Abstract
Dust aerosol has an impact on both the regional radiation balance and the global radiative forcing estimation. The Taklimakan Desert is the focus of the present research on the optical and micro-physical characteristics of the dust aerosol characteristics in Central Asia. However, our knowledge is still limited regarding this typical arid region. The DAO-K (Dust Aerosol Observation-Kashgar) campaign in April 2019 presented a great opportunity to understand further the effects of local pollution and transported dust on the optical and physical characteristics of the background aerosol in Kashgar. In the present study, the consistency of the simultaneous observations is tested, based on the optical closure method. Three periods dominated by the regional background dust (RBD), local polluted dust (LPD), and Taklimakan transported dust (TTD), are identified through the backward trajectories, combined with the dust scores from AIRS (Atmospheric Infrared Sounder). The variations of the optical and micro-physical properties of dust aerosols are then studied, while a direct comparison of the total column and near surface is conducted. Generally, the mineral dust is supposed to be primarily composed of silicate minerals, which are mostly very weakly absorbing in the visible spectrum. Although there is very clean air (with PM2.5 of 21 μg/m3), a strong absorption (with an SSA of 0.77, AAE of 1.62) is still observed during the period dominated by the regional background dust aerosol. The near-surface observations show that there is PM2.5 pollution of ~98 μg/m3, with strong absorption in the Kashgar site during the whole observation. Local pollution can obviously enhance the absorption (with an SSA of 0.72, AAE of 1.58) of dust aerosol at the visible spectrum. This is caused by the increase in submicron fine particles (such as soot) with effective radii of 0.14 μm, 0.17 μm, and 0.34 μm. The transported Taklimakan dust aerosol has a relatively stable composition and strong scattering characteristics (with an SSA of 0.86, AAE of ~2.0). In comparison to the total column aerosol, the near-surface aerosol has the smaller size and the stronger absorption. Moreover, there is a very strong scattering of the total column aerosol. Even the local emission with the strong absorption has a fairly minor effect on the total column SSA. The comparison also shows that the peak radii of the total column PVSD is nearly twice as high as that of the near-surface PVSD. This work contributes to building a relationship between the remote sensing (total column) observations and the near-surface aerosol properties, and has the potential to improve the accuracy of the radiative forcing estimation in Kashgar.
1. Introduction
Dust aerosols emitted from natural and anthropogenic sources [1,2] has important impacts on the global climate, human health, and biogeochemical cycles by changing the radiative budget, precipitation, snowmelt, as well as the concentration of airborne microorganisms [3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10]. The airborne dust can be transported over long distances [11], and the study of Biagio et al. [12] pointed out that the optical properties of dust aerosols varied from region to region. The properties of dust aerosol are determined by its parent soils [13,14] and aging on the transport path [12,15,16,17,18]. The Taklimakan Desert, as one of the largest dust sources in the world and a cause of the dust weather in Eastern Asia, is the focus of research on dust aerosol characteristics [19,20]. However, our knowledge of dust aerosol properties is very limited in this typical arid region of Central Asia. It is very valuable to carry out targeted observation experiments in this area.
As a margin city of the Tarim Basin, 150 km away from the western edge of the desert, Kashgar is a good place to observe the Taklimakan dust. Moreover, the floating dust produced by road construction and building construction [21,22], and the anthropogenic pollutants generated from industrial, traffic, and biomass burning, are also important components in Kashgar [20,23]. Yu et al. [24] reported that there was significant anthropogenic pollution during the sand storm in Kashgar in 2016. These local anthropogenic pollutants can coat the surface of dust, leading to changes in the optical and micro-physical properties [25,26]. Hence, Kashgar is selected as the study area to research the effects of local pollution and transported dust on background aerosol properties. It is of great importance for improving the accuracy of radiative forcing calculations in Central Asia [27].
This study is based on the international joint-observation experiment conducted in Kashgar in April 2019, during the DAO-K (Dust Aerosol Observation in Kashgar) campaign. The principal objective of the DAO-K campaign is to present a comprehensive view of the characterization of dust aerosol in Kashgar. Based on the DAO-K measurement, two studies have researched the dust aerosol profile and radiative forcing [20,28]. Our study mainly focuses on the absorption and size characteristics of total columnar and near-surface dust aerosols, trying to understand the effects of local pollution and transported dust on the optical and physical characteristics of background aerosol. The Single Scattering Albedo (SSA), the ratio of scattering to extinction, widely used in aerosol classification, is a common and important parameter in radiative transfer models [27]. The Absorption Angstrom Exponent (AAE) represents the spectral dependence of the absorption, which reflects the variation of different components in absorbing aerosols [29,30]. Both of the above optical parameters, together with scattering, extinction, and absorption coefficients, are investigated in this study. Meanwhile, we present a direct comparison between the total columnar and the near-surface dust aerosols. The detailed introduction of the study area and the simultaneous observations by instruments are recorded in Section 2.1. The overall experimental scheme as well as how to identify the dust aerosol source and how to perform the optical closure test are demonstrated in Section 2.2. Then, the results and analysis are displayed in Section 3. The optical closure test of the simultaneous observations is displayed in Section 4. Moreover, the variations on the computed AAE and retrieved complex refractive index are also discussed in this part. Finally, Section 5 summarizes the main points of the research.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.1.1. Study Area
The current research mainly pays attention to the effects of local pollutants and transported dust on the optical and micro-physical characterizations of both total column and near-surface dust aerosols in a typical arid region. The Dust Aerosol Observation in Kashgar, China (DAO-K campaign) was conducted in April 2019. The observation site (39.504° N, 75.930° E, the altitude of 1320 m) in Kashgar shown in Figure 1 is located in the global dust belt, which ranges from the Sahara over the Arabian Desert to the Gobi Desert [31]. It is strongly influenced by desert dust sources [32], especially in spring. Moreover, biomass burning and local pollutant emissions are also important sources for fine aerosol particles. Under different meteorological conditions, local emissions, transported dust, and/or background aerosols could potentially be observed at the site during the campaign.
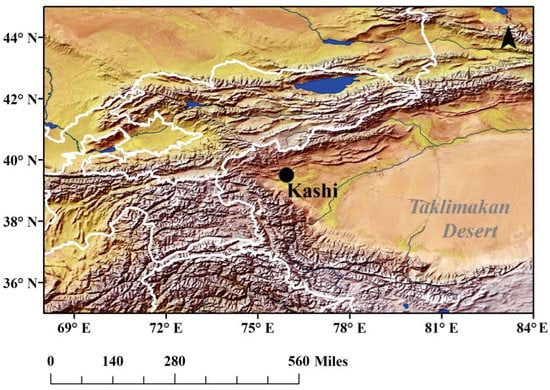
Figure 1.
The location of the site in Kashi (39.504° N, 75.930° E, altitude at 1320 m). The base map is the false color image of hill shade obtained from the Digital Elevation Model (DEM) data (with a spatial resolution of 1 km) through ArcGIS software under the default sun azimuth and altitude angles.
2.1.2. Simultaneous Observations by Instruments
The research data are obtained from many instruments simultaneously deployed in this campaign, in order to obtain aerosol optical and microphysical aerosol properties in the whole atmospheric column and near the surface. For the atmospheric total column observation, the sun–sky photometer is an excellent instrument to obtain the aerosol optical and micro-physical properties. The Single Scattering Albedo (SSA) is widely used as an important parameter for evaluating the aerosol absorption characteristic. The Particle Volume Size Distribution (PVSD), consisting of a fine mode and coarse mode, is a parameter that can effectively reflect the microphysical characteristics of the aerosol.
For the observation near the surface, four instruments are used in combination to obtain comprehensive information, such as the size distribution, absorption, scattering, and backscatter coefficients of aerosols. Hence, for dust aerosol in Kashgar, a comprehensive view of the variations in aerosol characterizations under different pollution episodes can be conducted. All of the instruments used in this study are listed in Table 1. The results analysis (in Section 3.2, Section 3.3 and Section 3.4.) of the near-surface observations (including GRIMM 1.129, Aurora 3000, AE 33, and BAM-1020) was conducted beginning on 2 April and ending on 30 April. As a result of the instrument issues of SONET CE 318, the comparison between the total column aerosol and the near-surface aerosol was conducted from 2 to 21 April.

Table 1.
List of instruments used and measurements conducted during the observation.
The sun–sky photometer CE318-DP (CIMEL Electronique Inc., Paris, France) is the standard instrument used in the SONET observation network, which is an automatic instrument for long-term continuous observation in the field. The instrument calibration is carried out once a year to ensure its data quality. More than 20 kinds of aerosol products can be provided by the CE318 Level 2.0 data, based on the multispectral and multiangle measurements. The particle volume size distribution and multi-spectral SSA (at 440 nm, 675 nm, 870 nm, and 1020 nm) retrievals (Level 2.0) are used during the observation period. Cloud screened by automatic procedures, the additional application of pre- and post-calibration coefficients and expert checking are applied. The SONET products have similar uncertainties to those of the AERONET (0.03 for SSA, 25% for PVSD with radii less than 7 μm) [32].
