concentrations, T2m, TP, SP, SSR, WS, WD and BLH as the independent variables. The equation of SR model is as follows:
where, Yi is O3_8h concentration, β0, β1, …, β10 are regression coefficients, X1i, X2i, …, X10i are the independent variable discussed above, μi is random variable.
The software of SPSS (version 22.0.0.0, IBM Corp, Armonk, NY, USA) was used for SR analysis.
2.3.2. Artificial Neural Network Model
An ANN is a computing system that consists of multiple interconnected processing elements. The flexibility and validity of the model are desirable. Additionally, this model is less demanding for input dataset [25]. The structure of the ANN model is shown in Figure 2. The output layer is O3_8h concentration. Following the principle of parsimony, hidden layers should be as few as possible [26], thus, we selected different numbers of nodes including 3, 4 and 5 to find the model that works best. 70% of the data were selected as training samples to complete the self-learning process and to construct an optimal ANN structure, and the remaining 30% of the data were the test samples to evaluate the performance of the established model. The activation function of the hidden layer is selected as hyperbolic tangent (tanh) and S-shaped growth curve (sigmoid), which are commonly used in ozone prediction using an ANN model [27,28,29,30]; the formulas are as follows:
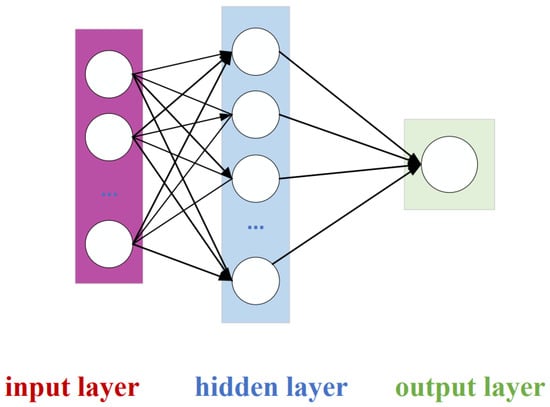
Figure 2.
Schematic diagram of artificial neural network.
In this study, neural network multilayer perceptron in IBM SPSS Statistics 22.0 (version 22.0.0.0, IBM Corp, Armonk, NY, USA) was used for ANN analysis.
2.3.3. Model Validation
The root mean square error (RMSE), mean absolute error (MAE) and coefficient of determination (R2) were used to evaluate the model performance. The formulas are as follows:
where, n is the number of measurements; ti is the simulated value; yi is the true value; yi-average is the average of the true values.
The value of R2 gives an estimate of the relationship between movements of a dependent variable based on an independent variable’s movements. It is between 0 and 1, and the closer it is to 1, the better the model fitting degree is. The MAE and the RMSE can be used to diagnose the variation in the errors in a set of forecasts. The greater difference between them, the greater the variance in the individual errors in the sample. The closer the values of the RMSE and MAE are to 0, the lower the error is and the better the model performance is.
In order to evaluate the performance of the model in predicting ozone pollution event when the concentration exceeds the limit value of 160 μg/m3, we calculated the probability of detection (POD), threat score (TS) and false alarm rate (FAR) of the two models. The higher the value of the POD and TS, the better the simulation is. The closer the FAR is to zero, the better the simulation is. The calculation formulas are as follows:
where, A represents the days when both the monitored and simulated O3 concentration are greater than 160 μg/m3; B represents the number of days when the monitored O3 concentration is greater than 160 μg/m3 and the simulated value is less than 160 μg/m3; C represents the number of days when the monitored O3 concentration is less than 160 μg/m3 and the simulated O3 concentration is greater than 160 μg/m3.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Ozone Concentration in Jing-Jin-Ji Region
Figure 3 shows the variation trend of the daily maximum O3_8h concentrations in Beijing, Tianjin and Hebei province from 2018 to 2020. It can be seen that the annual distribution of ozone concentration presents a shape of a single peak. The ozone concentration reaches the maximum in summer, which is mainly due to the acceleration of photochemical reaction process by high temperature and intense solar radiation in summer [10]. A slight downward trend of ozone concentration was observed from 2018 to 2020 (the annual averaged ozone concentrations are shown in Table 1). This may be related to that the strict plan named “The 2017 work plan for air pollution prevention and control in Beijing, Tianjin, Hebei, and surrounding areas” issued by China in 2017 [31]. The areas were urged to promote the use of new energy sources and restructure industry structure, which reduced emissions of industrial pollutants and controlled NOx emissions.
