Yearly Variations of Equivalent Black Carbon Concentrations Observed in Krakow, Poland
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Sampling and Method
2.1. Sampling Location
2.2. Sampling
2.3. Multi-Wavelength Absorption Black Carbon Instrument
3. Results and Discussion
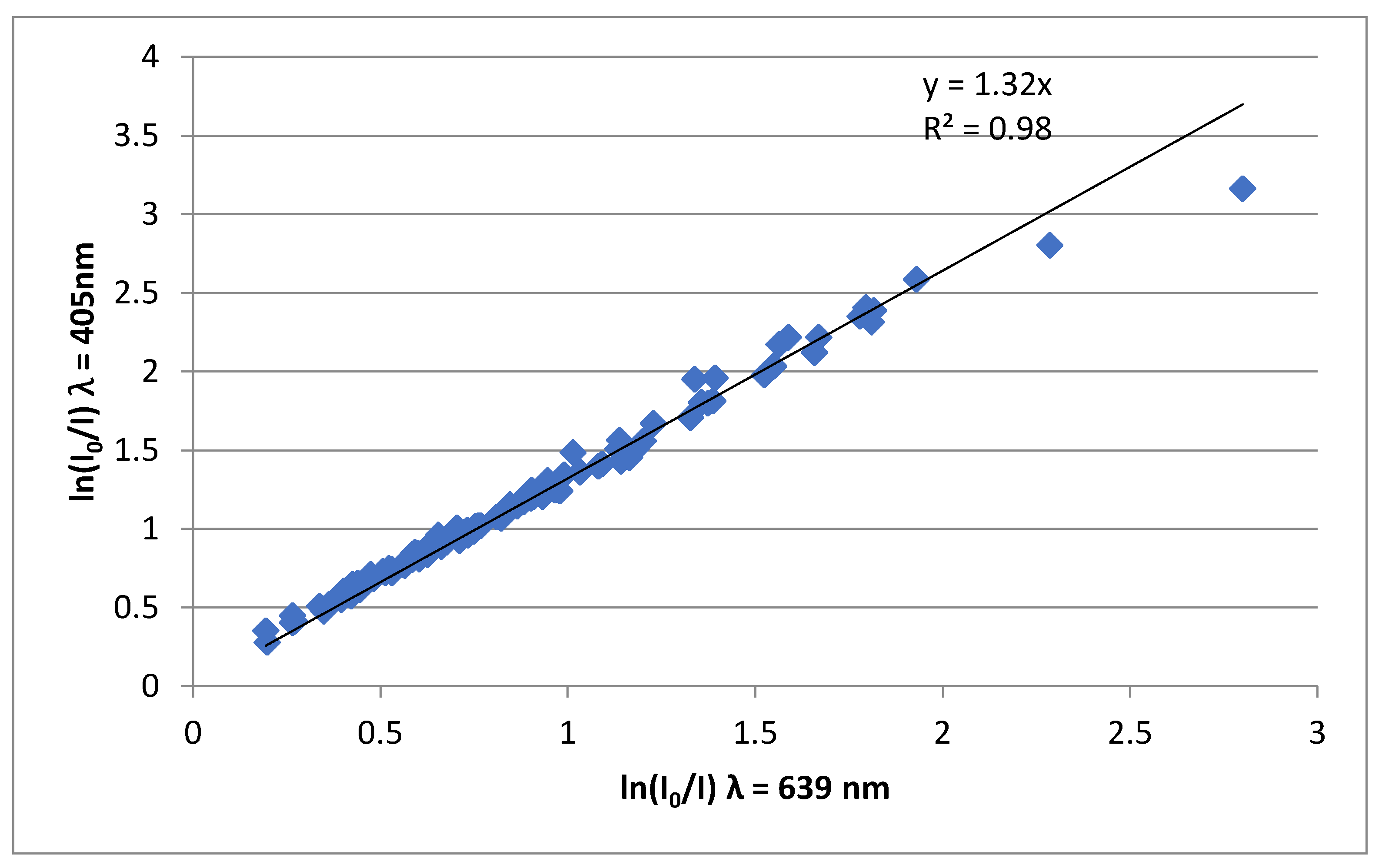
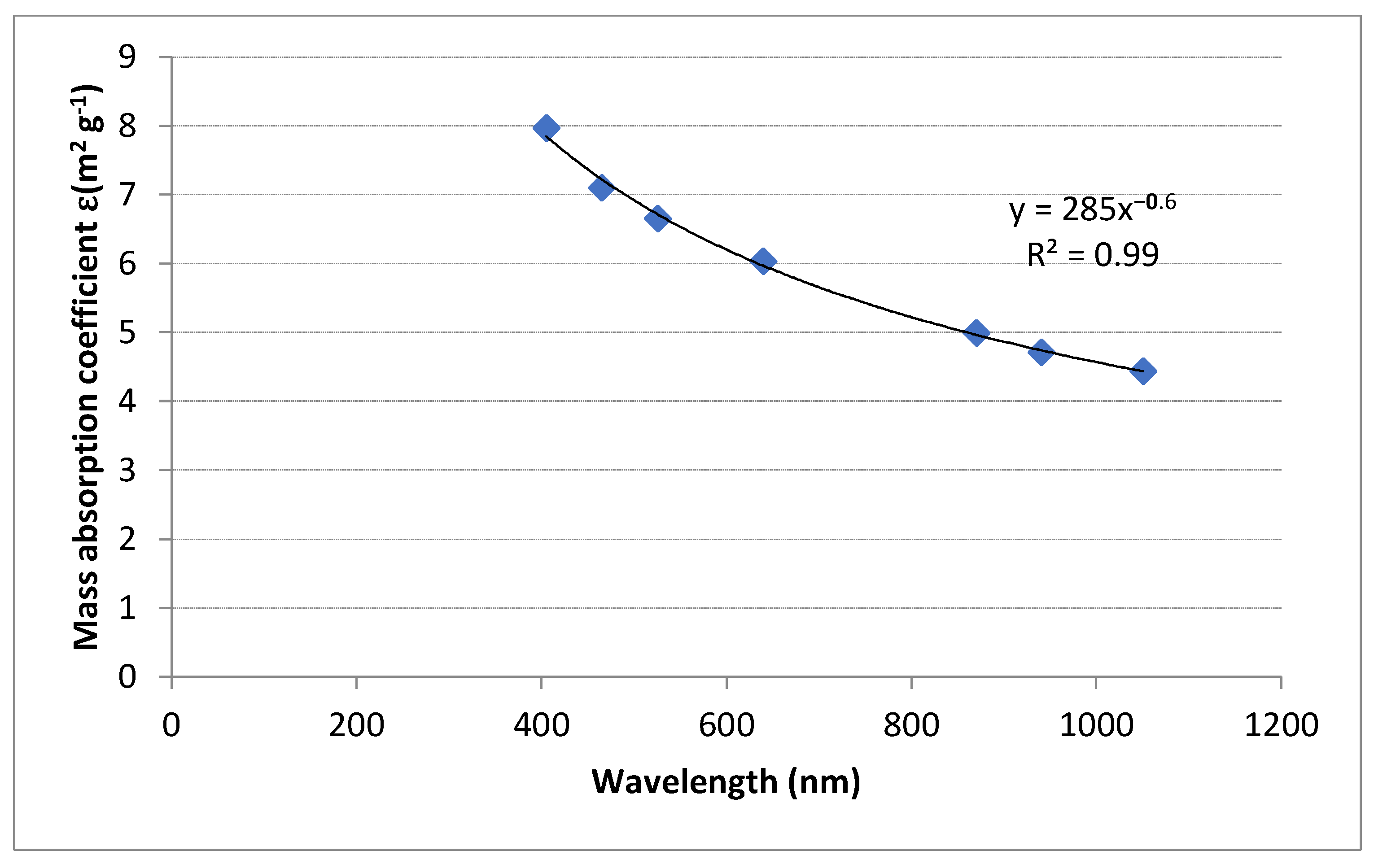
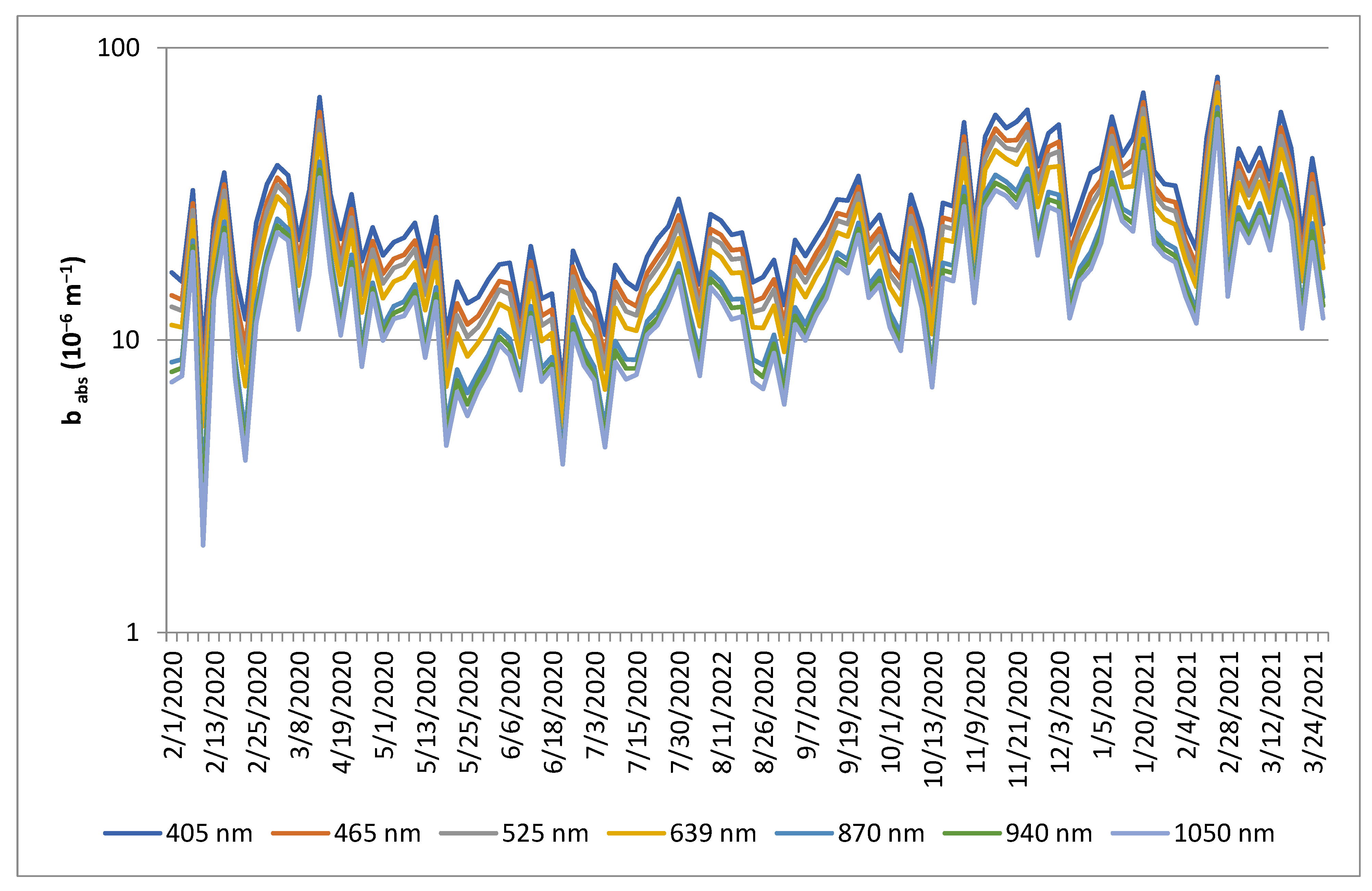
3.1. Mass Absorption Coefficients (ε) and Absorption Coefficients (babs)
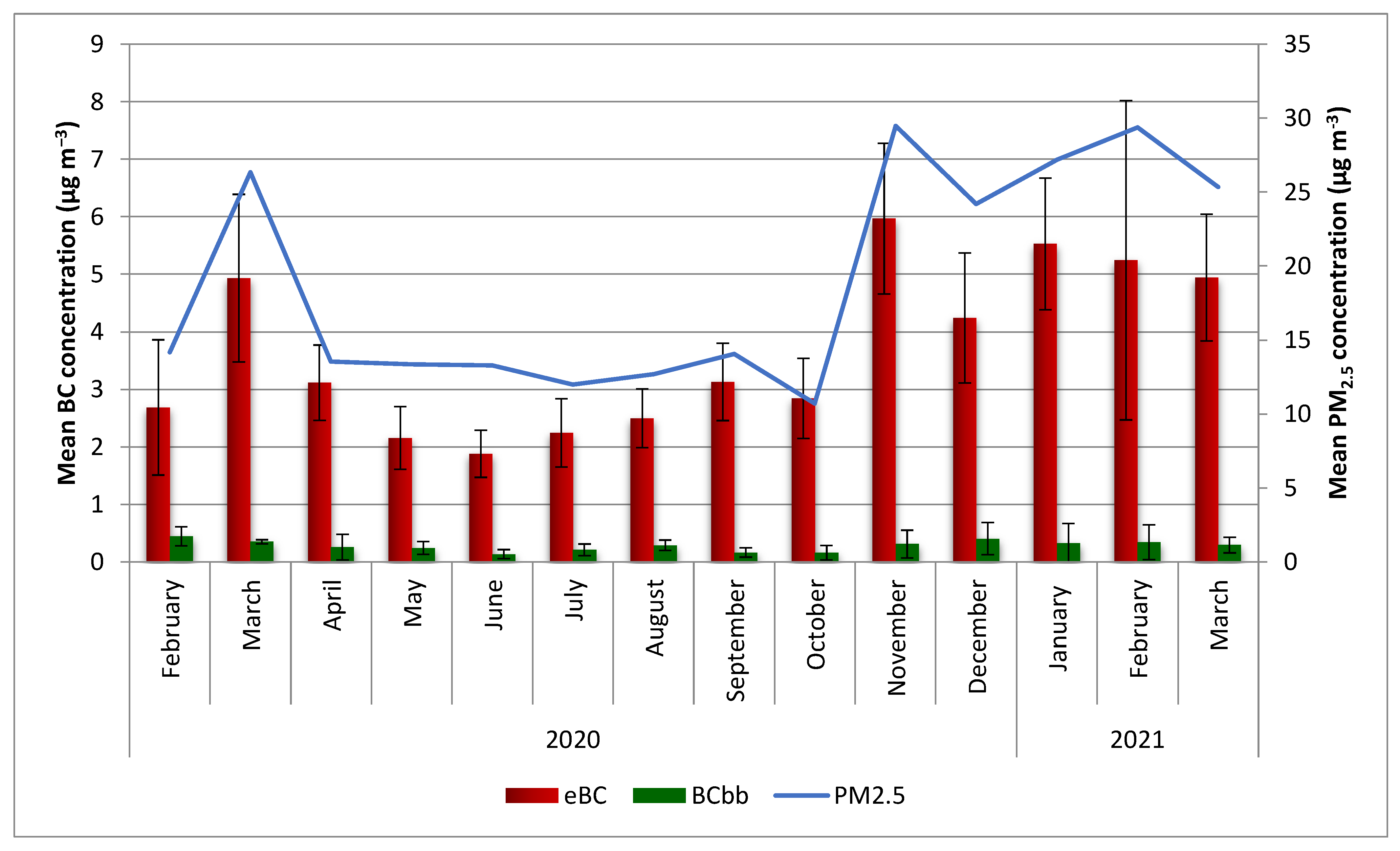
3.2. The E-Black Carbon Concentrations (eBC) and the Black Carbon Related to Biomass Burning (BCbb)
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Petzold, A.; Ogren, J.A.; Fiebig, M.; Laj, P.; Li, S.M.; Baltensperger, U.; Holzer-Popp, T.; Kinne, S.; Pappalardo, G.; Sugimoto, N.; et al. Recommendations for reporting black carbon measurements. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2013, 13, 8365–8379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Diapouli, E.; Kalogridis, A.C.; Markantonaki, C.; Vratolis, S.; Fetfatzis, P.; Colombi, C.; Eleftheriadis, K. Annual variability of black carbon concentrations originating from biomass and fossil fuel combustion for the suburban aerosol in Athens, Greece. Atmosphere 2017, 8, 234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- European Environment Agency. Status of Black Carbon Monitoring in Ambient Air in Europe; Publications Office of the European Union: Luxemburg, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Bond, T.C.; Bergstrom, R.W. Light Absorption by Carbonaceous Particles: An Investigative Review. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2006, 40, 27–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.S. EPA (U.S. Environmental Protection Agency). Report to Congress on Black Carbon; Department of the Interior, Environment, and Related Agencies Appropriations Act; U.S. Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2012.
- Jacobson, M.Z. Strong radiative heating due to the mixing state of black carbon in atmospheric aerosols. Nature 2001, 409, 695–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.; Ma, T.; Olson, M.R.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, T.; Wu, Y.; Schauer, J.J. Temporal variations of black carbon during haze and non-haze days in Beijing. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 33331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horvath, H. Atmospheric light absorption—A review. Atmos. Environ. Part A Gen. Top. 1993, 27, 293–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lack, D.; Moosmuller, H.; McMeeking, G.; Chakrabarty, R.; Baumgardner, D. Characterizing elemental, equivalent black, and refractory black carbon aerosol particles: A review of techniques, their limitations and uncertainties. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2013, 406, 99–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Petzold, A.; Schönlinner, M. Multi-angle absorption photometry—A new method for the measurement of aerosol light absorption and atmospheric black carbon. J. Aerosol Sci. 2004, 35, 421–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zioła, N.; Błaszczak, B.; Klejnowski, K. Temporal Variability of Equivalent Black Carbon Components in Atmospheric Air in Southern Poland. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taha, G.; Box, G.P.; Cohen, D.D.; Stelcer, E. Black carbon measurement using laser integrating plate method. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 266–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cohen, D.D. Summary of Light Absorbing Carbon and Visibility Measurements and Terms; ANSTO External Report ER-790; Australian Nuclear Science and Technology Organisation: Sydney, Australia, 2020; ISBN 1 921268 32 8. [Google Scholar]
- Atanacio, A.J.; Cohen, D.D.; Button, D.; Paneras, N.; Garton, D. Multi-wavelength Absorption Black Carbon Instrument (MABI) Manual. Available online: https://www.ansto.gov.au/media/2716/download (accessed on 8 February 2020).
