Abstract
The study concerns the quantitative evaluation of a satellite-based rain rate (RR) estimation algorithm using measurements from a network of ground-based meteorological stations across the Epirus Region, Greece, an area that receives among the maximum precipitation amounts over the country. The utilized version of the rain estimation algorithm uses the Meteosat-11 Brightness Temperature in five spectral regions ranging from 6.0 to 12.0 μm (channels 5–7, 9 and 10) to estimate the rain intensity on a pixel basis, after discriminating the rain/non-rain pixels with a simple thresholding method. The rain recordings of the meteorological stations’ network were spatiotemporally correlated with the satellite-based rain estimations, leading to a dataset of 2586 pairs of matched values. A statistical analysis of these pairs of values was conducted, revealing a Mean Error (ME) of −0.13 mm/h and a correlation coefficient (CC) of 0.52. The optimal computed Probability of False Detection (POFD), Probability of Detection (POD), the False Alarm Ratio (FAR) and the bias score (BIAS) are equal to 0.32, 0.88, 0.12 and 0.94, respectively. The study of the extreme values of the RR (the highest 10%) also shows satisfactory results (i.e., ME of 1.92 mm/h and CC of 0.75). The evaluation statistics are promising for operationally using this algorithm for rain estimation on a real-time basis.
1. Introduction
The accurate knowledge of the amount of regional rainfall is essential for many human activities, also being a vital component for natural ecosystems. Moreover, the rainfall produced by cloud storms has also a direct and significant impact on human life, infrastructure, and properties. Indeed, significant losses are caused by heavy rain events and flash floods [1,2,3]. One basic characteristic of the rainfall is its abrupt spatial and temporal variations that cause many difficulties, as well as its short- and long-range forecasting. Thus, in order to improve weather predictions, and to ensure better conditions of human life and various sectors of human activity, accurate and spatially complete rainfall records are necessary. Rain gauges, which are the only ground truth instrumentation to measure rainfall, operate over land only, and mainly in densely populated areas, and therefore cannot capture the strong spatial variations of rainfall since they provide only point measurements. All the rest of the scientific instrumentation for rainfall is based on remote sensing, providing rainfall data that ensure the desired extended spatial coverage but need to be evaluated against ground truth measurements. Specifically, the remotely sensed data coming from modern satellites or radars can be used to provide accurate rainfall estimations through suitable algorithmic procedures, even in areas with complex terrain and abrupt spatial land cover changes, where rainfall exhibits its strongest spatial and temporal variability [4,5].
A widely used type of remote sensing equipment to estimate the rainfall is weather radars. Modern weather radars are mostly doppler radars, capable (due to the different polarization combinations of the emitted signals) of detecting the motion, the size and the shape of rain droplets in addition to intensity of the precipitation [6,7,8]. The weather radars are operating using pulses in microwave spectra (active sensors) and record the backscattered radar reflectivity to estimate rainfall and its characteristics (e.g., precipitation droplet size). Nevertheless, their most significant limitations are the relatively high cost of buying and operating such instrumentation as well as the limited spatial coverage, which is usually smaller than 230 km [9].
Another way to estimate the rainfall amount is the use of Geostationary Earth Orbiting (GEO) weather satellites that provide image data at low or no cost and cover much larger areas than weather radars. At this point, it should be noted that the Low-Earth Orbit (LEO) satellites in their vast majority are not suitable for (near) real-time monitoring of precipitation, because their temporal resolution is not sufficient to capture the small life cycle of the precipitation occurrence, which—in most cases—last from a few minutes to a few hours. The only widely used LEO satellite solution to capture rainfall patterns with quite satisfactory temporal resolution (around 2–3 h) is the GPM (Global Precipitation Measurement) satellite mission [10,11,12], which is the successor of the TRMM (Tropical Rainfall Measuring Mission) mission [13,14]. Nevertheless, the rainfall datasets coming from the GPM satellite also lack in spatial resolution, in opposition to the weather satellites. Thus, rainfall datasets from LEO satellites are used mainly in climatology, and as validation products in methodologies and algorithms, which include initial data from radars and/or from weather satellites as a main (or exclusive) source of information.
The geostationary weather satellite instrumentation provides high temporal resolution (typically 5–15 min), which is necessary to capture the rapid growth and decay of precipitating clouds [15,16]. Operational applications, however, require quantitative rainfall determination from a variety of precipitating systems, which differ both dynamically and microphysically. This fact prompts for non-unique solutions based on the physics of precipitation formation processes [1]. The operational geostationary satellites are developed focusing on the Earth’s weather and atmosphere, covering large geographical areas, and monitoring the spatiotemporal evolution of phenomena and cloud patterns from scales ranging from the limits of their spatial resolution (1–3 km) up to the synoptic scale. The remote sensing instrumentation (passive instruments) on board of this category of satellites operates mainly from the visible (VIS) up to thermal infrared (IR) region. The multispectral image data that are recorded in high spatial and temporal resolution are utilized in various applications and studies dealing with weather and atmospheric processes. Such satellite-based data are also extremely useful since they produce rainfall estimates for locations where ground-based observations do not exist. Thus, especially during the last two decades, numerous techniques have been proposed for rain estimation using geostationary satellite data, which differ significantly in the channels used, the implemented statistical approaches, and the study domain for which they operate, thus leading to results with different accuracy [17,18,19,20,21,22]. On the other hand, despite their strong usefulness, the satellite rainfall estimates contain biases, since they are produced by algorithms that transform the sensors response into rainfall values, and therefore require thorough validation against ground truth measurements in order to be considered as reliable.
Several studies where MSG datasets are used to estimate rainfall in different geographical areas are already developed, which significantly differ in their technical approaches, spatiotemporal resolution of their final estimates, as well as their evaluation methodology [23,24,25,26,27].