GRIMM V1.129 (GRIMM Inc., Hochdorf, Germany) is an optical particle counter, which relies on the amount of incident light scattered at 90° by dry particles. The maximal number concentration measured by GRIMM is up to 2000 cm−3. During the observation, it operates at a flow rate of 1.2 L min−1 with a 5 min resolution. Particle number size distributions are measured by GRIMM with diameters ranging from 0.25 μm to 32 μm (with 31 bins), which has an uncertainty less than 10% [33].
The nephelometer Aurora 3000 (Ecotech Inc., Knoxfield, Australia) works at three wavelengths (635 nm, 525 nm, and 450 nm) and is capable of providing the scattering coefficient and hemispheric backscatter coefficient. The nephelometer has an LED light source, which is robust and reliable during observations. It measures all the scattered radiation in the scattering angle of 9°~170° to obtain the scattering coefficient, and the scattered radiation in the scattering angle of 90°~170° to obtain the backscatter coefficient. Aerosol particles are sampled with an interval of 5 min, and dried by a dryer. During the campaign, the nephelometer calibration was performed using zero check every day. The calibration uncertainty of Aurora 3000 is 2.5%, given in the user manual [34].
The particle absorption properties are measured by a dual spot aethalometer AE 33 (Magee Scientific Inc., Berkeley, CA, USA). It operates at 7 wavelengths of 370 nm, 470 nm, 520 nm, 590 nm, 660 nm, 880 nm, and 950 nm. The mass specific attenuation cross sections for BC (black carbon) at 7 wavelengths, given by the manufacturer, are 18.47 m2 g−1, 14.54 m2 g−1, 13.14 m2 g−1, 11.58 m2 g−1, 10.35 m2 g−1, 7.77 m2 g−1, and 7.16 m2 g−1, respectively. Then, the absorption coefficient can be calculated from the effective BC concentration and mass specific attenuation cross section. During the campaign, AE 33 operated at a flow rate of 3 L min−1 with a time resolution of 1 min. The calibration of AE33 was performed using zero check every day with the precision error of ~9% [35,36].
Ground-based PM2.5 is a good indicator of particulate pollution. The hourly PM2.5 was observed by monitor BAM-1020 (MetOne Inc., Grants Pass, OR, USA) with a moderate (10–15%) positive multiplicative bias through a PM2.5 size cut head [37]. The heater was used to dry out the sampled particles. The time-continuous PM2.5 mass concentration near the surface can be effective in identifying the typical periods for different polluted levels (National Ambient Air Quality Standard). It should be noted that dust pollution also contributes to the rise in the PM2.5 mass concentration.
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Experimental Scheme
As a mixture, the absorption characteristics of dust aerosol depends on chemistry, size, and local emissions [25]. The vertical change of the absorption characteristics of dust aerosol is an important issue. Although Hu et al. [20] analyzed the vertical change of aerosol extinction based on lidar observations in the DAO-K campaign, they did not show the vertical changes in the absorption characteristics. We compared the absorption characteristics of dust aerosols observed near the surface with those in the atmospheric column, indirectly indicating the difference between absorption near the surface and in the upper air. Thanks to the inversion of aerosol microphysical parameters by the sun–sky photometer, we can compare the Particle Volume Size Distribution (PVSD) and Single Scattering Albedo (SSA), in addition to the absorption characteristics. The detailed flowchart, including the optical closure and analysis process, is presented in Figure 2.
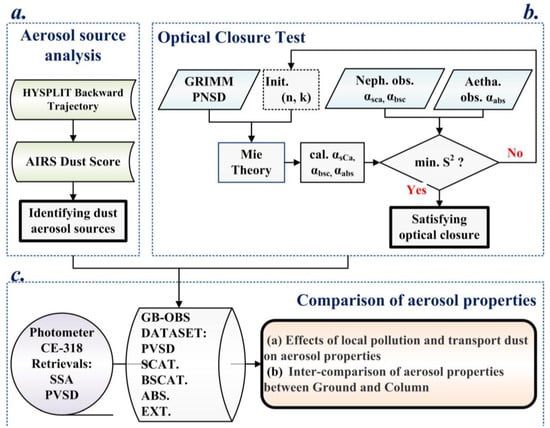
Figure 2.
Flowchart of the optical closure method and analytical framework. Step (a) represents the method for identifying aerosol sources, step (b) represents the method for optical closure test, step (c) represents the comparison and analysis of aerosol optical and micro-physical properties.
The detailed process mainly consists of three steps. Based on the key factors (backward trajectory and dust score data), the typical aerosol origins should be identified first. Here, the background dust, local polluted dust, and transported dust are taken into consideration. For the next step, an optical closure test should be conducted, in order to validate the consistency of the simultaneous observations (aerosol scattering coefficient, backscattering coefficient, absorption coefficient, and particle number size distribution data) obtained from different ground-based instruments. Finally, the variations in the optical and micro-physical properties of dust aerosols can be studied, and the direct comparison of total column and near surface can also be conducted.
2.2.2. Method for Identifying Aerosol Sources
The backward trajectory, dust scores, and PM2.5, are selected to classify the pollution episodes and transported dust. The backward trajectory is obtained by the Hybrid Single Particle Lagrangian Integrated Trajectory (HYSPLIT, [38]) model developed by NOAA (data can be found at the following website: http://ready.arl.noaa.gov/, accessed on 20 August 2021). The HYSPLIT model assumes that the parcel trajectory is formed through time integration and spatial difference when moving in the wind field. The HYSPLIT model uses the input meteorology field data (0.25° × 0.25°) provided by the Global Forecasting System. In this study, the backward trajectory modeled by HYSPLIT starts at 5:00 a.m. and ends at 5:00 a.m. on the next day. To explore whether air masses at different heights in the boundary layer come from the same source, the backward trajectories are initialized from the Kashgar site at 300, 500 m, and 1000 m. On the one hand, the air mass can be transported from relatively nearby regions, and pass through the near surface (less than 500 m) towards the Kashgar site. The air mass may mix with pollutants along its transport path. On the other hand, the air mass can be transported from a distant position, and pass through a higher altitude (1000~1500 m) towards the Kashgar site.
Then, the transported dust can be identified further with the dust score data. The dust score is obtained from the AIRS Level 2 product, which can indicate the distribution of dust aerosols. The AIRS Level 2 Dust Score product, with a spatial resolution of 13.5 km × 13.5 km, is observed at 1:30 a.m. and 1:30 p.m. The results show that different original sources are identified for three typical periods. Additionally, the significant PM2.5 pollution case can be distinguished by the upper limit value of 75 μg/m3, which is determined by the National Ambient Air Quality Standard. In this study, we mainly focus on the background dust, local polluted dust, and transported dust.
2.2.3. The Method Used for the Optical Closure Test
In order to validate the consistency of the measurements obtained from different ground instruments, we conducted an optical closure study [39,40] of the simultaneous measurements of aerosol scattering, backscattering, absorption coefficients, and particle number size distributions data during the DAO-K campaign. Based on the particle number size distribution measurements and Mie theory, the above optical parameters can be calculated. Then, the comparison between the optical calculations and the optical measurements was conducted (the so-called optical closure test). Particles are assumed to be spherical and chemically homogeneous during the whole treatment. The absorption efficiency Qabs, scattering efficiency Qsca, and backscattering efficiency Qbsc can be calculated based on the Mie theory. Then, by using Equation (1) proposed by Pettersson et al. [41], a look-up table of complex refractive index and optical parameters (scattering coefficient, backscattering coefficient, and absorption coefficient) can be built up.
where x represents the size parameter, proportional to the ratio of the particle size to the incident light wavelength. (n, k) represents the complex refractive index. Qopt represents the scattering efficiency, backscattering efficiency, or absorption efficiency of the aerosol particles, which depends on x and (n, k). N(Dp) represents the particle number size distribution.
In the look-up table, n ranges from 1.3 to 1.7 with a step of 0.005, and k ranges from 0.0005 to 0.1005 with a step of 0.00125. The two-dimensional contour plots of the scattering, backscattering, and absorption coefficients calculated with the fixed N(Dp) and an array of assumed (n, k) are shown in Figure 3.
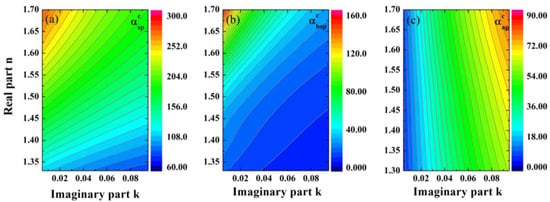
Figure 3.
The example of 2-D diagrams of (a) the scattering, (b) backscattering, and (c) absorption coefficients. The refractive index (n, k) can be retrieved from the corresponding observed optical coefficients.
With the same n, the scattering and backscattering coefficients decrease with k, and the absorption coefficient increases with k. With the same k, the scattering, backscattering, and absorption coefficients increase with n. Hence, an optimal (n, k) can be retrieved by minimizing S2 (Equation (2)), which is the fitting residual of the calculated and observed optical parameters.
where , , and are the observed scattering, backscattering, and absorption coefficients. , , and are the calculated scattering, backscattering, and absorption coefficients. If the differences between the calculated and observed values are less than the measurement uncertainties, the retrievals are acceptable [42].
