Abstract
Sea breezes are frequently observed in the South Carolina/Georgia region of the Southeastern United States (SEUS) and can reach upwards of 150km inland. This region is unique among the places frequently affected by sea breeze due to it being a continental location with relatively flat topography. The thermal gradient between land and water environments is a factor in introducing the sea breeze, but its role in the inland extent of sea breeze propagation isn’t as well known. We investigate the role of the thermal gradient in previously catalogued sea breeze events observed at the Savannah River Site (SRS) by taking differences of temperature measurements at inland and coastal weather stations for the days that the events occurred. We saw that the temperature differences for those days were much higher than in the non-sea breeze days during the mornings and afternoon. Numerical models were also used to conduct a sensitivity study on a sea breeze case, using simple modifications of the temperature gradient. We found that while the modifications did not stop the generation of a sea breeze circulation, the extent of the inland propagation was dependent on the magnitude of the thermal gradient.
1. Introduction
The mesoscale sea breeze is a coastal atmospheric phenomenon that is frequently observed in the Southeastern U.S. (SEUS; [1,2,3]). Sea breezes are primarily generated due to differing sensible heating rates between land and the water. This generates a gravity current that travels from the sea to the land, resulting in landward migration of the marine boundary layer, known as a “sea breeze front”. Later in the afternoon, the heating drivers of the sea breeze fronts are cut off from the original ocean circulation and the front migrates as a transient gravity current [4,5].
There are a multitude of factors attributed to the sea breeze circulation. For a sea breeze to occur, the land region must be significantly warmer to induce cross-shore winds from the generally along-shore flow from the coast. This is theorized to occur because the warmer onshore temperatures lead to rising motion, with the displaced continental air being replaced by air from the marine layer. When the continental air rises above the marine layer, it is often carried towards the water again, creating a “return flow” and, ultimately, a sea breeze circulation cycle [5]. Surface friction and terrain complexity impedes the near-surface flow which acts against the sea breeze circulation [6,7]. In the mid-latitudes, the Coriolis force is also a limiting factor in the inland extent of a sea breeze, as it redirects onshore flow to a direction that is parallel to the coast [8].
The prevalence of sea breezes varies across the SEUS due to surface moisture, land type, shape of the coastline [9], and some effects from urbanization [10]. The Savannah River region of Georgia and South Carolina (Figure 1) is unique in this sector of the country in that sea breezes frequently migrate hundreds of kilometers inland [11], permitted by relatively flat topography [12] blanketing much of the region southeast of the Appalachian Mountains [13]. This region stands out in contrast to other continental regions such as the California coast, which also frequently experiences sea breezes, but whose inland advection is limited by mountainous topography [14,15]. However, not every sea breeze in the Savannah River region that is initiated at the coast propagates that far inland, despite the topography favoring it. The inland extent of the sea breeze has been considered to be a function of many atmospheric factors (e.g., wind speed, vertical potential temperature gradient; [16]) but the magnitude of the horizontal thermal gradient over the land area has not been studied with regard to the inland propagation of some sea breeze fronts. The land–sea thermal gradient is crucial in the genesis of sea breeze events at the coast, furthermore it is hypothesized by this study that the intensity and speed of continued inland propagation beyond the initial genesis is fueled by the coastal–inland thermal gradient over the land.
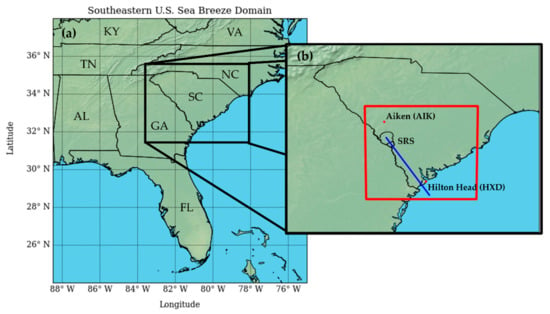
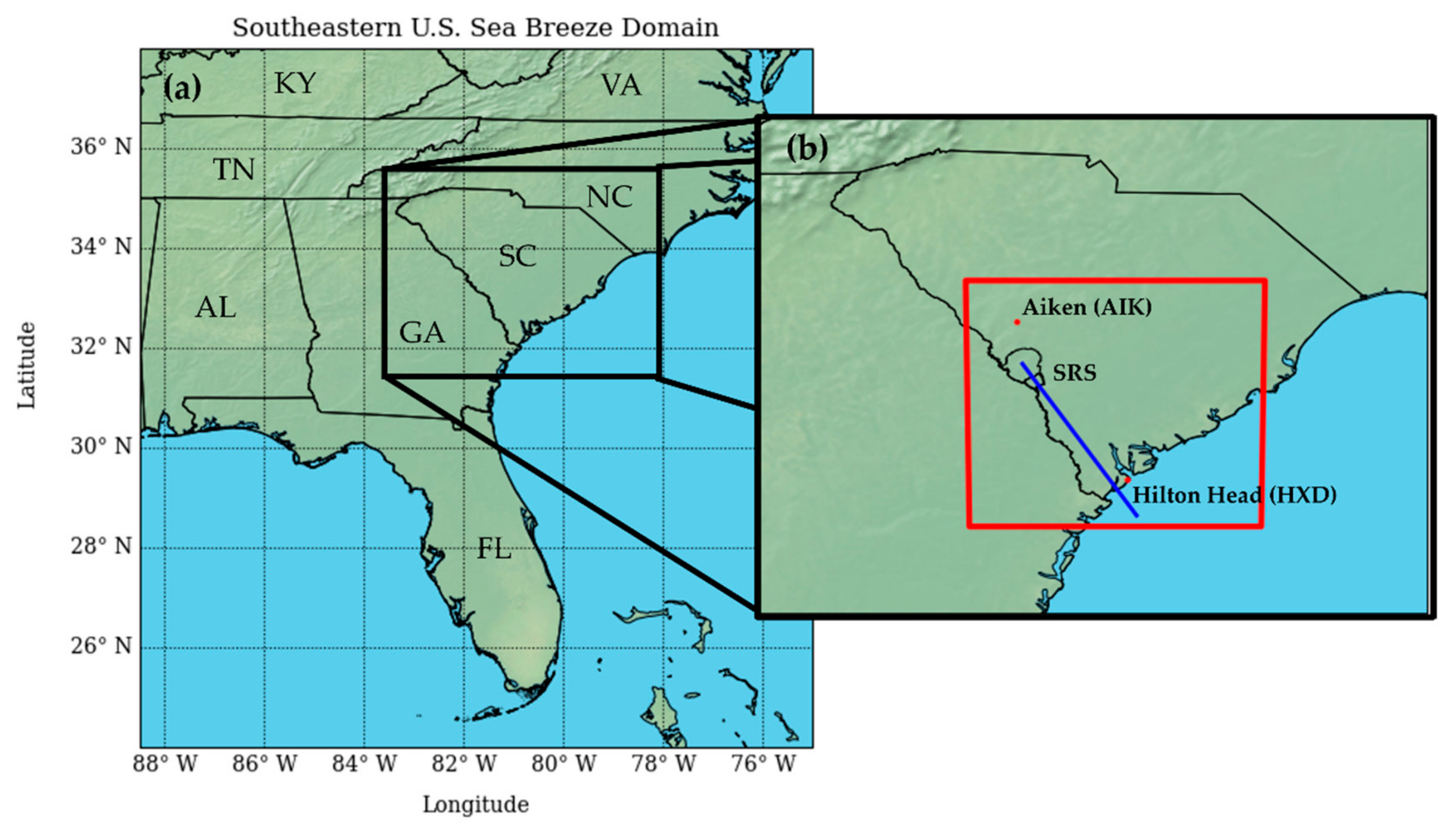
Figure 1.
(a) A view of the southeastern U.S. (SEUS) with each U.S. state labelled with its two-letter abbreviation. (b) A zoomed-in view of the Georgia/South Carolina region that frequently experiences sea breezes in the SEUS. The region on the South Carolina/Georgia border is the Savannah River Site (SRS). The red outline denotes the domain used for the WRF model in this study, with analyses featuring cross-sections along the blue line. The airport weather stations used for the observational analysis are marked with red circles and labelled on the map.
The goal of this study is to examine the horizontal thermal gradient from inland to coastal regions in the SEUS and to determine if it has influence on how far inland a sea breeze propagates in the Savannah River region. This is accomplished through a two-phased approach using observations and numerical models.
