Middle Latitude Geomagnetic Disturbances Caused by Hall and Pedersen Current Circuits Driven by Prompt Penetration Electric Fields
Abstract
1. Introduction
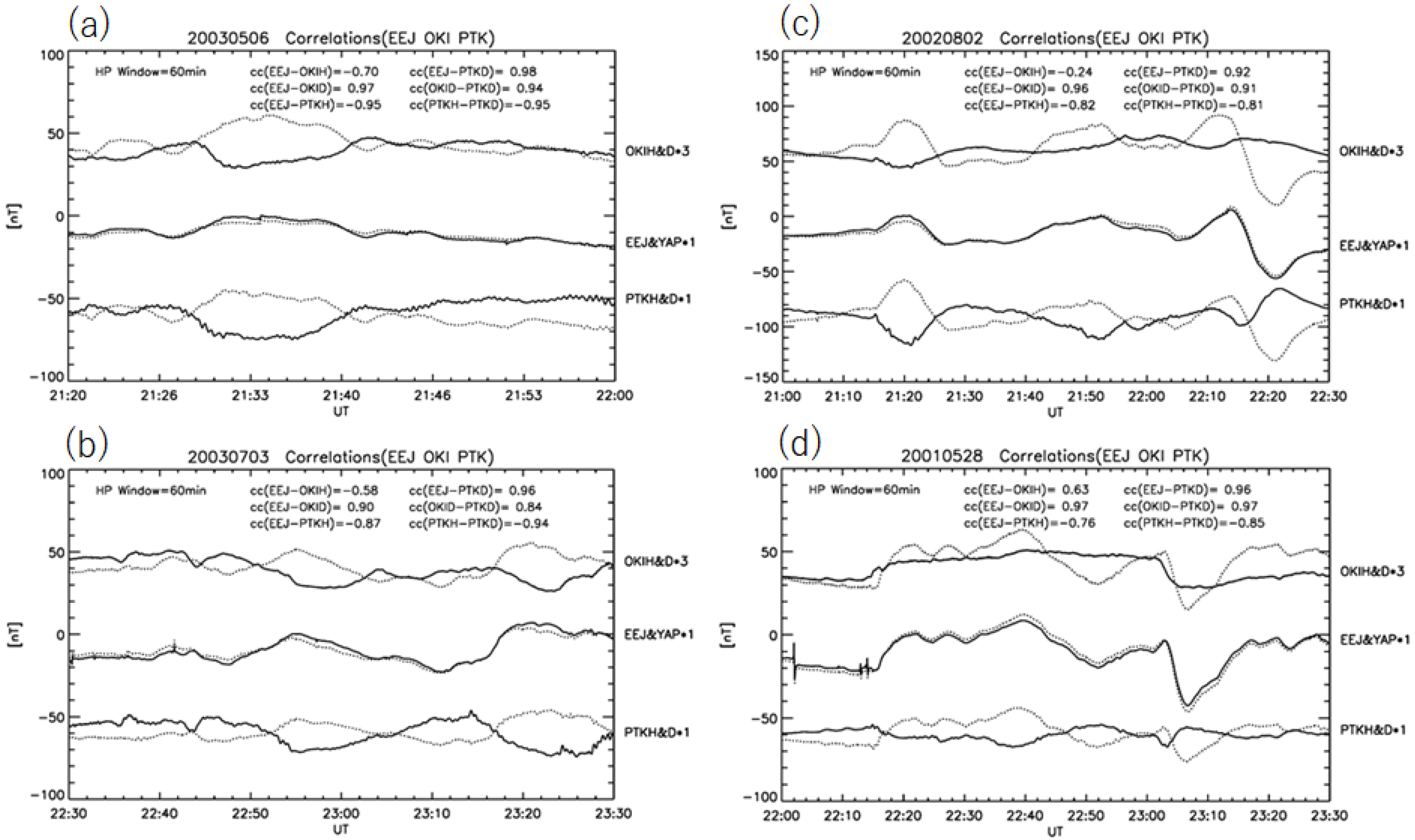
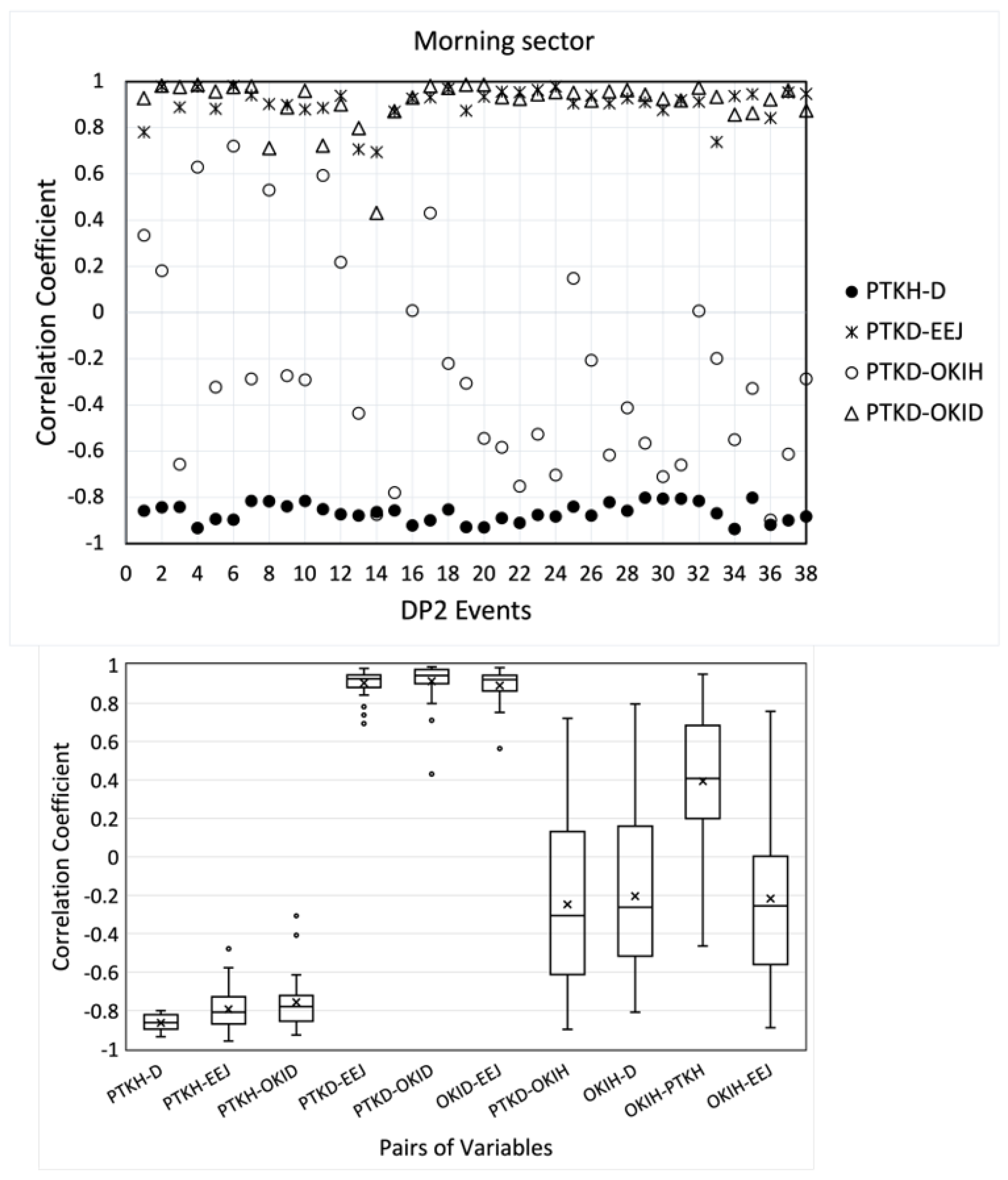
2. DP2 Events in the Morning Sector (0630-1030MLT)
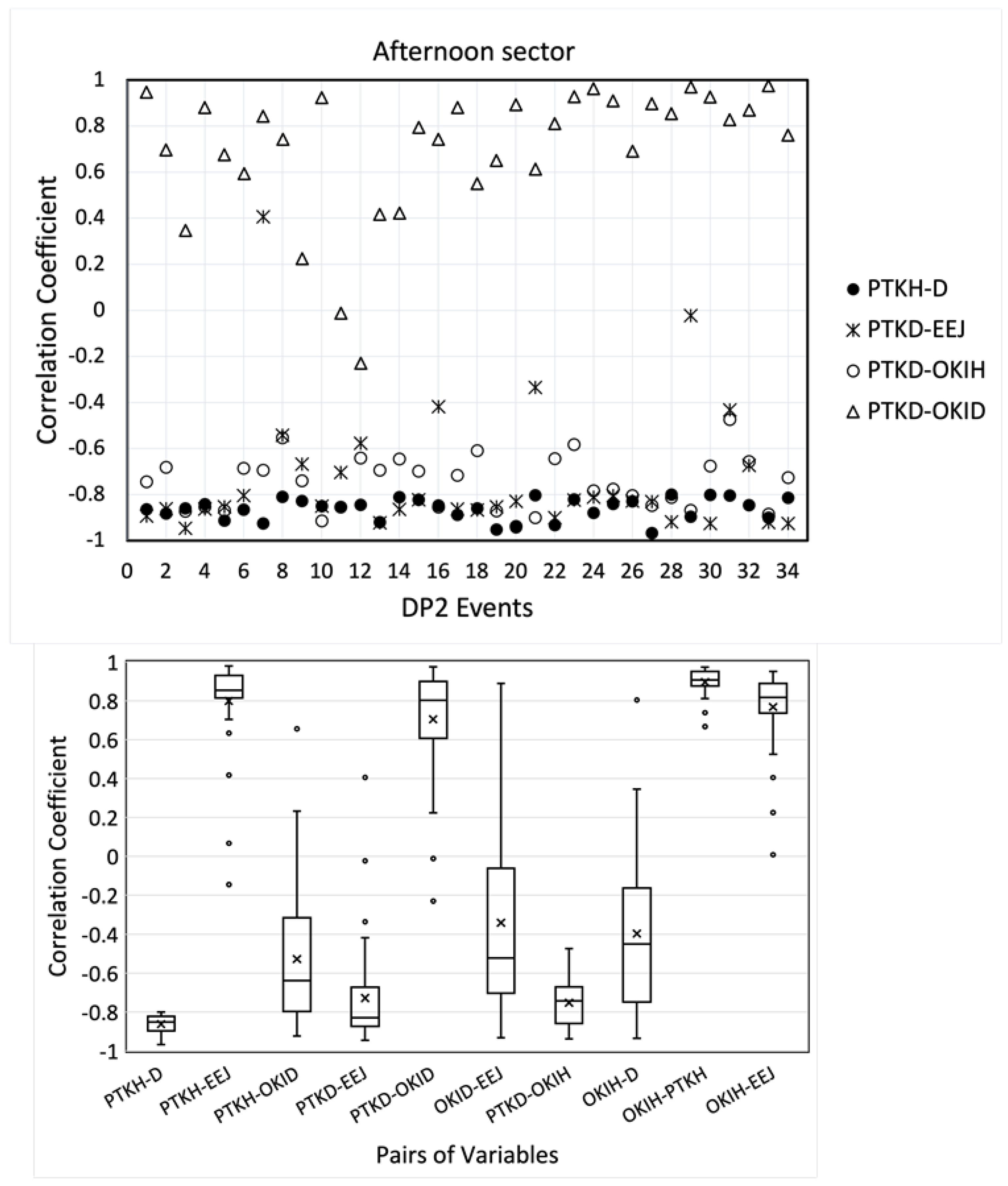
3. DP2 Events in the Afternoon (1330–1730MLT)
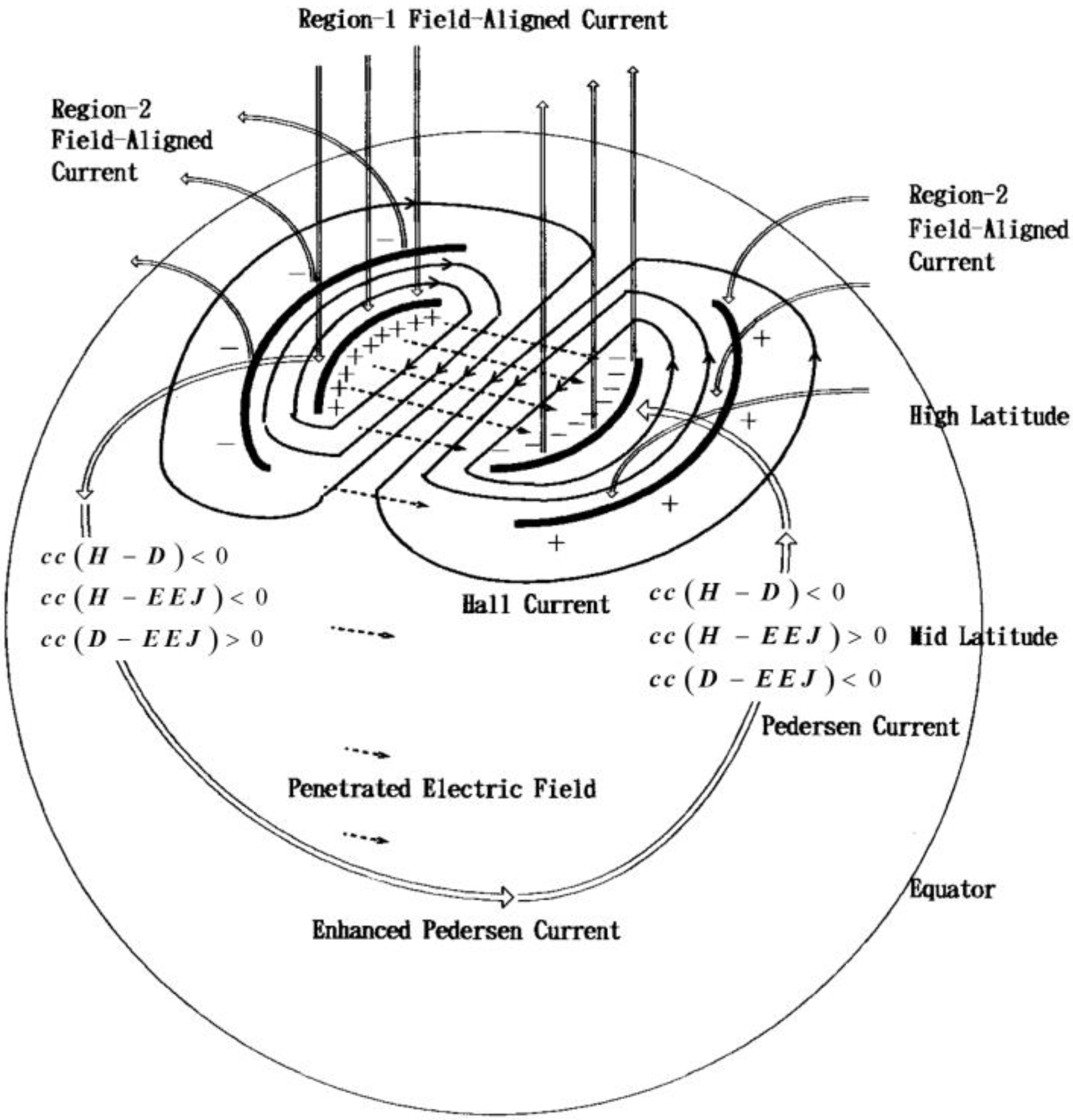
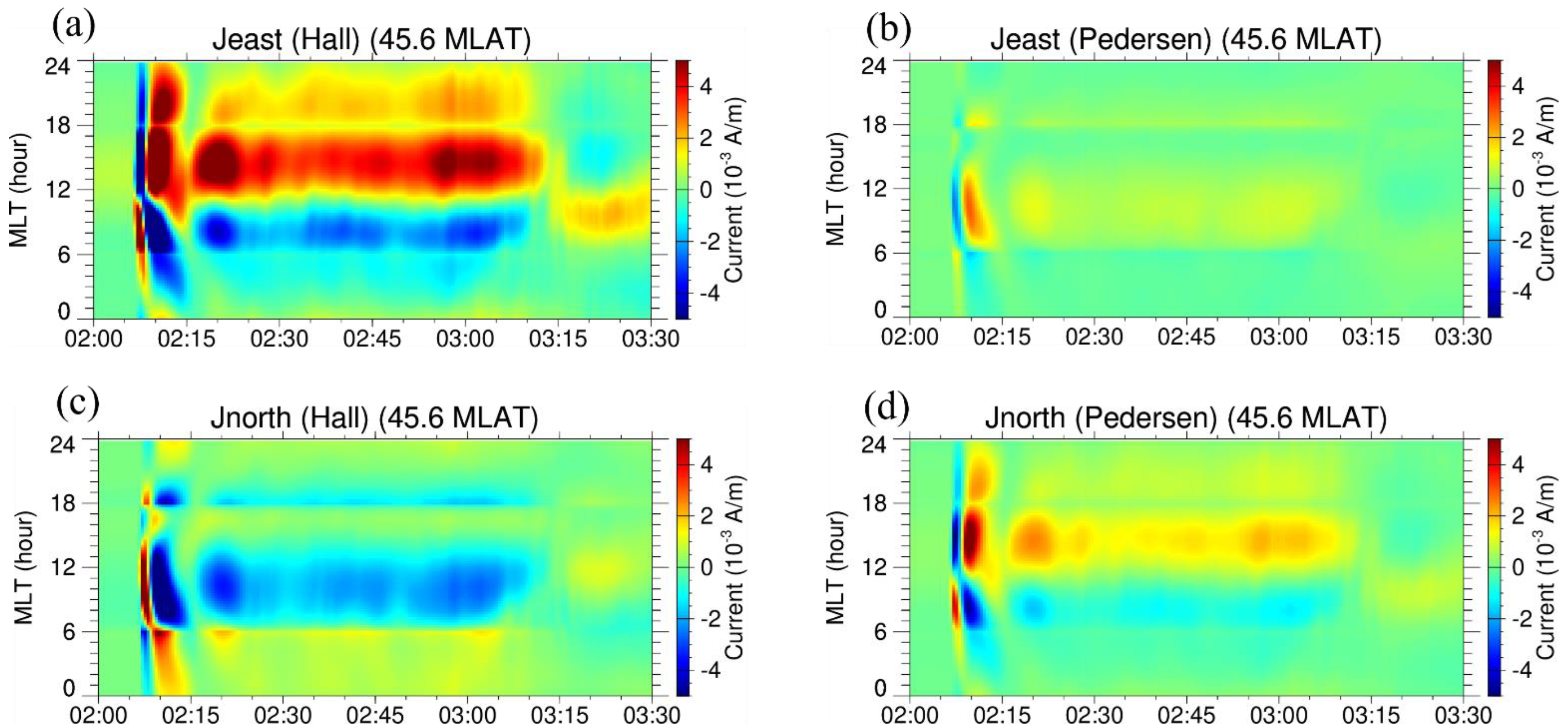
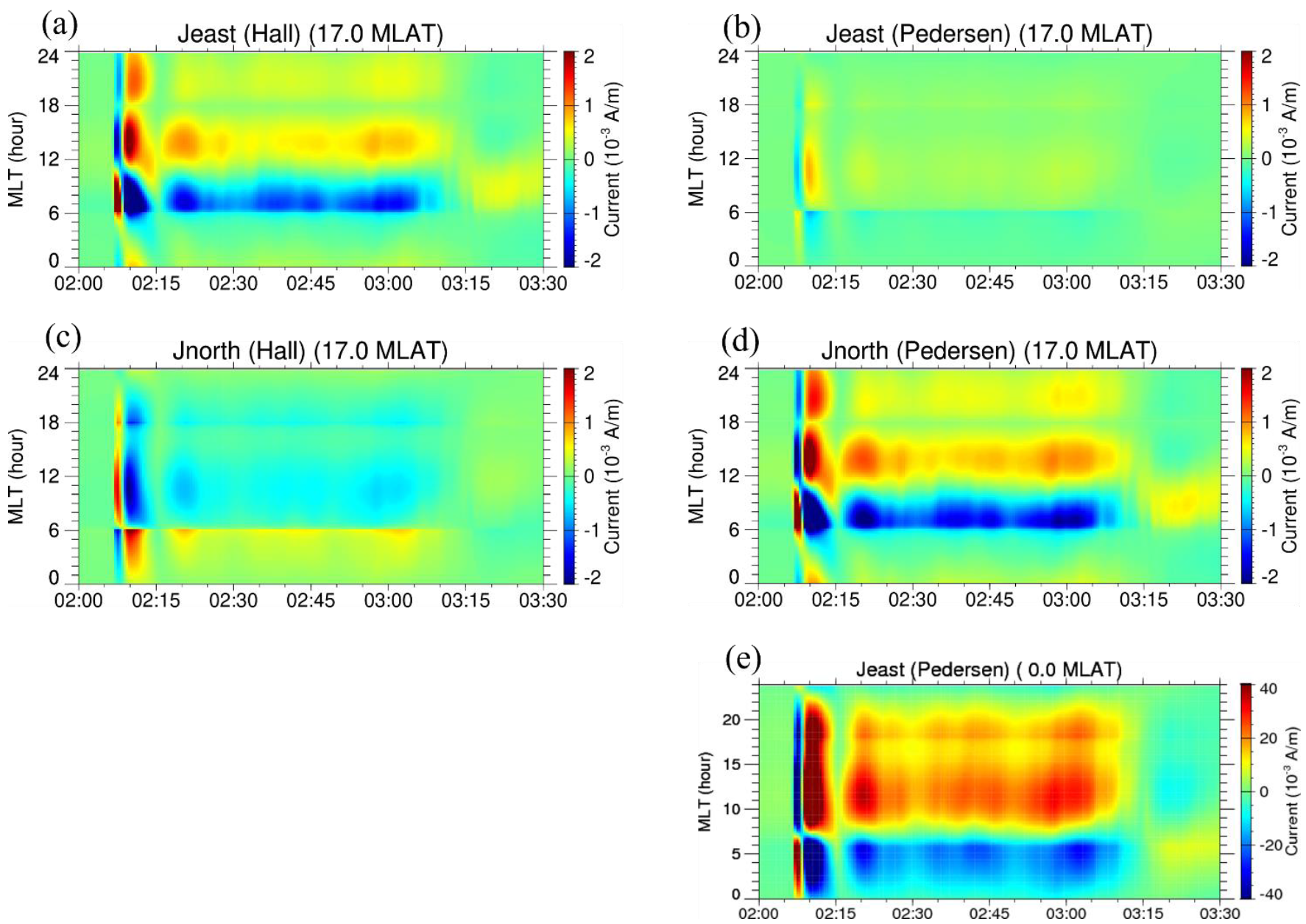
4. Reproduction of Hall and Pedersen-Cowling Currents
5. Summary and Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| SC | geomagnetic sudden commencement |
| PI | preliminary impulse |
| MI | main impulse |
| DL | stepwise low latitude magnetic disturbance |
| EEJ | equatorial electrojet |
| TM0 | zeroth-order transverse magnetic |
| MHD | magnetohydrodynamic |
| REPPU | Reproduce Plasma Universe |
| GML | geomagnetic latitude |
| MLT | magnetic local time |
References
- Nishida, A.; Iwasaki, N.; Nagata, T. The origin of fluctuations in the equatorial electrojet; A new type of geomagnetic variation. Ann. Geophys. 1966, 22, 478–484. [Google Scholar]
- Nishida, A. Coherence of geomagnetic DP2 magnetic fluctuations with interplanetary magnetic variations. J. Geophys. Res. 1968, 73, 5549–5559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kikuchi, T.; Lühr, H.; Kitamura, T.; Saka, O.; Schlegel, K. Direct penetration of the polar electric field to the equator during a DP2 event as detected by the auroral and equatorial magnetometer chains and the EISCAT radar. J. Geophys. Res. 1996, 101, 17161–17173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kikuchi, T.; Ebihara, Y.; Hashimoto, K.K.; Kataoka, R.; Hori, T.; Watari, S.; Nishitani, N. Penetration of the convection and overshielding electric fields to the equatorial ionosphere during a quasiperiodic DP 2 geomagnetic fluctuation event. J. Geophys. Res. 2010, 115, A05209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobea, A.T.; Amory-Mazaudier, C.; Do, J.M.; Luehr, H.; Hougninou, E.; Vassal, J.; Blanc, E.; Curto, J.J. Equatorial electrojet as part of the global circuit: A case-study from the IEEY. Ann. Geophys. 