Validation of MIGHTI/ICON Atmospheric Wind Observations over China Region Based on Meteor Radar and Horizontal Wind Model (HWM14)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Dataset
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Case Study
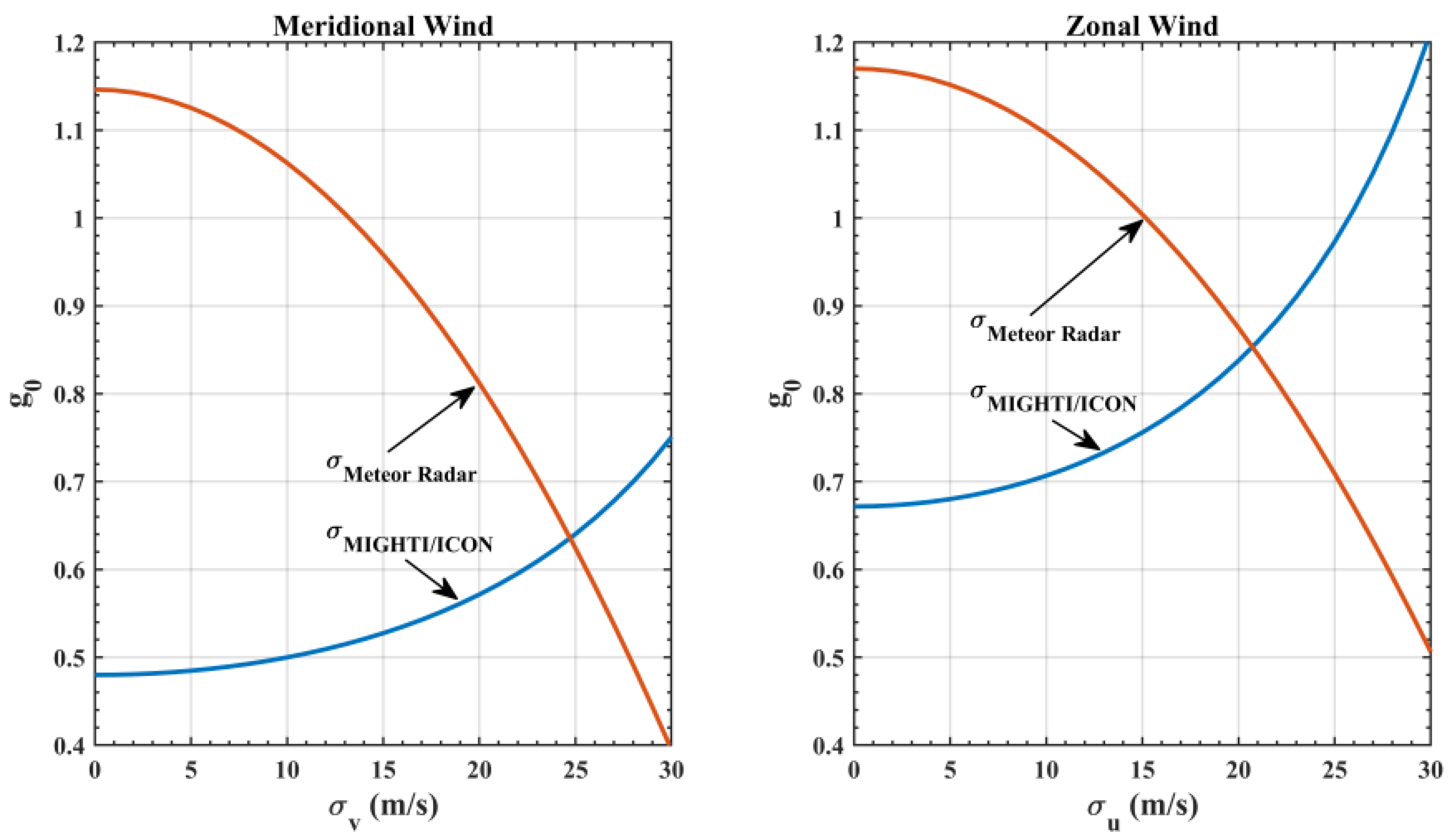
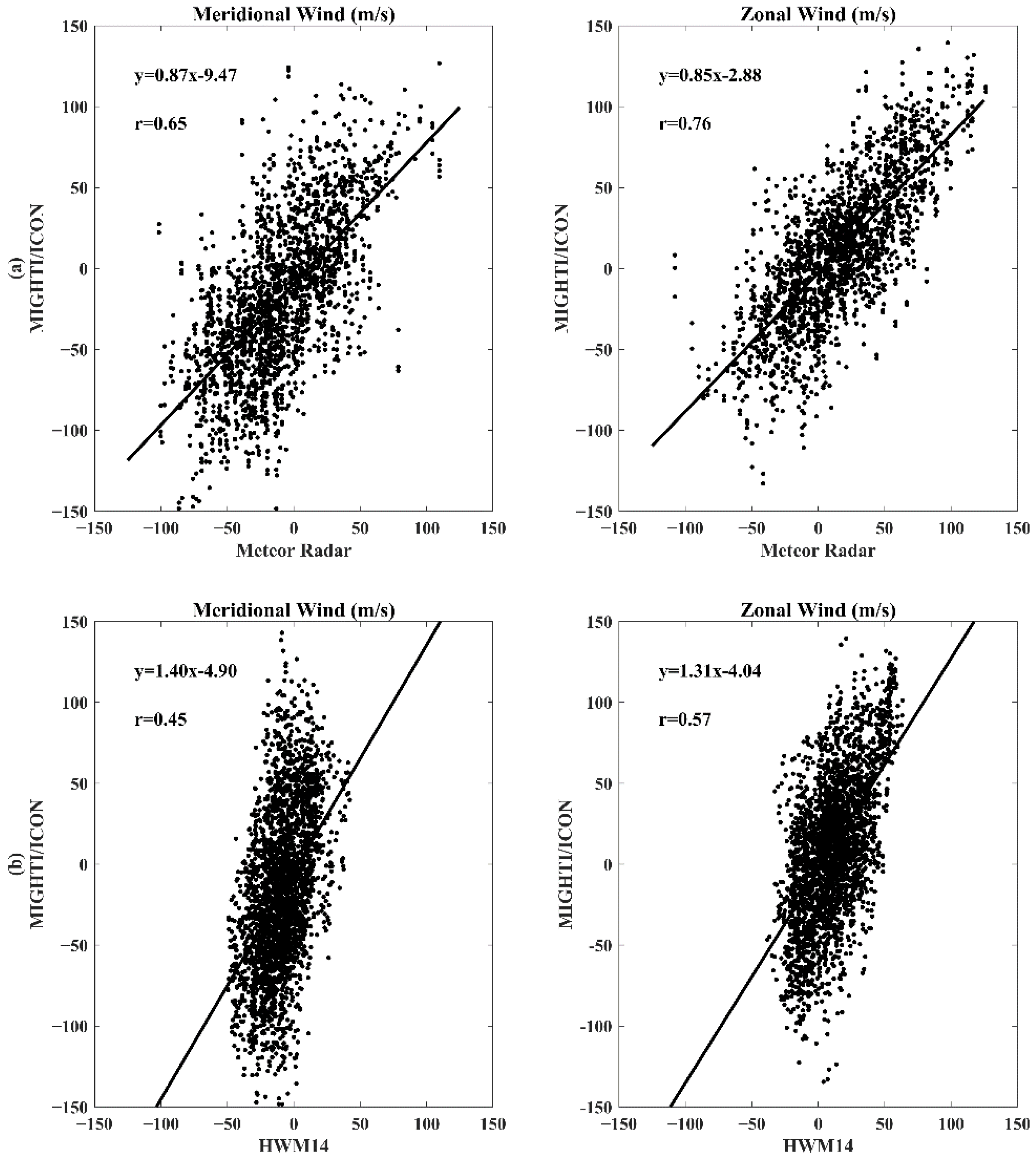
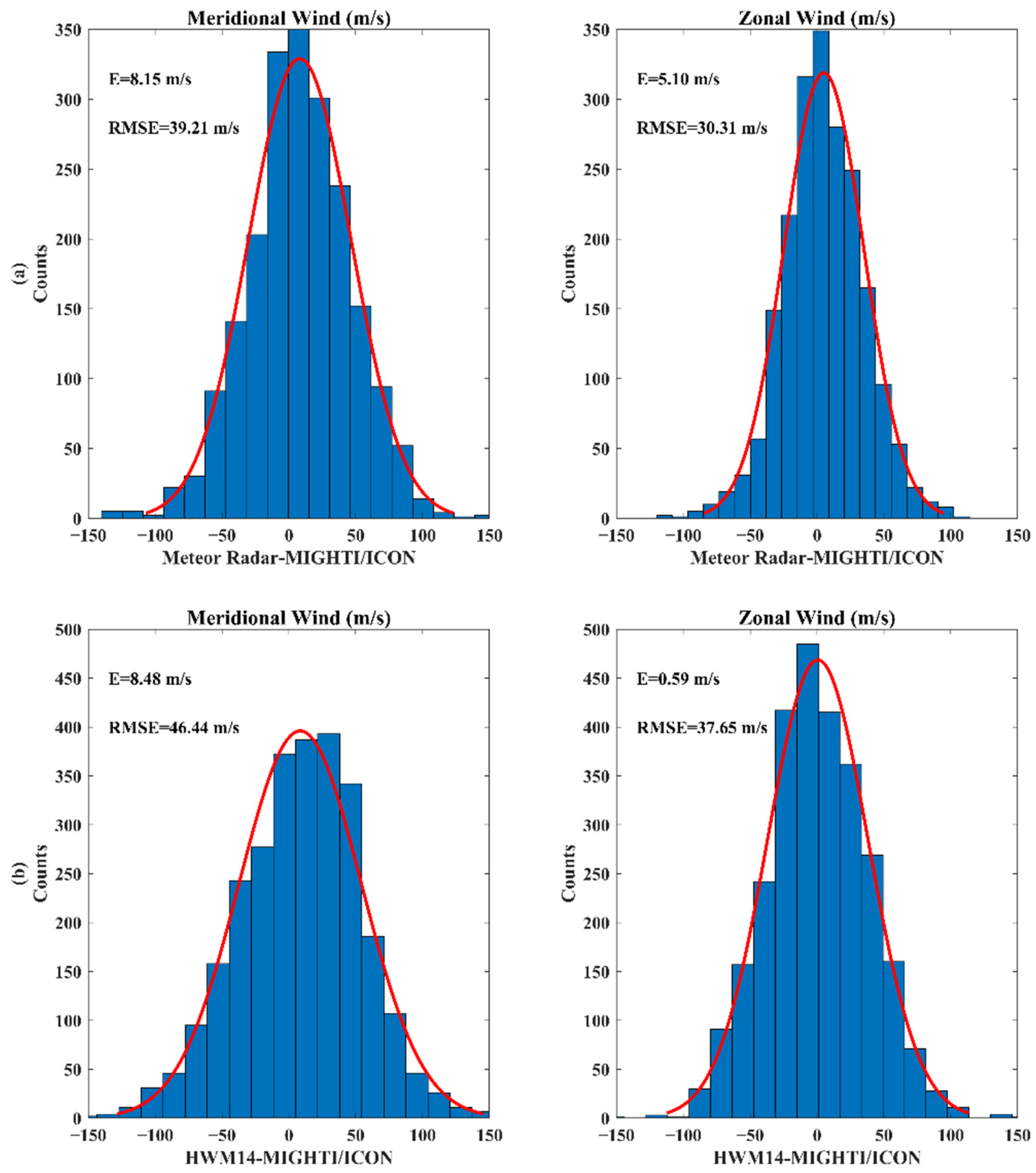
