Venus’ Cloud-Tracked Winds Using Ground- and Space-Based Observations with TNG/NICS and VEx/VIRTIS †
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Observations and Image Processing
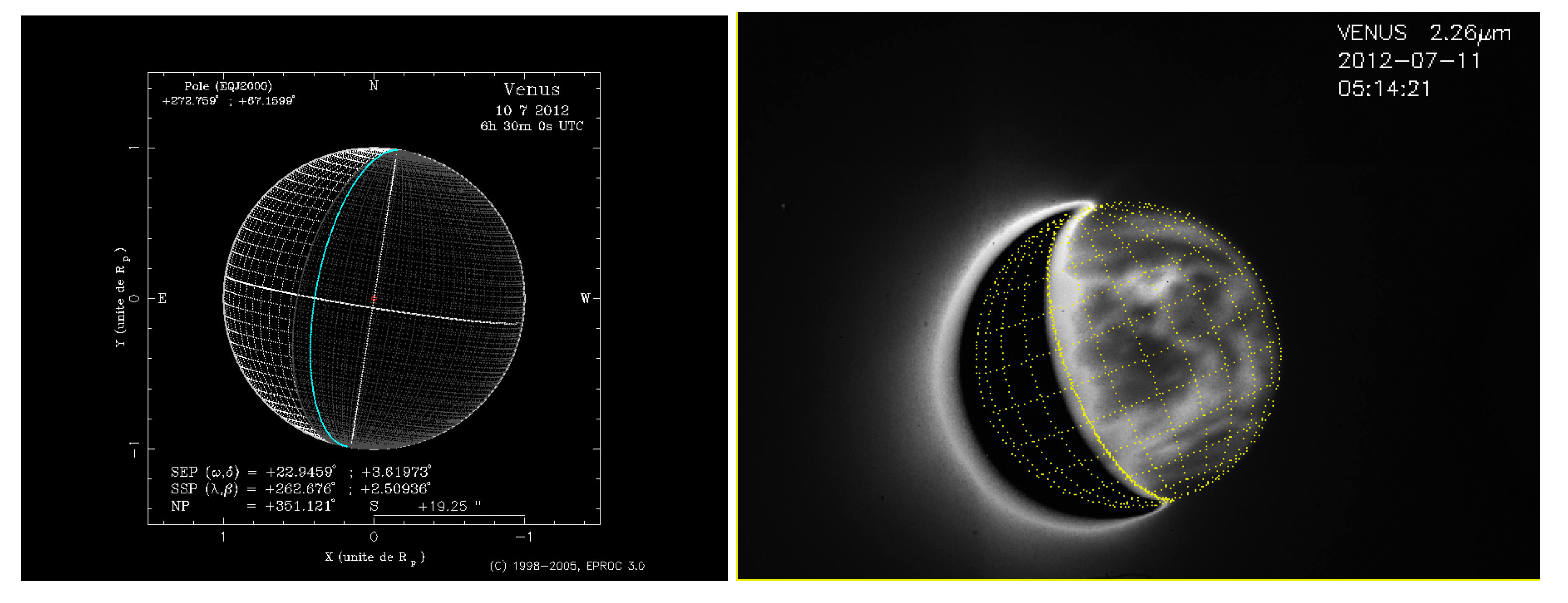
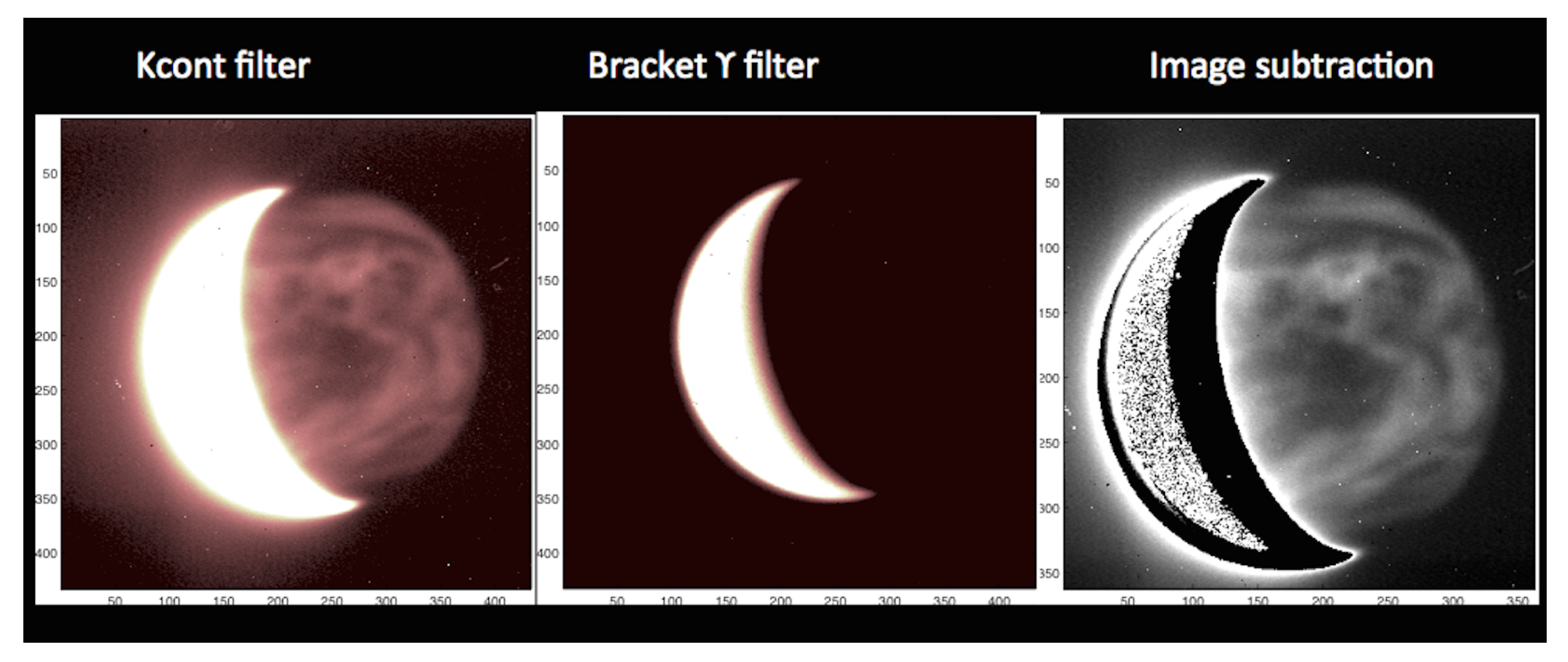
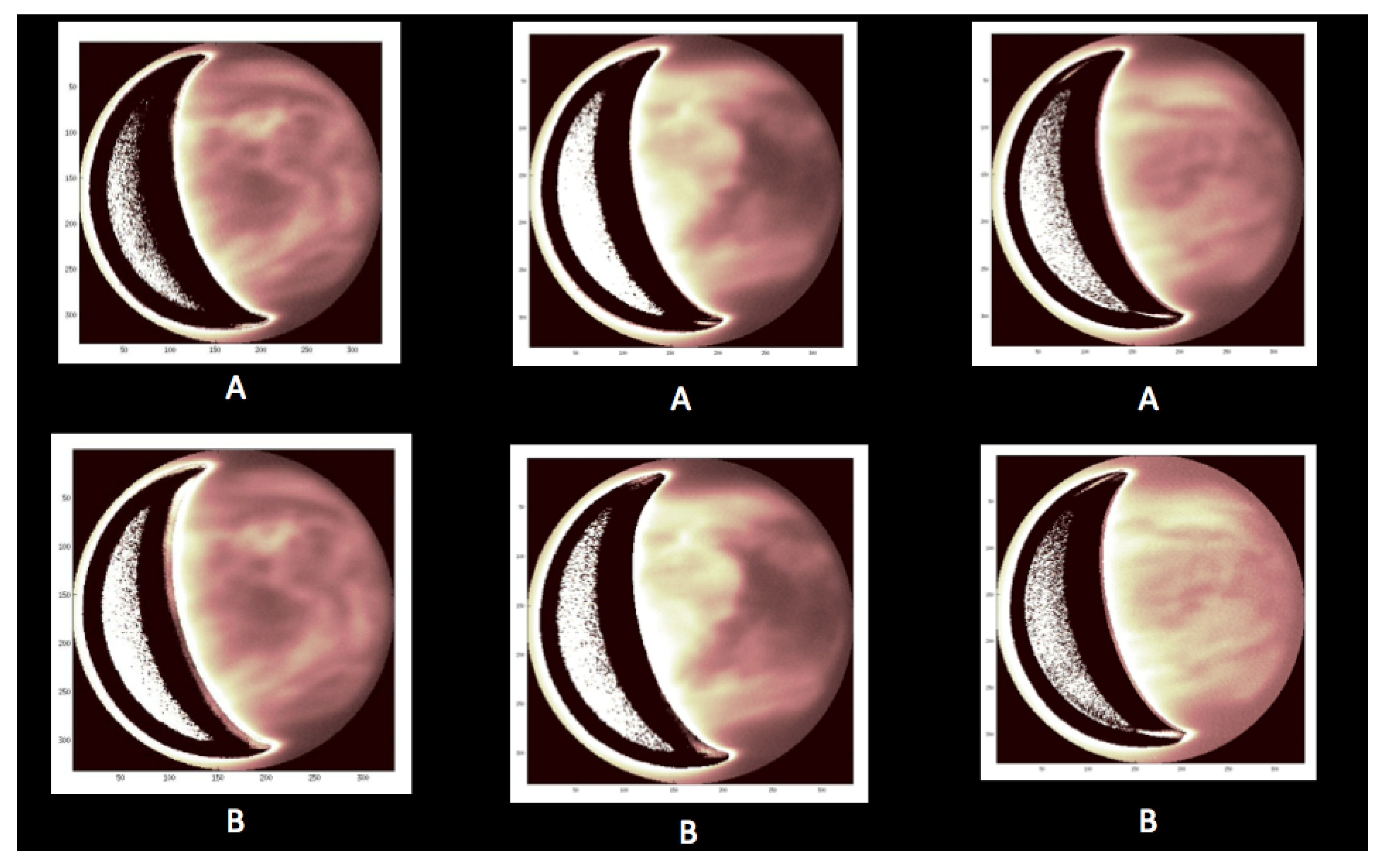
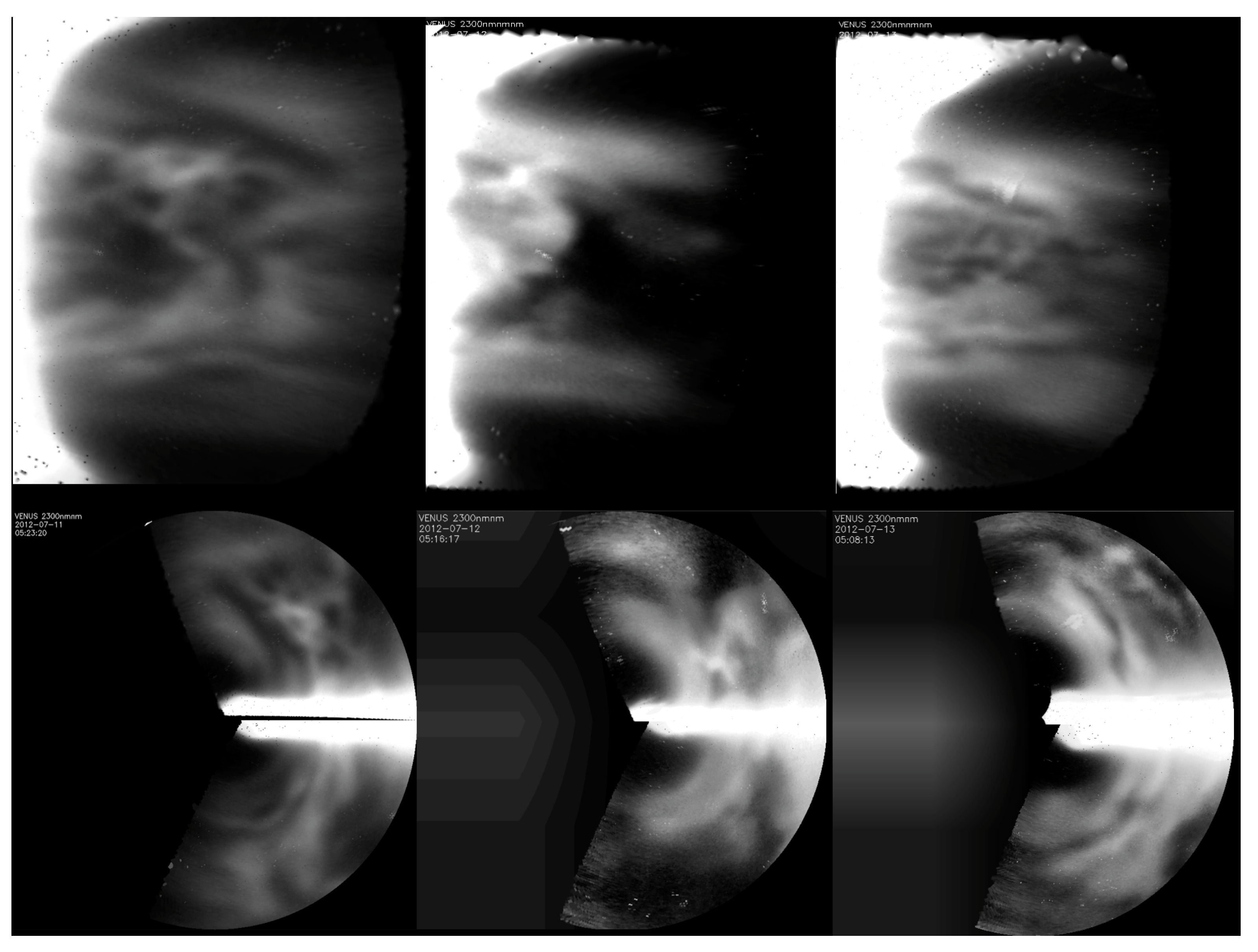
2.1. Ground-Based Observations with TNG/NICS
2.2. Coordinated Space-Based Observations with VEx/VIRTIS-M
3. Wind Determination Methods
3.1. Cloud-Tracked Winds on the Nightside Using TNG/NICS
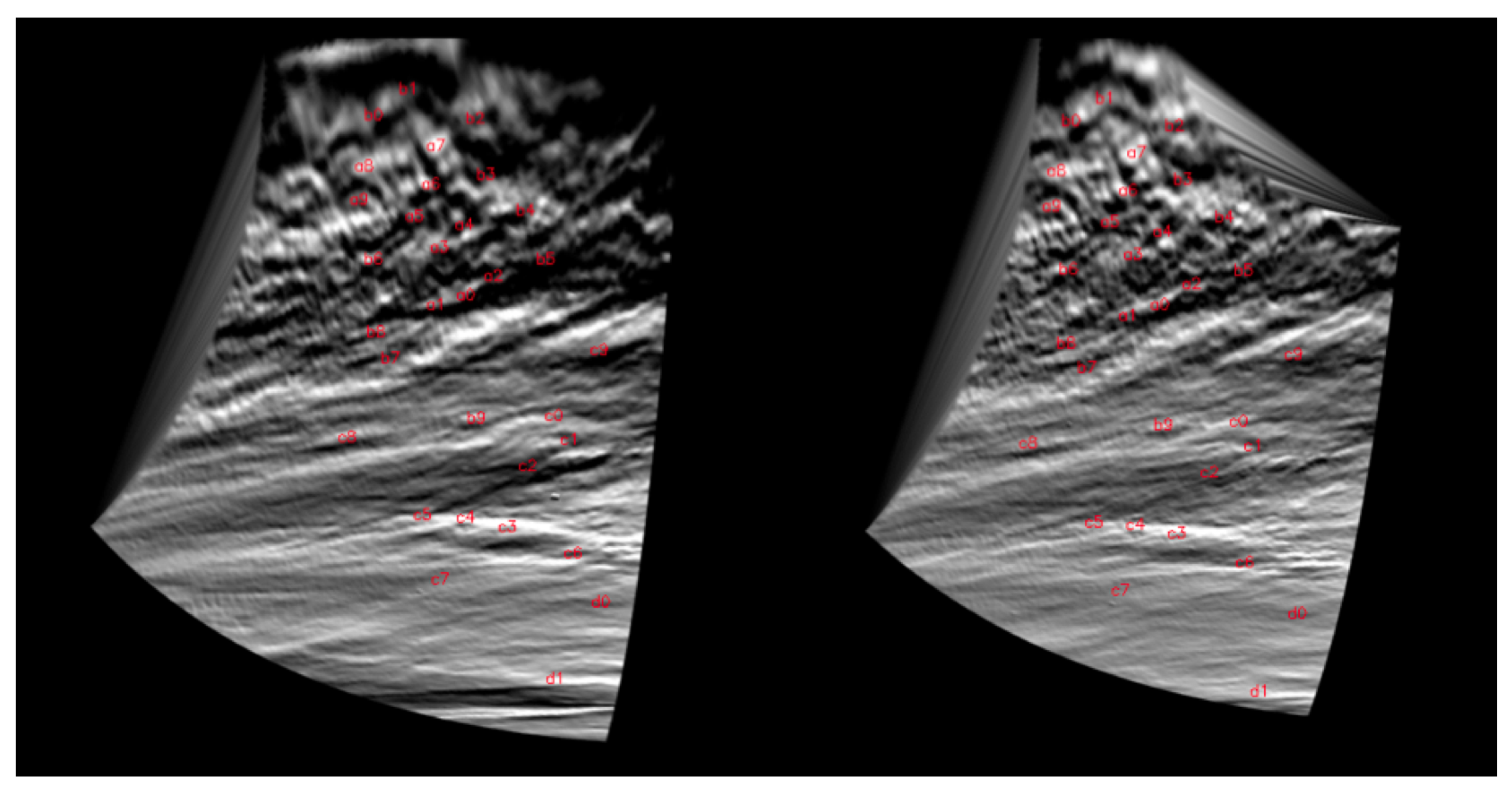
3.2. Cloud Tracking (CT) Wind Retrieval with VEx/VIRTIS-M
3.3. Cloud Tracking Method, Cloud Features Tracers, and Accuracy
4. Results
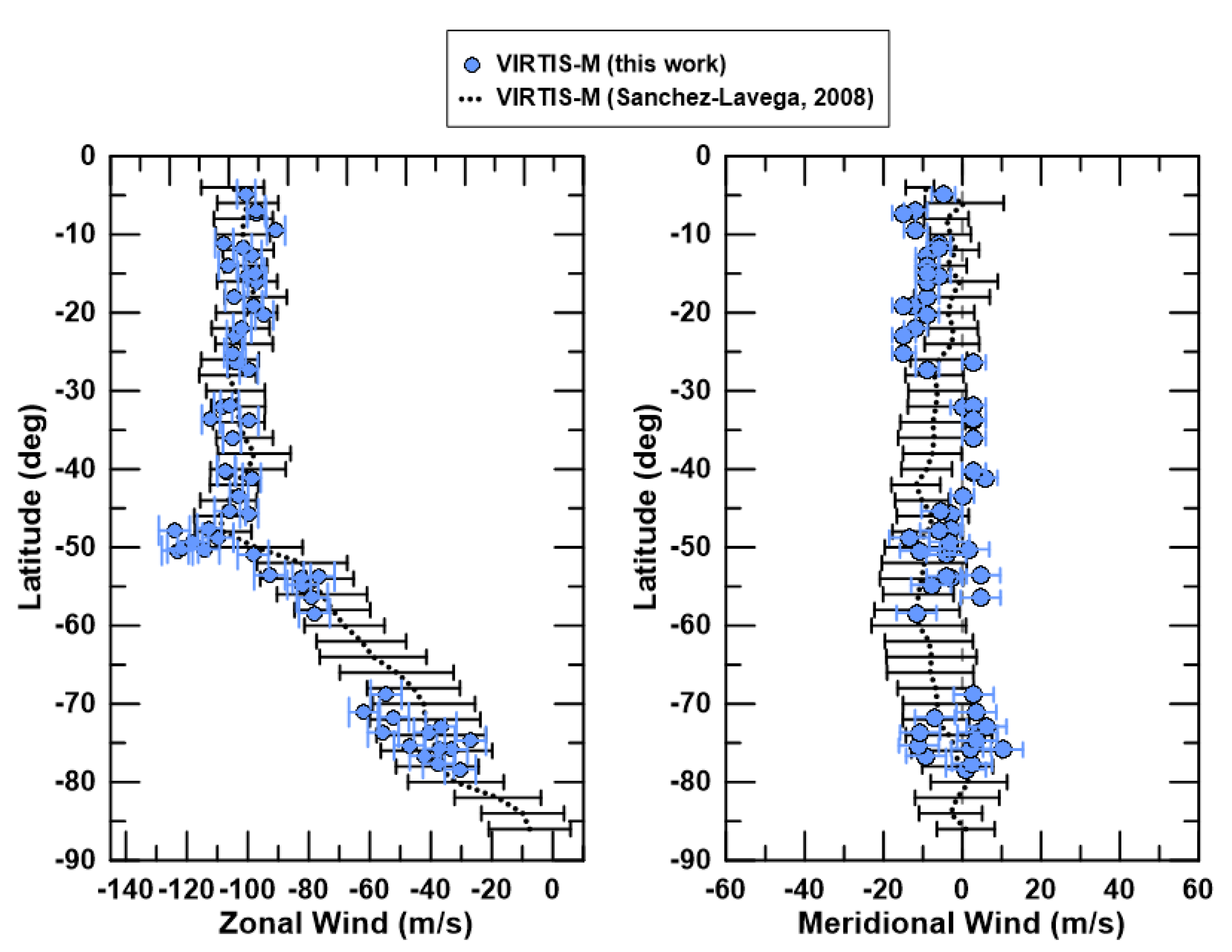
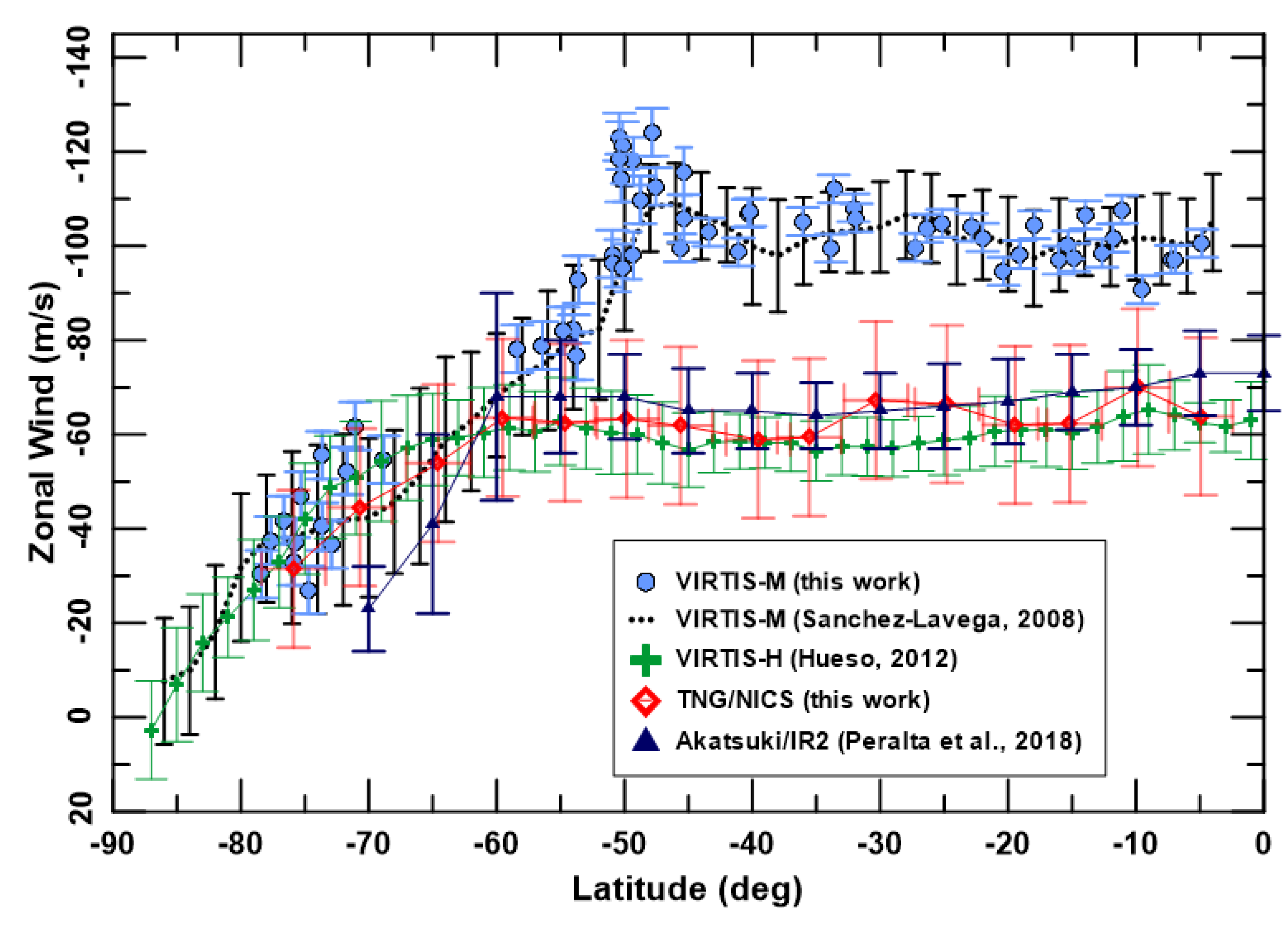
4.1. Winds at the Dayside Cloud Tops with VEx/VIRTIS-M
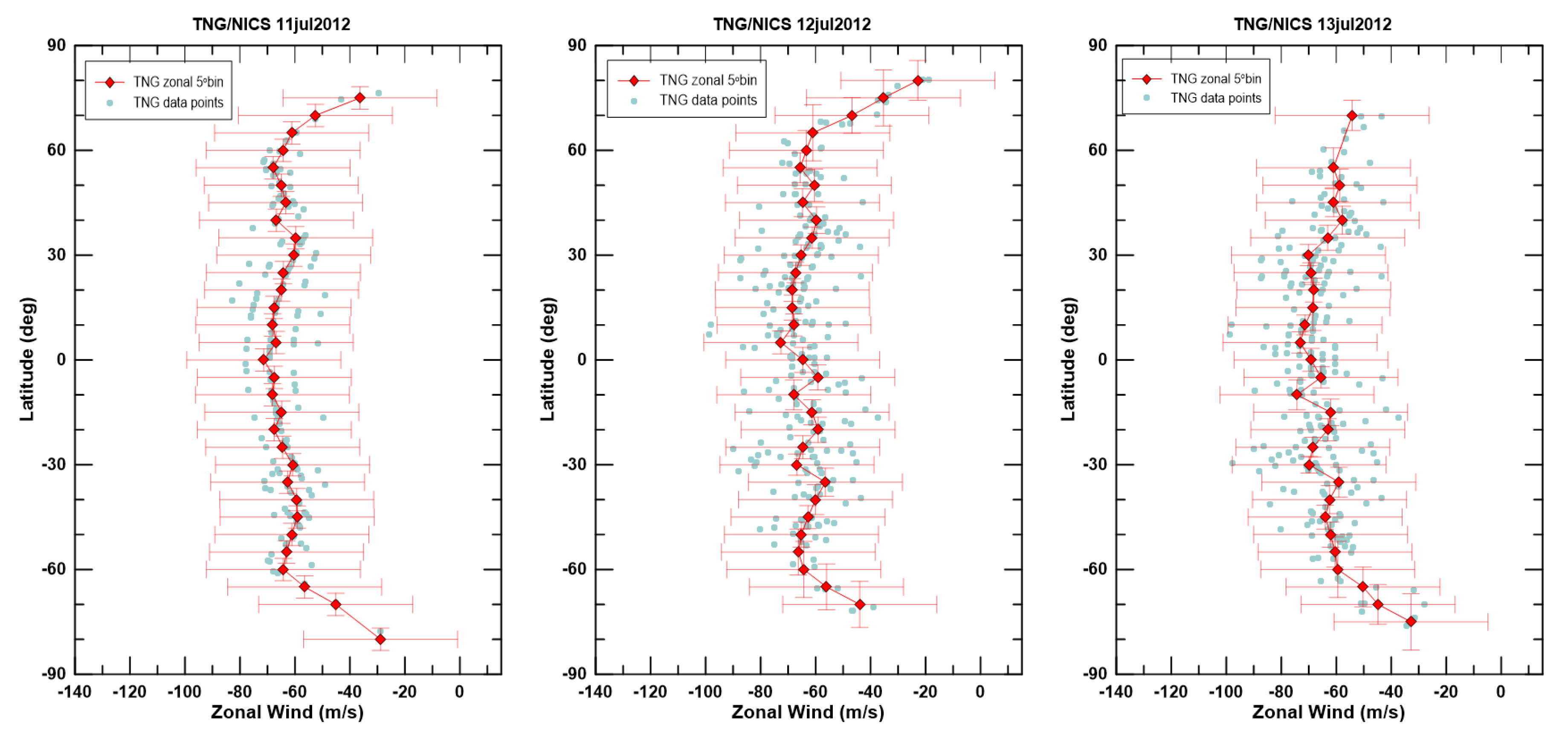
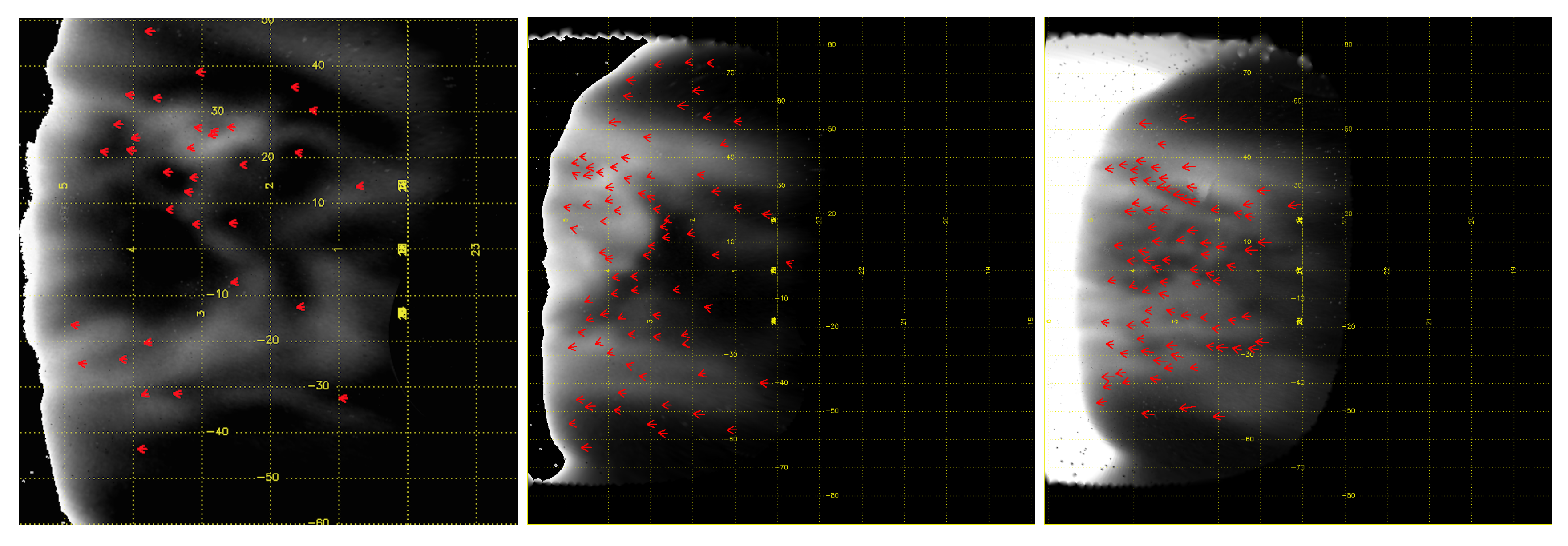
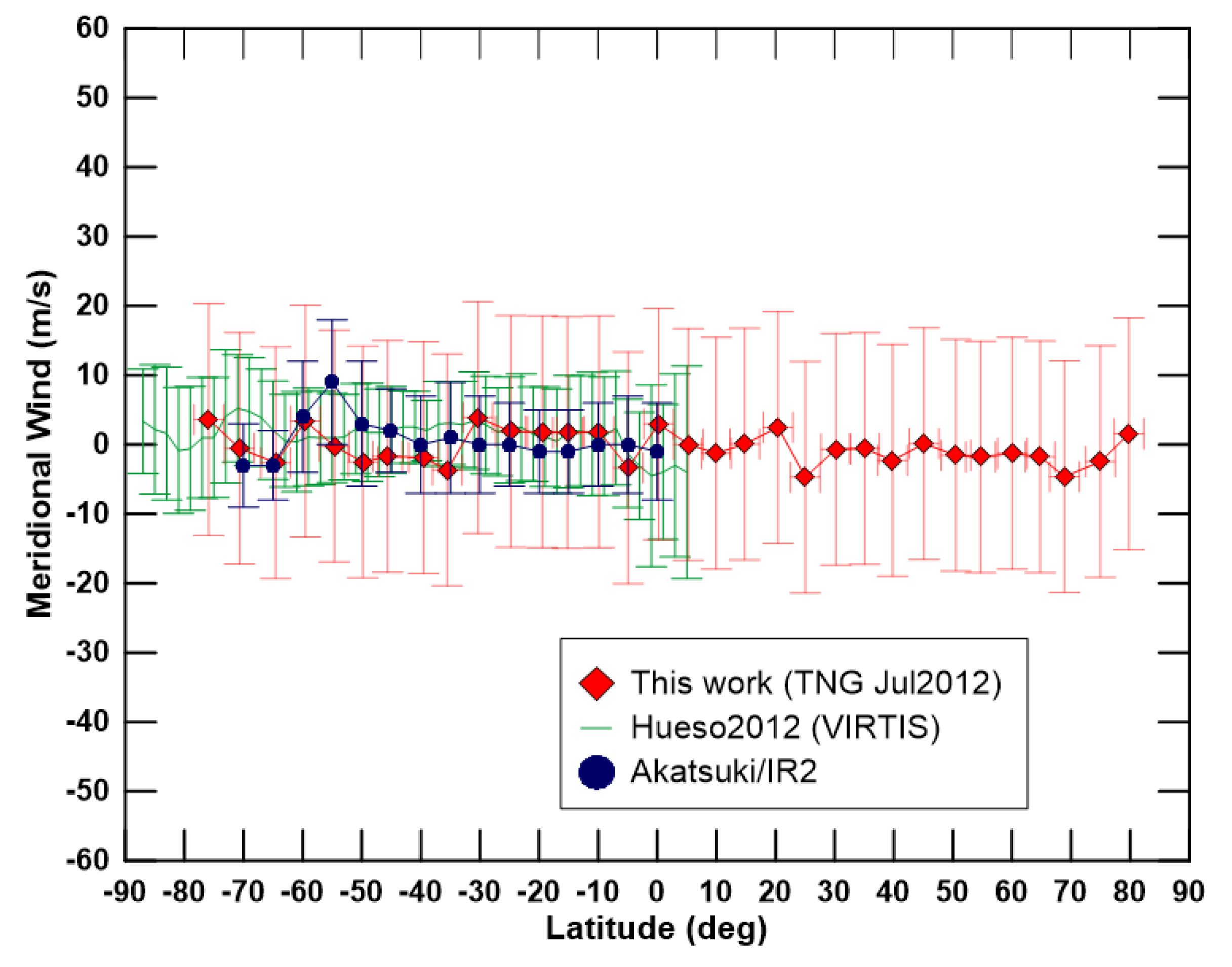
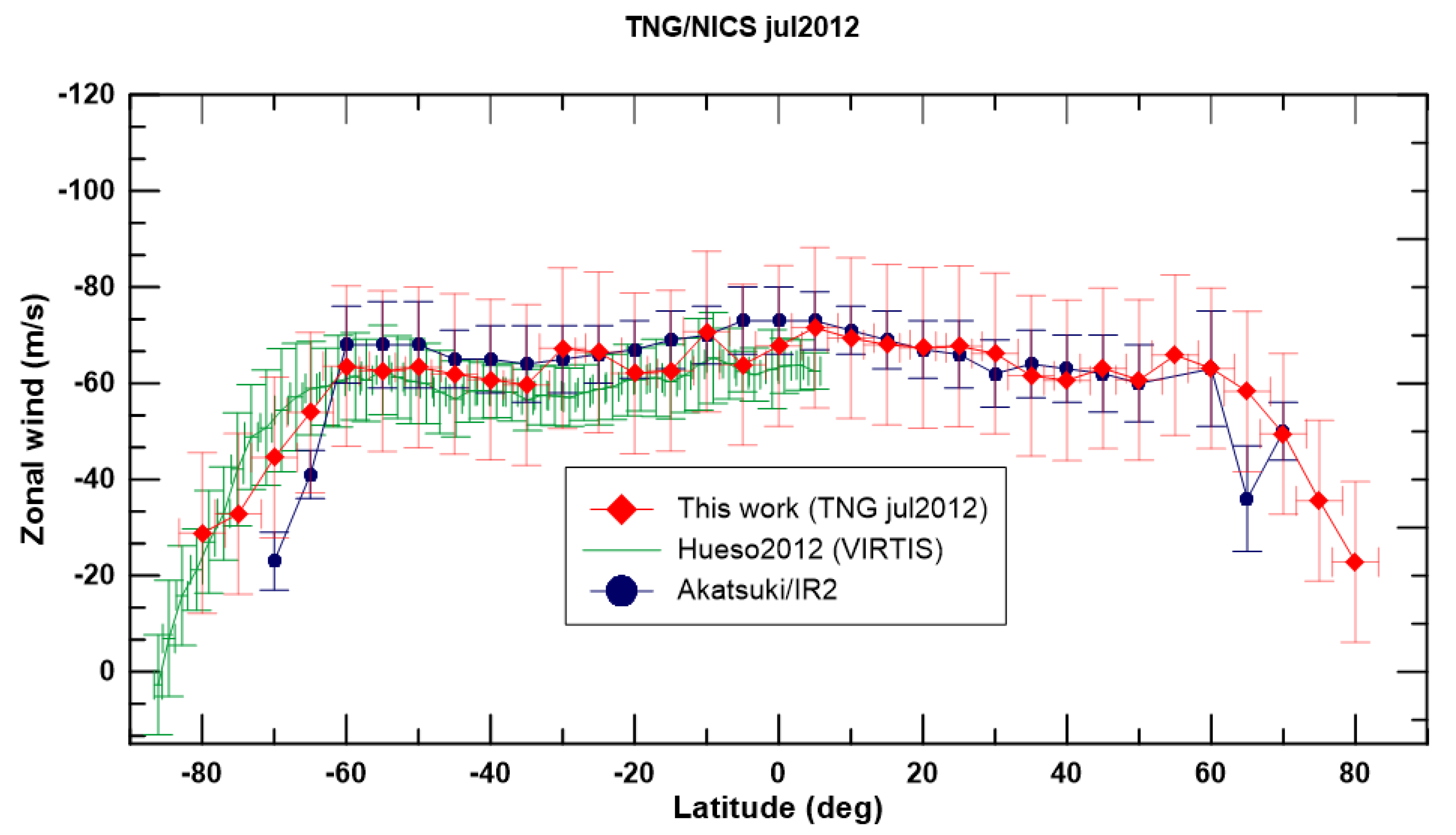
4.2. Cloud Patterns and Winds at the Nightside Lower Clouds with TNG/NICS
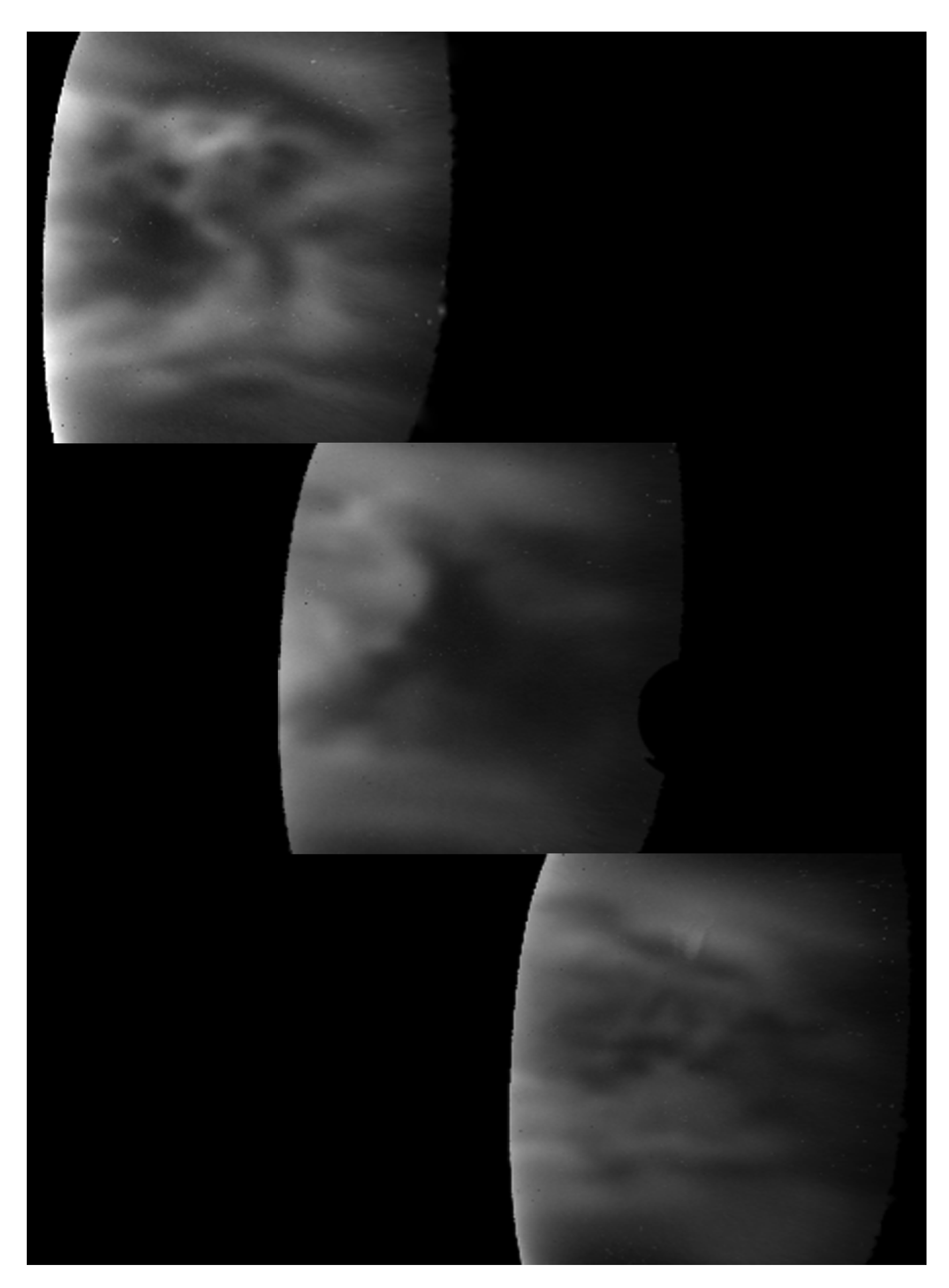
Morphology of the Nightside Lower Clouds with TNG/NICS Images
4.3. Was the Planetary-Scale Cloud Discontinuity Present?
Dynamics of the Nightside Lower Clouds with TNG/NICS Images