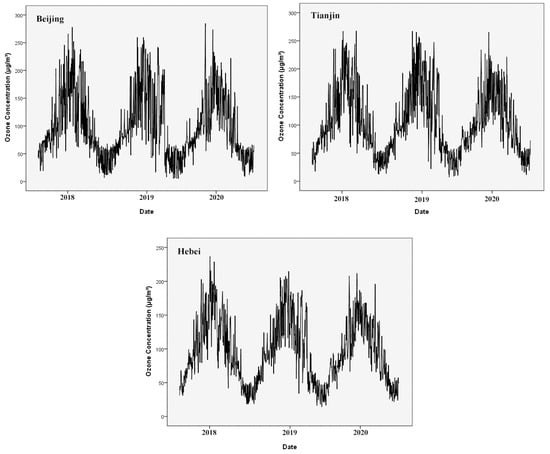
Figure 3.
Trend of O3_8h concentration from 2018 to 2020 in Jing-Jin-Ji region in China.

Table 1.
Annual averaged and standard deviation of ozone concentration from 2018 to 2020 in Jing-Jin-Ji region (μg/m³).
Figure 4 shows the distribution of ozone concentration in Jing-Jin-Ji region. Ozone concentrations in the southwestern Jing-Jin-Ji region were higher than those in the northeastern region. The reason is that the main industries in the southwestern area are steel, chemicals and coal, which are highly polluting industries [32]. The top ten value of O3_8h throughout the year are all observed in June with all values exceeded the standard of 160 μg/m3 in Ambient Air Quality Standard Ⅱ (GB3095-2012). The number of days that exceeded the 160 μg/m3 limited value in Jing-Jin-Ji region are shown in Table 2.
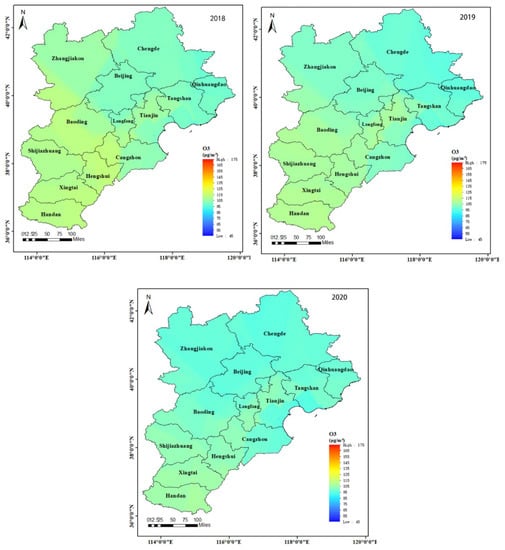
Figure 4.
Distribution of O3_8h concentration from 2018 to 2020 in Jing-Jin-Ji region in China.

Table 2.
Number of days exceeding the ozone limited value of 160 μg/m3 from 2018 to 2020 in Jing-Jin-Ji region in China.
As shown in Figure 5 and Table 3, the ozone concentration in Jing-Jin-Ji region showed a seasonal variation trend. Ozone concentration was the highest in summer, followed by spring and autumn, the concentration of ozone was the lowest in winter. The results were similar with the results reported by Cui et al., who analyzed ozone concentration in Beijing from 2013 to 2017 [33]. However, different seasonal variation characteristics of ozone concentration in Shanghai were reported by Li et al., with the highest ozone concentration in spring, followed by summer, autumn and winter [34]. The main reason is that Shanghai enters the “plum rain” season in July and August in summer, the overcast and rainy days lead to the decrease in solar radiation. Other changes in meteorological factors such as air humidity and temperature will affect the photochemical reaction of ozone, resulting in low ozone concentration in the corresponding month. In addition, ozone deposited in urban parks and greenery in rainy days was also influenced O3 variance in Shanghai [35]. Therefore, the rule of the highest ozone concentration in summer is not universally applicable in different areas. The influence of climate characteristics should also be considered.
