Using 3D Ray Tracing Technology to Study the Disturbance Effect of Rocket Plume on Ionosphere
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Kinetic Model
2.1. Neutral Gas Diffusion
2.2. Ion Chemical Reaction Process
2.3. Plasma Diffusion
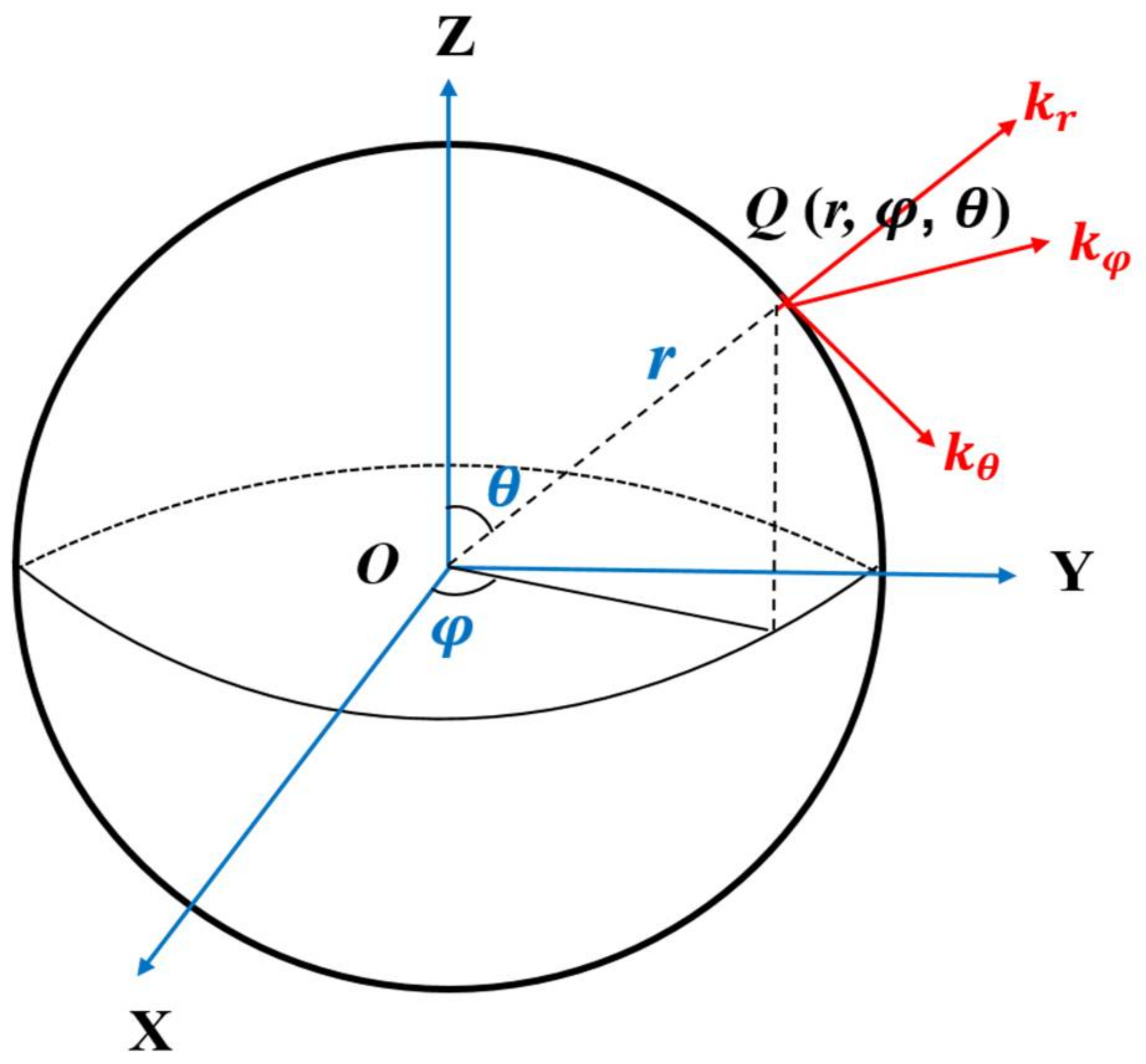
2.4. D Ray Tracing
3. Experimental Simulation and Parameter Setting
4. Simulation Results and Discussion
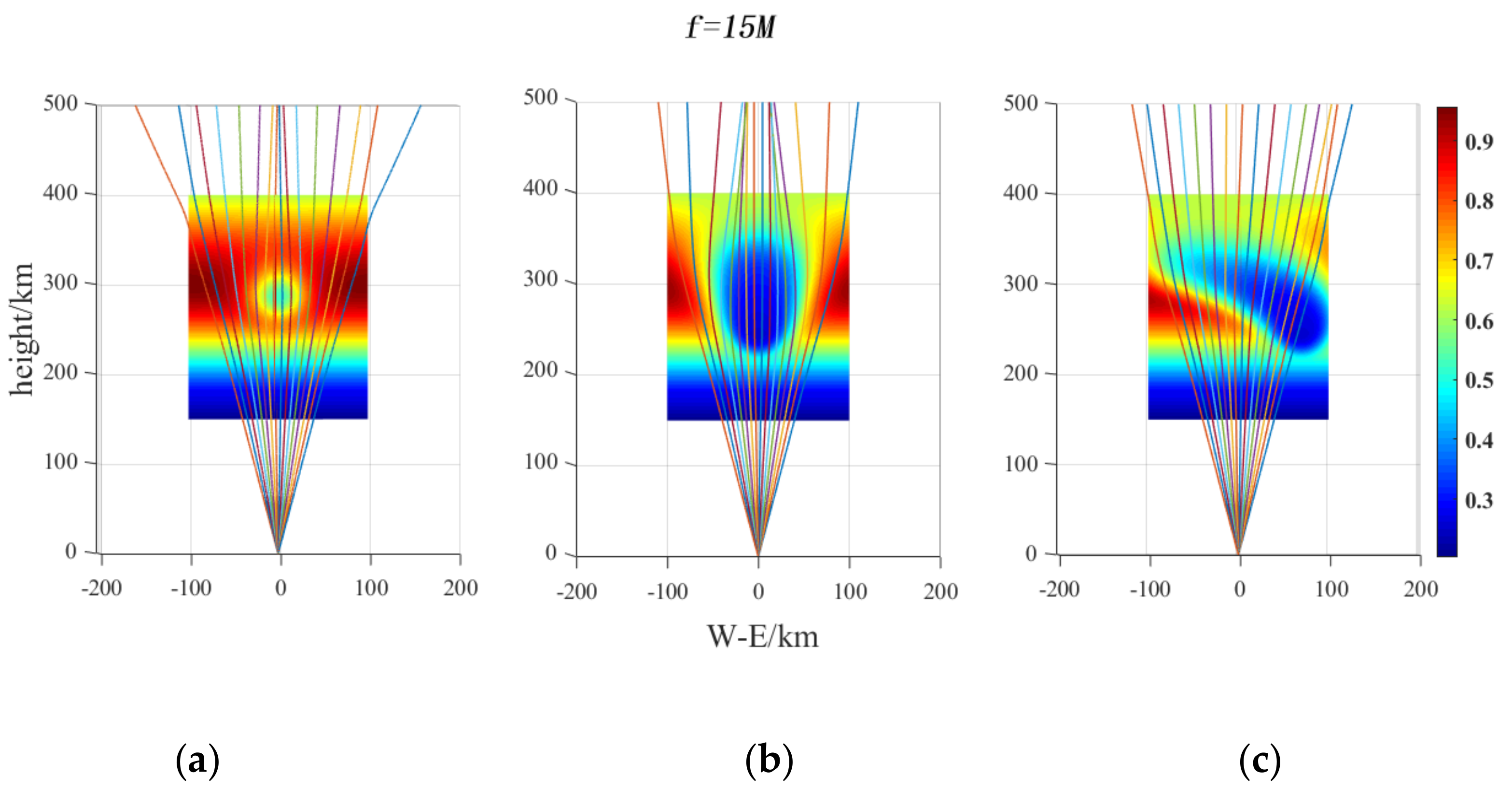
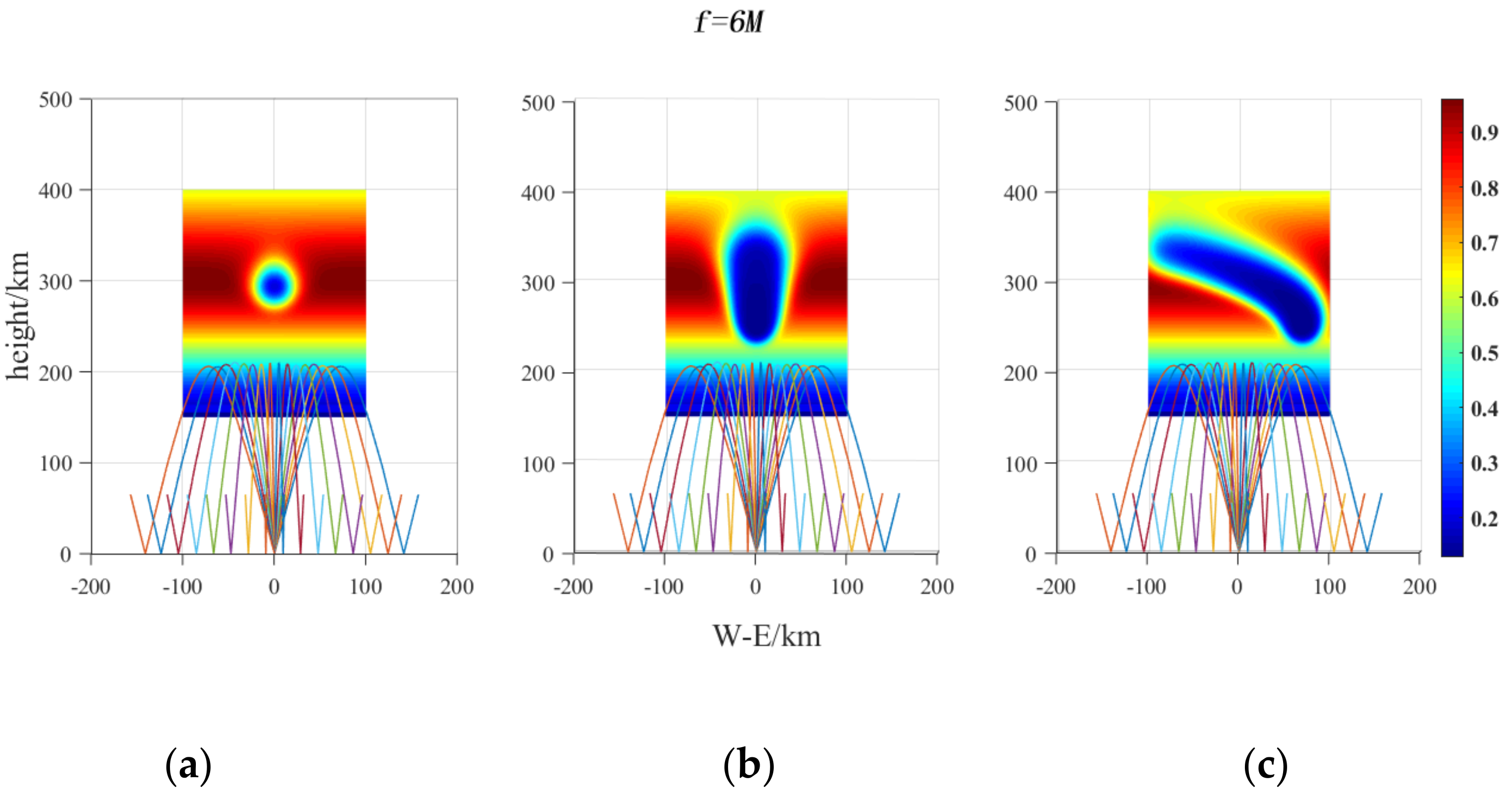
4.1. Disturbance Released by H2 in Different Paths and Its Influence on Radar Wave Propagation Path
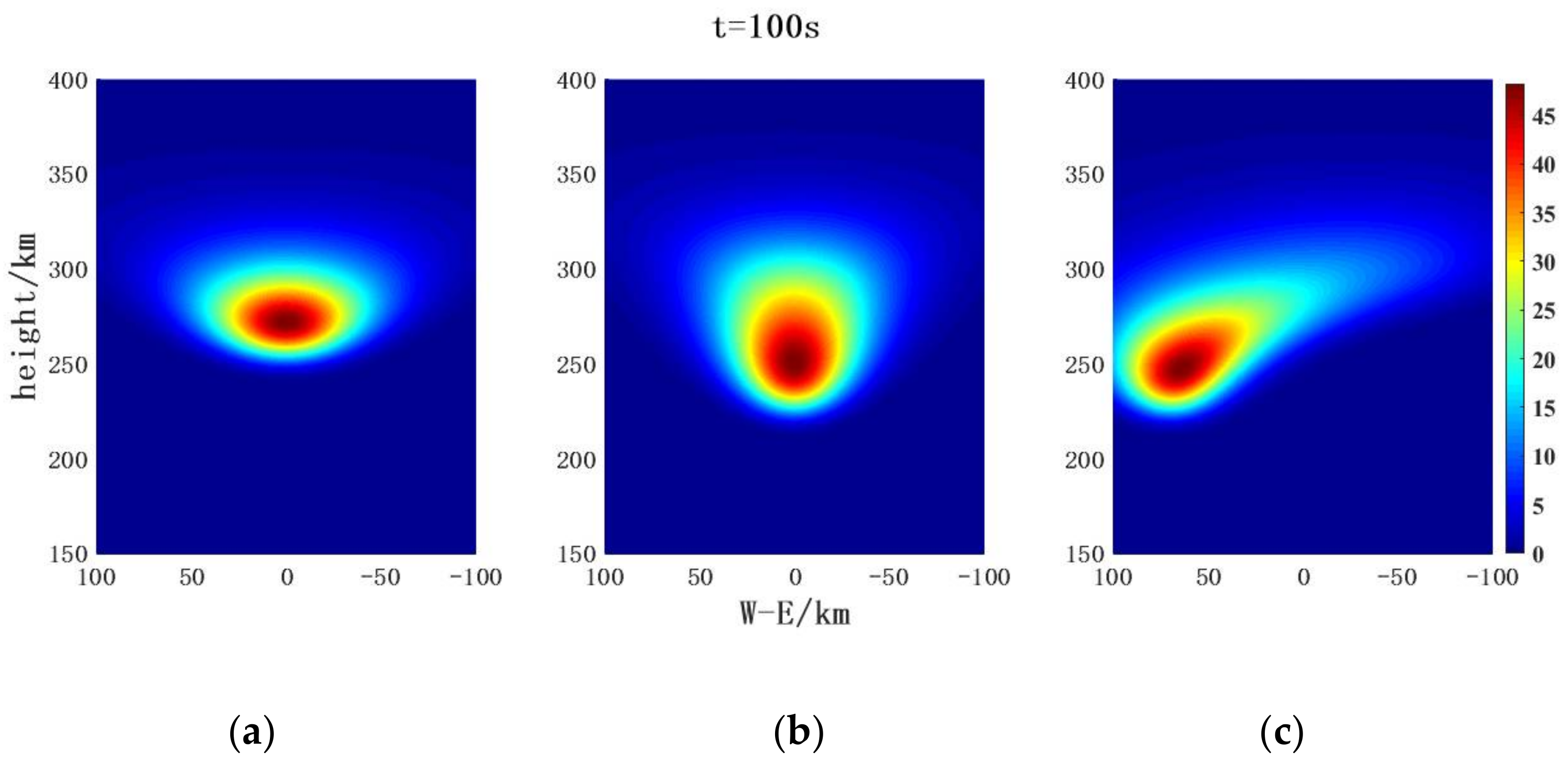
4.1.1. Simulation of Spatial Distribution of H2 after Release and Diffusion in Different Paths
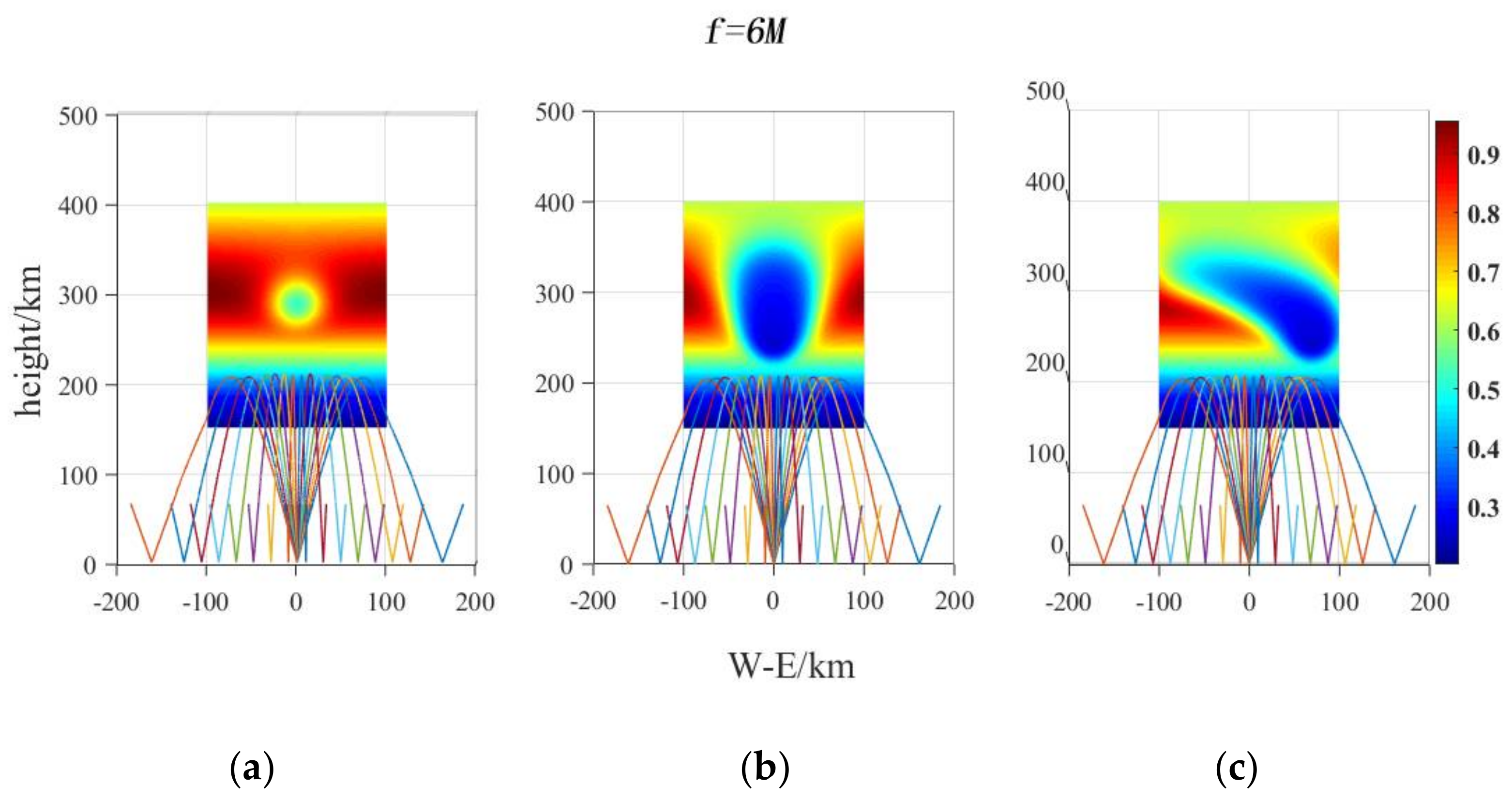
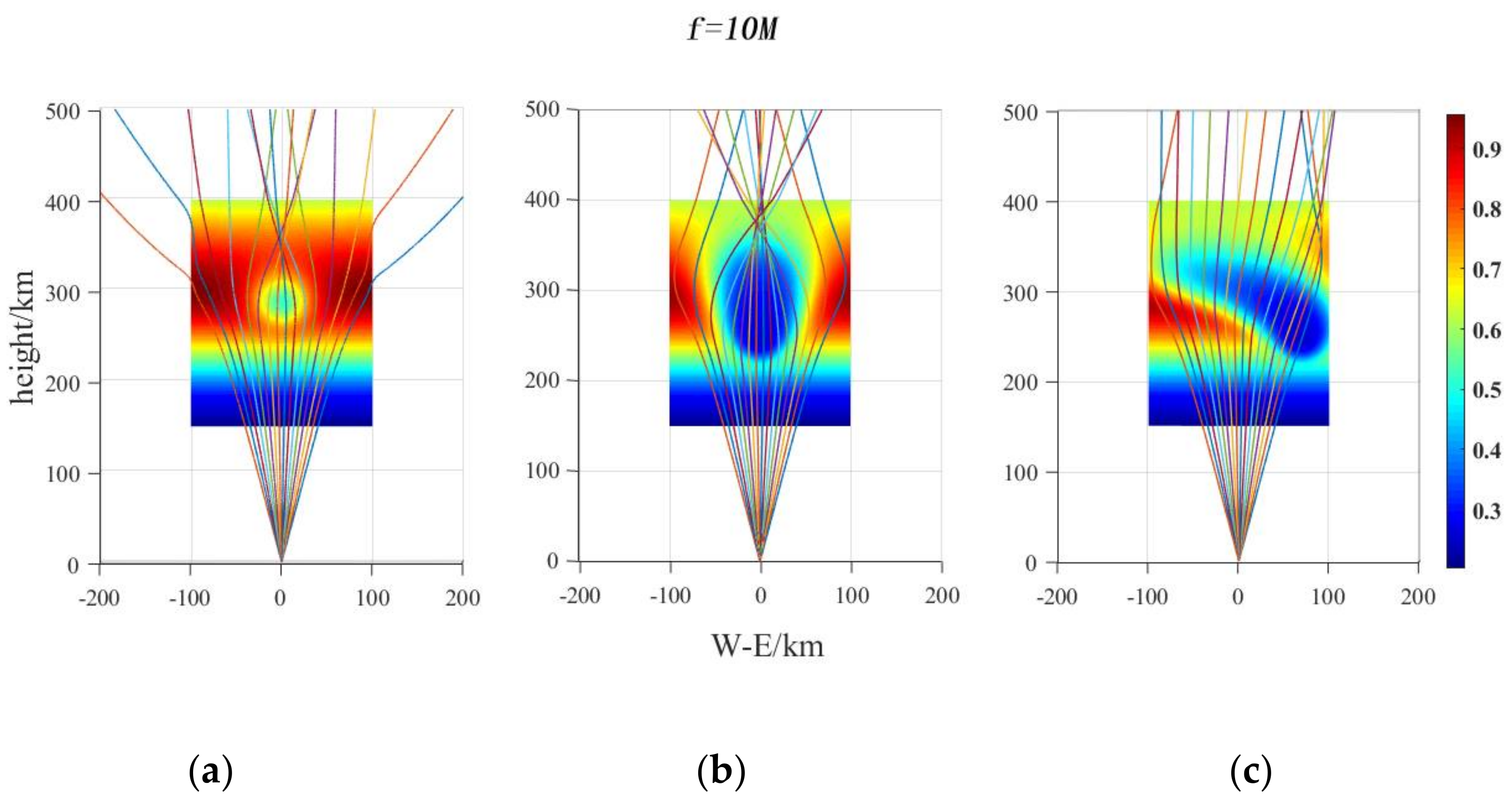
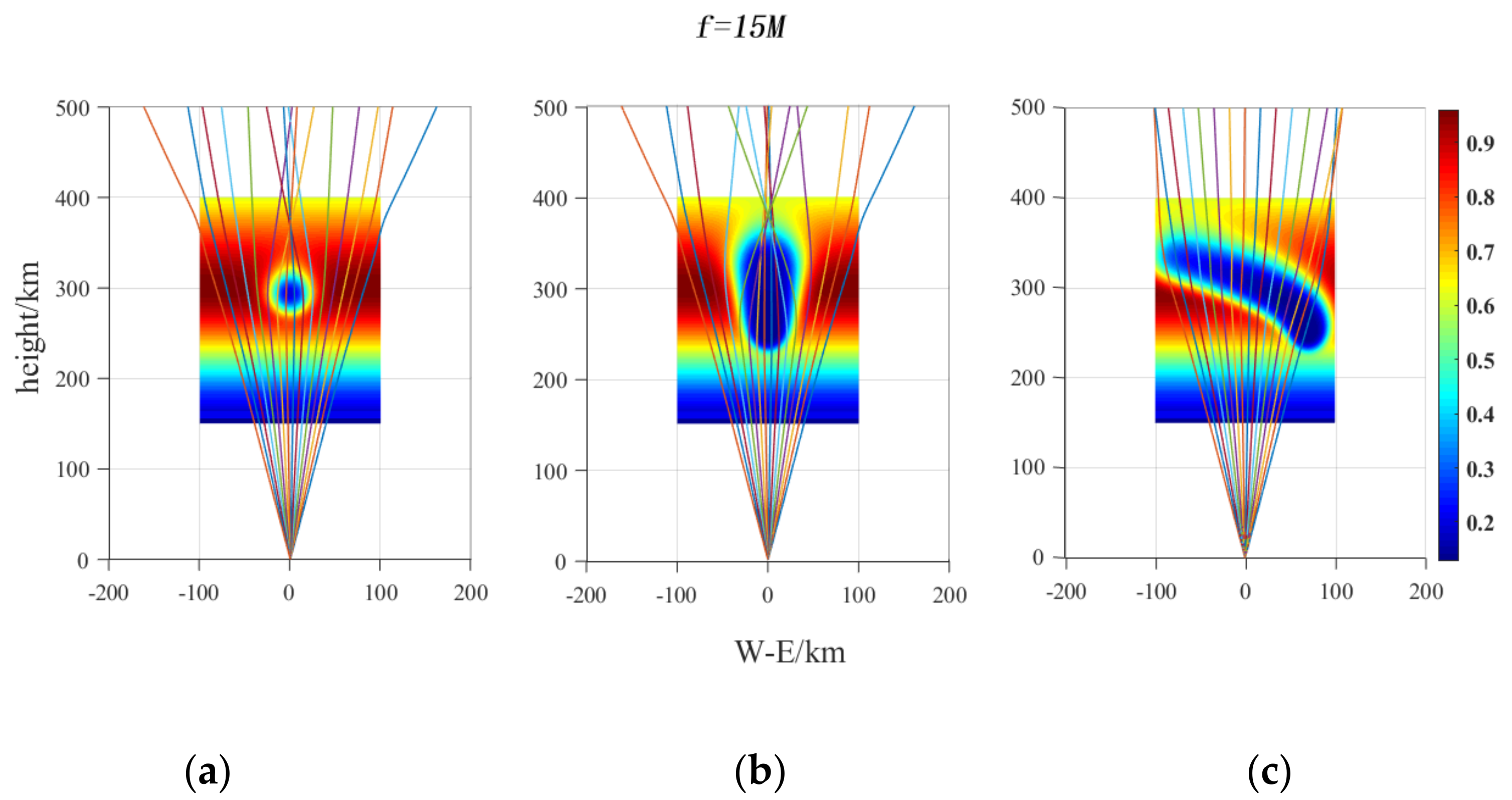
4.1.2. Ionospheric Disturbance Released by H2 in Different Paths and Its Influence on Radio Wave Propagation Path
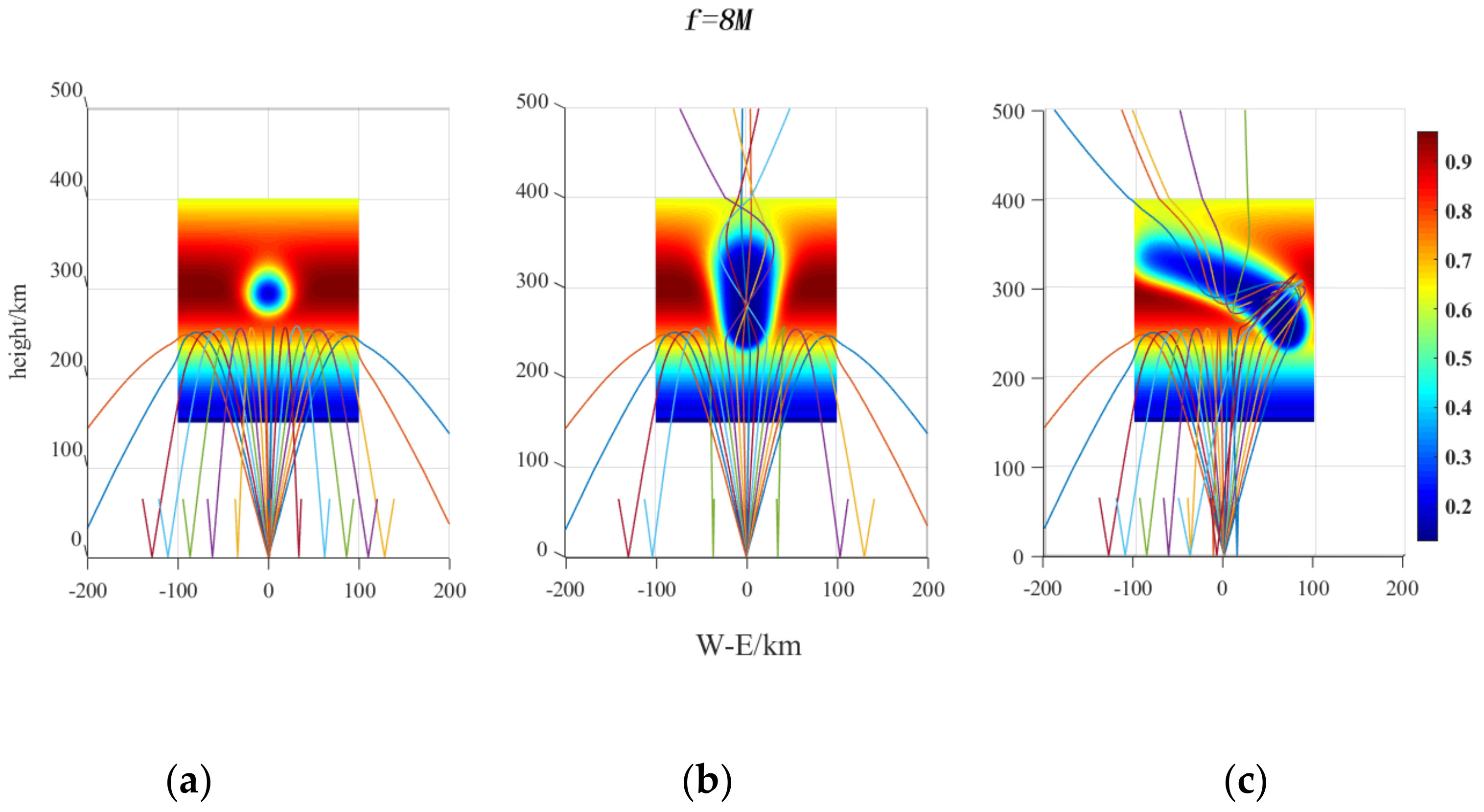
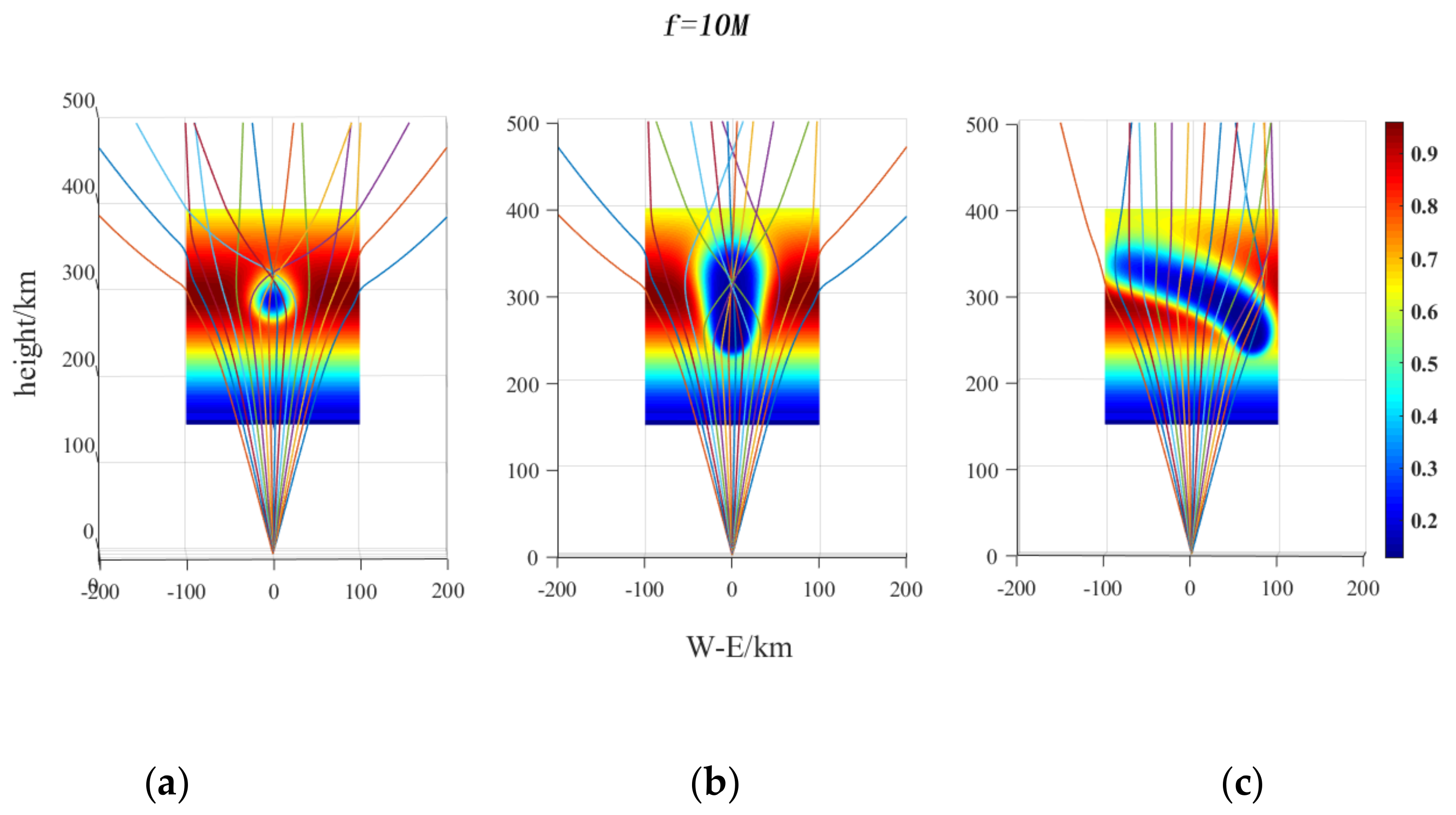
4.2. Disturbance Released by H2O in Different Paths and Its Influence on Radar Wave Propagation Path
4.2.1. Simulation of Spatial Distribution of H2O after Release and Diffusion in Different Paths
