Effect of Dust Types on the Eco-Physiological Response of Three Tree Species Seedlings: Eucalyptus camaldulensis, Conocarpus erectus and Bombax ceiba
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Site Description
2.2. Plant Materials
2.3. Measurement of Plant Growth Parameters
2.4. Measurement of Physiological Parameters
2.5. Measurement of Biochemical Parameters
2.6. Measurement of Chlorophyll and Carotenoids Contents
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Morphological Traits
3.2. Biomass Distribution
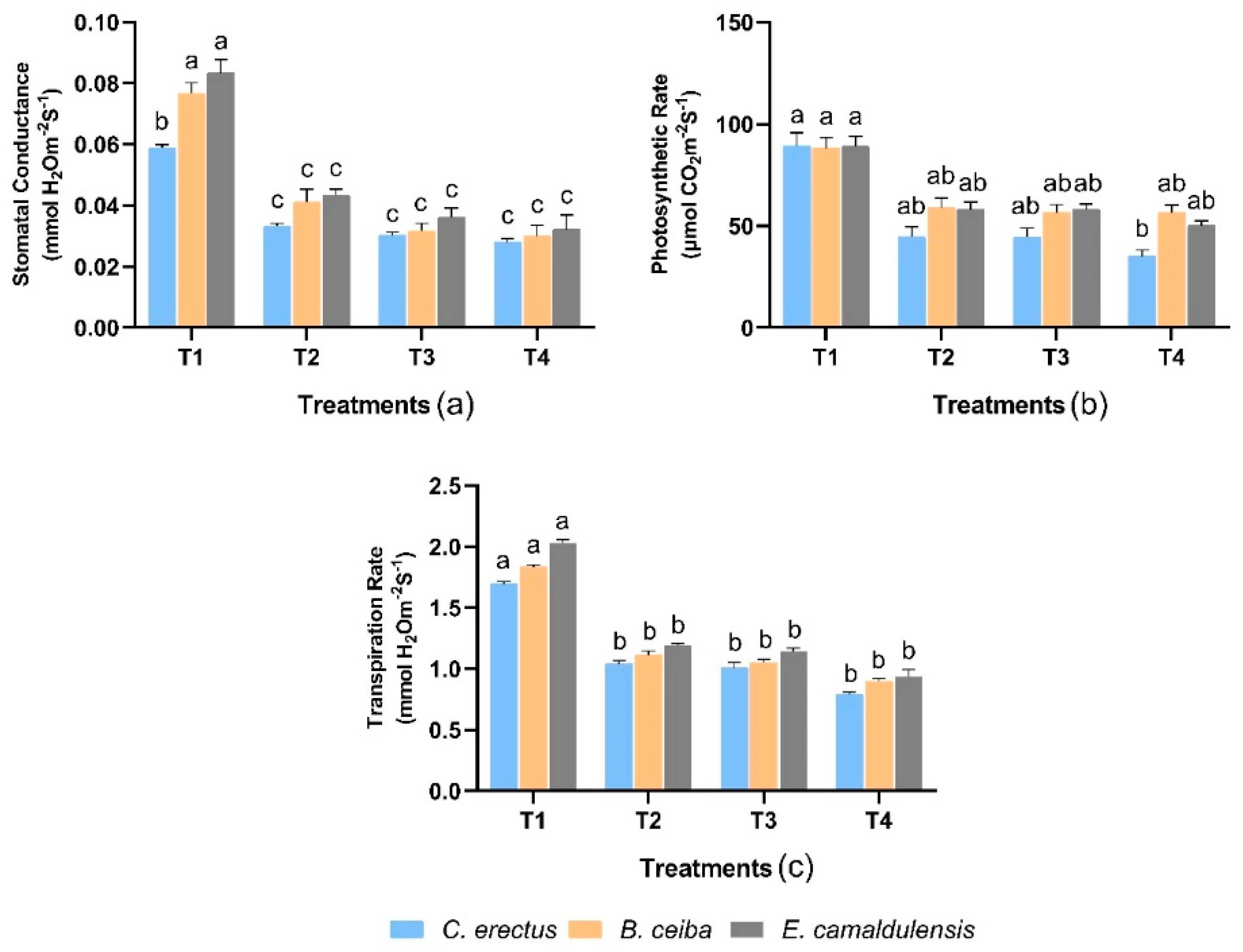
3.3. Physiological Traits
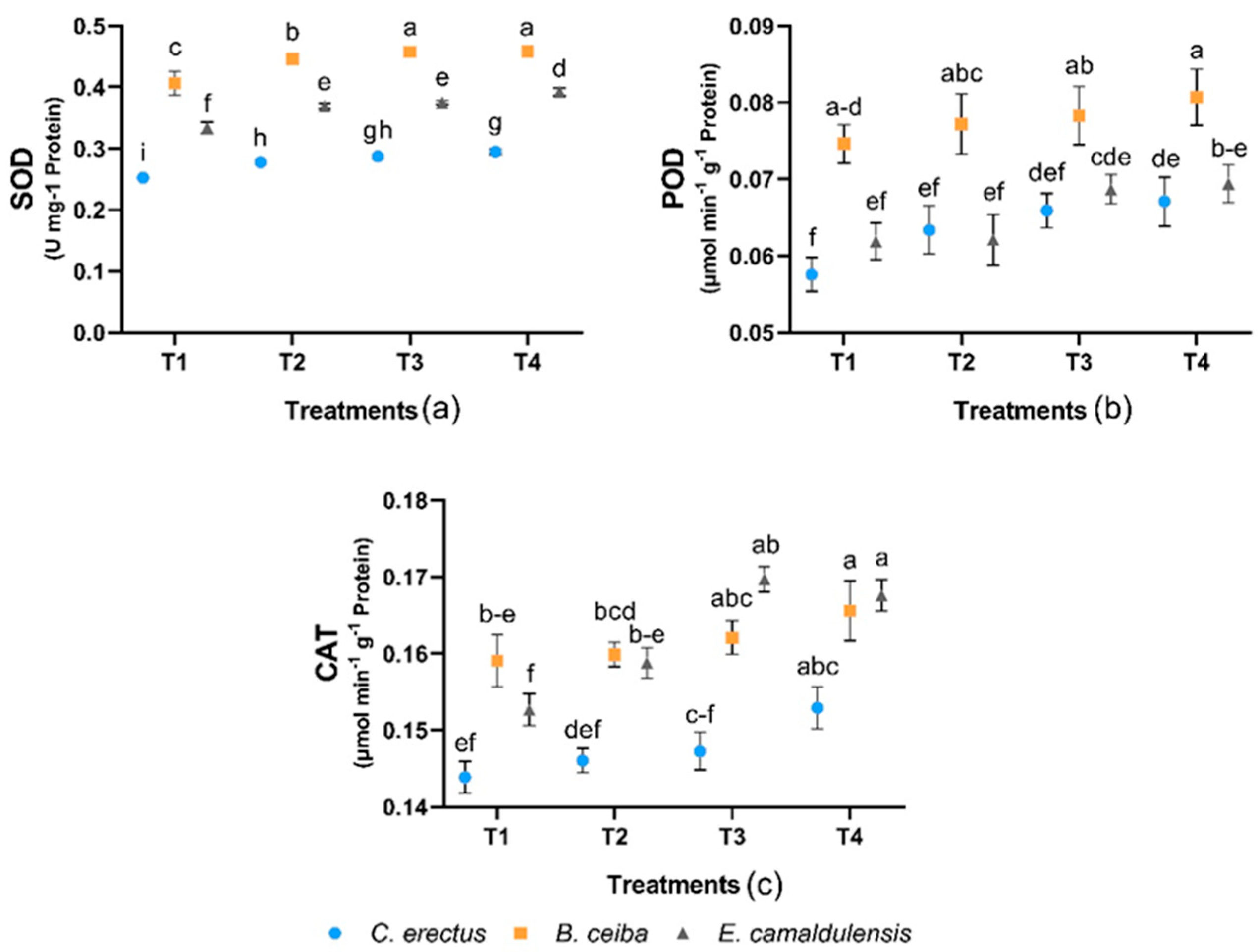
3.4. Enzyme Activities of Antioxidant Systems
3.5. Chlorophyll Content
3.6. Principal Component Analysis of Plant Growth Parameters, Plant Physiology and Plant Biochemical Contents
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Craven, D.; Gulamhussein, S.; Berlyn, G. Physiological and anatomical responses of Acacia koa (Gray) seedlings to varying light and drought conditions. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2010, 69, 205–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozlowski, T.T.; Kramer, P.J.; Pallardy, S.G. The Physiological Ecology of Woody Plant; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Shukla, S.; Sharma, R.; Sahu, M. Research article dust pollution affect morphophysiological traits of plant Mangifera indica Linn. Int. J. Bot. 2019, 15, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hess-Kosa, K. Indoor Air Quality: Sampling Methodologies; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Sett, R. Responses in plants exposed to dust pollution. Hortic. Int. J. 2017, 1, 53–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Areington, C.A.; Varghese, B.; Ramdhani, S. An assessment of morphological, physiological and biochemical biomarkers of industrial air pollution in the leaves of Brachylaena discolor. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2015, 226, 291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, H.; Yadav, M.; Kumar, N.; Kumar, A.; Kumar, M. Assessing adaptation and mitigation potential of roadside trees under the influence of vehicular emissions: A case study of Grevillea robusta and Mangifera indica planted in an urban city of India. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0227380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, K.; Amin, N.; Ahmad, I.; Shah, S.; Hussain, K. Dust particles induce stress, reduce various photosynthetic pigments and their derivatives in Ficus benjamina: A landscape plant. Int. J. Agric. Biol. 2017, 19, 1469–1474. [Google Scholar]