The first phase quantifies the seasonality of observed temperature differences between coastal and inland regions during sea breeze events that were confirmed to reach South Carolina’s Savannah River Site (SRS) by Viner et al. [13] (with the addition of 2021 sea breezes from the same team using the same methods). This phase of the study also examines other atmospheric quantities (moisture content and cloud cover), answering why the thermal gradients exist, or what causes them not to exist in certain cases.
The modeling phase introduces a more dynamic spatial approach over a singular case study of a previously observed sea breeze event. Several sensitivity simulations are conducted using the Weather Research & Forecasting (WRF) model [17], where different simple thermal gradients are applied to a real sea breeze case to determine whether changes to the temperature gradient over a large spatial extent can affect the intensity and the propagation speed of a sea breeze front.
2. Methods
The regional focus for this research is the area surrounding the Savannah River in the states of Georgia and South Carolina in the SEUS (Figure 1b). The area has relatively flat topography as it spans hundreds of kilometers southeast of the Appalachian Mountains. Observations are analyzed from the automated surface observing stations (ASOS) located at the Hilton Head Island Airport (HXD) and at the inland Aiken Regional Airport (AIK), both located in the state of South Carolina. The airports are around 185 km apart, which is around the distance that the sea breeze cases were confirmed to travel inland. The coastal HXD airport has an elevation of 5.9 m above sea level, whereas the inland AIK airport has an elevation of 161 m above sea level, with a mostly gradual slope of terrain in between the two locations featuring some occasional hills but no major topographical barriers. The location at SRS used for the model study has an elevation of 95 m above sea level, and there is also a mostly gradual increase in elevation between it and the coastal HXD airport.
2.1. Observations
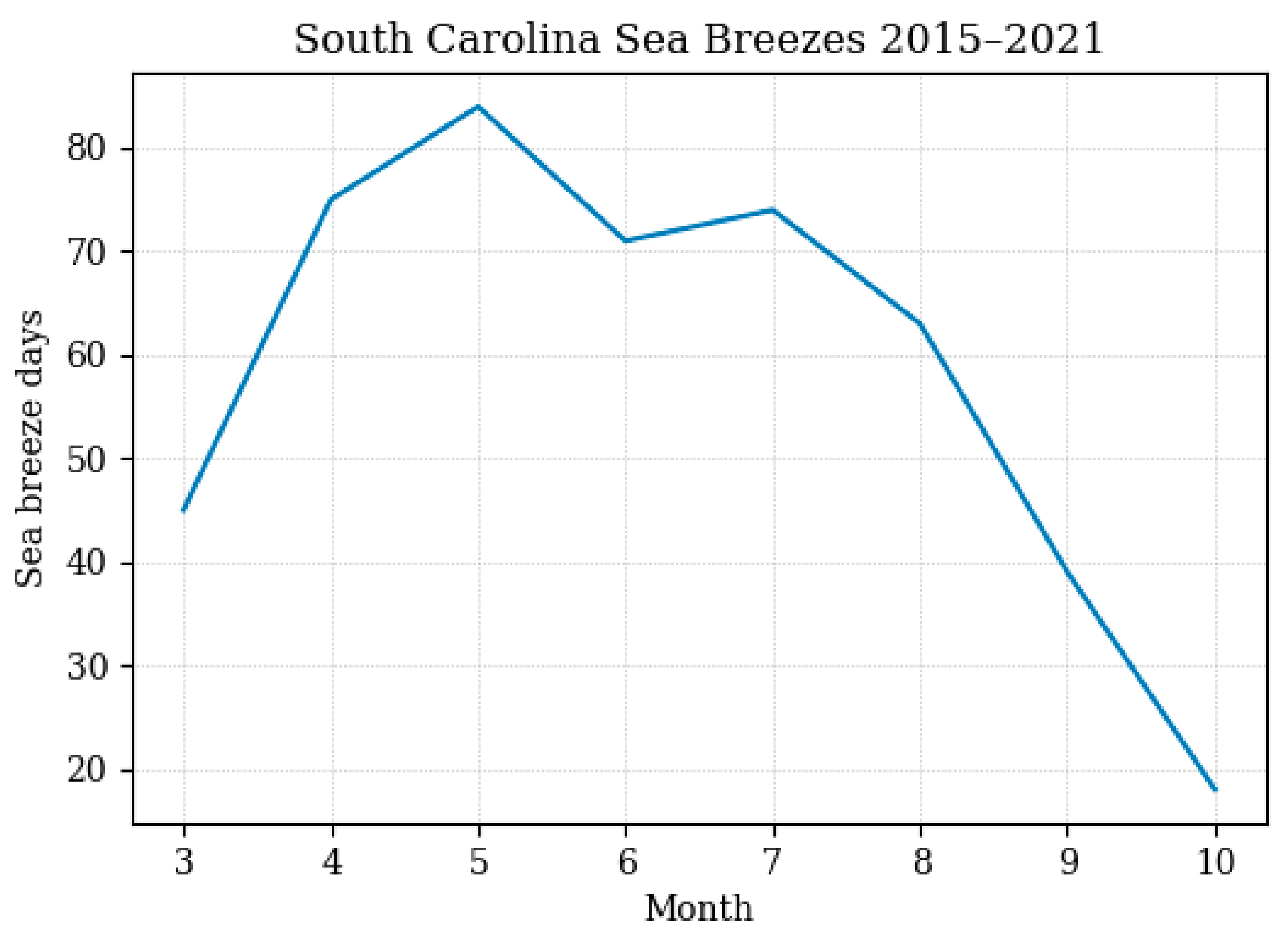
Using the methodology presented in Viner et al. [13], inland sea breeze events in South Carolina were categorized through dual verification of meteorological measurements and ceilometer backscatter [18] at the Savannah River Site (SRS, Figure 1b) and reflectivity from nearby radar stations. While the methodology doesn’t guarantee all sea breezes were verified and recorded, a total of 470 events ensures that there is a robust set of sea breeze events to conduct analyses and build associations. A majority of inland SEUS sea breezes occur from spring to fall [19], so all the observed sea breeze events are recorded through the months of March–October, in the years 2015–2021. Within this timeframe, the number of verified sea breezes is greatest in the months of April and May as seen in Figure 2.
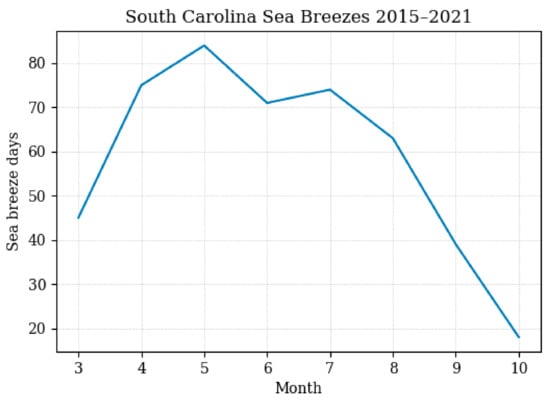
Figure 2.
Frequency of verified sea breeze events by month in the period of 2015–2021.
The thermal gradients for this study are approximated by taking the temperature difference between an inland weather station (AIK; Figure 1b) and a coastal weather station (HXD; Figure 1b). The gradient is quantified as the average hourly values for temperature at HXD subtracted from the average hourly values at AIK. For clarity, a positive value represents a warmer inland temperature while a negative value indicates a warmer coastal temperature. Further analyses are performed on both dew point and cloud cover, which are both averaged by hour for the seven years of 2015–2021 and are compared for both the days flagged as sea breeze (SB) days and the non-sea breeze (NSB) days.
Cloud fraction is decoded from the cloud cover indicators given in the ASOS reports. Although the cloud cover is reported categorically, the nominal categories refer to a range of numerical values. The specific cloud fraction is not given in the reports, therefore, values were assigned to each cloud cover category per report, and those fractions assigned were averaged per hour as were the other variables. Specific numerical values are assigned to each category (Table 1).

Table 1.
The numerical cloud fraction values assigned to the ASOS sky cover values for the observed analysis.
2.2. WRF Model Setup
Five WRF simulations were conducted to simulate the 21–22 May 2019 sea breeze event that was detected at SRS [13]. Each simulation utilized one domain with 1000-m grid spacing and spanned a resolution of 250 × 250 grid points, which is depicted by the red polygon in Figure 1. The first simulation, which will be referred to as the “control” simulation, was provided boundary conditions by initial analysis (hour 0) output from the hourly-updated High-Resolution Rapid Refresh (HRRR) operational weather model [20], which has three-kilometer grid spacing and spans the continental United States. The data produced by pre-processing were left unchanged for the control simulation, but simple horizontal temperature gradients were added for four additional sensitivity WRF simulations. The options used to configure WRF for this study are specified in Table 2.