Regarding satellite-based real-time rainfall estimation that covers Greece, the main operational service which exclusively uses satellites, is provided by the European Organization for the Exploitation of Meteorological Satellites (EUMETSAT) through its Satellite Application Facility (SAF) on Support to Operational Hydrology and Water Management (H SAF) and Numerical Weather Prediction (NWP SAF) and its relative products “H03B” (https://hsaf.meteoam.it/) (6 September 2021) and “CCR” (https://www.nwcsaf.org/) (4 July 2021), respectively. These data products provide at near-real time basis precipitation rate on ground but have a coarser spatial resolution (4.8 km at Nadir) of the raw Meteosat imagery, and are not validated in Greece [28]. Nevertheless, the precipitation patterns are strongly affected by the local topography, which requires the highest possible spatial resolution of precipitation products, which should be monitored on a real-time basis, and if possible nowcasted, especially in cases where heavy rainfall occurs. To this aim, the algorithm which was used in this study provides satellite-based rainfall estimations in exactly the same spatial and temporal resolution of Meteosat-11. Also, it is thoroughly validated using a representative relatively dense rain-gauge network of ground-based meteorological stations across the study domain of Epirus Region. This Greek area has a complex topography, being mountainous to a large part, while it receives the largest precipitation amounts all over Greece, exceeding 1000 mm/yr [29], and thus it is suitable for validating a satellite-based rainfall product under the most difficult conditions. During the cold period of the year, the region receives considerable precipitation amounts connected to the west to east movement of frontal depressions that are formed over the main cyclogenesis areas of the West and Central Mediterranean. Such depressions usually cause southwesterly flow over the region, which contributes to large precipitation amounts because of the upslope character of the flow and the associated adiabatic cooling and convective instability. During the warm period of the year, the intense radiative land heating associated with the high incoming solar radiation and the presence of much cooler air masses in the middle troposphere enhances atmospheric instability, contributing to the development of convective clouds, showers and thunderstorms and resulting in considerable precipitation amounts characterized by high spatial variability [30]. In Ioannina, which is the most populated city of the region, the total annual precipitation approaches 1100 mm, while for areas with higher altitudes the amounts are considerably larger.
This study provides analytical results of the quantitative evaluation procedure of rainfall estimations from a satellite-based rain estimation algorithm against reference data, namely measurements coming from a network of eight ground-based meteorological stations in the Epirus region, Greece, with complex terrain and frequent high rainfall amounts of convective nature. In Section 2, a brief description of the study domain, the algorithm, the data, as well as the methodologies used, is provided. Section 3 includes the discussion of the obtained results, while the study conclusions are provided in the last section.
2. Data, Tools and Methods
2.1. Data
Two different types of data were used in the study. The first one is the reference dataset, which consisted of measurements from eight different meteorological stations, dispersed across the whole Epirus Region (Greece). The stations’ network was installed in 2008 and belongs to Region of Epirus, and the stations are operated and supervised by the Laboratory of Meteorology and Climatology of the Department of Physics of the University of Ioannina. The exact locations of these stations are shown in Figure 1, while their coordinates and altitudes are provided in Table 1. At these stations, rainfall is recorded every 30 min with the use of Casella 0.2 mm tipping bucket rain gauges [31,32]. At this point, it is mentioned that 2586 cases (half-hourly rainfall measurements) for which the ground-based meteorological stations recorded rainfall values equal or higher of 0.1 mm/h, were finally used for the needs of the study.
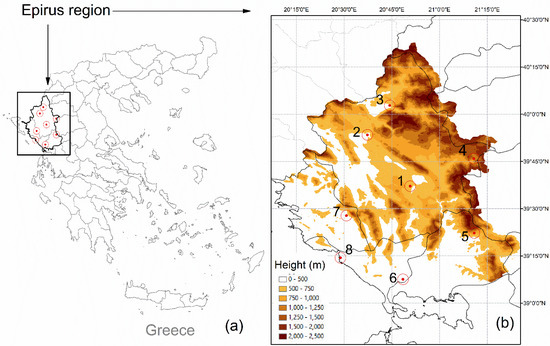
Figure 1.
(a) The study domain (Epirus Region, Greece). (b) The eight circles with red dots, show the locations of the meteorological stations whose rainfall measurements were used in the present study.

Table 1.
Descriptive information about the network of the meteorological stations whose measurements were used in the study.
The second type of data comes from the Meteosat geostationary satellite. The algorithm for rain estimation makes use of the multispectral imagery coming from the Meteosat-11 satellite. More specifically, image data of high spatial resolution (3 km in the sub satellite point) from the satellite instrument SEVIRI (Spinning Enhanced Visible and Infrared Imager) on board the Meteosat satellite platform at five different channels in the InfraRed spectral region (Table 2), were used.

Table 2.
Spectral characteristics of the five channels of SEVIRI instrument onboard the Meteosat satellite that are used in the satellite rain algorithm.
2.2. Tools
The algorithm used in the study is part of an automated satellite-based and autonomous system that uses exclusively five SEVIRI channels in order to detect and nowcast mesoscale cloud convection [33,34]. This system has been extended to provide dust estimates [35], while in the present study it was further extended to also provide rain estimations, the accuracy of which is evaluated in the present study. The rain rate is estimated by the satellite algorithm every 15 min. The selection of the specific five SEVIRI channels (Table 2) was made because their band combinations can be used during day/night (channels in the InfraRed region) to delineate cloud convection and in general cloud patterns with potential to produce heavy rainfall [36,37,38,39].
The basic operational principles of the RR estimation module of the satellite-based algorithm are the following. Firstly, a mask is applied on the SEVIRI multispectral data in order to characterize a specific pixel as rainy/not rainy. More specifically, if for a specific pixel: (i) the Brightness Temperature (BT) in channel 9 centered at 10.8 μm (BT10.8μm) is lower than 265 K, i.e., if BT10.8μm < 265 K, (ii) the Brightness Temperature Difference (BTD) between the channels 5 and 6, centered at 6.2 μm and 7.3 μm, respectively (BTD6.2μm–7.3μm) is larger than −20 K, i.e., if BTD6.2μm–7.3μm > −20 K, and (iii) the Brightness Temperature Difference (BTD) between the channels 9 and 10, centered at 10.8 μm and 12.0 μm respectively (BTD10.8μm–12.0μm) is smaller than 3 K, i.e., if BTD10.8μm–12.0μm < 3 K, then the pixel is considered as rainy, while if the three thresholds are not met the pixel is considered as not rainy. As abovementioned, the utilized set of criteria can delineate satisfactorily humid atmospheric areas in the middle to upper troposphere and greater areas of cloud convective cells, which are major source of heavy rainfall [36,37,38,39,40,41,42].