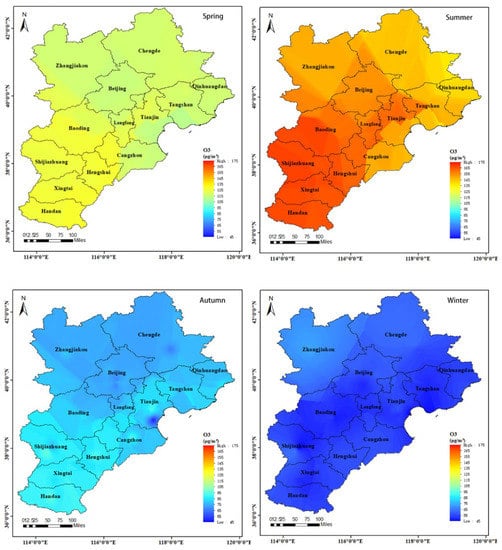
Figure 5.
Distribution of O3_8h concentration in different seasons during 2018 to 2020 in Jing-Jin-Ji region in China.

Table 3.
Averaged ozone concentrations and the standard deviation in different seasons from 2018 to 2020 in Jing-Jin-Ji region in China (μg/m³).
3.2. Ozone Concentration Simulated by Stepwise Regression Model
The performance of the SR model in Beijing, Tianjin and Hebei province is shown in Table 4. The averaged adjusted R2, RMSE and MAE values were 0.7564, 26.82 and 20.72, respectively. The performance of the SR model for the 11 cities in Hebei province is shown in Table S1 in the Supplementary Materials.

Table 4.
Performance of O3 concentration simulation using SR and ANN models.
Figure 6 shows the correlation between the simulated O3_8h concentrations by the SR model and the real monitoring value of O3_8h. Liu evaluated the performance of the SR method on the simulation of ozone concentration using input factors including solar radiation, NO2 and CO concentrations in Luwan district of Shanghai from May to August in 2017. Their results showed relatively higher errors (RMSE = 31.5 and MAE = 35.1) compared with the values obtained in this study, which is probably related to their smaller sample size and less input factors [36]. Zhang estimated the error and fitting degree between the simulated and the real O3 value in Hong Kong in different seasons by using the method of multiple linear regression. The mean value of R2 was 0.59 and the averaged RMSE was 25.9 [37]. In general, linear models such as the SR model perform poorly in predicting the nonlinear process of O3 formation, and the performance of the linear model on ozone concentration estimation is highly related to the selected input parameters.
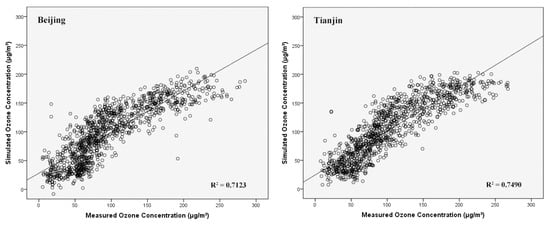
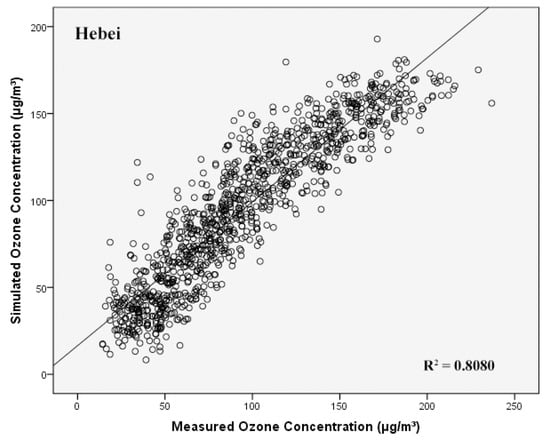
Figure 6.