5. Discussion and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mueller, N.T.; Helbert, J.; Erard, S.; Piccioni, G.; Drossart, P. Rotation period of Venus estimated from Venus Express VIRTIS images and Magellan altimetry. Icarus 2011, 217, 474–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ignatiev, N.I.; Titov, D.V.; Piccioni, G.; Drossart, P.; Markiewicz, W.J.; Cottini, V.; Manoel, N. Altimetry of the Venus cloud tops from the Venus Express observations. J. Geophys. Res. 2009, 114, E00B43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Titov, D.V.; Ignatiev, N.I.; McGouldrick, K.; Wilquet, V.; Wilson, C.F. Clouds and Hazes of Venus. Space Sci. Rev. 2018, 214, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lebonnois, S.; Hourdin, F.; Eymet, V.; Crespin, A.; Fournier, R.; Forget, F. Superrotation of Venus’ atmosphere analyzed with a full general circulation model. J. Geophys. Res. 2010, 115, E06006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez-Lavega, A.; Hueso, R.; Piccioni, G.; Drossart, P.; Peralta, J.; Perez-Hoyos, S.; Lebonnois, S. Variable winds on Venus mapped in three dimensions. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2008, 35, L13204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nakamura, M.; Imamura, T.; Ishii, N.; Abe, T.; Kawakatsu, Y.; Hirose, C.; Kamata, Y. AKATSUKI returns