Table 2.
The model parameterizations used in the WRF configuration for all the simulations done in this study.
Three different error metrics are used to determine how accurate the WRF control simulation represents the inland extent and timing of the sea breeze. Mean bias error (MBE) is used to determine if there are any sign biases in the data:
where P and O represent the predicted and observed values, respectively, and n is the number of values in the set. The result is either a positive or negative value of error in the units of the examined quantity. Root mean squared error (RMSE) is used to determine the magnitude of the error:
where the result is a positive magnitude of error in the units of the variable examined. Pearson’s correlation coefficient (PCC) is also used to determine the linear relationship between the predicted and observed values to determine if the trends in the data are consistent:
where the values represent the mean of predicted and observed values, respectively; the result is a unitless value between −1 and 1, where 1 is a perfect correlation, and −1 is a perfect inverse correlation. All three error metrics are used to examine temperature, dew point temperature (moisture), and both the zonal and meridional components of the horizonal wind.
In addition to the control run, four sensitivity simulations are analyzed utilizing four different temperature modification schemes to the initial meteorology produced by the initial pre-processing of the HRRR data. Although many sensitivity studies are conducted using the “idealized” configuration of WRF [27], these are conducted with the “real” configuration of WRF and analyses how changes in temperature gradient will affect the inland propagation of a sea breeze amongst an active mesoscale environment [28].
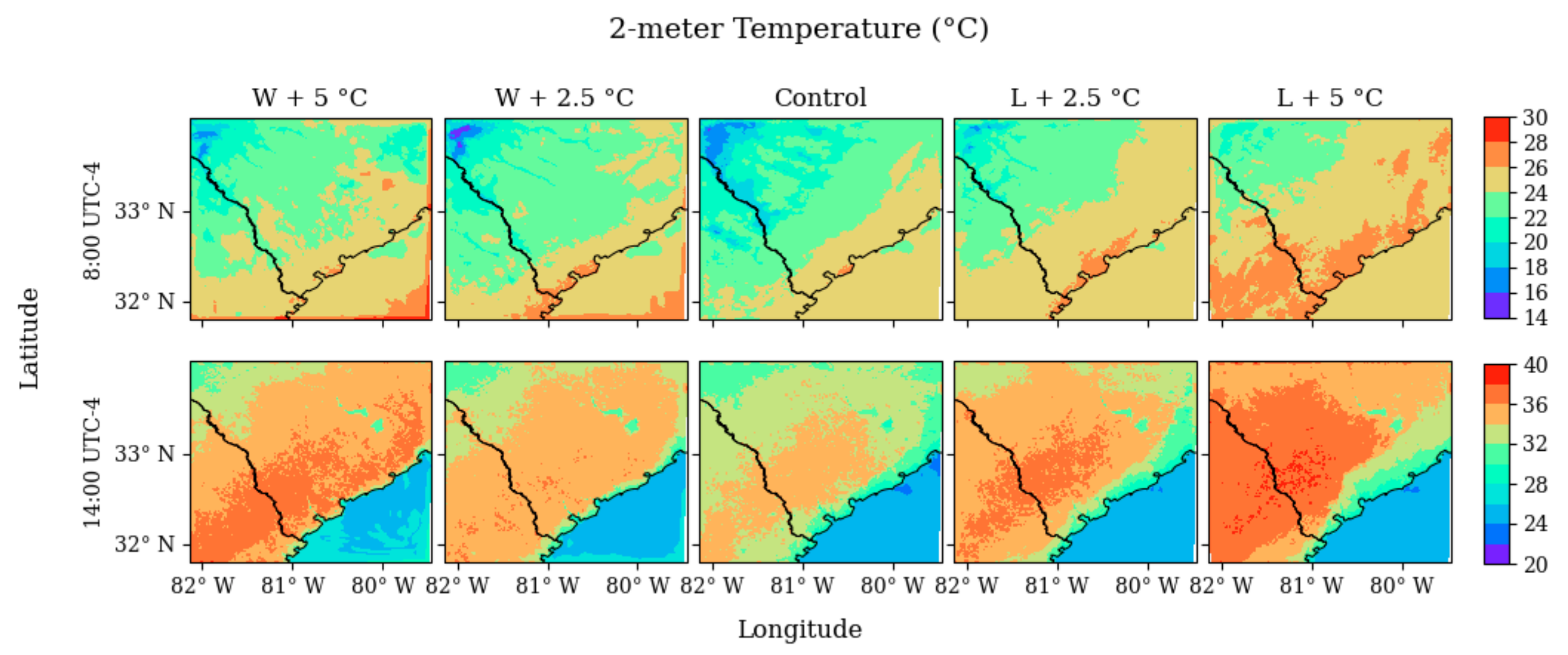
All four modification schemes add a different simple horizontal temperature gradient to the initial meteorology spanning the most northwesterly point on the domain to the most southeasterly point on the domain over all times of the simulation and over every vertical level. The first two modifications incorporated temperature gradients that were hotter towards the most southeastern point in the domain. The factor for these simulations was 0.005 °C and 0.01 °C per grid point in both directions, meaning that the point in the northwest corner was 2.5 °C and 5 °C warmer respectively for both simulations. These are referred to as the L + 2.5 °C and L + 5 °C simulations in the results (‘L’ referring to the land being 2.5 °C and 5 °C warmer, respectively). The remaining two modification schemes incorporated gradients of the same magnitude, but applied towards the southeasterly point of the domain. These two modifications are referred to as the W + 2.5 °C and W + 5 °C simulations (‘W’ referring to the water being 2.5 °C and 5 °C warmer, respectively). All modification schemes were applied to every hourly file ingested into WRF. The temperature differences over the domain among the five different modification schemes are shown in Figure 3.
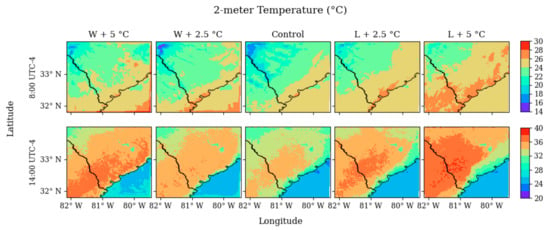
Figure 3.
WRF 2-m temperature output from 21 May 2019 at 08:00 local time (top) and at 14:00 local time (bottom) over each WRF domain modification scheme. Color tables are scaled for morning and afternoon temperature ranges, respectively.
While the temperature is modified for each sensitivity simulation, it’s important to keep variables consistent with each other. An important input variable that’s ingested into WRF is relative humidity, which is dependent on temperature and moisture content. The WRF pre-processed files accounted for specific humidity, so the saturation specific humidity for each grid point was re-calculated for each grid point. To accomplish this, the saturation vapor pressure is derived for each grid point using a simple formula derived by Huang [29]:
where T is temperature in degrees Celsius. The saturation vapor pressure is used to calculate saturation specific humidity (qs):
where P represents the pressure at the given point. Finally, relative humidity is calculated by taking the ratio of the original specific humidity to the newly calculated saturation specific humidity:
The WRF sensitivity output is analyzed through a cross-section from SRS to a point ~30 km offshore of Hilton Head Island, SC. Moisture content is quantified through dew point temperature, and the wind shift is represented by changes in the meridional component of the wind. These variables are the most important indicators of a sea breeze passage [13], and are averaged over the bottom 500 m of the atmosphere (above ground level) so that time can be used as a vertical axis in the plots.