3. Results and Analysis
3.1. Trajectory Analysis
Three representative periods (shown in Table 2) were selected during the observation. The aerosol origins were identified through the backward trajectories, combined with the dust score data. The results in Figure 4 show that air masses originated from different regions during the three typical periods. The first period started at 5:00 a.m. (Beijing time) on 6 April, and ended at 8:00 p.m. on 7 April, when the aerosols were identified as background dust. Figure 4a shows that the air masses originate from the border area between Tajikistan and Afghanistan, and pass through Kyrgyzstan. Although this region of Central Asia is heavily influenced by the dust emissions from deserts [43], there is no overlap between the backward trajectory and dust scores in the southwest of the observation site. Meanwhile, the air mass is transported at a high altitude level of 1~2.5 km, which is less affected by nearby surface pollutants. Therefore, it is likely that the aerosols observed during this period are regional background aerosols. Based on the above analysis, this period was selected and named as Period RBD (Regional Background Dust aerosol).

Table 2.
List of typical case periods with descriptions of the characteristics.
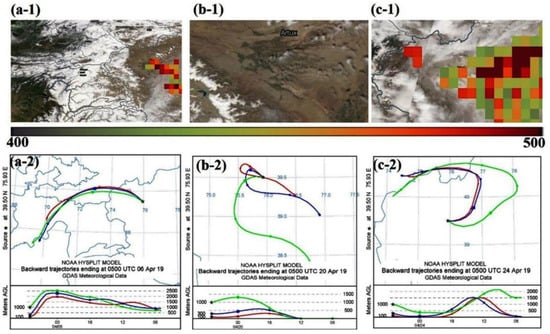
Figure 4.
(a-1), (b-1), and (c-1) represent the MODIS true-color images, combined with the AIRS Level 2 Dust Score product, at 1:30 a.m. and 1:30 p.m. on 6, 20, and 24 April 2019. (a-2), (b-2), and (c-2) represent the backward trajectories (starting at 5:00 a.m. on that day, and ending at 5:00 a.m. on the next day), at altitudes of 300 m, 500 m, and 1000 m.
The second period started at 5:00 a.m. on 20 April, and ended at 5:00 p.m. on 21 April. The dust aerosol was obviously affected by local anthropogenic pollution. In addition to the natural dust source, the emissions from industries and vehicles are major pollution sources in Kashgar. The work of Hofer et al. [43] also showed the non-negligible anthropogenic influence on the aerosols near the Tajikistan region. Figure 4b shows that the air mass is mainly obtained from local sources, with no dust scores in Kashgar. The local circulation, which is related to the topography, can carry high concentrations of surface air pollutants. The secondary particulate matter is an important source in Kashgar [24]. Additionally, the carbonaceous materials with light absorption from biomass combustion are a key emission source [23]. Then, this period was selected and named as Period LPD (Local Polluted Dust aerosol).
The third period was from 24 to 25 April, and the dust aerosol may have originated from long-distance transport. In Figure 4c, there are two stages presenting different aerosol origins. In the early stage (9:00 a.m.~6:00 p.m. on 24 April), dust particles were transported at a high altitude (~1 km, up to 1.5 km). The backward trajectory identified that the air masses pass through the Taklamakan Desert. The work of Hu et al. [20] pointed out that dust particles can be lifted from the Taklamakan desert by a low-pressure system, along with strong east or northeast winds. In the later stage, the main source was local dust. This also lead to the decrease in the PM2.5 mass concentration, extinction coefficient, scattering coefficient, and the SSA after 19:00 p.m. on 24 April (Figure 5). It is worth noting that the SSA was still maintained at a high level over a long period of time, because the transported dust was still dominant. Hence, this period was selected and named as Period TTD (Taklamakan Transported Dust aerosol).
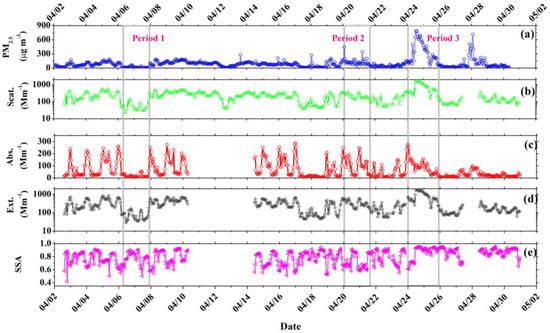
Figure 5.
(a) PM2.5, (b) scattering, (c) absorption, (d) extinction coefficient, and (e) SSA measurements during the campaign.
3.2. The Effects of Local Pollution and Transported Dust on the Optical Characteristics
3.2.1. Diurnal Variation of Optical Parameters during Typical Periods
The time series of the PM2.5 and optical measurements (scattering coefficient at 525 nm, absorption coefficient at 520 nm, extinction coefficient, and SSA at 520 nm) from 2 to 30 April are shown in Figure 5. Moreover, the mean values of the optical and physical parameters during the entire campaign and different typical periods are shown in Table 3. Dust is primarily composed of silicate minerals. Most of these are very weakly absorbing at the visible spectrum [44]. There was low fine-particle pollution during the period dominated by the regional background dust aerosol, but strong absorption was still observed. The mean value of PM2.5 and SSA was 98 μg/m3 and 0.79, respectively, during the entire campaign. Hence, there was slight pollution of fine particulate matter, with strong absorption mixed in with dust at the Kashgar site during the entire observation.

Table 3.
Mean optical and physical values during the entire observation and three periods.
In Period RBD, the PM2.5 measurements were always less than 70 μg m−3, with a mean value of 21 μg m−3 not exceeding Grade Ⅰ of the National Ambient Air Quality Standard (<35 μg m−3) in China. There was a medium absorption of background aerosol with a mean SSA value of 0.77 ± 0.12. Meanwhile, the near-surface aerosol loading was minimal, with the mean number concentration of 4.86 × 104/L, and the mean extinction coefficient of 66.07 ± 35.22 Mm−1. The mean scattering and absorption coefficients were 49.89 ± 27.78 Mm−1 and 16.19 ± 14.35 Mm−1, respectively.
In Period LPD, the large mean extinction (320.48 Mm−1), scattering (219.86 Mm−1), and absorption (100.51 Mm−1) coefficients were observed. The mean particle number concentration was 2.00 × 105/L. PM2.5, with a mean value of 125 μg m−3, exceeding Grade III of the National Ambient Air Quality Standard (>115 μg m−3) in China. The mean SSA value of 0.72 ± 0.11 was less than that of the background aerosol during Period 1. This implies that fine particles with stronger absorption increase, which may be related to primary soot emission [45]. Similar results were obtained by Guan et al. [46]. Although the increase in BC had no obvious contribution to the mass concentration of particulate matter, it lead to a significant decrease in the near-surface SSA.
Floating dust with the mean particle number concentration of 2.20 × 105/L occurred during Period TTD at the Kashgar site. The mean extinction coefficient was 817.93 Mm−1, the mean scattering coefficient was 727.56 Mm−1, and the mean absorption coefficient was 91.61 Mm−1. The PM2.5 pollution with a mean value of 337 μg m−3 exceeded Grade IV of the National Ambient Air Quality Standard (>250 μg m−3) in China. There was serious particulate pollution during this period. The mean SSA value was 0.86 ± 0.11, which was larger than that during Periods RBD (0.77) and LPD (0.79). Furthermore, the mean SSA value reached 0.91 ± 0.04, from 11:00 a.m. on 24 April to 11:00 p.m. on 25 April. This implies a strong scattering of the transported dust particles during this period. After 11:00 a.m. on 24 April, the PM2.5, extinction coefficient, scattering coefficient, and SSA values significantly increased. During the same period, the planetary boundary layer height (PBLH) retrieved from the Lidar profile was approximately 1.6 km, and the extinction coefficients (532 nm) at 0.8 km, 1.5 km, and 2 km were approximately 1000 ± 100 Mm−1, 1500 ± 200 Mm−1, and 1100 ± 100 Mm−1, respectively [20]. This indicates that the extinction increases with the altitude in the boundary layer.
Figure 6 shows the diurnal variation and frequency histogram of the aerosol optical and physical characteristics during Periods RBD, LPD, and TTD. An obvious diurnal variation of SSA was observed during these three periods. During the Period RBD, the particle extinction ability was weak, with most extinction coefficients less than 120 Mm−1. Meanwhile, the scattering and absorption coefficients were less than 100 Mm−1 and 35 Mm−1, respectively, and SSA values were mainly greater than 0.7 and less than 0.9. The SSA data records show high values on the morning of April 2 from 12:00 a.m. to 11:00 p.m. on 6 April. There was also a significant increase in the extinction and scattering coefficient values from 3:00 p.m. to 8:00 p.m. on 6 April. This implies an increase in the components with strong scattering characteristics. Increased extinction, scattering, and absorption coefficients were also obtained from 8:00 a.m. to 11:00 a.m. on 7 April, with decreased SSAs due to the increase in absorbing components.