to Venus. Earth Planets Space 2016, 68, 201668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fukuhara, T.; Futaguchi, M.; Hashimoto, G.L.; Horinouchi, T.; Imamura, T.; Iwagaimi, N.; Kouyama, T.; Murakami, S.-Y.; Nakamura, M.; Ogohara, K.; et al. Large stationary gravity wave in the atmosphere of Venus. Nat. Geosci. 2017, 10, 85–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horinouchi, T.; Kouyama, T.; Lee, Y.J.; Murakami, S.; Ogohara, K.; Takagi, M.; Imamura, T.; Nakajima, K.; Peralta, J.; Yamazaki, A. Mean winds at the cloud top of Venus obtained from two wavelength UV imaging by Akatsuki. Earth Planets Space 2018, 70, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peralta, J.; Navarro, T.; Vun, C.W.; Sánchez-Lavega, A.; McGouldrick, K.; Horinouchi, T.; Imamura, T.; Hueso, R.; Boyd, J.P.; Schubert, G.; et al. A long-lived sharp disruption on the lower clouds of Venus. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2020, 42, 705–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machado, P.; Widemann, T.; Luz, D.; Peralta, J. Wind circulation regimes at Venus’ cloud tops: Ground-based Doppler velocimetry using CFHT/ESPaDOnS and comparison with simultaneous cloud tracking measurements using VEx/VIRTIS in February 2011. Icarus 2014, 243, 