Relationship between the monitored and simulated concentrations of O3_8h based on the stepwise regression model during 2018 to 2020 in Jing-Jin-Ji region.
3.3. Ozone Concentration Simulated by ANN Model
The parameters used in the input layer are the parameters adopted in the SR discussed above the selected input parameters for Beijing, Tianjin and Hebei are shown in Table 5.

Table 5.
Input parameters for ANN in Beijing, Tianjin and Hebei province.
The input parameters for 11 cities in Hebei province are shown in Table S2 in the Supplementary Materials. Different network structures including number of nodes in hidden layer (3, 4 and 5 nodes) and activation function type (tanh or sigmoid) were applied to obtain the optimal structure. After evaluation, the performance of the ANN was best when the hidden layer contained 5 nodes and the activation function was tanh (see Table 6 and Table S3 in the Supplementary Materials). Table 7 shows the performance of the ANN model in Beijing, Tianjin and Hebei province. The results also showed that the performance of the ANN model can be improved by increasing the number of nodes in the hidden layer regardless of the activation function used.

Table 6.
Performance of the ANN on O3 concentration simulation with different network structures.

Table 7.
Performance of the ANN on O3 concentration simulation in different seasons using the optimal network structure.
In addition, the activation function of tanh (averaged RMSE = 23.16, averaged MAE = 17.12 and averaged adjusted R2 = 0.8306) can provide better results than those obtained by sigmoid function (averaged RMSE = 23.59, averaged MAE = 17.49 and averaged adjusted R2 = 0.8244). The correlation between the real and simulated ozone value by the optimal ANN structure is shown in Figure 7.
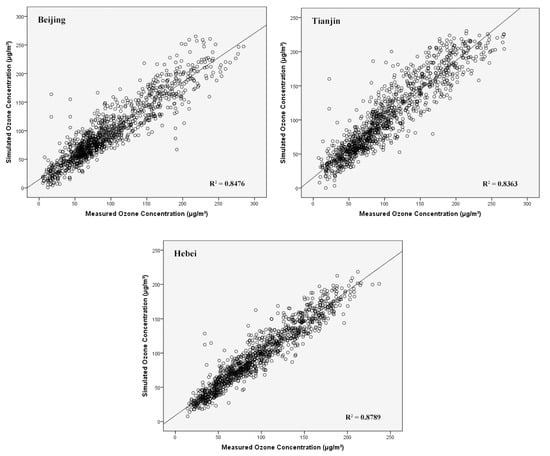
Figure 7.
Relationship between the monitored and simulated concentrations of O3_8h based on artificial neural network model.
The ANN model with 5 hidden nodes and activation function of tanh was thus used to predict ozone concentrations in different seasons. The performance of the ANN in different seasons for Beijing, Tianjin and Hebei province is shown in Table 7 and Figure 8. The corresponding results for 11 cities in Hebei province are shown in Table S4 and Figure S1 in the Supplementary Materials. Results indicated that the model performance in spring, autumn and winter is better, with lower simulating errors (averaged RMSE = 17.61, 17.68 and 9.31, averaged MAE = 12.02, 12.34 and 7.06, respectively, for spring, autumn and winter) and higher R2 (averaged adjusted R2 = 0.7851, 0.8379 and 0.7938, respectively, for spring, autumn and winter). The performance of the ANN model in summer (averaged RMSE = 26.40, averaged MAE = 20.08, averaged adjusted R2 = 0.6564) was relatively poorer than the other seasons. Our results indicated that the ANN model had limitations in estimating O3 concentration peaks, which mainly appeared in summer. This is probably due to the fact that the weights of input factors in the ANN model in the situations of high and low ozone levels are different [16]. Zhang et al. also found that the performance of the ANN model on ozone prediction in summer was worse than the results in other seasons [38]. Xue et al. predicted ozone concentration through BP neural network model in Tianjin, China using input factors of PM2.5, PM10, CO, temperature and wind direction [39]. The R2 was 0.597, which was lower than the R2 of 0.695 in this study [39]. This is probably due to the small amount of data used in their study. Hoshyaripour et al. simulated O3 concentration in Sao Paulo, Brazil using the method of the preceding selection-neural network (FS-ANN). The results showed that the R2 between real and simulated O3 values at two sampling points was 0.70 and 0.56, respectively. The corresponding RMSE values were 8.12 and 7.76 [40].
