Estimation of the Near-Surface Ozone Concentration with Full Spatiotemporal Coverage across the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Region Based on Extreme Gradient Boosting Combined with a WRF-Chem Model
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Study Area, Datasets, and Methodology
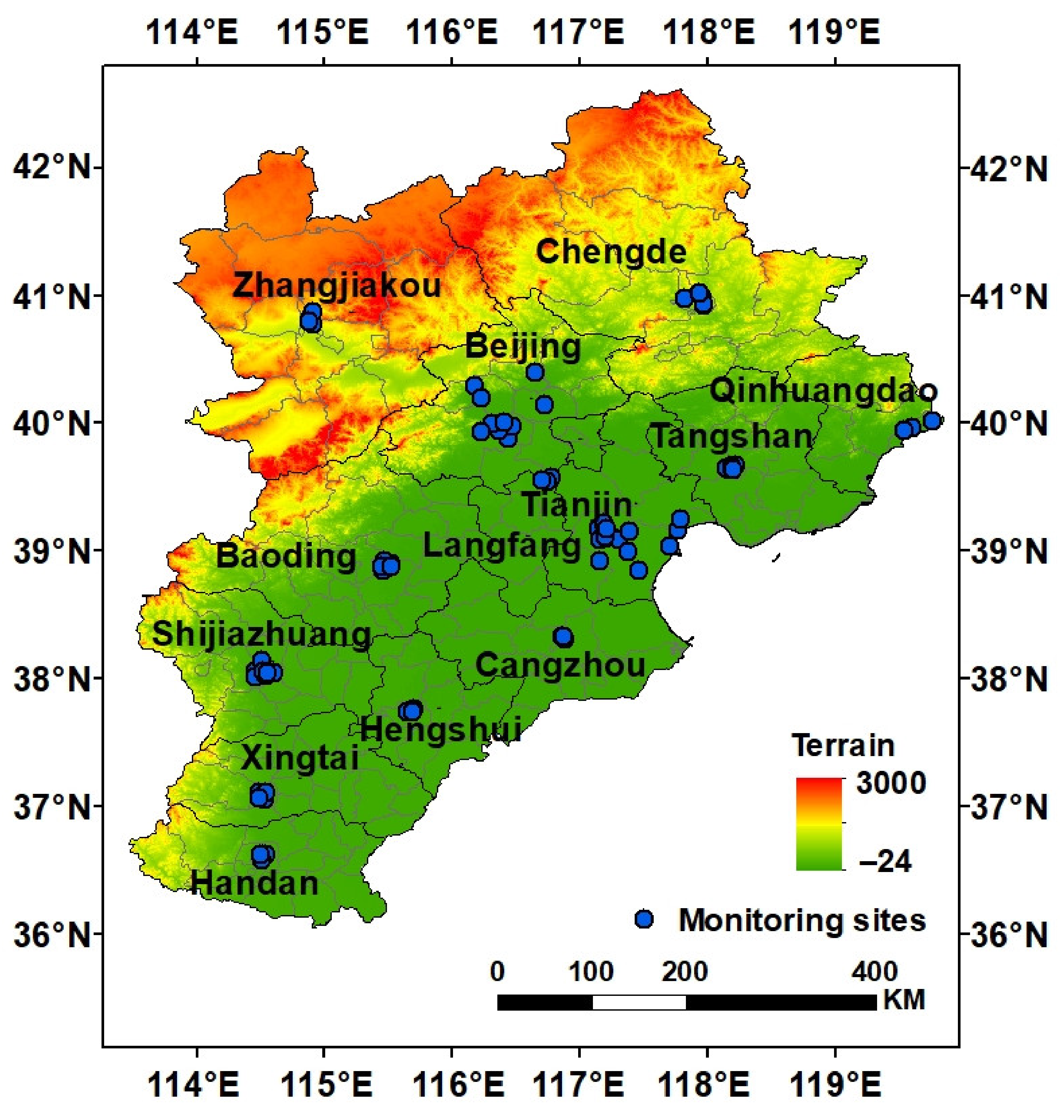
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Datasets
2.2.1. Near-Surface O3 Monitoring Data
2.2.2. WRF-Chem Simulation of O3
2.2.3. Other Auxiliary Data
2.3. Methodology
2.3.1. WRFC-XGB Model
2.3.2. Evaluation Method
3. Results and Discussion
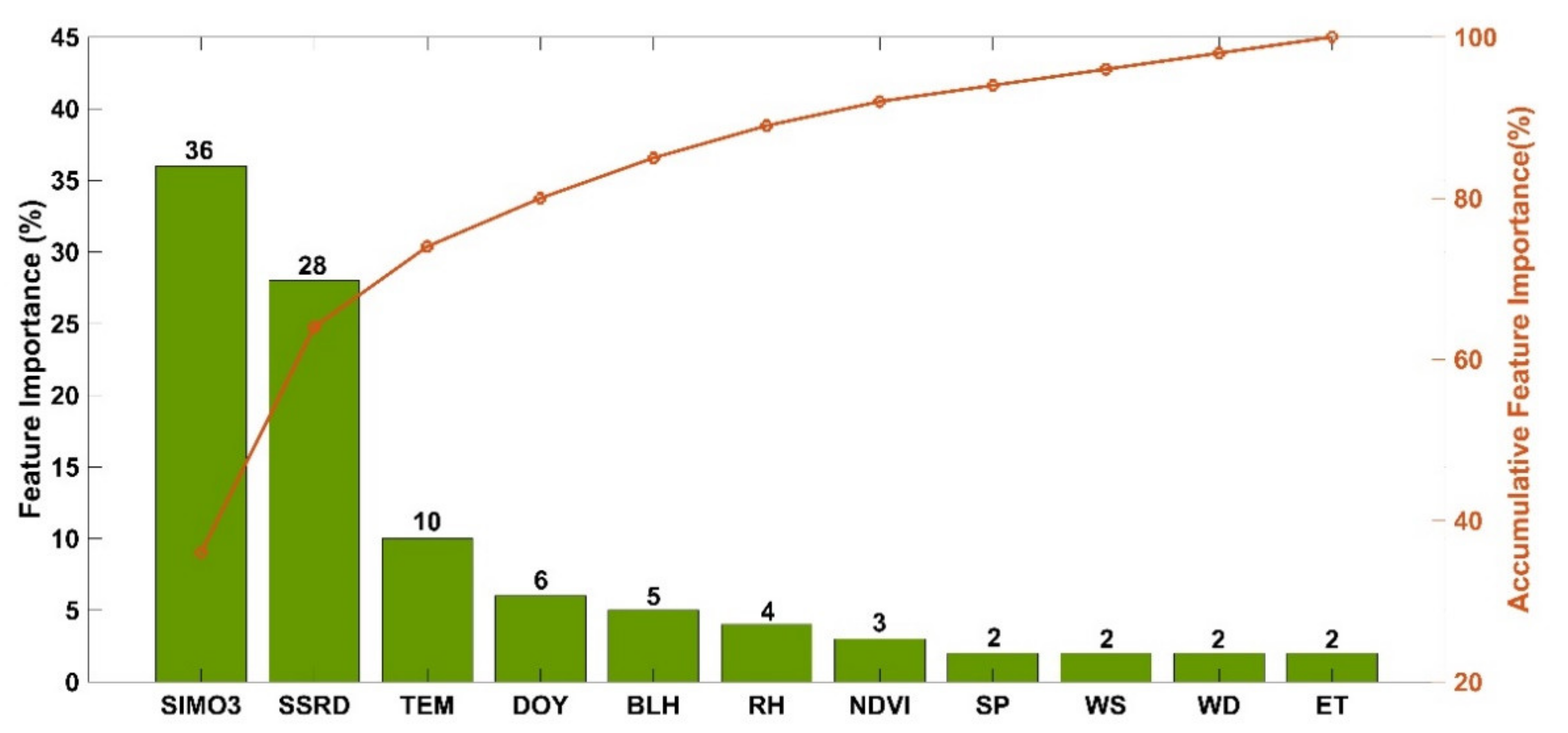
3.1. Feature Importance
3.2. Model Accuracy Evaluation
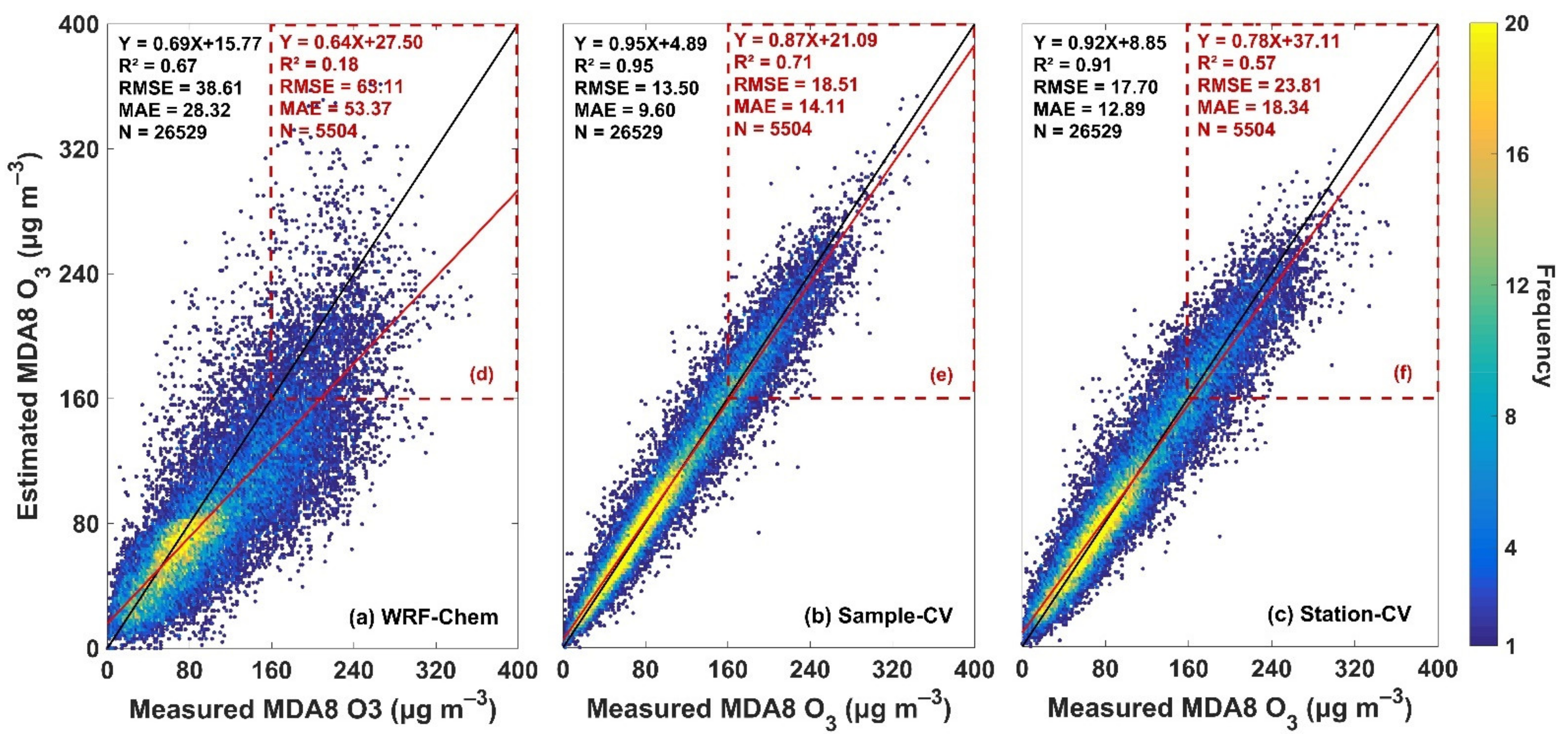
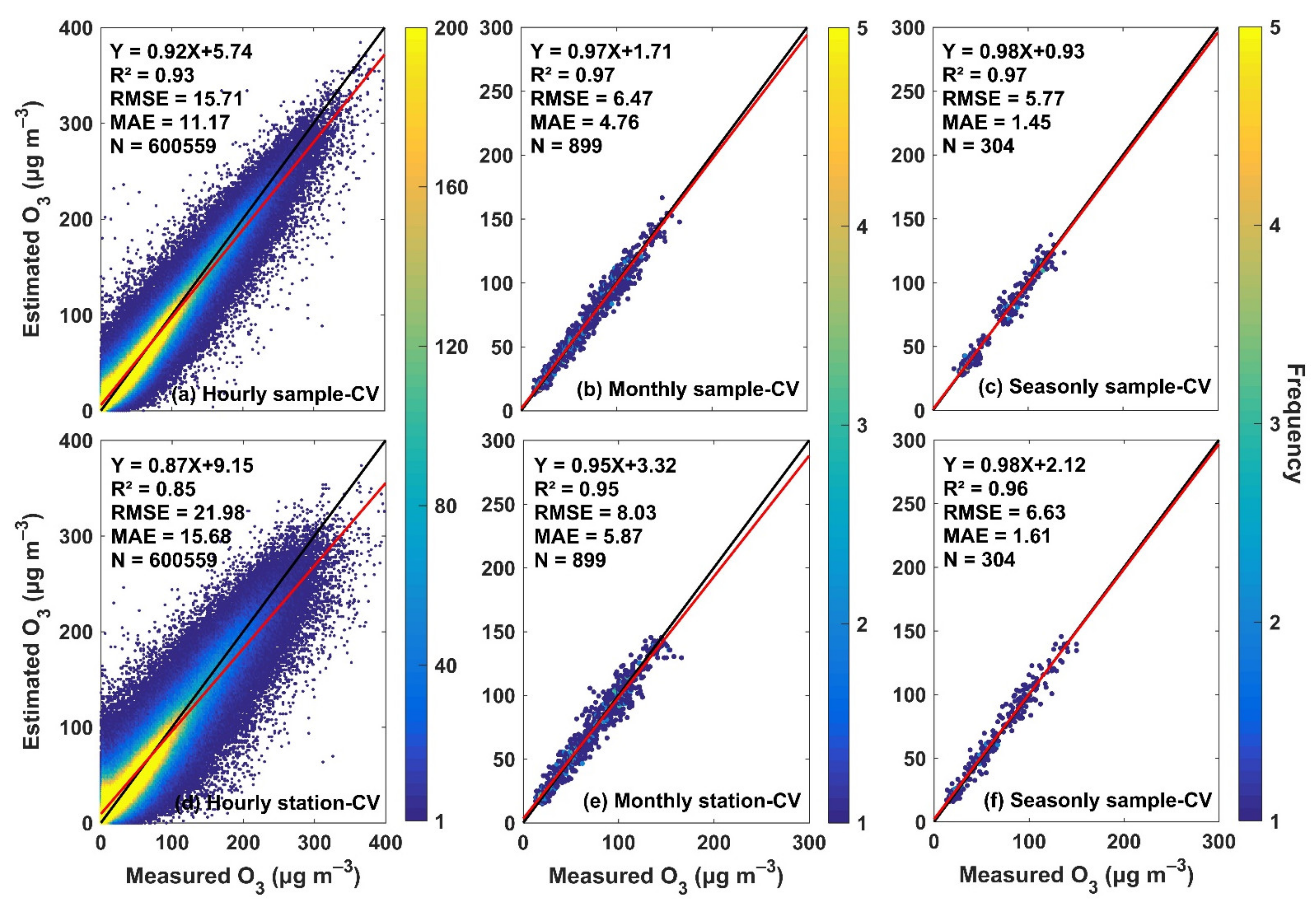
3.2.1. Overall Accuracy
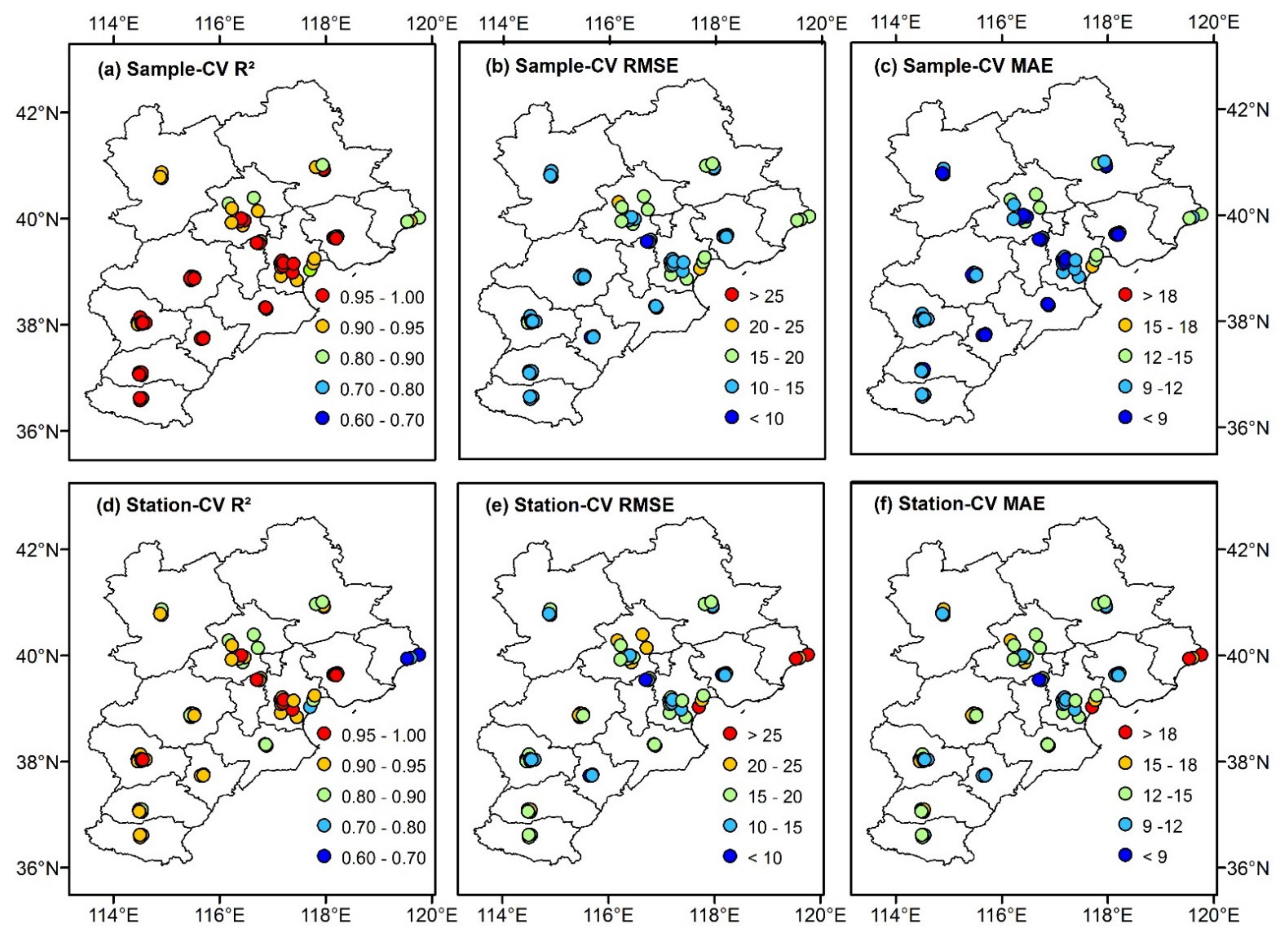
3.2.2. Spatial Consistency Verification
3.2.3. Temporal Consistency Verification
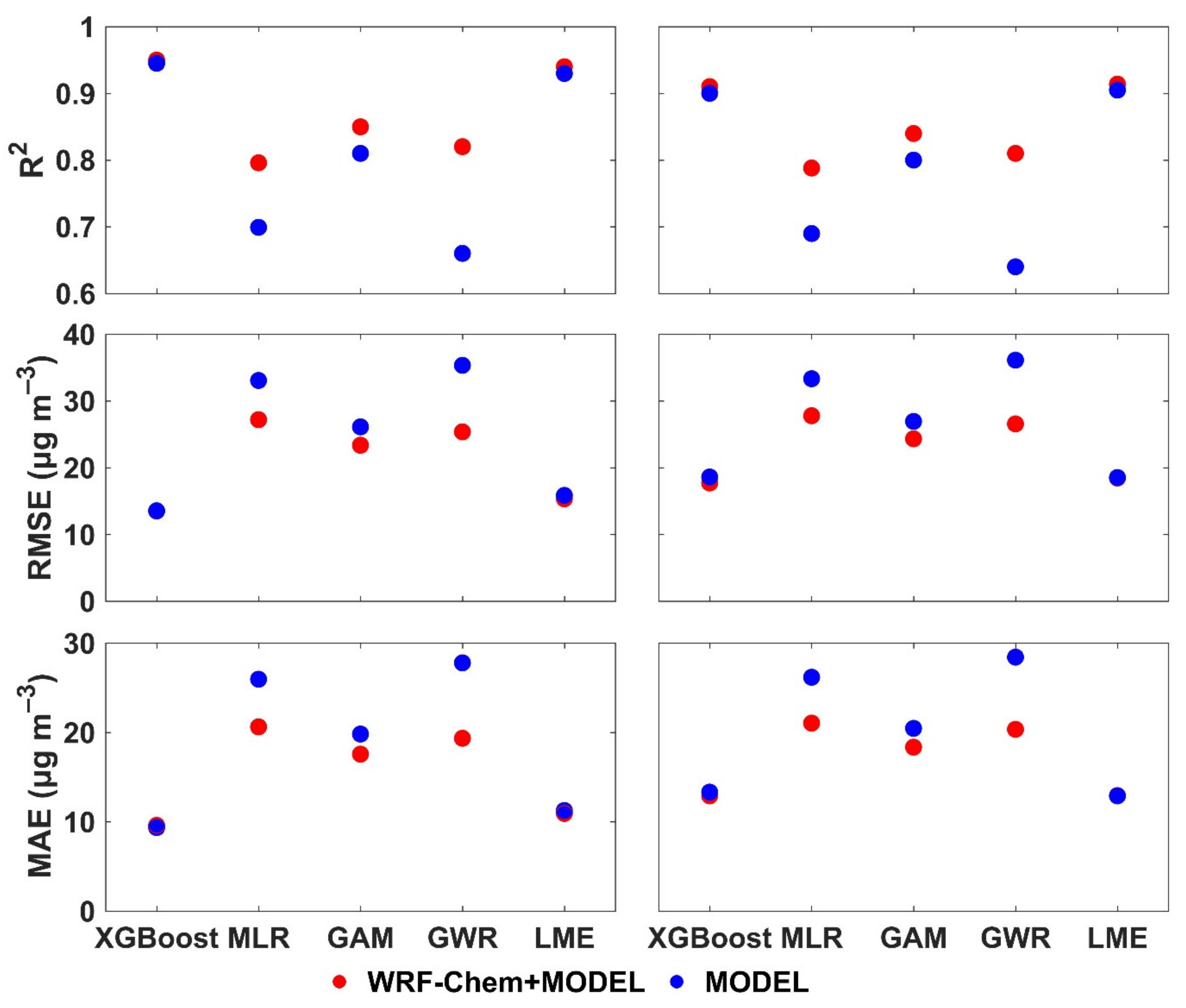
3.3. Comparison with Other Traditional Models and Studies
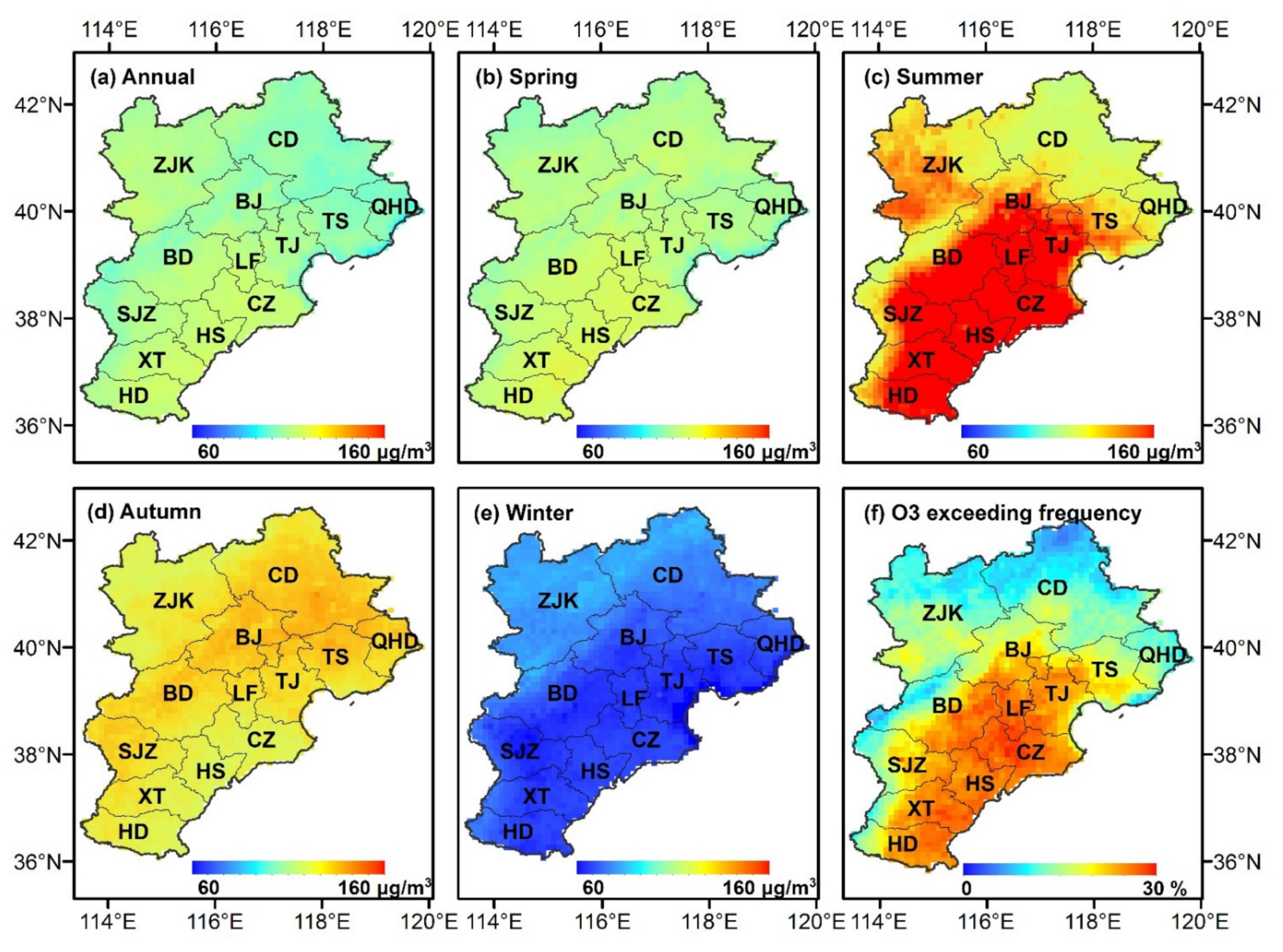
3.4. Spatial Distribution of MDA8 O3 in the BTH Region
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- U.S. Environmental Protection Agency. Integrated Science Assessment for Ozone and Related Photochemical Oxidants; U.S. Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2013.
- Jerrett, M.; Burnett, R.T.; Pope, C.A., III; Ito, K.; Thurston, G.; Krewski, D.; Shi, Y.; Calle, E.; Thun, M. Long-Term Ozone Exposure and Mortality. N. Engl. J. Med. 2009, 360, 1085–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sitch, S.; Cox, P.; Collins, W.; Huntingford, C. Indirect radiative forcing of climate change through ozone effects on the land-carbon sink. Nature 2007, 448, 791–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, Y.; Liao, H.; Yang, Y. Interannual and Decadal Changes in Tropospheric Ozone in China and the Associated Chemistry-Climate Interactions: A Review. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2019, 36, 975–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Xue, L.; Brimblecombe, P.; Lam, Y.F.; Li, L.; Zhang, L. Ozone pollution in China: A review of concentrations, meteorological influences, chemical precursors, and effects. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 575, 1582–1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, S.; Li, X.; Teng, Y.; Fu, H.; Chen, L.; Mao, J.; Zhang, H.; Gao, S.; Sun, Y.; Ma, Z.; et al. Estimation of health and economic benefits based on ozone exposure level with high spatial-temporal resolution by fusing satellite and station observations. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 255, 113267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, L.; Liu, S.; Ma, L.; Zhang, Z.; Du, J.; Zhou, Y.; Meng, F. Evaluating the meteorological normalized PM2.5 trend (2014–2019) in the “2+26” region of China using an ensemble learning technique. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 266, 115346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, B.; Tong, D.; Li, M.; Liu, F.; Hong, C.; Geng, G.; Li, H.; Li, X.; Peng, L.; Qi, J.; et al. Trends in China’s anthropogenic emissions since 2010 as the consequence of clean air actions. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 18, 14095–14111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xiang, S.; Liu, J.; Tao, W.; Yi, K.; Xu, J.; Hu, X.; Liu, H.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, H.; et al. Control of both PM2.5 and O3 in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei and the surrounding areas. Atmos. Environ. 2020, 224, 117259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, D.; Xie, M.; Chen, X.; Wang, T.; Zhan, C.; Ren, J.; Liu, Q. Modeling the Effects of Climate Change on Surface Ozone during Summer in the Yangtze River Delta Region, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Heal. 2019, 16, 1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, K.; Jacob, D.J.; Liao, H.; Shen, L.; Zhang, Q.; Bates, K.H. Anthropogenic drivers of 2013–2017 trends in summer surface ozone in China. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 116, 422–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, L.; Jacob, D.J.; Downey, N.V.; Wood, D.A.; Blewitt, D.; Carouge, C.C.; van Donkelaar, A.; Jones, D.B.; Murray, L.; Wang, Y. Improved estimate of the policy-relevant background ozone in the United States using the GEOS-Chem global model with 1/2° × 2/3° horizontal resolution over North America. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 45, 6769–6776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mathur, R.; Xing, J.; Napelenok, S.; Pleim, J.; Hogrefe, C.; Wong, D.; Gan, C.-M.; Kang, D. Multiscale Modeling of Multi-decadal Trends in Ozone and Precursor Species Across the Northern Hemisphere and the United States. In Air Pollution Modeling and its Application XXIV; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; pp. 239–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Zhang, L.; Chen, Y.; Zhou, M.; Zheng, B.; Li, K.; Liu, Y.; Lin, J.; Fu, T.-M.; Zhang, Q. Exploring 2016–2017 surface ozone pollution over China: Source contributions and meteorological influences. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2019, 19, 8339–8361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qiao, X.; Guo, H.; Wang, P.; Tang, Y.; Ying, Q.; Zhao, X.; Deng, W.; Zhang, H. Fine Particulate Matter and Ozone Pollution in the 18 Cities of the Sichuan Basin in Southwestern China: Model Performance and Characteristics. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2019, 19, 2308–2319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Adam-Poupart, A.; Brand, A.; Fournier, M.; Jerrett, M.; Smargiassi, A. Spatiotemporal Modeling of Ozone Levels in Quebec (Canada): A Comparison of Kriging, Land-Use Regression (LUR), and Combined Bayesian Maximum Entropy–LUR Approaches. Environ. Heal. Perspect. 2014, 122, 970–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefohn, A.S.; Knudsen, H.; McEvoy, L.R. The use of kriging to estimate monthly ozone exposure parameters for the Southeastern United States. Environ. Pollut. 1988, 53, 27–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L. An Application of a Shape Function Based Spatiotemporal Interpolation Method to Ozone and Population-Based Environmental Exposure in the Contiguous U.S. J. Environ. Inform. 