249–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machado, P.; Widemann, T.; Peralta, J.; Gonçalves, R.; Donati, J.; Luz, D. Venus cloud-tracked and doppler velocimetry winds from CFHT/ESPaDOnS and Venus Express/VIRTIS in April 2014. Icarus 2017, 285, 8–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves, R.; Machado, P.; Widemann, T.; Peralta, J.; Watanabe, S.; Yamazaki, A.; Silva, J. Venus’ cloud top wind study: Coordinated Akatsuki/UVI with cloud tracking and TNG/HARPS-N with Doppler velocimetry observations. Icarus 2020, 335, 113418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, D.A.; Crawford, J.W. Cloud structure on the dark side of Venus. Nature 1984, 307, 222–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crisp, D.; Sinton, W.M.; Hodapp, K.W.; Ragent, B.; Gerbault, F.; Goebel, J.H.; Probst, R.G.; Allen, D.A.; Pierce, K.; Stapelfeldt, K.R. The Nature of the Near-Infrared Features on the Venus Night Side. Science 1989, 246, 506–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chanover, N.J.; Glenar, D.A.; Hillman, J.J. Multispectral near-IR imaging of Venus nightside cloud features. J. Geophys. Res. 1998, 103, 31335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crisp, D.; McMuldroch, S.; Stephens, S.K.; Sinton, W.M.; Ragent, B.; Hodapp, K.W.; Probst, R.G.; Doyle, L.R.; Allen, D.A.; Elias, J. Ground-Based Near-Infrared Imaging