1998, 16, 698–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kobea, A.T.; Richmond, A.D.; Emery, B.A.; Peymirat, C.; Lühr, H.; Moretto, T.; Hairston, M.; Amory-Mazaudier, C. Electrodynamic coupling of high and low latitudes: Observations on May 27, 1993. J. Geophys. Res. 2000, 105, 22979–22989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sibeck, D.G.; Takahashi, K.; Yumoto, K.; Reeves, G.D. Concerning the origin of signatures in dayside equatorial ground magnetograms. J. Geophys. Res. 1998, 103, 6763–6769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, T. Generation mechanisms for magnetosphere-ionosphere current systems deduced from a three-dimensional MHD simulation of the solar wind-magnetosphere-ionosphere coupling processes. J. Geophys. Res. 1995, 100, 12057–12074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujita, S.; Tanaka, T.; Kikuchi, T.; Fujimoto, K.; Hosokawa, K.; Itonaga, M. A numerical simulation of the geomagnetic sudden commencement: 1. Generation of the field-aligned current associated with the preliminary impulse. J. Geophys. Res. 2003, 108, 1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujita, S.; Tanaka, T.; Kikuchi, T.; Fujimoto, K.; Itonaga, M. A Numerical Simulation of the Geomagnetic Sudden Commencement: 2. Plasma Processes in the Main Impulse. J. Geophys. Res. 2003, 108, 1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirono, M. A theory of diurnal magnetic variations in equatorial regions and conductivity of the ionosphere E region. J. Geomag. Geoelectr. Kyoto 1952, 4, 7–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, W.G.; Martyn, D.F. Electric currents in the ionosphere I. The conductivity. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. London. Ser. A 1953, 246, 281–294. [Google Scholar]
- Araki, T. A physical model of the geomagnetic sudden commencement, Solar Wind Sources of Magnetospheric Ultra-Low-Frequency Waves. Geophys. Monogr. 1994, 81, 183–200. [Google Scholar]