- Michalik, M.; Brzezanski, M.; Wilczyńska-Michalik, W.; Fisior, K.; Klimas, B.; Samek, L.; Pietras, B. Characterisation of solid particles emitted from diesel and petrol engines as a contribution to the determination of the origin of carbonaceous particles in urban aerosol. In IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering; IOP Publishing: Bristol, UK, 2016; Volume 148, p. 12079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wilczyńska-Michalik, W.; Rózańska, A.; Bulanda, M.; Chmielarczyk, A.; Pietras, B.; Michalik, M. Physicochemical and microbiological characteristics of urban aerosols in Krakow (Poland) and their potential health impact. Environ. Geochem. Health 2021, 43, 4601–4626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duc, H.N.; Shingles, K.; White, S.; Salter, D.; Chang, L.-C.; Gunashanhar, G.; Riley, M.; Trieu, T.; Dutt, U.; Merched, A.; et al. Spatial-Temporal Pattern of Black Carbon (BC) Emission from Biomass Burning and Anthropogenic Sources in New South Wales and the Greater Metropolitan Region of Sydney, Australia. Atmosphere 2020, 11, 570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuso, C.A.T.; Magtaas, R.A.H.; Punzalan, J.M.; Yee, J.R.; Bautista, A.T.; Pabroa, P.C.B. Air particulate matter, black carbon, and elemental concentrations and source apportionment in Calaca, Batangas. Philipp. J. Sci. 2020, 149, 117–127. [Google Scholar]