For each rainy pixel, a rain rate (mm/h) estimate is made by an automated internal module of the algorithm. For this scope, a set of linear equations are used, where the rain rate is the independent variable and the dependent variables are the BTs in the channels of 6.2, 7.3, 8.7 and 10.8 μm as well as the BTD6.2μm–7.3μm, and BTD10.8μm–12.0μm, forming a set of six different equations for the estimation of RR.
More analytically, the set of criteria that define the rainy pixels actually delineate a distribution of pixels in each different timeslot of the Meteosat multispectral imagery and for each different parameter. This means that the algorithm uses six different distributions of values related to the BTs of the 6.2, 7.3, 8.7 and 10.8 μm channels as well as the differences BTD6.2μm–7.3μm, and BTD10.8μm–12.0μm in each different timeslot (every 15-min). Then, the values of the percentiles 5%, 25%, 50%, 75% and 95% (P5%, P25%, P50%, P75%, P95%, respectively) for each parameter, are calculated. The next step is these values being linked with representative RR values and creating five different pairs of data which are used to calculate the least square equations for the six different parameters. The RR values are standard [43] and are based on the general theoretical concept that lower BT (and BTD) are linked with higher RR values as the cold/opaque cloud tops depict convective cloud patterns where heavy rainfall usually occur [39,40,41,42]. More specifically, for every different timeslot, the value of P5% for each parameter is linked with the RR = 1 mm/h, the value of P25% for each parameter is linked with the RR = 5 mm/h, the value of P50% for each parameter is linked with the RR = 10 mm/h, the value of P75% for each parameter is linked with the RR = 20 mm/h and the value of P95% for each parameter is linked with the RR = 30 mm/h. In this way, five pair of values for each parameter are used to calculate all the relative least square linear equations. Subsequently, the difference between the pixel value of the above-mentioned parameters and their relative quartiles of P25%, P50%, P75% (coming from the distribution of the pixel values that consist of the relative cloud pattern) are used to yield the RR estimation from the relative linear equation. More specifically, the minimum difference (Equation (1)) defines the linear equation/parameter that is the most representative and appropriate, which is finally used to provide the RR estimation (Equation (2)) on a pixel basis.
where is the rain rate estimate of a pixel, is the parameter (i.e., BTs of the 6.2., 7.3., 8.7 and 10.8 μm channels as well as the differences BTD6.2μm–7.3μm, and BTD10.8μm–12.0μm), is the pixel value (BT) of the “z” parameter in the position (row, column of the image file) , is the absolute value of the minimum distance of the pixel value and the quartile of the relative distribution (i.e., P25%, P50%, P75%).
Regarding the quality and the missing values/images during the examined period (year, 2019), a check for problems with the recordings of the ground-based meteorological stations, such as i.e., telemetry issues, erroneous values, etc., was made, in order to ensure the best quality of the reference dataset. This process includes the use the prevailing synoptic conditions and the adjacent stations recordings to ensure the validity of unexpectable recorded values. In order to avoid obstruction issues in the rain gauges, periodical checks are usually performed. Also, the availability of the satellite images during the study period has been checked (4.2% in total of the satellite images in the study period were missing due to faults in the receiving station and electricity power interruptions). At this point it is mentioned that the 10,000E Casella tipping bucket rain gauge is used. The bucket size is 0.2 mm. The accuracy of the measurements is ±2% at 1 L/hour. The network of the rain gauges is regularly maintained on a yearly basis. For an additional check of their proper operation, it is confirmed that the rainfall amount that corresponds to a specific volume of water entering the rain gauge is equal to the rainfall amount recorded by the rain gauge. Furthermore, the recorded amounts are often successfully used for the validation of numerical model forecasts [44].
Concerning the automated satellite-based system (where part of it is the RR algorithm) it should be noted that it has been developed through a series of steps and corresponding detailed analyses [34]. Although the accuracy of the system to detect, track and nowcast Mesoscale Convective Systems (MCS) was extensively checked, providing high accuracy [40,41,42], the multichannel approach of the RR estimation, which was previously referred and recently added to the main structure of the system, is validated for its accuracy for the first time and in the complex terrain (the topography and the land-sea distribution can result high spatiotemporal variability as well as heavy rainfall events) of the study domain (Figure 1).
2.3. Methods
In the present study, a thorough evaluation of the accuracy of RR estimation produced by the algorithm is performed using as reference ground-based rainfall measurements from a network of stations in the Epirus region (Figure 1). After the detailed checks for the quality and availability of the algorithm input and validation data, an automated procedure has been developed, outlined in Figure 2, which spatiotemporally correlates the two different datasets (satellite algorithm estimations and the ground measurements of RR). More analytically, every 30 min, the satellite-based rainfall estimations for the pixels where the rain gauges are located and were characterized as “Rainy” by the algorithm, were correlated with the relative (in time and space) half-hourly rainfall measurements. This procedure was applied for a large number of rainy days distributed throughout the year 2019, during which significant amounts of rainfall (RR ≥ 0.1 mm/h) were recorded in all of the eight ground-based meteorological stations. The result of this procedure was a final dataset of 2586 cases (half-hourly rainfall measurements) for which the ground-based meteorological stations recorded rainfall values equal or higher of 0.1 mm/h, and in parallel the pixels corresponding to these stations were found to satisfy the cloud mask criteria. It is noteworthy pointing out that there are days for which rain was recorded in all stations. In this way, heavy rain events with a large spatial extent over Epirus are studied.