- Sharifi, M.R.; Gibson, A.C.; Rundel, P.W. Surface dust impacts on gas exchange in Mojave Desert shrubs. J. Appl. Ecol. 1997, 34, 837–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farooq, T.H.; Yan, W.; Chen, X.; Shakoor, A.; Rashid, M.H.U.; Gilani, M.M.; He, Z.; Wu, P. Dynamics of canopy development of Cunninghamia lanceolata mid-age plantation in relation to foliar nitrogen and soil quality influenced by stand density. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2020, 24, e01209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Singh, P.; Mishra, R.; Singh, M. Leaf dust accumulation and its impact on chlorophyll content of Azadirachta indica and Bauhinia variegata developing in the proximity of jaypee cement plant, Rewa (Mp), India. Int. J. Biol. Innov. 2021, 3, 173–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nawaz, M.F.; Rashid, M.H.U.; Arif, M.Z.; Sabir, M.A.; Farooq, T.H.; Gul, S.; Gautam, N.P. Ecophysiological response of Eucalyptus camaldulensis to dust and lead pollution. N. Z. J. For. Sci. 2021, 51, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilbert, O. An alkaline dust effect on epiphytic lichens. Lichenologist 1976, 8, 173–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, D.; Everett, K. Road dust and its environmental impact on Alaskan taiga and tundra. Arct. Alp. Res. 1987, 19, 479–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaghate, D.; Hasan, M. Ambient lead levels in urban areas. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 1999, 62, 403–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rai, P.K. Impacts of particulate matter pollution on plants: Implications for environmental biomonitoring. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2016, 129, 120–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, B.; Sharma, S.; Bhardwaj, S. Plant-pollutant interactions with a special mention of dust accumulation by plants—A review. Nat. Environ. Pollut. Technol. 2017, 16, 375–384. [Google Scholar]
- Escobedo, F.J.; Wagner, J.E.; Nowak, D.J.; De la Maza, C.L.; Rodriguez, M.; Crane, D.E. Analyzing the cost effectiveness of Santiago, Chile’s policy of using urban forests to improve air quality. J. Environ. Manag. 2008, 86, 148–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, I.; Jabeen, B.; Nawaz, M.F.; Asif, M.; Rashid, M.H.U.; Hussain, M.; Farooq, T.H.; Ahmed, S.; Rafiq, M. Influence of salinity on the morphological behavior and ionic response of different commercially important bamboo species. Fresenius Environ. Bull. 2022, 31, 668–676. [Google Scholar]
- Bashir, M.; Uzair, M.; Chaudhry, B.A. A review of phytochemical and biological studies on Conocarpus erectus (Combretaceae). Pak. J. Pharm. Res. 2015, 1, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singare, P.U.; Talpade, M.S. Physiological responses of some plant species as a bio-indicator of roadside automobile pollution stress using the air pollution tolerance index approach. Int. J. Plant Res. 2013, 3, 9–16. [Google Scholar]
- Raina, A.K.; Rathore, V.; Sharma, A. Effect of stone crusher dust on leaves of Melia azedarach Linn. and Dalbergia sissoo Roxb. in Jammu (J&K). Nat. Environ. Pollut. Technol. 2008, 7, 279. [Google Scholar]