3. Results
3.1. Observed Results
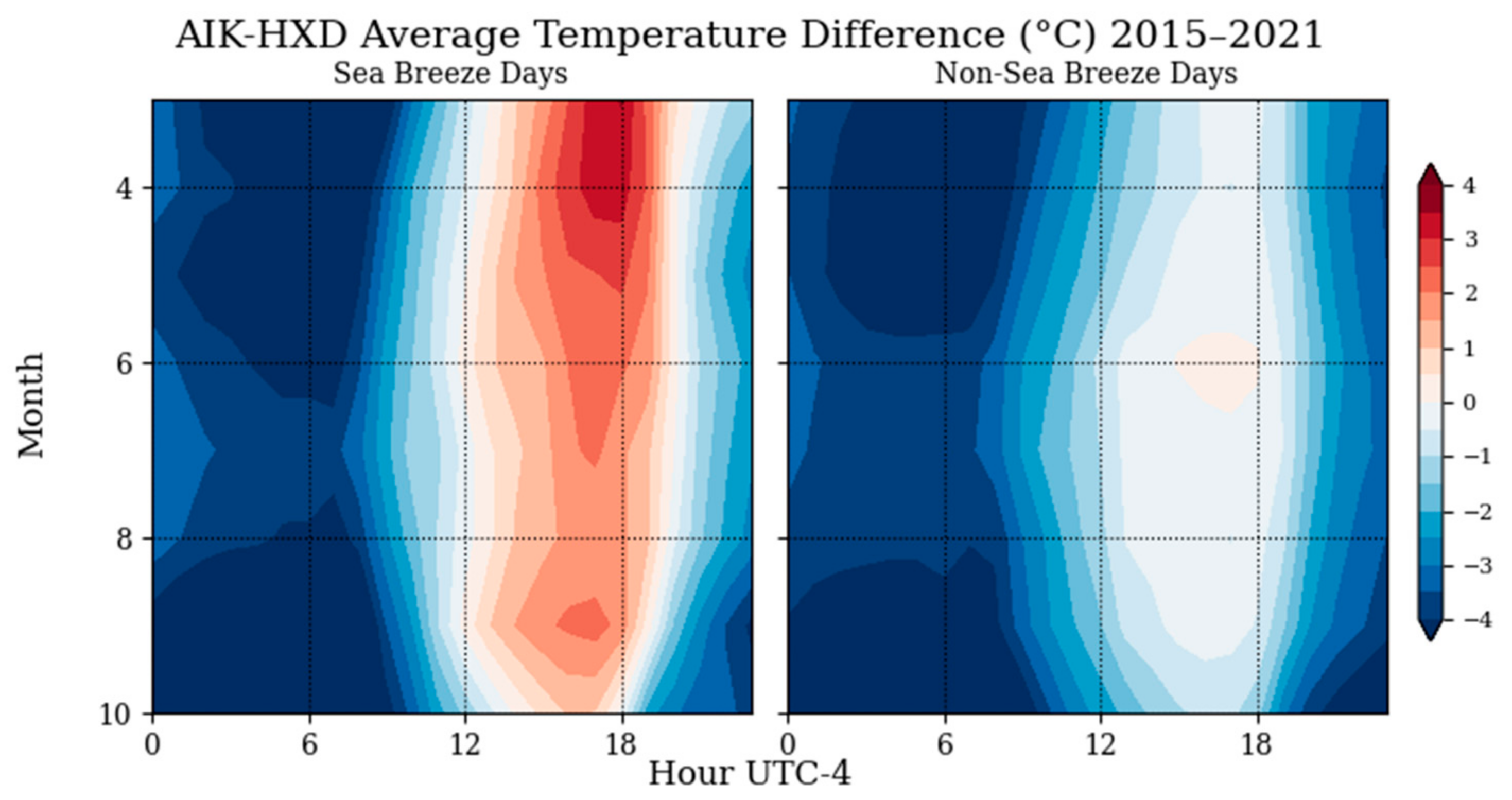
On the days where a sea breeze travels inland to SRS, Figure 4 shows that the temperature difference between the coastal and inland areas is higher in the afternoon-evening periods. The greatest differences are in the spring months of March and April, which is consistent with the higher inland sea breeze occurrence shown in Figure 2. On non-sea breeze days, there is almost no positive temperature difference between AIK and HXD throughout the morning and afternoon hours, except for a small one in the mid-afternoon in local time. It is important to note that the “non-sea breeze days” can include sea breeze events that did not reach as far inland and weren’t catalogued as sea breeze events at SRS [13]. Observed average temperature differences indicate that a thermal gradient is a requirement for sea breeze fronts to propagate inland.
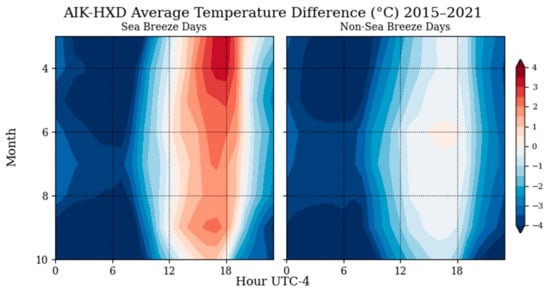
Figure 4.
Differences in average hourly temperature between an inland (Aiken) and a coastal (Hilton Head Island) weather station.
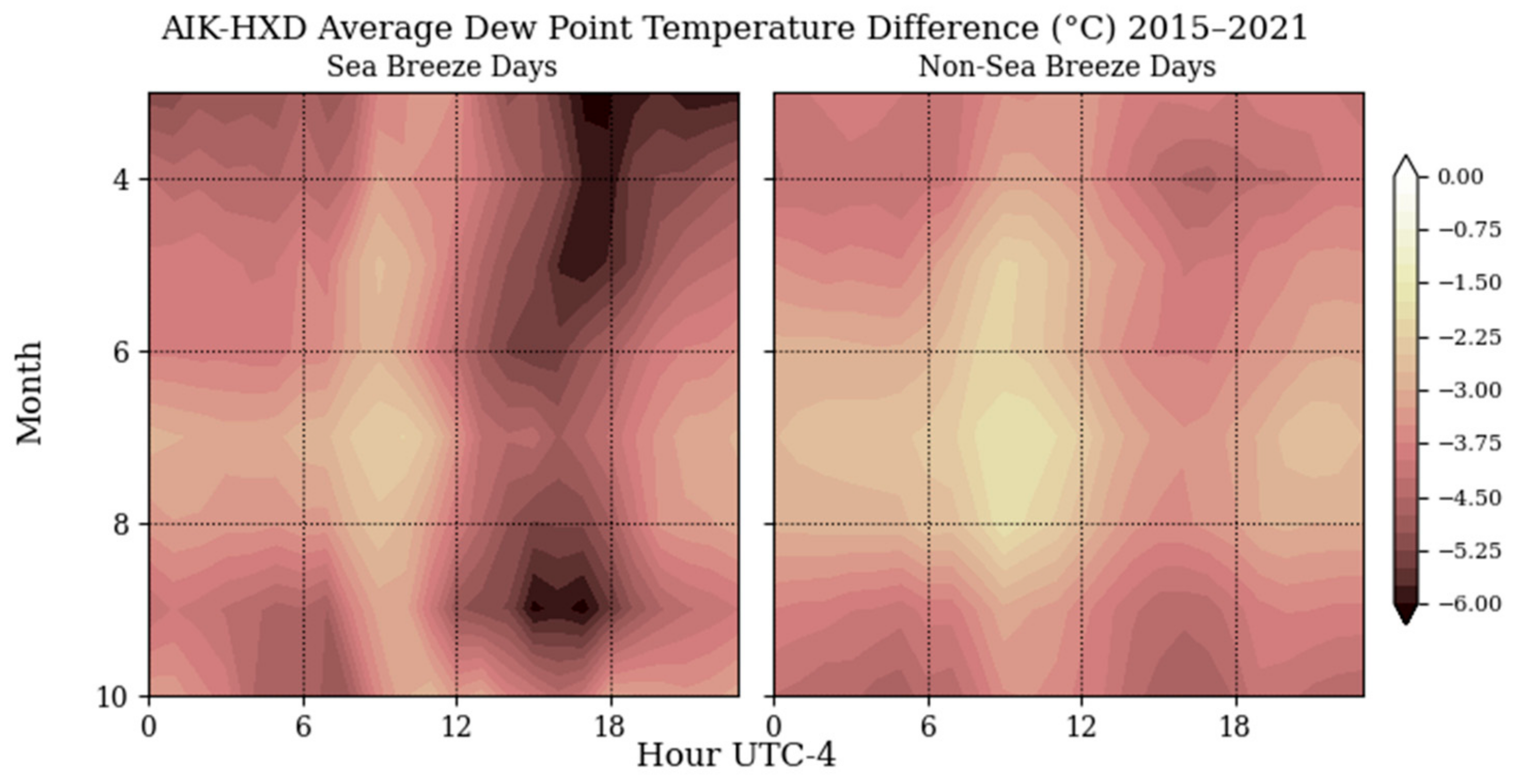
Figure 5 indicates a higher dew point difference in observed sea breeze days as well. The dew points in the coastal region of Hilton Head Island are generally higher than the inland region of Aiken. On days with inland sea breeze events, the dew point temperature difference in the morning hours from 6 to 12 local time is greater at AIK than as HDX by a few degrees. There is a much larger difference in dew points between AIK and HXD in the afternoon hours of 12 to 18 local time, which is when the largest temperature differences are seen as well. The differences reach their highest magnitudes in the afternoons of spring and early fall, which also aligns with the positive temperature differences. The air above the inland area tends to be drier after the genesis of the sea breeze front, just after the marine layer migrates onto the coast, which causes the larger difference in moisture content. The dew point differences between the two stations on sea breeze days are not as high in the summer months of July and August.