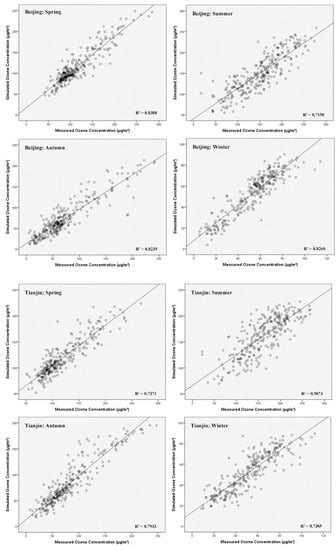
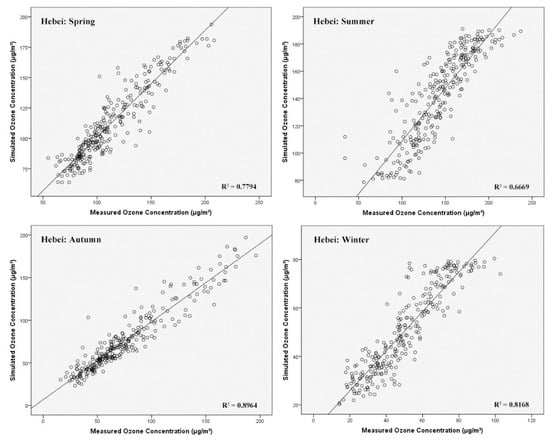
Figure 8.
Relationship between the monitored and simulated values of O3_8h based on the neural network model in each season in Jing-Jin-Ji region in China.
3.4. Model Contrast
Based on the R2, the RMSE and MAE values obtained by the two models, the ANN was more suitable for ozone concentration estimation due to its excellent ability of learning the nonlinear relationship between input and output variables [41]. In addition, with the help of SR model by selecting the most influenced factors that affect ozone concentration, the running time of the ANN was reduced and the over fitting phenomenon caused by high dimensional parameter sets was also avoided [25,42,43]. The performance of the ANN in each season was better than those obtained by the SR model. To compare the performance of the two models on simulating O3 concentration that exceeds the limited value of 160 μg/m3, the POD, TS and FAR values were calculated (see Table 8).

Table 8.
Prediction performance using SR and ANN models.
The POD and TS values in Beijing, Tianjin and Hebei province for the ANN were higher than those for the SR model, indicated that the ANN model had a stronger performance in predicting ozone exceedance. The FAR values for ANN and SR are similar. Among the 13 major cities in Jing-Jin-Ji region, only 3 cities’ FAR values of ANN model are slightly higher than those of the SR model. Comparison of prediction performance using SR and ANN models for 11 cities in Hebei province was shown in Table S5 in the Supplementary Materials. To sum up, the overall performance of the ANN is better than the SR model in simulating exceedance of ozone, thus the performance of the ANN on predicting ozone pollution events is better.