3.2. Statistical Study
3.3. Day/Night Differences
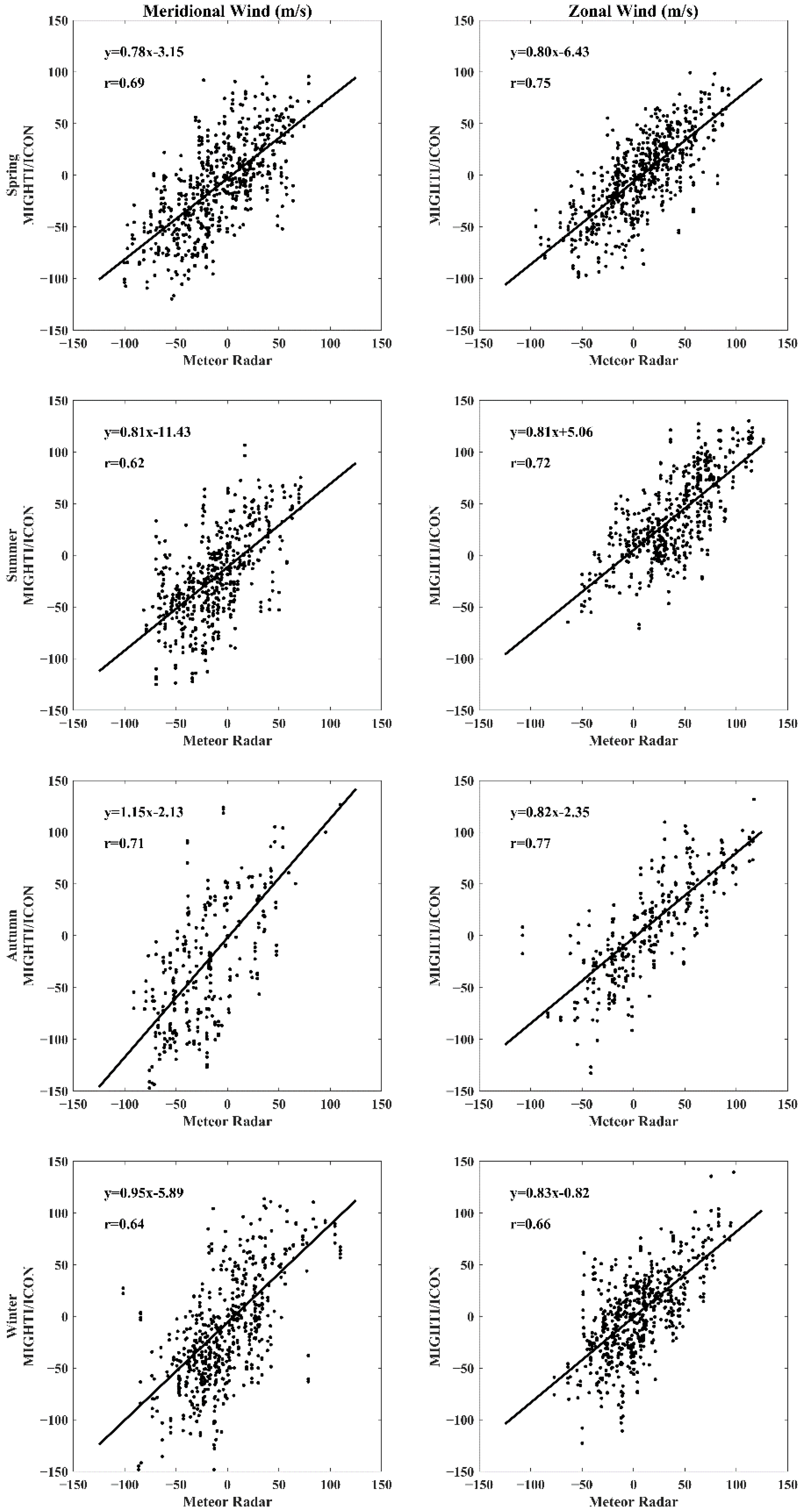
3.4. Seasonal Differences
4. Conclusions
- According to the statistical analysis of measurement results of MIGHTI/ICON, meteor radar, and HWM14 model, the measurement accuracy of zonal wind (r = 0.76, 0.57) from MIGHTI/ICON is better than that of meridional wind (r = 0.65, 0.45).