2008, 12, 120–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghazali, N.A.; Ramli, N.A.; Yahaya, A.S.; Yusof, N.F.F.M.; Sansuddin, N.; Al Madhoun, W.A. Transformation of nitrogen dioxide into ozone and prediction of ozone concentrations using multiple linear regression techniques. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2009, 165, 475–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sousa, S.; Martins, F.; Alvimferraz, M.; Pereira, M. Multiple linear regression and artificial neural networks based on principal components to predict ozone concentrations. Environ. Model. Softw. 2007, 22, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez-Mendoza, C.I.; Teodoro, A.; Cando, L.R. Spatial estimation of surface ozone concentrations in Quito Ecuador with remote sensing data, air pollution measurements and meteorological variables. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2019, 191, 155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.Y.; Zhao, L.M.; Cheng, M.M.; Chen, D.M. Estimating Ground-Level Ozone Concentrations in Eastern China Using Satellite-Based Precursors. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2020, 58, 4754–4763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, Y.; Luo, Y.Z.; Deng, X.F.; Grieneisen, M.L.; Zhang, M.H.; Di, B.F. Spatiotemporal prediction of daily ambient ozone levels across China using random forest for human exposure assessment. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 233, 464–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, G.; Chen, J.; Dong, G.-H.; Yang, B.-Y.; Liu, Y.; Lu, T.; Yu, P.; Guo, Y.; Li, S. Improving satellite-based estimation of surface ozone across China during 2008–2019 using iterative random forest model and high-resolution grid meteorological data. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2021, 69, 102807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, W.; Zhang, J.; Zhong, C.; Li, X.; Wei, J. Spatiotemporal PM2.5 variations and its response to the industrial structure from 2000 to 2018 in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 279, 123742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Li, Z.; Xue, W.; Sun, L.; Fan, T.; Liu, L.; Su, T.; Cribb, M. The ChinaHighPM10 dataset: Generation, validation, and spatiotemporal variations from 2015 to 2019 across China. Environ. Int. 2020, 146, 106290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Wang, Y.; Yuan, Q. Remote Sensing Estimation of Regional NO2 via Space-Time Neural Networks. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, G.; Xiao, Q.; Liu, S.; Liu, X.; Cheng, J.; Zheng, Y.; Xue, T.; Tong, D.; Zheng, B.; Peng, Y.; et al. Tracking Air Pollution in China: Near Real-Time PM2.5 Retrievals from Multisource Data Fusion. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 12106–12115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Fu, L.; Ji, M.; Lang, J.; Chen, D.; Cheng, S. Scenario analysis to vehicular emission reduction in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei (BTH) region, China. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 216, 470–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministry of Ecology and Environmental of the People’s Republic of China (MEE). National Urban Air Quality Status in 2018. 2018. Available online: http://www.mee.gov.cn/hjzl/dqhj/cskqzlzkyb/201809/P020180905326235405574.pdf (accessed on 4 March 2021).