Observations of Venus during the Galileo Encounter. Science 1991, 253, 1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Limaye, S.S.; Warell, J.; Bhatt, B.C.; Fry, P.M.; Young, E. Multi-observatory observations of night-side of Venus at 2.3 micron—Atmospheric circulation from tracking of cloud features. Bull. Astron. Soc. India 2006, 34, 189–201. [Google Scholar]
- Tavenner, T.; Young, E.F.; Bullock, M.A.; Murphy, J. Global mean cloud coverage on Venus in the near-infrared. Planet Space Sci. 2008, 56, 1435–1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlson, R.W.; Baines, K.H.; Encrenaz, T.; Taylor, F.W.; Drossart, P.; Kamp, L.W.; Pollack, J.B.; Lellouch, E.; Collard, A.D.; Calcutt, S.B.; et al. Galileo infrared imaging spectroscopy measurements at Venus. Science 1991, 253, 1541–1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hueso, R.; Sánchez-Lavega, A.; Piccioni, G.; Drossart, P.; Gérard, J.C.; Khatuntsev, I.; Zasova, L.; Migliorini, A. Morphology and dynamics of Venus oxygen airglow from Venus Express/visible and infrared thermal imaging spectrometer observations. J. Geophys. Res. Planets 2008, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hueso, R.; Peralta, J.; Sanchez-Lavega, A. Assessing the long-term variability of Venus winds at cloud level from VIRTIS-Venus Express. Icarus 2012, 217, 