- Trivedi, N.B.; Arora, B.R.; Padilha, A.L.; da Costa, J.M.; Dutra, S.L.G.; Chamalaun, F.H.; Rigoti, A. Global Pc5 geomagnetic pulsations of March 24, 1991, as observed along the American sector. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1997, 24, 1683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motoba, T.; Kikuchi, T.; Lühr, H.; Tachihara, H.; Kitamura, T.-I.; Hayashi, K.; Okuzawa, T. Global Pc5 caused by a DP2-type ionospheric current system. J. Geophys. Res. 2002, 107, A2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinohara, M.; Yumoto, K.; Yoshikawa, A.; Saka, O.; Solovyev, S.I.; Vershinin, E.F.; Trivedi, N.B.; Da Costa, J.M. The 210 MM Magnetic Observation Group Wave characteristics of daytime and nighttime Pi2 pulsations at the equatorial and low latitudes. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1997, 24, 2279–2282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imajo, S.; Yoshikawa, A.; Uozumi, T.; Ohtani, S.; Nakamizo, A.; Marshall, R.; Shevtsov, B.M.; Akulichev, V.A.; Sukhbaatar, U.; Liedloff, A.; et al. Pi2 pulsations observed around the dawn terminator. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2015, 120, 2088–2098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rastogi, R.G. Geomagnetic storms and electric fields in the equatorial ionosphere. Nature 1977, 268, 422–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kikuchi, T.; Lühr, H.; Schlegel, K.; Tachihara, H.; Shinohara, M.; Kitamura, T.–I. Penetration of auroral electric fields to the equator during a substorm. J. Geophys. Res. 2000, 105, 23251–23261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kikuchi, T.; Hashimoto, K.K.; Nozaki, K. Penetration of magnetospheric electric fields to the equator during a geomagnetic storm. J. Geophys. Res. 2008, 113, A06214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashimoto, K.K.; Kikuchi, T.; Watari, S.; Abdu, M.A. Polar-equatorial ionospheric currents driven by the region 2 field aligned currents at the onset of substorms. J. Geophys. Res. 2011, 116, A09217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.