- Grell, G.A.; Peckham, S.E.; Schmitz, R.; McKeen, S.A.; Frost, G.; Skamarock, W.C.; Eder, B. Fully coupled “online” chemistry within the WRF model. Atmos. Environ. 2005, 39, 6957–6975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Zhang, Q.; Tong, D.; Zheng, B.; Li, M.; Huo, H.; He, K.B. High-resolution inventory of technologies, activities, and emissions of coal-fired power plants in China from 1990 to 2010. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2015, 15, 13299–13317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tong, D.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, F.; Geng, G.; Zheng, Y.; Xue, T.; Hong, C.; Wu, R.; Qin, Y.; Zhao, H.; et al. Current Emissions and Future Mitigation Pathways of Coal-Fired Power Plants in China from 2010 to 2030. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 12905–12914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Tong, D.; Zheng, Y.; Cheng, J.; Qin, X.; Shi, Q.; Yan, L.; Lei, Y.; Zhang, Q. Carbon and air pollutant emissions from China’s cement industry 1990–2015: Trends, evolution of technologies and drivers. Atmos. Chem. Phys. Discuss. 2020, 21, 1627–1647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, L.; Zhang, Q.; Yao, Z.; Mauzerall, D.L.; Kang, S.; Du, Z.; Zheng, Y.; Xue, T.; He, K. Underreported coal in statistics: A survey-based solid fuel consumption and emission inventory for the rural residential sector in China. Appl. Energy 2018, 235, 1169–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, B.; Huo, H.; Zhang, Q.; Yao, Z.L.; Wang, X.T.; Yang, X.F.; Liu, H.; He, K.B. High-resolution mapping of vehicle emissions in China in 2008. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2014, 14, 9787–9805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guenther, A.; Karl, T.; Harley, P.; Wiedinmyer, C.; Palmer, P.I.; Geron, C. Estimates of global terrestrial isoprene emissions using MEGAN (Model of Emissions of Gases and Aerosols from Nature). Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2006, 6, 3181–3210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, L.; Zhang, J.; Lu, T.; Bao, M.; Deng, X.; Hu, X. Pollution patterns and their meteorological analysis all over China. Atmos. Environ. 2020, 246, 118108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balzarini, A.; Pirovano, G.; Honzak, L.; Žabkar, R.; Curci, G.; Forkel, R.; Hirtl, M.; José, R.S.; Tuccella, P.; Grell, G. WRF-Chem model sensitivity to chemical mechanisms choice in reconstructing aerosol optical properties. Atmos. Environ. 2015, 115, 604–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaveri, R.; Peters, L.K. A new lumped structure photochemical mechanism for large-scale applications. J. Geophys. Res. Earth Surf. 1999, 104, 30387–30415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.