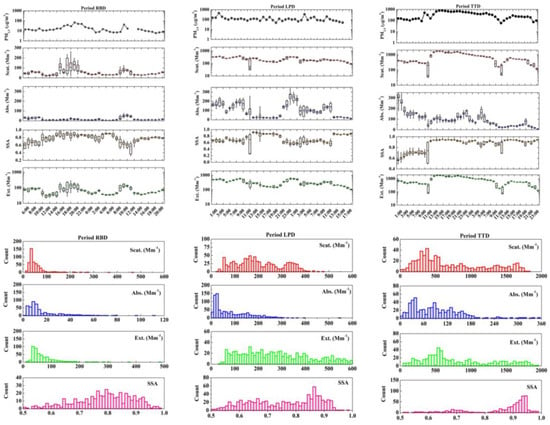
Figure 6.
The diurnal variation and frequency histogram of the aerosol optical and physical characteristics during the Period RBD, Period LPD, and Period TTD.
The particle absorption significantly increased during the Period LPD. Most of the absorption coefficient values ranged from 60 Mm−1 to 600 Mm−1. This was related to the increase in particles with SSA values between 0.6 and 0.7. The absorption and extinction coefficients had consistent diurnal variation trends, contrary to the SSA. This implies that the increase in local emitted primary particles (such as soot) with strong absorption characteristics, lead to a decrease in the SSA. The reported SSA values of soot, biomass burning, and other species can be found in Appendix A Table A1. The study by Kirchstetter et al. [47] also reported that polluted dust can absorb light in the visible spectrum. This was caused by the organic carbon from biomass burning, which can absorb at wavelengths below 600 nm, as well as black carbon from industrial burning, which can absorb throughout the visible spectrum. The extinction and absorption coefficients significantly increased from 0:00 a.m. to 11:00 a.m. on 20 April, and from 9:00 p.m. on 20 April to 11:00 a.m. on 21 April, while the SSA decreased due to the local emitted absorbing pollutants. The studies [46,48] pointed out that BC was another major contributor, in addition to iron oxides [49], to decreasing the dust SSA in a similar semi-arid region.
However, the shape of the SSA frequency histogram for the Period TTD was significantly different from that of the Periods BRD and LPD, which implies a difference of the aerosol’s origin. The scattering and extinction coefficients had similar values and diurnal variations. The scattering coefficient, extinction coefficient, and SSA had consistent diurnal variation trends, contrary to that of the absorption coefficient. The scattering coefficient, extinction coefficient, and SSA all significantly increased from 11:00 a.m. on 24 April to 8:00 a.m. on 25 April. The result also shows that the SSA of most particulate matter is greater than 0.9, which is at its highest for the whole campaign. In comparison to the local polluted dust, the effect of other particles (rather than the BC or absorbing OC reported in Table A1) in the transported dust could lead to an increase in the SSA [46]. Hence, the transported dust aerosol was dominated by primary and secondary particles with strong scattering characteristics. Moreover, the increase in the SSA can also be related to iron content and the hygroscopic growth of secondary pollutants [12].
3.2.2. The Variation of the Spectral Characteristics of the SSA during Typical Periods
The extinction, scattering, and absorption coefficients, and SSA at three wavelengths (450 nm, 525 nm, and 635 nm) during three periods are shown in Figure 7. The extinction (Figure 7a), scattering (Figure 7b) coefficients, and SSA (Figure 7d) increase with wavelength, whereas the absorption coefficient (Figure 7c) decreases with wavelength. From the relative spectral changes of the above parameters, the absorption coefficient and SSA had stronger spectral dependences. The spectral dependence of the SSA was similar during Periods LPD and RBD, but the aerosol absorption was stronger during Period LPD. Previous studies [23] pointed out that the strong absorption of aerosols in Kashgar mainly comes from carbonaceous aerosol emitted by biomass burning. In the carbonaceous aerosol, the spectral dependence of organic carbon was stronger than black carbon [47]. This may be the cause of the strong spectral absorption dependence during Periods RBD and LPD. Transported dust has a large SSA during Period TTD (data after 11:00 a.m. on 24 April). In comparison to the local emitted pollutants, dust particles from the Taklimakan Desert had stronger scattering characteristics. Moreover, the standard deviation of the SSA was small for the Period TTD, indicating that the fraction of various components was stable.
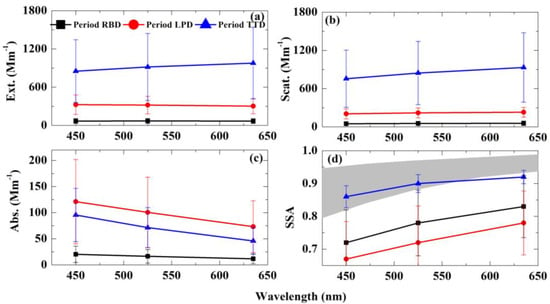
Figure 7.
Spectral extinction coefficient (a), spectral scattering coefficient (b), spectral absorption coefficient (c), and spectral SSA (d) during Periods RBD, LPD, and TTD. The gray-filled area in (d) represents the spectral SSAs of 19 dust aerosols sampled over 8 regions, reported by Biagio et al. [12].
The spectral SSA values of 19 dust aerosols sampled over 8 regions (Sahara, Sahel, Eastern Africa and the Middle East, Eastern Asia, North America, South America, Southern Africa, and Australia) were reported by Biagio et al. [12] and shown as a gray-filled area in Figure 7d. The observed SSAs in this study agree well with their results.
A slightly low SSA at 635 nm is also likely caused by the local polluted source, and also might be due to uncertainties in the sampling, measurements, and inversions additional to the different chemical components. The absorption strength of the dust mixture might be affected by the iron oxide content [50,51,52], as well as the carbonaceous and sulfate materials from combustion coalesced onto the dust particles [11,17]. In comparison to the Periods RBD and LPD, the SSA wavelength increases more slowly during the Period TTD. The different chemical compositions and larger size of the mineral aerosol particles can also have an obvious impact on the variation of the SSA in terms of the wavelength [25].
3.3. The Effects of Local Pollution and Transported Dust on the Particle Volume Size Distribution
The size of dust aerosol is related to the sandblasting (particle generation) mechanism and transported distance [53]. The daily mean particle volume size distributions (PVSDs) are presented in Figure 8a,c,e and the hourly mean total volume concentration in Figure 8b,d,f during three periods, which range from 5:00 a.m. (Beijing Time) that day to 5:00 a.m. on the next day. An obvious strong peak of coarse mode particles with radii of 0.8 μm ~3.25 μm, and a weak peak of coarse-mode particles with radii of 6~10 μm are observed for the daily mean PVSDs in Figure 8a,c,e. The peak concentration of the background dust aerosol (Period RBD) locates in the radius range of 1.25~3.25 μm in Figure 8a. More fine-mode particles could be emitted from local anthropogenic sources during Period LPD. Large coarse particles could decrease due to dry deposition during transport during Period TTD. Hence, the radius of the peak concentration ranges from 0.8 μm to 2.0 μm in Figure 8c,e, which is less than that of the background dust aerosol.
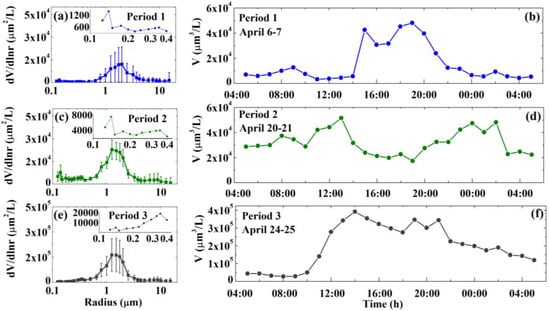
Figure 8.
The mean particle volume size distributions measured from GRIMM during (a) Period RBD also called Period 1, (c) Period LPD also called Period 2, and (e) Period TTD also called Period 3. Starts at 5:00 a.m. and ends at 5:00 a.m. on the next day. The mean total volume concentrations (b,d,f) during the three periods.
The viewpoints of the PVSDs with radii of 0.1 μm~0.4 μm are magnified, which are placed in the corresponding sub-figures in Figure 8a,c,e. There are three peaks of submicron fine-mode particles with radii of 0.14 μm, 0.17 μm, and 0.34 μm, which are evident of background and local emitted particles. Figure 8c shows that the fraction of submicron fine-mode particles with radii of 0.14 μm, 0.17 μm, and 0.34 μm increase during the Period LPD. This phenomenon is more obvious for hourly mean PVSDs. Meanwhile, three peaks of submicron fine-mode particles are also significant for the hourly mean PVSDs shown in Appendix A Figure A1. This is likely caused by the carbonaceous particles (e.g., soot) emitted by local combustion.
