Temporal Variation of NO2 and HCHO Vertical Profiles Derived from MAX-DOAS Observation in Summer at a Rural Site of the North China Plain and Ozone Production in Relation to HCHO/NO2 Ratio
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experiments and Methods
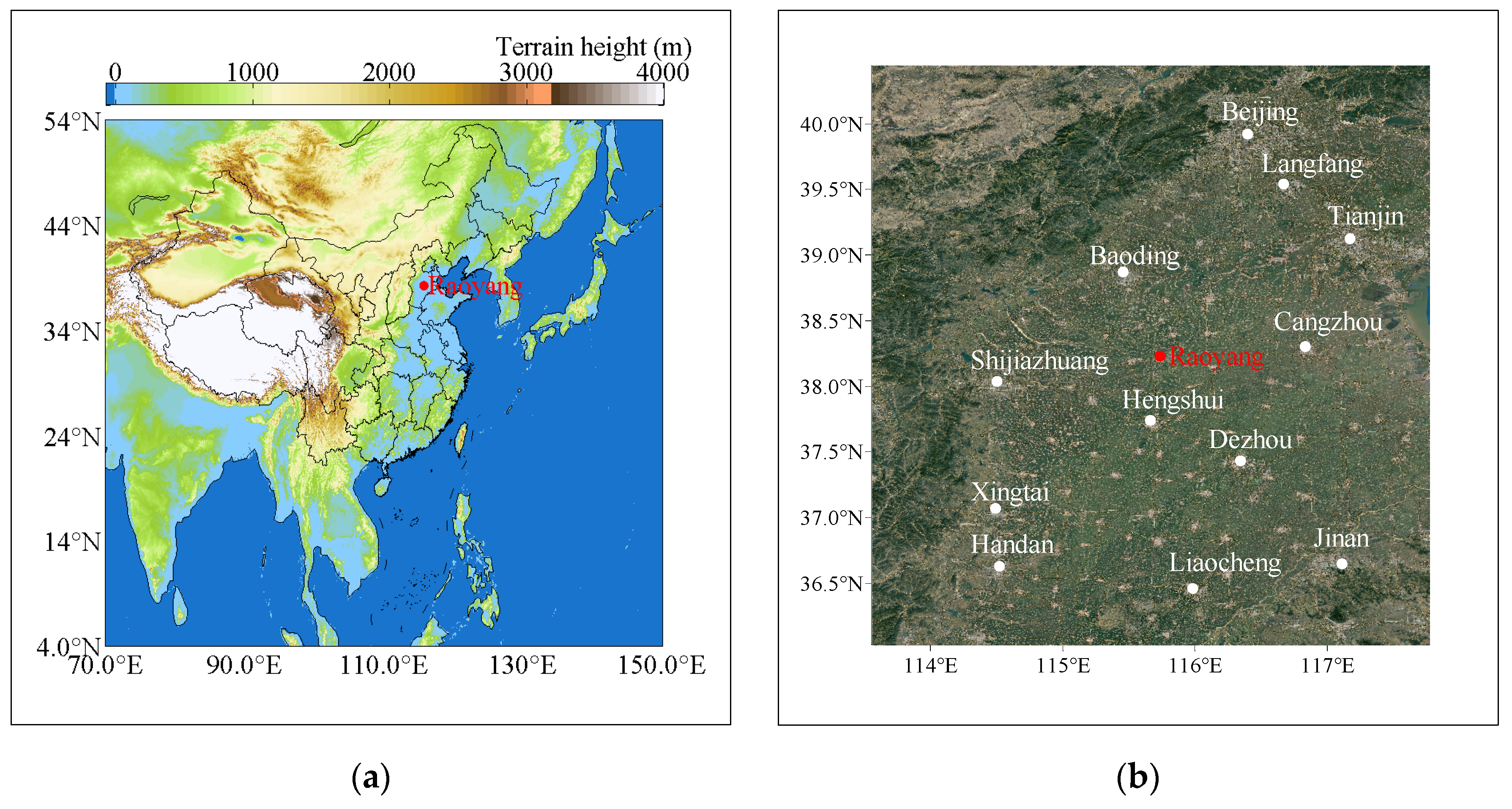
2.1. Site and Instrument
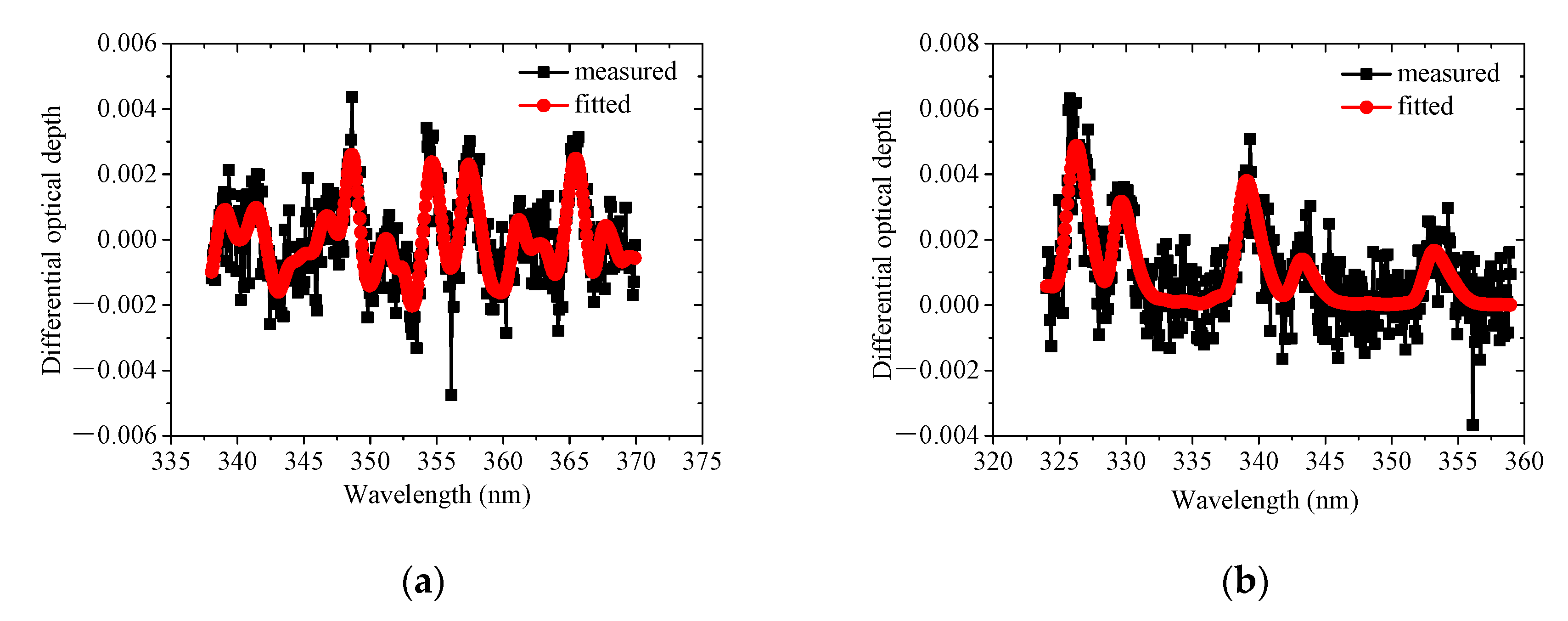
2.2. Spectral Analysis
2.3. Retrieval of NO2 and HCHO Vertical Profiles
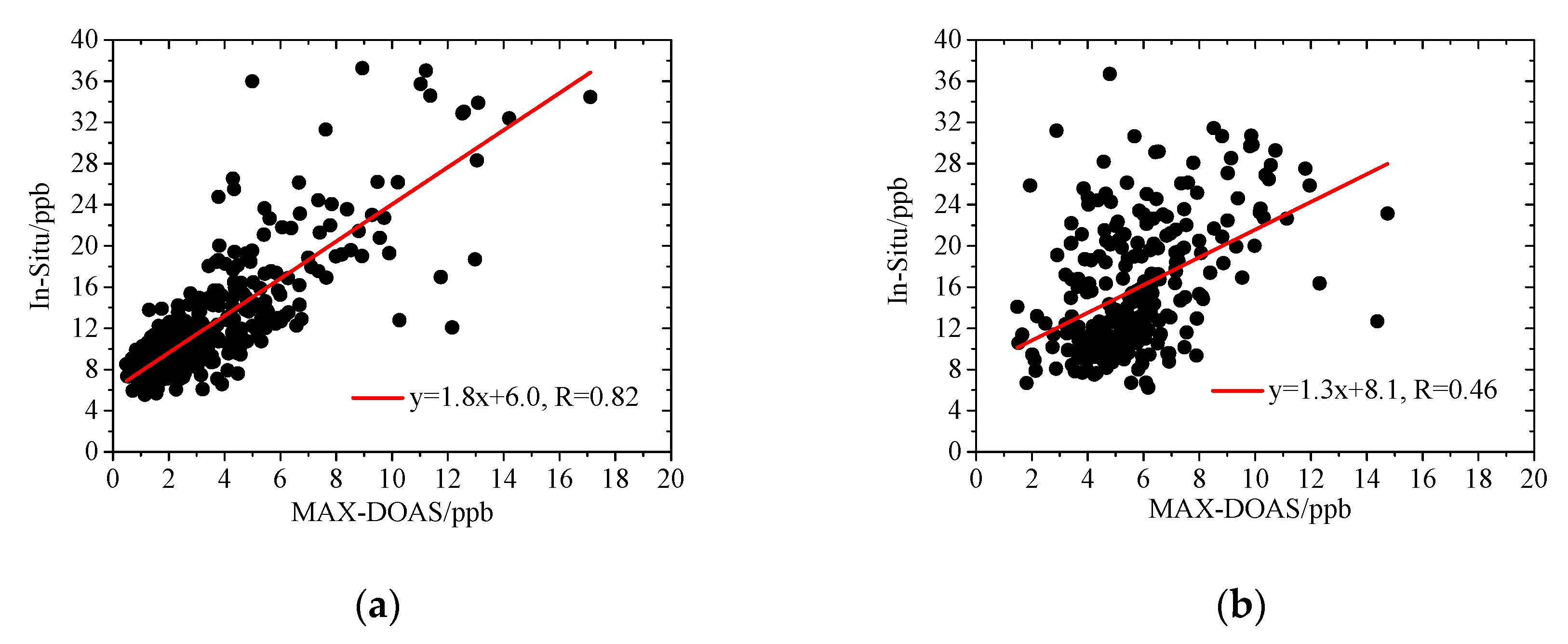
2.4. Ancillary Datasets
3. Results
3.1. Abundance and Overall Characteristics
3.2. Diurnal Variations
3.3. HCHO/NO2 Ratio
3.3.1. Vertical Profile and Diurnal Variation
3.3.2. Relationship to O3 Production and Meteorological Condition
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Seinfeld, J.H.; Pandis, S.N. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics: From Air Pollution to Climate Change, 3rd ed.; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2016; pp. 175–264. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, J.Z.; Wang, W.; Chen, Y.; Liu, H.J.; Yan, P.; Ding, G.A.; Wang, M.L.; Sun, J.; Lelieveld, J. The IPAC-NC field campaign: A pollution and oxidization pool in the lower atmosphere over Huabei, China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2012, 12, 3883–3908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ma, J.; Xu, X.; Zhao, C.; Yan, P. A review of atmospheric chemistry research in China: Photochemical smog, haze pollution, and gas-aerosol interactions. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2012, 29, 1006–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Zhou, X. Summertime tropospheric ozone over China simulated with a regional chemical transport model 2. Source contributions and budget. J. Geophys. Res. 2002, 107, ACH 2-1–ACH 2-11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Liu, H.; Hauglustaine, D. Summertime tropospheric ozone over China simulated with a regional chemical transport model 1. Model description and evaluation. J. Geophys. Res. 2002, 107, 4660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granier, C.; Bessagnet, B.; Bond, T.; D’Angiola, A.; Denier