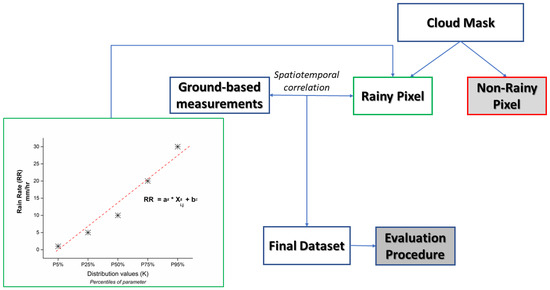
Figure 2.
Schematic flowchart of the procedure for the accuracy assessment of the satellite-based rain estimation algorithm using ground truth measurements from a network of meteorological stations over the Epirus Region (Greece).
During the accuracy assessment procedure of the satellite-based estimations, two different categories of statistics were calculated. Firstly, a set of indicative statistical scores, based on a 2 × 2 contingency table (Table 3), was calculated. These statistical scores were calculated using the Equations (1)–(4) based on the parameters of the contingency table. Such statistical scores are widely used to highlight the mean differences between the forecasts and the mean of the observations [11]. More specifically, the POD stands for the probability of detection, having a range of values [0, 1], where the perfect score value is 1. The FAR stands for the false alarm ratio, having a range of values [0, 1], where the perfect score value is 0. The POFD (range of values from 0 to 1, where the perfect score value is 0) stands for probability of false detection, and BIAS (range of values from 0 to ∞, where the perfect score value is 1) stands for the overall (systematic) bias. The symbols “H” (hit), “M” (miss), “CN” (correct negative), and “FA” (false alarm) are parameters that are presented in Table 3. From a practical standpoint, “H” refers to the number of correct rain estimates (measurements and estimates both found as rainy), “FA” refers to the total number of satellite estimated pixel values that were wrongly assigned with a value larger than zero (“rain”), while the corresponding real (ground/gauge) measurements were zero (“no rain”), “M” refers to the observed rainy values that were wrongly estimated as no-rainy, and finally, “CN” refers to the total number of paired values either (satellite and ground) not being rainy (no rain found in both measurements and estimates). These statistics were computed for the original dataset, and not the dataset of 2586 rain measurements of the year 2019, because, by definition, they are computed not only for rainy cases, but also for cases where either the rain gauge measurement or the correlated satellite estimate have zero (non-rain) rain value. It should be noted that different threshold values of the rainfall intensity were examined, which represent very low rain rates (actually, “no rain” values), ranging from 0.1 to 0.5 mm/h. After these tests, the optimum threshold value, which is most appropriate for evaluating the efficiency of the algorithm and discriminating between “rain/no-rain” events, was 0.3 mm/h. Applying this threshold value, the achieved statistical scores were 0.88, 0.32, 0.94 and 0.12 for POD, POFD, BIAS and FAR, respectively. These scores indicate a relatively good performance of the rain satellite algorithm in identifying the “rain/no-rain” events, proving the appropriateness of the selected threshold value of 0.3 mm/h. More analytically, the whole procedure captures correctly rainy events in the 88% of the total examined rainy cases (POD equal to 0.88). Moreover, the BIAS score value (“0.94”) which actually depicts level of agreement between the forecast and the truth, is very close to its perfect value (“1.0”), meaning a strong correspondence between the mean forecast and mean observation. On the other hand, the metric which represents the errors in capturing rainy events, is low (sPOFD and FAR of 0.32 and 0.12, respectively), which highlights the significant capability of the algorithm to detect rainy pixels.

Table 3.
Contingency table with calculated statistical scores (H, M, FA and CN) used to evaluate the ability of the satellite-based algorithm to estimate the presence/absence of rain over the study domain.
In the second part of the evaluation, a series of additional statistical parameters, used to evaluate the efficiency of the satellite-based algorithm to estimate the rainfall intensity, were calculated. These statistical parameters were calculated using the dataset of the 2586 rainy cases of the year 2019. More specifically, the Mean Error (ME), the Mean Absolute Error (MAE), the Root Mean Square Error, and the Pearson Correlation Coefficient, were calculated using the equations of Table 4. In these equations, the term “” are the rain rates calculated from the meteorological station (gauge) measurements, “” are the corresponding rain rates estimated by the satellite-based rain algorithm, and “n” is the total number of utilized matched (paired) values. It should be mentioned that the calculation of the statistics of Table 4 was made only for pairs with “” values larger than 0.3 mm/h, namely for a total number of 2303 cases, i.e., for 89.1% of all rainy cases). This choice was made because it is crucial to evaluate the accuracy of the rain algorithm exclusively in cases for which notable rainfall occurred.

Table 4.
Equations of statistical metrics used for the evaluation of the rain satellite algorithm.
3. Results and Discussion
Figure 3 displays, in a boxplot format, the main statistics, namely the mean values and associated standard deviations, as well as the percentiles of the rain rate values that are either measured by the gauges or estimated by the satellite algorithm. It is found that the difference between the mean values is equal to 0.3 mm/h, corresponding to only 1.8% of the measured value, while an excellent performance is also found for the estimated percentiles (maximum difference in the 90% percentile, equal to 9%). These results show the ability of the algorithm to appropriately estimate the rain rates recorded over the study region. The calculated statistical metrics of Table 4 are presented in Table 5. The scatterplot comparisons between the satellite-based and ground-based RR values are shown in Figure 4, both for the entire rainy dataset (2303 cases) and its extreme high values (highest 10% of the ground-based measurements). For the whole rainy dataset, which includes the selected 2303 cases (of the year 2019), the MAE is 1.35 mm/h and the ME is −0.13 mm/h. These values depict a satisfactory accuracy, while the small negative ME reveals a slight underestimation, which is, however, rather negligible, since it is significantly smaller than 1 mm/h. The RMSE is also quite small (1.92 mm/h), which also verifies the ability of the algorithm to reproduce the measured RR by the ground-based meteorological stations. The correlation coefficient (CC) is 0.52 (statistically significant at 0.05 confidence level), indicating a satisfactory linear relationship between the pairs of estimated and ground-truth RR values. Table 5 also gives the corresponding statistics (metrics of Table 4) for the high extremes of the examined distribution of RR values. As expected, for these highest values, the MAE and ME are larger values than for the whole dataset, but still remain quite small (MAE and ME equal to 2.87 and 1.92 mm/h, respectively). Also, the RMSE is small enough (3.2 mm/h) and the CC reach 0.75, being quite higher than the one for the whole rainy dataset (0.52), which underlines the very strong similarity between the satellite-based RR estimations and their corresponding ground-based measurements.