4.2.2. Ionospheric Disturbance Released by H2O in Different Paths and Its Influence on Radio Wave Propagation Path
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Booker, H. A local reduction of F-region ionization due to missile transit. J. Geophys. Res. 1961, 66, 1073–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendillo, M.; Hawkins, G.S.; Klobuchar, J.A. A Large-Scale Hole in the Ionosphere Caused by the Launch of Skylab. Science 1975, 187, 343–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendillo, M.; Hawkins, G.S.; Klobuchar, J.A. A sudden vanishing of the ionospheric F region due to the launch of Skylab. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1975, 80, 2217–2228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zinn, J.; Sutherland, C.D.; Stone, S.N.; Duncan, L.M.; Behnke, R. Ionospheric effects of rocket exhaust products—heaoc, skylab. J. Atmos. Sol.-Terr. Phys. 1982, 44, 1143–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savastano, G.; Komjathy, A.; Shume, E.; Vergados, P.; Ravanelli, M.; Verkhoglyadova, O.; Meng, X.; Crespi, M.G. Advantages of Geostationary Satellites for Ionospheric Anomaly Studies: Ionospheric Plasma Depletion Following a Rocket Launch. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, H.-S.; Feng, J.; Xu, Z.-W.; Wu, J.; Wu, Z.-S.; Xu, B.; Xue, K.; Xu, T.; Hu, Y.-L. A temporal three-dimensional simulation of samarium release in the ionosphere. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2016, 121, 10508–10519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Xu, Z.W.; Tang, W.; Xu, Z.-H.; Xue, K.; Xie, S.; Zheng, Y.; Wu, J.; Zhang, J.-D. Electromagnetic scattering by artificial plasma clouds in the ionosphere. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2020, 68, 4810–4819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Croft, T.A.; Hoogasian, H. Exact ray calculations in a quasi-parabolic ionosphere with no magnetic field. Radio Sci. 1968, 3, 69–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, K.; Rush, C.M. High-frequency ray paths in ionospheric layers with horizontal gradients. Radio Sci. 1985, 20, 95–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dyson, P.L.; Bennett, J.A. A model of the vertical distribution of the electron concentration in the ionosphere and its application to oblique propagation studies. J. Atmos. Terr. Phys. 1988, 50, 251–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norman, R.J.; Cannon, P.S. A