The Impact of Long-Range Transport of Biomass Burning Emissions in Southeast Asia on Southern China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Data and Methods
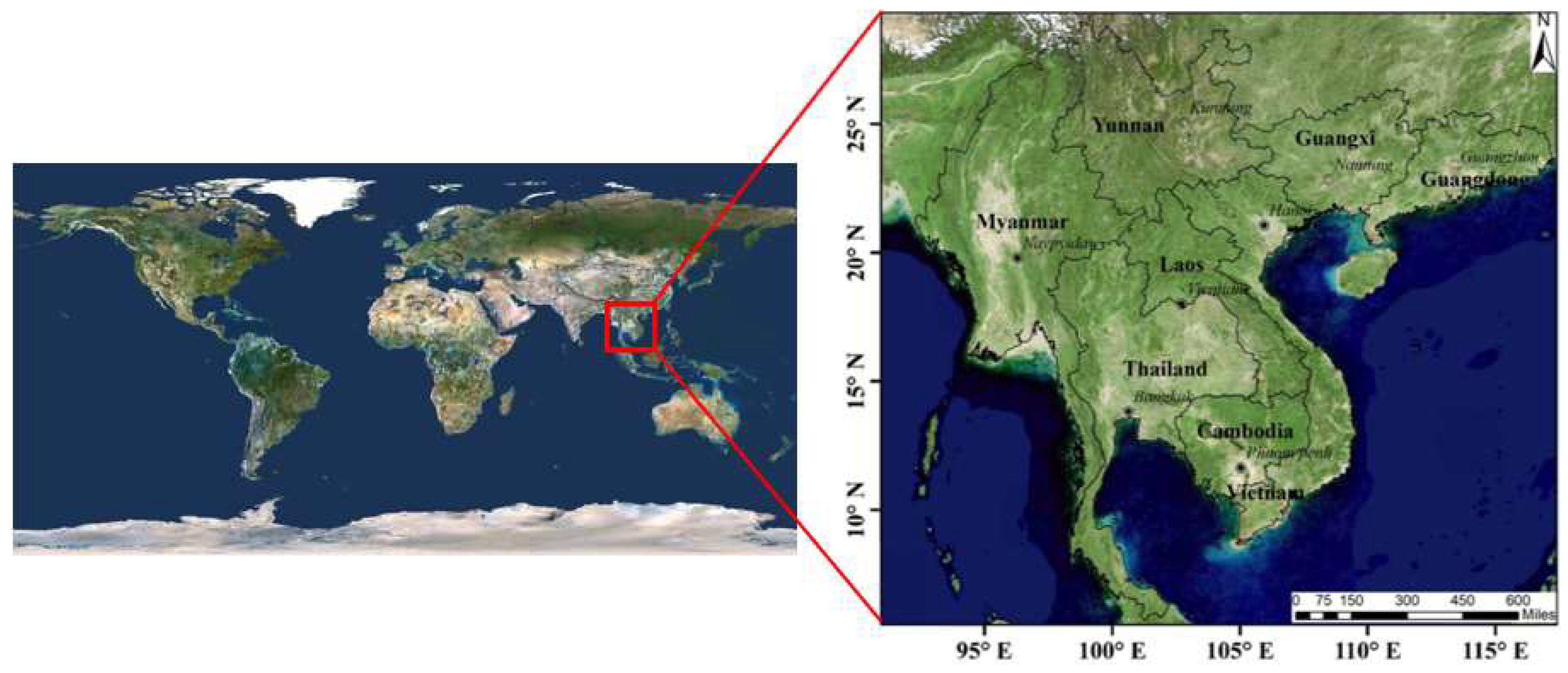
2.1. Description of the Study Area
2.2. MODIS Products about Fire Points and AOD