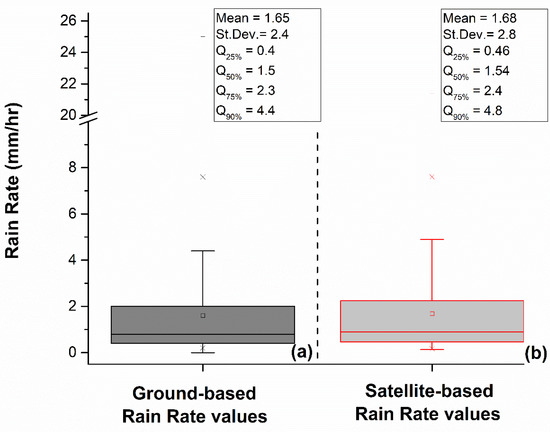
Figure 3.
Boxplot of the distribution of the rain rate values of (a) the dataset formed by the rainy measurements of the ground-based meteorological stations for the year 2019, used for the satellite algorithm evaluation and (b) the satellite-based rain rate estimations made by the satellite algorithm.

Table 5.
Evaluation statistics regarding the whole dataset as well as the high extremes (Q90%).
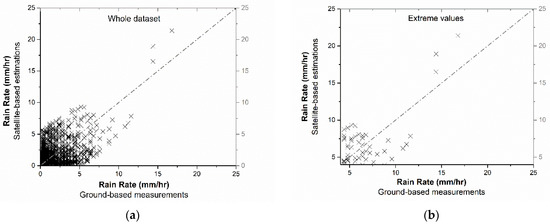
Figure 4.
Rain Rate comparisons between ground-based measurements and satellite-based estimations for (a) the whole rainy dataset (2303 pairs of values) and (b) the higher 10% (Q90%) of the distribution of RR values.
4. Case Study Analysis
Apart for the overall analysis, the results of which were presented in the previous section, a case study analysis was also made in order to further prove the efficiency of the satellite-based algorithm to provide accurate rain rate estimations. The results of this analysis refer to a recent significant precipitation event that took place over the study region on 26 May 2020. On 26 May 2020 (00:00 UTC), the surface pressure map (Figure 5a) shows the existence of a weak low-pressure system extending over the entire northern Greek peninsula. Moreover, the temperature isotherms at 500 hPa and 850 hPa have a local minimum over the greater areas of western and northern Greece at 06:00 UTC (Figure 5b and Figure 5c, respectively). The local minimum of atmospheric temperature at 500 hPa and 850 hPa was also persistent at 12:00 UTC. These conditions in the middle and lower atmosphere indicate atmospheric instability over the area of study, caused by the shallow low surface pressure system, which favored the development of mesoscale convective systems over the greater study area a few hours later (during noon and afternoon of the same day). The development of such convective systems is assisted by the daytime intense radiative heating of the land due to the intense solar radiation during this month of the year and leads to significant precipitation amounts. Indeed, as shown in Figure 6, the satellite-based algorithm detected large rain patterns over the study domain during the period 14:45–17:45 UTC of 26 May 2020. An organized MCS (Mesoscale Convective System) developed during noon over the greater area of the Epirus region produced notable amounts of rainfall, mainly during the examined three-hourly period. The estimated RR by the algorithm was significant from 14:45 to 16:45 UTC (Figure 6a–e), but shortly after the RR (as well its spatial extent) gradually decreased as the MCS started to dissipate (Figure 6f–h).
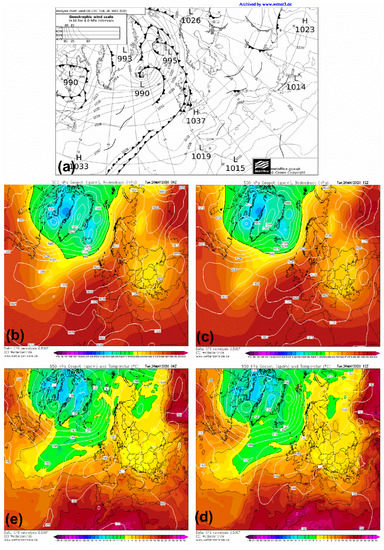
Figure 5.
Synoptic conditions on the examined day (26 May 2020). (a) Surface weather map on 26 May 2020 (00:00 UTC). Geographical distribution of: the 500 hPa geopotential height and sea-level pressure at 06:00 and 12:00 UTC (b,c) and the 850 hPa geopotential height and air temperature at 06:00 and 12:00 UTC (d,e).
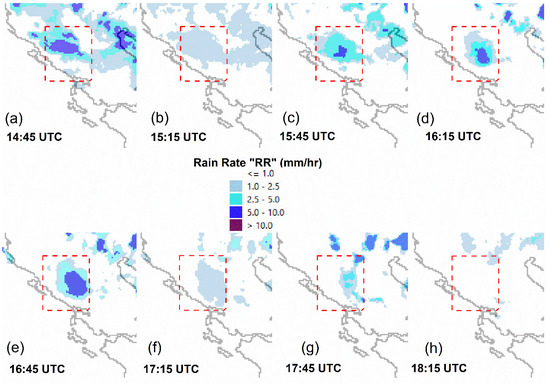
Figure 6.
Case study analysis used for testing the accuracy of the satellite-based algorithm to provide accurate rain rate estimations. (a–h) Rain rate estimations of the satellite-based algorithm over the greater Epirus region (red dashed rectangle).