585–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peralta, J.; Muto, K.; Hueso, R.; Horinouchi, T.; Sánchez-Lavega, A.; Murakami, S.Y.; Luz, D. Nightside Winds at the Lower Clouds of Venus with Akatsuki/IR2: Longitudinal, Local Time, and Decadal Variations from Comparison with Previous Measurements. Astrophys. J. Suppl. Ser. 2018, 239, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peralta, J.; Sánchez-Lavega, A.; Horinouchi, T.; McGouldrick, K.; Garate-Lopez, I.; Young, E.F.; Bullock, M.A.; Lee, Y.J.; Imamura, T.; Satoh, T.; et al. New cloud morphologies discovered on the Venus’s night during Akatsuki. Icarus 2019, 333, 177–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwagami, N.; Sakanoi, T.; Hashimoto, G.L.; Sawai, K.; Ohtsuki, S.; Takagi, S.; Takagi, K.; Ueno, M.; Kameda, S.; Murakami, S.-Y.; et al. Initial products of Akatsuki 1-μm camera. Earth Planets Space 2018, 70, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Acton, C.; Bachman, N.; Semenov, B.; Wright, E. A look towards the future in the handling of space science mission geometry. Planet Space Sci. 2018, 150, 9–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drossart, P.; Piccioni, G.; Gérard, J.C.; Lopez-Valverde, M.A.; Sanchez-Lavega, A.; Zasova, L.; Hueso, R.; Taylor, F.W.; Bézard, B.; Adriani, A.; et al. A dynamic upper