van der Gon, H.; Frost, G.J.; Heil, A.; Kaiser, J.W.; Kinne, S.; Klimont, Z.; et al. Evolution of anthropogenic and biomass burning emissions of air pollutants at global and regional scales during the 1980–2010 period. Clim. Change 2011, 109, 163–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.; Wang, P.; Ma, J.Z.; Zhu, S.; Pozzer, A.; Li, W. A high-resolution emission inventory of primary pollutants for the Huabei region, China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2012, 12, 481–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, D.S.; Köhler, I.; Grobler, E.; Rohrer, F.; Sausen, R.; Gallardo-Klenner, L.; Olivier, J.G.J.; Dentener, F.J.; Bouwman, A.F. Estimations of global NOx emissions and their uncertainties. Atmos. Environ. 1997, 31, 1735–1749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stavrakou, T.; Müller, J.F.; De Smedt, I.; Van Roozendael, M.; van der Werf, G.R.; Giglio, L.; Guenther, A. Evaluating the performance of pyrogenic and biogenic emission inventories against one decade of space-based formaldehyde columns. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2009, 9, 1037–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jin, X.M.; Holloway, T. Spatial and temporal variability of ozone sensitivity over China observed from the Ozone Monitoring Instrument. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2015, 120, 7229–7246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Liu, C.; Xie, Z.; Li, Y.; Huang, X.; Wang, S.; Xu, J.; Xie, P. A paradox for air pollution controlling in China revealed by “APEC Blue” and “Parade Blue”. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 34408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sun, Y.; Liu, C.; Palm, M.; Vigouroux, C.; Notholt, J.; Hu, Q.; Jones, N.; Wang, W.; Su, W.; Zhang, W.; et al. Ozone seasonal evolution and photochemical production regime in the polluted troposphere in eastern China derived from high-resolution Fourier transform spectrometry (FTS) observations. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 18, 14569–14583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, X.; Yan, B.; Du, C.; Cheng, C.; Zhao, H. Quantifying the interactive effects of meteorological, socioeconomic, and pollutant factors on summertime ozone pollution in China during the implementation of two important policies. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2021, 12, 101248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, G.; Liu, Y.; Huang, X.; Wang, Y.; Hu, B.; Zhang, Y.; Song, T.; Li, X.; Wu, S.; Li, Q.; et al. Aggravated ozone pollution in the strong free convection boundary layer. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 788, 147740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Gao, M.; Hu, Q.; Brasseur, G.P.; Carmichael, G.R. Stereoscopic Monitoring: A Promising Strategy to Advance Diagnostic and Prediction of Air Pollution. B. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2021, 102, E730–E737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Dörner, S.; Donner, S.; Böhnke, S.; De Smedt, I.; Dickerson, R.R.; Dong, Z.; He, H.; Li, Z.; Li, Z.; et al. Vertical profiles of NO2, SO2, HONO, HCHO, CHOCHO and aerosols derived from MAX-DOAS measurements at a rural site in the central western North China Plain and their relation to emission sources and effects of regional transport. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2019, 19, 5417–5449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, R.; Feng, T.; Guo, Y.; Wang, H.; Ming, R.; Wang, S.; Zhou, B. Study on ozone sensitivity in typical tropical region from DOAS ground-to-space measurements. Acta Sci. Circumstantiae 2021, 41, 2262–2271. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Luo, Y.; Dou, K.; Fan, G.; Huang, S.; Si, F.; Zhou, H.; Wang, Y.; Pei, C.; Tang, F.; Yang, D.; et al. Vertical distributions of tropospheric formaldehyde, nitrogen dioxide, ozone and aerosol in southern China by ground-based MAX-DOAS and LIDAR measurements during PRIDE-GBA 2018 campaign. Atmos. Environ. 