- MIGHTI/ICON horizontal wind measurement accuracy at 95–100 km is better than that at 100–110 km. The reason may be that the horizontal wind measurement accuracy from the meteor radar at 100–110 km is more inaccurate.
- Comparing the correlation coefficients between MIGHTI/ICON and meteor radar observations of horizontal wind, we find a better agreement at night (r = 0.67, 0.77) than during the day (r = 0.60, 0.68), and the consistency is better in spring and autumn than that in summer and winter.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rishbeth, H. Superrotation of the upper atmosphere. Rev. Geophys. 1972, 10, 799–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rishbeth, H.; Garriot, O. Introduction to Ionospheric Physics, 1st ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1969. [Google Scholar]
- Xiong, J.; Wan, W.; Ning, B.; Liu, L. Meteor radar observation of circulation near mesopause over Wuhan. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2003, 48, 1634–1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, J.; Wan, W.; Ning, B.; Liu, L. First results of the tidal structure in the MLT revealed by Wuhan meteor radar (30°40′ N, 114°30′ E). J. Atmos. Sol. Terr. Phys. 2004, 22, 675–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hocking, W.K.; Fuller, B.; Vandepeer, B. Real-time determination of Meteor-related parameters utilizing modern digital technology. J. Atmos. Sol. Terr. Phys. 2001, 63, 155–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holdsworth, D.A.; Reid, I.M.; Cervera, M.A. Buckland Park all-sky interferometric meteor radar. Radio Sci. 2004, 39, RS5009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, A.Z.; Hocking, W.K.; Franke, S.J.; Thayaparan, T. Comparison of Na lidar and meteor radar wind measurements at starfire optical range, NM, USA. J. Atmos. Sol. Terr. Phys. 2002, 64, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franke, S.J.; Chu, X.; Liu, A.Z.; Hocking, W.K. Comparison of meteor radar and Na Doppler lidar measurements of winds in the mesopause region above Maui, Hawaii. J. Geophys. Res. 2005, 110, D09S02. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, C.M.; Aso, T.; Tsutsumi, M.; Nozawa, S.; Manson, A.H.; Meek, C.E. A comparison of mesosphere and lower thermosphere neutral winds as determined by meteor and medium-frequency radar at 70°N. Radio Sci. 2005, 40, RS4001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Zhang, X.; Igarashi, K.; Zhang, D. A preliminary comparison of observations with MF radars in Wuhan and Yamagawa at 30–31°N. J. Atmos. Sol. Terr. Phys. 2006, 68, 1036–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.K.; Rokade, M.V.; Rao, R.K.; Gurubaran, S.; Patil, P.T. Comparative study of MLT mean winds using MF radars located at 16.8° N and 8.7° N. J. Earth Syst. Sci. 2010, 119, 461–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhadly, M.S.; Emmert, J.T.; Drob, D.P.; McCormack, J.P.; Niciejewski, R. Short-term and interannual variations of migrating diurnal and semidiurnal tides in the mesosphere and lower thermosphere. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2018, 123, 7106–7123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niciejewski, R.; Wu, Q.; Skinner, W.; Gell, D.; Cooper, M.; Marshall, A.; Killeen, T.; Solomon, S.; Ortland, D. TIMED Doppler Interferometer on the Thermosphere Ionosphere Mesosphere Energetics and Dynamics satellite: Data product overview. J. Geophys. Res. 2006, 111, A11S90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhadly, M.S.; Englert, C.R.; Drob, D.P.; Emmert, J.T.; Niciejewski, R.; Zawdie, K.A. Comparison of ICON/MIGHTI and TIMED/TIDI Neutral Wind Measurements in the Lower Thermosphere. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2021, 126, e2021JA029904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Englert, C.R.; Harlander, J.M.; Brown, C.M.; Marr, K.D.; Miller, I.J.; Stump, J.E.; Immel, T.J. Michelson Interferometer for Global High-resolution Thermospheric Imaging (MIGHTI): Instrument design and calibration. Space Sci. Rev. 2017, 212, 553–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harding, B.J.; Makela, J.J.; Englert, C.R.; Marr, K.D.; Harlander, J.M.; England, S.L.; Immel, T.J. The MIGHTI wind retrieval algorithm: Description and verification. Space Sci. Rev. 2017, 212, 585–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harlander, J.M.; Englert, C.R.; Brown, C.M.; Marr, K.D.; Miller, I.J.; Zastera, V.; Bach, B.W.; Mende, S.B. Michelson interferometer for global high-resolution thermospheric imaging (MIGHTI): Monolithic interferometer design and test. Space Sci. Rev. 2017, 212, 601–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makela, J.J.; Baughman, M.; Navarro, L.A.; Harding, B.J.; Englert, C.R.; Harlander, J.M.; Marr, K.D.; Benkhaldoun, Z.; Kaab, M.; Immel, T.J. Validation of ICON-MIGHTI thermospheric wind observations: 1. Nighttime Red-line Ground-Based Fabry-Perot Interferometers. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2021, 126, e2020JA028726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harding, B.J.; Chau, J.L.; He, M.; Englert, C.R.; Harlander, J.M.; Marr, K.D.; Makela, J.J.; Clahsen, M.; Li, G.; Ratnam, M.V.; et al. Validation of ICON-MIGHTI Thermospheric Wind Observations: 2. Green-Line Comparisons to Specular Meteor Radars. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2021, 126, e2020JA028947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Immel, T.J.; England, S.L.; Mende, S.B.; Heelis, R.A.; Englert, C.R.; Edelstein, J.; Sirk, M.M. The ionospheric connection explorer mission: Mission goals and design. Space Sci. Rev. 2018, 214, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.-J.J.; Harding, B.J.; Triplett, C.C.; Makela, J.J.; Marr, K.D.; Englert, C.R.; Harlander, J.M.; Immel, T.J. Errors from asymmetric emission rate in spaceborne, limb sounding Doppler interferometry: A correction algorithm with application to ICON/MIGHTI. Earth Space Sci. 2020, 7, e2020EA001164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drob, D.P.; Emmert, J.T.; Crowley, G.; Picone, J.; Shepherd, G.G.; Skinner, W.; Hays, P.; Niciejewski, R.J.; Larsen, M.; She, C.Y.; et al. An empirical model of the Earth’s horizontal wind fields: HWM07. J. Geophys. Res. 2008, 113, A12304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drob, D.P.; Emmert, J.T.; Meriwether, J.W.; Makela, J.J.; Doornbos, E.; Conde, M.; Hernandez, G.; Noto, J.; Zawdie, K.A.; McDonald, S.E.; et al. An update to the horizontal wind model(HWM): The quiet time thermosphere. Earth Space Sci. 2015, 2, 301–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emmert, J.T.; Drob, D.P.; Shepherd, G.G.; Hernandez, G.; Jarvis, M.J.; Meriwether, J.W.; Niciejewski, R.J.; Sipler, D.P.; Tepley, C.A. DWM07 global empirical model of upper thermospheric storm-induced disturbance winds. J. Geophys. Res. 2008, 113, A11319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Q.; Zhou, Y.; Du, Z.; Zhou, C.; Qiao, J.; Liu, Y.; Chen, G. A Comparison of Meteor Radar Observation over China Region with Horizontal Wind Model (HWM14). Atmosphere 2021, 12, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hocking, W.K.; Thayaparan, T.; Franke, S.J. Method for statistical comparison of geophysical data by multiple instruments which have differing accuracies. Adv. Space Res. 2001, 27, 1089–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojo, T.T.; Katamzi-Joseph, Z.T.; Chu, K.T.; Grawe, M.A.; Makela, J.J. A climatology of the nighttime thermospheric winds over Sutherland, South Africa. Adv. Space Res. 2022, 69, 209–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manson, A.H.; Meek, C.E.; Hall, C.M.; Nozawa, S.; Mitchell, N.J.; Pancheva, D.; Singer, W.; Hoffmann, P. Mesopause dynamics from the scandinavian triangle of radars within the PSMOS-DATAR Project. Ann. Geophys. 