2.3. Sentinel 5 Precursor TROPOMI CO Column Concentration Product
2.4. Suomi NPP OMPS Ultraviolet Aerosol Index Product
2.5. NCEP/NCAR Meteorological Datasets
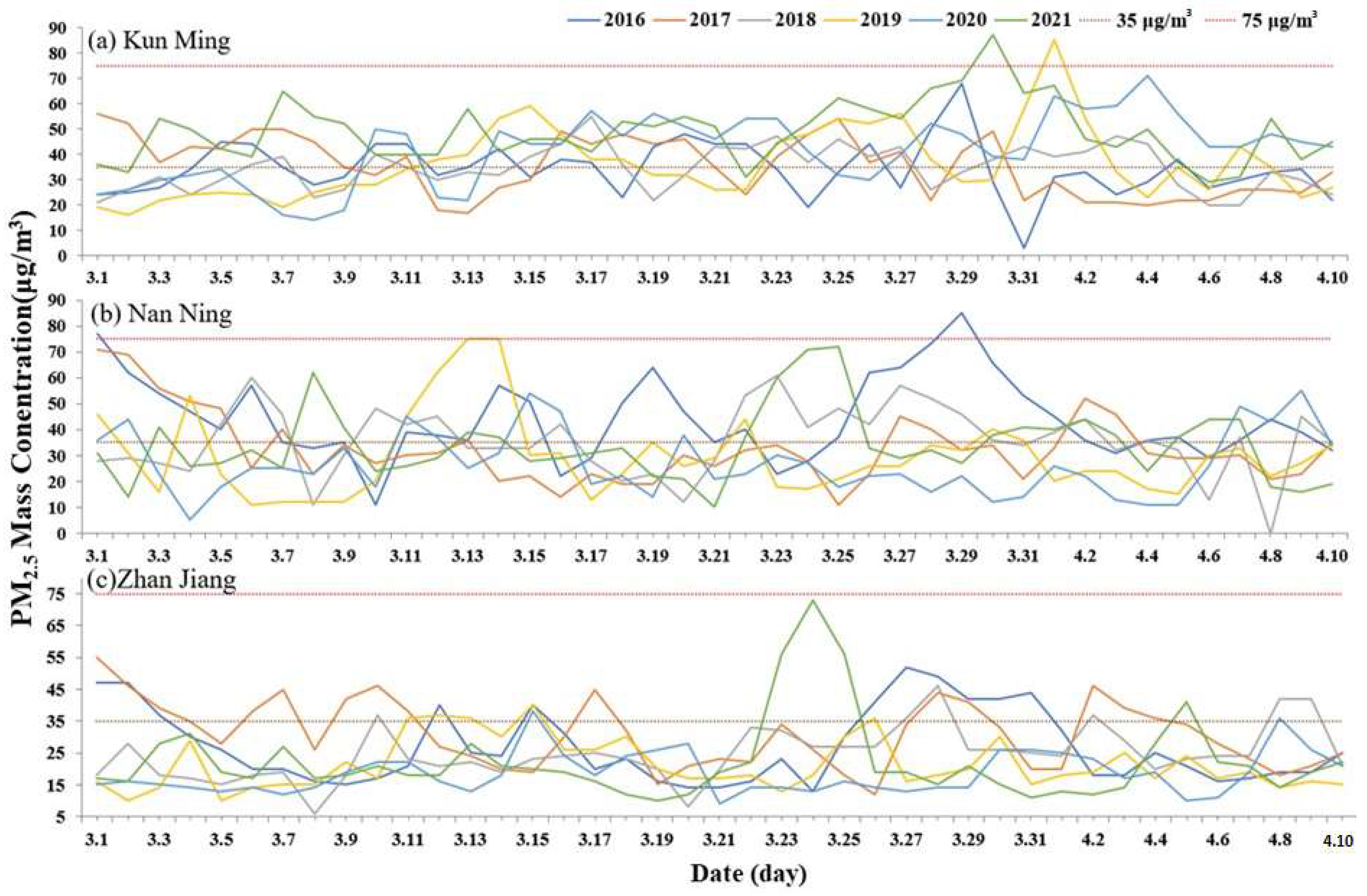
2.6. PM2.5 Data from Ground Stations
3. Results