2020, 226, 117384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, B.; Xie, P.; Xu, J.; Li, A.; Qin, M.; Hu, R.; Zhang, T.; Fan, G.; Tian, X.; Zhu, W.; et al. Vertical characteristics of NO2 and HCHO, and the ozone formation regimes in Hefei, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 823, 153425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanvir, A.; Javed, Z.; Jian, Z.; Zhang, S.; Bilal, M.; Xue, R.; Wang, S.; Bin, Z. Ground-Based MAX-DOAS Observations of Tropospheric NO2 and HCHO During COVID-19 Lockdown and Spring Festival Over Shanghai, China. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, J.; Zhao, T.; Luo, Y.; Miao, C.; Su, P.; Liu, F.; Zhang, G.; Qin, S.; Song, Y.; Bu, N.; et al. Identification of ozone sensitivity for NO2 and secondary HCHO based on MAX-DOAS measurements in northeast China. Environ. Int. 2022, 160, 107048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zong, R.; Yang, X.; Wen, L.; Xu, C.; Zhu, Y.; Chen, T.; Yao, L.; Wang, L.; Zhang, J.; Yang, L.; et al. Strong ozone production at a rural site in the North China Plain: Mixed effects of urban plumesand biogenic emissions. J. Environ. Sci. 2018, 71, 261–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, Z.; Lu, K.; Dong, H.; Hu, M.; Li, X.; Liu, Y.; Lu, S.; Shao, M.; Su, R.; Wang, H.; et al. Explicit diagnosis of the local ozone production rate and the ozone-NOx-VOC sensitivities. Sci. Bull. 2018, 63, 1067–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chi, X.; Liu, C.; Xie, Z.; Fan, G.; Wang, Y.; He, P.; Fan, S.; Hong, Q.; Wang, Z.; Yu, X.; et al. Observations of ozone vertical profiles and corresponding precursors in the low troposphere in Beijing, China. Atmos. Res. 2018, 213, 224–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, S.; Jin, J.; Ma, J.; Xu, X.; Ran, L.; Ma, Z.; Chen, J.; Guo, J.; Yang, P.; Wang, Y.; et al. Measuring the Vertical Profiles of Aerosol Extinction in the Lower Troposphere by MAX-DOAS at a Rural Site in the North China Plain. Atmosphere 2020, 11, 1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Yan, P.; Mao, J.; Zhang, X.; Tian, P.; Chang, H. Observation study on aerosol scattering phase function at Raoyang of Hebei, China. J. Appl. Meteorol. Sci. 2017, 28, 436–446. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, R.; Xu, X.; Jia, S.; Ma, R.; Ran, L.; Deng, Z.; Lin, W.; Wang, Y.; Ma, Z. Lower tropospheric distributions of O3 and aerosol over Raoyang, a rural site in the North China Plain. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2017, 17, 3891–3903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ran, L.; Deng, Z.; Xu, X.; Yan, P.; Lin, W.; Wang, Y.; Tian, P.; Wang, P.; Pan, W.; Lu, D. Vertical profiles of black carbon measured by a micro-aethalometer in summer in the North China Plain. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 16, 10441–10454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peng, W.; Wang, Y.; Gao, X.; Jia, S.; Xu, X.; Cheng, H.; Meng, Z. Characteristics of ambient formaldehyde at two rural sites in the North China Plain in summer. Res. Environ. Sci. 2016, 29, 1119–1127. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, S.; Ma, J.; Cheng, W.; Yan, P.; Zhou, H.; Zhou, L.; Yang, P. Tropospheric NO2 vertical column densities retrieved from ground-based MAX-DOAS measurements at Shangdianzi regional atmospheric background station in China. J. Environ. Sci. 2019, 80, 186–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Dörner, S.; Donner, S.; Jin, J.; Cheng, S.; Guo, J.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, J.; Liu, P.; Zhang, G.; et al. MAX-DOAS measurements of NO2, SO2, HCHO, and BrO at the Mt. Waliguan WMO GAW global baseline station in the Tibetan Plateau. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2020, 20, 6973–6990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.Z.; Beirle, S.; Jin, J.L.; Shaiganfar, R.; Yan, P.; Wagner, T. Tropospheric NO2 vertical column densities over Beijing: Results of the first three years of ground-based MAX-DOAS measurements (2008–2011) and satellite validation. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2013, 13, 1547–1567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jin, J.; Ma, J.; Lin, W.; Zhao, H.; Shaiganfar, R.; Beirle, S.; Wagner, T. MAX-DOAS measurements and satellite validation of tropospheric NO2 and SO2 vertical column densities at a rural site of North China. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 133, 12–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Platt, U.; Stutz, J. Differential Optical Absorption Spectroscopy, Principles and Applications; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2008; pp. 135–175. [Google Scholar]
- Hönninger, G.; Friedeburg, C.v.; Platt, U. Multi axis differential optical absorption spectroscopy (MAX-DOAS). Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2004, 4, 231–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; Lampel, J.; Xie, P.; Beirle, S.; Li, A.; Wu, D.; Wagner, T. Ground-based MAX-DOAS observations of tropospheric aerosols, NO2, SO2 and HCHO in Wuxi, China, from 2011 to 2014. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2017, 17, 2189–2215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ryan, R.G.; Rhodes, S.; Tully, M.; Schofield, R. Surface ozone exceedances in Melbourne, Australia are shown to be under NOx control, as demonstrated using formaldehyde:NO2 and glyoxal:formaldehyde ratios. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 749, 141460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Q.; Liu, C.; Hu, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Xing, C.; Su, W.; Ji, X.; Xiao, S. Evaluating the feasibility of formaldehyde derived from hyperspectral remote sensing as a proxy for volatile organic compounds. Atmos. Res. 2021, 264, 105777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duncan, B.N.; Yoshida, Y.; Olson, J.R.; Sillman, S.; Martin, R.V.; Lamsal, L.; Hu, Y.; Pickering, K.E.; Retscher, C.; Allen, D.J.; et al. Application of OMI observations to a space-based indicator of NOx and VOC controls on surface ozone formation. Atmos. Environ. 2010, 44, 2213–2223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Souri, A.H.; Nowlan, C.R.; Wolfe, G.M.; Lamsal, L.N.; Chan Miller, C.E.; Abad, G.G.; Janz, S.J.; Fried, A.; Blake, D.R.; Weinheimer, A.J.; et al. Revisiting the effectiveness of HCHO/NO2 ratios for inferring ozone sensitivity to its precursors using high resolution airborne remote sensing observations in a high ozone episode during the KORUS-AQ campaign. Atmos. Environ. 