On the same day (26 May 2020), the network of the meteorological stations recorded 13 different RR measurements during the examined period (Figure 7). At this point, it is noted that only RR values larger than 0.3 mm/h were taken into account because—as proven previously—this threshold value is the most suitable for discriminating rain/no rain values. The correlation of the RR estimations and the rain-gauge measurements is given in Figure 7. The statistical metrics for this case study (MAE, ME, RMSE and CC equal to 1.19, 0.8, 1.87 mm/h and 0.81, respectively) confirmed the satisfactory accuracy of the satellite-based algorithm and its ability to capture significant rainfall events in the study area. It is also mentioned that the statistics of the examined case study are of the same magnitude and are very close to the relative statistics that came from the quantitative analysis (Table 5).
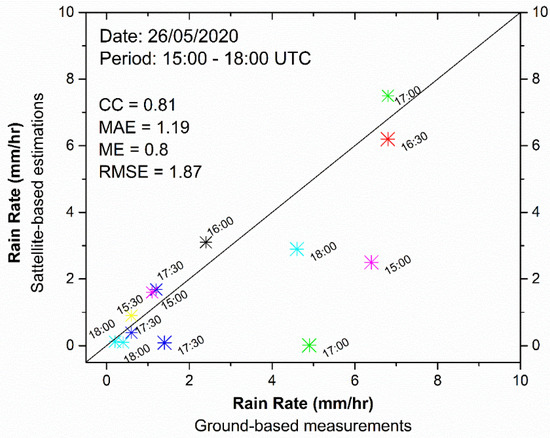
Figure 7.
Scatterplot comparison between the rain rates measured by the ground-based gauges (Figure 1) and estimated by the satellite-based algorithm on 26 May 2000 from 15:00 to 18:00 UTC. Different colors of the pairs of values are referred to different time (UTC).
5. Conclusions
This study assesses the accuracy of a satellite-based rain estimation algorithm using one-year (2019) measurements from a network of eight meteorological stations over the Epirus Region in Greece. Specific physico-geographical and climatological characteristics, such as the complex terrain, including elevation, slope, aspect and prevailing wind directions of the study domain, create intense spatial variability of the rainfall, which cannot be captured by the available meteorological stations. Thus, many areas, especially the remote ones, still lack sufficient and accurate information about rain rates. This information can be obtained from estimations of satellite-based algorithms like the one used in this study, provided that their accuracy is thoroughly evaluated.
At this point, it has to be noted that although similar studies can be found in the international literature, even the latest of them aim to provide improved rainfall estimates by using MSG datasets or provide aggregated (3-hourly up to daily) rainfall estimates based on MSG multispectral imagery [23,24,25,26]. The most recent and similar studies to the present work differ significantly regarding the geographical area they cover and the general approach of the rainfall estimation, though they provide similar statistical score values to ours, which actually confirm the accuracy limits attained in the present study. The difference between the present study and other similar ones [27,28] is that it presents an analytical evaluation over a complex terrain of the Greek peninsula, where for the first time an operational rainfall estimation product based on MSG data is provided, with the same spatiotemporal resolution of the initial Meteosat datasets. Also, the presented/applied methodology here is not using other data products or information from the visible spectrum like other studies [27,28] in order to be stand-alone, with stable accuracy during day and night and independent of discontinuities generated by using different sources of data from different satellites.
A two-phase procedure of the accuracy assessment of the satellite-based rain estimation algorithm was developed. Firstly, a set of statistical scores, which measure the efficiency of the algorithm to capture intensity, in terms of spatial extent and rain amounts, rainy events, was tested. The satisfactory statistical scores of POD, POFD, BIAS and FAR, equal to 0.88, 0.32, 0.94 and 0.12, respectively, prove the ability of the algorithm to successfully monitor such extended rainy events. In a second phase, a set of widely used statistical parameters were estimated, which evaluated quantitatively the correspondence of the pixel-based RR estimations to the ground-based measurements. The obtained results, namely the computed ME and MAE of -0.13 and 1.35 mm/h, respectively, also show the satisfactory performance of the satellite algorithm. Given the high spatio-temporal variability of the rain rate over the study region, the computed correlation coefficient (CC equal to 0.52) is quite satisfactory. The good performance of the satellite-based algorithm (ME, MAE and CC equal to 2.87, 1.92 mm/h and 0.75, respectively) was also confirmed for the highest RR values (above the 90th percentile, presented in Figure 3), which is important in relation to floods and landslides. The conclusions drawn regarding the good performance of the algorithm were corroborated by a case study analysis, which has shown the ability of the algorithm to monitor the spatial and temporal evolution of an intense rain event developed over the study region on 26th of May 2020. In summary, the presented satellite-based rain rate algorithm was proven to be an appropriate and useful tool, which can be used by the regional authorities for the real-time monitoring of severe precipitation events over the Epirus region and the release of relevant warnings and alerts, especially to sensitive sectors like tourism or agriculture.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, N.H. and S.K.; methodology, S.K.; software, S.K.; validation, S.K., C.J.L. and N.H.; formal analysis, S.K.; investigation, S.K.; resources, S.K, N.H, A.B. and C.J.L.; data curation, S.K, A.B. and C.J.L.; writing—original draft preparation, S.K.; writing—review and editing, N.H, S.K. and C.J.L.; visualization, S.K.; supervision, N.H.; project administration, N.H.; funding acquisition, N.H. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by European Regional Development Fund (ERDF), through Structural Funds and Cohesion Fund 2014–2020, Operational Program “Epirus”, Priority Axis “Strengthening regional competitiveness by developing innovation and ICT”, title “Development and use of digital systems, products and services by the Local Authorities” and specific title “Online platform for automatic information of the public and local authorities for possible occurrence of severe weather phenomena in Epirus Prefecture, Greece”, grant number MIS: 5032781.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Publicly available initial datasets were analyzed in this study. The data can be found in EUMETSAT (European Organization for the Exploitation of Meteorological Satellites) through the portal: https://eoportal.eumetsat.int and Wetterzedrale Organization, through the link: www.wetterzentrale.de (accessed on 30 May 2022).