atmosphere of Venus as revealed by VIRTIS on Venus Express. Nature 2007, 450, 641–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machado, P.; Widemann, T.; Peralta, J.; Gilli, G.; Espadinha, D.; Silva, J.E.; Brasil, F.; Ribeiro, J.; Goncalves, R. Venus Atmospheric Dynamics at Two Altitudes: Akatsuki and Venus Express Cloud Tracking, Ground-Based Doppler Observations and Comparison with Modelling. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peralta, J.; Hueso, R.; Sánchez-Lavega, A. A reanalysis of Venus winds at two cloud levels from Galileo SSI images. Icarus 2007, 190, 469–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peralta, J.; Lee, Y.J.; Hueso, R.; Clancy, R.T.; Sandor, B.; Sànchez-Lavega, A.; Imamura, T.; Omino, M.; Machado, P.; Lellouch, E.; et al. The Winds of Venus during the Messenger’s Flyby. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2017, 44, 3907–3915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garate-Lopez, I.; Lebonnois, S. Latitudinal Variation of Clouds’ Structure Responsible for Venus’ Cold Collar. Icarus 2018, 314, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Venus Coordinated Campaign Transit of Venus. 2012. Available online: https://lesia.obspm.fr/venus-atm-wiki/index.php/Venus_coordinated_campaign_Transit_of_Venus (accessed on 18 December 2021).