4. Conclusions
A downward trend of ozone concentration was found in the Jing-Jin-Ji region during 2018–2020. The seasonal variation trend of ozone concentration was obvious with the concentration peaks all obtained in summers. Air pollutants concentrations including NO2, CO, PM10, and PM2.5, and meteorological factors including T2m, SSR, TP, SP, BLH, WD, and WS were used as input parameters for SR and the ANN model for O3_8h concentration simulation. The correlation analysis between the real and simulated ozone concentration showed that values of R2, RMSE and MAE were 0.7324, 28.61, and 22.30, respectively, by the SR model. The hybrid model of SR and ANN models can significantly improve the simulation level of ozone estimation with R2 increased to 0.8299 and RMSE and MAE decreased to 22.87 and 16.92, respectively. The results show that the nonlinear ANN model is better than the linear model on simulating ozone concentration. The model performance in spring, autumn and winter was generally higher than that in summer, which indicated that the ANN has limitation in estimating high concentration of O3 that often occur in summer. The POD and TS values obtained by the ANN model were higher than those obtained by the SR model, indicating that the ANN model is better in forecasting ozone pollution events. The results of this study can provide a technical reference for using an ANN on predicting ozone concentration in other regions in China.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/atmos13091371/s1, Figure S1: Relationship between the simulated value of O3_8h and the actual monitored concentration of O3_8h in each season based on the neural network model with activation function of tanh; Table S1: Performance of O3 concentration simulation using SR and ANN models; Table S2: Input parameters for ANN in Shijiazhuang, Baoding, Cangzhou, Chengde, Handan, Hengshui, Langfang, Qinhuangdao, Tangshan, Xingtai and Zhangjiakou; Table S3: Performance of ANN on O3 concentration simulation with different network structures; Table S4: Performance of ANN on O3 concentration simulation in different seasons using the optimal network structure; Table S5: Prediction performance using SR and ANN models.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.G., L.C., Y.S. and H.Z.; Data curation, J.Y. and L.X.; Funding acquisition, S.G.; Methodology, J.Y. and L.X.; Resources, S.G. and L.C.; Software, J.M.; Supervision, L.C.; Visualization, J.Y.; Writing—original draft, J.Y.; Writing—review & editing, S.G. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The authors thank the Chinese National Natural Science Foundation (Grant No. 41907194) for funding this research.
Data Availability Statement
China National Environmental Monitoring Centre. China Air Quality Data (2018–2020). Available online: https://air.cnemc.cn:18007/ (accessed on 1 August 2022); European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts. ERA5-Land Hourly Data From 1950 to Present (2018–2020). Availa-ble online: https://cds.climate.copernicus.eu/cdsapp#!/dataset/reanalysis-era5-land?tab=form (accessed on 1 August 2022).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Li, X.; Li, S.; Liu, P.; Kong, Y.; Song, H. Spatial and temporal variations of ozone concentrations in China in 2016. Acta Sci. Circumstantiae 2018, 38, 1263–1274. [Google Scholar]
- Kaser, L.; Peron, A.; Graus, M.; Striednig, M.; Wohlfahrt, G.; Juráň, S.; Karl, T. Interannual variability of terpenoid emissions in an alpine city. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2022, 22, 5603–5618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, P.; Lyu, X.P.; Guo, H.; Cheng, H.R.; Jiang, F.; Pan, W.Z.; Wang, Z.W.; Liang, S.W.; Hu, Y.Q. Causes of ozone pollution in summer in Wuhan, Central China. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 241, 852–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faris, H.; Alkasassbeh, M.; Rodan, A. Artificial Neural Networks for Surface Ozone Prediction: Models and Analysis. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2014, 23, 341–348. [Google Scholar]
- Delia, M.P.; James, D.B.; Silvia, R.S.; Anne-Marja, N.; Jarmo, K.H. Plant Volatile Organic Compounds(VOCs) in Ozone (O3) Polluted Atmospheres: The Ecological Effects. J. Chem. Ecol. 2010, 36, 22–34. [Google Scholar]