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge the relative agencies and organizations regarding the provision of the datasets used in this study: EUMETSAT (European Organization for the Exploitation of Meteorological Satellites) for the free provision of the Meteosat multispectral satellite images (raw datasets) and Wetterzedrale (www.wetterzentrale.de, accessed on 30 May 2022) for the provision of free synoptic weather maps.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Karkani, A.; Evelpidou, N.; Tzouxanioti, M.; Petropoulos, A.; Santangelo, N.; Maroukian, H.; Spyrou, E.; Lakidi, L. Flash Flood Susceptibility Evaluation in human-affected areas using geomorphological methods—The Case of 9 August 2020, Euboea, Greece. A GIS-Based Approach. GeoHazards 2021, 2, 366–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esposito, G.; Matano, F.; Scepi, G. Analysis of Increasing Flash Flood Frequency in the Densely Urbanized Coastline of the Campi Flegrei Volcanic Area, Italy. Front. Earth Sci. 2018, 6, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kundzewicz, Z.W.; Pinskwar, I.; Brakenridge, G.R. Large floods in Europe, 1985–2009. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2013, 58, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buytaert, W.; Celleri, R.; Willems, P.; De Bievre, B.; Wyseure, G. Spatial and temporal rainfall variability in mountainous areas: A case study from the south Ecuadorian Andes. J. Hydrol. 2006, 329, 413–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbate, A.; Papini, M.; Longoni, L. Extreme Rainfall over Complex Terrain: An Application of the Linear Model of Orographic Precipitation to a Case Study in the Italian Pre-Alps. Geosciences 2021, 11, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saltikoff, E.; Friedrich, K.; Soderholm, J.; Lengfeld, K.; Nelson, B.; Becker, A.; Hollmann, R.; Urban, B.; Heistermann, M.; Tassone, C. An Overview of Using Weather Radar for Climatological Studies: Successes, Challenges, and Potential. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2019, 100, 1739–1752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schleiss, M.; Olsson, J.; Berg, P.; Niemi, T.; Kokkonen, T.; Thorndahl, S.; Nielsen, R.; Nielsen, J.; Bozhinova, D.; Pulkkinen, S. The accuracy of weather radar in heavy rain: A comparative study for Denmark, the Netherlands, Finland and Sweden. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2020, 24, 3157–3188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sokol, Z.; Szturc, J.; Orellana-Alvear, J.; Popová, J.; Jurczyk, A.; Célleri, R. The Role of Weather Radar in Rainfall Estimation and Its Application in Meteorological and Hydrological Modelling—A Review. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fienberg, K.; Foufoula-Georgiou, E. Atmospheric Water and Precipitation. In Encyclopedia of Inland Waters, 1st ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2009; Volume 1, pp. 651–660. [Google Scholar]
- Newell, D.A.; Rait, G.; Thach, T.; Berdanier, B.; Draper, D.; Kubitschek, M.; Krimchansky, S. GPM Microwave Imager Design, Predicted Performance and Status. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, IEEE International Symposium on Geoscience and Remote Sensing IGARSS, Honolulu, HI, USA, 25–30 July 2010; pp. 546–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, A.Y. Precipitation estimation using combined active/passive sensor information within the GPM framework. In Proceedings of the ECMWF-JCSDA Workshop on Assimilating Satellite Observations of Clouds and Precipitation into NWP Models, ECMWF, Reading, UK, 15–17 June 2010; pp. 69–78. [Google Scholar]
- Seto, S.; Iguchi, T. Applicability of the Iterative Backward Retrieval Method for the GPM DualFrequency Precipitation Radar. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2011, 9, 1827–1838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huffman, G.J.; Adler, R.F.; Bolvin, D.T.; Gu, G.; Nelkin, E.J.; Bowman, K.P.; Hong, Y.; Stocker, E.F.; Wolff, D.B. The TRMM multi-satellite rainfall analysis: Quasi-global, multi-year, combined-sensor rainfall estimates at fine scale. J. Hydrometeorol. 2007, 8, 38–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huffmann, G.; Bolvin, D. TRMM and Other Data Precipitation Rainfall Data Set Documentation. 2015. Available online: https://pmm.nasa.gov/sites/default/files/document_files/3B42_3B43_doc_V7.pdf (accessed on 8 April 2015).
- Thies, B.; Bendix, J. Satellite based remote sensing of weather and climate: Recent achievements and future perspectives. Meteorol. Appl. 2011, 18, 262–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNally, T.; Bonavita, M.; Thépaut, J.-N. The Role of Satellite Data in the Forecasting of Hurricane Sandy. Mon. Weather. Rev. 2014, 142, 634–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levizzani, V.; Amorati, R.; Meneguzzo, F. A Review of Satellite-Based Rainfall Estimation Methods. MUSIC—MUltiple-Sensor Precipitation Measurements, Integration, Calibration and Flood Forecasting Project, 2002. Technical Report, of the Research Project MUSIC-Multiple Sensor Precipitation Measurements, Integration, Calibration and Flood Forecasting, Deliverable 6.1. MUSIC—EVK1-CT-2000-00058, 04/02/2002. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/252272255_A_Review_of_Satellite_Based_Rainfall_Estimation_Methods (accessed on 30 May 2022).