- Alici, E.H.; Arabaci, G. Determination of SOD, POD, PPO and CAT enzyme activities in Rumex obtusifolius L. Annu. Res. Rev. Biol. 2016, 11, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, L.; Ma, K.; Zhang, S.; Lin, L.; Qu, L. Urban dust load impact on gas-exchange parameters and growth of Sophora japonica L. seedlings. Plant Soil Environ. 2015, 61, 309–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaturvedi, R.; Prasad, S.; Rana, S.; Obaidullah, S.; Pandey, V.; Singh, H. Effect of dust load on the leaf attributes of the tree species growing along the roadside. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2013, 185, 383–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomar, D.; Khan, A.A.; Ahmad, G. Response of potato plants to foliar application of cement dust. Trop. Plant Res. 2018, 5, 41–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javanmard, Z.; Tabari Kouchaksaraei, M.; Bahrami, H.; Hosseini, S.; Modarres Sanavi, S.; Struve, D.; Ammere, C. Soil dust effects on morphological, physiological and biochemical responses of four tree species of semiarid regions. Eur. J. For. Res. 2020, 139, 333–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, M.; Ghouse, A. Effects of coal-smoke pollutants from different sources on the growth, chlorophyll content, stem anatomy and cuticular traits of Euphorbia hirta L. Environ. Pollut. 1987, 47, 221–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, M.; Mahmooduzzafar; Nighat, F.; Khan, P.R. Photosynthetic, metabolic and growth responses of Triumfetta rhomboidea to coal-smoke pollution at different stages of plant ontogeny. J. Plant Interact. 2010, 5, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swami, A. Impact of automobile induced air pollution on roadside vegetation: A review. Essence-Int. J. Environ. Rehabil. Conserv. 2018, 9, 101–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Taani, A.A.; Nazzal, Y.; Howari, F.M. Assessment of heavy metals in roadside dust along the Abu Dhabi–Al Ain National Highway, UAE. Environ. Earth Sci. 2019, 78, 411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leghari, S.K.; Zaid, M.A.; Sarangzai, A.M.; Faheem, M.; Shawani, G.R. Effect of road side dust pollution on the growth and total chlorophyll contents in Vitis vinifera L.(grape). Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2014, 13, 1237–1242. [Google Scholar]
- Rai, P.K.; Singh, M.M. Lantana camara invasion in urban forests of an Indo–Burma hotspot region and its ecosustainable management implication through biomonitoring of particulate matter. J. Asia-Pac. Biodivers. 2015, 8, 375–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, K.; Ahmad, I.; Ara, G. Impact assessment of leaf pigments in selected landscape plants exposed to roadside dust. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 23055–23073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlík, M.; Pavlíková, D.; Zemanová, V.; Hnilička, F.; Urbanová, V.; Száková, J. Trace elements present in airborne particulate matter—Stressors of plant metabolism. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2012, 79, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rai, A.; Kulshreshtha, K.; Srivastava, P.; Mohanty, C. Leaf surface structure alterations due to particulate pollution in some common plants. Environmentalist 2010, 30, 18–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Zhang, X.; He, W.; Yan, X.; Yu, Q.; Xu, C.; Jiang, Q.O.; Huang, H.; Wang, R. Response of plant reflectance spectrum to simulated dust deposition and its estimation model. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 15803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siqueira-Silva, A.I.; Pereira, E.G.; Modolo, L.V.; Lemos-Filho, J.P.; Paiva, E.A.S. Impact of cement dust pollution on Cedrela fissilis Vell. (Meliaceae): A potential bioindicator species. Chemosphere 2016, 158, 56–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan-Yi, W.; Jia, H.; Jian-Ying, G.; Cheng-Jie, W.; Ming-Jiu, W. Coal dust reduce the rate of root growth and photosynthesis of five plant species in inner Mongolian grassland. J. Residuals Sci. Technol. 2016, 13, S63–S73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Moradi, A.; Taheri Abkenar, K.; Afshar Mohammadian, M.; Shabanian, N. Effects of dust on forest tree health in Zagros oak forests. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2017, 189, 549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, K.; Chaturvedi, S.N.; Chauhan, S. Plant Biodiversity, Microbial Interaction and Environmental Biology; Pointer Publishers: Jaipur, India, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Hirano, T.; Kiyota, M.; Aiga, I. Physical effects of dust on leaf physiology of cucumber and kidney bean plants. Environ. Pollut. 1995, 89, 255–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, L.-J.; Zhang, J.-H.; Gomez, H.; Murugan, R.; Hong, X.; Xu, D.; Jiang, F.; Peng, Z.Y. Reactive oxygen species-induced lipid peroxidation in apoptosis, autophagy, and ferroptosis. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2019, 2019, 5080843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; He, T.; Farrar, S.; Ji, L.; Liu, T.; Ma, X. Antioxidants maintain cellular redox homeostasis by elimination of reactive oxygen species. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2017, 44, 532–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Branicky, R.; Noë, A.; Hekimi, S. Superoxide dismutases: Dual roles in controlling ROS damage and regulating ROS signaling. J. Cell Biol. 2018, 217, 1915–1928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hendijani, A.K. Regulation of Pro-Longevity ROS by ROS-Handling Enzymes in C. elegans; McGill University: Montreal, QC, Canada, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Sakthi, V.; Andal, N.M.; Rengaraj, S.; Sillanpää, M. Removal of Pb (II) ions from aqueous solutions using Bombax ceiba saw dust activated carbon. Desalin. Water Treat. 2010, 16, 262–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Yu, H.; Yang, M.; Kong, D.; Zhang, Y. Effect of drought stress on lipid peroxidation, osmotic adjustment and antioxidant enzyme activity of leaves and roots of Lycium ruthenicum Murr. seedling. J. Plant Physiol. 2018, 65, 244–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siedlecka, A.; Krupa, Z. Functions of enzymes in heavy metal treated plants. In Physiology and Biochemistry of Metal Toxicity and Tolerance in Plants; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2002; pp. 303–324. [Google Scholar]