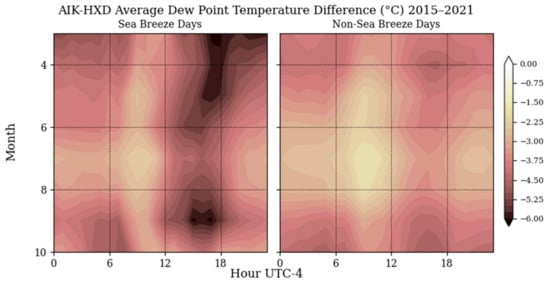
Figure 5.
Differences in average hourly dew point temperature between an inland (Aiken) and a coastal (Hilton Head Island) weather station.
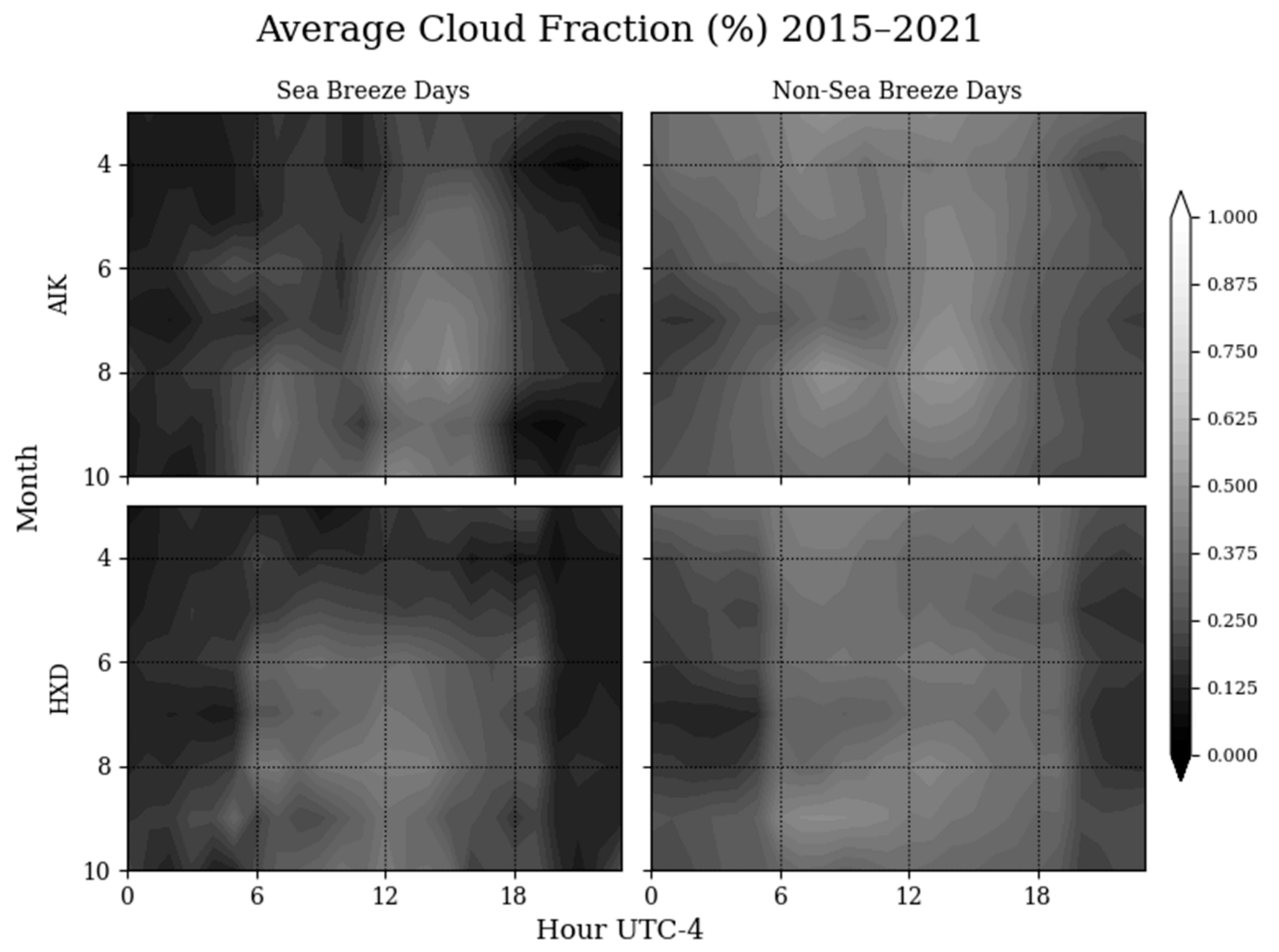
While the moisture content should play an important role in the generation of sea breezes, it is also important to examine cloud cover. Cloud cover for sea breeze days is noticeably less prevalent in the morning hours, especially over the land (Figure 6). This is important to note, because fewer clouds over land allows for more solar heating of the surface, which raises the temperature over the inland areas, thus inducing a higher temperature thermal gradient between the coastal and inland areas. Although it’s also less cloudy over the coastal region of Hilton Head, the climate could be moderated by the nearby Atlantic Ocean, which has a higher specific heat than the land, impeding the ability to induce a thermal gradient necessary for the genesis and inland advance of sea breeze fronts.
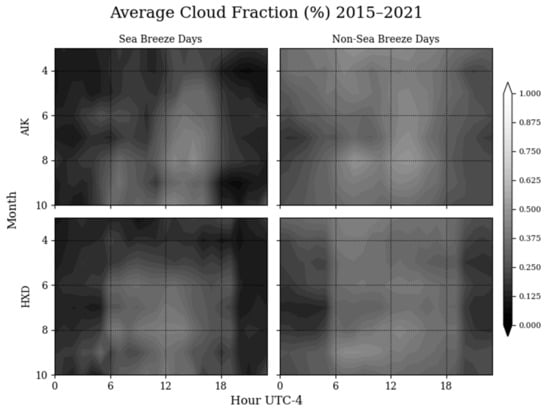
Figure 6.
Average cloud fraction by month and by hour for inland (Aiken) and coastal (Hilton Head) weather stations.