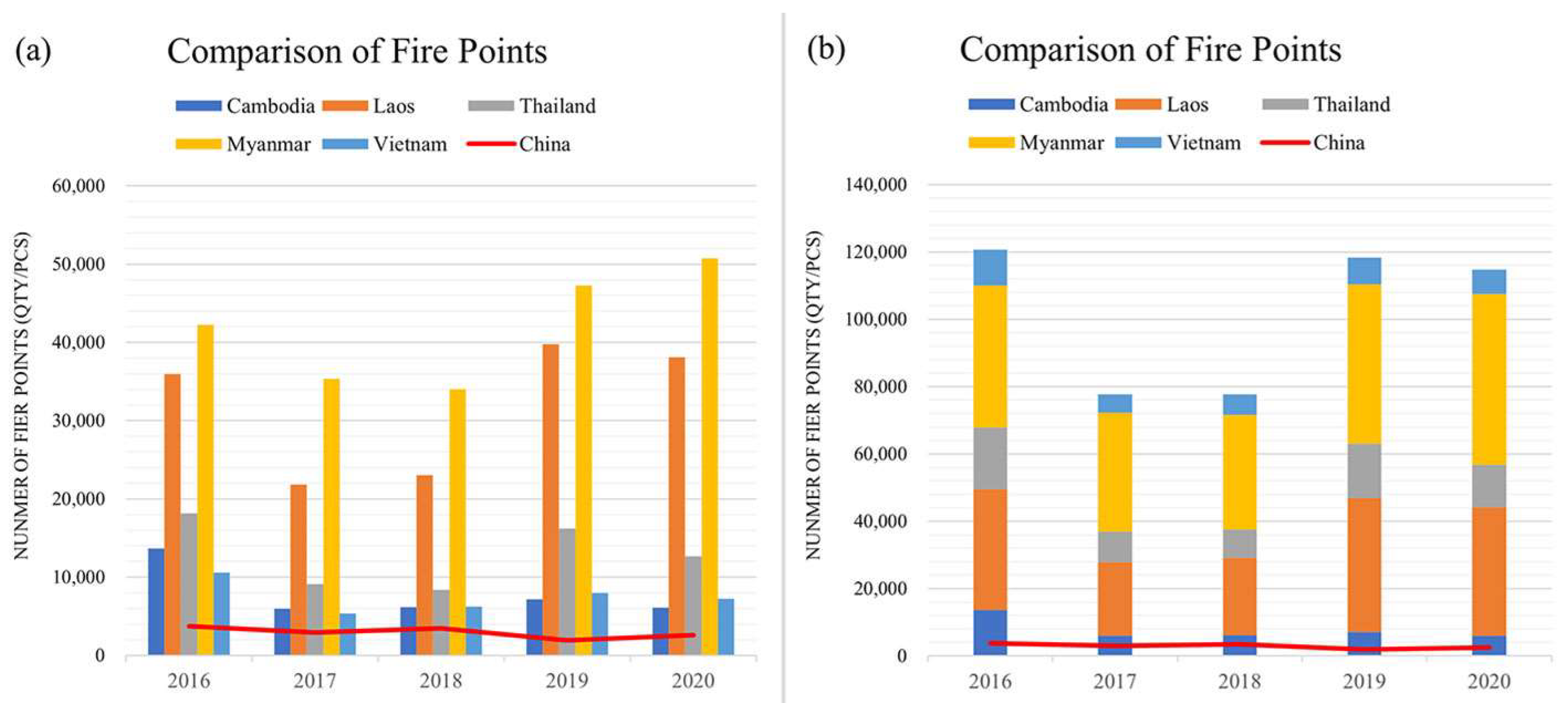
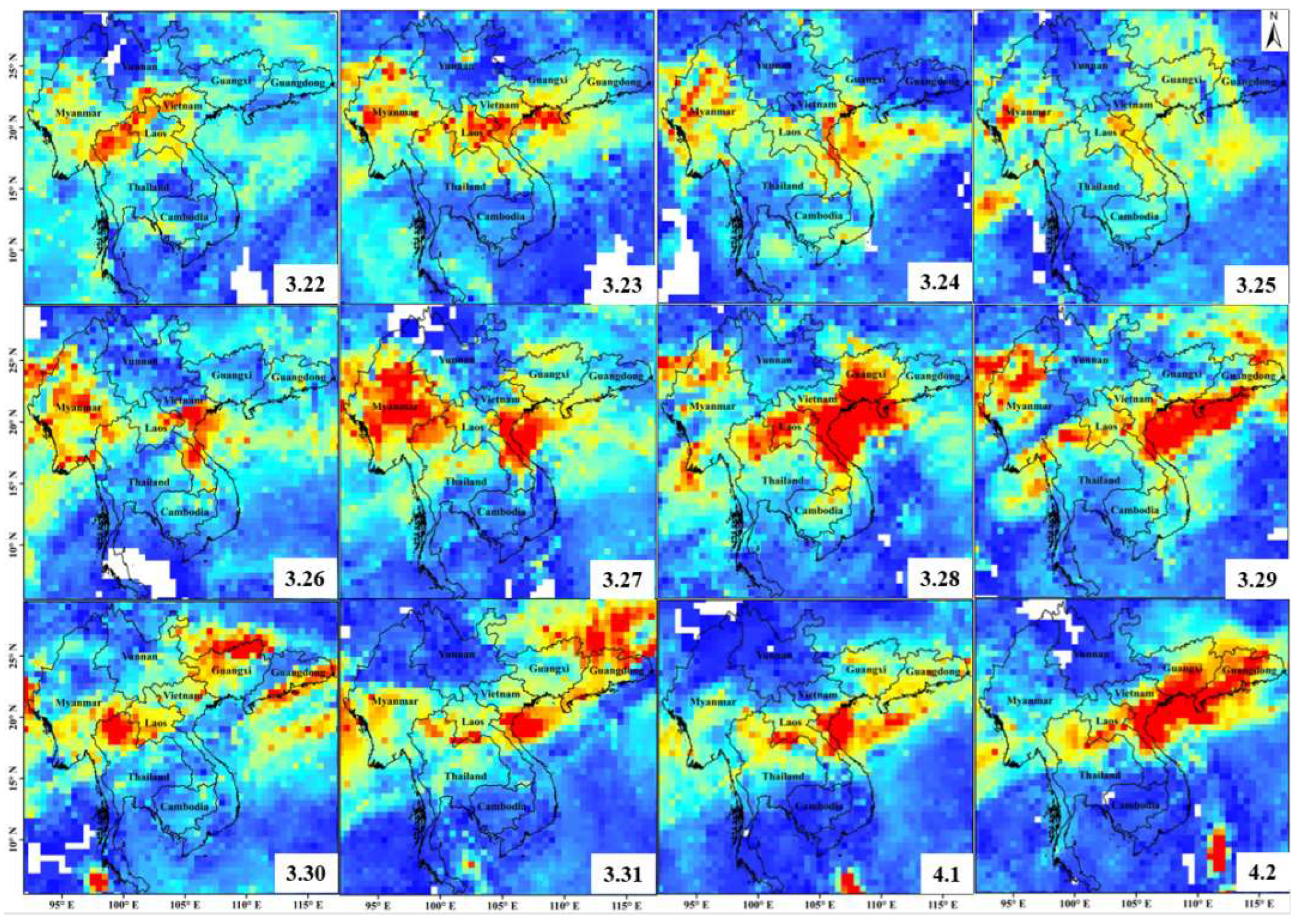
3.1. MODIS Fire Points Information Extraction
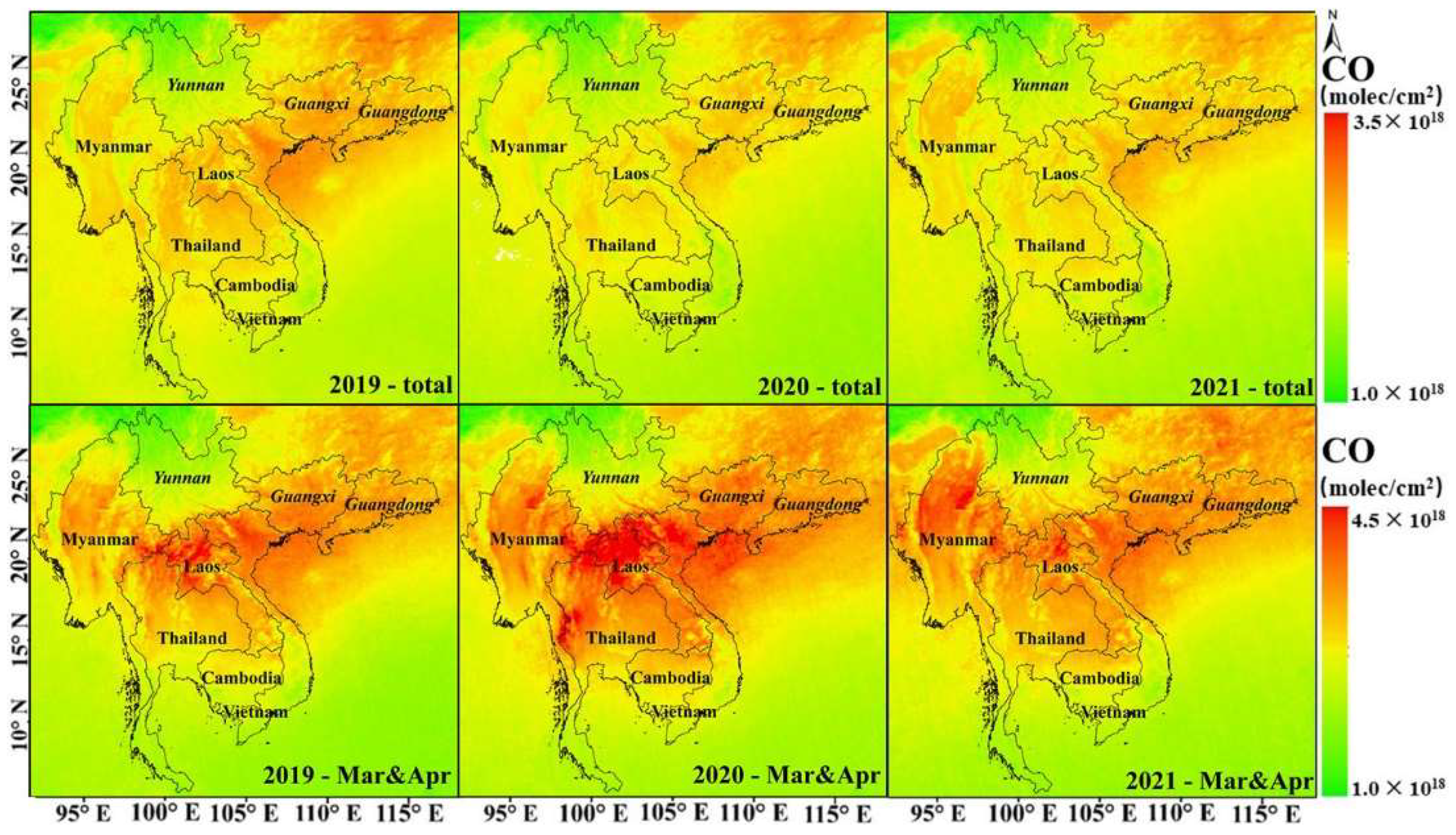
3.2. CO Column Concentration Change Analysis
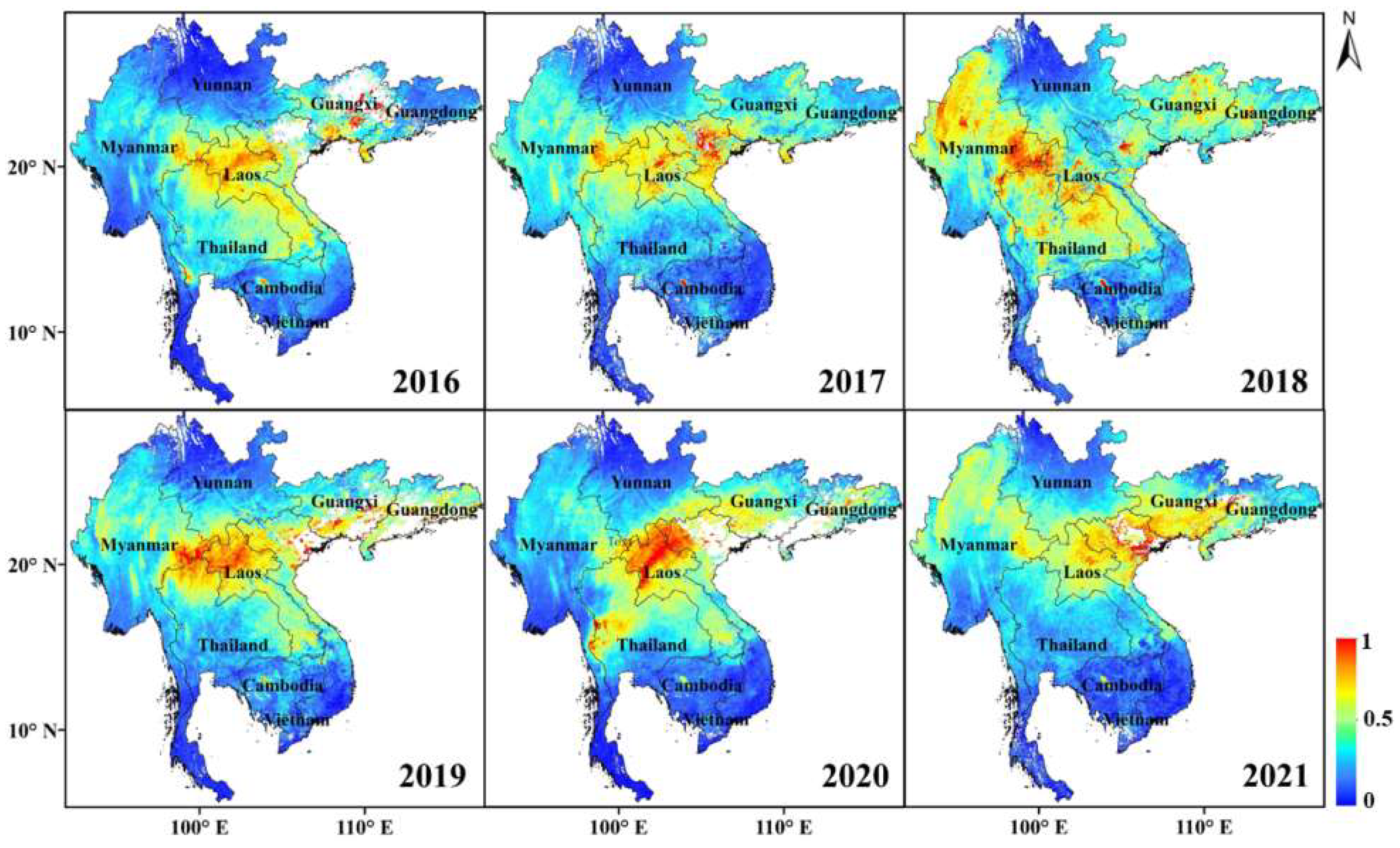
3.3. Distribution of MODIS AOD Products