- Farsiu, S.; Robinson, M.D.; Elad, M.; Milanfar, P. Fast and robust multiframe super resolution. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2004, 13, 1327–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendikoa, I.; Sánchez-Lavega, A.; Pérez-Hoyos, S.; Hueso, R.; Rojas, J.F.; Aceituno, J.; Aceituno, F.; Murga, G.; De Bilbao, L.; García-Melendo, E. PlanetCam UPV/EHU: A Two-channel Lucky Imaging Camera for Solar System Studies in the Spectral Range 0.38–1.7 μm. Astron. Instrum. Telesc. Obs. Site Charact. 2016, 128, 035002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sanchez-Lavega, A.; Peralta, J.; Gomez-Forrellad, J.M.; Hueso, R.; Pérez-Hoyos, S.; Mendikoa, I.; Rojas, J.F.; Horinouchi, T.; Lee, Y.J.; Watanabe, S. Venus Cloud Morphology and Motions from Ground-Based Images at the Time of the Akatsuki Orbit Insertion. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2016, 833, L7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mackay, C.D.; Baldwin, J.; Law, N.; Warner, P. High-resolution imaging in the visible from the ground without adaptive optics: New techniques and results. In Proceedings Ground-Based Instrumentation for Astronomy; SPIE Astronomical Telescopes + Instrumentation: Glasgow, UK, 2004; Volume 5492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lodieu, N.; Zapatero Osorio, M.R.; Martín, E.L. Lucky Imaging of M subdwarfs. Astron. Astrophys. 2009, 499, 729–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gallaway, M. An Introduction to Observational Astrophysics; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Hueso, R.; Legarreta, J.; Rojas, J.F.; Peralta, J.; Pérez-Hoyos, S.; Del Río-Gaztelurrutia, T.; Sánchez-Lavega, A. The Planetary Laboratory for Image Analysis (PLIA). Adv. Space Res. 2010, 46, 1120–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardesín, A. Study and Implementation of the End-to-End Data Pipeline for the VIRTIS Imaging Spectrometer on Board Venus Express: From Science Operation Planning to Data Archiving and Higher Level Processing. Ph.D. Thesis, Centro Interdipartimentale di Studi e Attività Spaziali (CISAS), Universita degli Studi di Padova, Padova, Italy, January 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Sánchez-Lavega, A.; Lebonnois, S.; Imamura, T.; Read, P.; Luz, D. The Atmospheric Dynamics of Venus. Space Sci. Rev. 2017, 212, 1541–1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatuntsev, I.; Patsaeva, M.; Titov, D.; Ignatiev, N.; Turin, A.; Limaye, S.; Markiewicz, W.; Almeida, M.; Roatsch, T.; Moissl, R. Cloud level winds from the Venus Express Monitoring Camera imaging. Icarus 2013, 226, 140–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hueso, R.; Peralta, J.; Garate-Lopez, I.; Bados, T.V.; Sanchez-Lavega, A. Six years of Venus winds at the upper cloud level from UV, visible and near-infrared observations from VIRTIS on Venus Express. Planet Space Sci. 2015, 113–114, 78–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peralta, J.; Iwagami, N.; Sánchez-Lavega, A.; Lee, Y.J.; Hueso, R.; Narita, M.; Imamura, T.; Miles, P.; Wesley, A.; Kardasis, E.; et al. Morphology and Dynamics of Venus’s Middle Clouds with Akatsuki/IR1. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2019, 46, 2399–2407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Acton, C.H. Ancillary Data Services of NASA’s Navigation and Ancillary Information Facility. Planet Space Sci. 1996, 44, 65–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bevington, P.R.; Robinson, D.K. Data Reduction and Error Analysis for the Physical Sciences, 2nd ed.; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- McGouldrick, K.; Momary, T.W.; Baines, K.H.; Grinspoon, D.H. Quantication of middle and lower cloud variability and mesoscale dynamics from Venus Express/VIRTIS observations at 1.74 microns. Icarus 2012, 217, 615–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satoh, T.; Sato, T.M.; Nakamura, M.; Kasaba, Y.; Ueno, M.; Suzuki, M.; Ohtsuki, S. Performance of Akatsuki/IR2 in Venus orbit: The first year. Earth Planets Space 2017, 69, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Horinouchi, T.; Murakami, S.; Satoh, T.; Peralta, J.; Ogohara, K.; Kouyama, T.; Young, E.F. Equatorial jet in the lower to middle cloud layer of Venus revealed by Akatsuki. Nat. Geosci. 2017, 10, 646–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Limaye, S.S.; Watanabe, S.; Yamazaki, A.; Yamada, M.; Satoh, T.; Sato, T.M.; Ocampo, A.C. Venus looks different at different wavelengths: Morphology from Akatsuki multispectral images. Earth Planets Space 2018, 70, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kashimura, H.; Sugimoto, N.; Takagi, M.; Matsuda, Y.; Ohfuchi, W.; Enomoto, T.; Nakajima, K.; Ishiwatari, M.; Sato, T.M.; Hashimoto, G.L.; et al. Planetary-scale streak structure reproduced in high-resolution simulations of the Venus atmosphere with a low-stability layer. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peralta, J.; Hueso, R.; Sánchez-Lavega, A. Characterization of mesoscale gravity waves in the upper and lower clouds of Venus from VEx-VIRTIS images. J. Geophys. Res. 2018, 113, E00B18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorinov, D.A.; Zasova, L.V.; Khatuntsev, I.V.; Patsaeva, M.V.; Turin, A.V. Winds in the Lower Cloud Level on the Nightside of Venus from VIRTIS-M (Venus Express) 1.74 μm Images. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preston, R.A.; Hildebrand, C.E.; Purcell, G.H., Jr.; Ellis, J.; Stelzried, C.T.; Finley, S.G.; Sagdeev, R.Z.; Linkin, V.M.; Kerzhanovich, V.V.; Altunin, V.I.; et al. Determination of Venus Winds by Ground-Based Radio Tracking of the VEGA Balloons. Science 1986, 231, 1414–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebonnois, S.; Sugimoto, N.; Gilli, G. Wave analysis in the atmosphere of Venus below 100-km altitude, simulated by the LMD Venus GCM. Icarus 2016, 278, 38–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gilli, G.; Lebonnois, S.; Gonzalez-Galindo, F.; Lopez-Valverde, M.A.; Stolzenbach, A.; Lefevre, F.; Chaufray, J.Y.; Lott, F. Thermal structure of the upper atmosphere of Venus simulated by a ground-to-thermosphere GCM. Icarus 2017, 281, 55–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilli, G.; Navarro, T.; Lebonnois, S.; Trucmuche, A. Venus’ upper atmosphere revealed by a GCM: II. Validation with temperature and densities measurements. Icarus 2021, 366, 114432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baso, C.J.D.; Ramos, A. Enhancing SDO/HMI images using deep learning. Astron. Astrophys. 2018, 614, A5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, X.; Chen, Z.; Song, W.; Li, F.; Yang, Y. Data Matching of Solar Images Super-Resolution Based on Deep Learning. Comput. Mater. Contin. 2021, 68, 4017–4029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dash, A.; Ye, J.; Wang, G. High Resolution Solar Image Generation Using Generative Adversarial Networks; Cornell University: Ithaca, NY, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt, D.; Gorceix, N.; Goode, P.R.; Marino, J.; Rimmele, T.; Berkefeld, T.; Wöger, F.; Zhang, X.; Rigaut, F.; von der Lühe, O. Clear widens the field for observations of the Sun with multi-conjugate adaptive optics. Astron. Astrophys. 2017, 597, L8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]

| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | (5) | (6) | (7) | (8) | (9) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Date | UT | Phase Angle | Ill. Fraction | Ang. Diam. | Ob-Lon/Lat | Airmass | Seeing | Pixel Size |
| () | (%) | () | () | () | (km) | |||
| 11 July 2012 | 05:18–07:48 | 119.9 | 25.63 | 38.07 | 24.16/ 3.64 | 2.98–1.28 | 0.8–0.7 | 41.3 |
| 12 July 2012 | 05:12–07:32 | 118.8 | 26.44 | 37.47 | 26.09/ 3.66 | 2.99–1.32 | 0.6–0.9 | 42.0 |
| 13 July 2012 | 05:01–07:27 | 117.7 | 27.35 | 36.89 | 28.05/ 3.68 | 3.02–1.35 | 0.8–1.1 | 42.7 |
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | (5) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| VEx Orbit | Date | Time Interval | Latitude | Solar Local Time |
| (yyyy/mm/dd) | (min) | Range | Range | |
| 2272 | 2012/07/11 | 49 | 40 S–80 S | 10 h–17 h |
| 2273 | 2012/07/11 | 60 | 0 S–55 S | 12 h–15 h |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Machado, P.; Peralta, J.; Silva, J.E.; Brasil, F.; Gonçalves, R.; Silva, M. Venus’ Cloud-Tracked Winds Using Ground- and Space-Based Observations with TNG/NICS and VEx/VIRTIS. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 337. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13020337
Machado P, Peralta J, Silva JE, Brasil F, Gonçalves R, Silva M. Venus’ Cloud-Tracked Winds Using Ground- and Space-Based Observations with TNG/NICS and VEx/VIRTIS. Atmosphere. 2022; 13(2):337. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13020337
Chicago/Turabian StyleMachado, Pedro, Javier Peralta, José E. Silva, Francisco Brasil, Ruben Gonçalves, and Miguel Silva. 2022. "Venus’ Cloud-Tracked Winds Using Ground- and Space-Based Observations with TNG/NICS and VEx/VIRTIS" Atmosphere 13, no. 2: 337. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13020337
APA StyleMachado, P., Peralta, J., Silva, J. E., Brasil, F., Gonçalves, R., & Silva, M. (2022). Venus’ Cloud-Tracked Winds Using Ground- and Space-Based Observations with TNG/NICS and VEx/VIRTIS. Atmosphere, 13(2), 337. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13020337