-Y.; Noh, Y.; Dudhia, J. A New Vertical Diffusion Package with an Explicit Treatment of Entrainment Processes. Mon. Weather Rev. 2006, 134, 2318–2341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, F.; Dudhia, J. Coupling an Advanced Land Surface–Hydrology Model with the Penn State–NCAR MM5 Modeling System. Part I: Model Implementation and Sensitivity. Mon. Weather Rev. 2001, 129, 569–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grell, G.A.; Dévényi, D. A generalized approach to parameterizing convection combining ensemble and data assimilation techniques. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2002, 29, 38-1–38-4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Morrison, H.; Thompson, G.; Tatarskii, V. Impact of Cloud Microphysics on the Development of Trailing Stratiform Precipitation in a Simulated Squall Line: Comparison of One- and Two-Moment Schemes. Mon. Weather Rev. 2009, 137, 991–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mlawer, E.J.; Taubman, S.J.; Brown, P.D.; Iacono, M.J.; Clough, S.A. Radiative transfer for inhomogeneous atmospheres: RRTM, a validated correlated-k model for the longwave. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1997, 102, 16663–16682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chou, M.-D.; Suarez, M.J. A Solar Radiation Parameterization for Atmospheric Studies. NASA Tech. Rep. Ser. Glob. Model. Data Assim. 1999, 15, 104606. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, T.; Guestrin, C. XGBoost: A Scalable Tree Boosting System. In Proceedings of the 22nd ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, San Francisco, CA, USA, 13–17 August 2016; pp. 785–794. [Google Scholar]
- Shtein, A.; Kloog, I.; Schwartz, J.; Silibello, C.; Michelozzi, P.; Gariazzo, C.; Viegi, G.; Forastiere, F.; Karnieli, A.; Just, A.C.; et al. Estimating Daily PM2.5 and PM10 over Italy Using an Ensemble Model. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 54, 120–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babak, O.; Deutsch, C.V. Statistical approach to inverse distance interpolation. Stoch. Hydrol. Hydraul. 2008, 23, 543–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Hong, J. A GAM for Daily Ozone Concentration in Seoul. Key Eng. Mater. 2005, 277–279, 497–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; Fu, Q.; Ma, Z.; Chen, L.; Zou, B.; Zhang, Y.; Xue, W.; Wang, J.; Wang, D.; Kan, H.; et al. Estimating ground-level PM 10 in a Chinese city by combining satellite data, meteorological information and a land use regression model. Environ. Pollut. 2015, 208, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özbay, B.; Keskin, G.A.; Doğruparmak, Ş.Ç.; Ayberk, S. Multivariate methods for ground-level ozone modeling. Atmos. Res. 2011, 102, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez, J.D.; Pérez, A.; Lozano, J.A. Sensitivity Analysis of k-Fold Cross Validation in Prediction Error Estimation. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2009, 32, 569–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, W.; Wei, J.; Zhang, J.; Sun, L.; Che, Y.; Yuan, M.; Hu, X. Inferring Near-Surface PM2.5 Concentrations from the VIIRS Deep Blue Aerosol Product in China: A Spatiotemporally Weighted Random Forest Model. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Gong, S.; Yu, Y.; Yu, L.; Wu, L.; Mao, H.; Song, C.; Zhao, S.; Liu, H.; Li, X.; et al. Air pollution characteristics and their relation to meteorological conditions during 2014–2015 in major Chinese cities. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 223, 484–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Shen, L.; Wu, S.; Mickley, L.; He, J.; Hao, J. Sensitivity of surface ozone over China to 2000–2050 global changes of climate and emissions. Atmos. Environ. 2013, 75, 374–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Im, U.; Markakis, K.; Poupkou, A.; Melas, D.; Unal, A.; Gerasopoulos, E.; Daskalakis, N.; Kindap, T.; Kanakidou, M. The impact of temperature changes on summer time ozone and its precursors in the Eastern Mediterranean. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2011, 11, 3847–3864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, Z.; Zhuang, Y.; Xie, X.; Chen, D.; Cheng, N.; Yang, L.; Li, R. Understanding long-term variations of meteorological influences on ground ozone concentrations in Beijing During 2006–2016. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 245, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilić, P.; Popović, Z.; Markić, D.N. Assessment of Meteorological Effects and Ozone Variation in Urban Area. Ecol. Chem. Eng. S 2020, 27, 373–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.; Lau, A.K.; Fung, J.C.; Song, Y.; Li, Y.; Tao, M.; Lu, X.; Ma, J.; Lao, X.Q. Removing the effects of meteorological factors on changes in nitrogen dioxide and ozone concentrations in China from 2013 to 2020. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 793, 148575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Liu, J.; Han, S.; Yao, Q.; Cai, Z. Study of the meteorological influence on ozone in urban areas and their use in assessing ozone trends in all seasons from 2009 to 2015 in Tianjin, China. Arch. Meteorol. Geophys. Bioclimatol. Ser. B 2019, 131, 1661–1675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.Y.; Ma, Z.W.; Liu, Y.; Shao, Y.C.; Zhao, W.; Bi, J. Spatiotemporal distributions of surface ozone levels in China from 2005 to 2017: A machine learning approach. Environ. Int. 2020, 142, 105823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajiloo, F.; Hamzeh, S.; Gheysari, M. Impact assessment of meteorological and environmental parameters on PM2.5 concentrations using remote sensing data and GWR analysis (case study of Tehran). Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 26, 24331–24345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, T.; Zheng, Y.; Geng, G.; Xiao, Q.; Meng, X.; Wang, M.; Li, X.; Wu, N.; Zhang, Q.; Zhu, T. Estimating Spatiotemporal Variation in Ambient Ozone Exposure during 2013–2017 Using a Data-Fusion Model. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 14877–14888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Cui, L.; Hongbo, F.; Li, J.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, J. Satellite-based estimation of full-coverage ozone (O3) concentration and health effect assessment across Hainan Island. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 244, 118773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- nbsp; Li, R.; Zhao, Y.L.; Zhou, W.H.; Meng, Y.; Zhang, Z.Y.; Fu, H.B. Developing a novel hybrid model for the estimation of surface 8 h ozone (O-3) across the remote Tibetan Plateau during 2005–2018. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2020, 20, 6159–6175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, R.; Ban, J.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, Y.; He, M.Z.; Li, S.; Shi, W.; Li, T. Random forest model based fine scale spatiotemporal O3 trends in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region in China, 2010 to 2017. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 276, 116635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, X.; Xiao, H.; Sun, H.; Liu, C.; Zhang, Z.; Xie, Y.; Liang, Y.; Wang, F. Characteristics of Ground-Level Ozone from 2015 to 2018 in BTH Area, China. Atmosphere 2020, 11, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Smiatek, G.; Steinbrecher, R. Temporal and spatial variation of forest VOC emissions in Germany in the decade 1994–2003. Atmos. Environ. 2006, 40, 166–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.; Wang, S.X.; Liu, H.; Xu, J.Y.; Fu, K.; Klimont, Z.; Hao, J.M.; He, K.B.; Cofala, J.; Amann, M.J.A.C. NOx emissions in China: Historical trends and future perspectives. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2013, 13, 9869–9897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, X.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Wang, Y.X.; Zhang, Q.Q.; Li, M.; Zheng, Y.X.; Geng, G.N.; Wallington, T.J.; et al. Attribution of PM2.5 exposure in Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei region to emissions: Implication to control strategies. Sci. Bull. 2017, 62, 957–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qi, J.; Zheng, B.; Li, M.; Yu, F.; Chen, C.; Liu, F.; Zhou, X.; Yuan, J.; Zhang, Q.; He, K. A high-resolution air pollutants emission inventory in 2013 for the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region, China. Atmos. Environ. 2017, 170, 156–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Barkjohn, K.K.; Norris, C.; Schauer, J.J.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, M.; Bergin, M. Using low-cost sensors to monitor indoor, outdoor, and personal ozone concentrations in Beijing, China. Environ. Sci. Process. Impacts 2019, 22, 131–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Domain | D01 | D02 |
|---|---|---|
| Horizontal resolution (km) | 27 | 9 |
| Domain size | 64 × 56 | 81 × 17 |
| Vertical resolution | 33 | 33 |
| Boundary layer scheme | YSU [41] | YSU |
| Land surface scheme | Noah [42] | Noah |
| Cumulus parameterization scheme | Grell-3D [43] | Grell-3D |
| Microphysics scheme | Morrison 2-mom [44] | Morrison 2-mom |
| Longwave radiation scheme | RRTM [45] | RRTM |
| Shortwave radiation scheme | Goddard [46] | Goddard |
| Chemical mechanism | CBMZ [40] | CBMZ |
| Model spin-up time (h) | 168 | 168 |
| Variable | DOY | TEM (k) | RH (%) | BLH (m) | ET (mm) | SP (hPa) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R | 0.33 ** | 0.72 ** | 0.14 ** | 0.28 ** | −0.61 ** | −0.18 ** |