- Bela, K.; Horváth, E.; Gallé, Á.; Szabados, L.; Tari, I.; Csiszár, J. Plant glutathione peroxidases: Emerging role of the antioxidant enzymes in plant development and stress responses. J. Plant Physiol. 2015, 176, 192–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horton, P.; Ruban, A. Molecular design of the photosystem II light-harvesting antenna: Photosynthesis and photoprotection. J. Exp. Bot. 2005, 56, 365–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, M.; Zhao, Y.-Q.; Zhang, Z.-W.; Chen, Y.-E.; Ding, C.-B.; Yuan, S. Light regulates transcription of chlorophyll biosynthetic genes during chloroplast biogenesis. Crit. Rev. Plant Sci. 2017, 36, 35–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prusty, B.; Mishra, P.; Azeez, P. Dust accumulation and leaf pigment content in vegetation near the national highway at Sambalpur, Orissa, India. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2005, 60, 228–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Parameters | Sand | Silt | Clay | pH | EC | TSS | Nitrogen | Phosphorous | Potassium | Organic Matter |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (%) | (%) | (%) | (dSm−1) | (mg/kg) | (%) | (mg/kg) | (mg/kg) | (%) | ||
| 0–15 cm | 40 | 45 | 15 | 8.0 | 1.7 | 1176 | 0.1 | 3.9 | 280 | 1.54 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nawaz, M.F.; Rashid, M.H.U.; Saeed-Ur-Rehman, M.; Gul, S.; Farooq, T.H.; Sabir, M.A.; Iftikhar, J.; Abdelsalam, N.R.; Dessoky, E.S.; Alotaibi, S.S. Effect of Dust Types on the Eco-Physiological Response of Three Tree Species Seedlings: Eucalyptus camaldulensis, Conocarpus erectus and Bombax ceiba. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 1010. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13071010
Nawaz MF, Rashid MHU, Saeed-Ur-Rehman M, Gul S, Farooq TH, Sabir MA, Iftikhar J, Abdelsalam NR, Dessoky ES, Alotaibi SS. Effect of Dust Types on the Eco-Physiological Response of Three Tree Species Seedlings: Eucalyptus camaldulensis, Conocarpus erectus and Bombax ceiba. Atmosphere. 2022; 13(7):1010. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13071010
Chicago/Turabian StyleNawaz, Muhammad Farrakh, Muhammad Haroon U. Rashid, Muhammad Saeed-Ur-Rehman, Sadaf Gul, Taimoor Hassan Farooq, Muhammad Azeem Sabir, Junaid Iftikhar, Nader R. Abdelsalam, Eldessoky S. Dessoky, and Saqer S. Alotaibi. 2022. "Effect of Dust Types on the Eco-Physiological Response of Three Tree Species Seedlings: Eucalyptus camaldulensis, Conocarpus erectus and Bombax ceiba" Atmosphere 13, no. 7: 1010. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13071010
APA StyleNawaz, M. F., Rashid, M. H. U., Saeed-Ur-Rehman, M., Gul, S., Farooq, T. H., Sabir, M. A., Iftikhar, J., Abdelsalam, N. R., Dessoky, E. S., & Alotaibi, S. S. (2022). Effect of Dust Types on the Eco-Physiological Response of Three Tree Species Seedlings: Eucalyptus camaldulensis, Conocarpus erectus and Bombax ceiba. Atmosphere, 13(7), 1010. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13071010