two-dimensional analytic ray tracing technique accommodating horizontal gradients. Radio Sci. 1997, 32, 387–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haselgrove, J. Ray Theory and a New Method of Ray Tracing; The Physical Society: London, UK, 1955; Volume 23, pp. 355–360. [Google Scholar]
- Jones, R.M. A three-dimensional ray-tracing computer program. Radio Sci. 1968, 3, 93–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelso, J.M. Ray Tracing in the ionosphere. Radio Sci. 1968, 3, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Zhao, Z.; Deng, F. Effects of the travelling ionospheric disturbance on skywave over-the-horizon radar coordinate registration. Syst. Eng. Electron. 2011, 33, 2222–2225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.G.; Zhao, Z.Y.; Zhang, Y.N. Ionospheric disturbances produced by chemical releases and the resultant effects on short-wave ionospheric propagation. J. Geophys. Res. 2011, 116, 395–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schunk, R.W.; Szuszczewicz, E.P. Plasma expansion characteristics of ionized clouds in the ionosphere: Macroscopic formulation. J. Geophys. Res. 1991, 96, 1337–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.G.; Zhao, Z.Y.; Zhang, Y.N. Study on ionospheric release effects of several typical chemicals. Acta Phys. Sin. 2010, 59, 8293–8303. [Google Scholar]