3.4. Analysis of a Typical Pollution Event in 2021
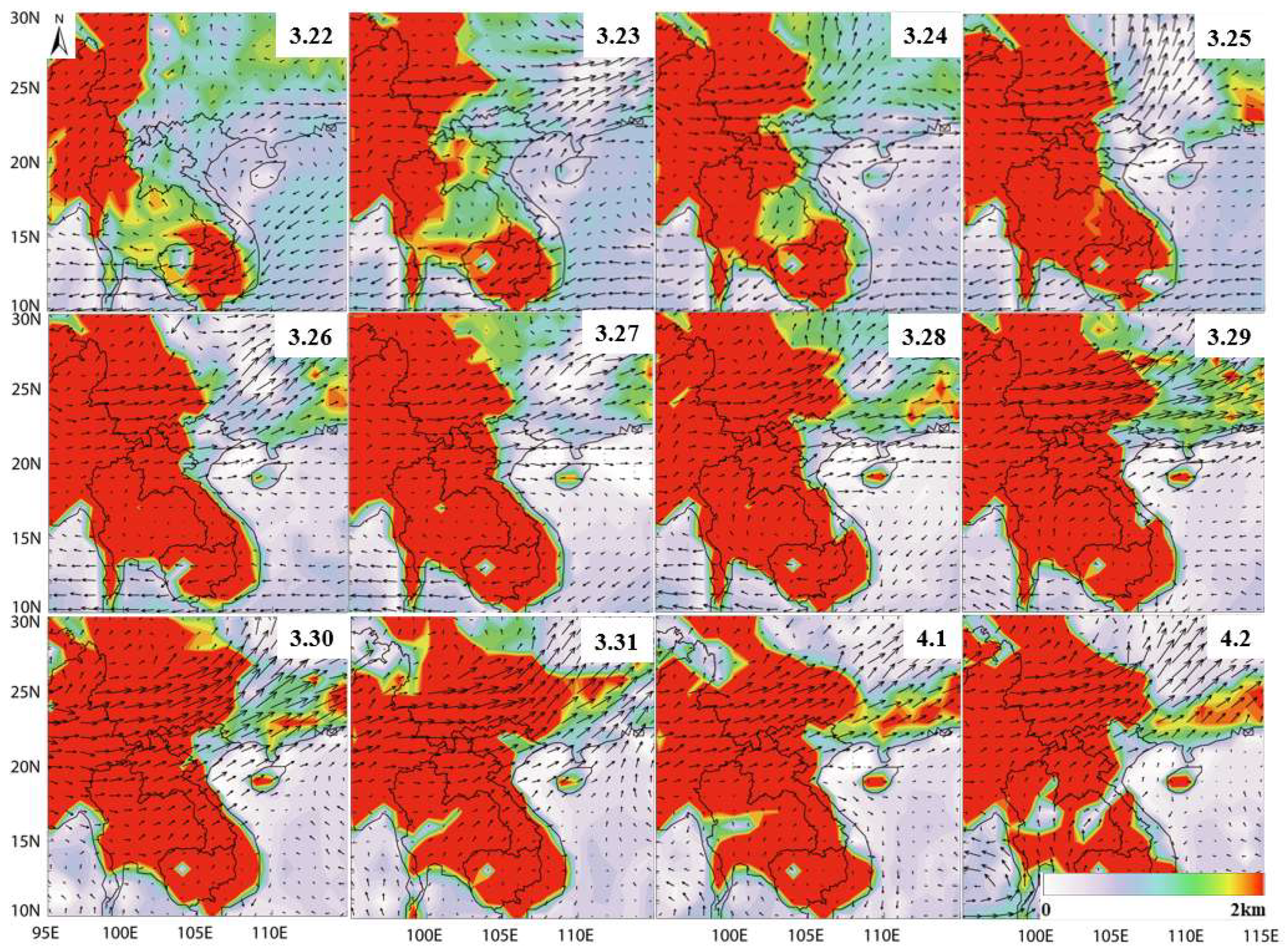
3.4.1. OMPS UVAI Change Trend
3.4.2. NCEP-Assisted Analysis of Meteorological Data
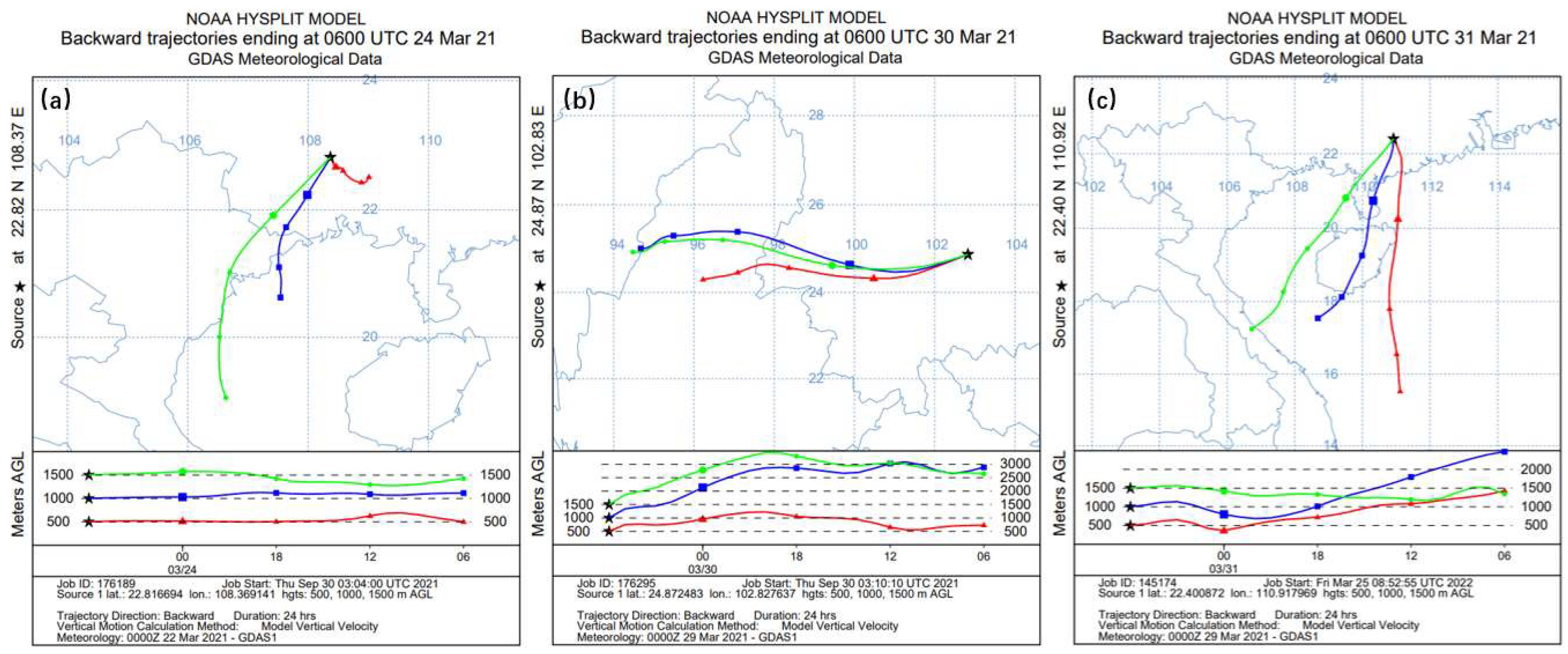
3.4.3. Validation
- Guangdong is affected by biomass burning in the Indochinese Peninsula to an extent. The main way is that pollutants are transferred from the Indochinese Peninsula to the South China Sea and then moved to the south of Guangdong under the action of wind.
- The polluted air masses in the upper atmosphere of Guangxi in China come from the Indochinese Peninsula and have a certain impact on the pollution index in the province.
- Affected by the spring southwest monsoon, the polluted air masses of different heights in Yunnan mainly come from Southeast Asia in the southwest.