- Chan, C.K.; Yao, X. Air pollution in mega cities in China. Atmos. Environ. 2008, 42, 1–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lelieveld, J.; Crutzen, P. Influences of cloud photochemical processes on tropospheric ozone. Nature 1990, 343, 227–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lengyel, A.; Héberger, K.; Paksy, L.; Bánhidi, O.; Rajkó, R. Prediction of ozone concentration in ambient air using multivariate methods. Chemosphere 2004, 57, 889–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- San José, R.; Stohl, A.; Karatzas, K.; Bohler, T.; James, P.; Pérez, J. A modelling study of an extraordinary night time ozone episode over Madrid domain. Environ. Model. Softw. 2005, 20, 587–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanis, P.; Hadjinicolaou, P.; Pozzer, A.; Tyrlis, E.; Dafka, S.; Mihalopoulos, N.; Lelieveld, J. Summertime free-tropospheric ozone pool over the eastern Mediterranean/Middle East. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2014, 14, 115–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdul-Wahab, S.A.; Bakheit, C.S.; Al-Alawi, S.M. Principal component and multiple regression analysis in modelling of ground-level ozone and factors affecting its concentrations. Environ. Model. Softw. 2005, 20, 1263–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajab, J.M.; MatJafri, M.; Lim, H. Combining multiple regression and principal component analysis for accurate predictions for column ozone in Peninsular Malaysia. Atmos. Environ. 2013, 71, 36–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bekesiene, S.; Meidute-Kavaliauskiene, I.; Vasiliauskiene, V. Accurate prediction of concentration changes in ozone as an air pollutant by multiple linear regression and artificial neural networks. Mathematics 2021, 9, 356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Keller, J.P.; Adar, S.D.; Kim, S.-Y.; Larson, T.V.; Olives, C.; Sampson, P.D.; Sheppard, L.; Szpiro, A.A.; Vedal, S. Development of long-term spatiotemporal models for ambient ozone in six metropolitan regions of the United States: The MESA Air study. Atmos. Environ. 2015, 123, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Alawi, S.M.; Abdul-Wahab, S.A.; Bakheit, C.S. Combining principal component regression and artificial neural networks for more accurate predictions of ground-level ozone. Environ. Model. Softw. 2008, 23, 396–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Bai, Z.; Liang, S.; Yu, H.; Chen, L.; Sun, Y.; Mao, J.; Zhang, H.; Ma, Z.; Azzi, M. Simulation of surface ozone over Hebei province, China using Kolmogorov-Zurbenko and artificial neural network (KZ-ANN) combined model. Atmos. Environ. 2021, 261, 118599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AhmadAali, K. Liaghat, A.M. Heydari, N. Bozorg-Haddad, O. Application of artificial neural network and adaptive neural-based fuzzy inference system techniques in estimating of virtual water. Int. J. Comput. Appl. 2013, 76, 12–19. [Google Scholar]
- Sha, L.-R.; Yang, Y. In ANN-based structure optimization with fatigue reliability constrains. Appl. Mech. Mater. 2012, 204, 3128–3131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arsić, M.; Mihajlović, I.; Nikolić, D.; Živković, Ž.; Panić, M. Prediction of ozone concentration in ambient air using multilinear regression and the artificial neural networks methods. Ozone Sci. Eng. 2020, 42, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shams, S.R.; Jahani, A.; Kalantary, S.; Moeinaddini, M.; Khorasani, N. The evaluation on artificial neural networks (ANN) and multiple linear regressions (MLR) models for predicting SO2 concentration. Urban Clim. 2021, 37, 100837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandyopadhyay, G.; Chattopadhyay, S. Single hidden layer artificial neural network models versus multiple linear regression model in forecasting the time series of total ozone. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 4, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AlOmar, M.K.; Hameed, M.M.; AlSaadi, M.A. Multi hours ahead prediction of surface ozone gas concentration: Robust artificial intelligence approach. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2020, 11, 1572–1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- China National Environmental Monitoring Centre. China Air Quality Data (2018–2020). Available online: https://air.cnemc.cn:18007/ (accessed on 1 August 2022).
- European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts. ERA5-Land Hourly Data From 1950 to Present (2018–2020). Available online: https://cds.climate.copernicus.eu/cdsapp#!/dataset/reanalysis-era5-land?tab=form (accessed on 1 August 2022).