3.2. WRF Simulation Results
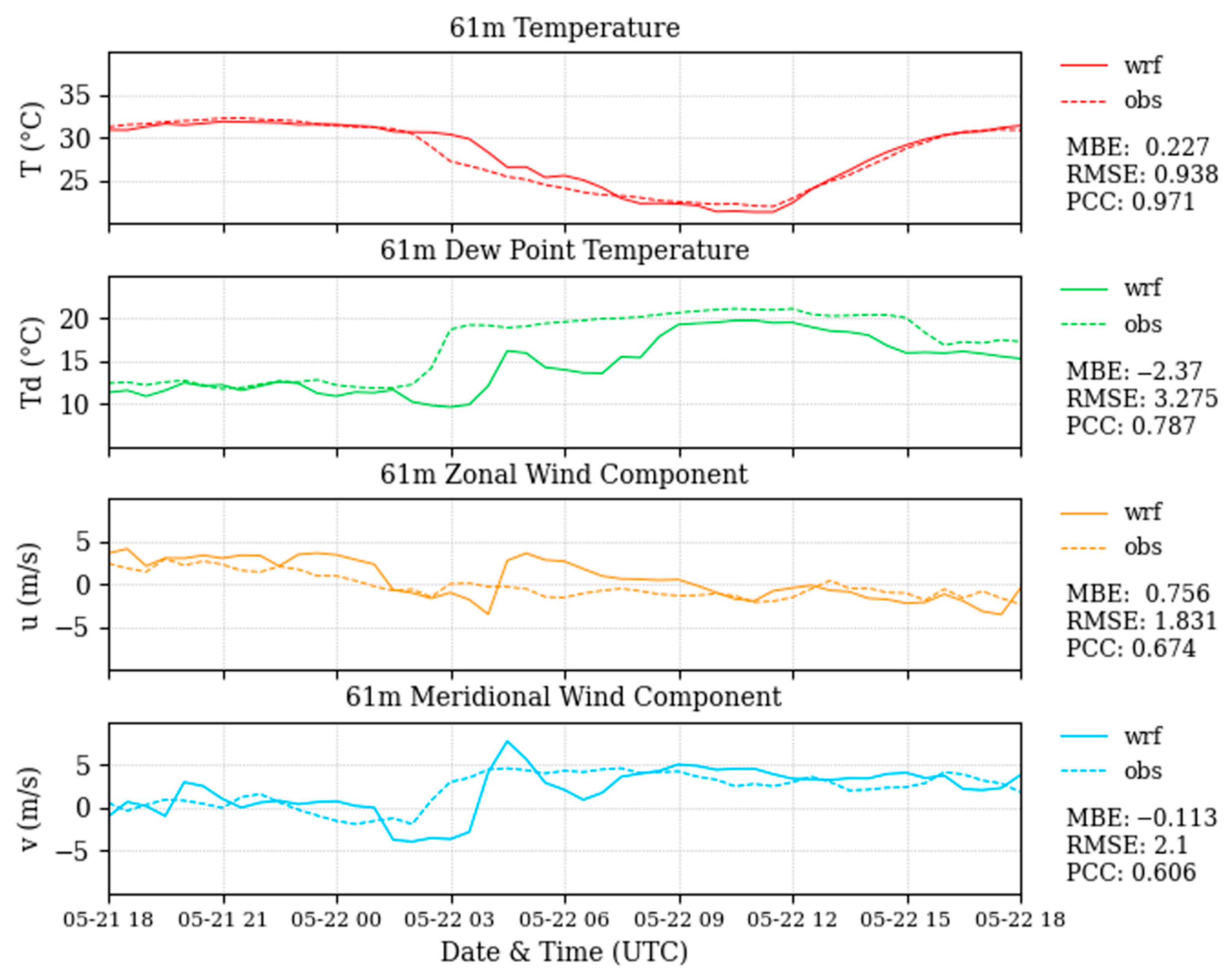
The control sea breeze simulation shows the generation of a sea breeze that begins 05/21 around noon local time (14 UTC), followed by the movement of the sea breeze front inland towards SRS that impacts the site before midnight local time (3 UTC). The model output underestimates the rise in dew points and overestimates the southerly wind shift at the site, both appearing slightly later in the night than observed by roughly one hour. The temperature decrease that is observed with the far inland passage of the sea breeze front over SRS is represented in the model output as well. Some error is potentially introduced by model boundary anomalies propagating inwards, which does seem to stall the arrival of the sea breeze compared to what is observed from the tower data. However, the WRF simulation does resolve the inland propagation of this sea breeze case and provides reasonable output to compare the modified simulations to (Figure 7).
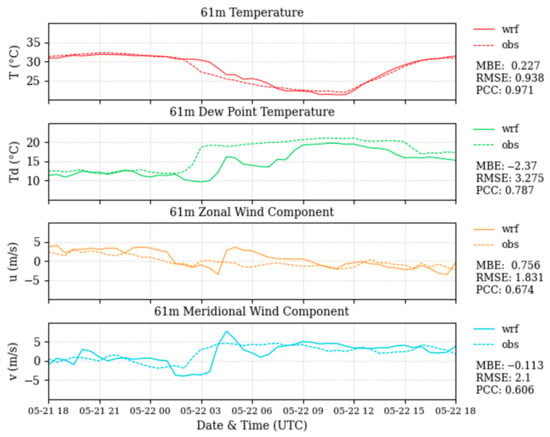
Figure 7.
A comparison between the data from a 61-m tower at SRS and the WRF simulated data interpolated to the location of the tower. For each variable, the observed value is denoted by a dashed line and the WRF simulated values is denoted by a solid line. Error statistics are displayed to the right of each figure.
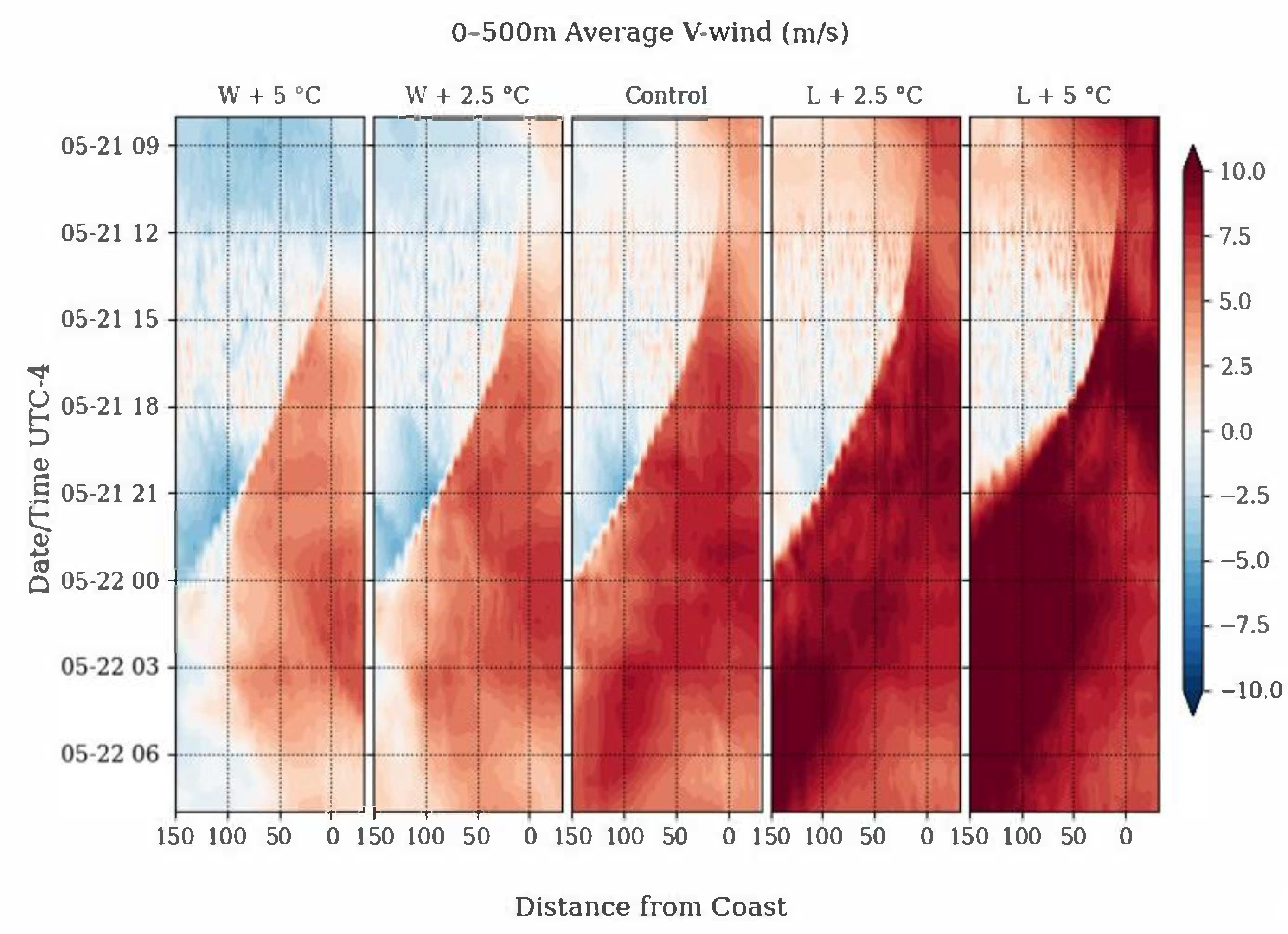
Due to the distance to the coast, the following sensitivity analyses are performed using a vertical cross section (depicted by the blue line on the map in Figure 1b) that spans from SRS to a point on the ocean ~30km offshore of Hilton Head Island, SC. Viner et al. [13] previously concluded that moisture content (denoted by dew point temperature) and wind were the two main physical indicators for the sea breeze passage. Additionally, the wind shift in this particular case was largely to a southerly direction. Given these facts, the analyses for these sensitivity studies focuses on the WRF output for dew point temperature and the meridional (north/south) wind component (also known as the “v-wind”) out of the many variables that WRF calculates. The lowest 500 m above ground level are averages for the analyses and plotted as a vertical time series as seen in Figure 8 and Figure 9:
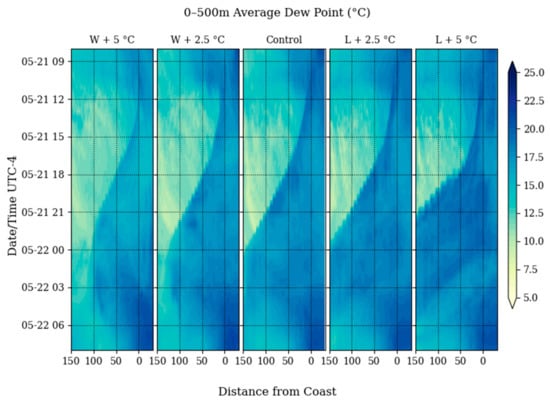
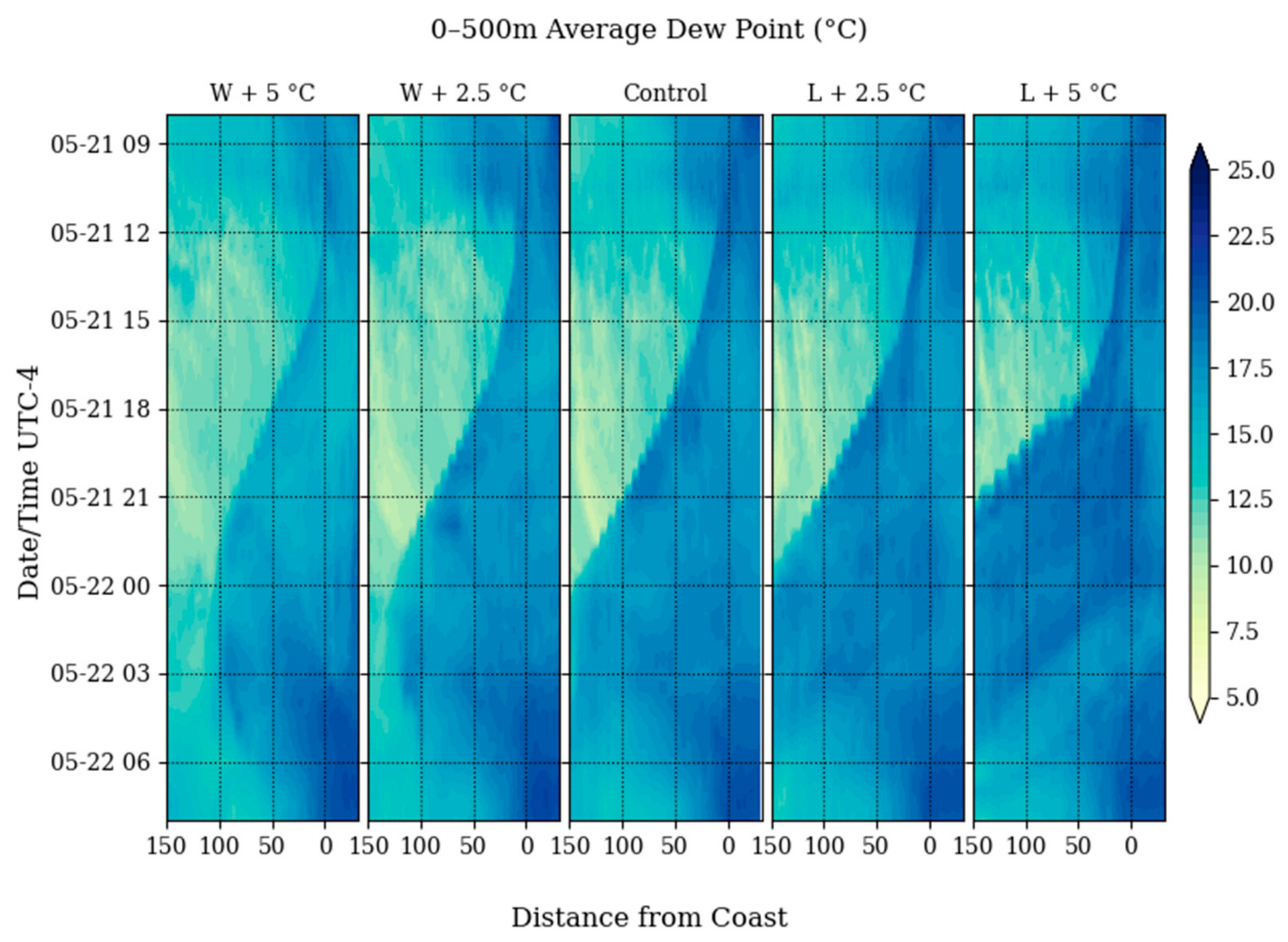
Figure 8.
Average Dew point over the lowest 500 m above the ground as a time series over a 24-h period from 21 May 2019 to 22 May 2019. SRS is located 150 km from the coast (left axis).
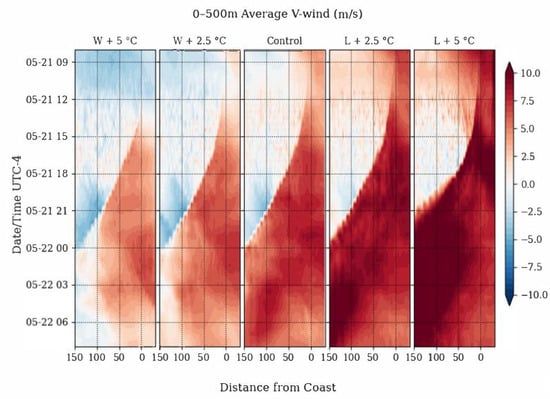
Figure 9.
Average meridional wind over the lowest 500 m above the ground as a time series over a 24-h period from 21 May 2019 to 22 May 2019. SRS is located 150 km from the coast (left axis).
The control simulation shows higher dew points over the ocean and the coastal region, with a genesis of the sea breeze at around 14 local time, with a clear sea breeze front advancing from the coast towards the inland regions. The front arrives at 0 local time in the Control simulation. The dew point shift is accompanied by a shift to southerly across-shore winds that carry the front inland.