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Adam, M.G.; Tran, P.T.; Bolan, N.; Balasubramanian, R. Biomass burning-derived airborne particulate matter in Southeast Asia: A critical review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 407, 124760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Othman, M.; Latif, M.T.; Hamid, H.H.A.; Uning, R.; Khumsaeng, T.; Phairuang, W.; Lung, S.C.C. Spatial–temporal variability and heath impact of particulate matter during a 2019–2020 biomass burning event in Southeast Asia. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 7630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, S.; Wang, X.; Zhang, X.; Guo, M.; Miura, M.; Xiao, Y. Influence of biomass burning on local air pollution in mainland Southeast Asia from 2001 to 2016. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 254, 112949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ito, A.; Ito, A.; Akimoto, H. Seasonal and interannual variations in CO and BC emissions from open biomass burning in Southern Africa during 1998–2005. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 2007, 21, GB2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiedinmyer, C.; Akagi, S.K.; Yokelson, R.J.; Emmons, L.K.; Al-Saadi, J.A.; Orlando, J.J.; Soja, A.J. The Fire INventory from NCAR (FINN)—A high resolution global model to estimate the emissions from open burning. Geosci. Model Dev. 2011, 4, 625–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Palacios-Orueta, A.; Chuvieco, E.; Parra, A.; Carmona-Moreno, C. Biomass Burning Emissions: A Review of Models Using Remote-Sensing Data. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2005, 104, 189–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Streets, D.G.; Yarber, K.F.; Woo, J.-H.; Carmichael, G.R. Biomass burning in Asia: Annual and seasonal estimates and atmospheric emissions. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 2003, 17, 1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, K.; Fu, J.S.; Hsu, N.C.; Gao, Y.; Dong, X.; Tsay, S.-C.; Lam, Y.F. Impact assessment of biomass burning on air quality in Southeast and East Asia during BASE-ASIA. Atmos. Environ. 2013, 78, 291–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Li, J.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Z. Modeling the Impacts of Biomass Burning in Southeast Asia on PM2.5 over China in Spring. Res. Environ. Sci. 2016, 29, 952–962. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, L.; Ding, A.; Cooper, O.; Huang, X.; Wang, W.; Zhou, D.; Wu, Z.; McClure-Begley, A.; Petropavlovskikh, I.; Andreae, M.O.; et al. ENSO and Southeast Asian biomass burning modulate subtropical trans-Pacific ozone transport. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2020, 8, nwaa132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Xia, X.; Che, H.; Wang, J.; Zhang, J.; Duan, Y. Study of aerosol optical properties at Kunming in southwest China and long-range transport of biomass burning aerosols from North Burma. Atmos. Res. 2016, 169, 237–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, R.; Zhu, J. Effects of biomass combustion and transportation over southeast Asia on aerosol radiation characteristics in southwest China. China Environ. Sci. 2020, 40, 1429–1436. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Bond, T.C.; Doherty, S.J.; Fahey, D.W.; Forster, P.M.; Berntsen, T.; DeAngelo, B.J.; Zender, C.S. Bounding the role of black carbon in the climate system: A scientific assessment. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2013, 118, 5380–5552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olivier, J.G.J.; Aardenne, J.A.V.; Dentener, F.J.; Pagliari, V.; Ganzeveld, L.N.; Peters, J.A.H.W. Recent trends in global greenhouse gas emissions: Regional trends 1970–2000 and spatial distribution of key sources in 2000. Environ. Sci. 2005, 2, 81–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ciais, P.; Sabine, C.; Bala, G.; Bopp, L.; Brovkin, V.; Canadell, J.; Thornton, P. Carbon and other biogeochemical cycles. In Climate Change 2013: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2013; pp. 465–570. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, H.; Lu, C.; Ciais, P.; Michalak, A.M.; Canadell, J.G.; Saikawa, E.; Huntzinger, D.N.; Gurney, K.R.; Sitch, S.; Zhang, B.; et al. The terrestrial biosphere as a net source of greenhouse gases to the atmosphere. Nature 2016, 531, 225–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Crutzen, P.J.; Andreae, M.O. Biomass burning in the tropics: Impact on atmospheric chemistry and biogeochemical cycles. Science 1990, 250, 1669–1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robinson, A.L.; Donahue, N.M.; Shrivastava, M.K.; Weitkamp, E.A.; Sage, A.M.; Grieshop, A.P.; Lane, T.E.; Pierce, J.R.; Pandis, S.N. Rethinking organic aerosols: Semivolatile emissions and photochemical aging. Science 2007, 315, 1259–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- May, A.A.; Levin, E.J.T.; Hennigan, C.J.; Riipinen, I.; Lee, T.; Collett, J.L.; Jimenez, J.L.; Kreidenweis, S.M.; Robinson, A.L. Gas-particle partitioning of primary organic aerosol emissions: 3. Biomass burning. J. Geophys. Res. 2013, 118, 11327–11338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, X.; Unger, N. Fire air pollution reduces global terrestrial productivity. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 5413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, N.H.; Sayer, A.M.; Wang, S.H.; Loftus, A.M.; Hsiao, T.C.; Sheu, G.R.; Chantara, S. Interactions between biomass-burning aerosols and clouds over Southeast Asia: Current status, challenges, and perspectives. Environ. Pollut. 2014, 195, 292–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.; Rosenfeld, D.; Yang, Y.; Zhao, C.; Leung, L.R.; Li, Z. Substantial contribution of anthropogenic air pollution to catastrophic floods in Southwest China. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2015, 42, 6066–6075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pope Iii, C.A.; Burnett, R.T.; Thun, M.J.; Calle, E.E.; Krewski, D.; Ito, K.; Thurston, G.D. Lung cancer, cardiopulmonary mortality, and long-term exposure to fine particulate air pollution. JAMA 2002, 287, 1132–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vincenti, B.; Paris, E.; Carnevale, M.; Palma, A.; Guerriero, E.; Borello, D.; Gallucci, F. Saccharides as Particulate Matter Tracers of Biomass Burning: A Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 4387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Ge, P.; Chen, M.; Tang, J.; Cao, M.; Cui, Y.; Nie, D. Tracers from biomass burning emissions and identification of biomass burning. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Y.; Bai, P.; Hayakawa, K.; Zhang, L.; Tang, N. Characteristics and Influencing Factors of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons Emitted from Open Burning and Stove Burning of Biomass: A Brief Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 3944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cong, Z.; Kawamura, K.; Kang, S.; Fu, P. Penetration of biomass-burning emissions from South Asia through the Himalayas: New insights from atmospheric organic acids. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 9580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ranjan, A.K.; Patra, A.; Gorai, A. Effect of lockdown due to SARS COVID-19 on aerosol optical depth (AOD) over urban and mining regions in India. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 745, 141024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takami, K.; Shimadera, H.; Uranishi, K.; Kondo, A. Impacts of biomass burning emission inventories and atmospheric reanalyses on simulated PM10 over Indochina. Atmosphere 2020, 11, 160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ziemke, J.R.; Oman, L.D.; Strode, S.A.; Douglass, A.R.; Olsen, M.A.; McPeters, R.D.; Bhartia, P.K.; Froidevaux, L.; Labow, G.J.; Witte, J.C. Trends in global tropospheric ozone inferred from a composite record of TOMS/OMI/MLS/OMPS satellite measurements and the MERRA-2 GMI simulation. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2019, 19, 3257–3269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lu, S.; Huang, H.-C.; Hou, Y.-T.; Tang, Y.; McQueen, J.; da Silva, A.; Chin, M.; Joseph, E.; Stockwell, W. Development of NCEP Global Aerosol Forecasting System: An overview and its application for improving weather and air quality forecasts. In NATO Science for Peace and Security Series: Air Pollution Modeling and Its Application XX; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2010; pp. 451–454. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.H.; Lin, N.H.; Chou, M.D.; Woo, J.H. Estimate of radiative forcing of Asian biomass-burning aerosols during the period of TRACE-P. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2007, 112, D10222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thepnuan, D.; Chantara, S.; Lee, C.-T.; Lin, N.-H.; Tsai, Y.I. Molecular markers for biomass burning associated with the characterization of PM2.5 and component sources during dry season haze episodes in Upper South East Asia. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 658, 708–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ooi, M.C.-G.; Chuang, M.-T.; Fu, J.S.; Kong, S.S.; Huang, W.-S.; Wang, S.-H.; Pimonsree, S.; Chan, A.; Pani, S.K.; Lin, N.-H. Improving prediction of trans-boundary biomass burning plume dispersion: From northern peninsular Southeast Asia to downwind western North Pacific Ocean. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2021, 21, 12521–12541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duncan, B.N.; Martin, R.V.; Staudt, A.C.; Yevich, R.; Logan, J.A. Interannual and seasonal variability of biomass burning emissions constrained by satellite observations. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2003, 108, ACH 1-1–ACH 1-22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kondo, Y.; Morino, Y.; Takegawa, N.; Koike, M.; Kita, K.; Miyazaki, Y.; Sachse, G.; Vay, S.; Avery, M.; Flocke, F. Impacts of biomass burning in Southeast Asia on ozone and reactive nitrogen over the western Pacific in spring. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2004, 109, D15S12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ma, Y.; Weber, R.; Lee, Y.N.; Orsini, D.; Maxwell-Meier, K.; Thornton, D.; Bandy, A.; Clarke, A.; Blake, D.; Sachse, G. Characteristics and influence of biosmoke on the fine-particle ionic composition measured in Asian outflow during the Transport and Chemical Evolution Over the Pacific (TRACE-P) experiment. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2003, 108, 8816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gadhavi, H.; Jayaraman, A. Absorbing aerosols: Contribution of biomass burning and implications for radiative forcing. Ann. Geophys. 2010, 28, 103–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tao, M.; Chen, L.; Wang, Z.; Tao, J.; Su, L. Satellite observation of abnormal yellow haze clouds over East China during summer agricultural burning season. Atmos. Environ. 2013, 79, 632–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, C.; Chan, L.; Chang, W.; Zheng, Y.; Cui, H.; Zheng, X.; Qin, Y.; Li, Y.S. Characteristics of a tropospheric ozone profile and implications for the origin of ozone over subtropical China in the spring of 2001. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2003, 108, 8800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, L.; Ding, S.; Qian, W.; Zhao, A.; Zhao, S.; Yang, Y.; Weng, G.; Tao, M.; Chen, H.; Zhao, S.; et al. The Impact of Long-Range Transport of Biomass Burning Emissions in Southeast Asia on Southern China. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 1029. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13071029
Zhang L, Ding S, Qian W, Zhao A, Zhao S, Yang Y, Weng G, Tao M, Chen H, Zhao S, et al. The Impact of Long-Range Transport of Biomass Burning Emissions in Southeast Asia on Southern China. Atmosphere. 2022; 13(7):1029. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13071029
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Lijuan, Sijia Ding, Wenmin Qian, Aimei Zhao, Shimin Zhao, Yi Yang, Guoqing Weng, Minghui Tao, Hui Chen, Shaohua Zhao, and et al. 2022. "The Impact of Long-Range Transport of Biomass Burning Emissions in Southeast Asia on Southern China" Atmosphere 13, no. 7: 1029. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13071029
APA StyleZhang, L., Ding, S., Qian, W., Zhao, A., Zhao, S., Yang, Y., Weng, G., Tao, M., Chen, H., Zhao, S., & Wang, Z. (2022). The Impact of Long-Range Transport of Biomass Burning Emissions in Southeast Asia on Southern China. Atmosphere, 13(7), 1029. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13071029