2020, 224, 117341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duncan, B.N.; Yoshida, Y.; Damon, M.R.; Douglass, A.R.; Witte, J.C. Temperature dependence of factors controlling isoprene emissions. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2009, 36, L05813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Archibald, A.T.; Neu, J.L.; Elshorbany, Y.F.; Cooper, O.R.; Young, P.J.; Akiyoshi, H.; Cox, R.A.; Coyle, M.; Derwent, R.G.; Deushi, M.; et al. Tropospheric Ozone Assessment Report: A critical review of changes in the tropospheric ozone burden and budget from 1850 to 2100. Elem. Sci. Anthropocene 2020, 8, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendrick, F.; Müller, J.-F.; Clémer, K.; Wang, P.; Mazière, M.D.; Fayt, C.; Gielen, C.; Hermans, C.; Ma, J.Z.; Pinardi, G.; et al. Four years of ground-based MAX-DOAS observations of HONO and NO2 in the Beijing area. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2014, 14, 765–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Javed, Z.; Liu, C.; Khokhar, M.F.; Tan, W.; Liu, H.R.; Xing, C.Z.; Ji, X.G.; Tanvir, A.; Hong, Q.Q.; Sandhu, O.; et al. Ground-Based MAX-DOAS Observations of CHOCHO and HCHO in Beijing and Baoding, China. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhu, S.; Li, X.; Yu, C.; Wang, H.; Wang, Y.; Miao, J. Spatiotemporal Variations in Satellite-Based Formaldehyde (HCHO) in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Region in China from 2005 to 2015. Atmosphere 2018, 9, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hou, Y.F.; Wang, L.T.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, S.X.; Liu, W.L.; Zhu, J.F. Analysis of the tropospheric column nitrogen dioxide over China based on satellite observations during 2008–2017. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2019, 10, 651–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
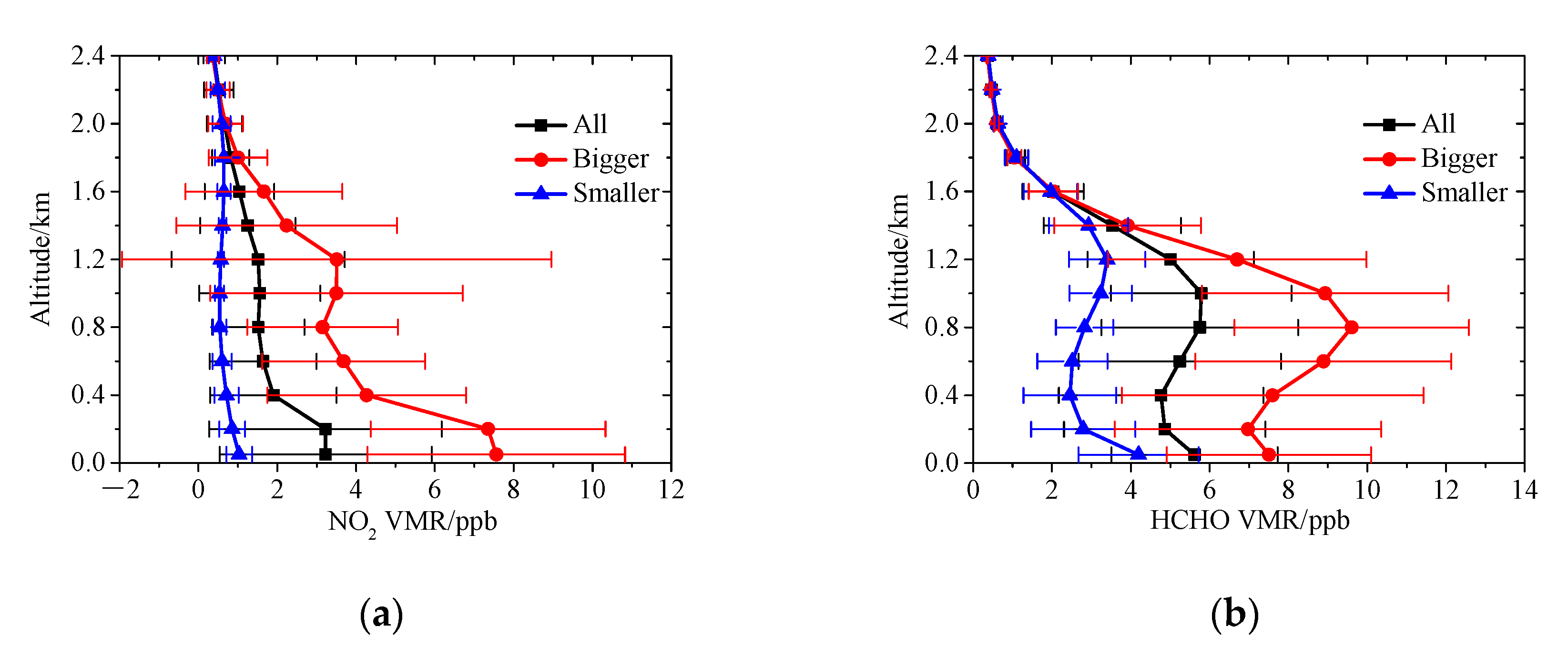
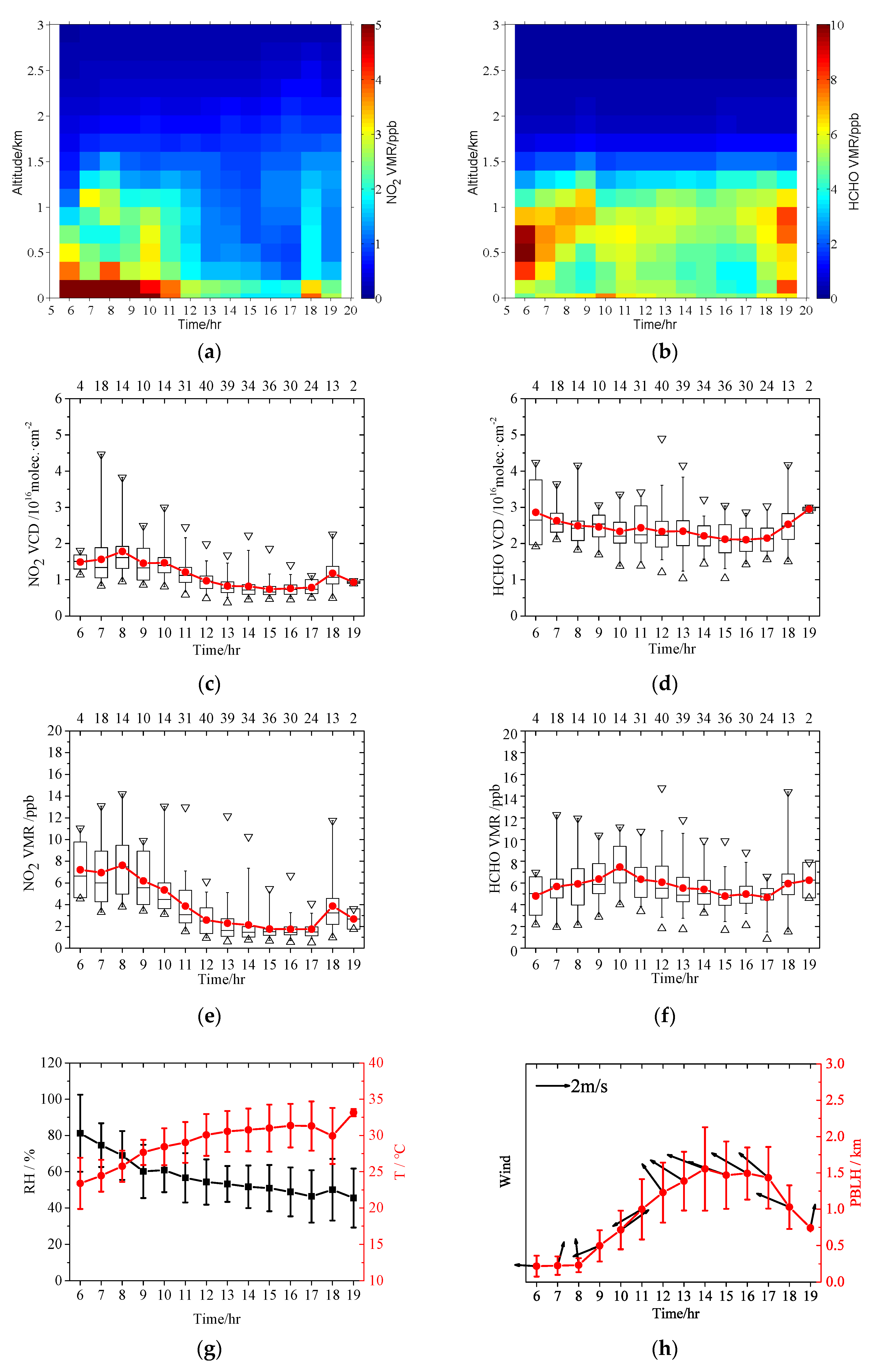