Meanwhile, similar diurnal variations of total volume concentrations between background and transported dust aerosols are observed in Figure 8b,f. The different diurnal variations of total volume concentrations are observed for the local emitted source in Figure 8d under the stable stratification conditions. The daily mean total volume concentrations are 1.6 × 104 μm3 L−1, 3.2 × 104 μm3 L−1, and 2.0 × 105 μm3 L−1 for Periods RBD, LPD, and TTD, respectively. The significant increase in the magnitude of the total volume concentration occurred in Period TTD due to the large amounts of transported particles. Due to the transported dust aerosol, the particle volume concentration significantly increases at 11:00 a.m. on 24 April in Figure 8f.
3.4. The Difference of the Optical and Micro-Physical Properties between the near Surface and Total Column
The aerosol vertical distributions are complex and related to chemical composition, topography, and meteorological conditions. Dust particles can be elevated to the free troposphere (above PBL) and transported over long distances. Meanwhile, regional circulations can also affect the aerosol vertical distribution, especially with high particulate concentrations. In this section, the observations, combined with a sun–sky photometer (CE318, CIMEL), allow the inter-comparison of particle volume size distribution between ground and column. The particle volume size distributions provided by CE318 are more smooth, due to the limits of the inversion algorithm.
Figure 9a,b shows similar particle volume size distributions between the ground and column aerosols. The peak radius of the PVSDns mainly ranges from 1 μm to 2 μm, with the mean value of 1.56 ± 0.67 μm. The peak radius of the PVSDcol mainly ranges from 1.5 μm to 4 μm, with the mean value of 2.84 ± 1.08 μm. The peak radius of the PVSDcol is nearly twice as great as that of the PVSDns. This implies that the average particle size in the column atmosphere is larger than that on the ground. This can be related to the elevated dust particles. In addition, the peaks of the submicron particle volume size distribution are only observed on the ground. This indicates that fine particles, which are related to the topographically generated local circulation, are mainly distributed near the ground. Meanwhile, a few particles with radii larger than 6 μm are found for background aerosols near the ground. We also found an obvious difference of SSAs at visible wavelengths between the ground and column.
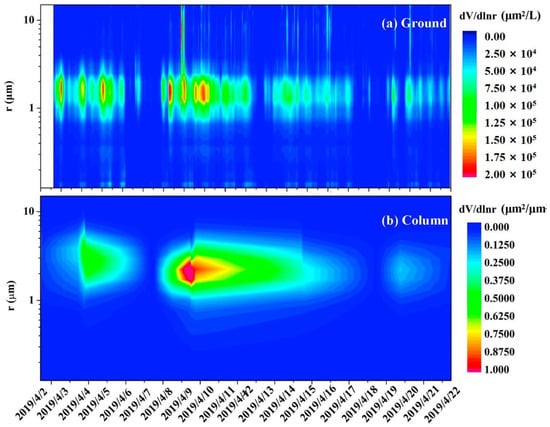
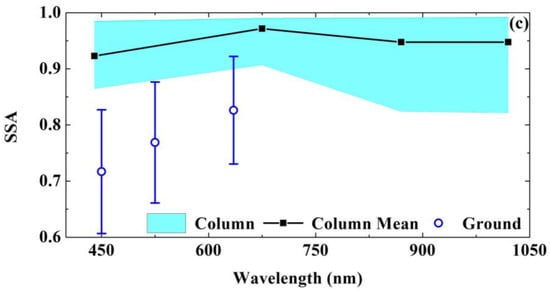
Figure 9.
Comparison of aerosol PVSD between (a) ground and (b) column. (c) Comparison of PVSD and spectral SSA between column and ground aerosols during the observation (from 2 to 21 April). The blue-filled area represents the spectral SSAcol inversions at 440 nm, 675 nm, 870 nm, and 1020 nm from CE318. The black line represents the mean spectral SSAcol. The blue circle and error bar represent the mean observed SSAns value and standard error at 450 nm, 525 nm, and 635 nm.
The sun–sky photometer CE318 can provide multi-wavelength (440 nm, 675 nm, 870 nm, and 1020 nm) SSA inversions of columnar aerosol particles. The results also show the inter-comparison of the mean spectral SSA values between the ground and column aerosols during the campaign. The blue-filled area represents the spectral SSAcol values inversed by the sun–sky photometer, and the black line represents the mean spectral SSAcol. The blue circle and error bar represent the mean observed SSAns value and standard deviation of near-surface particles at 450 nm, 525 nm, and 635 nm.
The SSA increases with wavelength (440 nm~675 nm) at visible spectrum for both the column and ground particles (Figure 9c). The SSAcol increases from 0.92 to 0.97. The SSAns increases from 0.72 to 0.83, which is obviously lower than the column aerosol due to much more small-sized particles with the stronger light absorption near the ground. The difference could also be related to the methodology or uncertainties. The SSAcol (440 nm) values have a range of 0.86 to 0.98. The results are close to the SSA values of column dust particles found by Parts et al. [54] for a range of 0.82 to 0.97 in south-western Spain. In the short-wave infrared bands, SSAcol are relatively constant (~0.95). The negative of SSA (440 nm) minus SSA (1020 nm) is a typical characteristic of dust particles [55,56]. We found that this feature appeared in 75% of the cases during the campaign.
4. Discussion
4.1. Analysis of the Absorption Angstrom Exponent
The Absorption Angstrom Exponent (AAE) describes the spectral dependence of the absorption coefficient, and can be calculated for any two wavelengths by using the following Equation (3) [29]. Table 4 shows that the relatively pure dust (e.g., Saharan dust and Asian dust) AAE values are close to 2.2 in some studies [30,57,58]. The strong light absorption of BC varies little with wavelength. Previous studies reported a BC AAE of 1.0, whether BC is fresh or aged [47,59]. Generally, the organic aerosol AAE is higher than BC AAE, but lower than pure dust AAE. Previous studies [60,61] reported that the AAE (a range of 300–700 nm) value of humic-like substances can be as high as 7.0 in biomass-burning aerosols, caused by the substantial increase in specific absorption towards shorter wavelengths.

Table 4.
The reported AAE values for various species in the previous studies.
The Mass Absorption Cross-Sections (MACs) are reported to be 14.54 m2/g and 10.35 m2/g at 470 nm (λ1) and 660 nm (λ2), respectively [35]. The spectral absorption coefficients (αabs,λ1, αabs,λ2) can be obtained from multiplying the BC concentration observed from AE33 by MACs. Then, the AAE can be calculated by Equation (3). The computed average AAE is 1.68 ± 0.28 during the whole observation (Figure 10), which is obviously lower than the AAE value of the pure dust. This implies the existence of BC and BrC [17,47,48]. The mean AAE value (1.58 ± 0.21) recorded during the period dominated by LPD, was similar to the values of 1.5 ± 0.1 for polluted dust, reported by Lee et al. [48] and Yang et al. [17]. In comparison to the RBD AAE (1.62 ± 0.29), the decrease in AAE may be caused by the increase in BC particles during the Period LPD. The daily mean AAE values were about 2.0 during the period dominated by TTD, which were the highest values during the whole observation. Similar AAE values of dust-dominated aerosols were also obtained in similar cases [30,57,58]. This can be attributed to the strong wavelength dependence of light absorption by pure dust particles.
where λ1 and λ2 are 470 nm and 660 nm, respectively.
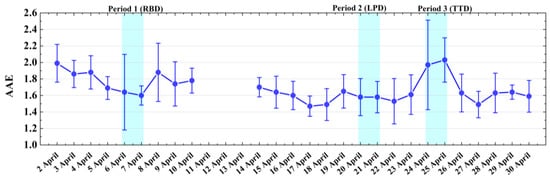
Figure 10.
Daily mean Absorption Angstrom Exponent (AAE470–660) from 2 to 30 April 2019.
4.2. Retrieval of the Complex Refractive Index
The consistency of the ground multi-instrument measurements was proved by the optical closure calculation from 2 to 21 April (shown in Figure 11). Except for the direct observations of the instrument, the extinction, scattering, and absorption coefficients can be also calculated from particle number size distribution measurements indirectly based on the Mie theory. The results also show that the deviation between the mean observation (216.47 Mm−1) and calculation (212.67 Mm−1) of the scattering coefficient is 7.68%. The deviation between the mean observation (56.02 Mm−1) and calculation (52.06 Mm−1) of backscattering coefficients is 4.46%. Meanwhile, the variation trend of the calculated results is consistent with that of the observation obtained from the nephelometer. The relatively large difference of observed (~79.01 Mm−1) and calculated (~46.14 Mm−1) absorption coefficients was found. However, the fitting residual error (Equation (2)) of all the retrieval results is less than 0.30, as shown in Figure 11. It is worth noting that particles are assumed as spherical and chemically homogeneous in this optical closure test. Hence, the large deviation between the calculations and observations is related to the use of this assumption during the whole treatment. Furthermore, different calibration principles among instruments also affected the consistency of the multi-instrument measurements to some extent.