-S. Statistical analysis of dayside equatorial ionospheric electric fields and electrojet currents produced by magnetospheric substorms during sawtooth events. J. Geophys. Res. 2012, 117, A02316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yizengaw, E.; Moldwin, M.B.; Zesta, E.; Magoun, M.; Pradipta, R.; Biouele, C.M.; Rabiu, A.B.; Obrou, O.K.; Bamba, Z.; De Paula, E.R. Response of the equatorial ionosphere to the geomagnetic DP 2 current system. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2016, 43, 7364–7372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Wang, H.; Yamazaki, Y.; Xiong, C. Effects of subauroral polarization streams on the equatorial electrojet during the geomagnetic storm on June 1, 2013. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2021, 126, e2021JA029681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Wang, H.; Yamazaki, Y. Effects of subauroral polarization streams on the equatorial electrojet during the geomagnetic storm on 1 June 2013: 2. Temporal variations. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2022, 127, e2021JA030180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamazaki, Y.; Maute, A. Sq and EEJ—A review on the daily variation of the geomagnetic field caused by ionospheric dynamo currents. Space Sci. Rev. 2017, 206, 299–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zheng, Z.; Zhang, K.; Wang, W. Influence of nonmigrating tides and geomagnetic field geometry on the diurnal and longitudinal variations of the equatorial electrojet. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2020, 125, e2019JA027631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamazaki, Y.; Harding, B.J.; Stolle, C.; Matzka, J. Neutral wind profiles during periods of eastward and westward equatorial electrojet. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2021, 48, e2021GL093567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kikuchi, T.; Araki, T.; Maeda, H.; Maekawa, K. Transmission of polar electric fields to the Equator. Nature 1978, 273, 650–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kikuchi, T.; Hashimoto, K.K.; Tomizawa, I.; Ebihara, Y.; Nishimura, Y.; Araki, T.; Shinbori, A.; Veenadhari, B.; Tanaka, T.; Nagatsuma, T. Response of the incompressible ionosphere to the compression of the magnetosphere during the geomagnetic sudden commencements. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2016, 121, 1536–1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kikuchi, T.; Chum, J.; Tomizawa, I.; Hashimoto, K.K.; Hosokawa, K.; Ebihara, Y.; Hozumi, K.; Supnithi, P. Penetration of the electric fields of the geomagnetic sudden commencement over the globe as observed with the HF Doppler sounders and magnetometers. Earth Planets Space 2021, 73, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashimoto, K.K.; Kikuchi, T.; Tomizawa, I.; Nagatsuma, T. Substorm overshielding electric field at low latitude on the nightside as observed by the HF Doppler sounder and magnetometers. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2017, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashimoto, K.K.; Kikuchi, T.; Tomizawa, I.; Hosokawa, K.; Chum, J.; Buresova, D.; Nose, M.; Koga, K. Penetration electric fields observed at middle and low latitudes during the 22 June 2015 geomagnetic storm. Earth Planets Space 2020, 72, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdu, M.A.; Sastri, J.H.; Lühr, H.; Tachihara, H.; Kitamura, T.; Trivedi, N.B.; Sobral, J.H.A. DP 2 electric field fluctuations in the dusk-time dip equatorial ionosphere. Geophys. Res. Let. 1998, 25, 1511–1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishimura, Y.; Kikuchi, T.; Wygant, J.; Shinbori, A.; Ono, T.; Matsuoka, A.; Nagatsuma, T.; Brautigam, D. Response of convection electric fields in the magnetosphere to IMF orientation change. J. Geophys. Res. 2009, 114, A09206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishimura, Y.; Kikuchi, T.; Shinbori, A.; Wygant, J.; Tsuji, Y.; Hori, T.; Ono, T.; Fujita, S.; Tanaka, T. Direct