2004, 22, 367–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobi, C.; Hoffmann, P.; Liu, R.Q.; Merzlyakov, E.G.; Portnyagin, Y.I.; Manson, A.H.; Meek, C.E. Long-term trends, their changes, and interannual variability of Northern Hemisphere midlatitude MLT winds. J. Atmos. Sol. Terr. Phys. 2012, 75, 81–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasebe, F.; Tsuda, T.; Nakamura, T.; Burrage, M.D. Validation of HRDI MLT winds with meteor radars. Ann. Geophys. 1997, 15, 1142–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Wu, Q.; Killeen, T.L.; Ortland, D.A.; Solomon, S.C.; Gablehouse, R.D.; Johnson, R.M.; Skinner, W.R.; Niciejewski, W.R.; Franke, S.J. TIMED Doppler interferometer (TIDI) observations of migrating diurnal and semidiurnal tides. J. Atmos. Sol. Terr. Phys. 2006, 68, 408–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.; Liu, L.; Wan, W.; Ning, B.; Xiong, J. Seasonal behavior of meteor radar winds over Wuhan. Earth Planet Space 2005, 57, 61–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wing, R.; Martic, M.; Triplett, C.; Hauchecorne, A.; Porteneuve, J.; Keckhut, P.; Courcoux, Y.; Yung, L.; Retailleau, P.; Cocuron, D. Gravity Wave Breaking Associated with Mesospheric Inversion Layers as Measured by the Ship-Borne BEM Monge Lidar and ICON-MIGHTI. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Altitude Range (km) | Day | Night | Vertical Resolution (km) | Along Track Resolution (km) | Wind Velocity Precision (m/s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 90–105 | x | x | 5 | 500 | 8.7 |
| 105–170 | x | 5 | 500 | 10 | |
| 170–200 | x | 30 | 500 | 10 | |
| 200–300 | x | x | 30 | 500 | 8.7 |
| Height (km) | Number of Samples | Meridional Wind Correlation Coefficient | Zonal Wind Correlation Coefficient |
|---|---|---|---|
| 94 km | 709 | 0.65 | 0.79 |
| 96 km | 697 | 0.66 | 0.78 |
| 98 km | 636 | 0.63 | 0.70 |
| 100 km | 502 | 0.48 | 0.48 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, Z.; Liu, Y.; Du, Z.; Fan, Z.; Sun, H.; Zhou, C. Validation of MIGHTI/ICON Atmospheric Wind Observations over China Region Based on Meteor Radar and Horizontal Wind Model (HWM14). Atmosphere 2022, 13, 1078. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13071078
Chen Z, Liu Y, Du Z, Fan Z, Sun H, Zhou C. Validation of MIGHTI/ICON Atmospheric Wind Observations over China Region Based on Meteor Radar and Horizontal Wind Model (HWM14). Atmosphere. 2022; 13(7):1078. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13071078
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Zhou, Yi Liu, Zhitao Du, Zhiqiang Fan, Haiyang Sun, and Chen Zhou. 2022. "Validation of MIGHTI/ICON Atmospheric Wind Observations over China Region Based on Meteor Radar and Horizontal Wind Model (HWM14)" Atmosphere 13, no. 7: 1078. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13071078
APA StyleChen, Z., Liu, Y., Du, Z., Fan, Z., Sun, H., & Zhou, C. (2022). Validation of MIGHTI/ICON Atmospheric Wind Observations over China Region Based on Meteor Radar and Horizontal Wind Model (HWM14). Atmosphere, 13(7), 1078. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13071078