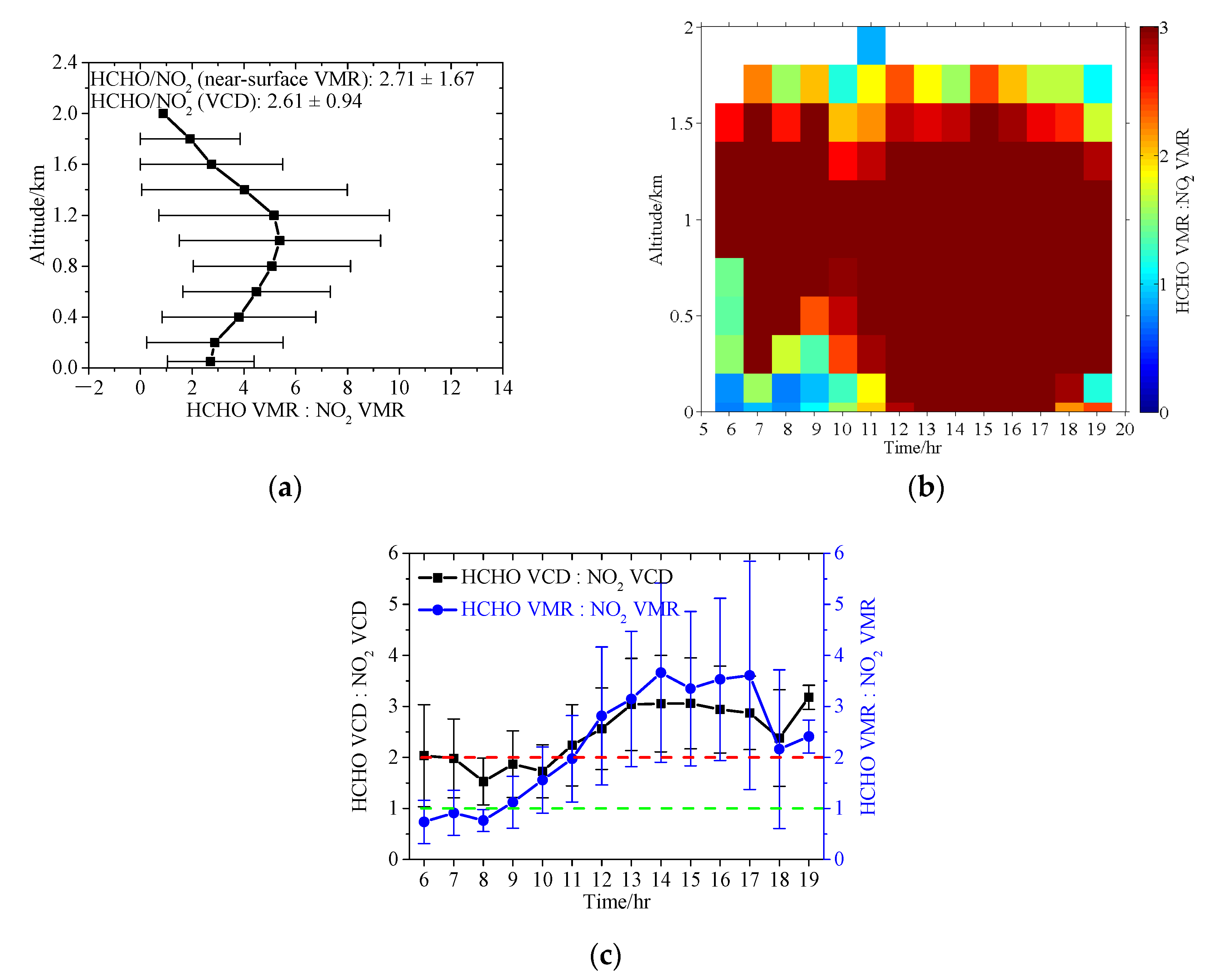
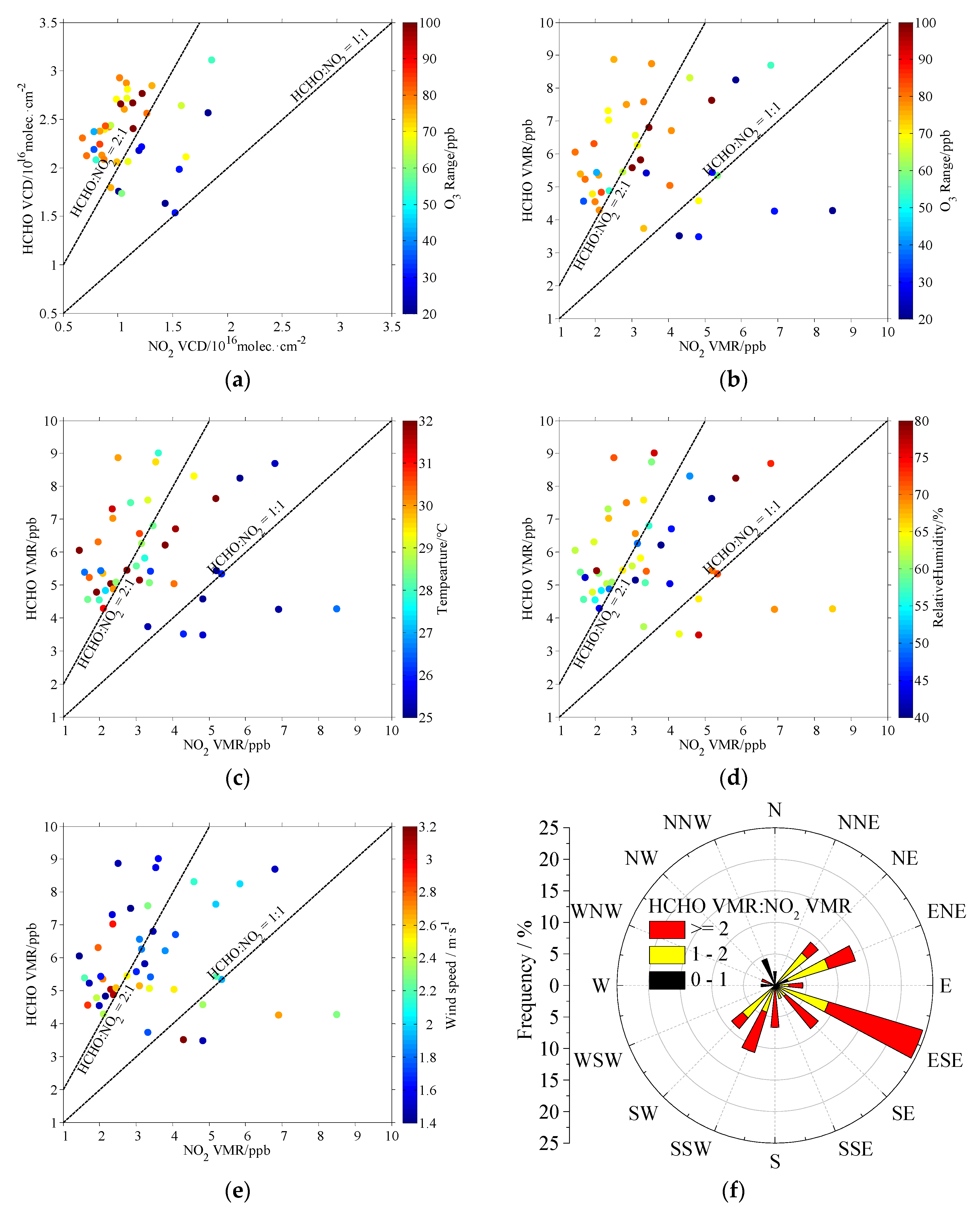
| Parameters | NO2 | HCHO | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| All | Larger | Smaller | All | Larger | Smaller | |
| VCD/1016 molec·cm−2 | 1.02 ± 0.51 | 2.03 ± 0.60 | 0.47 ± 0.04 | 2.32 ± 0.56 | 3.29 ± 0.46 | 1.51 ± 0.18 |
| VMR/ppb | 3.23 ± 2.70 | 7.56 ± 3.27 | 1.03 ± 0.33 | 5.62 ± 2.11 | 7.50 ± 2.59 | 4.20 ± 1.53 |
| Temperature/°C | 30 | 26 | 33 | 30 | 29 | 28 |
| RH/% | 55 | 66 | 42 | 55 | 61 | 58 |
| WD/° | 120 | 353 | 98 | 120 | 131 | 263 |
| WS/m·s−1 | 2.2 | 1.8 | 2.2 | 2.2 | 1.6 | 2.8 |
| PBLH/km | 1.16 | 0.46 | 1.56 | 1.16 | 0.99 | 0.95 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cheng, S.; Jin, J.; Ma, J.; Lv, J.; Liu, S.; Xu, X. Temporal Variation of NO2 and HCHO Vertical Profiles Derived from MAX-DOAS Observation in Summer at a Rural Site of the North China Plain and Ozone Production in Relation to HCHO/NO2 Ratio. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 860. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13060860
Cheng S, Jin J, Ma J, Lv J, Liu S, Xu X. Temporal Variation of NO2 and HCHO Vertical Profiles Derived from MAX-DOAS Observation in Summer at a Rural Site of the North China Plain and Ozone Production in Relation to HCHO/NO2 Ratio. Atmosphere. 2022; 13(6):860. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13060860
Chicago/Turabian StyleCheng, Siyang, Junli Jin, Jianzhong Ma, Jinguang Lv, Shuyin Liu, and Xiaobin Xu. 2022. "Temporal Variation of NO2 and HCHO Vertical Profiles Derived from MAX-DOAS Observation in Summer at a Rural Site of the North China Plain and Ozone Production in Relation to HCHO/NO2 Ratio" Atmosphere 13, no. 6: 860. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13060860
APA StyleCheng, S., Jin, J., Ma, J., Lv, J., Liu, S., & Xu, X. (2022). Temporal Variation of NO2 and HCHO Vertical Profiles Derived from MAX-DOAS Observation in Summer at a Rural Site of the North China Plain and Ozone Production in Relation to HCHO/NO2 Ratio. Atmosphere, 13(6), 860. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13060860