measurements of the Poynting flux associated with convection electric fields in the magnetosphere. J. Geophys. Res. 2010, 115, A12212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araki, T. Global structure of geomagnetic sudden commencements. Planet. Space Sci. 1977, 25, 373–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kikuchi, T. Evidence of transmission of polar electric fields to the low latitude at times of geomagnetic sudden commencements J. Geophys. Res. 1986, 91, 3101–3105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kikuchi, T.; Araki, T. Horizontal transmission of the polar electric field to the equator. J. Atmos. Terr. Phys. 1979, 41, 927–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kikuchi, T. Transmission line model for the near-instantaneous transmission of the ionospheric electric field and currents to the equator. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2014, 119, 1131–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kikuchi, T.; Tsunomura, S.; Hashimoto, K.; Nozaki, K. Field-aligned current effects on midlatitude geomagnetic sudden commencements. J. Geophys. Res. 2001, 106, 15–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsunomura, S. Characteristics of geomagnetic sudden commencement observed in middle and low latitudes. Earth Planets Space 1998, 50, 755–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, T. Magnetosphere-ionosphere convection as a compound system. Space Sci. Rev. 2007, 133, 1–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kikuchi, T. Penetration of the Magnetospheric Electric Fields to the Low Latitude Ionosphere, Space Physics and Aeronomy Collection Volume 3: Ionosphere Dynamics and Applications, Geophysical Monograph 260, 1st ed.; Huang, C., Lu, G., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, T.; Nakamizo, A.; Yoshikawa, A.; Fujita, S.; Shinagawa, H.; Shimazu, H.; Kikuchi, T.; Hashimoto, K.K. Substorm convection and current system deduced from the global simulation. J. Geophys. Res. 2010, 115, A05220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebihara, Y.; Tanaka, T.; Kikuchi, T. Counter equatorial electrojet and overshielding after substorm onset: Global MHD simulation study. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2014, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolf, R.A. Effects of ionospheric conductivity on convective flow of plasma in the magnetosphere. J. Geophys. Res. 1970, 75, 4677–4698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lühr, H.; Rother, M.; Häusler, K.; Alken, P.; Maus, S. The influence of nonmigrating tides on the longitudinal variation of the equatorial electrojet. J. Geophys. Res. 2008, 113, A08313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fejer, B.G.; Gonzales, A.C.; Farley, D.T.; Kelley, M.C.; Woodman, R.F. Equatorial electric fields during magnetically disturbed conditions 1. The effect of the interplanetary magnetic field. J. Geophys. Res. 1979, 84, 5797–5802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinbori, A.; Tsuji, Y.; Kikuchi, T.; Araki, T.; Watari, S. Magnetic latitude and local time dependence of the amplitude of geomagnetic sudden commencements. J. Geophys. Res. 2009, 114, A04217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.-S.; Foster, J.C.; Goncharenko, L.P.; Reeves, G.D.; Chau, J.L.; Yumoto, K.; Kitamura, K. Variations of low-latitude geomagnetic fields and Dst index caused by magnetospheric substorms. J. Geophys. Res. 2004, 109, A05219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamao, T. The structure of three-dimensional hydromagnetic waves in a uniform cold plasma. J. Geomagn. Geoelectr. 1964, 48, 89–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamao, T. Hydromagnetic interpretation of geomagnetic SSC*. Rep. Ionos. Space Res. Jpn. 1964, 18, 16–31. [Google Scholar]