| VIF | 1.20 | 5.34 | 3.10 | 2.58 | 4.07 | 1.33 |
| Variable | WD (°) | WS (m s−1) | SSRD (W m−2) | NDVI | SIMO3 (µg m−3) | |
| R | 0.07 ** | 0.05 ** | 0.72 ** | 0.43 ** | 0.82 ** | |
| VIF | 1.19 | 1.85 | 3.71 | 2.93 | 2.08 |
| Model | Spatial Resolution | Temporal Resolution | Study Area | Model Validation | Reference | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R2 | RMSE (µm m−3) | |||||
| GWR | 0.25° × 0.25° | Month | Eastern China | 0.77 | - | [22] (Zhang et al., 2020) |
| RF | 0.01° × 0.01° | Daily (MDA8H) | BTH | 0.84 (sample_CV10) | - | [61] (Ma et al., 2021) |
| RF | 0.01° × 0.01° | Daily (mean) | BTH | 0.84 (sample_CV10) | - | |
| RF | 0.01° × 0.01° | Hour (1hmax) | BTH | 0.81 (sample_CV10) | - | |
| Data fusion model | 0.1° × 0.1° | Daily (MDA8H) | China | 0.7 (sample_CV5) | 26 | [58] (Xue et al., 2020) |
| RF | 0.1° × 0.1° | Daily (MDA8H) | China | 0.69 (sample_CV10) | 26 | [23] (Zhan et al., 2018) |
| XGBoost | 0.1° × 0.1° | Daily (MDA8H) | China | 0.78 (sample_CV10) | 21.47 | [56] (Liu et al., 2020b) |
| XGBoost | 0.1° × 0.1° | Daily (MDA8H) | China | 0.64 (station_CV10) | 27.27 | [56] (Liu et al., 2020b) |
| XGBoost | 0.1° × 0.1° | Daily | Hainan Island | 0.59 (sample_CV10) | 24.14 | [59] (Li et al., 2020a) |
| RF-GAM | 0.25° × 0.25° | Daily (MDA8H) | Tibetan Plateau | 0.76 (sample_CV10) | 14.41 | [60] (Li et al., 2020b) |
| WRFC-XGB | 0.1° × 0.1° | Daily (MDA8H) | BTH | 0.95 (sample_CV10) | 13.50 | Our study |
| 0.1° × 0.1° | Daily (MDA8H) | BTH | 0.91 (station_CV10) | 17.70 | ||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hu, X.; Zhang, J.; Xue, W.; Zhou, L.; Che, Y.; Han, T. Estimation of the Near-Surface Ozone Concentration with Full Spatiotemporal Coverage across the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Region Based on Extreme Gradient Boosting Combined with a WRF-Chem Model. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 632. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13040632
Hu X, Zhang J, Xue W, Zhou L, Che Y, Han T. Estimation of the Near-Surface Ozone Concentration with Full Spatiotemporal Coverage across the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Region Based on Extreme Gradient Boosting Combined with a WRF-Chem Model. Atmosphere. 2022; 13(4):632. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13040632
Chicago/Turabian StyleHu, Xiaomin, Jing Zhang, Wenhao Xue, Lihua Zhou, Yunfei Che, and Tian Han. 2022. "Estimation of the Near-Surface Ozone Concentration with Full Spatiotemporal Coverage across the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Region Based on Extreme Gradient Boosting Combined with a WRF-Chem Model" Atmosphere 13, no. 4: 632. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13040632
APA StyleHu, X., Zhang, J., Xue, W., Zhou, L., Che, Y., & Han, T. (2022). Estimation of the Near-Surface Ozone Concentration with Full Spatiotemporal Coverage across the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Region Based on Extreme Gradient Boosting Combined with a WRF-Chem Model. Atmosphere, 13(4), 632. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13040632