- Gatsonis, N.A.; Hastings, D.E. A three-dimensional model and initial time numerical simulation for an artificial plasma cloud in the ionosphere. J. Geophys. Res. 1991, 96, 7623–7639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendillo, M.; Semeter, J.; Noto, J. Finite element simulation (FES): A computer modeling technique for studies of chemical modification of the ionosphere. Adv. Space Res. 1993, 13, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y. A Study on Ionospheric Effect of the Rocket Plume. Master’s Thesis, Wuhan University, Wuhan, China, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Ferguson, E.E. Rate constants of thermal energy binary ion-molecule reactions of aeronomic interest. At. Data Nucl. Data Tables 1973, 12, 159–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, D.N.; Bernhardt, P.A. Modeling the effects of an H2 gas release on the equatorial ionosphere. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 1978, 83, 4777–4790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Number | Parameter | Representation |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | n | Neutral gas number density |
| 2 | Neutral gas velocity | |
| 3 | P | Production rate of chemical substances |
| 4 | L | Chemical loss rate |
| 5 | S | Gas primitive function |
| 6 | m | Molecular mass of released gas |
| 7 | Acceleration of gravity | |
| 8 | Vertically upward unit vector | |
| 9 | T | Gas temperature |
| 10 | Neutral gas drift velocity | |
| 11 | Collision frequency | |
| 12 | k | Boltzmann constant |
| Number | Parameter | Representation cm3∙s−1 |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Number density of neutral gas | |
| 2 | Height of release point | |
| 3 | The amount of neutral gas molecules | |
| 4 | Atmospheric elevation | |
| 5 | Elevation of the released gas | |
| 6 | k | Boltzmann constant |
| 7 | T | Background gas temperature |
| 8 | Atmospheric average molecular weight | |
| 9 | Release the molecular weight of neutral gas | |
| 10 | g | Acceleration of gravity |
| 11 | αt | Loss item caused by chemical reaction |
| Number | Parameter | Representation |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | The number density of the plasma (mainly refers to O+) | |
| 2 | Plasma generation rate | |
| 3 | Plasma loss rate | |