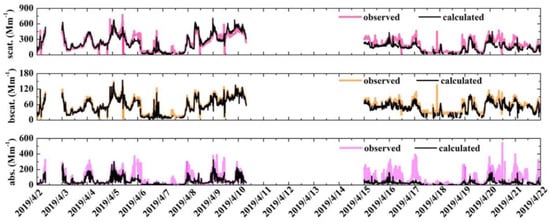
Figure 11.
The calculations (black lines) and the observations (colored lines) of the scattering, backscattering, and absorption coefficients at 532 nm from 2 to 21 April.
In addition to the performance of the consistency check, the complex refractive index can be simultaneously retrieved based on the optical closure method [39]. The real and imaginary parts of the retrieved complex refractive index from 2 to 21 April are shown in Figure 12. The lines and bars represent the daily mean real part n and imaginary part k of the complex refractive index at 532 nm. The real part of the refractive index varies from 1.58 to 1.69, with the average value of 1.64. There is a similarity of the real part of the refractive index between the total column and near-surface aerosols. The results also show that the imaginary part of the refractive index varies from 0.029 to 0.056, with an average value of 0.039. The large retrieval results of the imaginary part of the complex refractive index can indirectly prove the strong absorbability of aerosols in Kashgar. It is also found that the imaginary part of the refractive index decreases, following the decrease in the absorption coefficient.
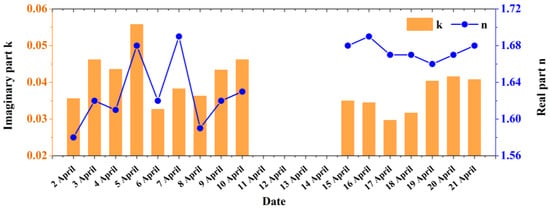
Figure 12.
Daily mean optimal retrievals of the complex refractive index based on the optical closure method at 532 nm from 2 to 21 April.
To make it clear, the k values of some materials are listed in Table 5. Compared with iron, iron-compound, and BC, the inherent absorption of mineral dust is obviously weaker at the visible spectrum. This also implies that the component with strong absorption (content of iron and BC) may exist in dust aerosol during the campaign, except for the transported dust event. Similar results were found in Lanzhou that determined that the transported dust event can weaken the effect of BC on the SSA [46]. However, even if aerosols originate from the same source, different coating states can cause significant differences in the absorbability [65,66].

Table 5.
Comparison of the imaginary part of the refractive index of ground aerosol particles to the literature data.
5. Conclusions
This research achieved two goals based on the Dust Aerosol Observation-Kashgar campaign conducted in April 2019, including (1) exploring the effects of local pollution and transported dust on the optical (e.g., single scattering albedo and absorption Angstrom exponent) and micro-physical (particle volume size distribution) characteristics of the background aerosols; and (2) presenting a direct comparison between the total columnar and the near-surface dust aerosol near the Taklimakan desert. Hence, the variations on the optical absorption of the background, polluted, and transported dust aerosols are reported in Kashgar. Meanwhile, a comprehensive inter-comparison between the total column and the near-surface aerosols was conducted based on the precise in-situ instruments.
The typical periods dominated by local polluted dust and transported dust were identified based on the auxiliary data, including the backward trajectory and dust score. By using the optical closure method, we proved that the simultaneous observations were consistent. Then, an analysis of the near-surface observations was conducted. The unexpected strongly absorbing aerosols were observed during the clean (regional background dust) and local polluted episodes. Furthermore, the low SSA (less than 0.80) and the weak wavelength dependence of absorption (low AAE of ~1.60) were observed, except for the transported dust events. This was likely caused by the soot coated by organic materials, which mixed with the airborne mineral dust. Compared with the regional background dust, the SSA values decreased from 0.77 to 0.72 when local pollution occurred. Meanwhile, more submicron particles with peak radii of 0.14 μm, 0.17 μm, and 0.34 μm were emitted by the local polluted source. The aerosols dominated by the transported dust had a stronger wavelength dependence of optical absorption (AAE of ~2.0). Meanwhile, the SSA (0.86) significantly increased as a result of the obvious decrease in the proportion of strong absorbing components. The above results can help to improve the estimation accuracy of radiative forcing.
Due to the existence of more small-sized particles with strong light absorption characteristics, the near-surface SSA was lower than the total column SSA at visible wavelengths. Both the total column SSA and the near-surface SSA increased with wavelength at the visible spectrum, which is consistent with other similar dust studies. Moreover, the SSA increased more slowly with wavelength during the period of transported dust. Due to the emission source and topography, the submicron fine-mode particles were mainly distributed near the ground. Furthermore, the peak radius of the total column PVSD was nearly twice as great as that of the near-surface PVSD. The above results can contribute to building relationships between the satellite (remote-sensed total column) observations and the near-surface aerosol properties.
Author Contributions
Y.W. created the published work, specifically writing the initial draft. Z.L., Y.Z. and Z.P. provided the critical review, commentary and revision. Z.L., Y.Z. and P.G. designed the experiments. K.L., J.C., Q.H. and Y.O. carried out the experiment. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant number 42101365). The National Key R&D Program of China (Grant number 2016YFE0201400); the National Outstanding Youth Foundation of China (Grant number 41925019); Hainan Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 418QN302); and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant number 41671367).
Data Availability Statement
Data will be available. The HYSPLIT model was run at https://www.ready.noaa.gov/HYSPLIT_traj.php (accessed on 20 August 2021), with the input meteorology field data (0.25° × 0.25°) provided by the Global Forecasting System (GFS). The satellite data from AIRS can be found in NASA’s GES DIS service center. All the other data presented in this study are available upon request of readers.
Acknowledgments
Thanks to the open-source HYSPLIT model developed by NOAA, as well as the dust scores data provided by NASA AIRS. Thanks to the long-term maintenance by the staff at the SONET Kashgar site. We have to thank the researchers who participated in this joint campaign. We acknowledge the colleagues at the Institute of Remote Sensing and Digital Earth for their kind help and for the financial support. And we thank the colleagues at the GPI RAS (Prokhorov General Physics Institute of the Russian Academy of Sciences), LOA, ESA/IDEAL+ project and IAP (Institute of Atmospheric Physics) for the participation and the efforts they made for the campaign.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Appendix A
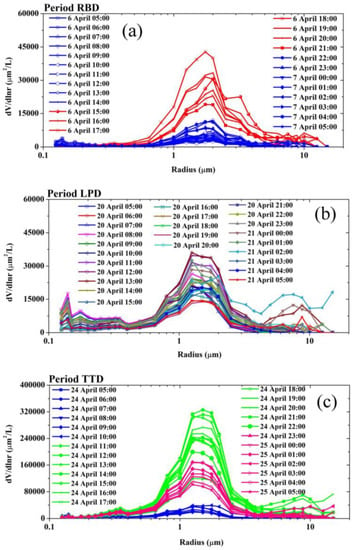
Figure A1.
The hourly mean PVSDs dominated by (a) the regional background dust (RBD), (b) the local polluted dust (LPD), and (c) the Taklimakan transported dust (TTD). There are three peaks of submicron fine-mode particles with radii of 0.14 μm, 0.17 μm, and 0.34 μm, which are evident for background and local emitted particles.

Table A1.
The reported SSA values at the wavelength of 550 nm in the previous studies. The SSA of BC is very low. The SSA value of heavily-coated (mainly with organic materials) BC may be dominated by the coating materials [69]. The carbonaceous components mixed in with dust can obviously decrease the SSA value. This may be a major contributor to the variation of the radiative forcing of mineral dust.
Table A1.
The reported SSA values at the wavelength of 550 nm in the previous studies. The SSA of BC is very low. The SSA value of heavily-coated (mainly with organic materials) BC may be dominated by the coating materials [69]. The carbonaceous components mixed in with dust can obviously decrease the SSA value. This may be a major contributor to the variation of the radiative forcing of mineral dust.