- Tobler, A.K.; Skiba, A.; Canonaco, F.; Močnik, G.; Rai, P.; Chen, G.; Bartyzel, J.; Zimnoch, M.; Styszko, K.; Nęcki, J.; et al. Characterization of non-refractory (NR) PM1 and source apportionment of organic aerosol in Kraków, Poland. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2021, 21, 14893–14906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manohar, M.; Atanacio, A.; Button, D.; Cohen, D. MABI—A multi-wavelength absorption black carbon instrument for the measurement of fine light absorbing carbon particles. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2021, 12, 133–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kebe, M.; Traore, A.; Manousakas, M.-I.; Vasilatou, V.; Ndao, A.; Wague, A.; Eleftheriadis, K. Source Apportionment and Assessment of Air Quality Index of PM2.5-10 and PM2.5 in at Two Different Sites in Urban Background Area in Senegal. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz, M.T.; Cruz, M.T.; Bañaga, P.A.; Betito, G.; Braun, R.A.; Stahl, C.; Aghdam, M.A.; Obiminda Cambaliza, M.; Dadashazar, H.; Hilario, M.R.; et al. Size-resolved composition and morphology of particulate matter during the southwest monsoon in Metro Manila, Philippines. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2019, 19, 10675–10696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Reche, C.; Querol, X.; Alastuey, A.; Viana, M.; Pey, J.; Moreno, T.; Rodriguez, S.; González, Y.; Fernández-Camacho, R.; de la Rosa, J.; et al. New considerations for PM, Black Carbon and particle number concentration for air quality monitoring across different European cities. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2011, 11, 6207–6227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stahl, C.; Cruz, M.T.; Bañaga, P.A.; Betito, G.; Braun, R.A.; Aghdam, M.A.; Cambaliza, M.O.; Lorenzo, G.R.; MacDonald, A.B.; Pabroa, P.C.; et al. An annual time series of weekly size-resolved aerosol properties in the megacity of Metro Manila, Philippines. Sci. Data 2020, 7, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, D.D.; Taha, G.; Stelcer, E.; Garton, D.; Box, G. The Measurement and Sources of Fine Particle Elemental Carbon at Several Key Sites in NSW over the Past Eight Years. In Proceedings of the 15th International Clean Air Conference, Sydney, Autralia, 27–30 November 2000; pp. 485–490. [Google Scholar]

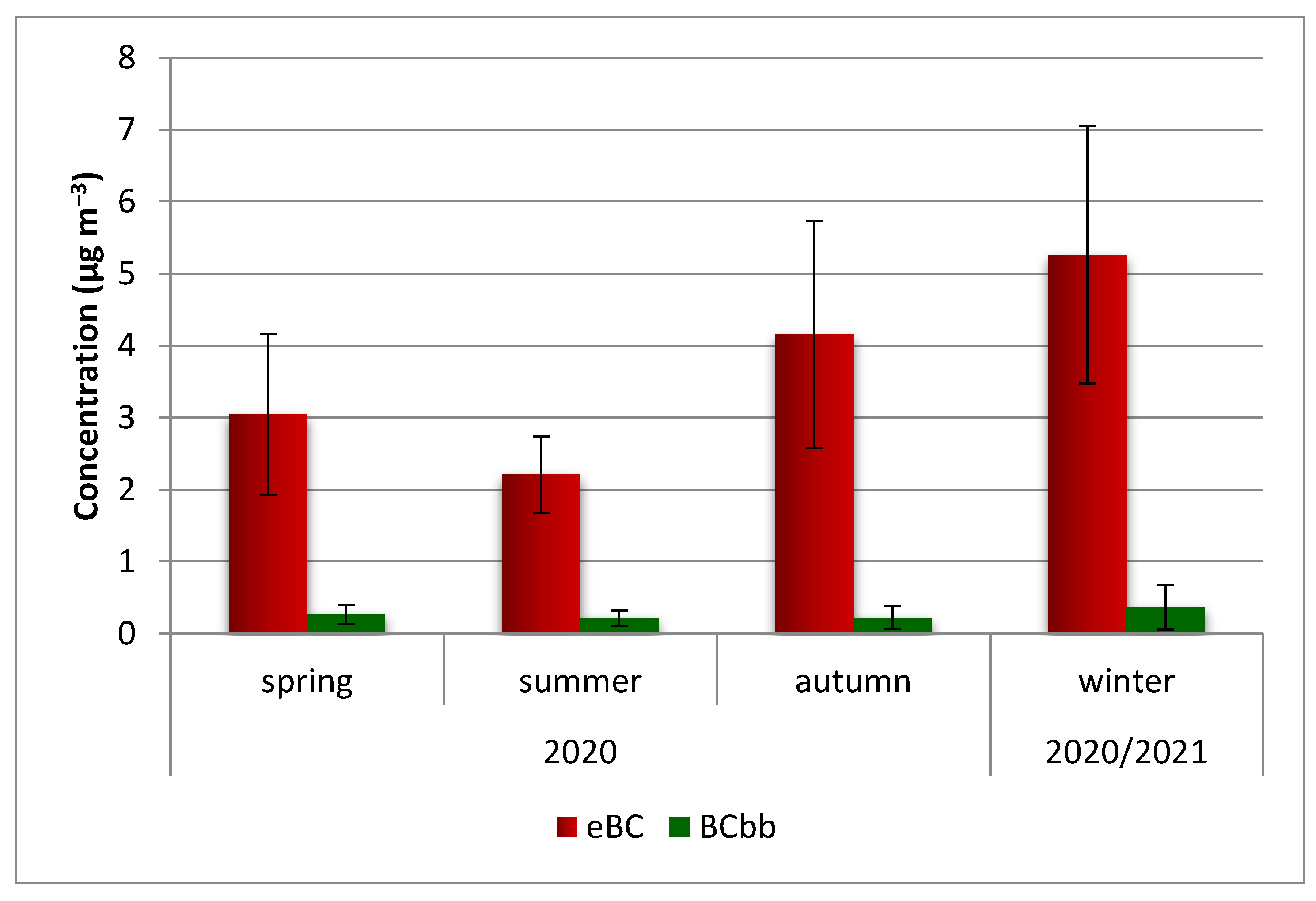
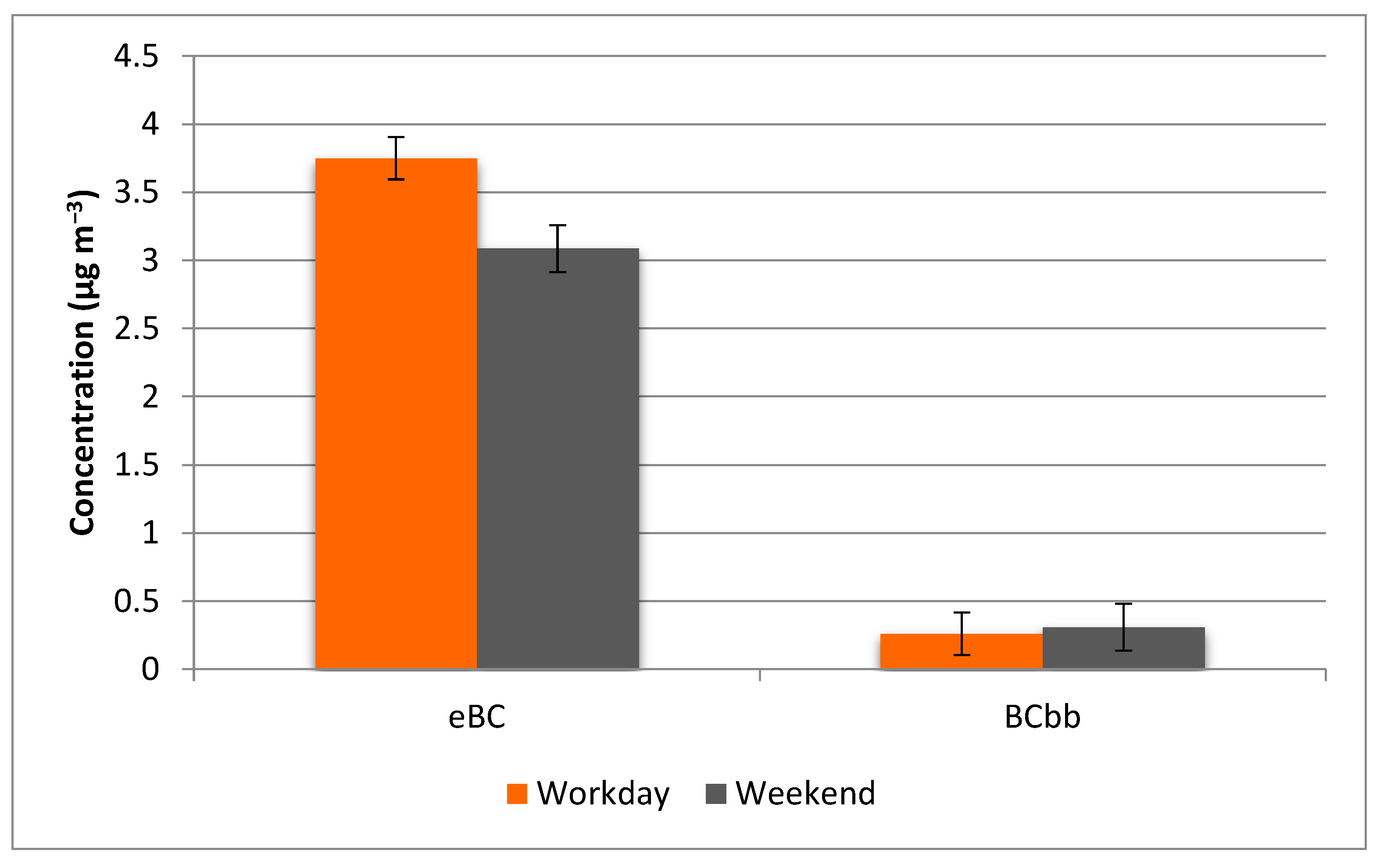
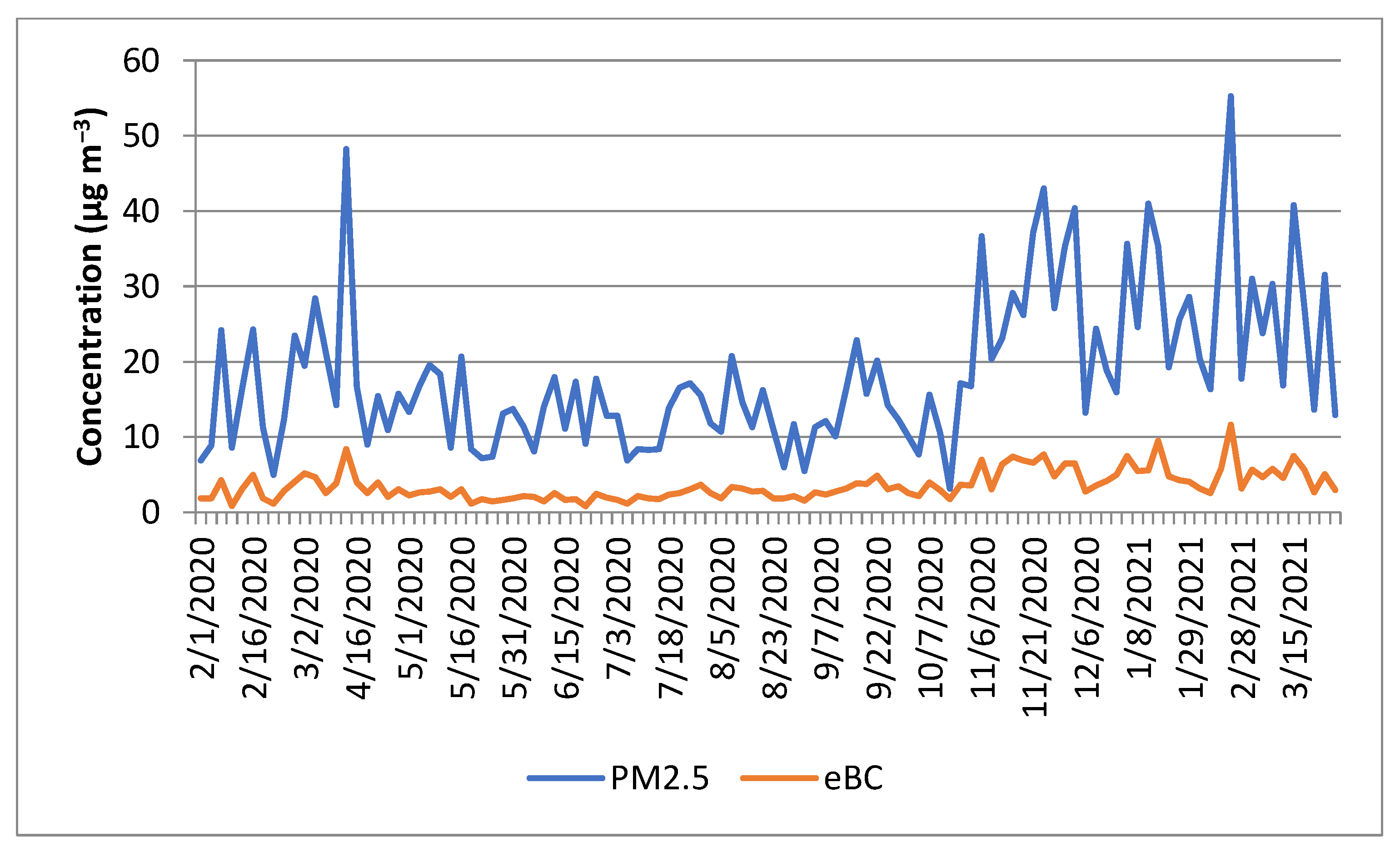
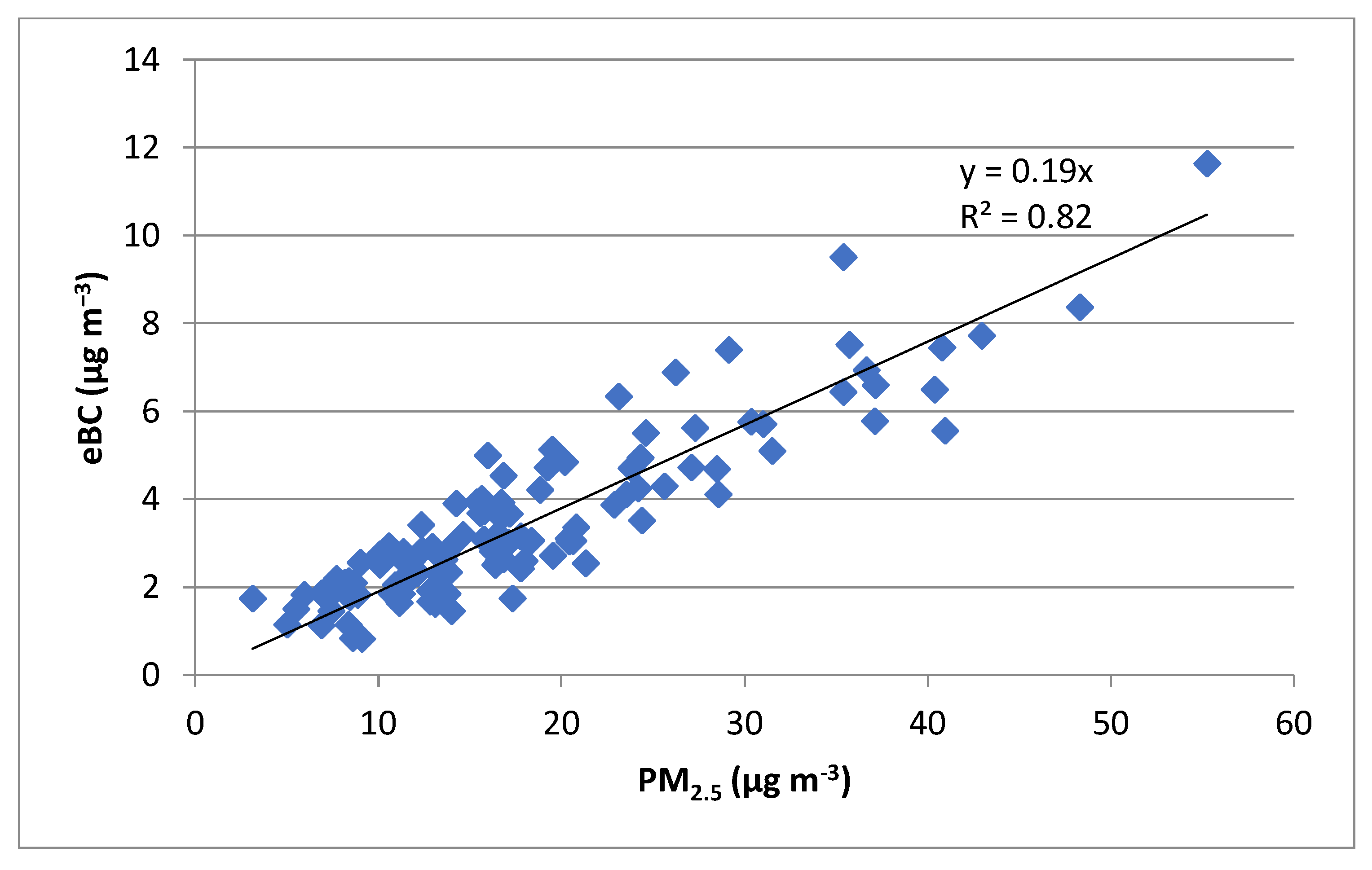