- Tu, J.; Song, P. On the momentum transfer from polar to equatorial ionosphere. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2019, 124, 6064–6073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kivelson, M.G.; Southwood, D.J. Hydromagnetic waves and the ionosphere. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1988, 15, 1271–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, T.; Iijima, T. Primary sources of large-scale Birkeland currents. Space Sci. Rev. 1979, 24, 347–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| STATION | COUNTRY | GEOGRAPHIC (deg) | GEOMAGNETIC (deg) | MLT UT+ | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Latitude | Longitude | Latitude | Longitude | |||
| PTK, Paratunka | Russia | 52.94° N | 158.25° E | 45.58° N | 221.13° E | 10.6 |
| OKI, Okinawa | Japan | 26.78° N | 128.25° E | 16.95° N | 198.69° E | 8.4 |
| YAP, Yap | Micronesia | 9.49° N | 138.09° E | 0.51° N | 209.45° E | 9.1 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kikuchi, T.; Hashimoto, K.K.; Tanaka, T.; Nishimura, Y.; Nagatsuma, T. Middle Latitude Geomagnetic Disturbances Caused by Hall and Pedersen Current Circuits Driven by Prompt Penetration Electric Fields. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 580. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13040580
Kikuchi T, Hashimoto KK, Tanaka T, Nishimura Y, Nagatsuma T. Middle Latitude Geomagnetic Disturbances Caused by Hall and Pedersen Current Circuits Driven by Prompt Penetration Electric Fields. Atmosphere. 2022; 13(4):580. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13040580
Chicago/Turabian StyleKikuchi, Takashi, Kumiko K. Hashimoto, Takashi Tanaka, Yukitoshi Nishimura, and Tsutomu Nagatsuma. 2022. "Middle Latitude Geomagnetic Disturbances Caused by Hall and Pedersen Current Circuits Driven by Prompt Penetration Electric Fields" Atmosphere 13, no. 4: 580. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13040580
APA StyleKikuchi, T., Hashimoto, K. K., Tanaka, T., Nishimura, Y., & Nagatsuma, T. (2022). Middle Latitude Geomagnetic Disturbances Caused by Hall and Pedersen Current Circuits Driven by Prompt Penetration Electric Fields. Atmosphere, 13(4), 580. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13040580