| SSA | λ (nm) | Species | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0.2 | 550 | Diesel soot | Schnaiter et al., 2003 [70] |
| 0.2–0.3 | 550 | BC fractal aggregates | Smith and Grainger et al., 2014 [71] |
| 0.7 | 550 | Biomass burning | Schnaiter et al., 2005 [62] |
| 0.3 | 550 | Soot with OC < 20% | Schnaiter et al., 2006 [69] |
| 0.7 | 550 | Soot with OC~50% | Schnaiter et al., 2006 [69] |
| 0.7 ± 0.18 | 870 | Fine particles over a Western Tibetan Plateau site | Zhang et al., 2021 [72] |
References
- Hand, J.L.; Gill, T.; Schichtel, B. Spatial and seasonal variability in fine mineral dust and coarse aerosol mass at remote sites across the United States. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2017, 122, 3080–3097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheuvens, D.; Schütz, L.; Kandler, K.; Ebert, M.; Weinbruch, S. Bulk composition of northern African dust and its source sediments—A compilation. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2013, 116, 170–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skiles, S.M.; Painter, T.H. Toward understanding direct absorption and grain size feedbacks by dust radiative forcing in snow with coupled snow physical and radiative transfer modeling. Water Resour. Res. 2019, 55, 7362–7378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christia, C.; Poma, G.; Besis, A.; Samara, C.; Covaci, A. Legacy and emerging organophosphοrus flame retardants in car dust from Greece: Implications for human exposure. Chemosphere 2018, 196, 231–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Svensson, J.; Ström, J.; Kivekäs, N.; Dkhar, N.B.; Tayal, S.; Sharma, V.P.; Jutila, A.; Backman, J.; Virkkula, A.; Ruppel, M. Light-absorption of dust and elemental carbon in snow in the Indian Himalayas and the Finnish Arctic. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2018, 11, 1403–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Wang, T.; Wang, W.; Li, Z.; Yan, H. Climate effects of dust aerosols over East Asian arid and semiarid regions. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2014, 119, 11398–11416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Creamean, J.M.; Suski, K.J.; Rosenfeld, D.; Cazorla, A.; DeMott, P.J.; Sullivan, R.C.; White, A.B.; Ralph, F.M.; Minnis, P.; Comstock, J.M. Dust and biological aerosols from the Sahara and Asia influence precipitation in the western US. Science 2013, 339, 1572–1578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hara, K.; Zhang, D. Bacterial abundance and viability in long-range transported dust. Atmos. Environ. 2012, 47, 20–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Liu, X.; Leung, L.; Johnson, B.; McFarlane, S.A.; Gustafson Jr, W.; Fast, J.D.; Easter, R. The spatial distribution of mineral dust and its shortwave radiative forcing over North Africa: Modeling sensitivities to dust emissions and aerosol size treatments. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2010, 10, 8821–8838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haas, D.; Kriso, A.; Fritz, T.; Galler, H.; Habib, J.; Ilieva, M.; Kropsch, M.; Ofner-Kopeinig, P.; Stonitsch, M.; Strasser, A. Background concentrations of cultivable, mesophilic bacteria and dust particles in the air in urban, rural and mountain regions. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 9572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandler, K.; Benker, N.; Bundke, U.; Cuevas, E.; Ebert, M.; Knippertz, P.; Rodriguez, S.; Schütz, L.; Weinbruch, S. Chemical composition and complex refractive index of Saharan Mineral Dust at Izaña, Tenerife (Spain) derived by electron microscopy. Atmos. Environ. 2007, 41, 8058–8074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Biagio, C.; Formenti, P.; Balkanski, Y.; Caponi, L.; Cazaunau, M.; Pangui, E.; Journet, E.; Nowak, S.; Andreae, M.O.; Kandler, K. Complex refractive indices and single-scattering albedo of global dust aerosols in the shortwave spectrum and relationship to size and iron content. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2019, 19, 15503–15531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skonieczny, C.; Bory, A.; Bout-Roumazeilles, V.; Abouchami, W.; Galer, S.J.; Crosta, X.; Stuut, J.B.; Meyer, I.; Chiapello, I.; Podvin, T. The 7–13 March 2006 major Saharan outbreak: Multiproxy characterization of mineral dust deposited on the West African margin. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2011, 116, D18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caquineau, S.; Gaudichet, A.; Gomes, L.; Legrand, M. Mineralogy of Saharan dust transported over northwestern tropical Atlantic Ocean in relation to source regions. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2002, 107, AAC 4-1–AAC 4-12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proestakis, E.; Amiridis, V.; Marinou, E.; Georgoulias, A.K.; Solomos, S.; Kazadzis, S.; Chimot, J.; Che, H.; Alexandri, G.; Binietoglou, I. Nine-year spatial and temporal evolution of desert dust aerosols over South and East Asia as revealed by CALIOP. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 18, 1337–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamouri, R.-E.; Ansmann, A.; Nisantzi, A.; Kokkalis, P.; Schwarz, A.; Hadjimitsis, D. Low Arabian dust extinction-to-backscatter ratio. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2013, 40, 4762–4766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Howell, S.; Zhuang, J.; Huebert, B. Attribution of aerosol light absorption to black carbon, brown carbon, and dust in China–interpretations of atmospheric measurements during EAST-AIRE. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2009, 9, 2035–2050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collaud Coen, M.; Weingartner, E.; Schaub, D.; Hueglin, C.; Corrigan, C.; Henning, S.; Schwikowski, M.; Baltensperger, U. Saharan dust events at the Jungfraujoch: Detection by wavelength dependence of the single scattering albedo and first climatology analysis. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2004, 4, 2465–2480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Kai, K.; Shibata, T.; Zhang, K.; Zhou, H. Validation of the dust layer structure over the Taklimakan Desert, China by the CALIOP space-borne lidar using ground-based lidar. Sola 2010, 6, 121–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Hu, Q.; Wang, H.; Goloub, P.; Li, Z.; Veselovskii, I.; Podvin, T.; Li, K.; Korenskiy, M. The characterization of Taklamakan dust properties using a multiwavelength Raman polarization lidar in Kashi, China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2020, 20, 13817–13834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Shen, Z.; Zhang, L.; Lei, Y.; Gong, X.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, T.; Xu, H.; Cui, S.; Wang, Q. Chemical source profiles of urban fugitive dust PM2. 5 samples from 21 cities across China. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 649, 1045–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, J.; Zhang, L.; Cao, J.; Zhang, R. A review of current knowledge concerning PM2.5 chemical composition, aerosol optical properties and their relationships across China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2017, 17, 9485–9518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Zhao, X.; Wang, J.; Yin, B.; Geng, C.; Wang, X.; Gu, C.; Huang, L.; Yang, W.; Bai, Z. Chemical characteristics of road dust PM2.5 fraction in oasis cities at the margin of Tarim Basin. J. Environ. Sci. 2020, 95, 217–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, H.; Yang, W.; Wang, X.; Yin, B.; Zhang, X.; Wang, J.; Gu, C.; Ming, J.; Geng, C.; Bai, Z. A seriously sand storm mixed air-polluted area in the margin of Tarim Basin: Temporal-spatial distribution and potential sources. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 676, 436–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Putaud, J.-P.; Van Dingenen, R.; Dell’Acqua, A.; Raes, F.; Matta, E.; Decesari, S.; Facchini, M.; Fuzzi, S. Size-segregated aerosol mass closure and chemical composition in Monte Cimone (I) during MINATROC. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2004, 4, 889–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falkovich, A.H.; Schkolnik, G.; Ganor, E.; Rudich, Y. Adsorption of organic compounds pertinent to urban environments onto mineral dust particles. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2004, 109, D02208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, P.; Zhang, L.; Ma, J.; Tang, K.; Xu, L.; Wang, Y.; Cao, X.; Liang, J.; Ji, Y.; Jiang, J.H. Radiative absorption enhancement of dust mixed with anthropogenic pollution over East Asia. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 18, 7815–7825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Li, Z.; Chang, W.; Ou, Y.; Goloub, P.; Li, C.; Li, K.; Hu, Q.; Wang, J.; Wendisch, M. Aerosol solar radiative forcing near the Taklimakan Desert based on radiative transfer and regional meteorological simulations during the Dust Aerosol Observation-Kashi campaign. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2020, 20, 10845–10864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reid, J.S.; Eck, T.F.; Christopher, S.a.; Koppmann, R.; Dubovik, O.; Eleuterio, D.; Holben, B.N.; Reid, E.A.; Zhang, J. A review of biomass burning emissions part III: Intensive optical properties of biomass burning particles. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2005, 5, 827–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russell, P.; Bergstrom, R.; Shinozuka, Y.; Clarke, A.; DeCarlo, P.; Jimenez, J.; Livingston, J.; Redemann, J.; Dubovik, O.; Strawa, A. Absorption Angstrom Exponent in AERONET and related data as an indicator of aerosol composition. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2010, 10, 1155–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ridley, D.A.; Heald, C.L.; Kok, J.F.; Zhao, C. An observationally constrained estimate of global dust aerosol optical depth. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 16, 15097–15117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Xu, H.; Li, K.; Li, D.; Xie, Y.; Li, L.; Zhang, Y.; Gu, X.; Zhao, W.; Tian, Q. Comprehensive study of optical, physical, chemical, and radiative properties of total columnar atmospheric aerosols over China: An overview of Sun–Sky Radiometer Observation Network (SONET) measurements. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2018, 99, 739–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heim, M.; Mullins, B.J.; Umhauer, H.; Kasper, G. Performance evaluation of three optical particle counters with an efficient “multimodal” calibration method. J. Aerosol Sci. 2008, 39, 1019–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, T.; Laborde, M.; Kassell, G.; Wiedensohler, A. Design and performance of a three-wavelength LED-based total scatter and backscatter integrating nephelometer. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2011, 4, 1291–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnott, W.P.; Hamasha, K.; Moosmüller, H.; Sheridan, P.J.; Ogren, J.A. Towards aerosol light-absorption measurements with a 7-wavelength aethalometer: Evaluation with a photoacoustic instrument and 3-wavelength nephelometer. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 17–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caubel, J.J.; Cados, T.E.; Kirchstetter, T.W. A new black carbon sensor for dense air quality monitoring networks. Sensors 2018, 18, 738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gobeli, D.; Schloesser, H.; Pottberg, T. Met one instruments BAM-1020 beta attenuation mass monitor US-EPA PM2.5 federal equivalent method field test results. In Proceedings of the Air & Waste Management Association (A&WMA) Conference, Kansas City, MO, USA, 4–27 June 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Draxler, R.R.; Hess, G. An overview of the HYSPLIT_4 modelling system for trajectories. Aust. Meteorol. Mag. 1998, 47, 295–308. [Google Scholar]