| 4 | The drift velocity of the plasma parallel to the direction of the magnetic field |
| Number | Parameter | Representation |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | The number density of the plasma (mainly refers to O+) | |
| 2 | Effective bipolar diffusion coefficient | |
| 3 | Ion diffusion coefficient | |
| 4 | )/2 | Plasma temperature |
| 5 | The elevation of plasma | |
| 6 | Plasma generation rate | |
| 7 | Plasma loss rate |
| Number | Parameter | Representation |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Point O | Geocentric position |
| 2 | OXYZ | Cartesian coordinate system |
| 3 | OXY | Equatorial plane |
| 4 | OX | Point to 0° longitude |
| 5 | OY | Point to 90°E |
| 6 | OZ | Point to the North Pole along the axis of the earth |
| 6 | The coordinate position of Q | |
| 7 | r | The distance from point Q to the center of the earth |
| 8 | The offset angle of the longitude of OX to Q point eastward | |
| 9 | Complementary angle of Q point latitude | |
| 10 | ) | Wave vector at point Q |
| 11 | Vertical ground up | |
| 12 | Pointing to the geographical true east | |
| 13 | Pointing to the geographic direction due south |
| Number | Parameter | Representation |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | P’ | The group path |
| 2 | c | The speed of light |
| 3 | ω = 2 π f | The angular frequency of the radio wave |
| 4 | f | The frequency of the radio wave |
| 5 | The angular frequency of the plasma | |
| 6 | Refractive index |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Q.; Li, Z.; Fang, H. Using 3D Ray Tracing Technology to Study the Disturbance Effect of Rocket Plume on Ionosphere. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 1150. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13071150
Li Q, Li Z, Fang H. Using 3D Ray Tracing Technology to Study the Disturbance Effect of Rocket Plume on Ionosphere. Atmosphere. 2022; 13(7):1150. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13071150
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Qingfeng, Zeyun Li, and Hanxian Fang. 2022. "Using 3D Ray Tracing Technology to Study the Disturbance Effect of Rocket Plume on Ionosphere" Atmosphere 13, no. 7: 1150. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13071150
APA StyleLi, Q., Li, Z., & Fang, H. (2022). Using 3D Ray Tracing Technology to Study the Disturbance Effect of Rocket Plume on Ionosphere. Atmosphere, 13(7), 1150. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13071150