- Russo, A.; Lind, P.G.; Raischel, F.; Trigo, R.; Mendes, M. Neural network forecast of daily pollution concentration using optimal meteorological data at synoptic and local scales. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2015, 6, 540–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, M.; Yin, L.; Ning, J. Artificial neural network model for ozone concentration estimation and Monte Carlo analysis. Atmos. Environ. 2018, 184, 129–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chattopadhyay, S.; Bandyopadhyay, G. Artificial neural network with backpropagation learning to predict mean monthly total ozone in Arosa, Switzerland. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2007, 28, 4471–4482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mekparyup, J.; Saithanu, K. Application of Artificial Neural Network Models to Predict the Ozone Concentration at the East of Thailand. Int. J. Appl. Environ. Sci. 2014, 9, 1291–1296. [Google Scholar]
- Chattopadhyay, S.; Bandyopadhyay, G. Artificial Neural Network to predict mean monthly total ozone in Arosa, Switzerland. arXiv 2006, arXiv:nlin/0608043. [Google Scholar]
- Paschalidou, A.; Iliadis, L.; Kassomenos, P.; Bezirtzoglou, C. Neural modelling of the tropospheric ozone concentrations in an urban site. In Proceedings of the 10th International Conference Engineering Applications of Neural Networks, Thessaloniki, Greece, 29–31 August 2007; pp. 436–445. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Zhao, W.; Zhang, T.; Qiu, Y.; Ma, P.; Li, L.; Wang, L.; Wang, M.; Zheng, D.; Zhao, W. Analysis of the Characteristics of Ozone Pollution in the North China Plain from 2016 to 2020. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Feng, Y.P.; Cui, J.S.; Liu, D.X.; Chen, J.; Tian, L.; He, B.W.; Shen, M.Y. Spatio-temporal evolution patterns and potential source areas of ozone pollution in Shijiazhuang. Acta Sci. Circumstantiae 2020, 40, 3081–3092. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, M.; An, X.; Sun, Z.; Wang, B.; Wang, C.; Ren, W.; Li, Y. Characteristics and meteorological conditions of ozone pollution in Beijing. Ecol. Environ. Monit. Three Gorges 2019, 4, 25–35. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J. Seasonal Characteristics of Air Pollution and Weekend Effect in Shanghai. Master’s Thesis, The University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, China, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Juráň, S.; Šigut, L.; Holub, P.; Fares, S.; Klem, K.; Grace, J.; Urban, O. Ozone flux and ozone deposition in a mountain spruce forest are modulated by sky conditions. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 672, 296–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.-H. Analysis and Multvariate Nonlinear Prediction Model of Ground-level Ozone Time Series in Shanghai. Master’s Thesis, East China Normal University, Shanghai, China, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Ding, W. Prediction of air pollutants concentration based on an extreme learning machine: The case of Hong Kong. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2017, 14, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W. Prediction of Ozone Concentration Based on C-PSODE Algorithm and BP Neural Network. Master’s Thesis, Zhejiang Gongshang University, Hangzhou, China, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, S.-Q. Prediction and Visualization of Air Quality Based on Error Back Propagation Neural Network Model. Master’s Thesis, Tianjin University, Tianjin, China, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Hoshyaripour, G.; Brasseur, G.; Andrade, M.d.F.; Gavidia-Calderón, M.; Bouarar, I.; Ynoue, R.Y. Prediction of ground-level ozone concentration in São Paulo, Brazil: Deterministic versus statistic models. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 145, 365–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borges, A.S.; Andrade, M.d.F.; Guardani, R. Ground-level ozone prediction using a neural network model based on meteorological variables and applied to the metropolitan area of São Paulo. Int. J. Environ. Pollut. 2012, 49, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Li, Q.; Zhu, Y.; Hou, J.; Jin, L.; Wang, J. Artificial neural networks forecasting of PM2. 5 pollution using air mass trajectory based geographic model and wavelet transformation. Atmos. Environ. 2015, 107, 118–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goulier, L.; Paas, B.; Ehrnsperger, L.; Klemm, O. Modelling of urban air pollutant concentrations with artificial neural networks using novel input variables. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).