- Kassianov, E.; Barnard, J.; Pekour, M.; Berg, L.K.; Shilling, J.; Flynn, C.; Mei, F.; Jefferson, A. Simultaneous retrieval of effective refractive index and density from size distribution and light-scattering data: Weakly absorbing aerosol. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2014, 7, 3247–3261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abo Riziq, A.; Erlick, C.; Dinar, E.; Rudich, Y. Optical properties of absorbing and non-absorbing aerosols retrieved by cavity ring down (CRD) spectroscopy. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2007, 7, 1523–1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettersson, A.; Lovejoy, E.R.; Brock, C.A.; Brown, S.S.; Ravishankara, A. Measurement of aerosol optical extinction at 532nm with pulsed cavity ring down spectroscopy. J. Aerosol Sci. 2004, 35, 995–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Zhao, W.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, S.; Fang, B.; Chen, W.; Venables, D.S.; Wang, X.; Pu, W.; Wang, X. Optical properties of atmospheric fine particles near Beijing during the HOPE-J 3 A campaign. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 16, 6421–6439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofer, J.; Althausen, D.; Abdullaev, S.F.; Makhmudov, A.N.; Nazarov, B.I.; Schettler, G.; Engelmann, R.; Baars, H.; Fomba, K.W.; Müller, K. Long-term profiling of mineral dust and pollution aerosol with multiwavelength polarization Raman lidar at the Central Asian site of Dushanbe, Tajikistan: Case studies. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2017, 17, 14559–14577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falkovich, A.H.; Ganor, E.; Levin, Z.; Formenti, P.; Rudich, Y. Chemical and mineralogical analysis of individual mineral dust particles. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2001, 106, 18029–18036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, Z.; Chen, Y.; de Leeuw, G.; Zhang, C.; Xie, Y.; Li, K. Improved inversion of aerosol components in the atmospheric column from remote sensing data. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2020, 20, 12795–12811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, X.; Zhang, N.; Tian, P.; Tang, C.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, M.; Guo, Y.; Du, T. Wintertime vertical distribution of black carbon and single scattering albedo in a semi-arid region derived from tethered balloon observations. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 807, 150790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirchstetter, T.W.; Novakov, T.; Hobbs, P.V. Evidence that the spectral dependence of light absorption by aerosols is affected by organic carbon. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2004, 109, D21208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Yoon, S.-C.; Kim, S.-W.; Kim, Y.P.; Ghim, Y.S.; Kim, J.-H.; Kang, C.-H.; Kim, Y.J.; Chang, L.-S.; Lee, S.-J. Spectral dependency of light scattering/absorption and hygroscopicity of pollution and dust aerosols in Northeast Asia. Atmos. Environ. 2012, 50, 246–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, T.L.; Ogren, J.A. Determining aerosol radiative properties using the TSI 3563 integrating nephelometer. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 1998, 29, 57–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wu, G.; Zhang, C.; Xu, T.; Zhou, Q. What is the real role of iron oxides in the optical properties of dust aerosols? Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2015, 15, 12159–12177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moosmüller, H.; Engelbrecht, J.P.; Skiba, M.; Frey, G.; Chakrabarty, R.K.; Arnott, W.P. Single scattering albedo of fine mineral dust aerosols controlled by iron concentration. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2012, 117, D11210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lafon, S.; Sokolik, I.N.; Rajot, J.L.; Caquineau, S.; Gaudichet, A. Characterization of iron oxides in mineral dust aerosols: Implications for light absorption. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2006, 111, D21207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahowald, N.M.; Baker, A.R.; Bergametti, G.; Brooks, N.; Duce, R.A.; Jickells, T.D.; Kubilay, N.; Prospero, J.M.; Tegen, I. Atmospheric global dust cycle and iron inputs to the ocean. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 2005, 19, GB4025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prats, N.; Cachorro, V.; Sorribas, M.; Mogo, S.; Berjón, A.; Toledano, C.; De Frutos, A.; De la Rosa, J.; Laulainen, N.; De la Morena, B. Columnar aerosol optical properties during “El Arenosillo 2004 summer campaign”. Atmos. Environ. 2008, 42, 2643–2653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foyo-Moreno, I.; Alados, I.; Guerrero-Rascado, J.L.; Lyamani, H.; Pérez-Ramírez, D.; Olmo, F.; Alados-Arboledas, L. Contribution to column-integrated aerosol typing based on Sun-photometry using different criteria. Atmos. Res. 2019, 224, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubovik, O.; Holben, B.; Eck, T.F.; Smirnov, A.; Kaufman, Y.J.; King, M.D.; Tanré, D.; Slutsker, I. Variability of absorption and optical properties of key aerosol types observed in worldwide locations. J. Atmos. Sci. 2002, 59, 590–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergstrom, R.W.; Pilewskie, P.; Russell, P.B.; Redemann, J.; Bond, T.C.; Quinn, P.K.; Sierau, B. Spectral absorption properties of atmospheric aerosols. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2007, 7, 5937–5943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eck, T.F.; Holben, B.; Sinyuk, A.; Pinker, R.; Goloub, P.; Chen, H.; Chatenet, B.; Li, Z.; Singh, R.P.; Tripathi, S.N. Climatological aspects of the optical properties of fine/coarse mode aerosol mixtures. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2010, 115, D19205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gadhavi, H.; Jayaraman, A. Absorbing aerosols: Contribution of biomass burning and implications for radiative forcing. Ann. Geophys. 2010, 28, 103–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, C.; Kim, S.-W.; Lee, M.; Yoon, S.-C.; Lee, S. Carbonaceous aerosol AAE inferred from in-situ aerosol measurements at the Gosan ABC super site, and the implications for brown carbon aerosol. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2012, 12, 6173–6184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffer, A.; Gelencsér, A.; Guyon, P.; Kiss, G.; Schmid, O.; Frank, G.; Artaxo, P.; Andreae, M. Optical properties of humic-like substances (HULIS) in biomass-burning aerosols. Atmos. Chem. Phys. Discuss. 2005, 5, 7341–7360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schnaiter, M.; Schmid, O.; Petzold, A.; Fritzsche, L.; Klein, K.-F.; Andreae, M.O.; Helas, G.; Thielmann, A.; Gimmler, M.; Möhler, O. Measurement of wavelength-resolved light absorption by aerosols utilizing a UV-VIS extinction cell. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 249–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Zhang, X.; Mao, M.; Yin, Y.; Tang, S. The absorption Ångstrom exponent of black carbon with brown coatings: Effects of aerosol microphysics and parameterization. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2020, 20, 9701–9711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, A.; McNaughton, C.; Kapustin, V.; Shinozuka, Y.; Howell, S.; Dibb, J.; Zhou, J.; Anderson, B.; Brekhovskikh, V.; Turner, H. Biomass burning and pollution aerosol over North America: Organic components and their influence on spectral optical properties and humidification response. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2007, 112, D12S18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiraiwa, M.; Kondo, Y.; Iwamoto, T.; Kita, K. Amplification of light absorption of black carbon by organic coating. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 46–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lack, D.A.; Cappa, C.D.; Cross, E.S.; Massoli, P.; Ahern, A.T.; Davidovits, P.; Onasch, T.B. Absorption enhancement of coated absorbing aerosols: Validation of the photo-acoustic technique for measuring the enhancement. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 1006–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goel, V.; Mishra, S.K.; Pal, P.; Ahlawat, A.; Vijayan, N.; Jain, S.; Sharma, C. Influence of chemical aging on physico-chemical properties of mineral dust particles: A case study of 2016 dust storms over Delhi. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 267, 115338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.; Dey, S.; Tripathi, S.; Tare, V.; Holben, B. Variability of aerosol parameters over Kanpur, northern India. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2004, 109, D23206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schnaiter, M.; Gimmler, M.; Llamas, I.; Linke, C.; Jäger, C.; Mutschke, H. Strong spectral dependence of light absorption by organic carbon particles formed by propane combustion. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2006, 6, 2981–2990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schnaiter, M.; Horvath, H.; Möhler, O.; Naumann, K.-H.; Saathoff, H.; Schöck, O. UV-VIS-NIR spectral optical properties of soot and soot-containing aerosols. J. Aerosol Sci. 2003, 34, 1421–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, A.; Grainger, R. Simplifying the calculation of light scattering properties for black carbon fractal aggregates. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2014, 14, 7825–7836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Tang, C.; Huang, J.; Du, T.; Guan, X.; Tian, P.; Shi, J.; Cao, X.; Huang, Z.; Guo, Q. Unexpected high absorption of atmospheric aerosols over a western Tibetan Plateau site in summer. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2021, 126, e2020JD033286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).