| Period | PM2.5 (μg m−3) | eBC (μg m−3) | BCbb (μg m−3) | eBC/PM2.5 (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Spring | 16.5 ± 0.2 | 3.0 ± 1.1 | 0.3 ± 0.1 | 20 ± 8 |
| Summer | 12.6 ± 0.1 | 2.2 ± 0.5 | 0.2 ± 0.1 | 19± 5 |
| Autumn | 19.2 ± 0.7 | 4.2 ± 1.6 | 0.22 ± 0.16 | 24 ± 9 |
| Winter | 27.6 ± 0.2 | 5.3 ± 1.8 | 0.4 ± 0.3 | 21 ± 8 |
| Annual | 18.2 ± 0.6 | 3.5 ± 1.5 | 0.25 ± 0.15 | 21 ± 10 |
| Full period | 18.4 ± 0.6 | 3.6 ± 1.5 | 0.3 ± 0.2 | 21 ± 10 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ryś, A.; Samek, L. Yearly Variations of Equivalent Black Carbon Concentrations Observed in Krakow, Poland. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 539. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13040539
Ryś A, Samek L. Yearly Variations of Equivalent Black Carbon Concentrations Observed in Krakow, Poland. Atmosphere. 2022; 13(4):539. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13040539
Chicago/Turabian StyleRyś, Anna, and Lucyna Samek. 2022. "Yearly Variations of Equivalent Black Carbon Concentrations Observed in Krakow, Poland" Atmosphere 13, no. 4: 539. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13040539
APA StyleRyś, A., & Samek, L. (2022). Yearly Variations of Equivalent Black Carbon Concentrations Observed in Krakow, Poland. Atmosphere, 13(4), 539. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13040539