In the L + 2.5 °C simulation, there is a negligible difference in the timing of the genesis of the sea breeze front. However, average southerly meridional winds in the first 500 m above ground tend to increase with the enhanced thermal gradient. In the L + 5 °C simulation, the gradient is enhanced enough to cause the front to advance inland at a faster rate and arrive at SRS significantly earlier than it did in either the control or the L + 2.5 °C simulations. This indicates that enhancing the temperature of the land influences the intensity of the moisture transport.
When the air over the ocean is heated up in the W + 2.5 °C and W + 5 °C simulations, there is still a genesis and propagation of the sea breeze front, but it noticeably “stalls out” before reaching SRS. The winds are significantly weaker than in the control simulation and eventually the transfer of moisture stops at ~25 km away from SRS (~125 km inland from the coast) in the W + 2.5 °C simulation, and ~50 km (~100 km inland from the coast) away from SRS in the W + 5 °C simulation. After 2 local time in both simulations, northerly coastal flow becomes predominant again, allowing an early retreat of the sea breeze front.
Observationally, it is shown that inland sea breeze events require a large thermal gradient. Modification of the thermal gradient over a spatial domain shows that the strength of the sea breeze is dependent on it. Through the parameters of the model simulations, it is shown that while the sea breeze genesis isn’t stopped by dampening the thermal gradient over the domain, the extent of the inland propagation of the sea breeze front is altered.
4. Conclusions
The thermal gradient between the land and the sea has long been understood to be an important factor in the generation of sea breezes [3,5]. Through observational evidence, the horizontal inland–coastal thermal gradient plays a role in the inland advancement of sea breezes in the SEUS as well. When examining confirmed inland-penetrating sea breeze events, there is a significant temperature difference between inland and coastal surface stations that isn’t present during days in which there is not an observed sea breeze at SRS, ~150 km inland from the coast. Cloud cover seems to be a factor in determining the thermal gradient responsible for generating inland sea breeze events.
The modeling perspective shows a more dynamic response when modifying the thermal gradient. A simple modification of the air over all vertical levels does not have a large impact on the timing of the sea breeze genesis, but does have a significant influence on the strength and the propagation speed of the sea breeze fronts. Increasing the gradient further inland will allow for a stronger sea breeze front, whereas increasing the gradient towards the coast will generate a weaker front that terminates earlier and does not have the inland reach.