- Levizanni, V.; Schmetz, J.; Lutz, H.L.; Kerkmann, J.; Alberoni, P.P.; Cervino, M. Precipitation estimations from geostationary orbit and prospects for METEOSAT Second Generation. Meteorol. Appl. 2001, 8, 23–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sehad, M.; Ameur, S. A multilayer perceptron and multiclass support vector machine based high accuracy technique for daily rainfall estimation from MSG SEVIRI data. Adv. Space Res. 2020, 66, 1250–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazri, M.; Labadi, K.; Brucker, J.M.; Ameur, S. Improving satellite rainfall estimation from MSG data in Northern Algeria by using a multi-classifier model based on machine learning. J. Hydrol. 2020, 584, 124705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouaita, B.; Moussaoui, A.; Bachari, N.E.I. Rainfall estimation from MSG images using fuzzy association rules. J. Intell. Fuzzy Syst. 2019, 37, 1357–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tapiador, F.J.; Marcos, C.; Sancho, M.J. The Convective Rainfall Rate from Cloud Physical Properties Algorithm for Meteosat Second-Generation Satellites: Microphysical Basis and Intercomparisons using an Object-Based Method. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turini, N.; Thies, B.; Bendix, J. Estimating High Spatio-Temporal Resolution Rainfall from MSG1 and GPM IMERG Based on Machine Learning: Case Study of Iran. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumah, K.K.; Hoedjes, C.B.J.; David, N.; Maathuis, H.P.B.; Gao, H.O.; Bob, Z.S. Combining MWL and MSG SEVIRI Satellite Signals for Rainfall Detection and Estimation. Atmosphere 2020, 11, 884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouallouche, F.; Lazri, M.; Ameur, S. Improvement of rainfall estimation from MSG data using Random Forests classification and regression. Atmos. Res. 2018, 21, 62–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sist, M.; Schiavon, G.; Del Frate, F. A New Data Fusion Neural Network Scheme for Rainfall Retrieval Using Passive Microwave and Visible/Infrared Satellite Data. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 4686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bensafi, N.; Lazri, M.; Ameur, S. Novel WkNN-based technique to improve instantaneous rainfall estimation over the north of Algeria using the multispectral MSG SEVIRI imagery. J. Atmos. Sol. Terr. Phys. 2019, 183, 110–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EUMETSAT, H-SAF. Product Validation Report (PVR-03B) for product H03B. 2 May 2017, Technical Report, Doc.No: SAF/HSAF/PVR-03B. Available online: https://navigator.eumetsat.int/product/EO:EUM:DAT:0017 (accessed on 30 May 2022).
- Hatzianastassiou, N.; Katsoulis, B.D.; Prevmatikos, J.D.; Antakis, V. Spatial and Temporal Variation of Precipitation in Greece and Surrounding Regions Based on Global Precipitation Climatology Project Data. J. Clim. 2008, 21, 1349–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotsias, G.; Lolis, C.J.; Hatzianastassiou, N.; Levizzani, V.; Bartzokas, A. On the connection between large-scale atmospheric circulation and winter GPCP precipitation over the Mediterranean region for the period 1980-2017. Atmos. Res. 2020, 233, 104714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartzokas, A.; Kotroni, V.; Lagouvardos, K.; Lolis, C.J.; Gkikas, A.; Tsirogianni, M.I. Weather forecast in north-western Greece: RISKMED warnings and verification of MM5 model. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2010, 10, 383–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Christofilakis, V.; Tatsis, G.; Votis, C.T.; Chronopoulos, S.K.; Kostarakis, P.; Lolis, C.J.; Bartzokas, A. Rainfall Measurements Due to Radio Frequency Signal Attenuation at 2 GHz. J. Signal Inf. Process. 2018, 9, 192–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolios, S.; Feidas, H. An automated nowcasting system of Mesoscale Convective Systems for the Mediterranean basin using Meteosat imagery. Part I: System description. Meteorol. Appl. 2011, 20, 287–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolios, S. Study of Mesoscale Cloud System Oscillations Capable of Producing Convective Gravity Waves. Climate 2018, 6, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolios, S.; Hatzianastassiou, N. Quantitative Aerosol Optical Depth detection during dust outbreaks from Meteosat imagery using an Artificial Neural Network model. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgado, G.; Machado, A.T.L.; Carlos, F.; Angelis, F.C.; Bottino, M.J.; Redaño, Á.; Lorente, J.; Gimeno, L.; Nieto, R. Basis for a Rainfall Estimation Technique Using IR–VIS Cloud Classification and Parameters over the Life Cycle of Mesoscale Convective Systems. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2008, 47, 1500–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhib, S.; Mannaerts, C.M.; Bargaoui, Z.; Retsios, V.; Maathuis, B.H.P. Evaluating the MSG satellite Multi-Sensor Precipitation Estimate for extreme rainfall monitoring over northern Tunisia. Weather Clim. Extrem. 2017, 16, 14–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Xu, J.; Tang, G.; Yang, Y.; Hong, Y. Infrared Precipitation Estimation Using Convolutional Neural Network. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2020, 58, 8612–8625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Risyanto, F.; Lasmono, F.; Teguh, H.T. Himawari-8 rainfall estimation from infrared channels based on machine learning methods. AIP Conf. Proc. 2021, 2366, 050004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolios, S.; Kalimeris, A. Study of Cloud Convection during the Mediterranean Tropical-Like Cyclones: The Medicane Case of September 2018. In Proceedings of the 15th International Conference on Meteorology, Climatology and Atmospheric Physics (COMECAP), Ioannina, Greece, 27–30 September 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Kolios, S. A Satellite-Based Automated System to Detect and Forecast Cloud Storms Focused on the Protection of the Greek Agricultural Sector. In Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Information and Communication Technologies in Agriculture, Food and Environment, Kavala, Greece, 17–20 September 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Kolios, S.; Feidas, H. An automated nowcasting system of mesoscale convective systems for the Mediterranean basin using Meteosat imagery. Part II: Verification statistics. Meteorol. Appl. 2012, 20, 296–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latupapua, H.; Latupapua, A.; Wahab, A.; Alaydrus, M. Wireless Sensor Network Design for Earthquake’s and Landslide’s Early Warnings. Indones. J. Electr. Eng. Comput. Sci. 2018, 11, 437–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sindosi, O.A.; Bartzokas, A.; Kotroni, V.; Lagouvardos, K. Verification of precipitation forecasts of MM5 model over Epirus, NW Greece, for various convective parameterization schemes. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2012, 12, 1393–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).