Overall, this study conclusively showed that there is a connection between the inland–coastal thermal gradient and the occurrence, intensity, and speed of inland advecting sea breezes. Through this conclusion, the study introduces compelling ideas that can be researched further. While the observational portion of this study shows that the temperature difference of two points at the coast and further inland is connected to the occurrence of sea breeze events with the propagation length of the distance between those points, a more rigorous analysis of factors contributing to a thermal gradient can be accomplished utilizing a spatially resolute set of observations between the coastal and inland Savannah River regions in South Carolina. With a robust set of observations, potentially more sea breeze cases can be found and catalogued [30]. Either through manual analysis or through a trained machine learning model, the inland propagational extent of the sea breeze can be quantified for each catalogued event [31]. With a more comprehensive dataset of sea breeze events paired with a record of their quantified propagational extent, statistical methods could then be used to determine if a more spatially observed thermal gradient is a factor in the propagation length of sea breezes.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, J.W., S.N. and B.V.; methodology, J.W., S.N. and B.V.; software, J.W.; formal analysis, J.W., S.N. and B.V.; investigation, J.W., S.N. and B.V.; data curation, J.W., S.N. and B.V.; writing—original draft preparation, J.W.; writing—review and editing, J.W., S.N. and B.V.; visualization, J.W.; supervision, S.N.; project administration, S.N.; funding acquisition, S.N. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the Laboratory Directed Research and Development (LDRD) program within the Savannah River National Laboratory (SRNL). This document was prepared in conjunction with work accomplished under Contract No. DE-AC09-08SR22470 with the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) Office of Environmental Management (EM). This work was produced by Battelle Savannah River Alliance, LLC under Contract No. 89303321CEM000080 with the U.S. Department of Energy. Publisher acknowledges the U.S. Government license to provide public access under the DOE Public Access Plan (http://energy.gov/downloads/doe-public-access-plan (accessed on 2 May 2022)).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author. The data are not publicly available due to database access restrictions.
Acknowledgments
We acknowledge the efforts of Steve Chiswell, who leads SRNL’s atmospheric research program.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Case, J.L.; Wheeler, M.M.; Manobianco, J.; Weems, J.W.; Roeder, W.P. A 7-yr climatological study of land breezes over the Florida spaceport. J. Appl. Meteorol. 2005, 44, 340–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hill, C.M.; Fitzpatrick, P.J.; Corbin, J.H.; Lau, Y.H.; Bhate, S.K. Summertime Precipitation Regimes Associated with the Sea Breeze and Land Breeze in Southern Mississippi and Eastern Louisiana. Weather. Forecast. 2010, 25, 1755–1779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, L.D.; Koziara, M. Surface Thermodynamic Gradients Associated with Gulf of Mexico Sea-Breeze Fronts. Adv. Meteorol. 2018, 2018, 2601346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buckley, R.L.; Kurzeja, R.J. An observational and numerical study of the nocturnal sea breeze. Part I: Structure and circulation. J. Appl. Meteorol. 1997, 36, 1577–1598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, S.T.K.; Keim, B.D.; Talbot, R.W.; Mao, H. Sea breeze: Structure, forecasting, and impacts. Rev. Geophys. 2003, 41, 1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Melas, D.; Lavagnini, A.; Sempreviva, A.M. An investigation of the boundary layer dynamics of Sardinia Island under sea-breeze conditions. J. Appl. Meteorol. 2000, 39, 516–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, T.T.; Epifanio, C.C.; Zhang, F.Q. Topographic Effects on the Tropical Land and Sea Breeze. J. Atmos. Sci. 2012, 69, 130–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rotunno, R. On the Linear-Theory of the Land and Sea Breeze. J. Atmos. Sci. 1983, 40, 1999–2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steele, C.J.; Dorling, S.R.; von Glasow, R.; Bacon, J. Modelling sea-breeze climatologies and interactions on coasts in the southern North Sea: Implications for offshore wind energy. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2015, 141, 1821–1835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shepherd, J.M.; Carter, W.M.; Manyin, M.; Messen, D.; Burian, S. The impact of urbanization on current and future coastal convection: A case study for Houston. Environ. Plan. 2010, 37, 284–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Simpson, J.E.; Mansfield, D.A.; Milford, J.R. Inland Penetration of Sea-Breeze Fronts. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 1977, 103, 47–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muppa, S.K.; Anandan, V.K.; Kesarkar, K.A.; Rao, S.V.B.; Reddy, P.N. Study on deep inland penetration of sea breeze over complex terrain in the tropics. Atmos. Res. 2012, 104, 209–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viner, B.; Noble, S.; Qian, J.H.; Werth, D.; Gayes, P.; Pietrafesa, L.; Bao, S.W. Frequency and Characteristics of Inland Advecting Sea Breezes in the Southeast United States. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banta, R.M. Sea Breezes Shallow and Deep on the California Coast. Mon. Weather Rev. 1995, 123, 3614–3622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wagner, N.L.; Riedel, T.P.; Roberts, J.M.; Thornton, J.A.; Angevine, W.M.; Williams, E.J.; Lerner, B.M.; Vlasenko, A.; Li, S.M.; Dube, W.P.; et al. The sea breeze/land breeze circulation in Los Angeles and its influence on nitryl chloride production in this region. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2012, 117, D00V24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arritt, R.W. Effects of the Large-Scale Flow on Characteristic Features of the Sea Breeze. J. Appl. Meteorol. 1993, 32, 116–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Skamarock, W.C.; Klemp, J.B.; Dudhia, J.; Gill, D.O.; Liu, Z.; Berner, J.; Wang, W.; Powers, J.G.; Duda, M.G.; Barker, D.M.; et al. A Description of the Advanced Research WRF Version 4; National Center for Atmospheric Research: Boulder, CO, USA, 2019; p. 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinbeck, S.; Viner, B.; Rivera-Giboyeaux, A. Meteorological Monitoring Program at the Savannah River Site; Savannah River National Laboratory: Jackson, SC, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Qian, J.H.; Viner, B.; Noble, S.; Werth, D. Precipitation Characteristics of Warm Season Weather Types in the Southeastern United States of America. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benjamin, S.G.; Weygandt, S.S.; Brown, J.M.; Hu, M.; Alexander, C.R.; Smirnova, T.G.; Olson, J.B.; James, E.P.; Dowell, D.C.; Grell, G.A.; et al. A North American Hourly Assimilation and Model Forecast Cycle: The Rapid Refresh. Mon. Weather Rev. 2016, 144, 1669–1694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, G.; Field, P.R.; Rasmussen, R.M.; Hall, W.D. Explicit Forecasts of Winter Precipitation Using an Improved Bulk Microphysics Scheme. Part II: Implementation of a New Snow Parameterization. Mon. Weather Rev. 2008, 136, 5095–5115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudhia, J. Numerical Study of Convection Observed during the Winter Monsoon Experiment Using a Mesoscale Two-Dimensional Model. J. Atmos. Sci. 1989, 46, 3077–3107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mlawer, E.J.; Taubman, S.J.; Brown, P.D.; Iacono, M.J.; Clough, S.A. Radiative transfer for inhomogeneous atmospheres: RRTM, a validated correlated-k model for the longwave. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1997, 102, 16663–16682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nakanishi, M.; Niino, H. Development of an Improved Turbulence Closure Model for the Atmospheric Boundary Layer. J. Meteorol. Soc. Jpn 2009, 87, 895–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mitchell, K. The Community Noah Land-Surface Model (LSM); University Center of Atmospheric Research: Boulder, CO, USA, 2005; p. 26. [Google Scholar]
- Kusaka, H.; Kondo, H.; Kikegawa, Y.; Kimura, F. A simple single-layer urban canopy model for atmospheric models: Comparison with multi-layer and slab models. Bound Lay Meteorol. 2001, 101, 329–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steele, C.J.; Dorling, S.R.; von Glasow, R.; Bacon, J. Idealized WRF model sensitivity simulations of sea breeze types and their effects on offshore windfields. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2013, 13, 443–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lombardo, K.; Sinsky, E.; Jia, Y.; Whitney, M.M.; Edson, J. Sensitivity of Simulated Sea Breezes to Initial Conditions in Complex Coastal Regions. Mon. Weather Rev. 2016, 144, 1299–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.H. A Simple Accurate Formula for Calculating Saturation Vapor Pressure of Water and Ice. J. Appl. Meteorol. Clim. 2018, 57, 1265–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novak, D.R.; Colle, B.A. Observations of multiple sea breeze boundaries during an unseasonably warm day in metropolitan New York City. B Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2006, 87, 169–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azorin-Molina, C.; Tijm, S.; Chen, D.L. Development of selection algorithms and databases for sea breeze studies. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2011, 106, 531–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).